Preparation and properties of gelatin@poly(L-lactic acid) core-shell nanofibers
-
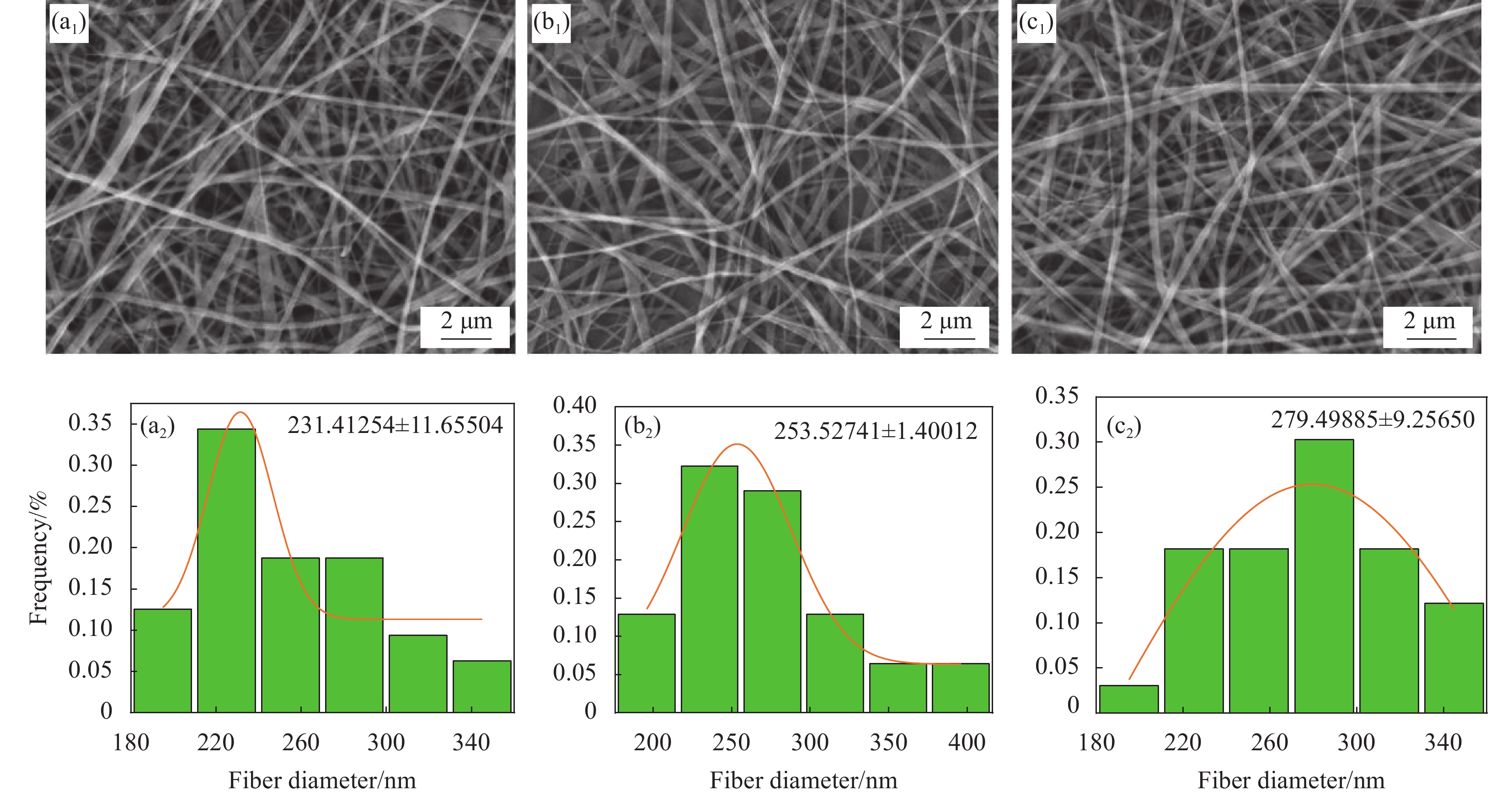
摘要: 同轴静电纺丝技术是基于传统静电纺丝技术改进,其制备的纤维材料不仅具有高比表面积,还具有特殊的核壳结构,能将活性分子等包覆在核内,保持其生物活性,达到缓释目的。本文通过同轴静电纺丝技术,制备具有核壳结构的明胶(Gelatin,GEL)@左旋聚乳酸(Poly(L-lactic acid),PLLA)纳米纤维膜。利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、激光共聚焦显微镜(LSCM)、拉伸测试及接触角测试等对纳米纤维膜的形貌结构和性能进行表征。探讨了静电纺丝工艺参数对纳米纤维形貌的影响,并考察了纳米纤维膜的生物相容性。结果表明:所制备的GEL@PLLA核壳纳米纤维表面光滑且有明显的核壳结构,增大核层与壳层流速比,纳米纤维的平均直径从231.41 nm增大到279.49 nm;增加纺丝电压,纤维直径逐渐减小;增加接收距离,纤维直径先减小后增大;核壳结构的GEL@PLLA纤维膜接触角为126.7°,与纯GEL纤维膜相比,表现为疏水性;力学测试结果显示GEL@PLLA核壳纳米纤维具有较好的柔性和弹性;体外细胞培养结果显示,第4代骨髓间充质干细胞(BMSCs)能在GEL@PLLA核壳纤维膜上黏附和增殖,表明该核壳纳米纤维膜具有较好的生物相容性。本文可为纤维膜进一步应用于药物控释系统及生物医用领域奠定基础。Abstract: Coaxial electrospinning technology is based on the improvement of traditional electrospinning technology. The fiber material prepared by it not only has a high specific surface area, but also has a special core-shell structure, which can encapsulate active molecules, maintain their biological activity, and achieve the goal of sustained release. This article uses coaxial electrospinning technology to prepare gelatin (GEL)@poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) nanofiber membranes with core-shell structure. The morphology, structure, and properties of nanofiber membranes were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), laser confocal microscopy (LSCM), tensile testing, and contact angle testing. The influence of electrospinning process parameters on the morphology of nanofibers was explored, and the biocompatibility of nanofiber membranes was investigated. The results showed that the surface of the prepared GEL@PLLA core-shell nanofibers was smooth and had a clear core-shell structure. Increasing the flow velocity ratio between the core-shell layers increases the average diameter of the nanofibers from 231.41 nm to 279.49 nm. Increasing the spinning voltage gradually reduces the fiber diameter. By increasing the receiving distance, the fiber diameter decreases first and then increases. The contact angle of the GEL@PLLA fiber membrane is 126.7°, which exhibits hydrophobicity compared to pure GEL fiber membrane. The mechanical test results show that GEL@PLLA core-shell nanofibers have good flexibility and elasticity. The results of in vitro cell culture showed that bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) can adhere and proliferate on the GEL@PLLA fiber membrane, indicate that the core-shell nanofiber membrane has good biocompatibility. This study can lay the foundation for the further application of fiber membranes in drug-controlled release systems and biomedical fields.
-
Key words:
- gelatin /
- poly(L-lactic acid) /
- coaxial electrospinning /
- core shell structure /
- nanofiber /
- drug-controlled release
-
图 1 不同核壳溶液推进速度比下GEL@PLLA核壳纤维的SEM图像和直径分布图:((a1), (a2)) 1 : 3;((b1), (b2)) 1 : 4;((c1), (c2)) 1 : 5
Figure 1. SEM images and diameter distribution of GEL@PLLA core-shell fibers under different propulsion velocity ratios of core shell solutions: ((a1), (a2)) 1 : 3; ((b1), (b2)) 1 : 4; ((c1), (c2)) 1 : 5
表 1 明胶(GEL)@左旋聚乳酸(PLLA)静电纺丝工艺参数
Table 1. Electrospinning process parameters of gelatin (GEL)@poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA)
Sample Velocity of flow
(core/shell)/(mm·s−1)Voltage/kV Needle-collector
distance/cmS1 1∶3 17 15 S2 1∶4 17 15 S3 1∶5 17 15 S4 1∶4 19 15 S5 1∶4 15 15 S6 1∶4 17 10 S7 1∶4 17 20 表 2 纤维的断裂伸长率和拉伸强度对比
Table 2. Comparison of elongation at break and tensile strength of fibers
Sample Elongation at break/% Tensile strength/MPa GEL 10.3383 1.7544 PLLA 9.2204 2.2772 GEL@PLLA 18.2957 1.8158 -
[1] GE J C, KIM J Y, YOON S K, et al. Fabrication of low-cost and high-performance coal fly ash nanofibrous membranes via electrospinning for the control of harmful substances[J]. Fuel,2019,237:236-244. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.09.068 [2] MIN L L, YANG L M, WU R X, et al. Enhanced adsorption of arsenite from aqueous solution by an iron-doped electrospun chitosan nanofiber mat: Preparation, characterization and performance[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019,535:255-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.09.073 [3] TONG H W, ZHANG X, WANG M. A new nanofiber fabrication technique based on coaxial electrospinning[J]. Materials Letters,2012,66(1):257-260. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.08.095 [4] ZHANG K, LI Z, KANG W, et al. Preparation and characterization of tree-like cellulose nanofiber membranes via the electrospinning method[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,183:62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.032 [5] LI W, SHI L, ZHOU K, et al. Facile fabrication of porous polymer fibers via cryogenic electrospinning system[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2019,266:551-557. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.11.035 [6] 李超, 宦思琪, 李庆德, 等. 纤维素纳米晶体对同轴电纺PMMA/PAN复合纳米纤维性能的影响[J]. 林业工程学报, 2017, 2(2):107-113.LI Chao, HUAN Siqi, LI Qingde, et al. Effect of cellulose nanocrystals on the properties of coaxial electrospun PMMA/PAN composite nanofibers[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2017,2(2):107-113(in Chinese). [7] DZIEMIDOWICZ K, SANG Q, WU J, et al. Electrospinning for healthcare: Recent advancements[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2021,9(4):939-951. doi: 10.1039/D0TB02124E [8] DING Y, LI W, CORREIA A, et al. Electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate/poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/sol-gel-derived silica hybrid scaffolds with drug releasing function for bone tissue engineering applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(17):14540-14548. [9] WEN P, WEN Y, ZONG M H, et al. Encapsulation of bioactive compound in electrospun fibers and its potential application[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(42):9161-9179. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b02956 [10] GARLOTTA D. A literature review of poly(lactic acid)[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2001,9(2):63-84. doi: 10.1023/A:1020200822435 [11] WU J, LIU S, ZHANG M, et al. Coaxial electrospinning preparation and antibacterial property of polylactic acid/tea polyphenol nanofiber membrane[J]. Journal of Industrial Textiles,2022,51(2):1778S-1792S. doi: 10.1177/15280837211054219 [12] LIU J, LI T, ZHANG H, et al. Electrospun strong, bioactive, and bioabsorbable silk fibroin/poly(L-lactic-acid) nanoyarns for constructing advanced nanotextile tissue scaffolds[J]. Materials Today Bio,2022,14:100243. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100243 [13] XIONG F, WEI S, SHENG H, et al. In situ polydopamine functionalized poly-L-lactic acid nanofibers with near-infrared-triggered antibacterial and reactive oxygen species scavenging capability[J]. International Journal of Biologi-cal Macromolecules,2022,201:338-350. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.024 [14] GUO J, SU W, JIANG J, et al. Enhanced tendon to bone healing in rotator cuff tear by PLLA/CPS composite films prepared by a simple melt-pressing method: An in vitro and in vivo study[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,165:526-536. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.02.003 [15] LYU Y, XU Y, SANG X, et al. PLLA-gelatin composite fiber membranes incorporated with functionalized CeNPs as a sustainable wound dressing substitute promoting skin regeneration and scar remodeling[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2022,10(7):1116-1127. doi: 10.1039/D1TB02677A [16] SINGH Y P, DASGUPTA S, BHASKAR R. Preparation, characterization and bioactivities of nano anhydrous calcium phosphate added gelatin-chitosan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science-Polymer Edition,2019,30(18):1756-1778. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2019.1663474 [17] XU Z, LIU P, LI H, et al. In vitro study on electrospun lecithin-based poly(L-lactic acid) scaffolds and their biocompatibility[J]. Journal of Biomaterials Science-Polymer Edition,2020,31(17):2285-2298. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2020.1802837 [18] JUNKA R, YU X. Polymeric nanofibrous scaffolds laden with cell-derived extracellular matrix for bone regeneration[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications,2020,113:110981. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110981 [19] PORRELLI D, MARDIROSSIAN M, MUSCIACCHIO L, et al. Antibacterial electrospun polycaprolactone membranes coated with polysaccharides and silver nanoparticles for guided bone and tissue regeneration[J]. ACS Applied Materials& Interfaces,2021,13(15):17255-17267. [20] MIGUEZ M, SABAROTS M G, CID M P, et al. Fabrication and characterization of gelatin/calcium phosphate electrospun composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2022,23(7):1915-1923. doi: 10.1007/s12221-022-4166-4 [21] LYU Y, SANG X, TIAN Z, et al. Electrospun hydroxyapatite loaded L-polylactic acid aligned nanofibrous membrane patch for rotator cuff repair[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,217:180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.061 [22] 张晓莉, 汤克勇, 郑学晶. 同轴静电纺丝法制备PVA-胶原微纳米纤维[J]. 丝绸, 2016, 53(6):6-10.ZHANG Xiaoli, TANG Keyong, ZHENG Xuejing. Preparation of PVA-collagen micro and nano fibers by coaxial electrospinning[J]. Silk,2016,53(6):6-10(in Chinese). [23] ANAYA M J M, BOLDRINI P L C, DE MIRANDA B P G, et al. Novel polycaprolactone (PCL)-type I collagen core-shell electrospun nanofibers for wound healing applications[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Biomaterials,2023,111(2):366-381. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35156 [24] HAJIKHANI M, EMAM-DJOMEH Z, ASKARI G. Fabrication and characterization of mucoadhesive bioplastic patch via coaxial polylactic acid (PLA) based electrospun nanofibers with antimicrobial and wound healing application[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,172:143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.051 [25] 崔志香, 涂建炳, 司军辉, 等. 同轴静电纺丝制备PCL-PLA芯-壳结构复合纤维及其形态分析[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2015, 33(6):786-790, 830.CUI Zhixiang, TU Jianbing, SI Junhui, et al. Preparation and morphology analysis of PCL-PLA core-shell compo-site fiber by coaxial electrospinning[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2015,33(6):786-790, 830(in Chinese). [26] 董宇涵, 辜鹏程, 张子阳, 等. 肌腱仿生用定向PLLA微纳米纤维的静电纺丝工艺参数研究[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2022, 30(5):10-17.DONG Yuhan, GU Pengcheng, ZHANG Ziyang, et al. Study on electrospinning process parameters of directional PLLA micronanofibers for tendon bionics[J]. Materials Science and Technology,2022,30(5):10-17(in Chinese). [27] HE Z, RAULT F, VISHWAKARMA A, et al. High-aligned PVDF nanofibers with a high electroactive phase prepared by systematically optimizing the solution property and process parameters of electrospinning[J]. Coatings,2022,12(9):1310. doi: 10.3390/coatings12091310 [28] BUCHKO C J, CHEN L C, SHEN Y, et al. Processing and microstructural characterization of porous biocompatible protein polymer thin films[J]. Polymer,1999,40(26):7397-7407. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00866-0 [29] 杜馨禹, 魏亮, 孙润军, 等. 工艺参数对PLA/CA复合纳米纤维形貌与直径的影响[J]. 合成纤维, 2022, 51(5):26-32.DU Xinyu, WEI Liang, SUN Runjun, et al. The influence of process parameters on the CA/PLA composite nanofibers morphology and diameter[J]. Synthetic Fiber,2022,51(5):26-32(in Chinese). [30] 杜江华, 杨婷婷, 郭生伟, 等. 有序PEO/PHB核壳超细纤维的制备及性能[J]. 材料工程, 2021, 49(10):123-131.DU Jianghua, YANG Tingting, GUO Shengwei, et al. Preparation and properties of ordered PEO/PHB core-shell microfiber[J]. Materials Engineering,2021,49(10):123-131(in Chinese). [31] 仲宣树, 刘宗建, 耿雪, 等. 材料表面性质调控细胞黏附[J]. 化学进展, 2022, 34(5):1153-1165.ZHONG Xuanshu, LIU Zongjian, GENG Xue, et al. Surface properties of materials regulate cell adhesion[J]. Progress in Chemistry,2022,34(5):1153-1165(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: