Properties of microwave absorbers formed by fused deposition modeling with Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composite wire
-
摘要: 具有轻质高强、宽吸收带、薄厚度和热稳定性的电磁吸收材料是实现微波吸收应用的核心要求。本文以聚乳酸(PLA)为基体,Fe3O4和多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)为填料,通过球磨混合和熔融挤出法制备出Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合线材,利用熔融沉积成型(FDM)制备出Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料。采用XRD、SEM和矢量网络分析仪分别对复合材料的物相结构、微观形貌和电磁特性进行了表征,并研究了Fe3O4含量对复合材料吸波性能的影响。Fe3O4与MWCNTs-PLA复合形成的复合吸波材料质量轻、稳定性好、介电性能可调,因其良好的阻抗匹配和电磁波衰减能力而表现出优异的宽带吸收能力。实验结果表明:Fe3O4含量达到25wt%,厚度为1.4 mm时,反射损耗达到−48.5 dB,有效吸收带宽达到6.78 GHz (10.38~17.16 GHz),表现出优异的微波吸收性能。Abstract: Electromagnetic absorbing materials with light weight, high strength, wide absorption band, thin thickness and thermal stability are the core requirements for microwave absorption applications. In this paper, Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composite wires were prepared by ball milling mixing and melt extrusion using polylactic acid (PLA) as matrix, Fe3O4 and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) as fillers, and Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composites were prepared by melt deposition molding (FDM). The phase structure, microstructure and electromagnetic properties of the composites were characterized by XRD, SEM and vector network analyzer, respectively. The composite absorbing material of Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA has light weight, good stability, and adjustable dielectric properties, which exhibits excellent broadband absorption ability due to its good impedance matching and electromagnetic wave attenuation ability. The experimental results show that when the Fe3O4 content reaches 25wt% and the thickness is 1.4 mm, the reflection loss reaches −48.5 dB and the effective absorption bandwidth reaches 6.78 GHz (10.38-17.16 GHz), showing excellent microwave absorption performance.
-
Keywords:
- dielectric loss /
- magnetic loss /
- Fe3O4 /
- carbon nanotube /
- impedance matching
-
Janus材料因其独特的结构或组成的不对称性展现出很多特殊的功能,近年来为人们所广泛关注[1-4]。目前,Janus材料在乳化剂[5]、自驱动马达[6]、药物释放[7]、催化[8]和柔性可穿戴[9]等众多领域都展现出巨大的应用前景。自1991年被诺贝尔奖获得者De Gennes[1]首次提出以来,经过30多年的发展,已经有多种不同组成或形貌结构的Janus材料被合成出来,从组成来分类,主要有聚合物/聚合物型、无机物/无机物型及聚合物/无机物型;从形貌来区分,包括颗粒状[10]、棒状[11]、片状[12]、锥状[13]及雪人状[14]等。
不同于传统Janus材料,Janus中空球在空间结构上中心对称,其非对称性体现在内外表面的化学组成和性质上,这种独特的结构使其可以用作特殊微容器,用于分离富集、传输和受限反应等[15-19]。但是,研究发现,完整致密的壳层会限制微球和环境之间的物质传输[15]。因此,为了提高Janus微球和环境之间的物质传输速率,引入了贯穿壳层的孔道,即Janus笼。目前,已经有多种功能Janus笼被制备出来,作为高效传输的微反应容器,在水处理、催化,环境响应富集释放等方向展现出一定的应用前景[20-23]。
课题组在之前的工作中,最早提出了乳液界面溶胶凝胶法制备二氧化硅Janus中空球的方法[24]。进而在此基础上通过两种表面活性剂在乳液界面发生微相分离在中空球表面形成通孔,同时引入磁性纳米粒子并在中空球内腔接枝温敏性聚合物,得到热敏性的聚合物-无机物复合功能Janus笼[22]。但是,在之前的研究中也发现,Janus笼的表面孔径很难调控,孔径也只能限制在50 nm以下,如果想要通过增加致孔表面活性剂的量得到更大孔径的笼,不仅孔径变化不大,而且还会导致壳层局部呈不连续结构,在表面形成二氧化硅小颗粒,进而破坏球形结构,无法得到完整的中空球。
基于这些考虑,在此提出了新的研究思路,先用烷基和末端带卤素基团的硅烷偶联剂代替带活性双键的硅烷偶联剂,壳层依旧引入磁性纳米颗粒,先制备出支撑性良好、孔径大范围可调的无机Janus笼,进而利用可控自由基聚合代替自由基聚合,在更温和的反应条件下在内腔接枝pH响应性聚合物,得到支撑性好、孔径大范围可调的功能有机/无机功能复合Janus笼,并验证了其可以在改变环境pH的条件下实现对油相的可控吸收和释放,以及在磁操控下实现装载物的定向传输,有望用于药物装载和体内靶向释放等领域。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
无水三氯化铁(FeCl3,分析纯)、油酸钠(分析纯)、油酸(分析纯)、吐温80(Tween 80,化学纯)、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS,化学纯)、铜粉(分析纯)和52#石蜡(熔点50~52℃)购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES,98%)、香豆素-6 (98%)、荧光素5-异硫氰酸酯(FITC,95%)、三乙胺(99%)、正辛基三乙氧基硅烷(98%)和2-溴-2-甲基丙酰溴(98%)购自北京百灵威科技有限公司;正硅酸乙酯(分析纯)、甲醇(分析纯)、正癸烷(分析纯)和甲苯(分析纯)购自西陇科学股份有限公司;1, 1-双十八烷基-3, 3, 3, 3-四甲基吲哚羰花青高氯酸盐(dil-C18,98%)和甲基丙烯酸二乙氨基乙酯(DEAEMA,>98.5%)购自西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司(Sigma-Aldrich);三[2-(二甲氨基)乙基]胺(Me6TREN,97%)购自梯希爱(上海)化成工业发展有限公司(TCI);预水解的苯乙烯马来酸酐共聚物水溶液(HSMA,10wt%)为自制。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
(1) 磁性无机Janus笼的制备。取0.3 g合成的油溶性磁性Fe3O4颗粒[25]、1.1 g APTES、0.88 g正辛基三乙氧基硅烷和5.2 g正硅酸乙酯加入到25 g正癸烷中混合均匀作为油相;将15 mL 10wt%的HSMA的水溶液加入75 mL水中,用2 mol/L HCl调pH为3~4。然后再加入0.03 g Tween 80,混合均匀,作为水相。混合水油两相,用高速剪切机(Fluko FA25,德国Fluko)在12000 r/min的速度下剪切乳化3 min。将剪切所得乳液转移至三口瓶中,70℃反应12 h,得到磁性无机Janus笼。
(2) 末端Br基硅烷偶联剂的合成。将4.31 g APTES和2.55 g三乙胺(TEA)加入到20 mL甲苯中,通氮气30 min。再将5.95 g溴代异丁酰溴(BiBB)溶解于10 mL甲苯中,加入到恒压漏斗中。在冰浴条件下,缓慢的将溴代异丁酰溴甲苯溶液缓慢滴加到体系中,磁力搅拌过夜后,离心除去下层白色沉淀后,旋蒸除去甲苯,即得到末端为溴基的硅烷偶联剂。
(3) pH响应性磁性复合Janus笼的制备。将10 mg 铜粉和50 mg上述步骤(1)合成的磁性无机Janus笼分散到36 mL水中,通氮气30 min。将0.2 g DEAEMA和30 μL配体Me6TREN分散到18 mL甲醇中,通氮气30 min后和水相混合,在50℃水浴中反应12 h。磁分离,用乙醇洗涤3次,真空干燥,得到内表面接枝有PDEAEMA的磁性聚合物/无机磁性复合Janus笼。
1.2.2 复合Janus笼pH响应性吸释实验
(1) 复合Janus笼对油相的pH响应性吸释和磁分离。在0.2 g甲苯中加入少量油溶性荧光染料dil-C18染色,在样品瓶中将10 mg磁性复合Janus笼分散在5 g水中,再加入染色甲苯,调节pH至5,此时水油两相明显分层,再调节pH至9,振荡吸附,甲苯层消失,用磁铁吸附,吸附有甲苯的复合Janus笼即在磁铁一侧的瓶壁处富集,将pH调回5,振荡静置后用磁铁吸附,甲苯层重新出现;同样在0.2 g甲苯中加入少量油溶性荧光染料dil-C18染色,在样品瓶中将10 mg磁性复合Janus笼分散在5 g水中,再加入染色甲苯,调节pH至5,此时水油两相明显分层,保持pH值不变,振荡后用磁铁吸附,甲苯无法被复合Janus笼吸附。
(2) 复合Janus笼在荧光显微镜下的pH响应性吸释:将50 mg磁性复合Janus笼分散在10 g水中,加入水溶性荧光燃料FITC进行染色标记。将0.5 g加入少量香豆素-6荧光染料染色的甲苯加入到溶解有10 mg表面活性剂SDS的10 g水中,超声乳化得到水包油乳液。将FITC标记的复合Janus笼水分散液加入到乳液中,调节pH至9左右,避光搅拌,分别在磁分离复合Janus笼前后在荧光显微镜(Olympus IX83,日本Olympus)下观察;再调节pH至5左右,避光搅拌,同样分别在磁分离复合Janus笼前后在荧光显微镜下观察。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 磁性无机Janus笼的制备、孔径调节与表征
在之前制备复合Janus笼时,课题组是将硅烷前驱体和聚合物单体同时溶解在油相中,一步得到有机/无机复合Janus多孔球[22]。但是多孔球的孔径只能在50 nm左右且难以调节,对应的致孔表面活性剂Tween 80在水相的浓度在0.22wt%以下,当Tween 80浓度继续升高时,会使多孔球外表面生成SiO2小颗粒,进而破坏球形结构。
本文用正辛基三乙氧基硅烷代替含活性双键的硅烷偶联剂作为球壳内侧接枝亲油基团的硅前驱体,同时将制备的油溶性Fe3O4纳米颗粒分散在油相中,得到外侧为氨基,内侧为烷基的磁性无机Janus笼。样品分别在扫描电子显微镜(SEM,带有元素分析 EDX的Quanta FEG 250,美国 FEI)和透射电子显微镜(TEM,JEM-1011,日本 JEOL)下进行观察,如图1所示。Janus笼的直径约为1~3 μm,孔径约为200~400 nm (图1(a)、图1(b)),同时不同于内侧接枝活性双键的无机Janus笼,即使没有聚合物的支撑,内侧为正辛基硅烷修饰的Janus笼也不会塌缩。进而对无机Janus笼进行超声粉碎,可以得到表面具有孔道的磁性Janus片(图1(c))。对得到的Janus片进行包埋切片,在TEM下观察,如图1(d)所示,可以看到磁性纳米粒子镶嵌在壳层中。
调节致孔表面活性剂Tween 80的加入量,即可对Janus笼球壳表面的通孔孔径进行调节。如图2所示,Tween 80在水相的浓度分别为0.01wt% (图2(a))、0.02wt% (图2(b))、0.04wt% (图2(c))和0.08wt% (图2(d))时,其表面孔径可从40 nm左右增加到约1 μm。
![]() 图 1 内侧修饰正辛基的磁性无机Janus笼的SEM图像 (a) 和TEM图像 (b);由磁性无机Janus笼破碎得到的Janus多孔片的SEM图像 (c) 和甲基丙烯酸甲酯(MMA)包埋切片后的TEM图像 (d)Figure 1. SEM image (a) and TEM image (b) of magnetic organic Janus cage with octyl group grafted onto interior surface; SEM image (c) of Janus porous nanosheets crushed from magnetic inorganic Janus cage and cross section TEM image (d) of slice of magnetic inorganic Janus cage after embedding in methyl methacrylate (MMA) and section
图 1 内侧修饰正辛基的磁性无机Janus笼的SEM图像 (a) 和TEM图像 (b);由磁性无机Janus笼破碎得到的Janus多孔片的SEM图像 (c) 和甲基丙烯酸甲酯(MMA)包埋切片后的TEM图像 (d)Figure 1. SEM image (a) and TEM image (b) of magnetic organic Janus cage with octyl group grafted onto interior surface; SEM image (c) of Janus porous nanosheets crushed from magnetic inorganic Janus cage and cross section TEM image (d) of slice of magnetic inorganic Janus cage after embedding in methyl methacrylate (MMA) and section在之前的工作中,即使Tween 80的含量提高近10倍,孔径的大小变化也不明显[22],相比之下,本文孔径对Tween 80的量变化更敏感。这是由于在之前工作中,由于无机/有机壳层是一锅法制备,因而在油相中加入了大量的聚合物单体,其和Tween 80相容性比烷烃溶剂要差,使Tween 80在界面的微相分区面积较小,即使浓度增加,对分区面积影响也不大,因而难以对孔径进行大范围调节,继续增加Tween 80的浓度只能破坏壳层。而本文先构建无机壳层,油相中只添加了硅前驱体,同时用烷基硅烷偶联剂代替带有活性双键的硅前驱体,使油相和Tween 80非极性部分的基团极性相近,使Tween 80微区可以在界面更加铺展,因而能够通过改变Tween 80的量来实现孔径的大范围调节。为了进一步验证,在不改变其他条件,仅仅不添加聚合物单体的情况下重复之前的制备过程,如图3所示,腔内不一步接枝聚合物时,制备的无机笼的孔径明显变大且孔径对Tween 80的含量更加敏感,但是失去聚合物的支撑,无机笼壳层本身支撑性差,呈塌缩状态。
![]() 图 3 (a) 水相中Tween 80添加量为0.22wt%制备的无机/有机复合Janus笼的SEM图像;(b) 水相中Tween 80添加量为0.04wt%制备的无机笼的SEM图像Figure 3. (a) SEM image of the polymer/inorganic composite Janus cages synthesized at 0.22wt% of Tween 80 in aqueous phase; (b) SEM image of inorganic Janus cages synthesized at 0.04wt% of Tween 80 without addition of monomer in aqueous phase
图 3 (a) 水相中Tween 80添加量为0.22wt%制备的无机/有机复合Janus笼的SEM图像;(b) 水相中Tween 80添加量为0.04wt%制备的无机笼的SEM图像Figure 3. (a) SEM image of the polymer/inorganic composite Janus cages synthesized at 0.22wt% of Tween 80 in aqueous phase; (b) SEM image of inorganic Janus cages synthesized at 0.04wt% of Tween 80 without addition of monomer in aqueous phase2.2 磁性pH响应性聚合物/无机复合Janus笼的制备
研究发现,用带烷基的硅前驱体替代带活性双键的硅前驱体能够得到支撑性良好的无机笼,但是单纯的烷基链修饰内侧使得无机笼没有活性位点去接枝功能性的聚合物,限制了Janus笼的应用。考虑到自由基聚合难以控制,本工作基于“铜媒介”可控自由基聚合法(CuCRP)代替自由基聚合,在笼内侧接枝了pH响应性聚合物[26]。
为了在无机Janus笼内表面接枝聚合物,先要在内侧修饰上卤素基团。通过氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷和溴代异丁酰溴在等物质的量的条件下进行反应,制备出末端为溴基的硅烷偶联剂。对产物进行核磁共振(1H NMR,Bruker Avance III 400 HD,德国 Bruker)表征,各个H原子峰已在图4(a)中标注,其中,化学位移在6.96×10−6的峰对应着酰胺上与N相连的H,且积分结果为1 ,证明末端为溴基的硅烷偶联剂成功合成。再以摩尔比1∶1的比例将合成的末端Br基硅烷偶联剂和正辛基三乙氧基硅烷一起加入油相作为亲油一侧的修饰基团,得到内表面接枝Br基的Janus笼。如图4(b)所示,对Janus笼进行EDX元素分析,证明Br的成功引入。
![]() 图 4 (a) 合成的末端带Br基的硅烷偶联剂的核磁共振图谱;(b) 内表面接枝Br基的磁性无机Janus笼的SEM图像及内嵌EDX图谱(方框为元素分析所选区域)Figure 4. (a) 1H NMR spectrum of synthesized silane end with Br group; (b) SEM image and inset EDX spectrum of magnetic inorganic Janus cage with Br group grafted onto the interior surface (Box is the selected area for element analysis)
图 4 (a) 合成的末端带Br基的硅烷偶联剂的核磁共振图谱;(b) 内表面接枝Br基的磁性无机Janus笼的SEM图像及内嵌EDX图谱(方框为元素分析所选区域)Figure 4. (a) 1H NMR spectrum of synthesized silane end with Br group; (b) SEM image and inset EDX spectrum of magnetic inorganic Janus cage with Br group grafted onto the interior surface (Box is the selected area for element analysis)成功在壳层内侧引入溴基以后,采用“铜媒介”可控自由基聚合法(CuCRP)制备pH响应性Janus笼[26],将磁性无机Janus笼分散在水相,pH响应性单体DEAEMA和配体分散在甲醇中,混溶后加入铜粉作为催化剂,壳层内侧的溴基引发聚合,接枝上pH响应性聚合物PDEAEMA,即得到pH响应的磁性聚合物/无机复合Janus笼。其反应体系温和简单,在水和甲醇混溶体系就可以聚合油溶性单体,更加清洁无污染,反应体系耐氧性高。在扫描电镜下观察,其形貌未有明显变化(图5(a))。将接枝功能聚合物的复合Janus笼用预聚物甲基丙烯酸甲酯(MMA)包埋,再进行切片并在TEM下观察,如图5(b)所示,发现Janus笼壳层内出现衬度较低的一层,说明PDEAEMA仅接枝在Janus笼的内表面(为了便于观察,包埋切片的Janus笼未复合磁性纳米颗粒)。将复合Janus笼超声破碎得到复合多孔片,发现内侧接枝聚合物之后变得粗糙(图5(c)),用HF刻蚀除去无机层,得到聚合物笼(图5(d))。
对复合Janus笼分别进行红外图谱(FTIR,Bruker EQUINOX 55,德国 Bruker)和热失重(TGA, Perkin-Elmer Pyris 1, 美 国 Perkin-Elmer)分析。其红外图谱如图6(a)所示,接枝聚合物后的Janus笼(曲线2)对比于无机磁性Janus笼(曲线1),在1725 cm−1出现新的特征峰,对应着聚合物PDEAEMA的酯基峰。此外,1050~1150 cm−1对应着二氧化硅Si—O—Si的非对称伸缩振动峰,1633 cm−1对应的为氨基的特征峰,595 cm−1对应着的Fe—O特征峰。通过TGA分析可测得复合Janus笼中聚合物的含量(图6(b))。图中曲线1为无机磁性Janus笼的热失重曲线,其残余63.1wt%,失重的原因主要为有机基团热解和硅前驱体进一步缩合造成。而曲线2为接枝聚合物后的复合Janus笼的曲线,其热解后残余36.8wt%,因而计算出复合Janus笼中聚合物质量含量为41.7wt%。
![]() 图 5 (a) 内表面接枝聚甲基丙烯酸二乙氨基乙酯(PDEAEMA)的磁性无机/有机复合Janus笼的SEM图像;(b) 未复合磁性纳米颗粒的内表面接枝PDEAEMA无机/有机复合Janus笼切片的TEM图像;(c) 复合Janus笼破碎后的多孔片的SEM图像;(d) 用HF酸刻蚀除去无机壳层后的有机笼的SEM图像Figure 5. (a) SEM image of magnetic composite Janus cage with polydiethylaminoethyl methacrylate (PDEAEMA) grafted onto interior surface; (b) Cross-section TEM image of composite Janus cage with PDEAEMA grafted onto interior surface (without Fe3O4 nanoparticles); (c) SEM image of Janus porous nanosheets crushed from composite Janus cage; (d) SEM image of organic cage obtained by etching inorganic shell with HF
图 5 (a) 内表面接枝聚甲基丙烯酸二乙氨基乙酯(PDEAEMA)的磁性无机/有机复合Janus笼的SEM图像;(b) 未复合磁性纳米颗粒的内表面接枝PDEAEMA无机/有机复合Janus笼切片的TEM图像;(c) 复合Janus笼破碎后的多孔片的SEM图像;(d) 用HF酸刻蚀除去无机壳层后的有机笼的SEM图像Figure 5. (a) SEM image of magnetic composite Janus cage with polydiethylaminoethyl methacrylate (PDEAEMA) grafted onto interior surface; (b) Cross-section TEM image of composite Janus cage with PDEAEMA grafted onto interior surface (without Fe3O4 nanoparticles); (c) SEM image of Janus porous nanosheets crushed from composite Janus cage; (d) SEM image of organic cage obtained by etching inorganic shell with HF![]() 图 6 (a) 磁性无机Janus笼(曲线1)和磁性有机/无机复合Janus笼(曲线2)的FTIR图谱;(b) 磁性无机Janus笼(曲线1)和磁性有机/无机复合Janus笼(曲线2)的在空气中的热失重曲线Figure 6. (a) FTIR spectra of magnetic inorganic Janus cage ( curve 1) and magnetic composite Janus cage (curve 2); (b) Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves in air of magnetic inorganic Janus cage (curve 1) and magnetic composite Janus cage (curve 2)
图 6 (a) 磁性无机Janus笼(曲线1)和磁性有机/无机复合Janus笼(曲线2)的FTIR图谱;(b) 磁性无机Janus笼(曲线1)和磁性有机/无机复合Janus笼(曲线2)的在空气中的热失重曲线Figure 6. (a) FTIR spectra of magnetic inorganic Janus cage ( curve 1) and magnetic composite Janus cage (curve 2); (b) Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) curves in air of magnetic inorganic Janus cage (curve 1) and magnetic composite Janus cage (curve 2)2.3 磁性pH响应性聚合物/无机复合Janus笼用于油水分离、传输和响应性吸释
PDEAEMA为pH响应性聚合物,pKa约为7.2,当环境pH值大于其pKa时,PDEAEMA表现为疏水,反之则为亲水。Janus笼接枝pH响应性聚合物后,可以通过调节pH值来改变Janus笼内部的亲疏水环境,实现磁操控的pH响应性油水分离,进而可用于药物在体内的靶向释放等。
首先对复合Janus笼进行磁操控pH响应性吸释和磁分离实验,如图7所示。先将油溶性荧光染料dil-C18加入到少量甲苯中以便后续观察,将甲苯加入到分散有复合Janus笼的水中并调节水相pH值为5,两者不互溶形成界限分明的两相(图7(a))。再将水相pH值调至9,振荡吸附,甲苯和水相分层消失,体系呈浑浊的均相,再用磁铁进行磁分离,发现不再出现两相分层,而是甲苯都随着复合Janus笼被吸附在瓶壁上(图7(b))。将pH调回5,振荡后静置,再用磁铁进行磁分离,发现油水分相重新出现,当环境变为酸性时,油相重新被Janus笼释放出来(图7(c))。作为对照,保持水相pH值为5不变,重复上述实验,发现油相无法在酸性条件下被复合笼吸入(图7(d)、图7(e))。由此,复合Janus笼可对环境中的油进行pH响应性的吸释并可在磁操控下定向运输。
![]() 图 7 内表面接枝PDEAEMA的磁性复合Janus笼对油相的pH响应性及磁操控分离实验:(a) 分散有复合Janus笼的水(下层)和甲苯(上层)分相照片,甲苯中加入1, 1-双十八烷基-3, 3, 3, 3-四甲基吲哚羰花青高氯酸盐 (dil-C18)染料以便于观察,水相pH值为5;(b) 调节pH至9,振荡后磁分离吸收甲苯的复合Janus笼的照片;(c) 调节pH至5,振荡静置后磁铁吸附复合Janus笼的照片;(d) 分散有复合Janus笼的水(下层)和经dil-C18染色的甲苯(上层)分相照片,水相pH值为5;(e) 保持pH为5不变,振荡静置后磁铁吸附复合Janus笼的照片Figure 7. pH-responsive absorption and release of the oil and magnetic manipulation of magnetic composite Janus cage with PDEAEMA grafted onto interior surface: (a) Immiscible mixture of toluene (top)/aqueous dispersion of composite Janus cage (bottom), oil soluble dye 1, 1'-dioctadecyl-3, 3, 3', 3'-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine perchlorate (dil-C18) is added in toluene and the pH value of aqueous dispersion is 5; (b) pH value is modulated to 9 and oil contained magnetic Janus cages are collected by magnets after vibration; (c) pH value is modulated back to 5 and magnetic Janus cages are collected by magnets after vibration with the release of dyed oil; (d) Immiscible mixture of toluene (top)/aqueous dispersion of composite Janus cage (bottom), oil soluble dye dil-C18 is added in toluene and the pH value of aqueous dispersion is 5; (e) pH value remains to be 5 and magnetic Janus cages are collected by magnets after vibration while dyed oil remains unchanged
图 7 内表面接枝PDEAEMA的磁性复合Janus笼对油相的pH响应性及磁操控分离实验:(a) 分散有复合Janus笼的水(下层)和甲苯(上层)分相照片,甲苯中加入1, 1-双十八烷基-3, 3, 3, 3-四甲基吲哚羰花青高氯酸盐 (dil-C18)染料以便于观察,水相pH值为5;(b) 调节pH至9,振荡后磁分离吸收甲苯的复合Janus笼的照片;(c) 调节pH至5,振荡静置后磁铁吸附复合Janus笼的照片;(d) 分散有复合Janus笼的水(下层)和经dil-C18染色的甲苯(上层)分相照片,水相pH值为5;(e) 保持pH为5不变,振荡静置后磁铁吸附复合Janus笼的照片Figure 7. pH-responsive absorption and release of the oil and magnetic manipulation of magnetic composite Janus cage with PDEAEMA grafted onto interior surface: (a) Immiscible mixture of toluene (top)/aqueous dispersion of composite Janus cage (bottom), oil soluble dye 1, 1'-dioctadecyl-3, 3, 3', 3'-tetramethylindodicarbocyanine perchlorate (dil-C18) is added in toluene and the pH value of aqueous dispersion is 5; (b) pH value is modulated to 9 and oil contained magnetic Janus cages are collected by magnets after vibration; (c) pH value is modulated back to 5 and magnetic Janus cages are collected by magnets after vibration with the release of dyed oil; (d) Immiscible mixture of toluene (top)/aqueous dispersion of composite Janus cage (bottom), oil soluble dye dil-C18 is added in toluene and the pH value of aqueous dispersion is 5; (e) pH value remains to be 5 and magnetic Janus cages are collected by magnets after vibration while dyed oil remains unchanged进而在荧光显微镜下观察复合Janus笼对油相pH响应性的吸释过程,如图8所示。将甲苯加入香豆素-6荧光染料标记后再用十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)为乳化剂和水乳化得到水包油乳液,乳液液滴在荧光显微镜下呈现蓝色。将pH响应性复合Janus笼先用FITC进行荧光标记,染料可吸附在Janus笼壳层便于后续观察。再将标记后的Janus笼加入上述荧光标记的水和甲苯的乳液中,分散均匀,调节pH为9左右,避光搅拌后再置于荧光显微镜下观察,发现蓝色的甲苯液滴(圆圈内)被吸入到Janus笼腔体内(图8(a)),磁分离Janus笼后取水相置于荧光显微镜下观察,蓝色液滴消失(图8(b)),证明在pH=9的条件下,Janus笼将甲苯完全吸入腔内;把pH调至5,壳层内聚合物由疏水转变为亲水,甲苯被挤出,此时在荧光显微镜下仅仅看到Janus笼呈现绿色的光圈,腔内蓝色液滴消失(图8(c)),磁分离后对水相取样观察,出现蓝色液滴(球形),证明甲苯被Janus笼响应性释放(图8(d)),说明复合Janus笼可通过改变环境pH值可以实现可控的油水分离。
![]() 图 8 pH=9时复合Janus笼吸附荧光染色甲苯的荧光显微镜图像(a)和用磁铁分离吸附甲苯的Janus笼后,上层水样的荧光显微镜图像(b); pH=5时Janus笼释放出甲苯后的荧光显微镜图像(c)和磁铁分离Janus笼后上层水样的荧光显微镜图像(d)Figure 8. Fluorescence microscopy images of the Janus composite cage after absorption of toluene with pH of the circumstance of 9 (a) and the supernatant water after magnetic collection of the Janus cage (b); Fluorescence microscopy images of the Janus composite cage after release of toluene with pH of the circumstance of 5 (c) and the supernatant water after magnetic collection of the Janus cage (d)
图 8 pH=9时复合Janus笼吸附荧光染色甲苯的荧光显微镜图像(a)和用磁铁分离吸附甲苯的Janus笼后,上层水样的荧光显微镜图像(b); pH=5时Janus笼释放出甲苯后的荧光显微镜图像(c)和磁铁分离Janus笼后上层水样的荧光显微镜图像(d)Figure 8. Fluorescence microscopy images of the Janus composite cage after absorption of toluene with pH of the circumstance of 9 (a) and the supernatant water after magnetic collection of the Janus cage (b); Fluorescence microscopy images of the Janus composite cage after release of toluene with pH of the circumstance of 5 (c) and the supernatant water after magnetic collection of the Janus cage (d)3. 结 论
(1) 通过乳液界面溶胶凝胶和两种表面活性剂在界面微相分离先制备磁性无机Janus笼,内部修饰的烷基基团使无机笼壳层具有良好支撑性,同时可通过调节吐温80 (Tween 80)含量实现孔径在40 nm~1 μm可调,进一步利用同样修饰在内表面的卤素基团,通过“Cu媒介”的活性自由基聚合法在温和的反应条件下成功在内表面接枝pH响应性聚合物得到功能无机/有机复合Janus笼。
(2) 将复合Janus笼用于油水分离,证明了其可通过调控环境pH来实现对油相的响应性吸收和释放。这种pH敏感性的微容器且表面带有增强传质的孔道,有望用于药物的装载和体内靶向释放等领域。
-
图 5 不同Fe3O4含量的Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料SEM图像:(a) 6%MWCNTs/PLA;(b) 10%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA;(c) 15%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA;(d) 20%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA;((e), (f)) 25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA
Figure 5. SEM images of Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composites with different Fe3O4 contents: (a) 6%MWCNTs/PLA; (b) 10%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA; (c) 15%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA; (d) 20%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA; ((e), (f)) 25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA
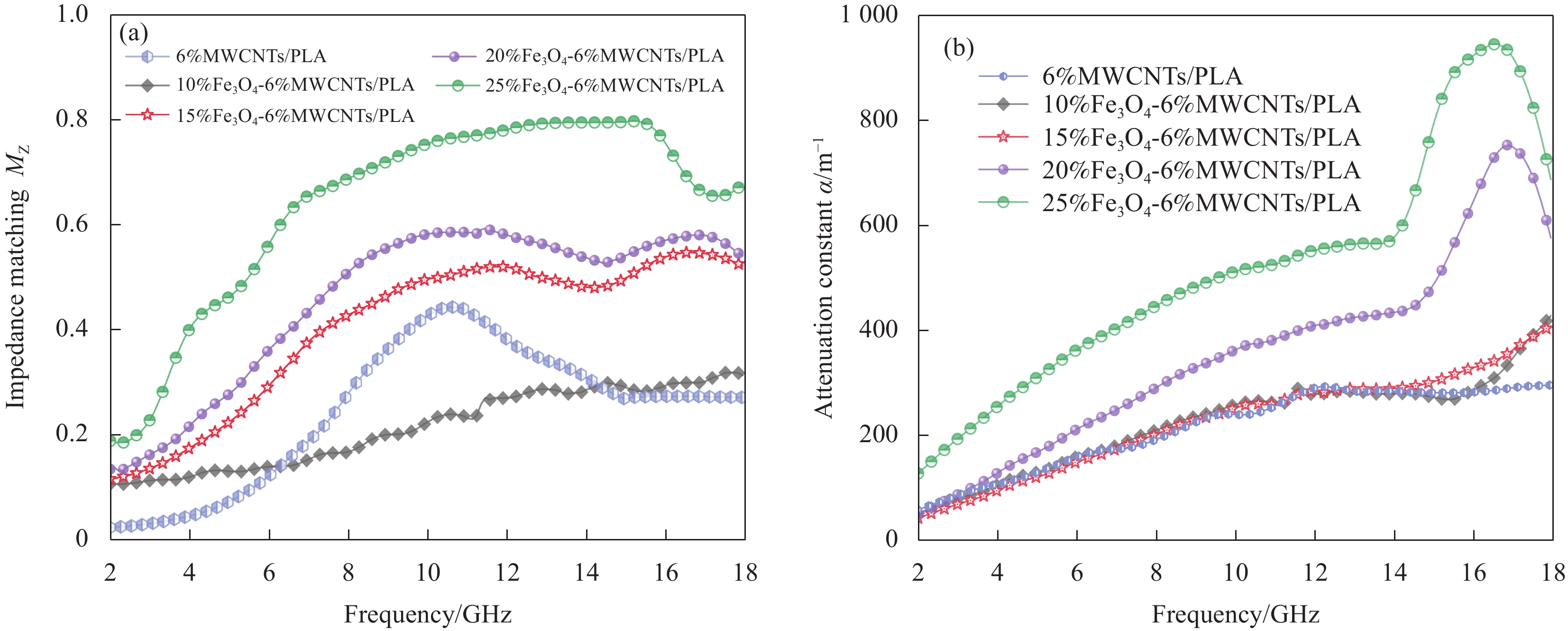
图 7 Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料的电磁参数:(a) 复介电常数实部;(b) 复介电常数虚部;(c) 介电损耗角正切;(d) 复磁导率实部;(e) 复磁导率虚部;(f) 磁损耗角正切
Figure 7. Electromagnetic parameters of Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composites: (a) Real part of complex permittivity; (b) Imaginary part of complex permittivity; (c) Dielectric loss tangent; (d) Real part of complex permeability; (e) Imaginary part of complex permeability; (f) Magnetic loss tangent
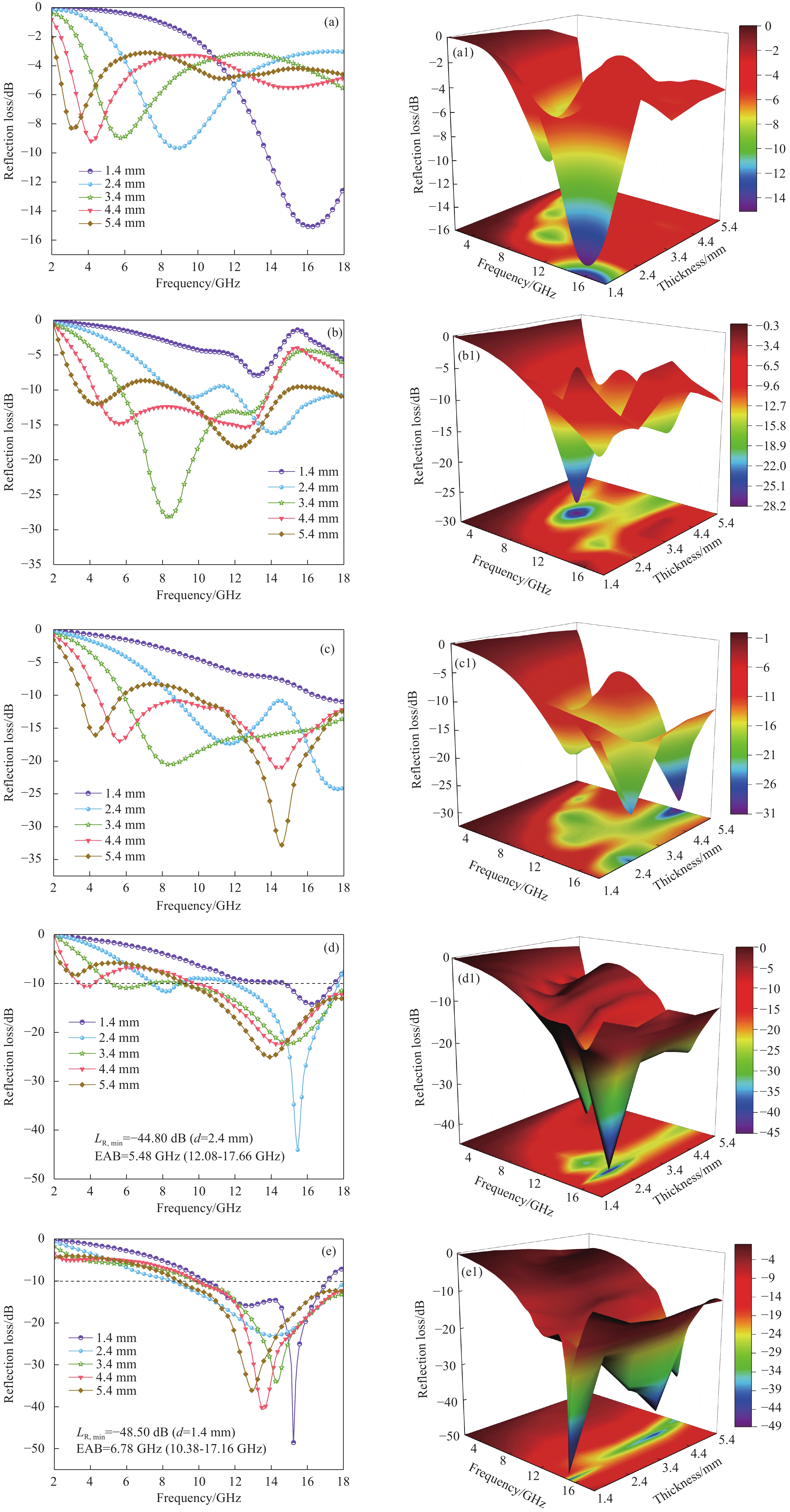
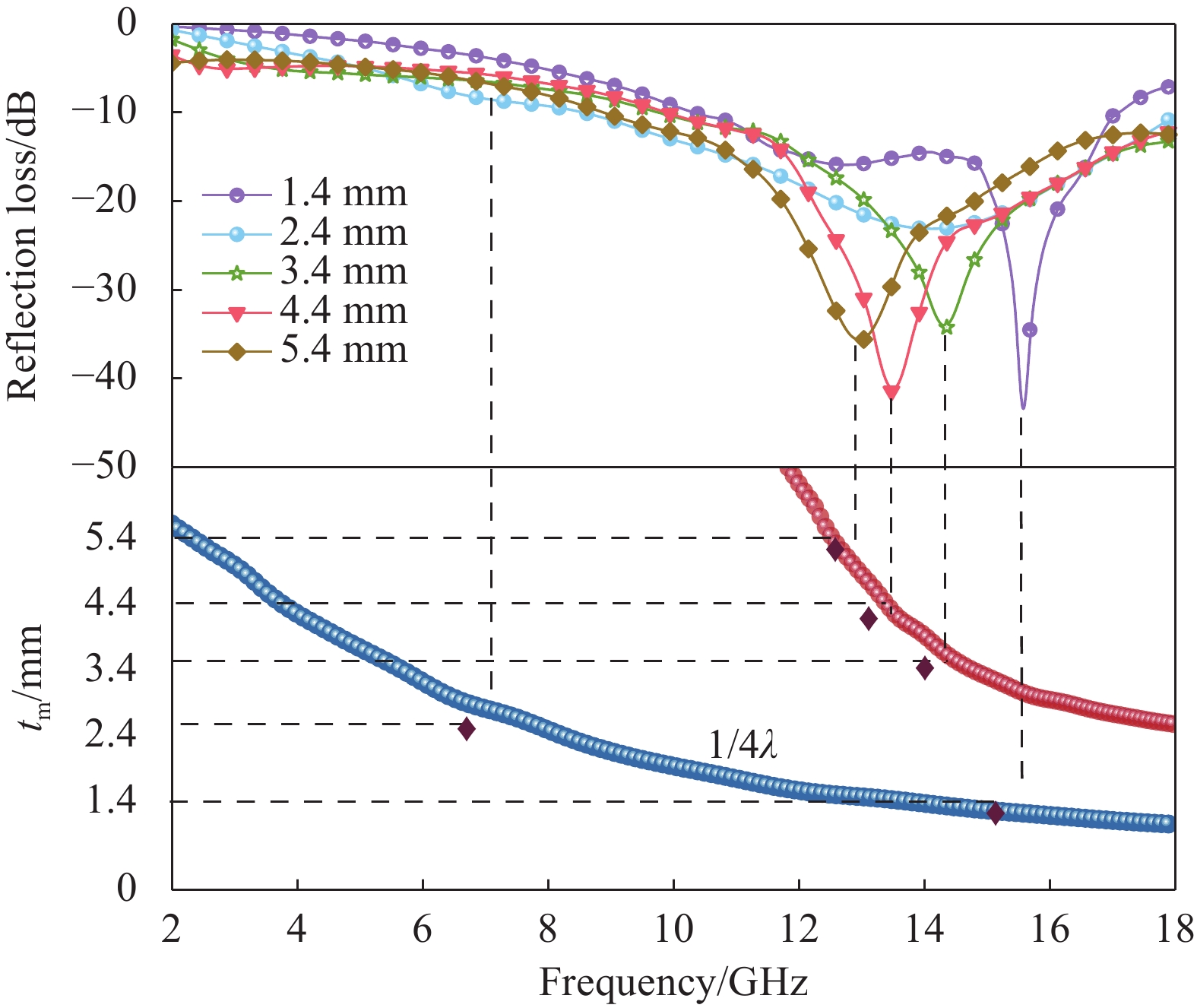
图 10 6%MWCNTs/PLA ((a), (a1))、10%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((b), (b1))、15%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((c), (c1))、20%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((d), (d1))和25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((e), (e1))的反射损耗曲线图与3D颜色映射曲面图
Figure 10. Reflection loss curves and 3D color mapping surfaces of 6%MWCNTs/PLA ((a), (a1)), 10%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((b), (b1)), 15%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((c), (c1)), 20%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((d), (d1)), 25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA ((e), (e1))
LR, min—Minimal reflection loss; d—Thickness; EAB—Effective absorption bandwidth
表 1 Fe3O4-多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)/聚乳酸(PLA)复合材料的成分
Table 1 Ingredients of Fe3O4-multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)/polylactic acid (PLA) composites
Sample Mass fraction/wt% PLA MWCNTs Fe3O4 6%MWCNTs/PLA 94 6 0 10%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA 84 6 10 15%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA 79 6 15 20%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA 74 6 20 25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA 69 6 25 表 2 Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合粉末DSC曲线对应的数据
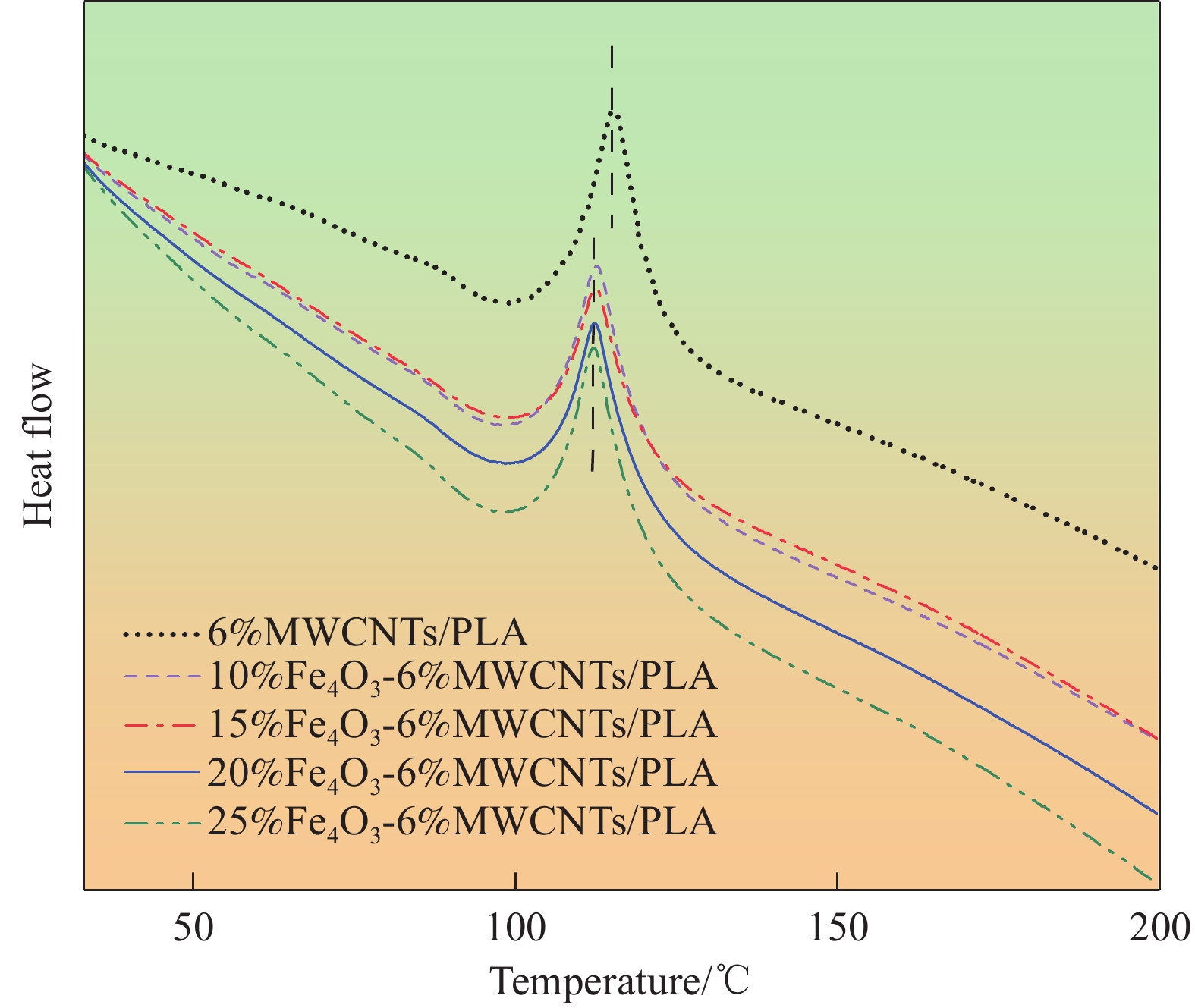
Table 2 DSC data of Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composite powders
Sample Tm/℃ Tc/℃ Tg/℃ 6%MWCNTs/PLA 113.2 98.88 86.48 10%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA
15%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA
20%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA
25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA112.6
112.8
112.7
112.798.47
98.37
98.34
98.3785.67
85.68
85.65
85.45Notes: Tm—Melting temperature; Tc—Crystallization temperature; Tg—Glass transition temperature. 表 3 近3年文献中报道的Fe3O4复合材料与本文制备的复合材料吸波性能对比
Table 3 Comparison of the absorbing properties of Fe3O4 composites reported in the literature in the past three years and the composites prepared in this paper
Material Loading/wt% Matrix LR, min/dB (Thickness) EAB/GHz Ref. Fe3O4@f-GNPs
RGO-Fe3O4
CF/Fe3O4
Fe3O4/MDCF
Palygorskite/Fe3O4
Fe3O4@Ti3C2Tx/CNTs
Fe3O4/RGO@PANI
Fe3O4@RGO
Fe3O4@2H-MoS2
ZnO/Fe3O4
25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA70
35
50
70
50
20
60
60
60
70
31Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
Paraffin
PLA−25.00 (2 mm)
−34.40 (1.6 mm)
−19.00 (1.5 mm)
−26.45 (5 mm)
−40.41 (5.9 mm)
−40.01 (2 mm)
−46.49 (2.5 mm)
−49.40 (1.75 mm)
−50.00 (1.9 mm)
−51.10 (2.2 mm)
−48.50 (1.4 mm)2.40
3.80
4.80
4.28
4.80
5.80
4.25
3.96
4.20
5.28
6.78[34]
[33]
[35]
[36]
[38]
[39]
[40]
[43]
[47]
[49]
This workNotes: EAB—Effective absorption bandwidth (LR, min≤−10 dB); f-GNPs—Graphene nanosheets; RGO—Graphene; CF—Foamed carbon; MDCF—Reticulated foam carbon; CNTs—Carbon nanotubes; PANI—Polyaniline. -
[1] FENG W X, LIU Y Y, BI Y X, et al. Recent advancement of magnetic MOF composites in microwave absorption[J]. Synthetic Metals,2023,294:117307. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2023.117307
[2] HUANG Y, JI J D, CHEN Y, et al. Broadband microwave absorption of Fe3O4-BaTiO3 composites enhanced by interfacial polarization and impedance matching[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,163:598-605. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.01.008
[3] SUN Y, ZHANG J W, ZONG Y, et al. Crystalline-amorphous permalloy@iron oxide core-shell nanoparticles decorated on graphene as high-efficiency, lightweight, and hydrophobic microwave absorbents[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(6):6374-6383.
[4] WANG Z J, WU L N, ZHOU J G, et al. Magnetite nanocrystals on multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a synergistic microwave absorber[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2013,117(10):5446-5452. DOI: 10.1021/jp4000544
[5] YANG H J, CAO W Q, ZHANG D Q, et al. NiO hierarchical nanorings on SiC: Enhancing relaxation to tune microwave absorption at elevated temperature[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(13):7073-7077. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b01122
[6] ZHANG X J, WANG G S, CAO W Q, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption property of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)-MnFe2O4 nanocomposites and polyvinylidene fluoride[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2014,6(10):7471-7478.
[7] CHE R, PENG L M, DUAN X, et al. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes[J]. Advanced Materials,2004,16(5):401-405. DOI: 10.1002/adma.200306460
[8] CHANG Q, LIANG H S, SHI B, et al. Microstructure induced dielectric loss in lightweight Fe3O4 foam for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. IScience,2022,25(3):103925. DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103925
[9] DENG Y F, ZHENG Y, ZHANG D F, et al. A novel and facile-to-synthesize three-dimensional honeycomb-like nano-Fe3O4@C composite: Electromagnetic wave absorption with wide bandwidth[J]. Carbon,2020,169:118-128. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.021
[10] LIANG C B, SONG P, MA A J, et al. Highly oriented three-dimensional structures of Fe3O4 decorated CNTs/reduced graphene oxide foam/epoxy nanocomposites against electromagnetic pollution[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,181:107683. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107683
[11] BHASKARA RAO B V, JENA M, AEPURU R, et al. Superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Fe3O4 modified graphene assembled porous carbon (mGAPC) based hybrid foam[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2022,290:126512. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126512
[12] YIN J H, XU X H, JI J D, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/CuS composites[J]. Physica Status Solidi A: Applications and Materials Science,2022,219(22):2200189.
[13] LIU P B, HUANG Y, ZHANG X. Synthesis and excellent microwave absorption properties of graphene/polypyrrole composites with Fe3O4 particles prepared via a co-precipitation method[J]. Materials Letters,2014,129:35-38. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.04.194
[14] NIU Y, GUO A P, WANG S W, et al. Enhanced wave absorption properties of the flexible composites (MWCNTs/PVDF) with low filler content[J]. Science of Advanced Materials,2017,9(12):2090-2095. DOI: 10.1166/sam.2017.3122
[15] WANG H, XING H L, LIU Q C, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of CeO2/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2018,29(22):19308-19315. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-018-0057-2
[16] WANG X X, FU K, WEN X Y, et al. Oxygen vacancy boosted microwave absorption in CeO2 hollow nanospheres[J]. Applied Surface Science,2022,598:153826. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153826
[17] 熊益军, 王岩, 王强, 等. 一种基于3D打印技术的结构型宽频吸波超材料[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(8):106-133. XIONG Yijun, WANG Yan, WANG Qiang, et al. Structural broadband absorbing metamaterial based on three-dimensional printing technology[J]. Acta Physica Sinica,2018,67(8):106-133(in Chinese).
[18] MEI H, YANG W Q, YANG D, et al. Metamaterial absorbers towards broadband, polarization insensitivity and tunability[J]. Optics and Laser Technology,2022,147:107627. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107627
[19] 刘洋子健, 夏春蕾, 张均, 等. 熔融沉积成型3D打印技术应用进展及展望[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2017, 45(3):130-133. LIU Yangzijian, XIA Chunlei, ZHANG Jun, et al. Application progress and prospect of fused deposition modeling 3D printing technology[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2017,45(3):130-133(in Chinese).
[20] WU T Y, HUAN X H, JIA X L, et al. 3D printing nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical property and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption capability via the introduction of ZIF-derivative modified carbon fibers[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2022,233:109658. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109658
[21] YIN L X, TIAN X Y, SHANG Z T, et al. Ultra-broadband metamaterial absorber with graphene composites fabricated by 3D printing[J]. Materials Letters,2019,239:132-135. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.12.087
[22] 吴海华, 胡正浪, 李雨恬, 等. 铁镍合金/聚乳酸复合材料的熔融沉积成形制备及其电磁吸收性能和力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):158-168. WU Haihua, HU Zhenglang, LI Yutian, et al. Electromagnetic absorption properties and mechanical properties of Fe-Ni alloy/polylactic acid composites fabricated by fused deposition modeling[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):158-168(in Chinese).
[23] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料拉伸性能的测定第4部分: 各向同性和正交各向异性纤维增强复合材料的试验条件: GB/T 1040.4—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Determination of tensile properties of plastics—Part 4: Test conditions for isotropic and orthotropic fiber-reinforced composites: GB/T 1040.4—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006(in Chinese).
[24] 叶喜葱, 欧阳宾, 杨超, 等. 石墨烯-羰基铁粉线材的制备及其吸波性能分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3292-3302. YE Xicong, OUYANG Bin, YANG Chao, et al. Preparation of graphene-carbonyl iron powder wire and analysis of its wave absorption performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3292-3302(in Chinese).
[25] ZHU Y F, NI Q Q, FU Y Q. One-dimensional barium titanate coated multi-walled carbon nanotube heterostructures: Synthesis and electromagnetic absorption properties[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(5):3748-3756. DOI: 10.1039/C4RA11784K
[26] PRASAD C, MURTHY P K, KRISHNA R H H, et al. Bio-inspired green synthesis of RGO/Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using Murrayakoenigii leaves extract and its application for removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2017,5(5):4374-4380. DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.026
[27] MALEKI S T, BABAMORADI M, ROUHI M, et al. Facile hydrothermal synthesis and microwave absorption of halloysite/polypyrrole/Fe3O4[J]. Synthetic Metals,2022,290:117142. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2022.117142
[28] TABAR MALEKI S, SADATI S J. Synthesis and investigation of hyperthermia properties of Fe3O4/HNTs magnetic nanocomposite[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications,2022,145:110000. DOI: 10.1016/j.inoche.2022.110000
[29] SAINI P, CHOUDHARY V, SINGH B P, et al. Polyaniline-MWCNT nanocomposites for microwave absorption and EMI shielding[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2009,113(2-3):919-926. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.08.065
[30] 叶喜葱, 高琦, 何恩义, 等. 熔融沉积成形锰锌铁氧体/聚乳酸复合材料的力学和吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(5):2759-2771. YE Xicong, GAO Qi, HE Enyi, et al. Mechanical and microwave absorbing properties of Mn-Zn ferrite/polylactic acid composites formed by fused deposition modeling[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2023,40(5):2759-2771(in Chinese).
[31] SHU R W, WU Y, ZHANG J B, et al. Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped cobalt/cobalt oxide/carbon/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,193:108027. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108027
[32] ZHAO X N, NIE X Y, LI Y, et al. A layered double hydroxide-derived exchange spring magnet array grown on graphene and its application as an ultrathin electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2019,7(39):12270-12277. DOI: 10.1039/C9TC03254A
[33] DU Z H, CHEN X B, ZHANG Y W, et al. One-pot hydrothermal preparation of Fe3O4 decorated graphene for microwave absorption[J]. Materials,2020,13(14):3065. DOI: 10.3390/ma13143065
[34] JIANG S, QIAN K, YU K J, et al. Controllable synthesis and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4@f-GNPs nanocomposites[J]. Composites Communications,2020,20:100363. DOI: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.100363
[35] LIANG Y Q, YIN X Q, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Electromagnetic response and microwave absorption properties of CF/Fe3O4 absorbing composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2022,33(4):2152-2165. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-021-07422-z
[36] JIANG S, QIAN K, YU K J, et al. Study on ultralight and flexible Fe3O4/melamine derived carbon foam composites for high-efficiency microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Physics Letters,2021,779:138873. DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138873
[37] SHU R W, WAN Z L, ZHANG J B, et al. Facile design of three-dimensional nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite foams as lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorbers[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(4):4689-4698.
[38] WANG S, REN H D, LIAN W, et al. Purification and dissociation of raw palygorskite through wet ball milling as a carrier to enhance the microwave absorption performance of Fe3O4[J]. Applied Clay Science,2021,200:105915. DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105915
[39] ZHANG C, WU Z C, XU C Y, et al. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotubes hollow microsphere with confined magnetic nanospheres for broadband microwave absorption[J]. Small,2022,18(3):2104380. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202104380
[40] CAI H P, FENG C C, XIAO H B, et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4/RGO@PANI with three-dimensional flower-like nanostructure and microwave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,893:162227. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162227
[41] LIU X G, GENG D Y, MENG H, et al. Microwave-absorption properties of ZnO-coated iron nanocapsules[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2008,92(17):214-216.
[42] WANG Y M, WANG L D, WU H J, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of α-Fe₂O₃-filled ordered mesoporous carbon nanorods[J]. Materials,2013,6(4):1520-1529. DOI: 10.3390/ma6041520
[43] QIAN C Y, LIANG X H, WU M, et al. Lightweight chain-typed magnetic Fe3O4@RGO composites with enhanced microwave-absorption properties[J]. Nanomaterials,2022,12(20):3699. DOI: 10.3390/nano12203699
[44] DU J H, ZHAO L, ZENG Y, et al. Comparison of electrical properties between multi-walled carbon nanotube and graphene nanosheet/high density polyethylene composites with a segregated network structure[J]. Carbon,2011,49(4):1094-1100. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2010.11.013
[45] ZHANG H X, SHI C, JIA Z R, et al. FeNi nanoparticles embedded reduced graphene/nitrogen-doped carbon composites towards the ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,584:382-394. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.122
[46] XU D W, YANG S, CHEN P, et al. 3D nitrogen-doped porous magnetic graphene foam-supported Ni nanocomposites with superior microwave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,782:600-610. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.239
[47] WANG H P, ZHOU Y, XING H N, et al. Construction of flower-like core-shell Fe3O4@2H-MoS2 heterostructures: Boosting the interfacial polarization for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Ceramics International,2022,48(7):9918-9926. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.196
[48] JIAN X, WU B, WEI Y F, et al. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/GCs composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(9):6101-6109.
[49] SU Z W, DAI P, YANG M N, et al. ZnO/Fe3O4 nanoparticles encapsulated in N-doped porous carbon for extraordinary microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2023,52(2):1233-1241. DOI: 10.1007/s11664-022-10074-2
[50] CAO F H, XU J, LIU M J, et al. Regulation of impedance matching feature and electronic structure of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2022,108:1-9.
[51] LI N N, SHU R W, ZHANG J B, et al. Synthesis of ultralight three-dimensional nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/zinc ferrite composite aerogel for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,596:364-375. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.143
[52] LI N, XIE X, LU H X, et al. Novel two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx/Ni-spheres hybrids with enhanced microwave absorption properties[J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(17):22880-22888. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.331
[53] ZHANG X, WANG H H, HU R, et al. Novel solvothermal preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene modified by in situ coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,484:383-391. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.264
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 孙鹤,何欣,骆彤雨,吉欣,廖琪玲,张玉霞,周洪福. ABS/CNTs/Fe_3O_4复合材料及其双峰泡沫的电磁屏蔽性能研究. 中国塑料. 2024(08): 46-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孔祥恺,吴佩琨,严寒,郑方羽,王李志,刘强春,鞠治成. 生物质碳管/高岭岩-双废材料的复合及其吸波应用. 复合材料学报. 2024(10): 5389-5399 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)
-
目的
随着电子技术和通信技术的飞速发展,微波辐射也加重了环境污染,严重威胁着电子设备的正常运行,同时也对人类健康产生了危害,而具有轻质高强、宽吸收带、薄厚度和热稳定性的电磁吸收材料是实现微波吸收应用的核心要求。本文以聚乳酸(PLA)为基体,FeO和多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)为填料,通过球磨混合和熔融挤出法制备出FeO-MWCNTs/PLA复合线材,利用熔融沉积成形(FDM)制备出FeO-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料,并研究FeO的添加量对复合材料的电磁吸收性能的影响。
方法第一步确定复合材料的配比,将FeO含量定为10wt%~25wt%,MWCNTs含量定为6wt%。然后利用卧式行星球磨机将不同配比粉末进行球磨混合3.5h,得到不同FeO含量的FeO-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料。第二步将球磨后的FeO复合粉末利用单螺杆挤出机制作直径约为1.75mm的FDM 3D打印线材。将挤出机的机筒一区、机筒二区和模口温度分别设置为155℃、165℃、185℃,冷却水槽的温度为20℃,螺杆转速20r/min,牵引速度为5r/min。第三步采用熔融沉积成形(FDM)3D打印机,打印外径7mm、内径3mm、厚度2.5mm的同轴环和(1BA型)拉伸试样。打印层厚0.1mm,填充密度100%,沉积角度45°,打印速度30mm/s,喷头温度180℃,热床温度50℃。采用XRD,SEM和矢量网络分析仪分别对复合材料的物相结构、微观形貌和电磁特性进行了表征。
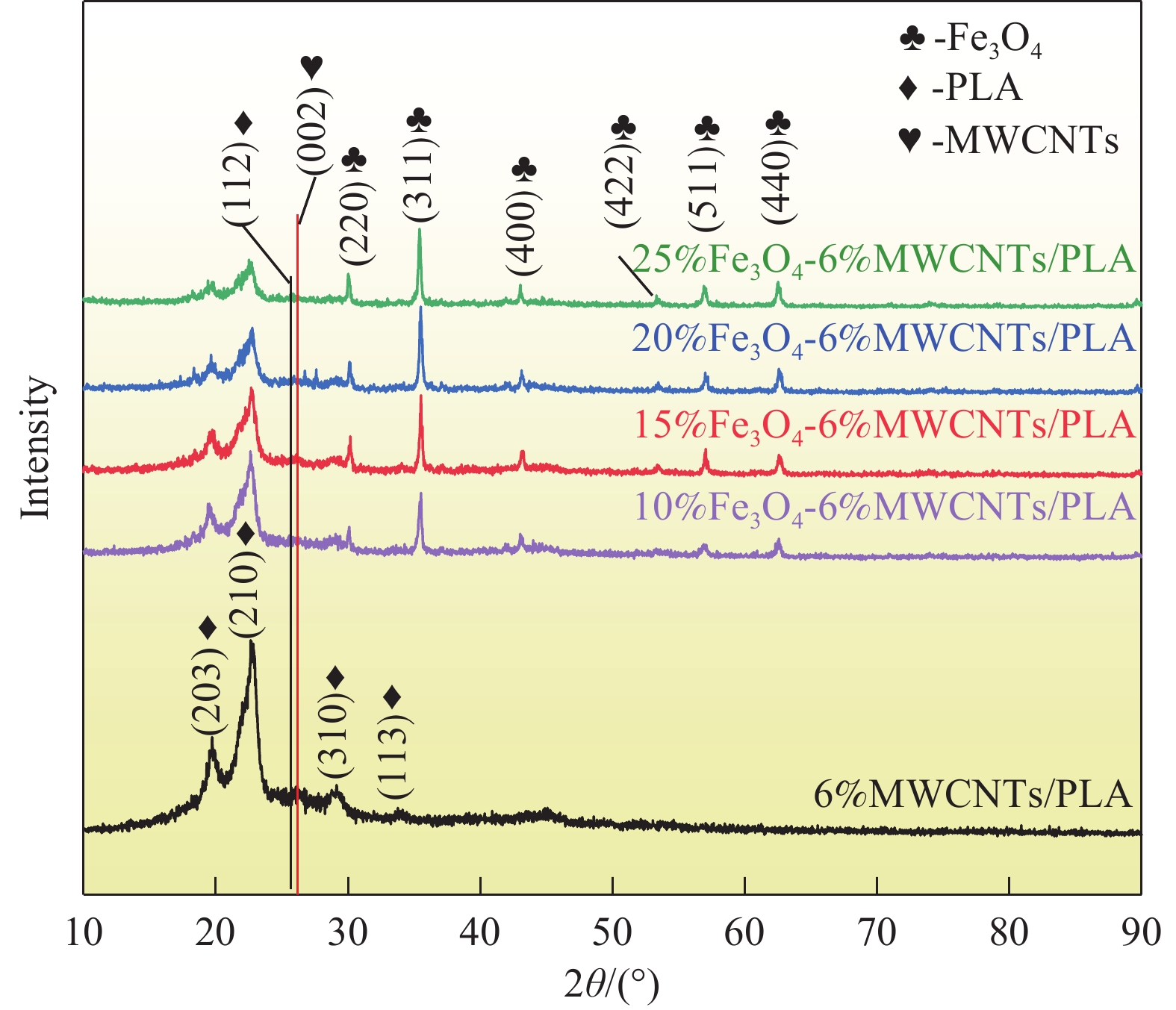
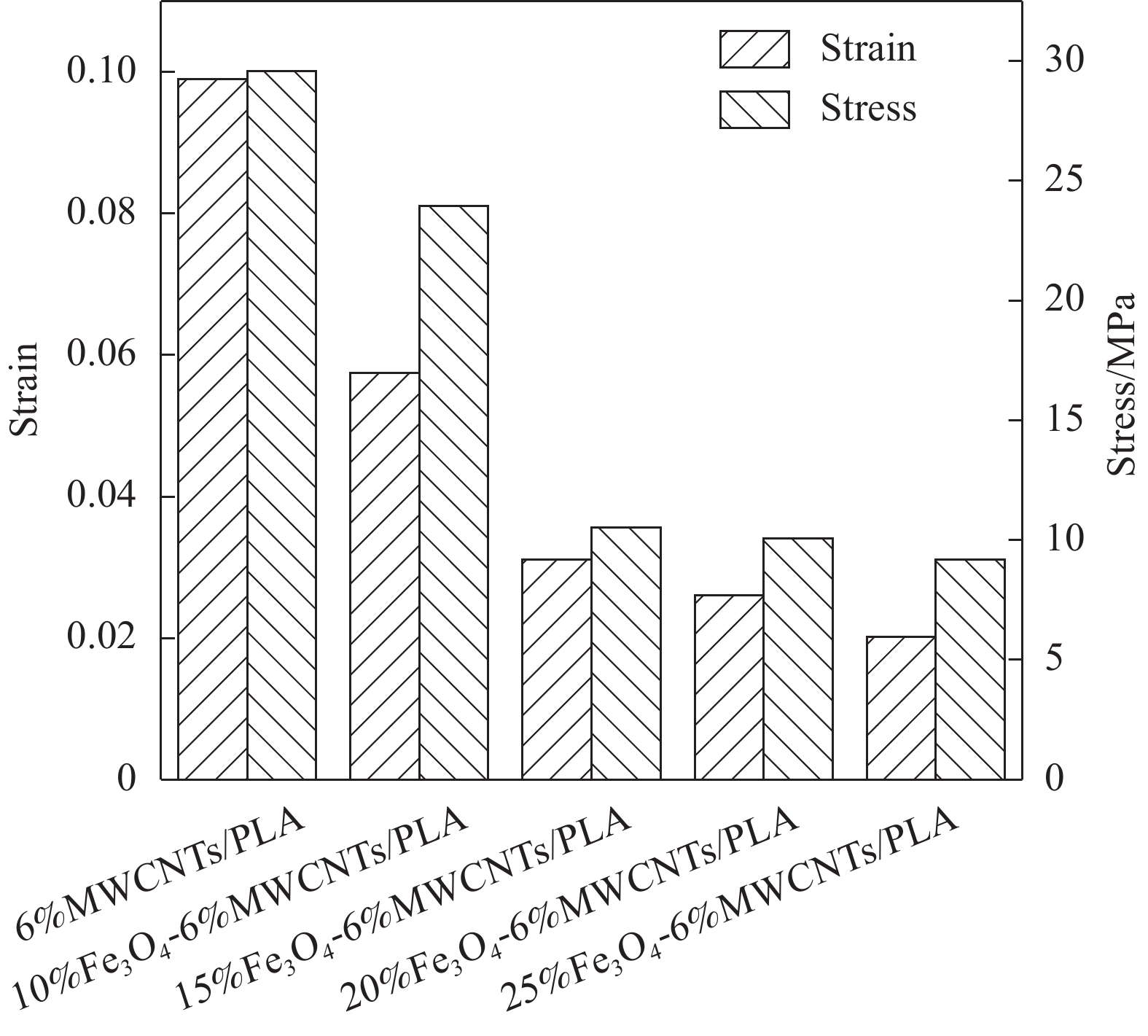
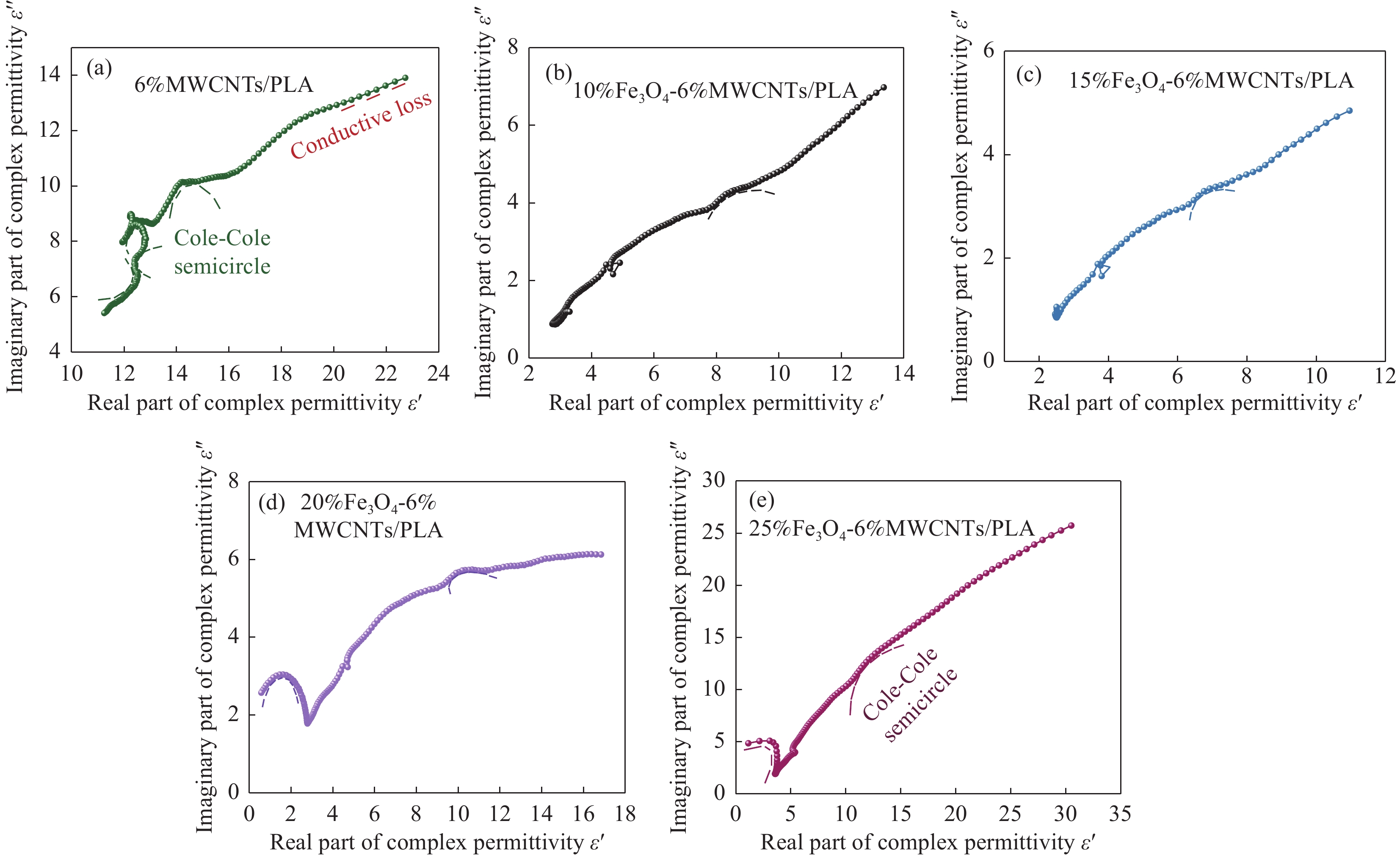
结果从复合材料的XRD图谱中可以看出,衍射峰的峰强度都随着FeO含量的增加而增加,未观察到来自其他相的衍射峰,表明所制备的FeO-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料中各组分保持其原有的物相结构不变。随着FeO含量的增长,复合材料的热稳定性基本保持不变,从SEM图中可以清晰的看到,FeO颗粒与MWCNTs紧密附着。随着FeO含量的增加,复合材料表面呈现大量堆叠层状缺陷,易于形成极化中心并引起极化弛豫。且随着FeO的增多,PLA内部的完整性被割裂,这些裂纹在拉伸过程中导致应力集中,从而使复合材料的承载能力下降和变形增加。与MWCNTs/PLA相比,FeO-MWCNTs/PLA复合材料表现出显著增强的微波吸收性能,且随着FeO含量增加,复合材料吸波性能逐渐增强,当FeO含量为25wt%,复合材料吸波性能最佳,在吸波体厚度为1.4mm时,最佳反射损耗值达到了-48.5dB,与此同时,有效吸收带宽达到了6.78GHz(10.38~17.16GHz)。而在FeO-MWCNTs/PLA内部存在大量的缺陷有利于提高偶极极化,促成介电常数随FeO的增加而提高。FeO颗粒的引入也显著改善了复合材料的涡流效应、固有共振和交换共振等磁损耗。
结论通过球磨混合和熔融挤出法制备出Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合线材,再利用熔融沉积(FDM)成型,其制备方法具有简单、快速、环保等特点。复合材料优异的吸波性能主要由于多壁碳纳米管的介电损耗产生相应的介电弛豫过程,以及引入的FeO使得复合材料拥有了优异的磁损耗,两者的协同效应,充分展现了良好的阻抗匹配和高衰减能力。
-
本文采用四氧化三铁和多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)作为吸波剂,通过与PLA球磨混合后熔融挤出Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA复合线材,经熔融沉积成形(FDM)制备出复合材料。MWCNTs优异的介电性能有利于提高复合材料的介电损耗能力从而使微波吸收性能显著提升,Fe3O4可改善磁损耗能力,两者的协同,使Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA具有良好的阻抗匹配和高衰减能力,表现出高效的微波吸收性能。当四氧化三铁含量为25wt%时,吸波性能最佳,吸波体厚度1.4mm对应反射损耗值达到最大值-48.5dB,对应有效吸收带宽6.78GHz(10.38-17.16GHz),在1.4mm~5.4mm下的反射损耗均可以达到-20dB(99%吸收率)。

反射损耗曲线(a)与反射损耗/厚度/频率映射示意图(b)(25%Fe3O4-6%MWCNTs/PLA)





 下载:
下载: