可氧化再生的“核-壳”结构磁性吸附剂Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2对水中氧氟沙星的吸附机制
doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210722.002
Adsorption mechanism of ofloxacin in water with "core-shell" magnetic adsorbent Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2 capable of oxidation regeneration
-
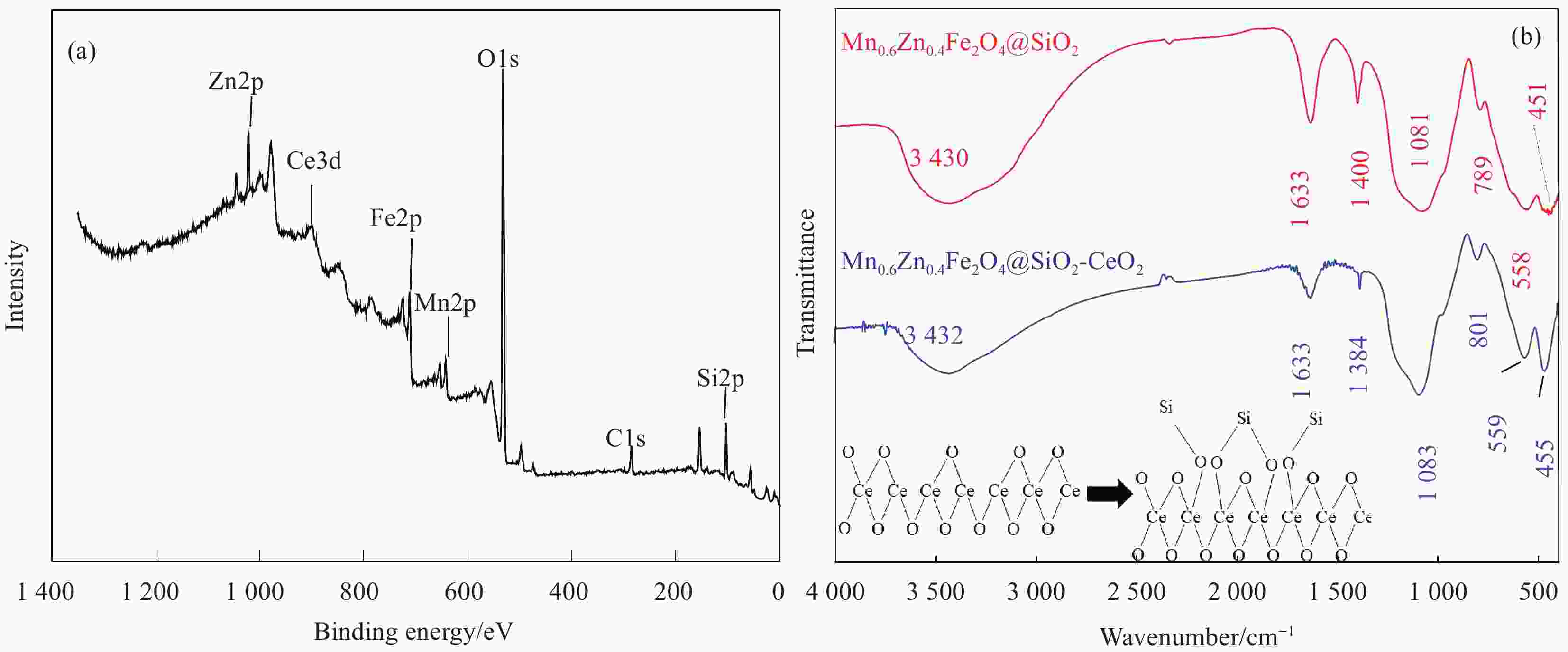
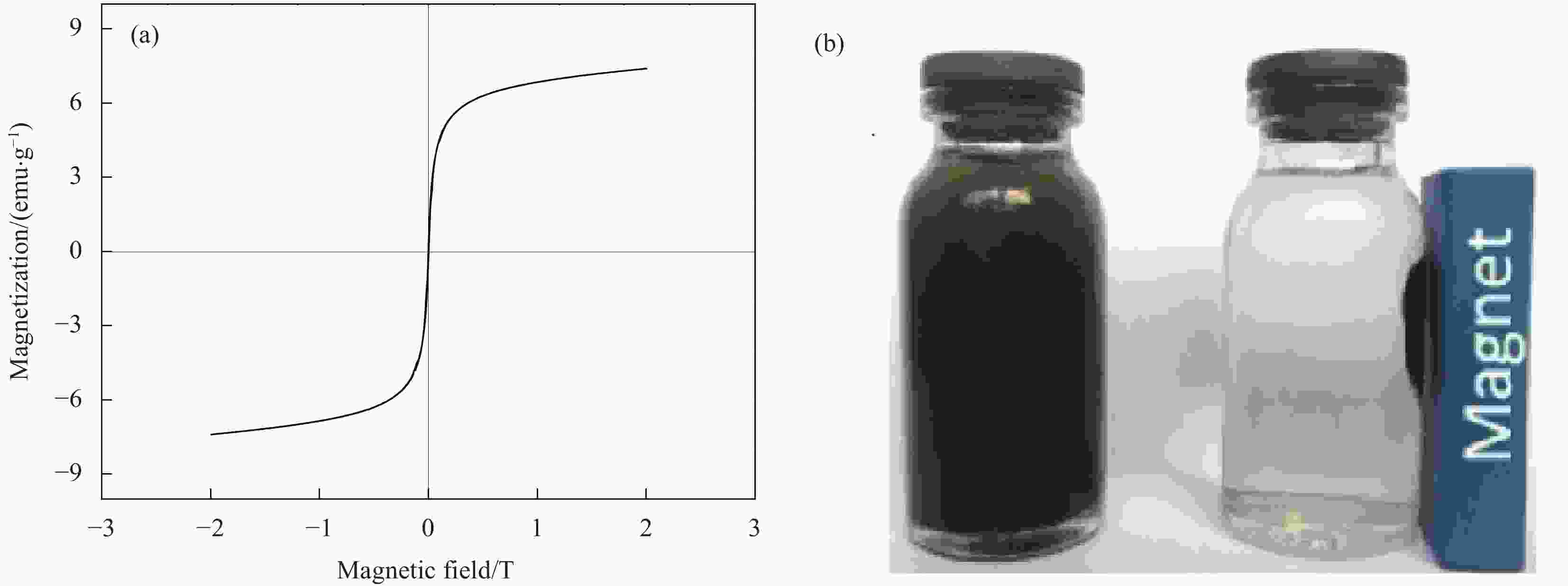
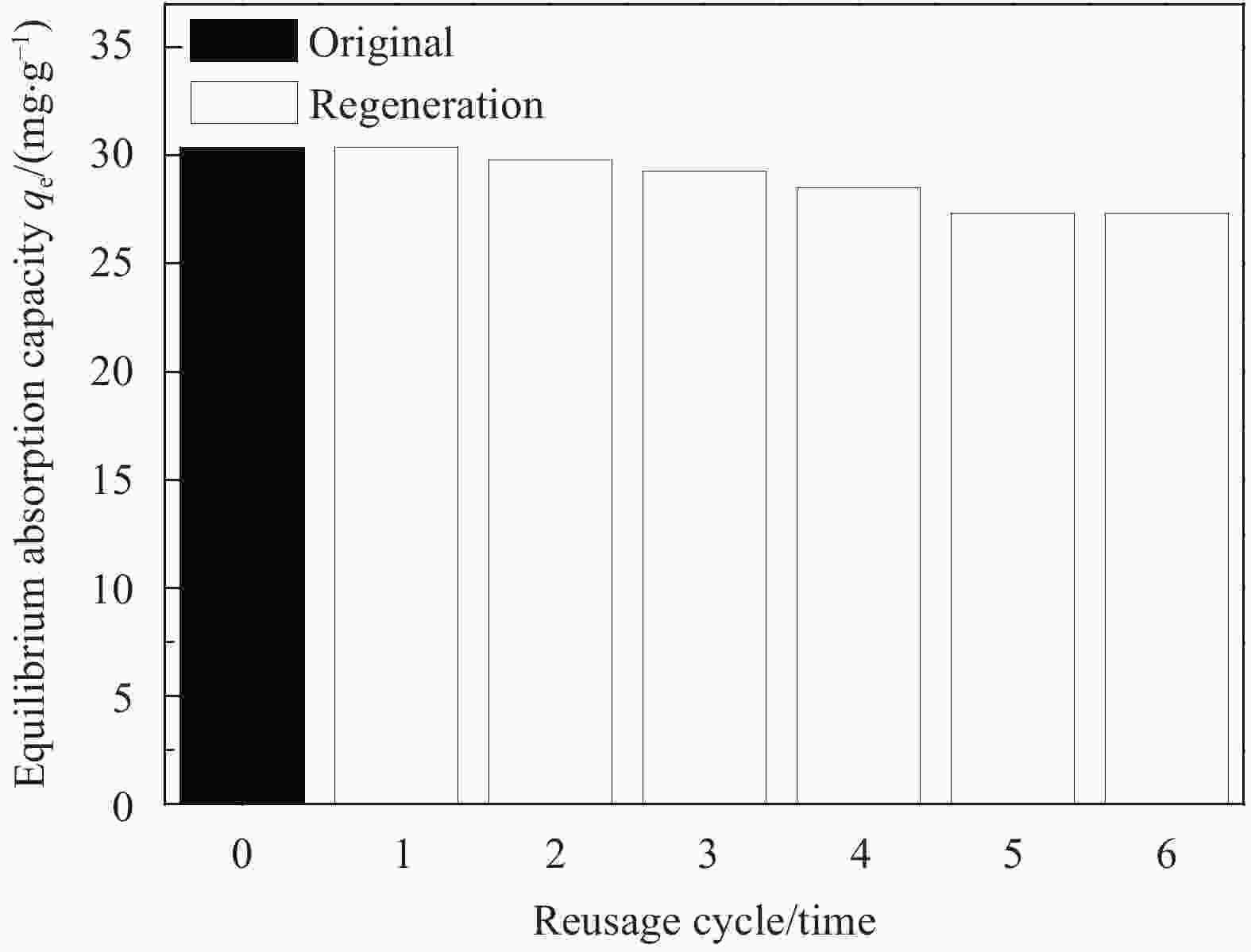
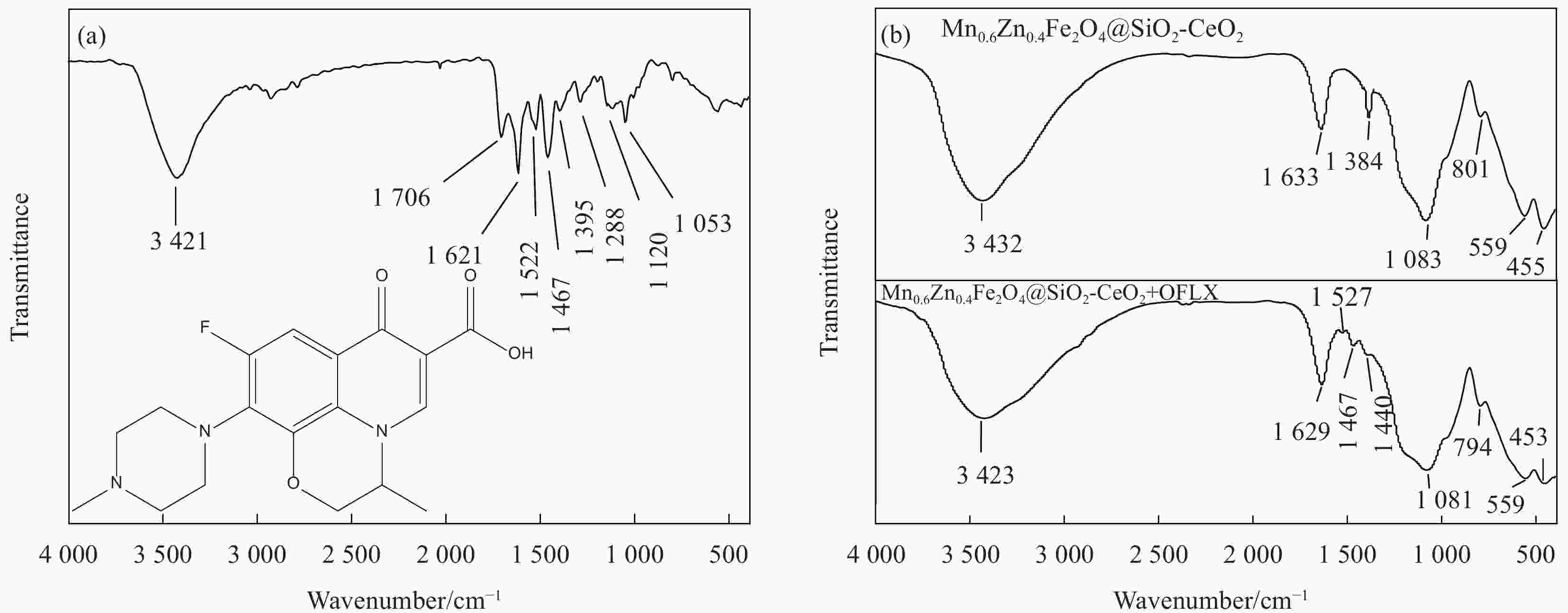
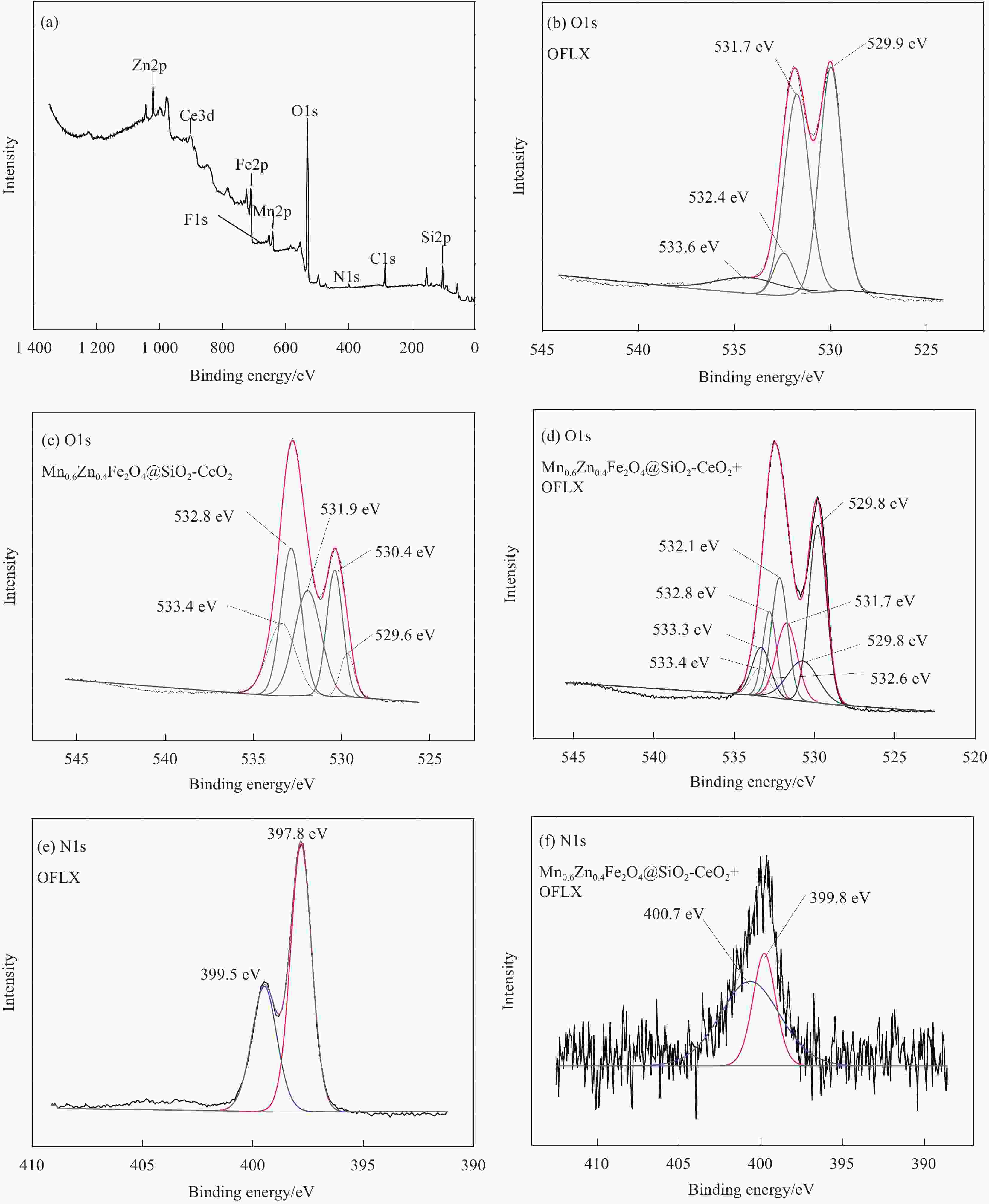
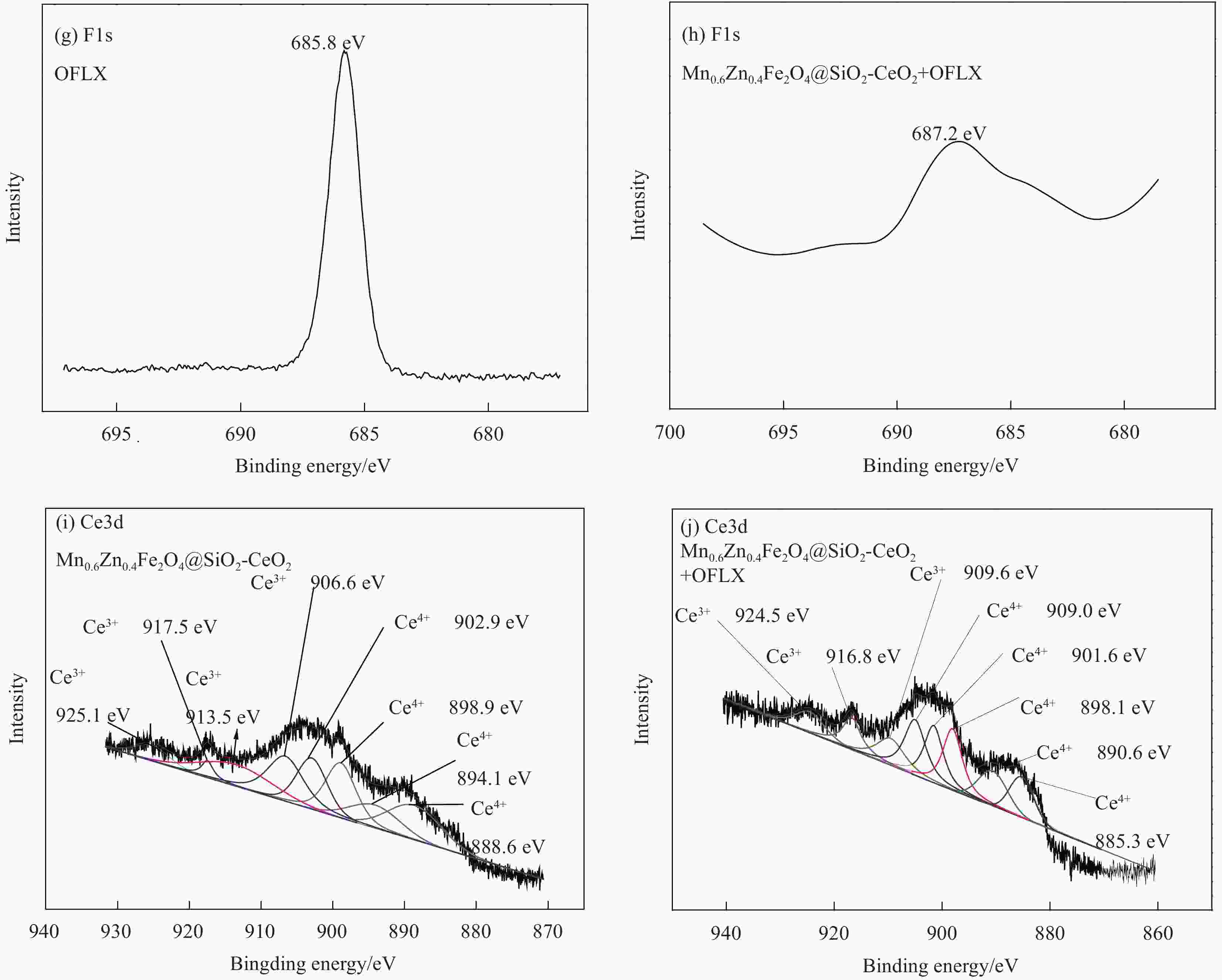
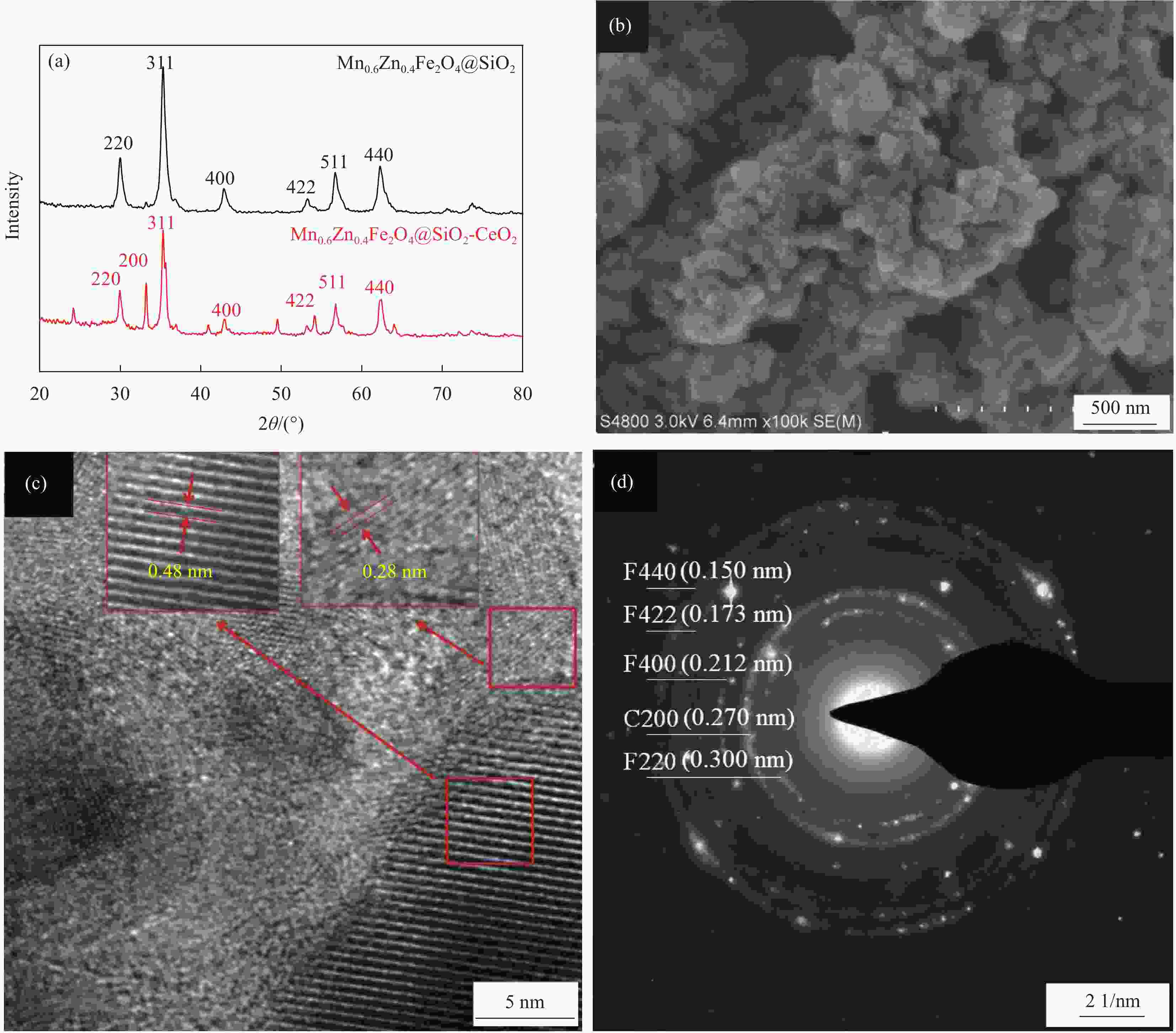
摘要: 为去除水中难生物降解的氧氟沙星(OFLX),突破吸附剂固液分离和再生难的瓶颈,采用SiO2和CeO2功能化修饰Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4磁性纳米颗粒,制备得到磁性纳米复合物吸附剂Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2,利用XRD、FTIR、SEM、TEM、和振动样品磁强计等对Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2进行了系统表征。3种动力学模型(拟一级动力学、拟二级动力学和颗粒内扩散模型)、3种等温线模型(Langmuir、Freundlich和D-R模型)和吸附热力学的研究结果表明:该吸附过程的速率由颗粒内扩散和液膜扩散等多种因素共同控制;该吸附过程以物理吸附为主,化学吸附为吸附速率控制步骤;吸附过程可自发进行,为放热和熵减小的过程。FTIR和XRD的表征结果表明,π-π共轭作用、分子间氢键和配位作用等是Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2和OFLX之间的主要相互作用力。经6次吸附-氧化原位再生循环后,Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2对OFLX平衡吸附量为27.00 mg·g−1。研究结果可为难生物降解的OFLX的控制技术研究提供基础理论数据。Abstract: In order to remove ofloxacin (OFXL), which is difficult to biodegrade in water, and break through the bottleneck of solid-liquid separation and regeneration of adsorbents, Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles were modified by SiO2 and CeO2 to prepare Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2 magnetic nanocompsite adsorbents. The as-prepared Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2 were systematically characterized using XRD, FTIR, SEM, TEM, vibration sample magnetometer. The investigation results of three kinetic models (quasi-first-order kinetics, quasi-second-order kinetics, and intraparticle diffusion models), three isotherm models (Langmuir, Freundlich and D-R models) and adsorption thermodynamics show that the adsorption rate is controlled by multiple factors such as intra-particle diffusion and liquid film diffusion; the adsorption process is dominated by physical adsorption, and the chemical adsorption is the rate-controlling step; the adsorption process is spontaneously and exothermic with entropy increase. The characterization results of FTIR and XRD spectroscopy indicate that the interaction forces between Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2 and OFLX include π-π conjugation, hydrogen bonding and coordination. After six cycles of adsorption-oxidation regeneration in situ, the equilibrium adsorption capacity of Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2 for OFLX is 27.00 mg·g−1. The research results can provide basic theoretical data on the control technology of nonbiodegradable OFLX.
-
Key words:
- magnetic adsorbent /
- CeO2 /
- oxidation regeneration /
- ofloxacin /
- adsorption mechanism /
- "core-shell" structure
-
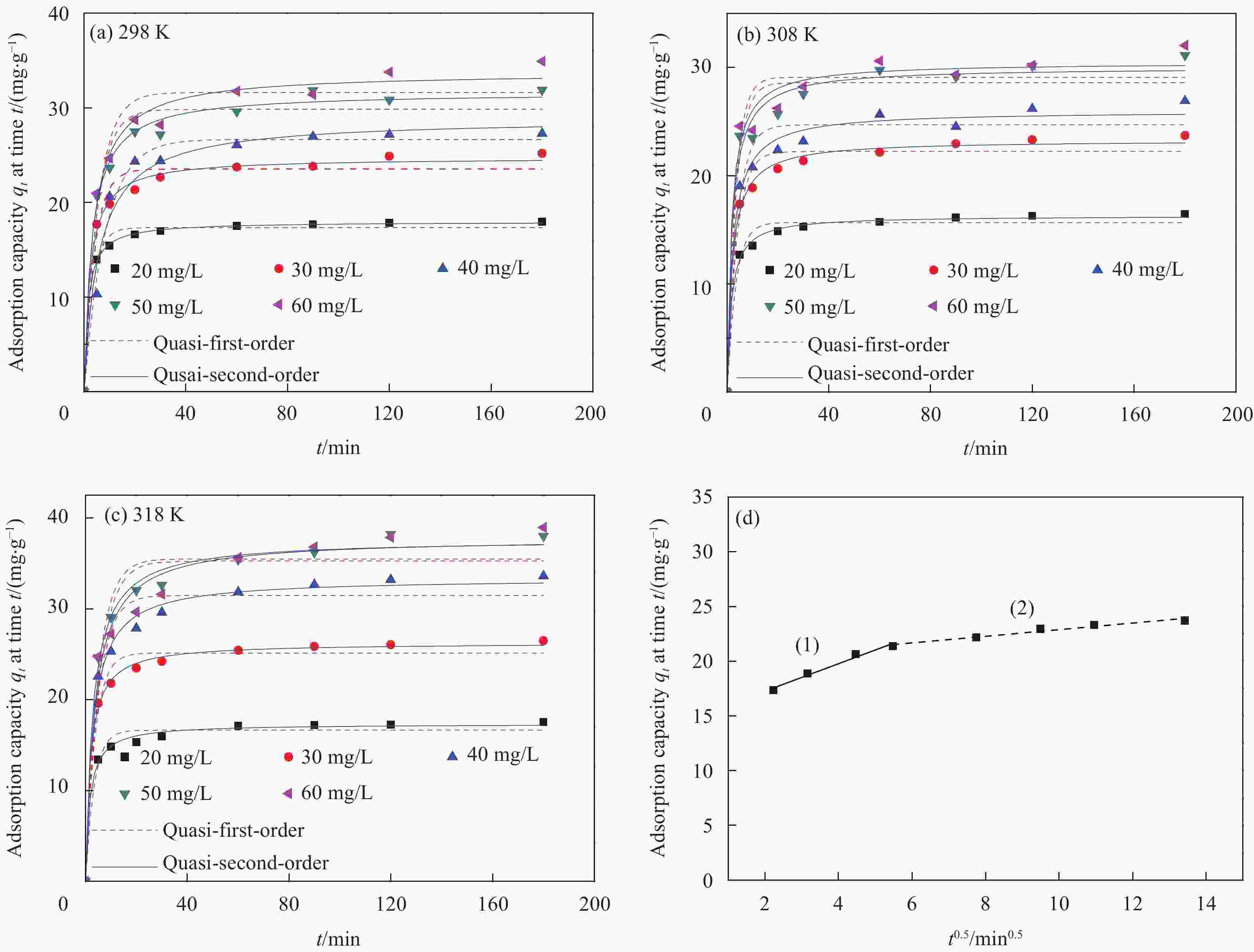
表 1 Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2吸附OFLX的吸附动力学拟合结果
Table 1. Fitting results of adsorption kinetics of OFLX by Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2
Temperature/K qe,exp/ (mg·g−1) Quasi-first-order kinetic model Quasi-second-order kinetic model qe,cal/(mg·g−1) K1/min−1 R2 qe,cal/(mg·g−1) K2/min−1 R2 298 25.17 23.54 −0.2419 0.9691 24.74 0.01784 0.9943 308 23.72 22.24 −0.2638 0.9712 23.29 0.02166 0.9946 318 26.49 25.15 −0.2702 0.9792 26.26 0.02039 0.9976 Notes: qe,exp—Experimental amount of OFLX removed per unit mass of adsorbent; K1, K2—Quasi-first-order kinetic constant and quasi-second-order kinetic constant; qe,cal—Calculation amount of OFLX removed per unit mass of adsorbent. 表 2 Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2吸附OFLX的吸附等温线模型的拟合结果
Table 2. Fitting results of adsorption isotherms models of OFLX by Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2
Temperature/K Langmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) b/(L·mg−1) R2 Kf/(mg·g−1) n/(mg·g−1) R2 298 33.98 0.7189 0.9651 16.81 4.430 0.9899 308 35.47 0.3340 0.9944 13.72 3.650 0.9941 318 46.01 0.3322 0.9961 16.51 3.226 0.9735 Notes: qm—Langmuir adsorption maximum; b—Langmuir coefficient of distribution of the adsorption; Kf—Freundlich coefficient of distribution of the adsorption; n—Freundlich isotherm constant. 表 3 Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2的D-R等温吸附模型的拟合结果
Table 3. Fitting results of D-R isotherm adsorption model of Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2
Temperature/K qm/(mg·g−1) k/10−7(mol2·kJ−2) E/(kJ·mol−1) R2 298 41.89 0.462 3.29 0.8089 308 62.43 0.102 7.00 0.9280 318 87.18 1.050 2.18 0.9973 Notes: qm—D-R adsorption maximum; k—Adsorption energy constant; E—Free energy of adsorption. 表 4 Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2吸附OFLX的热力学参数
Table 4. Thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of OFLX by Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2
Temperature/K lnKd ΔGΘ/(kJ·mol−1) ΔHΘ/(kJ·mol−1) ΔSΘ/(J·mol−1·K−1) 298 4.817 −11.93 −43.8 −107.83 308 3.675 −9.41 318 3.411 −9.02 Notes: Kd—Adsorption thermodynamic equilibrium constant; ΔGΘ—Gibbs free energy variation of the adsorption process; ΔHΘ—Enthalpy change of the adsorption process; ΔSΘ—Entropy change of theadsorption process. 表 5 不同吸附材料对OFLX吸附性能比较
Table 5. Comparison of the adsorption performance of OFLX by different adsorption materials
Adsorption material BET/(m2·g−1) Balance time/min qe/(mg·g−1) Reference Magnetic biochar 254 1440 22.00 [32] Zrconium-based MOFs 519 120 35.46 [33] Shell polysacchar/biochar composites 141 1300 6.64 [34] MCM41 1026 120 39.20 [35] Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4@SiO2-CeO2 169 120 30.38 This report Notes: BET—Specific surface area; MOFs—Metal organic framework; MCM41—Ordered mesoporous molecular sieve. -
[1] LIANG R, LUO S, JING F, et al. A simple strategy for fabrication of Pd@MIL-100(Fe) nanocomposite as a visible-light-driven photocatalyst for the treatment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs)[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2015,176:240-248. [2] PERES M S, MANIERO M G, GUIMARAES J R. Photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin and evaluation of the residual antimicrobial activity[J]. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences,2015,14(3):556-562. [3] SHE P F, LUO Z, CHEN L H, et al. Efficacy of levofloxacin against biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with respiratory tract infections in vitro[J]. MicrobiologyOpen,2019,8(5):e00720. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.720 [4] ASHTON D, HILTON M, THOMAS K V. Investigating the environmental transport of human pharmaceuticals to streams in the United Kingdom[J]. Science of the total environment,2004,333(1-3):167-184. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.04.062 [5] YU R B, WU Z C. High adsorption for ofloxacin and reusability by the use of ZIF-8 for wastewater treatment[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2020,308:110494. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110494 [6] SHOKOOHI R, GHOBADI N, GODINI K, et al. Antibiotic detection in a hospital wastewater and comparison of their removal rate by activated sludge and earthworm-based vermifilteration: Environmental risk assessment[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2020,134:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.10.020 [7] DING J Q, HE Y, WANG P C, et al. Performances of simultaneous removal of trace-level ofloxacin and sulfamethazine by different ozonation-based treatments[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,277:124120. [8] CHEN D N, XIE Z J, ZENG Y Q, et al. Accelerated photocatalytic degradation of quinolone antibiotics over Z-scheme MoO3/g-C3N4 heterostructure by peroxydisulfate under visible light irradiation: Mechanism, kinetic and products[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers,2019,104:250-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2019.08.007 [9] NASUHOGLU D, RODAYAN A, BERK D, et al. Removal of the antibiotic levofloxacin (LEVO) in water by ozonation and TiO2 photocatalysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,189:41-48. [10] FENG C S, CHEN C, ZHU Y, et al. Degradation of ofloxacin using peroxymonosulfate activated by nitrogen-rich graphitized carbon microspheres: Structure and performance controllable study[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2021,99:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.06.003 [11] MA P L, LIU Q J, LIU P L, et al. Green synthesis of Fe/Cu oxides composite particles stabilized by pine needle extract and investigation of their adsorption activity for norfloxacin and ofloxacin[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2020,217:1-18. [12] 孙宏伟, 陈建峰. 我国化工过程强化技术理论与应用研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2011, 30(1):1-15.SUN H W, CHEN J F. Advances in fundamental study and application of chemical process intensification technology in China[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2011,30(1):1-15(in Chinese). [13] ZHENG C F, ZHENG H L, WANG Y J, et al. Modified magnetic chitosan microparticles as novel superior adsorbents with huge “force field” for capturing food dyes[J]. Jour-nal of hazardous materials,2019,367:492-503. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.120 [14] YUAN Y, WU Y, WANG H, et al. Simultaneous enrichment and determination of cadmium and mercury ions using magnetic PAMAM dendrimers as the adsorbents for magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of hazardous materials,2020,386:121658. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121658 [15] ROTO R, YUSRAN Y, KUNCAKA A. Magnetic adsorbent of Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiol group for chloroauric ion adsorption[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,377:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.099 [16] BANIAMERIAN H, TEIMOORI M, SABERI M. Fe2O3/TiO2/Activated carbon nanocomposite with synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology,2021,44(1):130-139. [17] WANG R, YU J, HAO Q. Activated carbon/Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 composites: Facile synthesis, magnetic performance and their potential application for the removal of methylene blue from water[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2018,132:215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2018.01.027 [18] 姜德彬, 余静, 叶芝祥, 等. 磁性纳米复合物对水中亚甲基蓝的吸附及其机理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(6):1763-1772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.06.025JIANG D B, YU J, YE Z X, et al. Adsorption and mechanism of methylene blue from water by magnetic nanocomposites[J]. China Environmental Science,2016,36(6):1763-1772(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.06.025 [19] LV Z J, ZHONG Q, OU M. Utilizing peroxide as precursor for the synthesis of CeO2/ZnO composite oxide with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,376:91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.280 [20] 李小军, 李绪翠. 紫外分光光度法测定氧氟沙星片的含量[J]. 药品评价, 2005, 04(2):63-64.LI X J, LI X C. Content determination of ofloxacin in tablets by UV-spectrohotometry[J]. Drug evaluation,2005,04(2):63-64(in Chinese). [21] JIN B F, WEI Y C, ZHAO Z, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous CeO2/Al2O3-supported Au nanoparticle catalysts: Effects of CeO2 nanolayers on catalytic activity in soot oxidation[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2017,38(9):1629-1641. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(17)62798-0 [22] HAN Z T, SANI B, MROZIK W, et al. Magnetite impregnation effects on the sorbent properties of activated carbons and biochars[J]. Water research,2015,70:394-403. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.12.016 [23] 奚丽荷, 江海军, 朱忠其, 等. CeO2掺杂TiO2光催化剂的性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2007, 7:1146-1148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2007.07.029XI L H, JIANG H J, ZHU Z Q, et al. Study on properties of CeO2-doped TiO2[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2007,7:1146-1148(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2007.07.029 [24] BOKARE A, CHOI W. Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes[J]. Journal of hazardous materials,2014,275:121-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054 [25] WU Y, LUO H, WANG H. Adsorption properties of modified sawdust for conge red removal from wastewater[J]. Huanjing Kexue Xuebao/Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2014,34(7):1680-1688. [26] 马锋锋, 赵保卫, 刁静茹. 小麦秸秆生物炭对水中Cd2+的吸附特性研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(2):551-559.MA F F, ZHAO B W, DIAO J R. Adsorptive characteristics of cadmium onto biochar produced from pyrolysis of wheat straw in aqueous solution[J]. China Environmental Science,2017,37(2):551-559(in Chinese). [27] 苏龙, 张海波, 程红艳, 等. 木耳菌糠生物炭对阳离子染料的吸附性能研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(2):693-703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.02.023SU L, ZHANG H B, CHENG H Y, et al. Study on adsorption properties of biochar derived from spent Auricularia auricula substrate for cationic dyes[J]. China Environmental Science,2021,41(2):693-703(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.02.023 [28] ZULFIKAR M A, AFRITA S, WAHYUNINGRUM D, et al. Preparation of Fe3O4-chitosan hybrid nano-particles used for humic acid adsorption[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management,2016,6:64-75. [29] PATHAK P D, MANDAVGANE S A. Preparation and characterization of raw and carbon from banana peel by microwave activation: application in citric acid adsorption[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2015,3(4):2435-2447. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2015.08.023 [30] SHEN S B, PAN T L, LIU X Q, et al. Adsorption of Rh (III) complexes from chloride solutions obtained by leaching chlorinated spent automotive catalysts on ion-exchange resin Diaion WA21J[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,179(1-3):104-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.064 [31] REZA R, AHMARUZZAMAN M, SIL A, et al. Comparative adsorption behavior of ibuprofen and clofibric acid onto microwave assisted activated bamboo waste[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2014,53(22):9331-9339. [32] 赵华轩, 郎印海. 磁性生物炭对水中CIP和OFL的吸附行为和机制[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(8):3729-3735.ZHAO H X, LANG Y H. Behaviors and mechanisms of CIP and OFL adsorption by magnetic biochar[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(8):3729-3735(in Chinese). [33] 崔颖, 孙国峰, 任苏瑜, 等. 锆基MOF材料用于水中抗生素的吸附研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(3):103-108.CUI Y, SUN G F, REN S Y, et al. Zrconium-based MOFs for antibiotics adsorption in water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2019,42(3):103-108(in Chinese). [34] ZHU C, LANG Y, LIU B, et al. Ofloxacin adsorption on chitosan/biochar composite: Kinetics, isotherms, and effects of solution chemistry[J]. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds,2018:1-11. [35] 李鹤然, 宋立娜, 胡贝贝, 等. 介孔硅材料MCM41对盐酸左氧氟沙星的吸附行为[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2017, 34(4):285-289+296.LI H R, SONG L N, HU B B, et al. Experimental and kinetic studies on levofloxacin hydrochloride adsorption by MCM41[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,2017,34(4):285-289+296(in Chinese). [36] 王新欣, 孟昭福, 刘欣, 等. BS-18两性修饰膨润土对四环素和诺氟沙星复合污染的吸附[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 3:1-11.WANG X X, MENG Z F, LIU X, et al. Adsorption of BS-18 amphoterically modified bentonite to tetracycline and norfloxacin combined pollutants[J]. Environmental Science,2020,3:1-11(in Chinese). [37] 鲁浩, 杜姣姣, 肖剑, 等. 霍州和兴和褐煤的热溶解聚及其有机氧的赋存形态[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(8):897-904. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.08.001LU H, DU J J, XIAO J, et al. Thermal dissolution of Huozhou and Xinghe lignites and the occurrence forms of organic oxygen in them[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2018,46(8):897-904(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2018.08.001 [38] 李忠, 文春梅, 郑华艳, 等. 载体表面性质对Cu2O/AC催化剂结构和活性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(1):145-152.LI Z, WEN C M, ZHENG H Y, et al. Effects of the active carbon surface properties on the structure and catalytic activity of Cu2O/AC catalyst[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2010,31(1):145-152(in Chinese). [39] CHIANG Y C, LEE C Y, LEE H C. Surface chemistry of polyacrylonitrile-and rayon-based activated carbon fibers after post-heat treatment[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2007,101(1):199-210. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2006.03.007 [40] WANG T Q, JIANG Z F, AN T C, et al. Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic bacterial inactivation by ultrathin carbon-coated magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles[J]. Environmental science & technology,2018,52(8):4774-4784. [41] 胡强, 熊志波, 白鹏, 等. 铈钛掺杂促进铁氧化物低温SCR脱硝性能的机理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(8):2304-2310. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.08.009HU Q, XIONG Z B, BAI P, et al. Promotional mechanism of cerium oxide and titanium oxide doping on the low-temperature NH3-SCR activity of iron oxide[J]. China Environmental Science,2016,36(8):2304-2310(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.08.009 -





 下载:
下载: