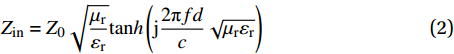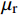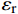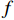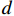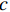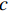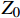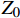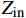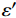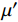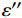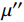Preparation and microwave absorption properties of porous charcoal/ Fe3O4 composites
-
摘要: 为了改善Fe3O4吸波材料密度大和吸波频带窄等问题,以马尾松木材为原料,采用去木质素及高温原位生长法制备了多孔木炭(WPC)/Fe3O4复合材料,通过变化碳化温度来调控复合材料的电磁特性与微波吸收性能。微观形貌、结构和电磁参数等结果表明:WPC/Fe3O4复合材料保有木材天然的三维孔结构,Fe3O4粒子均匀负载于多孔木炭的炭壁与孔道中;升高碳化温度(630~690℃)可增强材料的电导率与电磁衰减能力,但温度过高会引起材料阻抗失配。670℃制备的复合材料微波衰减能力强且阻抗匹配特性好,最小反射损耗为−49.5 dB,有效吸收频宽为6.24 GHz(9.04~15.28 GHz),主要衰减机制归结于复合材料的电导损耗、极化弛豫及介电与磁损耗的协同作用。WPC/Fe3O4复合材料优异的吸波性能在电磁波吸收领域具有良好前景,可促进速生木材的高值化与功能化应用。Abstract: In order to improve the shortages of big density and narrow absorption bandwidth of Fe3O4 absorbing material, in this study, wood-based porous charcoal (WPC)/Fe3O4 composites were prepared from fast-growing masson pine wood by delignification and high temperature in-situ growth methods. The microwave absorption properties of the composites were regulated by tailoring the carbonization temperature. The results of micromorphology, structure and electromagnetic parameters show that, the WPC/Fe3O4 composites retain the natural three-dimensional porous structure of wood with Fe3O4 particles evenly loaded in the carbon walls and channels of WPC. The increment of carbonization temperature (630-690℃) can enhance the electric conductivity and microwave attenuation capacity of the composites, but too high temperature causes the impedance mismatching. The composite prepared at 670℃ exhibits excellent microwave absorption performance with a minimum reflection loss of −49.5 dB and an effective absorption bandwidth of 6.24 GHz (9.04-15.28 GHz), due to its strong attenuation capability and good impedance matching characteristics. The main dissipation mechanism includes conductive loss, polarization relaxation, and synergistic effect of dielectric and magnetic loss. The strong reflection loss and wide effective absorption bandwidth of WPC/Fe3O4 composite suggest a good prospect in electromagnetic absorption field, which can promote the value-added and functional application of fast-growing wood.
-
Keywords:
- pine wood /
- Fe3O4 /
- porous structure /
- impedance matching /
- wave absorption performance /
- attenuation mechanism
-
在无线通信和国防隐身领域,日益突出的电磁辐射与干扰对人类身体健康、电子设备正常运转、信息泄露等方面造成了严重威胁[1-2]。吸波材料因能大幅吸收或衰减投射到其表面的电磁波能量而引起了广泛关注。开发高性能(宽、薄、轻、强)、可持续的吸波材料是当下解决电磁污染的关键所在,也是研究热点[3-5]。
铁氧体作为一种典型的磁损耗型吸波材料,不仅具有高的磁导率和矫顽力,同时具备吸收强、成本低、制备简单等优点[6-7]。其中,Fe3O4是目前研究最多也最成熟的磁性氧化物,具有高表面活性、高饱和磁化强度及良好的磁损耗,但其单独使用时存在密度大、阻抗匹配特性差、吸波频带窄等不足[8-9]。通过与导电材料(如石墨烯、多孔碳、碳纳米管、导电高分子等)复合,既能促进缺陷的产生,增强极化效应,改善单组分的阻抗匹配特性,也可以实现电、磁损耗机制的协同效应[10-12]。例如,通过化学气相沉积法在碳纤维表面原位生长碳纳米管(CNTs),后热沉积Fe3O4纳米颗粒制备出的Fe3O4/CNTs@碳纤维(Cf)复合材料,其反射损耗在C波段可达−43.02 dB[13]。
木材具有以微米级轴向管胞与横向纹孔构成的三维贯穿网络结构,比表面积大,孔隙丰富。碳化木材中的孔径都远小于2~18 GHz电磁波的波长(2.5~75 cm),故电磁波能大量进入木炭内部并迅速发生衰减[14]。它独特的通直孔道亦有助于满足材料的阻抗匹配特性,降低材料密度,拓展电磁波在材料内的散射与反射路径,是一种优良的磁损耗吸波剂(如Fe3O4)载体。
木材细胞壁的主要成分是纤维素、半纤维素和木质素。研究表明,木材去木质素处理可以大量暴露亲水官能团并丰富木材细胞壁内的纳米孔隙[15-16],因而,有助于铁氧体溶液快速的深入木材细胞壁中。本文通过脱除马尾松木材中的木质素,采用简单的浸渍和高温原位生长法获得多孔木炭(WPC)/Fe3O4复合材料。研究了不同碳化温度对复合材料结构、微观形貌、电磁参数及吸波性能的影响。制备的WPC670/Fe3O4复合材料展现出优异的微波吸收性能(最小反射损耗RL=−49.5 dB,有效频宽为6.24 GHz),是一种有潜力的轻质吸波材料。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
马尾松木材(Pinus massoniana Lamb.)购自广西柳州,初始含水率为10%~15%;材料制备过程中所用主要原料与试剂有:九水合硝酸铁(Fe(NO3)3·9H2O),分析纯,购于广东西陇化工股份有限公司;无水乙醇,分析纯,购于天津市恒兴化学试剂制造有限公司及蒸馏水。
1.2 WPC/Fe3O4复合材料制备
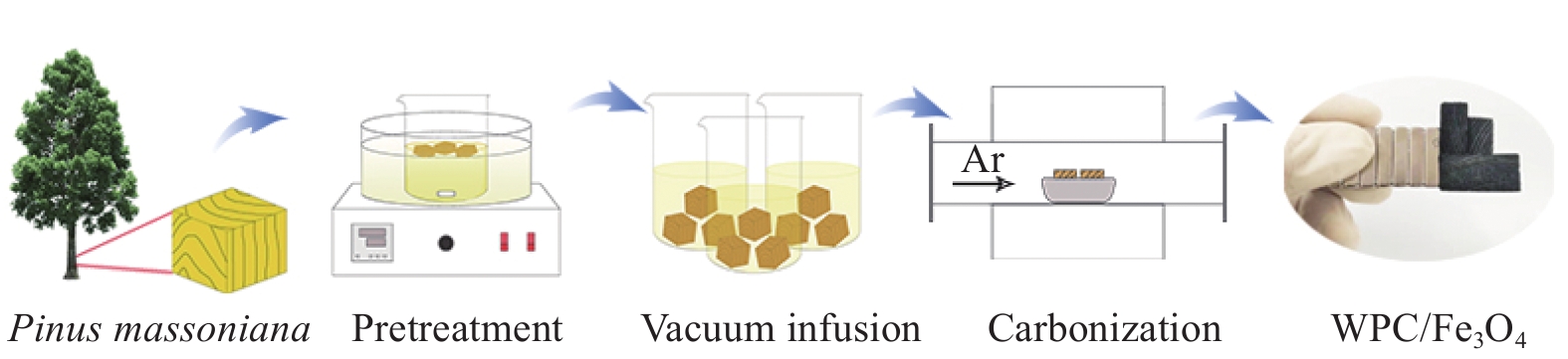
将马尾松木块置入酸性NaClO2溶液(5wt%)中,75℃处理5.5 h后用蒸馏水清洗多次至pH≈7,接着冷冻干燥。取500 mg冻干木块放入含有1.45 mmol的Fe(NO3)3·9H2O溶液中浸泡24 h,取出,冷冻干燥48 h。冻干后的样品置于刚玉舟内,并在充满Ar气的管式炉中以5℃/min的速率升温至预设温度(630℃、650℃、670℃、690℃)并保温3 h,然后以相同速率降至室温,得到不同温度条件下的多孔木炭/铁氧体复合材料,标记为WPCx/Fe3O4(x代表碳化温度,例如WPC630/Fe3O4表示样品的碳化温度为630℃),具体制备过程见图1。对照样(Control)是将脱木素冻干木块直接放在充满Ar气的管式炉中升温至670℃并保温3 h获得。
1.3 材料表征
采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,Zeiss Sigma 300,德国卡尔蔡司股份有限公司)在12.5 kV加速电压下观察样品的微观形貌,并利用EDS进行区域元素定性分析。使用X射线衍射仪(XRD,Bruker D8 Advance,德国布鲁克股份公司)表征样品的元素组成和晶型结构。测试时,将粉末样品置于玻璃载片上压制均匀,利用Cu靶Kα射线作为辐射源,扫描速度为5°/min,步距为0.02°,管电压为40 kV,管电流为40 mA。采用X射线光电子能谱(XPS,Thermo Scientific K-Alpha,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司)与热重分析仪(TG,Pyris 6,美国珀金埃尔默股份有限公司)表征样品元素状态和化学组成。使用双电测四探针测试仪(RTS-9,中国苏州晶格电子有限公司)测试样品的电阻率。
1.4 电磁参数测试
利用矢量网络分析仪(AV3672B-S,中国电子科技集团公司)获取样品测试环在2~18 GHz频率范围内的相对复介电常数实部(ε')、虚部(ε'')及复磁导率实部(μ')、虚部(μ'')。测试采用同轴法且每个样品均重复测试2~3次。测试之前,先将WPCx/Fe3O4样品与一定比例的熔融态石蜡混合均匀(质量比为15∶85),并在特制模具中压制出内径与外径分别为3.04 mm和7.00 mm的测试环。根据测得的电磁参数,利用传输线理论对电磁波吸收性能进行评价。主要评价指标是反射损耗(RL),可由以下公式推导[17-18]:
RL=20lg|Zin−Z0||Zin+Z0| (1) Zin=Z0√μrεrtanh(j2πfdc√μrεr) (2) μr=μ′−jμ″ (3) {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{r}}={\varepsilon }{{'}}-{\rm{j}}\varepsilon {''} (4) 式中:RL为反射损耗(dB);
{\mu }_{\mathrm{r}} 为复磁导率;{\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{r}} 为复介电常数;f 为电磁波频率(GHz);d 为松木炭厚度(mm);c 为光速,c =(299792.50±0.10) km/s;{Z}_{0} 为自由空间阻抗,{Z}_{0} =376.73031 Ω;{Z}_{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} 为吸收体的输入阻抗(Ω);{\varepsilon }{{'}} 、\mu {'} 与{\varepsilon }{{''}} 、\mu {''} 分别对应复介电常数、复磁导率的实部与虚部。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的结构与微观形貌
WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的XRD图谱如图2(a)所示。可知,所有样品在2θ=30.1°、35.5°、43.1°、53.6°、57.0°、62.7°处均可观察到较强衍射峰,它们分别对应Fe3O4的(220)、(311)、(400)、(422)、(511)、(400)晶面(JCPDS 74-0748),说明Fe3O4成功载入多孔木炭中。WPC690/Fe3O4的Fe3O4衍射峰偏弱,并且在2θ=44.7°处出现了关于Fe的(100)晶面衍射峰(JCPDS 50-1275)。这可能由于在较高温度下,部分Fe3+被C还原成单质Fe。此外,WPC690/Fe3O4样品在2θ=26°附近出现了石墨碳尖峰,而其他三个样品没有,表明在Fe元素的催化作用下,木炭在较低温度下(690℃)就能由无定形态转变成石墨化碳结构[19]。石墨碳和铁单质峰的出现意味着WPC690/Fe3O4拥有较其他样品强的导电性,而强的导电性往往不利于材料与空气的阻抗匹配[20]。
使用四探针测试仪测得WPC/Fe3O4-石蜡复合材料(样品含量为15wt%)的电导率,结果如图2(b)所示。随着碳化温度的增加,复合材料的电导率呈现增大趋势。当温度从630℃增至670℃时,样品的电导率增长缓慢(10−3~5.36×10−2 S·m−1)。当温度升至690℃时,样品的电导率显著提高至2.25 S·m−1,较670℃样品增大了41倍,这归因于WPC690/Fe3O4样品中石墨化碳的形成。
在空气介质中对WPC670/Fe3O4样品进行TG测试,结果如图2(c)所示。在所测温度范围内,WPC670/Fe3O4的TG曲线可分为两个阶段:室温~100℃为第一阶段,样品轻微的质量损失率(4.0wt%),主要源自水分的蒸发;第二阶段主要发生在350~550℃之间,此阶段样品质量损失率达79.9wt%,归因于样品中主要元素C的氧化与降解。此后样品的质量几乎无变化,最终固体残余量为16.1wt%,残余固体成分为Fe2O3。碳基复合材料中,碳的相对含量主要由氧化降解过程决定,故可计算出样品中碳相对含量为80.4%。
以污染碳(电子结合能为284.8 eV)为内标,得到WPCx/Fe3O4复合材料的XPS全谱图,如图3(a)所示。WPC670 /Fe3O4主要由C、O、Fe三种元素组成,其原子分数分别为85.83at%、11.36at%、2.81at%。图3(b)~3(d)是采用高斯-洛伦兹函数对样品的C1s、O1s和Fe2p进行高分辨谱分峰拟合得到的结果。图3(b)中,C1s能谱主要分为284.8 eV、286.6 eV、289.9 eV三个峰,分别对应于C−C/C=C、C−O和O=C−O键[21]。图3(c)中,O1s能谱峰可分成530.5 eV (Fe−O和H−O)和533.3 eV(表面吸附水)两个峰。在Fe2p能谱中(图3(d)),两个分裂峰出现在711.0 eV和724.7 eV处,分别对应于Fe2p3/2与Fe2p1/2的结合能,进一步证实了Fe3O4的存在[9],与711.0 eV和724.7 eV处,分别对应于Fe2p3/2与Fe2p1/2 的结果相符。
采用SEM对WPC670/Fe3O4复合材料进行微观形貌观察,结果如图4所示。图4(a)中,WPC670/Fe3O4完好地保留了木材的通直孔结构(孔径约10~20 μm),这有利于电磁波在材料表面的入射与在材料内部的多重反射[11]。图4(b)和图4(c)中,可观察到样品的碳质管壁上附着了大量的Fe3O4粒子,因此WPC670/Fe3O4形成了比WPC670更丰富的异质界面(如WPC-Fe3O4、Fe3O4-空气界面等),这有利于增强复合材料的界面极化弛豫。从WPC670/Fe3O4的EDS元素分布图可知(图4(d)~4(f)),Fe元素均匀分布于多孔木炭碳壁与孔道中,O元素主要分布在多孔木炭碳壁中,少量分布在孔道中。
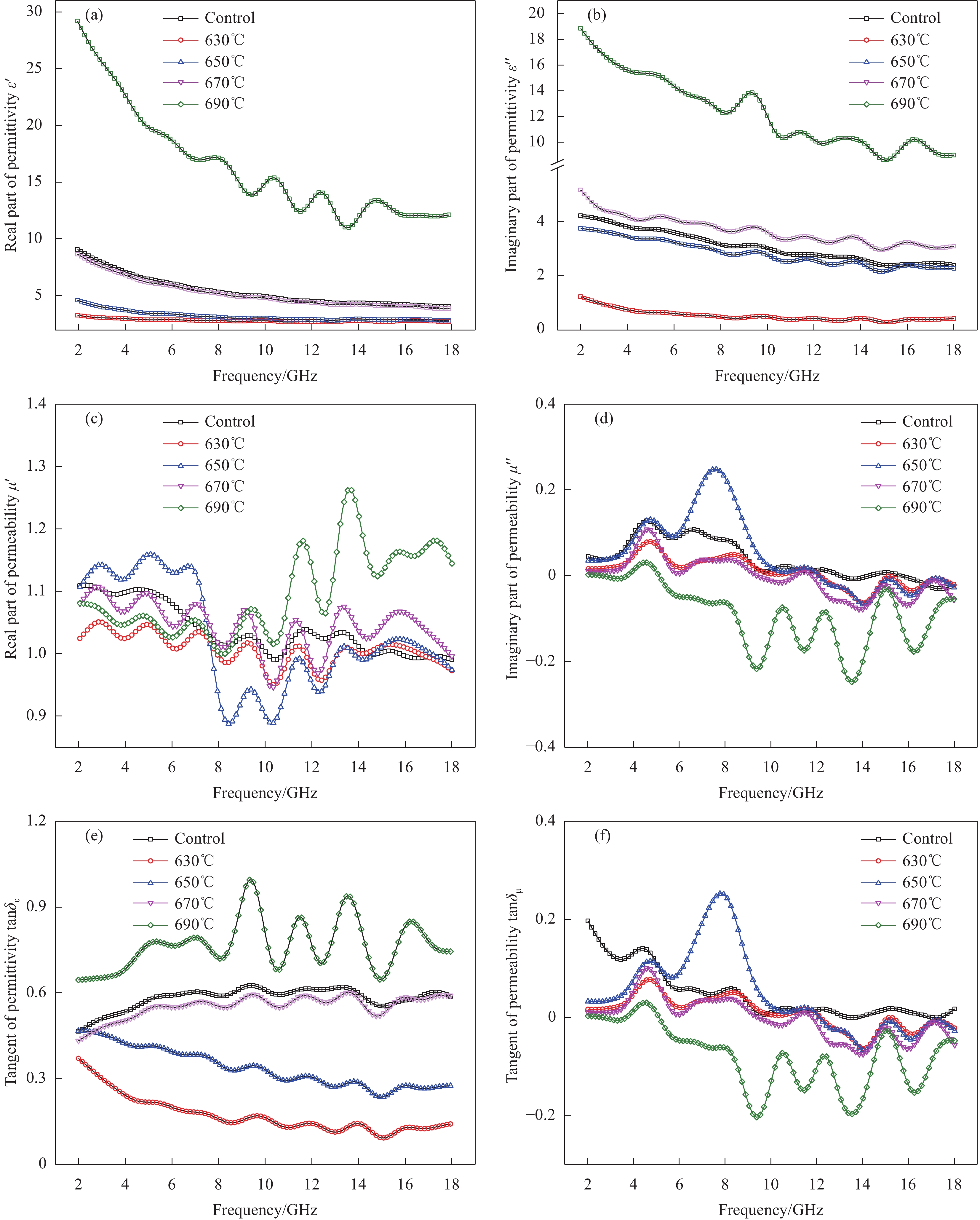
2.2 WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的电磁参数
材料与电磁场的作用可通过相对复介电常数(εr)和相对复磁导率(μr)两个参数来描述。利用矢量网络分析仪测定WPCx/Fe3O4在2~18 GHz频段内的电磁参数,得到其复介电常数和复磁导率随频率的变化曲线,如图5所示。由图5(a)和图5(b)可知,WPCx/Fe3O4的复介电常数实部(ε')、虚部(ε'')均随频率增加呈现下降趋势。以WPC670/Fe3O4为例,当频率从2 GHz增加至18 GHz时,它的复介电常数实部从8.63降至3.82,虚部则从3.75降至2.26。这是因感应电荷在外加电磁场频率增加时出现滞后所引起的频散现象[22]。WPCx/Fe3O4的复介电常数实部、虚部均随温度增加呈逐渐增大趋势。WPC630/Fe3O4的ε'与ε''值分别为2.69~3.23与0.39~1.20,而WPC690/Fe3O4的ε'与ε''值均远大于其他样品,分别为12.07~29.17与9.00~18.86。这表明升高碳化温度可增强WPCx/Fe3O4对电磁波的介电损耗作用。与对照样(WPC670)相比,WPC670/Fe3O4的ε''值稍高,这可能是由于Fe元素的催化作用增强了WPC670/Fe3O4的电导率。WPCx/Fe3O4复合材料在宽频内的共振峰来源于多重极化弛豫损耗[23-24]。
图5(c)和图5(d)中,除WPC690/Fe3O4外,其他样品的复磁导率实部与虚部随频率增大有小幅度的下降,其范围分别为1.0~1.1、−0.05~0.25。WPC690/Fe3O4的μ'值随频率增加呈波动增大,这可能由于少量单质铁的存在提高了磁导率和铁磁共振。μ''值在部分频段为负值,这可以根据麦克斯韦方程理论解释:磁场可由交变电场向外辐射的电磁诱导产生,当诱导产生的磁场超过材料中磁粒的损耗能力时,会导致多余的磁场被辐射出来,于是产生负的磁导率虚部[25-26]。磁导率曲线中的波动主要源自材料对电磁波的自然共振和交换共振损耗[27-28]。与对照样相比,WPC670/Fe3O4的磁导率实部与虚部呈现更明显的共振峰,表明Fe3O4的引入增强了复合材料的磁损耗。
图5(e)和图5(f)分别为WPCx/Fe3O4的介电损耗因子和磁损耗因子随频率的变化曲线。图5(e)中,随碳化温度的升高,WPCx/Fe3O4的介电损耗因子逐渐增大,这是由于高温样品大的电导率引起了介电损耗的增强。以10 GHz为例,WPC630/Fe3O4、WPC650/Fe3O4、WPC670/Fe3O4、WPC690/Fe3O4的介电损耗因子值分别为0.17、0.33、0.58、0.82。图5(f)中,WPCx/Fe3O4的磁损耗因子变化趋势与磁导率虚部基本一致,除WPC690/Fe3O4外的磁损耗因子差异较小。
2.3 WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的吸波性能
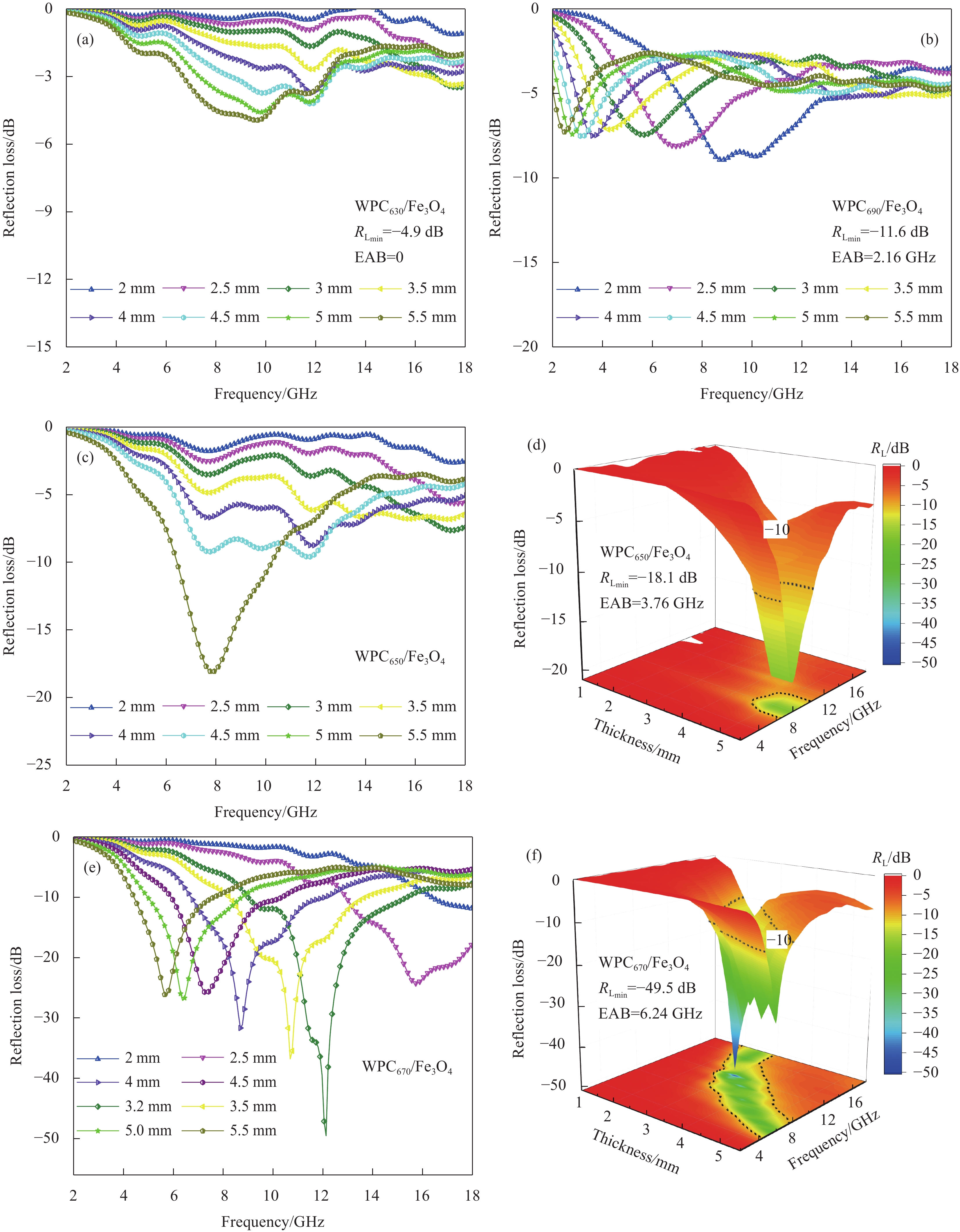
材料的吸波性能主要以RL和RL<−10 dB时对应的有效吸收(EAB)两个指标来评价。根据测得的电磁参数计算WPCx/Fe3O4在不同厚度下的反射损耗值,如图6所示。
碳化温度从630℃升至670℃时,WPCx/Fe3O4的最小反射损耗值从−4.9 dB降至−49.5 dB,吸波性能逐渐增强。图6(a)中,WPC630/Fe3O4在2~5.5 mm厚度范围内的反射损耗峰值均未低于−10 dB,表明它基本不具备吸收电磁波的能力。图6(c)、图6(d)中,WPC650/Fe3O4的吸波性能也较差,仅在匹配厚度为5.5 mm时能够实现有效吸波,它的最低反射损耗值为−18.1 dB,有效吸收频宽为3.76 GHz(6.40~10.16 GHz)。随着温度继续升高,WPC670/Fe3O4的吸波性能出现明显提升,如图6(e)和图6(f)所示。它在厚度为3.2 mm、频率为12.16 GHz处具有最低反射损耗为−49.5 dB,对应有效频宽覆盖了6.24 GHz(9.04~15.28 GHz);当匹配厚度为3.5 mm时,它的最低反射损耗为−36.8 dB,对8.24~13.60 GHz频段电磁波的吸收率亦能达90%以上。而对照样的最小反射损耗为−41.3 dB,有效带宽为5.76 GHz,表明引入Fe3O4能够强化材料对电磁波的吸收。值得注意的是,WPC670/Fe3O4在2.5~5.5 mm之间的反射损耗峰值均低于−20 dB,对4.4~18 GHz(13.60 GHz)频段电磁波的吸收率达99%以上,表现出了对电磁波的高效与宽频吸收。WPC670/Fe3O4的性能在掺量、厚度、反射损耗和有效频宽方面都优于已报道的若干碳基吸波材料(表1)。但是,当碳化温度升高至690℃时,WPC690/Fe3O4的吸波性能显著变差(图6(b)),其最低反射损耗值仅为−11.6 dB。这可能由于材料高的导电性引起了阻抗失配,使入射电磁波在界面被反射而无法深入材料内部发生衰减[29]。
表 1 碳基吸波材料的性能对比Table 1. Comparison of microwave absorption properties of carbon-based materialsSample Filler content/wt% RL
/dBThickness
/mmEffective absorption bandwidth/GHz Ref. PC 70 −42.4 2 1.76 [30] PFSL 50 −43.8 3 5.3 [20] RHPC/Fe 25 −21.8 1.4 5.6 [31] Fe3O4/rGO 50 −45 3 − [32] HPC/Co 30 −52.6 2.8 2.5 [24] Co/C fiber 33 −31 2 3.2 [33] Ni(OH)2/BPC 50 −23.6 6 2 [34] Fe3O4/WPC 50 −51.3 2 5.8 [35] HCF@CZ-CNTs 10 −53.5 2.9 2.64 [36] WPC670/Fe3O4 15 −49.5 3.20 6.24 (9.04-15.28) This work Notes: PC—Porous carbon; PFLS—Pyrolytic functionalized loofah sponge; RHPC—Rice husk-based porous carbon; rGO—Reduced graphene oxide; HPC—Hierarchical porous carbon; C fiber—Carbon fiber; BPC—Biomass porous carbon; HCF@CZ-CNTs—Hierarchical carbon fiber coated with Co/C nano-dodecahedron particles where CNTs were anchored. 2.4 WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的吸波机制分析
材料的阻抗匹配特性与衰减特性是影响其吸波性能的重要因素。图7(a)为WPCx/Fe3O4复合材料在3.2 mm厚度下的归一化阻抗(Z=|Zin/Z0|)。可知,WPCx/Fe3O4的Z值随频率增加呈先增大后减小的趋势。WPC630/Fe3O4和WPC650/Fe3O4的Z峰值分别为3.92、2.32,远远超过1,表明材料与空气阻抗失配。WPC690/Fe3O4的Z值在整个频段内小于0.5,同样阻抗失配。WPC670/Fe3O4与对照样的Z值接近于1,意味着它们的阻抗匹配特性较好[37]。由此可见,碳化温度对材料的阻抗匹配系数影响显著,温度过低或过高均不利于满足WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的阻抗匹配特性。
图7(b)反映了WPCx/Fe3O4复合材料衰减常数(α)随频率的变化关系。可知,WPCx/Fe3O4的衰减常数随频率增加呈增大趋势,且温度越高,衰减常数越大。例如,在10 GHz处,WPC630/Fe3O4、WPC650/Fe3O4、WPC670/Fe3O4和WPC690/Fe3O4的衰减常数分别约29、60、122和257。可见,升高碳化温度可显著增强WPCx/Fe3O4复合材料对电磁波的衰减能力。WPC690/Fe3O4虽然有最强的电磁波衰减能力,但由于阻抗匹配特性差,造成大部分电磁波在界面发生直接反射,因此未能实现对电磁波的高效吸收。WPC670/Fe3O4不仅有良好的阻抗匹配特性且对电磁波的衰减能力强,故展现出最优的吸波性能。
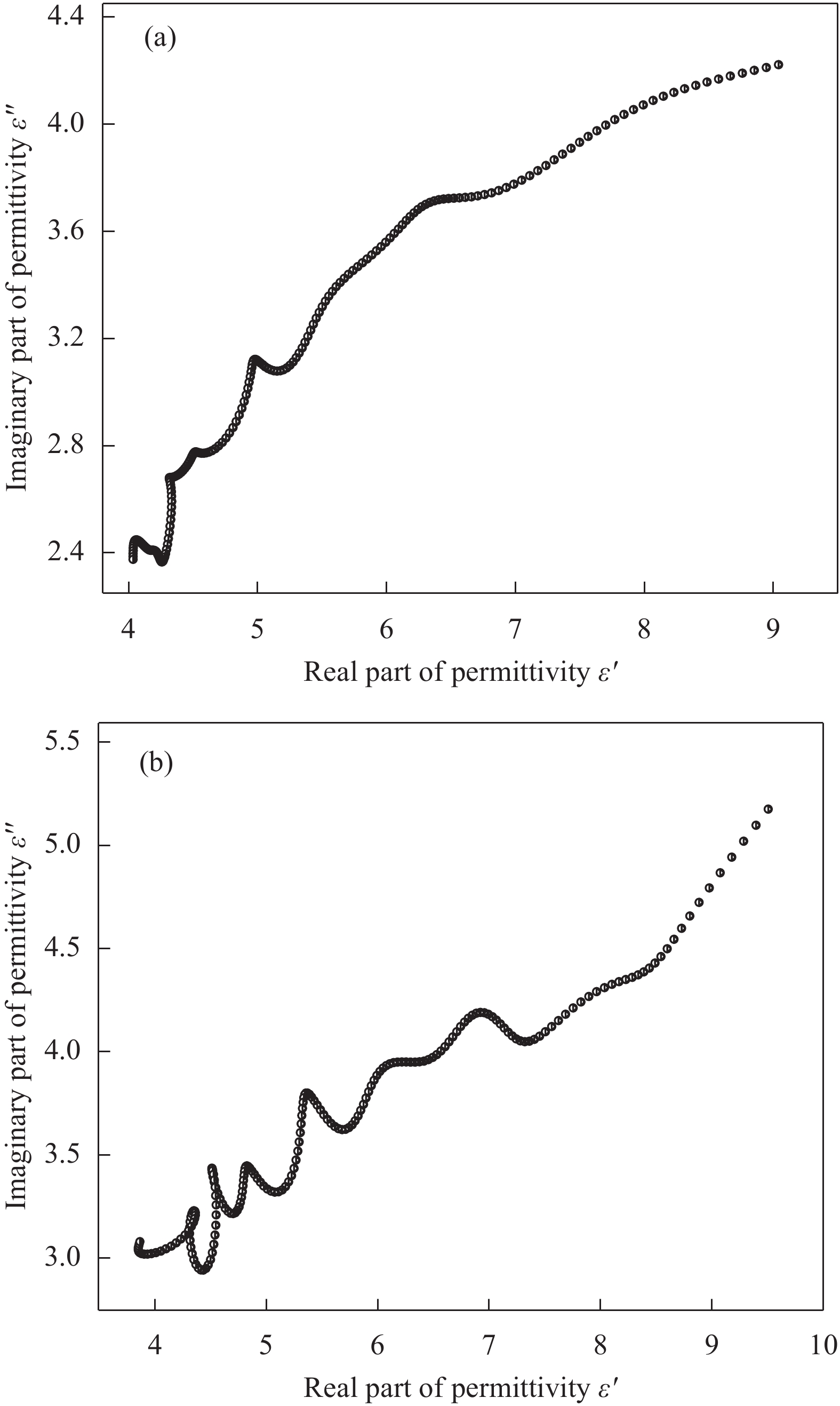
碳/磁复合材料的电磁衰减能力主要与介电损耗与磁损耗有关。介电损耗主要源于电导损耗和极化弛豫,而2~18 GHz频段内的极化弛豫衰减机制包括界面极化与偶极子极化,损耗机制可由德拜弛豫方程解释[38-39]。以介电常数实部为横坐标、虚部为纵坐标,绘制Cole-Cole半圆曲线,如图8所示。图中,曲线半圆代表极化损耗,而长直线代表电导损耗[40]。WPCx/Fe3O4与对照样中都观察到了长直线和多个半圆,说明电导损耗和极化损耗为所制备材料的主要吸波损耗机制。极化损耗主要源于材料缺陷处不均匀的电荷分布导致的偶极子极化和界面处电子聚集引起的界面极化。与对照样相比,WPC670/Fe3O4中观察到更多半圆弧,这可能由于磁性粒子的引入使复合材料增加了更多的异质界面与缺陷(如C-Fe3O4、Fe3O4-石蜡、Fe3O4-空气等),因而展现出更强的极化弛豫过程。
材料的磁损耗通常包括涡流损耗、共振损耗、磁滞损耗和畴壁共振等[41]。一般来说,磁滞损耗出现在弱磁场中,畴壁共振仅出现在兆赫兹低频率范围内,因此在本研究中不予考虑。为进一步研究WPCx/Fe3O4的磁损耗特性,引入涡流系数C0(C0=μ''(μ')−2f−1)。当C0是一个常数则表示材料的磁损耗机制主要为涡流损耗[42]。如图9(a)所示,在2~18 GHz内,WPCx/Fe3O4的C0值随频率波动较大,出现多个共振峰,表明涡流损耗不是主要磁损耗机制。WPCx/Fe3O4的磁损耗可能是由共振损耗引起,即源于低频率下的自然共振与高频率下的交换共振[9]。
图9(b)中反映了WPC670/Fe3O4的反射损耗与λ/4对应厚度随频率的变化关系。可以看出,随着厚度的增加,WPC670/Fe3O4的反射损耗峰逐渐向低频移动。同时,RL峰值与对应频率下的计算厚度与模拟厚度几乎完全吻合,即符合 1/4波长模型[43]。证实了半波相消理论为WPC670/Fe3O4复合材料的吸波机制之一。
综上所述,WPC/Fe3O4复合材料优异的吸波性能主要归因于以下几个方面:(1) WPC的多孔结构不仅利于电磁波大量进入,也扩展了电磁波在材料内的传输路径;(2) 复合材料中碳框架可提供较强的电导损耗,磁性Fe3O4粒子可增加自然共振与交换共振损耗,丰富的缺陷与异质界面可促进极化损耗;(3) 碳化温度适中,使WPC670/Fe3O4阻抗匹配和衰减常数之间存在一种平衡,并且有良好的电磁波干涉损耗能力,提高了吸波性能。
3. 结 论
(1)以马尾松木材为原料,采用去木质素及高温原位生长法制备了多孔木炭(WPC)/Fe3O4复合材料。微观形貌和结构结果表明,复合材料保有木材天然的通直三维孔结构,Fe3O4粒子均匀负载于多孔木炭的碳壁与孔道中。
(2) 调节碳化温度可有效调控复合材料的电磁特性与微波吸收性能。升高碳化温度(630~690℃)可增强WPC/Fe3O4复合材料的电导率与微波衰减能力,但温度过高会引起材料阻抗失配。670℃条件下,复合材料阻抗匹配和衰减常数之间达到平衡,有最佳的吸波性能。
(3) WPC670/Fe3O4复合材料的最小反射损耗值为−49.5 dB,有效吸收带宽为6.24 GHz (9.04~15.28 GHz),在2~5.5 mm厚度范围内对电磁波的有效吸波频宽达到13.60 GHz(4.4~18 GHz)。其主要衰减机制可归结于复合材料的电导损耗、极化弛豫及介电与磁损耗的协同作用。
-
表 1 碳基吸波材料的性能对比
Table 1 Comparison of microwave absorption properties of carbon-based materials
Sample Filler content/wt% RL
/dBThickness
/mmEffective absorption bandwidth/GHz Ref. PC 70 −42.4 2 1.76 [30] PFSL 50 −43.8 3 5.3 [20] RHPC/Fe 25 −21.8 1.4 5.6 [31] Fe3O4/rGO 50 −45 3 − [32] HPC/Co 30 −52.6 2.8 2.5 [24] Co/C fiber 33 −31 2 3.2 [33] Ni(OH)2/BPC 50 −23.6 6 2 [34] Fe3O4/WPC 50 −51.3 2 5.8 [35] HCF@CZ-CNTs 10 −53.5 2.9 2.64 [36] WPC670/Fe3O4 15 −49.5 3.20 6.24 (9.04-15.28) This work Notes: PC—Porous carbon; PFLS—Pyrolytic functionalized loofah sponge; RHPC—Rice husk-based porous carbon; rGO—Reduced graphene oxide; HPC—Hierarchical porous carbon; C fiber—Carbon fiber; BPC—Biomass porous carbon; HCF@CZ-CNTs—Hierarchical carbon fiber coated with Co/C nano-dodecahedron particles where CNTs were anchored. -
[1] XU H L, YIN X W, ZHU M, et al. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(7):6332-6341. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b15826
[2] ZHANG N, HUANG Y, LIU X D, et al. High efficiency microwave absorption nanocomposites of multiple-phase core-shell CoNi alloy@C loaded on rGO conducting network[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,115:283-293. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.10.012
[3] LIU P B, GAO S, ZHANG G Z, et al. Hollow engineering to Co@N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(27):2102812. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202102812
[4] ZHANG H X, SHI C, JIA Z R, et al. FeNi nanoparticles embedded reduced graphene/nitrogen-doped carbon composites towards the ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,584:382-394. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.122
[5] LIU X D, HUANG Y, DING L, et al. Synthesis of covalently bonded reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2021,72:93-103. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.09.012
[6] 赵佳, 姚艳青, 杨煊赫, 等. 铁氧体及其复合吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11):2684-2699. ZHAO Jia, YAO Yanqing, YANG Xuanhe, et al. Research progress of ferrite and its composite absorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(11):2684-2699(in Chinese).
[7] HUANG L, LI J J, WANG Z J, et al. Microwave absorption enhancement of porous C@CoFe2O4 nanocomposites derived from eggshell membrane[J]. Carbon,2019,143:507-516. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.11.042
[8] SHAO Y Q, LU W B, CHEN H, et al. Flexible ultra-thin Fe3O4/MnO2 coreshell decorated CNT composite with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,144:111-117. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.015
[9] LIU J L, LIANG H S, WU H J. Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2020,130:105760. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105760
[10] LI J S, XIE Y Z, LU W B, et al. Flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing composite based on 3D rGO-CNT-Fe3O4 ternary films[J]. Carbon,2018,129:76-84. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.11.094
[11] ZHOU X F, ZHANG C H, ZHANG M, et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon foams composites with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,127:105627. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105627
[12] WANG H S, SHI P P, RUI M, et al. The green synthesis rGO/Fe3O4/PANI nanocomposites for enhanced electromagnetic waves absorption[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2020,139:105476. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.105476
[13] 李焕然, 马关胜, 杨智伟, 等. Fe3O4/CNTs@Cf 复合材料的制备及其吸波性能的研究[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(4):4023-4029. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.04.005 LI Huanran, MA Guansheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Preparation of Fe3O4/CNTs@Cf composite material and its microwave absorbing properties[J]. Functional Materials,2021,52(4):4023-4029(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.04.005
[14] XI J B, ZHOU E Z, LIU Y J, et al. Wood based straightway channel structure for high performance microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2017,124:492-498. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.07.088
[15] GUAN H, CHANG Z Y, WANG X Q. Highly compressible wood sponges with a spring-like lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(10):10365-10373. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05763
[16] LI X J, CAO M, PANG X N, et al. Microtubule-based hierarchical porous carbon for lightweight and strong wideband microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2021,9(5):1649-1656. DOI: 10.1039/D0TC04486E
[17] WANG X X, MA T, SHU J C, et al. Confinedly tailoring Fe3O4 clusters-NG to tune electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption with broadened bandwidth[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,332:321-330. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.101
[18] GAO S, ZHANG G Z, WANG Y, et al. MOFs derived magnetic porous carbon microspheres constructed by core-shell Ni@C with high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2021,88:56-65. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2021.02.011
[19] LI X J, HE L L, LI Y S, et al. Catalytic graphite mechanism during CVD diamond film on iron and cobalt alloys in CH4-H2 atmospheres[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2019,360:20-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.12.120
[20] LIU L Y, SHUANG Y, HU H Y, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on loofah sponge derived hierarchically porous carbons[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2019,7(1):1228-1238. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04907
[21] MA F W, MA D, WU G, et al. Construction of 3D nanostructure hierarchical porous graphitic carbons by charge-induced self-assembly and nanocrystal-assisted catalytic graphitization for supercapacitors[J]. Chemical Communications,2016,52(40):6673-6676. DOI: 10.1039/C6CC02147F
[22] 张艳. 生物质碳材料及生物质碳/磁性粒子复合材料的微波吸收性能研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2020. ZHANG Yan. Research on the microwave absorption properties of biomass carbon materials and biomass carbon/magnetic particle composite materials[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2020(in Chinese).
[23] LIU P B, GAO S, WANG Y, et al. Magnetic porous N-doped carbon composites with adjusted composition and porous microstructure for lightweight microwave absorbers[J]. Carbon,2021,173:655-666. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.043
[24] LIU T S, LIU N, GAI L X, et al. Hierarchical carbonaceous composites with dispersed Co species prepared using the inherent nanostructural platform of biomass for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2020,302:110210. DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110210
[25] WANG C, HAN X J, XU P, et al. The electromagnetic property of chemically reduced graphene oxide and its application as microwave absorbing material[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2011,98:072906. DOI: 10.1063/1.3555436
[26] YAN F, ZHANG S, ZHANG X, et al. Growth of CoFe2O4 hollow nanoparticles on graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2018,6(47):12781-12787. DOI: 10.1039/C8TC04222E
[27] XU D W, XIONG X H, CHEN P, et al. Superior corrosion-resistant 3D porous magnetic graphene foam-ferrite nanocomposite with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2019,469:428-436. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.019
[28] NI S B, SUN X L, WANG X H, et al. Low temperature synthesis of Fe3O4 micro-spheres and its microwave absorption properties[J]. Materials Chemistry Physics,2010,124(1):353-358. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.06.046
[29] CHENG Y, CAO J M, LI Y, et al. The out-side-in approach to construct Fe3O4 nanocrystals/mesoporous carbon hollow spheres core-shell hybrids toward microwave absorption[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(1):1427-1435. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03846
[30] QIU X, WANG L X, ZHU H L, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nanoporous carbon[J]. Nanoscale,2017,9(22):7408-7418. DOI: 10.1039/C7NR02628E
[31] FANG J Y, SHANG Y S, CHEN Z, et al. Rice husk-based hierarchically porous carbon and magnetic particles composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave attenuation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2017,5(19):4695-4705. DOI: 10.1039/C7TC00987A
[32] ZHU L Y, ZENG X J, LI X P, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4/graphene composites with good electromagnetic microwave absorbing performances[J]. Journal of Magnetism& Magnetic Materials,2016,426:114-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.063
[33] LI W X, QI H X, GUO F, et al. Co nanoparticles supported on cotton-based carbon fibers: A novel broadband microwave absorbent[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,772:760-769. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.075
[34] WANG H Y, ZHANG Y L, WANG Q Y, et al. Biomass carbon derived from pine nut shells decorated with NiO nanoflakes for enhanced microwave absorption properties[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(16):9126-9135. DOI: 10.1039/C9RA00466A
[35] GAO S S, AN Q D, XIAO Z Y, et al. Significant promotion of porous architecture and magnetic Fe3O4 NPs inside honey comb like carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. RSC Advance,2018,8(34):19011-19023. DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00913a
[36] YANG M L, YUAN Y, LI Y, et al. Dramatically enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of hierarchical CNT/Co/C fiber derived from cotton and metal-organic-framework[J]. Carbon,2020,161:517-527. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.073
[37] LV H L, ZHANG H Q, ZHAO J, et al. Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures[J]. Nano Research,2016,9:1813-1822. DOI: 10.1007/s12274-016-1074-1
[38] WU Z C, TIAN K, HUANG T, et al. Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(13):11108-11115. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b17264
[39] ZHANG X J, WANG G S, WEI Y Z, et al. Polymer-composite with high dielectric constant and enhanced absorption properties based on graphene-CuS nanocomposites and polyvinylidene fluoride[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2013,1(39):12115-12122. DOI: 10.1039/c3ta12451g
[40] 谢文瀚, 耿浩然, 柳扬, 等. MoS2/生物质碳复合材料的制备与吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5): 2238-2248. XIE Wenhan, GENG Haoran, LIU Yang, et al. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of MoS2/biomass carbon composite [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(5): 2238-2248(in Chinese).
[41] TONG G X, LIU Y, CUI T T, et al. Tunable dielectric properties and excellent microwave absorbing properties of elliptical Fe3O4 nanorings[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2016,108(7):072905. DOI: 10.1063/1.4942095
[42] ZHAO B, SHAO G, FAN B B, et al. Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core-shell structure[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2015,17(4):2531-2539. DOI: 10.1039/C4CP05031B
[43] SHENG A, YANG Y Q, YAN D X, et al. Self-assembled reduced graphene oxide/nickel nanofibers with hierarchical core-shell structure for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2020,167:530-540. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.107
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 武志红,任安文,刘一军,薛群虎,牛丹,常吉进. 生物质衍生碳基复合吸波材料的分类、吸波机制与研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2024(08): 3910-3934 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 简煜,范勋娥,邱柏杨,田迅东,杨喜. 铁氧体/芦苇秆炭复合材料的制备与吸波性能. 复合材料学报. 2024(10): 5351-5360 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 朱培,张晓民,俞洁,杨爽,陈天星,贺攀阳. 粉煤灰磁珠Fe含量和研磨粒径对Fe_3C@C-CNTs复合材料结构和吸波性能的影响. 复合材料学报. 2023(01): 342-354 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 叶永盛,丁迪,吴海华,何恩义,殷诗浩,胡正浪,杨超. 石墨烯增强Fe_3O_4/乙基纤维素复合微球吸波性能. 航空学报. 2023(11): 301-315 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)
-




 下载:
下载: