Preparation and adsorption mechanism of NHFO@pumice for ammonia nitrogen
-
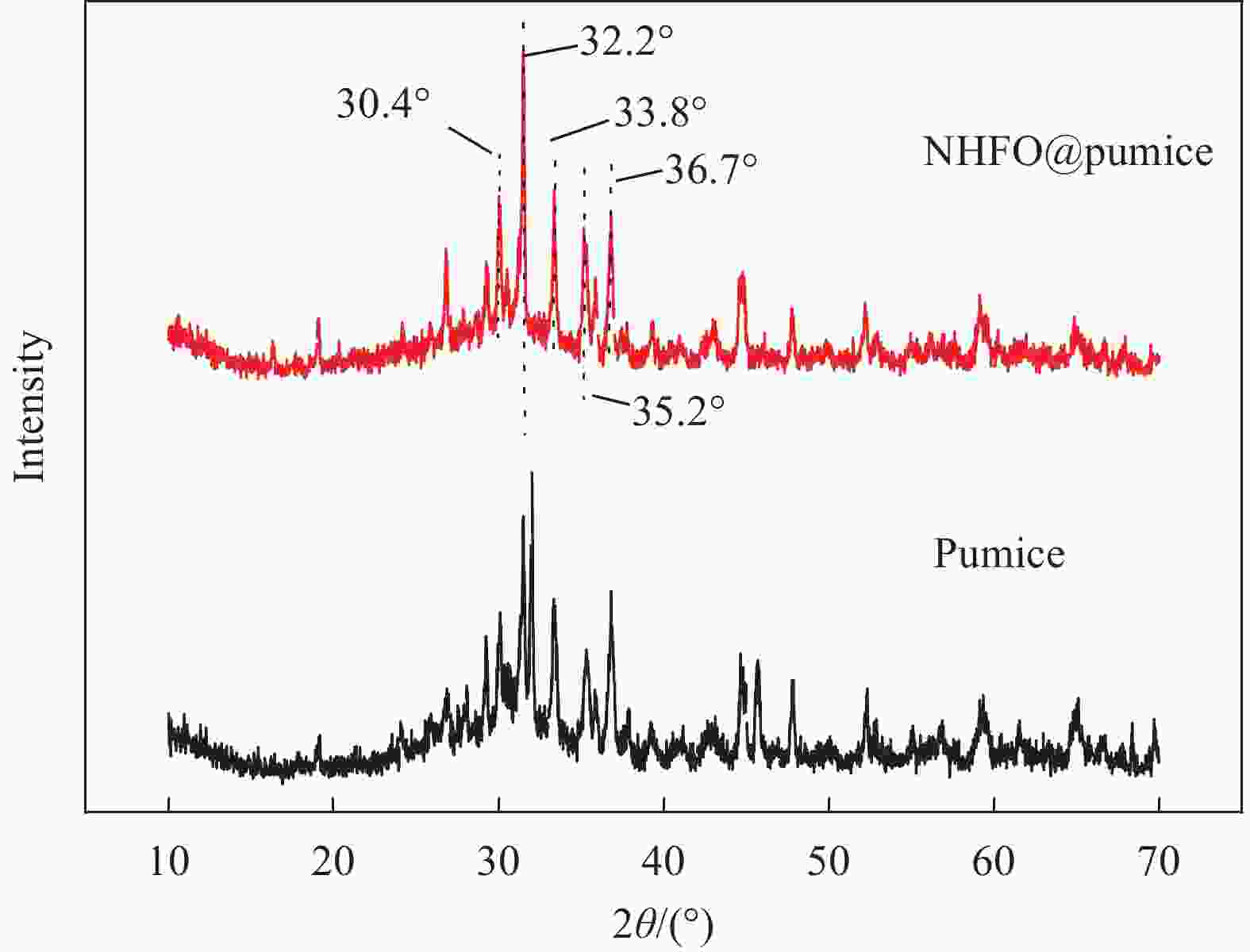
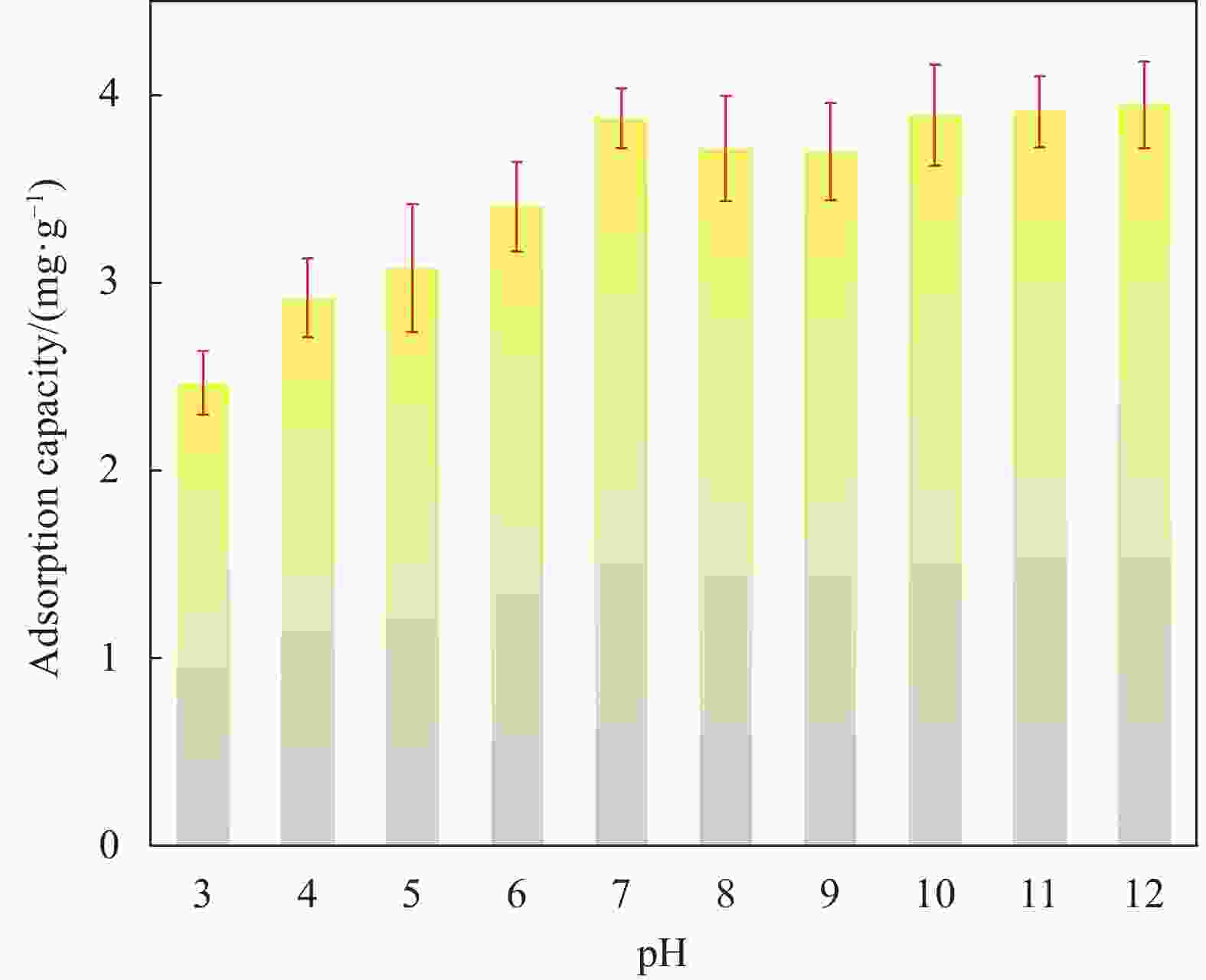
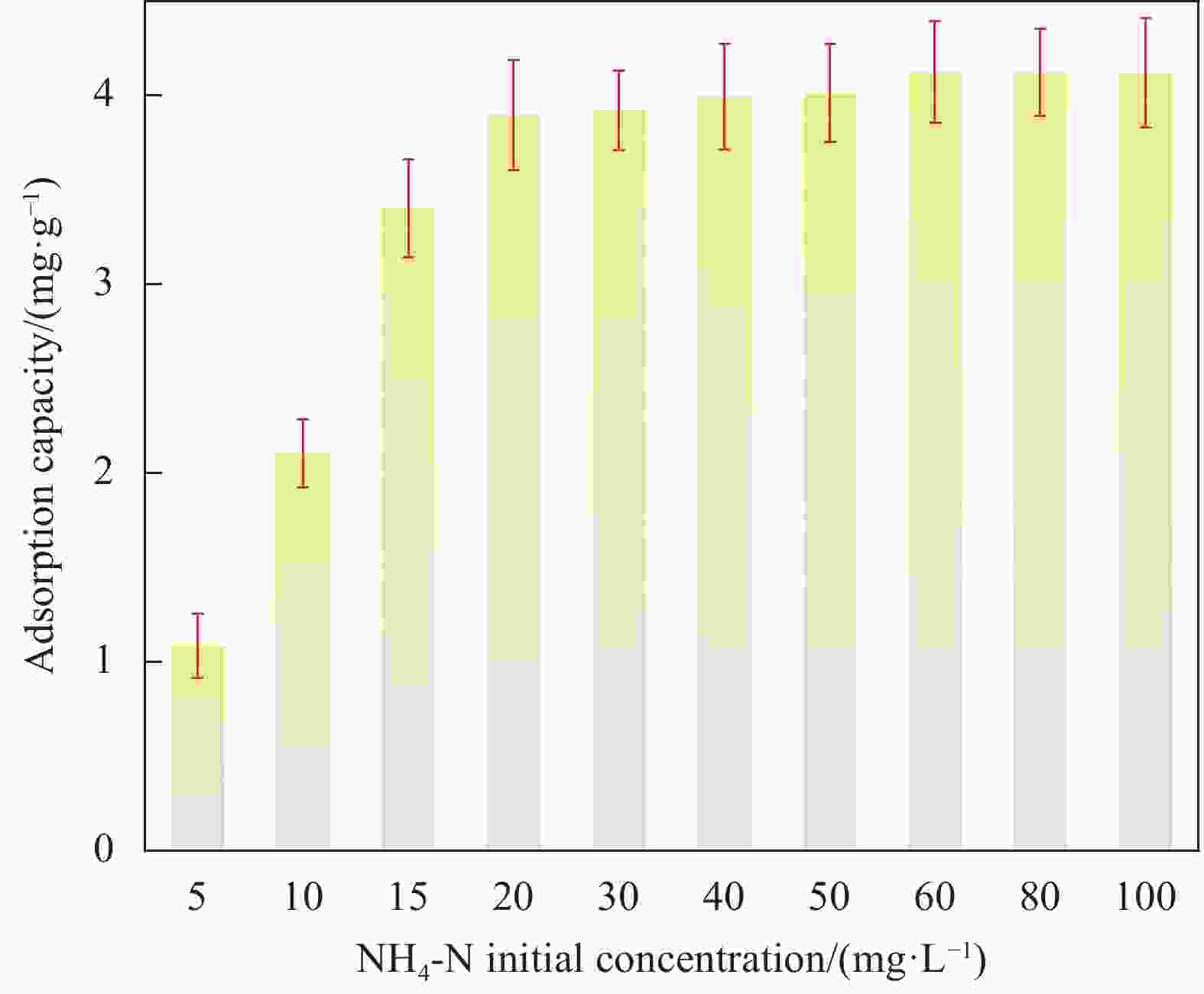
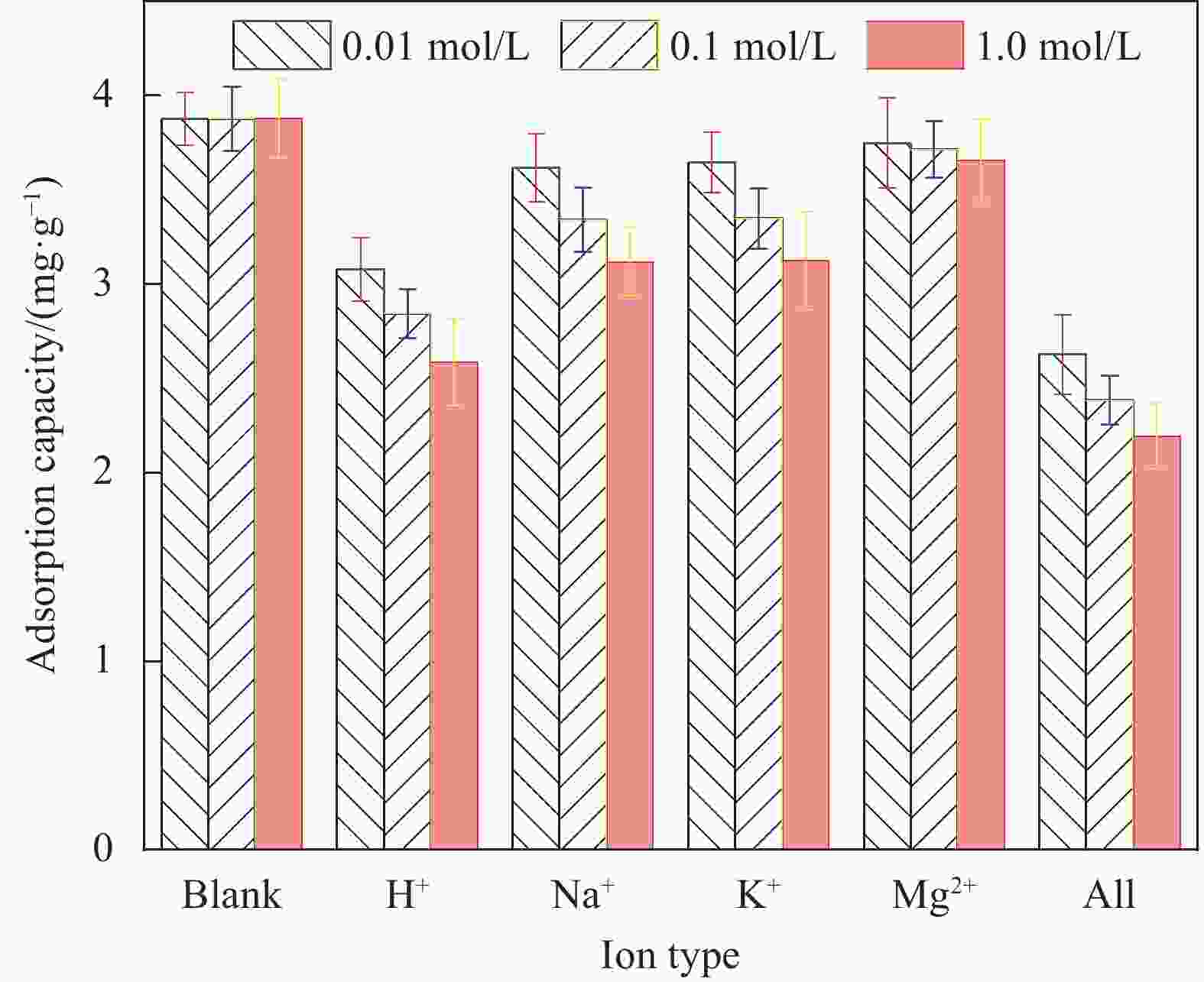
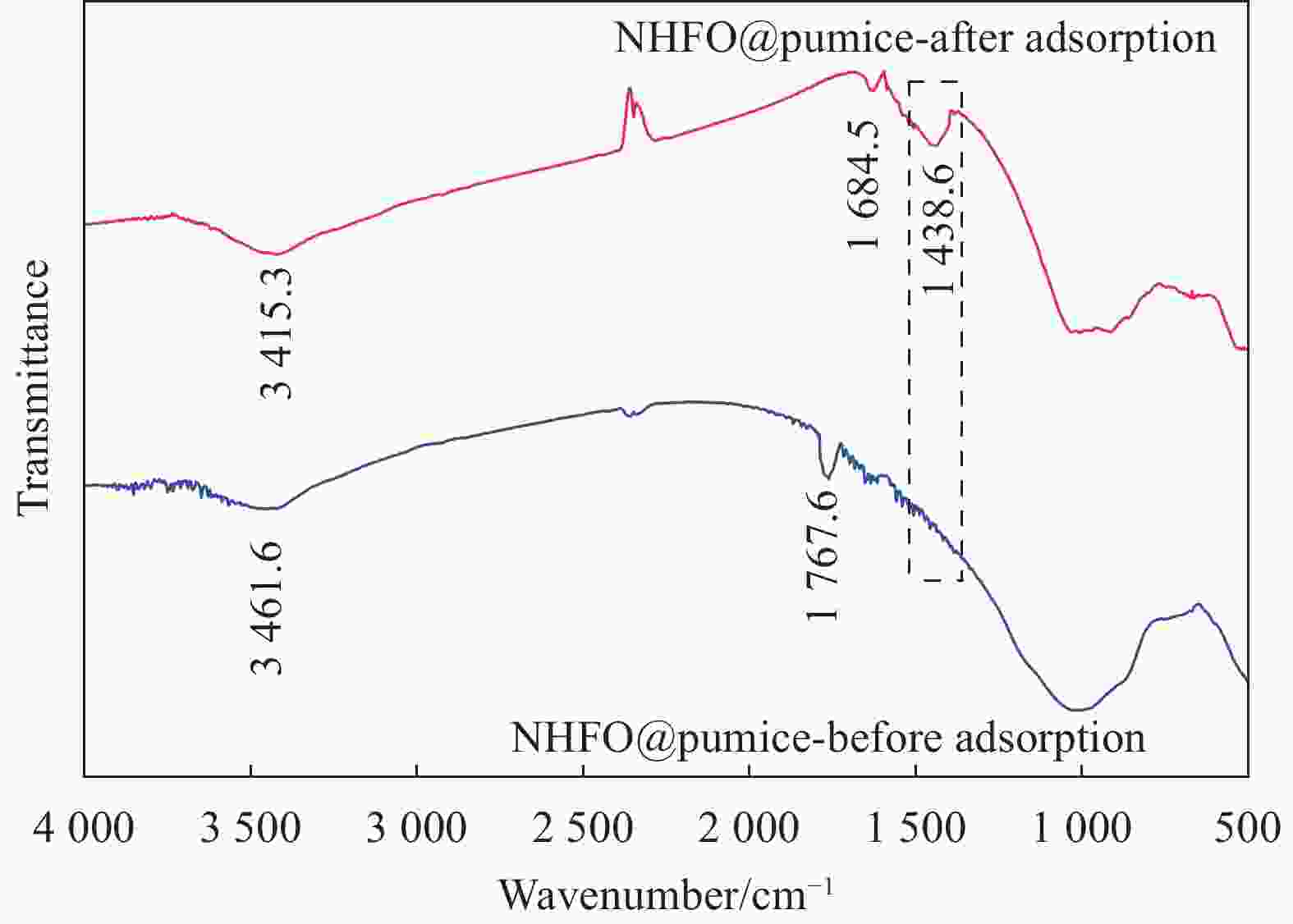
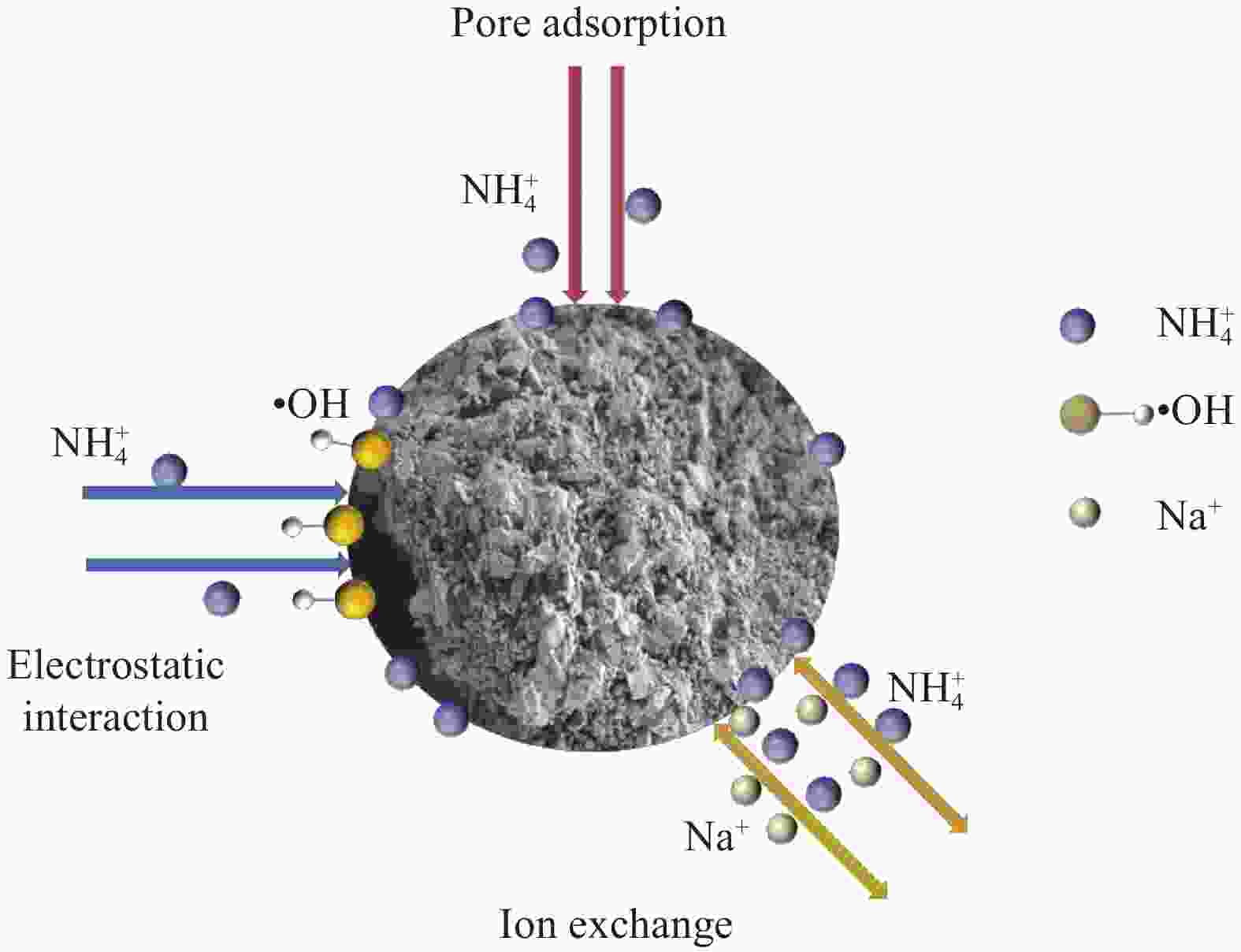
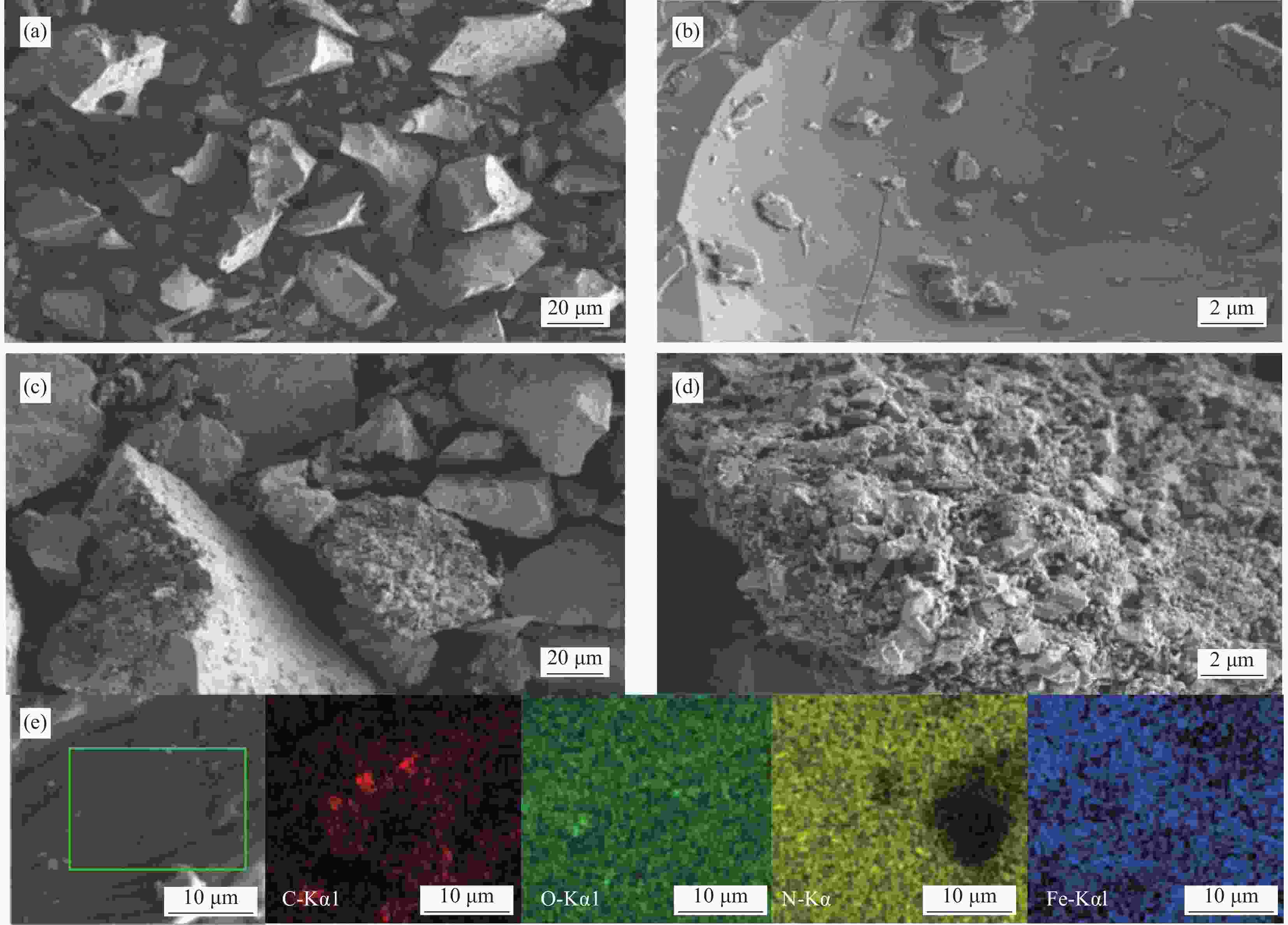
摘要: 蜂巢石与纳米水合氧化铁(NHFO)是水处理中常用的吸附剂,研究采用共沉淀法将NHFO负载到蜂巢石上,探究其对氨氮的吸附性能及机制。实验探究了初始氨氮浓度、初始pH值及共存阳离子(H+、Na+、K+、Mg2+)对NHFO@蜂巢石吸附氨氮的影响。采用SEM-EDS、XRD等手段表征NHFO@蜂巢石的形貌及结构。结果显示:氨氮初始浓度为20 mg/L,pH值7左右时具有较好的吸附能力;共存离子对氨氮的吸附有抑制作用,抑制强度为H+>Na+>K+>Mg2+。SEM-EDS、XRD、FTIR等表征手段证实了NHFO成功负载在蜂巢石上,吸附过程符合Langmuir吸附等温线(R2=0.9886)和准二级动力学模型(R2=0.9969)。研究表明:氨氮主要通过羟基和NH4+的静电作用、离子交换和孔隙吸附共同实现的。该研究为吸附法处理氨氮废水提供了理论依据。Abstract: Both pumice and nano hydrous iron oxide (NHFO) are commonly used adsorbents in water treatment. In this study, NHFO was loaded onto pumice by co-precipitation method to explore its adsorption performance and mechanism of ammonia nitrogen. The effects of initial ammonia concentration, initial pH value and co-existing ions (H+, Na+, K+, Mg2+) on NHFO@pumice adsorption of ammonia nitrogen were investigated. SEM-EDS and XRD were used to characterize the morphology and structure of NHFO@honeycomb. The results show that the initial concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 20 mg/L and the pH value is around 7. The co-existing ions have an inhibitory effect on the adsorption of ammonia nitrogen, and the inhibitory strength is H+>Na+>K+>Mg2+. SEM-EDS, XRD, FTIR and other characterization methods confirmed that NHFO was successfully loaded on the honeycomb, and the adsorption process was consistent with Langmuir adsorption isotherm (R2=0.9886) and quasi second-order kinetic model (R2=0.9969). The mechanism of ammonia nitrogen adsorption mainly includes electrostatic interaction of hydroxyl group and NH4+, ion exchange and pore adsorption. This study provides a theoretical basis for the treatment of ammonia-nitrogen water by adsorption.
-
Key words:
- pumice /
- nano hydrous iron oxide /
- adsorption /
- ammonia nitrogen /
- mechanisms
-
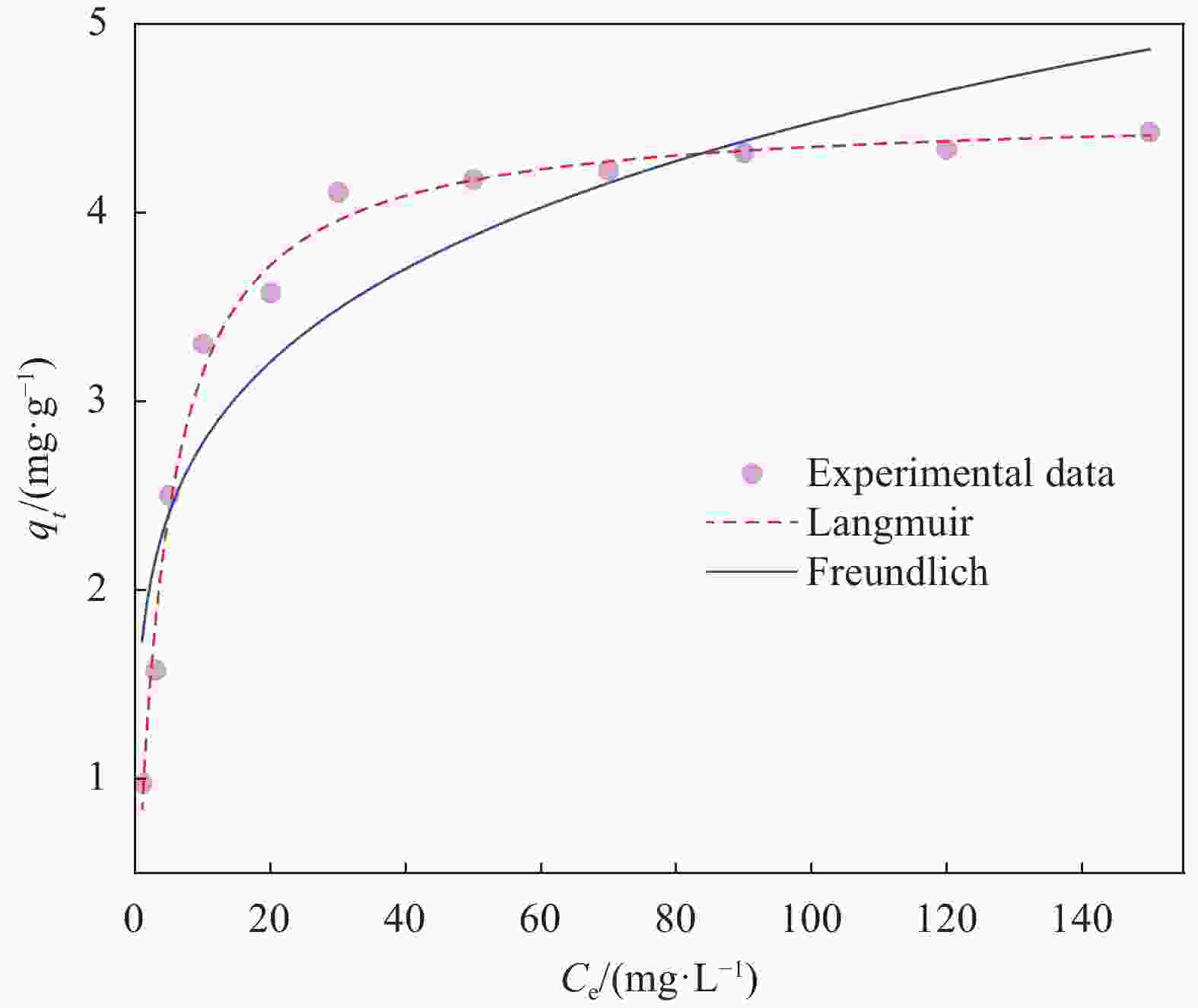
表 1 NHFO@蜂巢石复合材料吸附等温线模型参数
Table 1. Adsorption isotherm model parameters of NHFO@pumice stone composites
Langmuir Freundich qm/(mg·g−1) KL R2 KF n R2 4.5393±0.0692 0.2277±0.0189 0.9886 1.7285±0.2401 0.2066±0.0341 0.8560 Notes: qm—Maximal adsorption capacity; KL—Langmuir constant; KF—Freundlich constant; n—The constant of the adsorption model; R2—Variance. 表 2 NHFO@蜂巢石复合材料吸附动力学模型参数
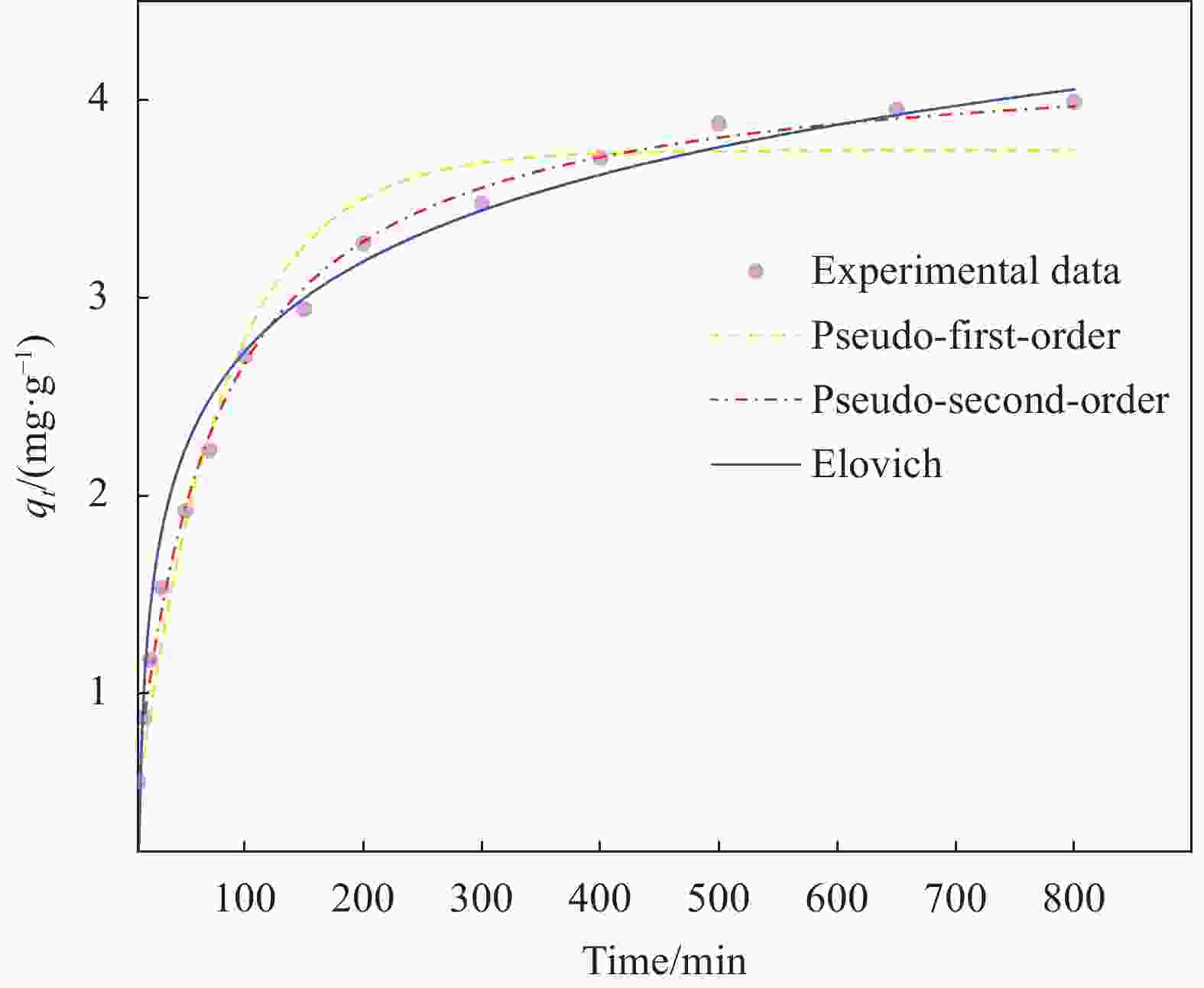
Table 2. Adsorption kinetics model parameters of NHFO@pumice stone composites
Pseudo-first-order qm k1 R2 3.7459±0.0919 0.0137±0.0012 0.9678 Pseudo-second-order qm k2 R2 4.2650±0.0451 0.0039±0.0002 0.9969 Elovich a b R2 0.0484±0.0267 −0.6115±0.0083 0.8786 Notes: k1—Pseudo-first-order kinetic constant; k2—Pseudo-second-order kinetic constant; a—Initial adsorption rate (mg/(g·min)); b—Desorption constant. 表 3 NHFO@蜂巢石吸附前后成分相对含量(XPS全谱)
Table 3. Relative contents of NHFO@pumice before and after adsorption (Full spectrum of XPS)
Sample Atomic ratio/at% C N O Fe Al Si Na NHFO@pumice-before adsorption 39.30 0.49 42.50 1.41 5.10 6.60 2.43 NHFO@pumice-after adsorption 36.82 2.73 43.15 2.51 4.73 5.92 1.04 -
[1] ZHAO J G, LI H B, LIU C Q, et al. Eutrop-hication evaluation of water body at Huailai section of the Yongding River[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Research,2018,9(6):66-72, 78. [2] 曾青云, 薛丽燕, 曾繁钢, 等. 氨氮废水处理技术的研究现状[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2018, 9(4):83-88. doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2018.04.014ZENG Qingyun, XUE Liyan, ZENG Fangang, et al. Research progress of treatment technology for ammonia nitrogen wastewater[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering,2018,9(4):83-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2018.04.014 [3] YU R T, ZHOU J C, XIE Z P, et al. Mechanism of ammonium adsorption from wastewater by modified bentonite and optimization by response surface[J]. Bioremediation Journal, 2018, 22(1-2): 16-24. [4] 牛乙涛, 包国庆, 吴纯鑫, 等. 功能化纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的制备及其对Pb(II)的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(6): 3350-3365.NIU Yitao, BAO Guoqing, WU Chunxin, et al. Preparation of functionalized nano composites Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS and its adsorption to Pb(II)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(6): 3350-3365(in Chinese). [5] REN Z J, JIA B, ZHANG G M, et al. Study on adsorption of ammonia nitrogen by iron-loaded activated carbon from low temperature wastewater[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 262: 127895. [6] TURAL B, ERTAŞ E, GÜZEL M, et al. Effect of structural differences of pumice on synthesis of pumice-supported nFe0: Removal of Cr(VI) from water[J]. Applied Water Science, 2021, 11(7): 1-11. [7] ZHANG Y, XU G S, XU M D, et al. Preparation of MgO porous nanoplates modified pumice and its adsorption performance on fluoride removal[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,884:160953. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160953 [8] ALAM M M, ALOTHMAN Z A, NAUSHAD M, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal kinetics through pyridine based Th(IV) phosphate composite cation exchanger using particle diffusion controlled ion exchange phenomenon[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2014,20(2):705-709. [9] 徐宝龙, 周根陶, 郑永飞. 针铁矿-四方纤铁矿-水体系氧同位素分馏的实验研究[J]. 地球化学, 2002, 31(4):366-374. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2002.04.009XU Baolong, ZHOU Gentao, ZHENG Yongfei. Experimental study on oxygen isotope fractionation of goethite-tetracycline iron-water system[J]. Geochimica,2002, 31(4):366-374(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2002.04.009 [10] LIU Y Q, CHEN Z H, YIN X S, et al. Selective and efficient removal of As(V) and As(III) from water by resin-based hydrated iron oxide[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2023,1273:134361. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134361 [11] DZYAZKO Y S, ROZHDESTVENSKA L M, KUDELKO K O, et al. Hydrated iron oxide embedded to natural zeolite: Effect of nanoparticles and microparticles on sorption properties of composites[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution,2022,233(6):205. doi: 10.1007/s11270-022-05681-y [12] XU Q Y, LI W P, MA L, et al. Simultaneous removal of ammonia and phosphate using green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles dispersed onto zeolite[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,703(C):135002. [13] ZHANG H L, ELSKENS M, CHEN G X, et al. Influence of seawater ions on phosphate adsorption at the surface of hydrous ferric oxide (HFO)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 721: 137826. [14] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 水质 氨氮的测定 纳氏试剂分光光度法: HJ 535—2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2009.Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Water quality. Determination of ammonia nitrogen. Nessler's reagent spectrophotometry: HJ 535—2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2009(in Chinese). [15] LIN K N, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y B, et al. Determination of ammonia nitrogen in natural waters: Recent advances and applications[J]. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 24: e00073. [16] HE Y H, LIN H, DONG Y B, et al. Zeolite supported Fe/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles for simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate: Synergistic effect and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,347:669-681. [17] ZHOU H Y, QU L M. Adsorption of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater by tailing loaded manganese oxide material[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications,2022,144:109886. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109886 [18] CHENG H M, ZHU Q, XING Z P. Adsorption of ammonia nitrogen in low temperature domestic wastewater by modification bentonite[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,233:720-730. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.079 [19] REN S G, HUANG S Y, LIU B X. Enhanced removal of ammonia nitrogen from rare earth wastewater by NaCl modified vermiculite: Performance and mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 302: 134742. [20] 孙健, 徐兆郢, 赵平歌, 等. 水合氧化铁负载量对丙烯酸树脂基复合吸附剂的结构及除磷影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(8): 2595-2604.SUN Jian, XU Zhaoying, ZHAO Pingge, et al. Effect of hydrated ferric oxide loadings on structure and phosphate adsorption of acrylic polymer supported composite adsorbents[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(8): 2595-2604(in Chinese). [21] ALSHAMERI A, HE H P, ZHU J X, et al. Adsorption of ammonium by different natural-clay minerals: Characterization, kinetics and adsorption isotherms[J]. Applied Clay Science,2018,159:83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.007 [22] ZHANG Y, YU F, CHENG W P, et al. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of the removal of ammoniacal nitrogen by zeolite X/activated carbon composite synthesized from elutrilithe[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 481: 1936829. [23] POSSATO L G, ACEVEDO M D, PADRÓ C L, et al. Activation of Mo and V oxides supported on ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts followed by in situ XAS and XRD and their uses in oxydehydration of glycerol[J]. Molecular Catalysis,2020,481:110158. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.07.029 [24] CHENG Y, HUANG T L, SHI X X, et al. Removal of ammonium ion from water by Na-rich birnessite: Performance and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences,2016,57:402-410. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.11.015 [25] 贺银海. 沸石同步脱氮除磷功能调控及机理研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2018.HE Yinhai. Study on the functional regulationand mechanism of simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus by natural zeolite[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2018(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: