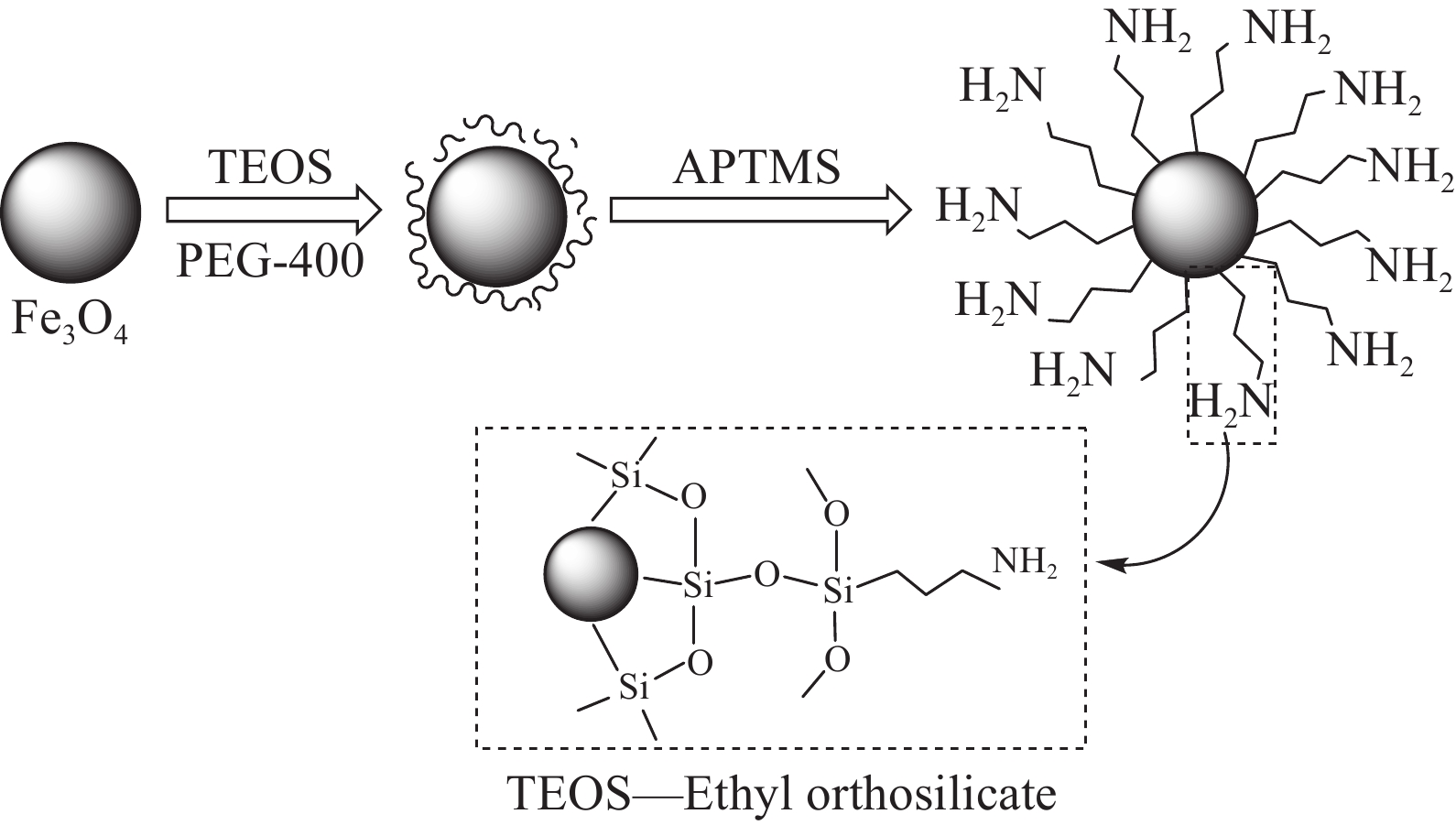
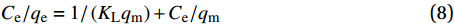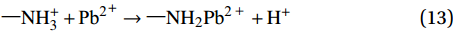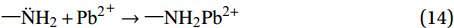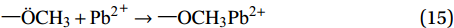Preparation of functionalized nanocomposites Fe3O4@SiO2-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane and its adsorption to Pb(Ⅱ)
-
摘要: 为解决磁性纳米Fe3O4颗粒易腐蚀、团聚等问题,对其进行功能化修饰改进。在超声波辐照下以FeCl3和FeSO4为原料,氨水为沉淀剂,然后加入正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)和3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS)进行功能化修饰,制备得到SiO2包覆的氨基功能化纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,并采用TEM、FTIR、VSM、TGA、低温氮吸附、XRD等对其进行表征测试,证实了超声波辐照下制备的复合材料具有磁响应强度强、耐酸碱性强、分散性高、比表面积大、粒径小等特点,同时探究了纳米复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附性能。结果表明:溶液初始pH值为5.86,吸附剂投加量为1.0~1.5 g·L−1时Pb(Ⅱ)吸附效果较好;Langmuir模型适合模拟该等温吸附过程,吉布斯自由能变∆G0<0,吸附过程是一个自发过程;准二级动力学可以较好地描述Pb(Ⅱ)在复合材料上的吸附行为,准二级动力学常数k2=0.0401 g·mg−1·min−1,达到吸附平衡时的吸附量qe=80.041 mg·g−1;推测得到吸附机制主要为离子交换和络合吸附。Abstract: In order to solve the indefects that magnetic nano-Fe3O4 particles were corroded and agglomerated easily, functional modification was carried out. FeCl3 and FeSO4 were used as raw materials and ammonia as preci-pitant in the presence of ultrasonic irradiation, then functionalized by ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS) to prepare SiO2-coated amino-functional nanocomposites Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS. The magnetic nanocomposites were characterized by TEM, FTIR, VSM, TGA, low temperature nitrogen adsorption and XRD, etc. The characterized results show that the magnetic nanocomposites prepared by ultrasonic strengthening method have the characteristics of strong magnetic response, strong acid and alkali resistance, high dispersion, large specific surface area and small particle size.Meanwhile, the adsorption effects of magnetic nanocomposites for Pb(Ⅱ) were investigated. The results show that the initial pH value of the solution and the dosage of adsorbent have greatest effects on the adsorption effect of Pb(Ⅱ) with the initial pH value of the solution 5.86 and the dosage of adsorbent 1.0-1.5 g·L−1. The Langmuir model is suitable for simulating the isothermal adsorption process, and the adsorption process is a spontaneous process when Gibbs free energy change ∆G0<0. The adsorption behavior of Pb(Ⅱ) can be well described by quasi-second-order kinetics on the composites, Quasi-second-order kinetic constant k2=0.0401 g·mg−1·min−1, equilibrium adsorption capacity qe=80.041 mg·g−1; it is speculated that the adsorption mechanism is mainly complex adsorption and ion exchange.
-
Keywords:
- ultrasonic /
- magnetic nanocomposites /
- complex adsorption /
- adsorption kinetics /
- lead ions
-
随着社会工业化进程的不断加快,以Pb(Ⅱ)为代表的重金属离子污染问题日益严重[1]。自然环境中的Pb(Ⅱ)较稳定,不易降解和代谢,易被农作物吸收并聚集,导致植物根系功能丧失,影响植物的正常生长[2-3],同时也会通过生物链被人体摄取,对人体消化系统、神经系统、生殖系统等具有巨大的毒害作用[4-5]。
目前有效去除水体中Pb(Ⅱ)污染的方法主要有吸附法、生物法、离子交换法及化学沉淀法等[6]。吸附法较其他方法来说更加简便、高效,但传统吸附剂存在着不易回收和选择性差等缺点。随着纳米技术的发展,磁性纳米Fe3O4颗粒能有效解决这些缺点[7],然而纳米Fe3O4颗粒也存在着一些其他问题,如颗粒易被氧化腐蚀和易发生团聚等[8-9]。为了解决这些问题,需对其进行一些功能化修饰,比如引入氨基、羧基、磺酸基等基团,能有效改善颗粒易氧化腐蚀等问题[10-12]。Zhang等[13]通过多步法先以FeCl3和C6H5Na3O7为前驱体通过溶剂热法制得Fe3O4,干燥后以硅酸正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)、3-氨丙基-三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS)为功能化试剂制得Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2,结果显示氨基功能化后对Pb(Ⅱ)的饱和吸附量达到215 mg·g−1;雷婷[14]同样采用上述多步法先制得Fe3O4纳米微球,干燥后以多巴胺(DA)、二巯基琥珀酸(DMSA)为功能化试剂制备得到巯基功能化复合材料Fe3O4@聚多巴胺(PDA)-DMSA,对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附容量达52.91 mg·g−1。此外,已有的研究证实纳米材料制备过程中引入超声波,利用其“声空化”作用能有效解决纳米颗粒易团聚等问题,提高吸附剂颗粒的分散性,增大有效比表面积,从而提高吸附效率[15-16]。目前来说,利用单个基团来修饰磁性纳米颗粒的研究较多,但在超声波辐照下利用官能团和负载材料协同改善磁性纳米Fe3O4颗粒缺点的制备技术研究较少,且大多数Fe3O4纳米复合材料的合成方法均是采用多步法,较繁琐。
因此,本文在超声波辐照下采用一步法以FeCl3和FeSO4为原料,氨水为沉淀剂,TEOS为硅源,APTMS为硅烷化试剂,以化学沉淀法制备得到氨基功能化纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,采用TEM、FTIR、XRD、低温氮吸附等对复合材料进行表征,同时对其抗酸碱性能进行了测试,探究了复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果,通过实验数据模拟吸附等温线并建立了吸附动力学模型,经分析推测得到其吸附机制,以便为实际工业应用提供基础参考数据。
1. 实验部分
1.1 原材料
FeCl3·6H2O(≥99.0%)、FeSO4·7H2O (99.0%~101.0%)、NH3·H2O(25.0%~28.0%)、硅酸正硅酸乙酯(TEOS,≥99.5%)、3-氨丙基-三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS,≥98.0%)、聚乙二醇(PEG-400)、NaOH(≥97.0%)、邻二氮菲(≥98.0%)、二甲酚橙(≥98.0%)均为分析纯,购于麦克林试剂公司;六次甲基四胺(≥99.5%)、HNO3(65.0%~68.0%)均为分析纯,购于国药集团化学试剂公司;Pb(NO3)2(≥99.0%,分析纯)广东光华科技公司;NaCl(≥99.5%)、MgCl2(≥98.0%)、无水CaCl2(≥96.0%)均为分析纯,购于太仓美达试剂公司;HCl (36.0%~38.0%,优级纯)富宇精细化工公司。
1.2 实验步骤
在氮气氛围条件下,FeCl3·6H2O和FeSO4· H2O以2∶3摩尔比加到250 mL三口烧瓶中,加入脱氧去离子水,在超声波(40 kHz,150 W)辐照下搅拌20 min混合均匀,用恒压滴液漏斗滴加一定量1 moL·L−1的氨水;滴加完毕后加入1~2 mL PEG-400(非离子表面活性剂,用以改善颗粒的分散性和稳定性),加入2 mL TEOS和1.75 mL APTMS,再在超声波辐照下,恒温循环浴槽(HWS-20 A,上海百典仪器设备有限公司)控温313 K、450 r·min−1转速搅拌反应4 h。反应结束后,用脱氧去离子水多次洗涤纳米颗粒至洗液为中性。磁分离得到固体并置于60℃真空干燥箱(DZF-6050,上海一恒科学仪器有限公司)内干燥12 h,即制得纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,反应式见图1。
1.3 Pb(Ⅱ)浓度测定方法
采用二甲酚橙分光光度法[17]测定Pb(Ⅱ)浓度,首先在10 mL容量瓶中配制一系列浓度梯度为1.0、2.0、4.0、6.0、8.0、10.0 mg·L−1的Pb(Ⅱ)溶液,然后在25 mL容量瓶中依次加入1 mL Pb(Ⅱ)上清液、2 mL 2 g·L−1二甲酚橙溶液、4 mL 400 g·L−1六次亚甲基四胺溶液和1.5 mL 1.5 g·L−1邻二氮菲溶液,显色10 min后用脱氧去离子水定容并摇匀,以相应试剂空白组做参比,于λ=574 nm处测吸光度,作出Pb(Ⅱ)标准曲线。吸附完成后取样,并经该法测定其吸光度,然后根据标准曲线计算吸附后的Pb(Ⅱ)浓度。
1.4 纳米复合材料的表征
X射线衍射(XRD)表征:将待测复合材料研磨成粉末后用X射线衍射仪(Rigaku Ultima IV,日本理学公司)进行XRD实验,扫描速度为2°·min−1,Cu靶,扫描范围为20°~80°。
透射电子显微镜(TEM)表征:将待测复合材料粉末分散在无水乙醇中并超声15 min,取微量试样溶液滴在铜网上,制成电镜试样,通过透射电子显微镜(JEM 2100,日本电子公司)观测样品的形貌、尺寸、分散性。
红外(FTIR)表征:取少许待测样品与溴化钾以1∶100质量比例混合,充分研磨压片后用傅里叶红外光谱仪(Thermo Scientific Nicolet 10,热电公司)扫描,扫描范围为4000~400 cm−1。
热重分析(TGA)表征:取待测样取0.01 g待测样品于小坩埚中,缓慢移入样品台,在惰性气体N2的保护下,温度从298 K升至1273 K,使用TGA热重分析仪(耐驰STA 449 F5,德国耐驰科学仪器商贸(上海)有限公司)测量其质量的变化。
磁滞回线(VSM)表征:待测样品于60℃下真空干燥12 h后,在298 K、−20 kOe~20 kOe条件下测定样品磁滞回线。
低温氮吸附表征:将少量待测样品在氢气流中活化5 h,在液氮温度77.40 K下以氮气为吸附气体进行低温氮吸附测定材料的比表面积及孔径分布。
1.5 吸附实验
用脱氧去离子水配制100 mg·L−1 Pb(Ⅱ)溶液,取20 mL Pb(Ⅱ)溶液(pH=5.86)于锥形瓶中,用HCl、NaOH调节至所需pH值,加入一定量的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS进行吸附实验。在恒温培养振荡器(TQZ-312,上海精宏实验设备有限公司)中振荡9 h,振荡频率180 r·min−1,温度283~313 K。吸附完成后使用强磁分离,取上清液测定吸附后的Pb(Ⅱ)浓度,每组吸附实验重复进行3次,取平均值以减小实验误差。通过下式计算吸附容量。
q=C0−CemV (1) 其中:C0为Pb(Ⅱ)溶液初始浓度(mg·L−1);q为吸附容量(mg·g−1);Ce为吸附平衡时溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)浓度(mg·L−1);m为复合材料用量(mg);V为Pb(Ⅱ)溶液体积(mL)。
1.6 吸附热力学
分别取浓度为50 mg·L−1、100 mg·L−1、150 mg·L−1的Pb(Ⅱ)溶液20 mL于不同锥形瓶中,溶液初始pH值为5.86,加入0.03 g Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,分别在283 K、293 K、303 K和313 K下吸附9 h。结束后用磁铁分离得到Pb(Ⅱ)上清液,测定Pb(Ⅱ)浓度,每组吸附实验重复进行3次取平均值,据下式计算热力学参数吉布斯自由能变∆G0(kJ·mol−1)、焓变∆H0(kJ·mol−1)和熵变∆S0(J·mol−1·K−1)。
K0=qe/Ce (2) ΔG0=−RTlnK0 (3) lnK0=ΔS0R−ΔH0RT (4) 其中:qe为吸附平衡时的吸附量(mg·g−1);K0为热力学平衡常数;R为气体常数;T为热力学温度(K)。
1.7 吸附动力学
取50 mL浓度为100 mg·L−1 的Pb(Ⅱ)溶液,溶液初始pH值为5.86,加入0.06 g Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,温度为313 K,在恒温培养振荡器中振荡9 h,进行吸附动力学研究。设定一系列时间梯度取上清液测定溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)浓度,每组吸附实验重复进行3次取平均值,分别用准一级动力学模型(5)、准二级动力学模型(6)和颗粒内扩散模型(7)对数据进行拟合。
ln(qe−qt)=lnqe−k1t (5) tqt=1k2q2e+tqe (6) qt=kpt1/2+C (7) 其中:qt为t时刻的吸附量(mg·g−1);t为吸附时间(min);k1为准一级动力学常数(min−1);k2为准二级动力学常数(g·mg−1·min−1);kp为内扩散速率常数(mg·(g·min1/2)−1);C为涉及到厚度、边界层的常数。
1.8 吸附等温线实验
分别取浓度为100 mg·L−1、200 mg·L−1、300 mg·L−1、400 mg·L−1、500 mg·L−1、600 mg·L−1 、800 mg·L−1、1000 mg·L−1的Pb(Ⅱ)溶液各20 mL于不同锥形瓶中,溶液初始pH值为5.86,加入0.03 g Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,分别在288 K、298 K、308 K下吸附9 h。结束后用磁铁分离得到Pb(Ⅱ)上清液并测定其浓度,每组吸附实验重复进行3次,用三种模型Langmuir(8)、Freundlich(9)和Temkin(10)分别对数据进行拟合。
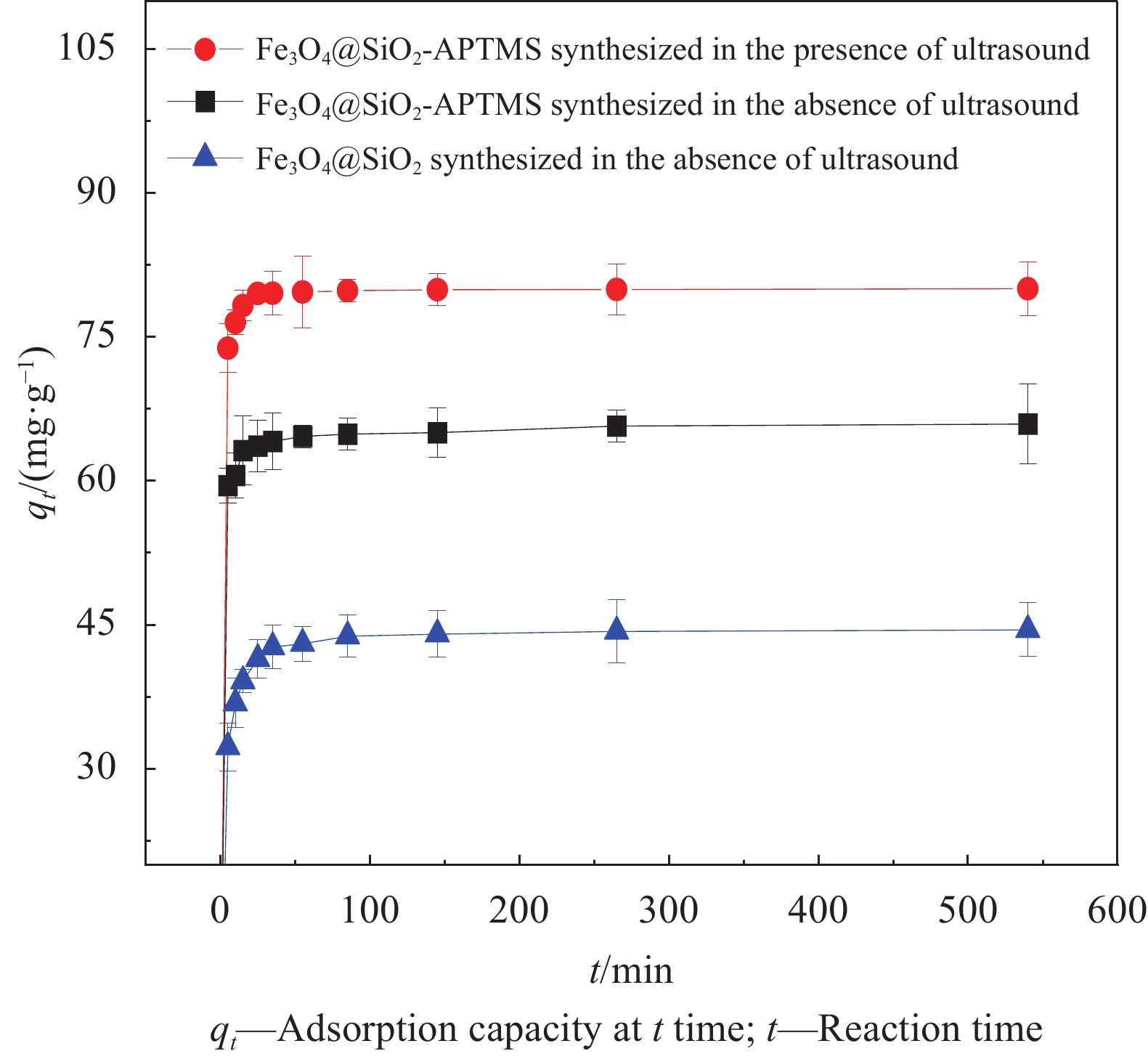
Ce/qe=1/(KLqm)+Ce/qm (8) lgqe=lgKF+(1/n)lgCe (9) qe=B1lnKt+B1lnCe (10) 其中:KL为Langmuir吸附系数(L·mg−1);qm为饱和吸附量(mg·g−1);Kt、Bl为Temkin吸附等温系数;KF为Freundlich吸附系数(mg1−(1/n)·L1/n·g−1)。
1.9 脱附与重复利用实验
吸附动力学实验结束后,将分离出来的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS浸泡于0.1 mol·L−1的HNO3中,在超声波辐照下分散脱附2 h,再用脱氧去离子水洗涤至中性,于60℃真空烘箱内干燥12 h。取干燥后的复合材料再次进行吸附反应并测定上清液中Pb(Ⅱ)浓度,重复此操作5次。
1.10 抗酸碱腐蚀性实验
取无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS各 1.25 g,分别加入到15 mL自来水、0.1 mol·L−1 HCl、1 mol·L−1 HCl、0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH、1 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液中,常温静置浸泡24 h;再取两种材料各1.25 g分别加入15 mL自来水、1 mol·L−1 HCl、1 mol·L−1 NaOH中,313 K下分别搅拌72 h和96 h,通过测量Fe和有机碳的溶解量来判断材料的耐酸碱性,其中Fe溶解量采用二氮杂菲分光光度法测量,APTMS溶解量用总有机碳分析仪(TOC-L,日本岛津公司)来检测。
1.11 不同重金属离子选择性吸附实验
取浓度均为100 mg·L−1的Pb(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)、Ni(Ⅱ)的混合溶液20 mL于锥形瓶中,溶液初始pH值为5.86,温度为313 K,加入0.02 g复合材料,在恒温培养振荡器中振荡9 h,设定一系列时间梯度取上清液测定溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)和Ni(Ⅱ)浓度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 样品表征
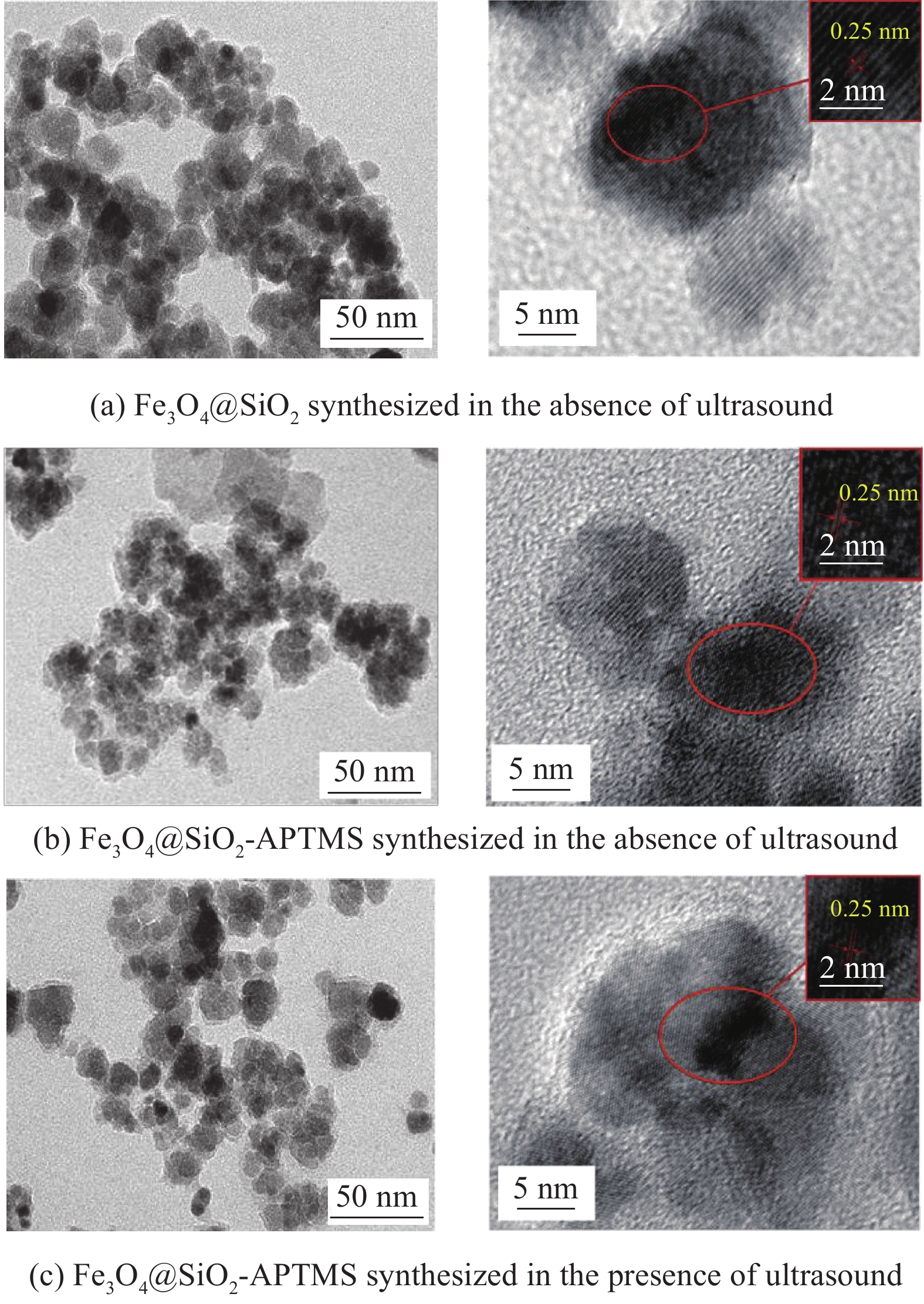
图2为无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS和超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的TEM图像。通过Digital Micrograph软件测得晶格条纹间距为0.25 nm,比对标准PDF卡(JCPDS,75-1610)对应Fe3O4的(311)晶面,图2(c)中的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS颗粒粒径较小,中间部分颜色深,为纳米Fe3O4,周围颜色浅,为有机包裹层,表明SiO2、APTMS成功包裹在了复合材料表面。用ImageJ软件测量得到图2(c)中的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS颗粒平均粒径为13 nm,其分散性明显要高于图2(a)中的Fe3O4@SiO2及图2(b)中的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,可见超声波辐照能提高纳米复合材料的分散性。
图3(a)为无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS和超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的XRD图谱。比对标准卡片,图中存在Fe3O4典型特征峰,分别在30.1°、35.5°、43.3°、53.4°、57.2°、62.6°和74.8°处对应纳米Fe3O4颗粒7个不同的晶面,在20°~25°附近出现衍射宽峰,说明颗粒中存在无定型SiO2,无其他杂质峰,表明材料较纯。功能化改性未改变晶体构型,不会引起颗粒晶相的变化[18]。通过Jade软件计算得到图3(a)中无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS及超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的平均晶粒大小分别为11.35 nm、12.11 nm、13.85 nm。
图3(b)为无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS和超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的FTIR图谱。可知,582.4 cm−1为Fe—O键振动吸收峰;786.3 cm−1为N—H键面外弯曲振动峰,表明氨基已成功接枝在材料表面;1097.3 cm−1为Si—O振动峰;由于SiO2与APTMS发生反应,导致图3(b)中c曲线1097.3 cm−1处峰强度减小;1405.4 cm−1处为—CH3弯曲振动峰;2929.5 cm−1为C—H键伸缩振动峰[19]。超声波辐照下制备的复合材料氨基特征峰强度明显强于无超声波辐照制备的,可能是由于超声辐照下APTMS更易稳定包裹在材料表面。
图3(c)、图3(d)为无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS和超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的热重分析曲线。从图3(c)可看出,a、b曲线中随着温度升高,纳米复合材料的质量损失率逐渐增加,随后在1148 K趋于平缓,c曲线在1253 K质量损失才慢慢趋于平缓。图3(d)为材料的差热曲线。可知,3条曲线在373 K时出现波谷,原因可能是复合材料表面的游离水离去;b、c曲线在573 K时出现波谷,可能是表面有机包裹层的热分解导致,其中曲线c中的质量损失明显大于b,说明在超声波辐照下,纳米复合材料表面有更多的有机包裹层,这与FTIR图谱得出的结论一致;973 K出现的波谷判断为表面APTMS包裹层分解完毕,SiO2包裹层开始分解。表面游离水的质量可根据a曲线质量变化得到约为5wt%;b曲线的质量总损失约为17.5wt%,其中SiO2-APTMS包裹层占比约为12.5wt%;c曲线的质量总损失约为26.5wt%,SiO2-APTMS包裹层占比约为22.5wt%,明显大于b曲线,证实超声波辐照下更多的SiO2-APTMS包裹在Fe3O4表面。
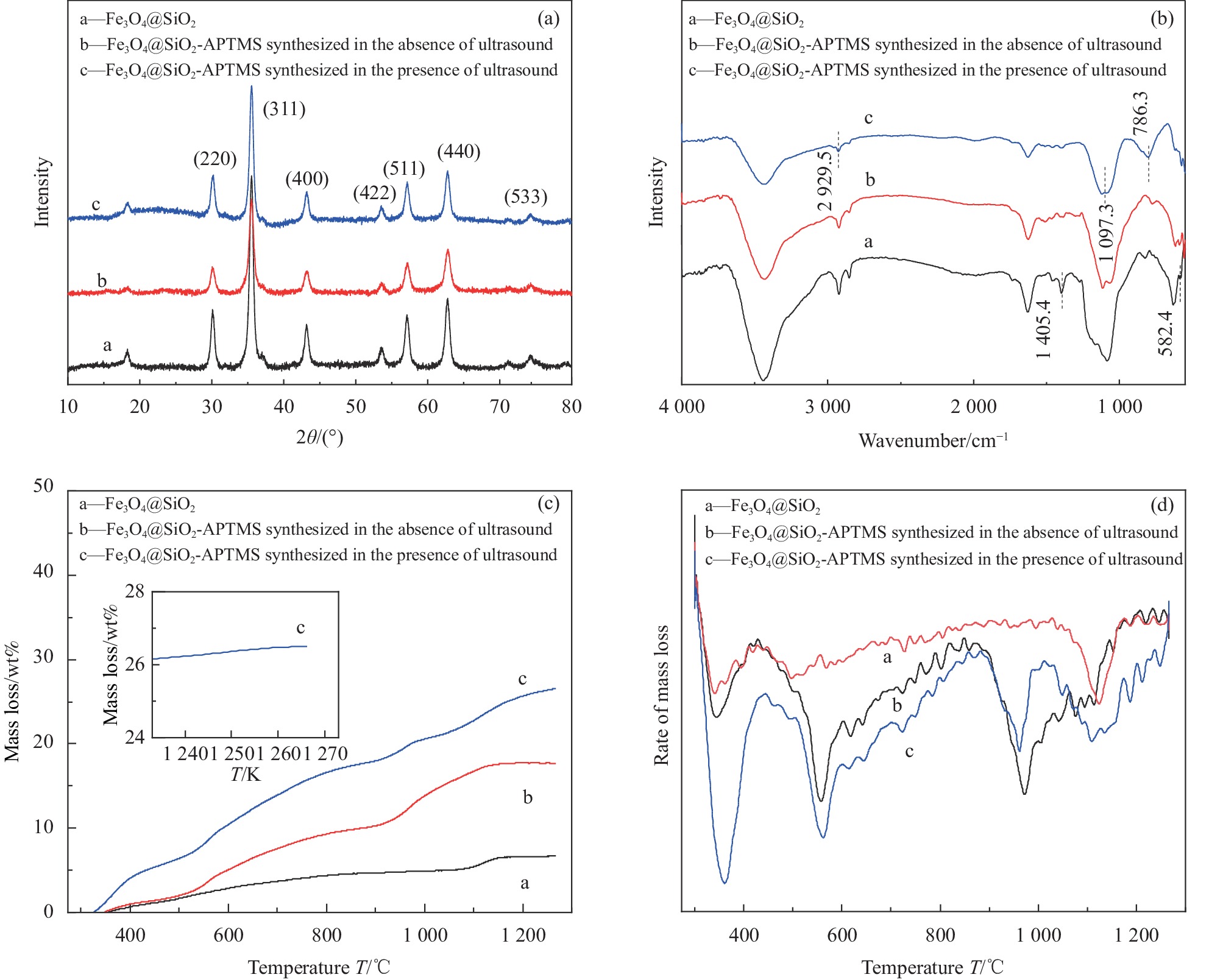
图4为无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS和超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的磁滞回线图谱。可知,3种材料的饱和磁强度分别为12.0 emu·g−1、9.0 emu·g−1和5.5 emu·g−1。说明在引入APTMS后,材料饱和磁强度降低,超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的饱和磁强度更低,可能是超声波辐照下材料表面有机层增多。但材料经30 s仍能从液体中分离,说明该材料的磁响应强度良好,便于分离和回收处理。
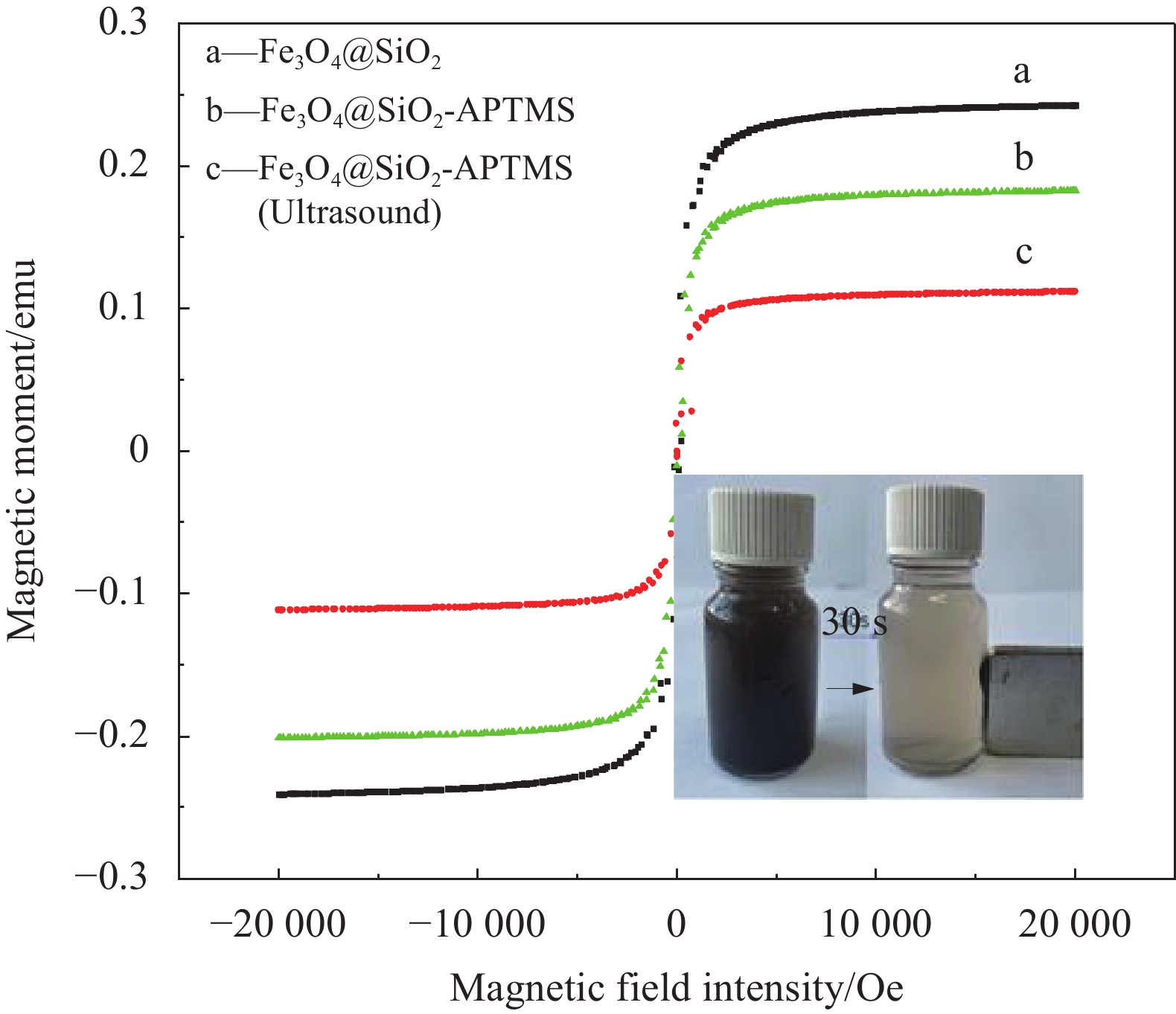
2.2 制备方法对吸附剂吸附效果对比
图5为无超声波辐照制备的Fe3O4@SiO2、Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS和超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果。可以看出,无超声波辐射下的 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果明显高于Fe3O4@SiO2;超声波强化后的材料平衡吸附量均大于无超声强化的材料。这说明引入APTMS和在超声波辐照下制备材料可以提高材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果,可能是由于APTMS上的官能团能够增强材料与Pb(Ⅱ)之间的相互作用力[20],超声波辐射使颗粒分散程度增大,增大了复合材料比表面积。
SiO2本身表面具有丰富的羟基,APTMS为硅烷化试剂,常搭配SiO2使用,直接使用APTMS与Fe3O4复合的较少,需要加入甲醇在Fe3O4表面引入羟基,而且 Fe3O4@APTMS难以控制粒径大小,更容易团聚[21]。因此制备了复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2和 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS,并探究其对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附。从对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果可知,超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS具有优异的吸附性能,后续实验均采用超声辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS。
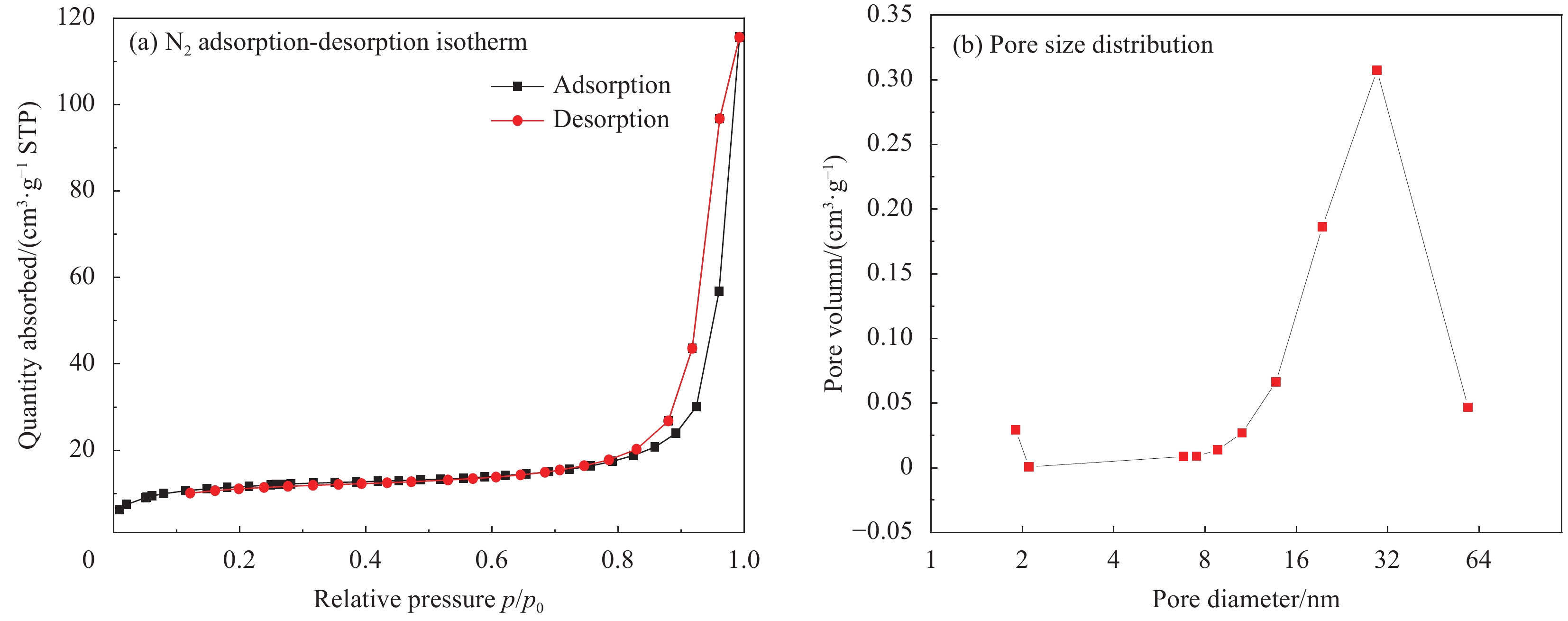
在低温77.4 K条件下,通过N2吸附脱附测得Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS比表面积为138 m2·g−1,平均孔径大小16.64 nm(BET),23.76 nm(BJH),对比Fe3O4的比表面积42 m2·g−1, Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS拥有更大的比表面积。图6为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的N2吸附脱附等温线及孔径分布图。可知,纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS的孔径主要分布在在19~30 nm,在0<p/p0<0.1低压力区时等温线出现拐点,说明进行的是单层吸附,材料表面有少量微孔;在0.1<p/p0<0.8中压力区时等温线十分平缓,为多层吸附,而高压区,等温线逐渐变阧,出现滞回环且没有平台出现,说明出现毛细孔凝聚现象,且吸附剂的中孔数量较多,大小均一,该N2吸附脱附等温线为Ⅳ型和H3型滞回环[22-23]。
制备过程中超声波的引入有利于SiO2和APTMS有效包裹在Fe3O4表面,使颗粒分散程度增大,从而增大复合材料比表面积。表1对比了本文的复合材料和已报道文献[24-26]中材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果,可见本文的复合材料有明显优势。
表 1 不同吸附剂对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果比较Table 1. Comparison of adsorption effects of different adsorbents for Pb (Ⅱ)2.3 复合材料投加量对Pb(Ⅱ) 吸附的影响
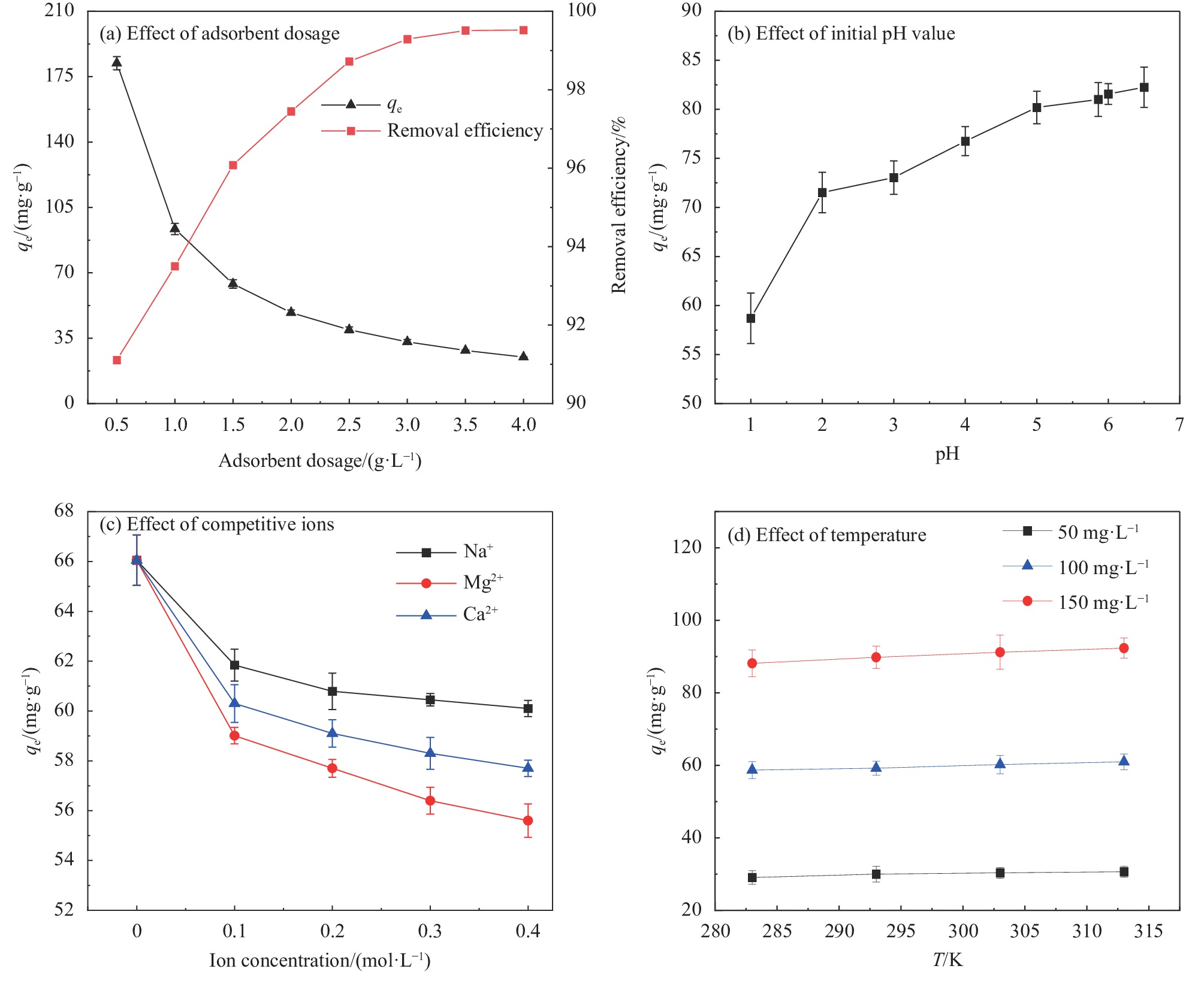
图7(a)为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS投加量对吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的影响。可知,随着复合材料投加量越多,Pb(Ⅱ)去除率越大,当投加量>2.5 g/L时Pb(Ⅱ)去除率逐渐趋于平稳,复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的平衡吸附量逐渐下降。
根据平衡移动的原理可以得到,所加入的复合材料越多,可提供的吸附位点也越多,吸附的Pb(Ⅱ)的量增大,溶液的吸附平衡浓度降低,但却使单位质量复合材料的吸附量减少,复合材料的利用率降低[27]。考虑Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的去除率、吸附剂的经济成本及利用率,吸附剂投加量选在1.0~1.5 g·L−1较优。
2.4 溶液初始pH值对吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的影响
溶液初始pH值大于7时,会生成Pb(Ⅱ)的氢氧化物沉淀,造成假性吸附,对实验结果产生影响,故在初始pH值<7的情况下探讨对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附。图7(b)为溶液初始pH值对Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的影响。可知,溶液初始pH值对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附影响较大,随着初始pH值的逐渐增大,复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的平衡吸附量呈上升趋势。可能是由于低pH值下复合材料上的—NH2易与H+发生质子化作用,由于静电的排斥作用抑制了复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附[28]。未调节pH时Pb(Ⅱ)溶液的pH值为5.86,此时复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量为81.013 mg·g−1,继续增大pH值,材料对Pb(Ⅱ)吸附量增幅较小,同时为了实验操作简便后续吸附实验溶液初始pH值均为5.86。
2.5 竞争性阳离子对吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的影响
图7(c)为不同浓度的竞争性阳离子对纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的影响。可知,随着其他阳离子浓度增大,Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量减小,并且Na+对吸附的影响小于Mg2+和Ca2+。可能是由于离子强度的增大提高了传质阻力,不同价态阳离子与复合材料的相互作用力不同,阳离子价态越高,其与复合材料作用力越强,占据一部分吸附点位,降低了复合材料与Pb(Ⅱ)间的作用力,对吸附产生一定的干扰[29]。
2.6 吸附热力学
图7(d)为温度对Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的影响。可知,随着温度的升高,复合材料对溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量逐渐增大,表明升温有利于吸附进行。
由lnK0对1/T作图,计算得到热力学参数吉布斯自由能∆G0、熵变∆S0和焓变∆H0,结果见图8、表2[30]。
从表2中可知该吸附过程的ΔG0<0,ΔS0>0,ΔH0>0;说明Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附是一个自发的熵增吸热过程。
2.7 吸附动力学
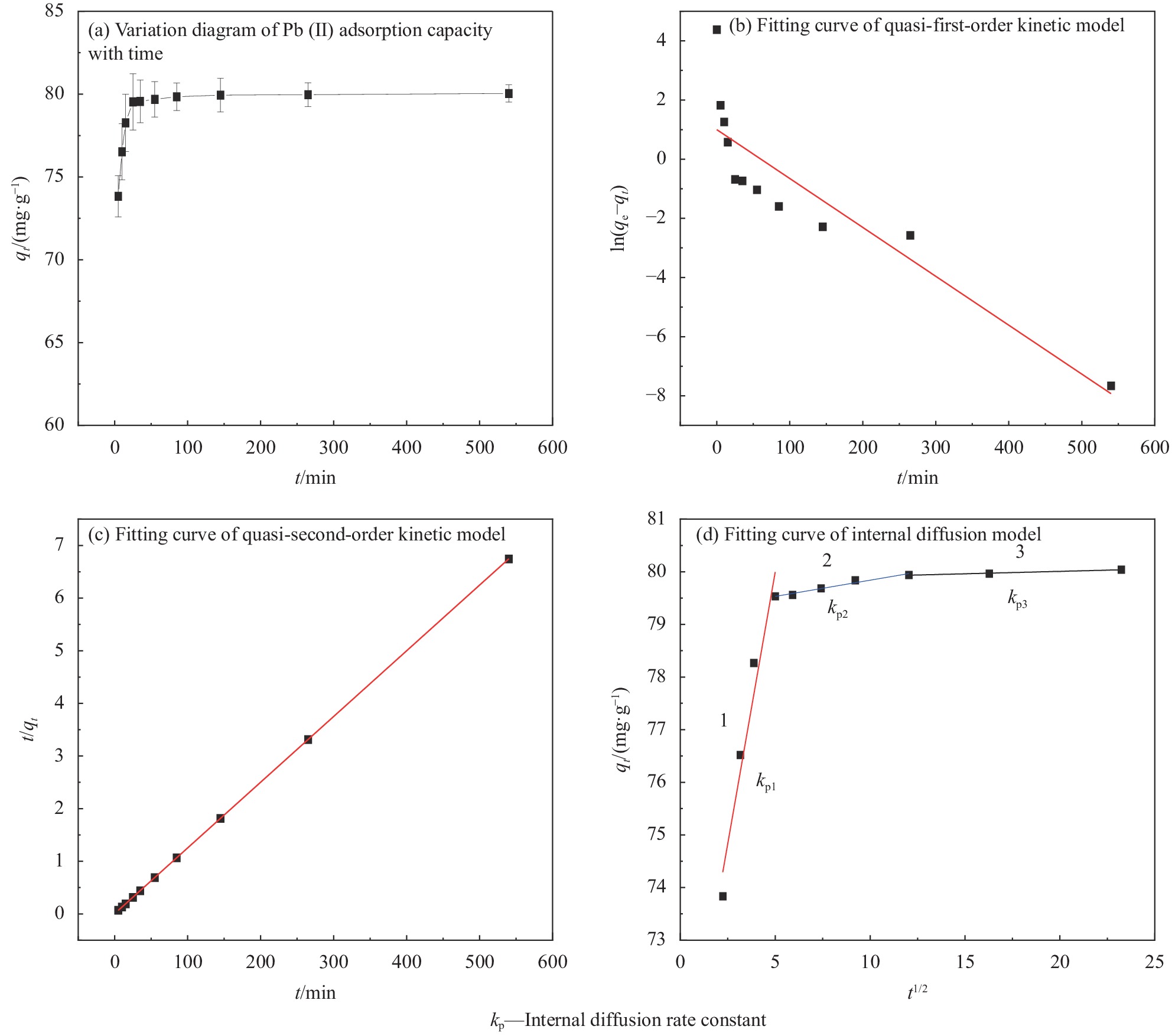
图9为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量随时间变化图和动力学模型拟合曲线。
由图9(a)可知,开始时复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附速度较快,大约100 min就能达到吸附平衡。为进一步了解吸附机制,以准一、准二级动力学方程和内扩散方程对吸附数据进行拟合并阐述Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附过程,拟合结果见图9(b)~9(d)和表3[31]。
表 2 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)热力学常数Table 2. Thermodynamic constants of Pb(Ⅱ) adsorbed by Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMSC0/(mg·L−1) ΔG0/(kJ·mol−1) ΔH0/(kJ·mol−1) ΔS0/(J·mol−1·K−1) 283 K 293 K 303 K 313 K 50 −3.555 −4.373 −4.827 −5.292 12.513 57.125 100 −3.746 −4.067 −4.609 −5.115 9.391 46.227 150 −3.767 −4.313 −4.871 −5.423 11.871 55.271 Notes: C0—Initial concentration of Pb (Ⅱ) solution; ∆G0—Gibbs free energy change; ∆H0—Enthalpy change; ∆S0—Entropy change. 表 3 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)吸附动力学方程拟合结果Table 3. Fitting results of Pb (Ⅱ) adsorption kinetic equation by Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMSQuasi-first order kinetics Quasi-second-order kinetics Internal diffusion equation k1 qe,cal qe,exp R2 k2 qe,cal qe,exp R2 kp C R2 0.0165 2.714 80.041 0.789 0.0401 79.99 80.041 0.999 kp1=2.0639 69.675 0.952 kp2=0.0616 79.223 0.969 kp3=0.0092 79.823 0.980 Notes: qe,cal—Theoretical saturated adsorption capacity; qe,exp—Experimental saturated adsorption capacity; k1—Quasi-first-order kinetic constant; k2—Quasi-second-order kinetic constant; C—Constant related to thickness and boundary layer. 准一和准二级动力学方程拟合相关系数R2依次为0.789、0.999。准二级动力学方程线性相关性更好,能更准确地描述Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附行为。准二级动力学方程以吸附剂和吸附质之间的化学吸附为主要步骤,表明该吸附过程主要受Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS表面活性官能团影响,其吸附力包括静电吸附、离子交换及形成化学键等作用[32]。通过准二级动力学方程计算得到平衡吸附量为79.99 mg·g−1,与实验测定值80.041 mg·g−1非常相近。
由图9(d)可知,内扩散方程拟合后分为3个阶段的线性关系且截距C≠0,不经过原点,说明内扩散不是控制吸附过程的唯一步骤而由多阶段控制[33]。吸附初期主要是外扩散阻力,材料表面有较多吸附位点,Pb(Ⅱ)由液相扩散到Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS表面,这一阶段短时间内即可完成,具有较快的扩散速率,即吸附阶段;在Pb(Ⅱ)吸附到复合材料的表面后由于吸附位点被占据,Pb(Ⅱ)开始由材料表面向内部扩散,分为中孔内扩散和微孔内扩散且kp2>kp3,这个过程需要耗费较长的时间才能逐渐趋于平衡状态,即内扩散阶段。kp1>kp2>kp3 说明吸附速率逐渐变小,内扩散阶段主导着整个吸附过程的反应。
2.8 吸附等温线实验
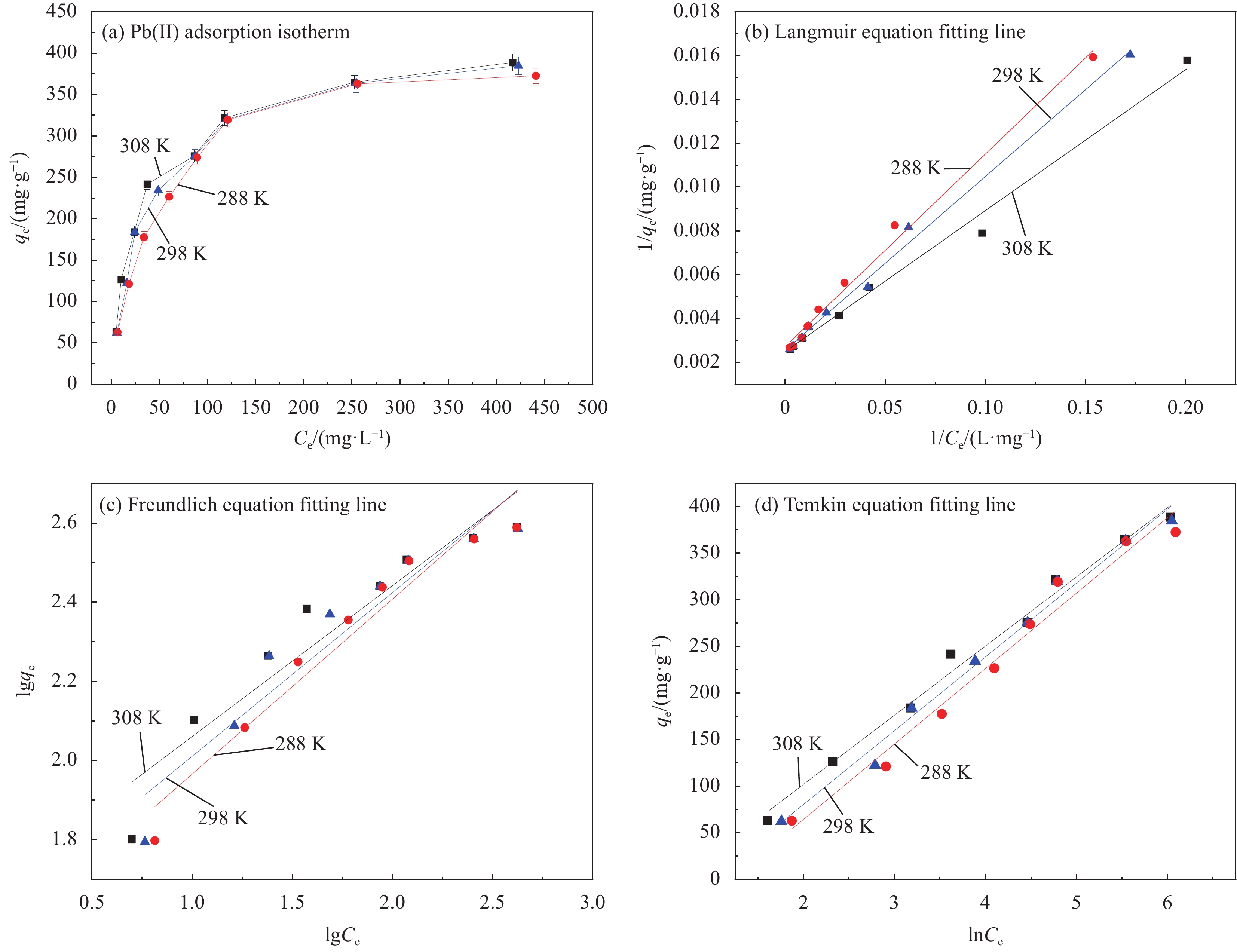
图10(a)为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附等温线。可知,随着Pb(Ⅱ)平衡浓度的增大,纳米复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量快速增加,之后趋于平缓达到饱和吸附,298 K时饱和吸附量为384.76 mg·g−1。
对各吸附数据依次用Langmuir、Freundlich和Temkin模型进行拟合[34],拟合图见图10(b)~10(d),拟合相关参数结果见表4。通过比较表4中3种等温吸附模型拟合的线性相关系数R2可知Langmuir模型的线性相关性更好,能更好地描述复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附过程。Langmuir模型吸附效果可用下式中分离常数RL表示:
表 4 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附等温线拟合结果Table 4. Adsorption isotherm fitting results of Pb(Ⅱ) by Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMST/K Langmuir Freundlich Temkin KL qm RL R2 KF R2 Kt Bl R2 308 0.0387 401.606 0.0252-0.615 0.991 47.83 0.905 0.534 74.27 0.989 298 0.0323 390.625 0.0312-0.570 0.993 39.57 0.916 0.373 79.25 0.988 288 0.0311 366.300 0.0300-0.602 0.995 33.41 0.946 0.299 81.02 0.977 Notes: KL—Langmuir adsorption coefficient (L·mg−1); KF—Freundlich adsorption coefficient (mg1−(1/n)·L1/n·g−1); Kt, Bl—Temkin adsorption isotherm constant; qm—Saturated adsorption capacity (mg·g−1); RL—Separation constant; R2—linear correlation coefficient. RL=11+KLC0 (11) 表中计算出的RL值均大于0小于1,有利于反应的进行,表明Pb(Ⅱ)易于被Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附,该复合材料的吸附性能较好。
2.9 重复利用实验
图11为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS循环使用次数对Pb(Ⅱ)吸附的影响。可知随着循环使用次数的增加,复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量减小,可能是由于在超声波辐照解吸脱附时,材料表面仍有部分Pb(Ⅱ)未被洗脱出来,仍占据吸附位点[35];另外超声波辐照解吸可能造成材料表面部分有机层的脱落,影响其吸附性能,导致材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量减少。5次重复使用后其平衡吸附量仅减小了6.25%,变化不大,说明纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS有着性质稳定、可回收、重复使用的特点。
2.10 耐酸碱性实验
复合材料耐酸碱腐蚀性研究结果见表5。可知,Fe3O4@SiO2在强酸条件下Fe的溶解量为25.542 mg·L−1,说明其易被强酸腐蚀,由于SiO2的存在使Fe3O4@SiO2抗碱性增强,Fe的溶解量只有0.276 mg·L−1;而Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS在强酸条件下,Fe的溶解量只有2.729 mg·L−1,说明Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS能较好地保护Fe。通过总有机碳(TOC)分析可知,在强酸、强碱条件下Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS中均只有3.5%左右的APTMS溶解,说明本实验制备的复合材料耐酸碱腐蚀性良好;升温和搅拌对复合材料的耐酸碱性影响不大,基本可以忽略,可见 APTMS包裹层有利于保护复合材料。
3. 吸附机制
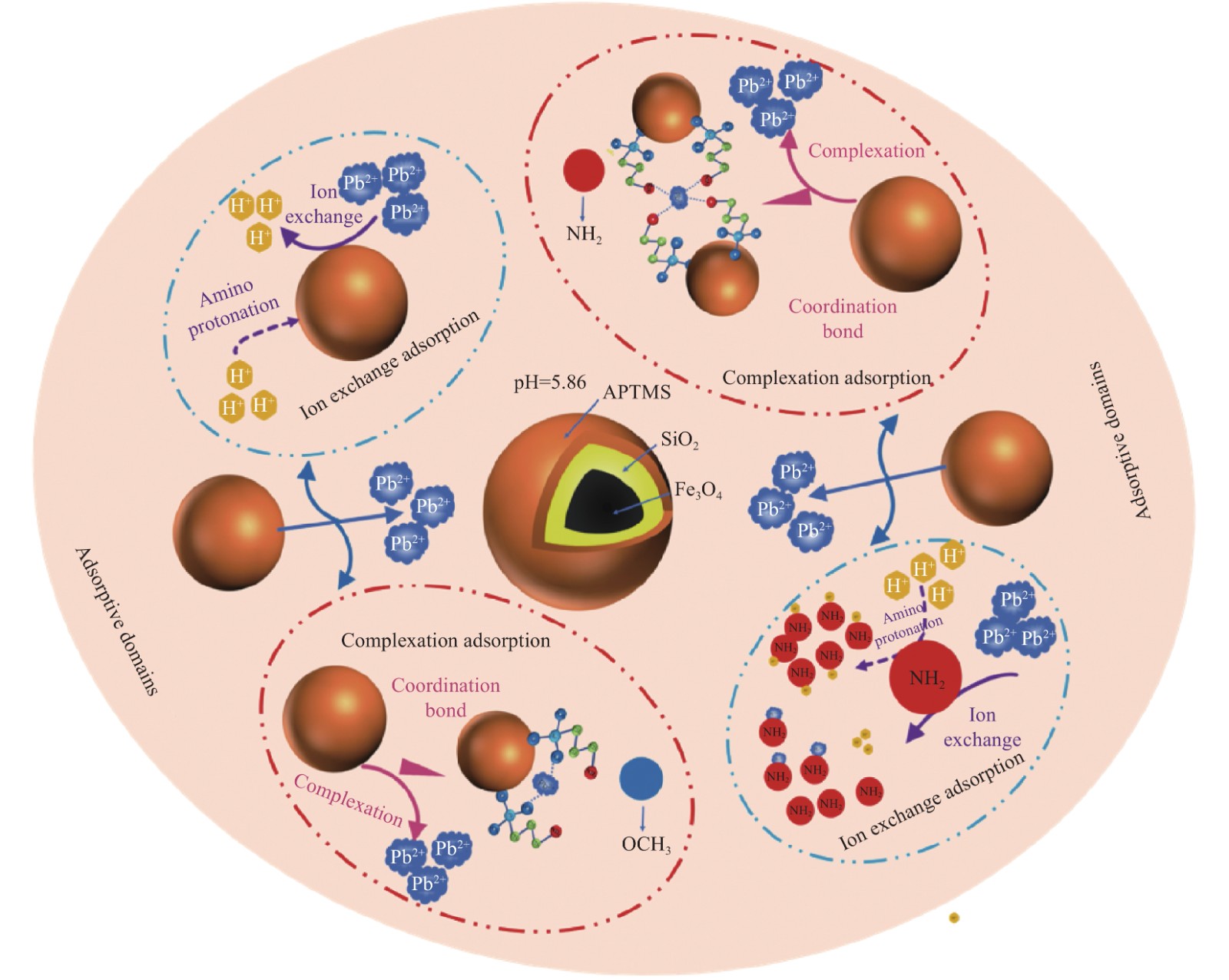
图12为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)前后的FTIR图谱。可知, 1383.2 cm−1处为脂肪族—CH3变形振动,吸附后此处峰强度增强;1097.3 cm−1处为Si—O振动峰,786.3 cm−1为N—H键的弯曲振动,吸附后此两处的峰值减小,可能是由于APTMS上—OCH3/—NH2可以和Pb(Ⅱ)形成稳定的络合物。
由动力学实验结果可知,纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的过程符合准二级动力学模型,即该纳米复合材料在吸附Pb(Ⅱ)时主要为化学吸附,判断其吸附机制为络合吸附;此外复合材料表面APTMS包裹层富含的—NH2与溶液中的H+发生质子化反应,再与Pb(Ⅱ)发生离子交换,进而使Pb(Ⅱ)被吸附[36-37]。
吸附机制可用如下方程式来表示可能发生的主要化学反应[38-39]。
表 5 复合材料耐酸碱腐蚀性研究Table 5. Study on acid and alkali corrosion resistance of compound materialsCondition Solution Fe3O4@SiO2 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS Fe/(mg·L−1) Fe/(mg·L−1) TOC/(mg·L−1) 298 K, soak, 24 h Water 0.135 0.015 0.025 0.1 mol·L−1 HCl 3.598 0.206 3.420 1 mol·L−1 HCl 25.542 2.729 8.866 0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.137 0.149 6.712 1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.276 0.186 8.106 313 K, stirring, 72 h Water 0.138 0.016 0.027 1 mol·L−1 HCl 24.842 2.629 8.886 1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.281 0.189 8.126 313 K, stirring, 96 h Water 0.140 0.017 0.029 1 mol·L−1 HCl 25.552 2.749 8.916 1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.296 0.191 8.173 Note: TOC—Total organic carbon. 离子交换:
\rm —NH_{\text{2}} + {H^ + } \to —NH_{3 }^ + (12) \rm —NH_{3}^ + + {\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}^ + \to —NH_2P{{\text{b}}^{{\text{2 + }}}} + {H}^ + (13) 络合反应:
\rm —\ddot NH_{\text{2}} + {\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}^ + \to —NH_{\text{2}}P{{\text{b}}^{{\text{2}} + }} (14) \rm —\ddot OCH_{\text{3}} + {\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}^ + \to —OCH_{\text{3}}P{{\text{b}}^{{\text{2}} + }} (15) 综上,推测Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)的机制为:(1) APTMS上的—NH2发生质子化反应与溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)发生离子交换吸附;(2) 溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)与复合材料表面上的APTMS上—OCH3/—NH2发生络合反应生成络合物,即发生络合吸附,具体吸附机制见图13。超声波辐照下制备的Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS中含有大量的—OCH3/—NH2,Pb(Ⅱ)与—OCH3/—NH2所形成的络合物受酸效应影响小,络合作用强稳定性大[40],初始溶液pH为5.86,用于离子交换的H+本身浓度很小,而且—NH2质子化作用后与Pb(Ⅱ)之间会有静电斥力[28],因此吸附机制以络合吸附为主。
4. 选择性实验
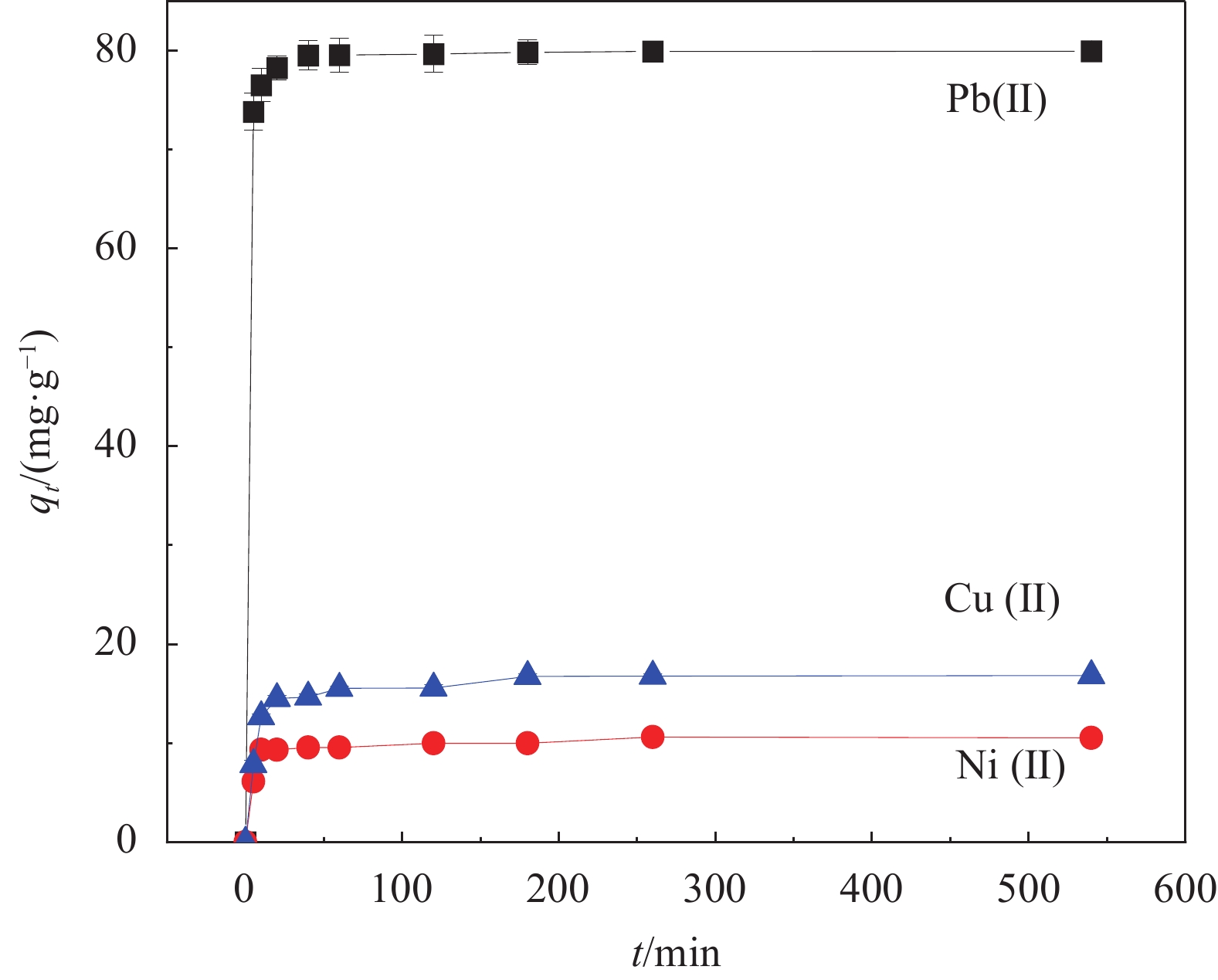
图14为Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附3种重金属离子的混合溶液时各离子吸附量随时间变化的曲线。可知,复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量为80 mg·g−1左右,而对于Cu(Ⅱ)和Ni(Ⅱ)的吸附量却不足18 mg·g−1,可见Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附量远远高于Cu(Ⅱ)和Ni(Ⅱ)的吸附量。
Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)和Ni(Ⅱ)的吸附机制相同,主要为金属离子与—OCH3/—NH2发生络合反应生成络合物,吸附量的大小可能与所形成络合物的稳定性有关, Pb(Ⅱ)相比Cu(Ⅱ)和Ni(Ⅱ)与活性基团的络合作用更强,形成络合物更稳定性 [41]。因此,Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对同浓度的混合溶液中的Pb(Ⅱ)具有良好的选择吸附性。
5. 结 论
(1) 超声波辐照下制备的纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷(APTMS)为球形颗粒,分散性和比表面积得到显著增强,具有良好的抗酸碱性和磁响应强度。
(2) 确定了纳米复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的较佳吸附条件:溶液初始pH值为5.86,吸附剂投加量为1.0~1.5 g·L−1;Langmuir模型能较好地反映其对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附过程;对Pb (Ⅱ)的吸附是一个自发的熵增吸热过程;准二级动力学方程的拟合效果最好。
(3) 纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附有良好选择性。
(4) 纳米复合材料对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附机制包括离子交换和络合吸附,其中络合吸附占主导作用。
-
表 1 不同吸附剂对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附效果比较
Table 1 Comparison of adsorption effects of different adsorbents for Pb (Ⅱ)
表 2 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS吸附Pb(Ⅱ)热力学常数
Table 2 Thermodynamic constants of Pb(Ⅱ) adsorbed by Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS
C0/(mg·L−1) ΔG0/(kJ·mol−1) ΔH0/(kJ·mol−1) ΔS0/(J·mol−1·K−1) 283 K 293 K 303 K 313 K 50 −3.555 −4.373 −4.827 −5.292 12.513 57.125 100 −3.746 −4.067 −4.609 −5.115 9.391 46.227 150 −3.767 −4.313 −4.871 −5.423 11.871 55.271 Notes: C0—Initial concentration of Pb (Ⅱ) solution; ∆G0—Gibbs free energy change; ∆H0—Enthalpy change; ∆S0—Entropy change. 表 3 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)吸附动力学方程拟合结果
Table 3 Fitting results of Pb (Ⅱ) adsorption kinetic equation by Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS
Quasi-first order kinetics Quasi-second-order kinetics Internal diffusion equation k1 qe,cal qe,exp R2 k2 qe,cal qe,exp R2 kp C R2 0.0165 2.714 80.041 0.789 0.0401 79.99 80.041 0.999 kp1=2.0639 69.675 0.952 kp2=0.0616 79.223 0.969 kp3=0.0092 79.823 0.980 Notes: qe,cal—Theoretical saturated adsorption capacity; qe,exp—Experimental saturated adsorption capacity; k1—Quasi-first-order kinetic constant; k2—Quasi-second-order kinetic constant; C—Constant related to thickness and boundary layer. 表 4 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附等温线拟合结果
Table 4 Adsorption isotherm fitting results of Pb(Ⅱ) by Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS
T/K Langmuir Freundlich Temkin KL qm RL R2 KF R2 Kt Bl R2 308 0.0387 401.606 0.0252-0.615 0.991 47.83 0.905 0.534 74.27 0.989 298 0.0323 390.625 0.0312-0.570 0.993 39.57 0.916 0.373 79.25 0.988 288 0.0311 366.300 0.0300-0.602 0.995 33.41 0.946 0.299 81.02 0.977 Notes: KL—Langmuir adsorption coefficient (L·mg−1); KF—Freundlich adsorption coefficient (mg1−(1/n)·L1/n·g−1); Kt, Bl—Temkin adsorption isotherm constant; qm—Saturated adsorption capacity (mg·g−1); RL—Separation constant; R2—linear correlation coefficient. 表 5 复合材料耐酸碱腐蚀性研究
Table 5 Study on acid and alkali corrosion resistance of compound materials
Condition Solution Fe3O4@SiO2 Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS Fe/(mg·L−1) Fe/(mg·L−1) TOC/(mg·L−1) 298 K, soak, 24 h Water 0.135 0.015 0.025 0.1 mol·L−1 HCl 3.598 0.206 3.420 1 mol·L−1 HCl 25.542 2.729 8.866 0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.137 0.149 6.712 1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.276 0.186 8.106 313 K, stirring, 72 h Water 0.138 0.016 0.027 1 mol·L−1 HCl 24.842 2.629 8.886 1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.281 0.189 8.126 313 K, stirring, 96 h Water 0.140 0.017 0.029 1 mol·L−1 HCl 25.552 2.749 8.916 1 mol·L−1 NaOH 0.296 0.191 8.173 Note: TOC—Total organic carbon. -
[1] 徐峥. 重金属污染水体的环境保护处理技术分析[J]. 信息记录材料, 2021, 22(9):235-237. DOI: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2021.09.111 XU Zheng. Analysis of environmental protection treatment technology of water body polluted by heavy metals[J]. Information Recording Material,2021,22(9):235-237(in Chinese). DOI: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2021.09.111
[2] TADJARODI A, ABBASZADEH A, TAGHIZADEHB M, et al. Solid phase extraction of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions based on a novel functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles with the aid of multivariate optimization methodology[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2015,49:416-421. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.013
[3] 郭健, 姚云, 赵小旭, 等. 粮食中重金属铅离子、镉离子的污染现状及对人体的危害[J]. 粮食科技与经济, 2018, 43(3):33-35, 85. GUO Jian, YAO Yun, ZHAO Xiaoxu, et al. Pollution status and harm to human body of heavy metal lead ion and cadmium ion in grain[J]. Grain Science, Technology and Economy,2018,43(3):33-35, 85(in Chinese).
[4] CENDROWSKIA K, SIKORAB P, ZIELINSKAA B, et al. Chemical and thermal stability of core-shelled magnetite nanoparticles and solid silica[J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,407:391-397. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.118
[5] 许端平, 陈丽媛, 孔岳. 纳米级四氧化三铁回收水中铅离子实验[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(1):75-77, 82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.01.018 XU Duanping, CHEN Liyuan, KONG Yue. Experiment on recovery of lead ion from water by nanometer iron tetroxide[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2021,50(1):75-77, 82(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.01.018
[6] 罗超. 二氧化锰和四氧化三铁对碳纳米管改性及其对Cd(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2014. LUO Chao. Modification of carbon nanotubes by manganese dioxide and ferric oxide and their adsorption for Cd(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅵ)[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2014(in Chinese).
[7] LIU J, ZHANG J, XING L, et al. Magnetic Fe3O4/attapulgite hybrids for Cd(II) adsorption: Performance, mechanism and recovery[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,412(14):125-237.
[8] DUGOSZ O, SZOSTAK K, KRUPINSKI M, et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles and their application for the photodegradation of anionic and cationic dyes[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2021,18(3):561-574. DOI: 10.1007/s13762-020-02852-4
[9] JIN S Y, PARK B C, HAM W S, et al. Effect of the magnetic core size of amino-functionalized Fe3O4-mesoporous SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles on the removal of heavy metal ions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A,2017,531:133-140.
[10] 王朝辉, 杨芳. 磺酸基功能化磁性纳米粒子的制备、表征及除去水中Cu(II)的研究[J]. 化学工程师, 2012, 202(7):15-19. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1124.2012.07.005 WANG Zhaohui, YANG Fang. Preparation, characterization and removal of Cu(II) from water by sulfonic acid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Engineer,2012,202(7):15-19(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1124.2012.07.005
[11] 赵永纲, 沈昊宇, 李勍, 等. 氨基功能化纳米Fe3O4磁性高分子吸附剂对废水中Cr(VI)的吸附研究[J]. 化学学报, 2009, 67(13):1509-1514. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2009.13.018 ZHAO Yonggang, SHEN Haoyu, LI Gou, et al. Study on the adsorption of Cr(VI) in wastewater by amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer adsorbent[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2009,67(13):1509-1514(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2009.13.018
[12] LIN S, LIU L, YANG Y, et al. Comparison of the adsorption preference using superparamagnetic Fe3O4-SH nanoparticles to remove aqueous heavy metal contaminants[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2017,125:319-327. DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2017.07.027
[13] ZHANG J, ZHAI S, SHI L, et al. Pb(II) removal of Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 core-shell nanomaterials prepared via a controllable sol-gel process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,215:461-471.
[14] 雷婷. 官能化磁性Fe3O4纳米颗粒的制备及其对污水中重金属离子的吸附性能研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2020. LEI Ting. Preparation of functional magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their adsorption properties for heavy metal ions in wastewater[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2020(in Chinese).
[15] ABAZARI R, MAHJOUB A R, MOLAIE S, et al. The effect of different parameters under ultrasound irradiation for synthesis of new nanostructured Fe3O4@bio-MOF as an efficient anti-leishmanial in vitro and in vivo conditions[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2018,43:248-261. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.01.022
[16] ZHAO D M, LI M, ZHANG D X, et al. Reductive dechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by Pd/Fe nanoparticles prepared in the presence of ultrasonic irradiation[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2013,20:864-871.
[17] 窦国金, 郑莹, 麦欣欣, 等. 二甲酚橙分光光度法测定化学镀镍液中的铅浓度[J]. 材料保护, 2012, 45(5):72-74, 88. DOI: 10.16577/j.cnki.42-1215/tb.2012.05.001 DOU Guojin, ZHENG Ying, MAI Xinxin, et al. Determination of lead in electroless nickel plating bath by xylenol orange spectrophotometry[J]. Material Protection,2012,45(5):72-74, 88(in Chinese). DOI: 10.16577/j.cnki.42-1215/tb.2012.05.001
[18] TA T K H, TRINH M T, LONG N V. Synthesis and surface functionalization of Fe3O4-SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles with 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane and 1, 1’-carbonyldiimidazole for bio-applications[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2016,504:376-383.
[19] 聂阳, 王永花, 胡良锋, 等. Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2磁性复合材料对水中全氟化合物的检测研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 2016(1):1-7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2016.01.001 NIE Yang, WANG Yonghua, HU Liangfeng, et al. Detection of perfluorinated compounds in water by Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 magnetic composites[J]. Journal of Analysis and Testing,2016(1):1-7(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2016.01.001
[20] 关桦楠, 宋岩, 龚德状. 功能化Fe3O4纳米粒子去除水中Cu2+的研究[J]. 化学工程师, 2018, 32(10):11-14. GUAN Hua'nan, SONG Yan, GONG Dezhuang. Study on removal of Cu2+ from Water by Functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Engineer,2018,32(10):11-14(in Chinese).
[21] 胡超凡, 贾丽. 硅烷化试剂修饰Fe3O4磁性微粒的研究进展[J]. 激光生物学报, 2009, 18(4):561-569. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2009.04.026 HU Chaofan, JIA Li. Research progress of Fe3O4 magnetic particles modified by silanization reagents[J]. Journal of Laser Biology,2009,18(4):561-569(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2009.04.026
[22] 陈华军, 王锐, 丁梧秀, 等. 聚乙二醇聚合度对介孔η-Al2O3纤维形貌及吸附能力的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(3):845-850. CHEN Huajun, WANG Rui, DING Wuxiu, et al. Effect of degree of polymerization of polyethylene glycol on the morphology and adsorption capacity of mesoporous η-Al2O3 fiber[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(3):845-850(in Chinese).
[23] 何飞, 赫晓东, 李垚. 掺杂二氧化硅干凝胶孔结构的分形特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007(1):81-85. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.014 HE Fei, HE Xiaodong, LI Yao. Fractal characteristics of pore structure of doped silica xerogel[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2007(1):81-85(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.014
[24] 李美兰, 豆小喻, 何娇, 等. 羧基化磁性Fe3O4复合材料的制备及其对水体中Pb2+的吸附研究[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(10):37-44. LI Meilan, DOU Xiaoyu, HE Jiao, et al. Preparation of carboxylated magnetic Fe3O4 composites and their adsorption of Pb2+ in water[J]. China Plastics,2021,35(10):37-44(in Chinese).
[25] 刘崇敏, 黄益宗, 于方明, 等. 改性沸石及添加CaCl2和MgCl2对重金属离子Pb2+吸附特性的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(5):803-809. LIU Chongmin, HUANG Yizong, YU Fangming, et al. Effect of modified zeolite and addition of CaCl2 and MgCl2 on the adsorption characteristics of heavy metal ion Pb2+[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2013,32(5):803-809(in Chinese).
[26] 孙玉坤. 功能化Fe3O4@PAMAM纳米复合材料的制备及其对重金属离子的去除[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. SUN Yukun. Preparation of functionalized Fe3O4@PAMAM nanocomposites and their removal of heavy metal ions[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese).
[27] 曹玮, 周航, 邓贵友, 等. 改性谷壳生物炭负载磁性Fe去除废水中Pb2+的效果及机制[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017(3):1437-1444. DOI: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511081 CAO Wei, ZHOU Hang, DENG Guiyou, et al. Effect and mechanism of Pb2+ removal from wastewater by magnetic Fe loaded with modified chaff biochar[J]. Journal of Envi-ronmental Engineering,2017(3):1437-1444(in Chinese). DOI: 10.12030/j.cjee.201511081
[28] FENG Z G, ZHU S, GODOI D, et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ on carboxyl-terminated suerparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2012,84(8):3764-3770. DOI: 10.1021/ac300392k
[29] 张立志, 易平, 方丹丹, 等. 超顺磁性纳米Fe3O4@SiO2功能化材料对镉的吸附机制[J]. 环境科学, 2021(6):2917-2927. ZHANG Lizhi, YI Ping, FANG Dandan, et al. Adsorption mechanism of cadmium on superparamagnetic nano-Fe3O4@SiO2 functionalized materials[J]. Environmental Science,2021(6):2917-2927(in Chinese).
[30] NASROLLAHZADEH M, ISSAABADI Z, SAJADI S M. Green synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4 nanocomposite using Hibiscus tiliaceus L. extract and its application for reductive catalysis of Cr(VI) and nitrocompounds[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2018,197:253-260. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.010
[31] MA J, JIA K F, CHENG G L, et al. Solid-phase extraction of Pb(II) ions based on L-cysteine functionalized Fe3O4/SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering,2016,142(11):04016062. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001062
[32] AKPOMIE K G, DAWODU F A. Efficient abstraction of nickel (II) and manganese (II) ions from solution onto an alkaline-modified montmorillonite[J]. Journal of Taibah University for Science,2014,8(4):343-356. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtusci.2014.05.001
[33] 刘嘉丽. 氨基改性Fe3O4@mC复合材料的制备及其对Pb2+的吸附性能研究[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2020. LIU Jiali. Preparation of amino modified Fe3O4@mC composites and their adsorption properties for Pb2+[D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2020(in Chinese).
[34] XIANG W, LIU X J, XIAO C W, et al. Triethylenetetramine-modified hollow Fe3O4/SiO2/chitosan magnetic nanocomposites for removal of Cr(VI) ions with high adsorption capacity and rapid rate[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2020,297(C):110041.
[35] ZHANG W B, DENG M, SUN C X, et al. Ultrasound-enhanced adsorption of chromium(VI) on Fe3O4 magnetic particles[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research,2014,53(1):333-339. DOI: 10.1021/ie401497k
[36] CRUZLOPES L P, MACENA M, ESTEVES B, et al. Ideal pH for the adsorption of metal ions Cr6+, Ni2+, Pb2+ in aqueous solution with different adsorbent materials[J]. Open Agriculture,2021,6(1):115-123. DOI: 10.1515/opag-2021-0225
[37] 王彦惠, 冷阳春, 成建峰, 等. Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2粒子对铀(Ⅵ)在阿拉善水相中的吸附性能研究[J]. 核科学与工程, 2020, 40(4):688-695. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2020.04.025 WANG Yanhui, LENG Yangchun, CHENG Jianfeng, et al. Study on the adsorption of uranium(VI) by Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 particles in alxa aqueous phase[J]. Nuclear Science and Engineering,2020,40(4):688-695(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0918.2020.04.025
[38] 包炳钦, 张军, 宋卫锋, 等. 磁性复合凝胶球对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附特性与机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6):1929-1938. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200924.001 BAO Bingqin, ZHANG Jun, SONG Weifeng, et al. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of magnetic compo-site gel spheres for Pb(Ⅱ)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(6):1929-1938(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200924.001
[39] 王申宛, 钟爽, 郑丽丽, 等. 共热解法制备方解石/生物炭复合材料及其吸附Pb(II)性能和机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(12):4282-4293. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210309.002 WANG Shenwan, ZHONG Shuang, ZHENG Lili, et al. Calcite/biochar composites prepared by co-pyrolysis and their adsorption properties and mechanism of Pb(Ⅱ)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(12):4282-4293(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210309.002
[40] 李安生. 聚天冬氨酸的合成及其与金属离子络合沉淀的研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2005. LI Ansheng. Synthesis of polyaspartic acid and its complexation with metal ions[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern University, 2005(in Chinese).
[41] 刘立华, 周智华, 吴俊, 等. 两性高分子螯合絮凝剂与Cu(Ⅱ)、Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)、Ni(Ⅱ)的螯合稳定性[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013(1):79-87. LIU Lihua, ZHOU Zhihua, WU Jun, et al. The chelating stability of amphoteric polymer chelating flocculant with Cu (Ⅱ), Pb(Ⅱ), Cd (Ⅱ) and Ni(Ⅱ)[J]. Journal of Environmental Science,2013(1):79-87(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 张颖,叶宇航,司文帅. 磁性二氧化硅复合材料制备及其对磺酰脲类除草剂的吸附研究. 化学研究与应用. 2025(02): 482-487 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 崔灿,牛姣姣,杨莲,周凌云,王环江,谢雅典. β-环糊精改性磁性棕榈纤维生物炭高效去除水中Pb(Ⅱ). 复合材料学报. 2024(03): 1378-1390 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 郝新丽,郑钰涛,周亚红,周靖凯,代雨函,马佳莹,李启航. Birnessite型二氧化锰纳米花吸附水中Pb~(2+)性能研究. 功能材料. 2024(05): 5086-5092 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 胡娟,肖楠,李文强,曾向宏,陈莉,陈敏剑,周远建. 2023年国内有机硅进展. 有机硅材料. 2024(03): 73-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘永侠,焦朋朋,王晴,杨丹,于晓娜,姜东良,王盛谕,吴昊. 磁性吸附剂Fe_3O_4@SiO_2-NH_2的制备及其对Cd~(2+)的吸附性能研究. 离子交换与吸附. 2024(05): 394-403 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 单书月,罗中秋,周新涛,尚波,田鑫聪,阎崔蓉. 钢渣构筑Fe-CSH吸附溶液中Pb(Ⅱ)、Cu(Ⅱ)、Zn(Ⅱ)性能及机理. 化工进展. 2024(10): 5867-5880 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 朱浩,杜春艳,曹姣,周璐,余关龙,严蓉,杨玉. 磁性硅酸盐纳米材料在光催化降解有机污染物中的研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2024(11): 5812-5823 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 田甜,付义乐,关丽,王溢源,周军. 海藻酸钠-羧甲基纤维素-氧化石墨烯复合气凝胶的制备及其对Pb(Ⅱ)的吸附. 复合材料学报. 2023(10): 5792-5802 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 黄健,孙运运,张华,奚姗姗,王金花,张佳妹,何春华,罗涛,余韵韩. NHFO@蜂巢石的制备及其吸附氨氮机制. 复合材料学报. 2023(11): 6130-6138 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 杨帆,付东,李鹏,谢洋,隋新,黄波. 磁性分子印迹聚合物中磁核的制备和表征. 黑龙江大学工程学报. 2022(04): 42-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-




 下载:
下载: