Prediction of the effective elastic properties for plain woven fabric composite based on the structural parameters
-
摘要: 经向纤维束与纬向纤维束纵横交错引起的纤维弯曲(也称为波纹)是平纹机织复合材料固有特征。首先,提出了一种精确描述平纹机织复合材料单胞3D结构特征的数学表达式。其次,基于经典层合板理论和等应力假设,考虑平纹机织复合材料厚度方向非对称引起的弯曲-拉伸耦合效应及单胞结构特征,建立了含结构参数的平纹机织复合材料等效弹性性能多参数解析模型。通过数个典型算例验证了建立的多参数解析模型,结果表明:该多参数解析模型预测值与相关文献中有限元模型预测值、解析模型预测值、实验值等均吻合较好;该多参数解析模型预测值尤其是Z向弹性性能预测值,比文献中解析模型预测值更接近于实验值。在此基础上,进一步探讨了纤维束波纹比(包括纤维束波动方向波纹比与纤维束横截面波纹比)、经向与纬向纤维束构成的预成形体厚度、纤维束中弯曲部分的长度、相邻纤维束之间间距等结构参数对平纹机织复合材料弹性性能影响。该多参数解析模型建模方法为研究纺织复合材料力学性能提供了参考。Abstract: The warp and fill fiber strands interlacing in two mutually orthogonal directions to one another results in the fiber curvature, namely the waviness, which is the inherent characteristic of plain woven fabric composite. First, a mathematical description was developed to accurately represent the 3D architecture morphology of the unit cell for plain woven fabric composite. Next, an analytical multi-parameter model of plain woven fabric composite was established based on the classical lamination theory and iso-stress assumption. Meanwhile, the bending-extension coupling effect due to asymmetry along the thickness-direction as well as the architecture morphology of the unit cell was embedded in this model. The validation of several typical cases shows that the predicted effective elastic properties of plain woven fabric composite agree well with the numerical values of the finite element model, the results of the analytical model and the experimental data cited in the related literatures. Also, the predictions of the analytical multi-parameter model, especially the Z-direction ones, are more approaching to the experimental data than counterparts of other analytical models aforementioned. Furthermore, the influence of the structural parameters such as the waviness ratio of the fiber strand containing both the undulation direction and the cross section, the thickness of the preform consisting of the warp and fill fiber strands, the length of the curved section of the fiber strand and the spacing between the adjacent fiber strands on the elastic properties of plain woven fabric composite is elaborated. The present approach of the analytical multi-parameter model provides a reference for evaluating the mechanical properties of textile composite.
-
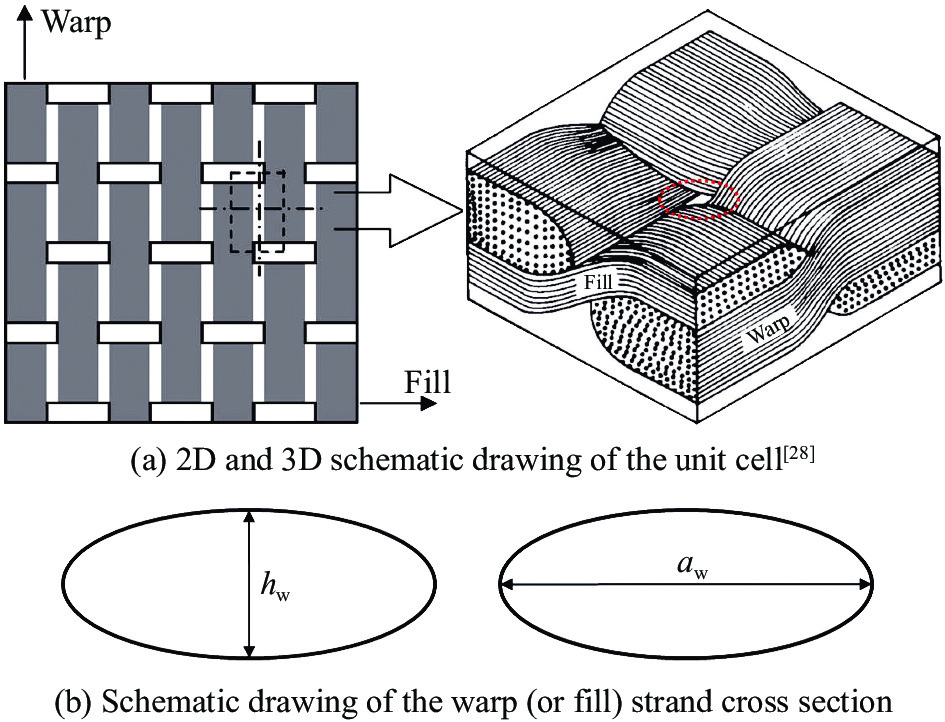
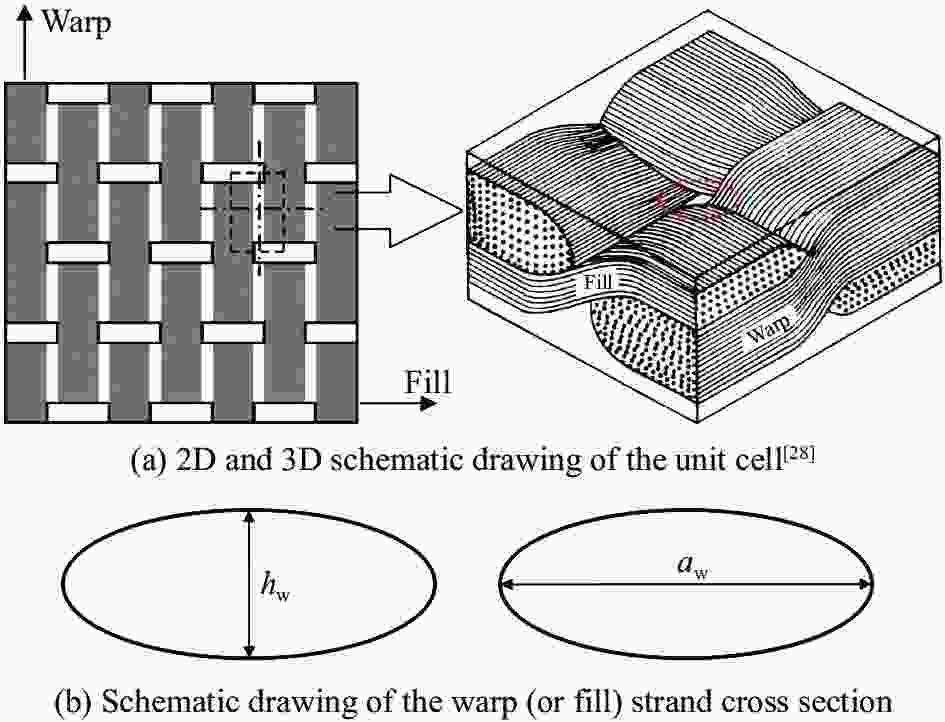
图 2 平纹机织复合材料单胞横截面
The subscript ‘f’ refers to fill strand, and the subscript ‘w’ refers to warp strand; a, h, u, θ—Width and thickness of the fiber strand cross-section, length of the curved section of the fiber strand within the unit cell, and the local off-axis angle of the fiber strand, respectively; g—Spacing between the adjacent fiber strands within the unit cell; ht and h—Thickness of the preform consisting of the warp and fill fiber strands and the total thickness for the unit cell, respectively
Figure 2. Cross section of unit cell for plain woven fabric composite
表 1 E玻璃纤维/乙烯基酯树脂复合材料及其组分材料弹性常数
Table 1. Elastic constants for E-glass/vinyl ester composite and the constituents
(a) Elastic constants of E-glass/vinyl ester composite[15] E1/GPa E2=E3/GPa G12=G13/GPa G23/GPa v21=v31 v23 57.5 18.8 7.44 7.26 0.25 0.29 Notes: E1, E2, E3—Moduli in 1-, 2- and 3-direction, respectively; G12, G13, G23—Shear moduli in 1-2, 1-3 and 2-3 plane, respectively; v21, v31, v23—Major Poisson’s ratios in 1-2, 1-3 and 2-3 plane, respectively. (b) Elastic constants of the constituent fiber and resin matrix[13] Constitute E/GPa G/GPa v E-glass fiber 73.0 30.40 0.20 Vinyl ester resin matrix 3.4 1.49 0.35 Note: E, G, v—Elastic modulus, the shear modulus and the major Poisson’s ratio of the constituents, respectively. 表 2 本文模型中E玻璃纤维/乙烯基酯树脂平纹机织复合材料单胞的结构参数
Table 2. Unit-cell structural parameters of E-glass/vinyl ester plain woven fabric composite in present model
af=aw/mm hf=hw/mm gf=gw/mm ht=h/mm lx=ly/mm uf=uw/mm 0.6 0.05 0 0.10 0.6 0.6 Note: lx, ly—Length, width of the unit cell, respectively. 表 3 E玻璃纤维/乙烯基酯树脂平纹机织复合材料弹性性能
Table 3. Elastic properties of E-glass/vinyl ester plain woven fabric composite
Results Ex=Ey/GPa Ez/GPa Gyz=Gxz/GPa Gxy/GPa vyx vzx=vzy Present model 25.52 13.03 4.82 5.28 0.14 0.31 Experimental data[13] 24.80±1.10 8.50±2.60 4.20±0.70 6.50±0.80 0.10±0.01 0.28±0.07 Analytical model[13] 25.33 13.46 5.24 5.19 0.12 0.29 Analytical model[15] 25.80 13.26 5.02 5.12 0.15 0.31 Notes: Ex, Ey, Ez—Moduli in X-, Y- and Z-direction, respectively; Gxy, Gyz, Gxz—Shear moduli in X-Y, Y-Z and X-Z plane, respectively; νyx, vzx, νzy—Major Poisson’s ratios in X-Y, X-Z and Y-Z plane, respectively. 表 4 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维(UHMWPE)/环氧树脂复合材料及其树脂基体弹性常数[31]
Table 4. Elastic constants of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene fiber (UHMWPE)/epoxy composite and the constituent resin matrix[31]
Material E1/GPa E2=E3/GPa G12=G13/GPa G23/GPa v21=v31 v23 PE/epoxy 6.4029 2.5381 1.14950 0.91055 0.2334 0.39372 Epoxy resin matrix 1.0000 1.0000 0.38462 0.38462 0.3000 0.30000 表 5 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维/环氧树脂平纹机织复合材料弹性性能
Table 5. Elastic properties of UHMWPE/epoxy plain woven fabric composite
Results Ex=Ey/GPa Ez/GPa Gyz=Gxz/GPa Gxy/GPa vyx vzx=vzy Present model 3.213 2.084 0.805 0.870 0.151 0.332 Finite element model[27] 3.410 2.210 0.818 0.856 0.163 0.301 表 6 E玻璃纤维/乙烯基酯树脂平纹机织复合材料单胞结构参数
Table 6. Structural parameters of the unit cell for E-glass/vinyl ester plain woven fabric composite
Case af=aw/mm hf=hw/mm gf=gw/mm h/mm lx=ly/mm uf=uw/mm 1# 0.6
0-0.30
h=ht=hf+hw0.6 0.6 2# 0.6
0-0.050 0.10 0.6 0.6 3# 0.6 0.05 0 0.10 0.6
0-0.64# 0.6 0.05
0-0.50.10 0.6 0.6 表 7 纤维束中弯曲部分的长度对E玻璃纤维/乙烯基酯树脂平纹机织复合材料弹性性能影响(案例3#)
Table 7. Effects of the length of the curved section of the fiber strand on elastic properties of E-glass/vinyl ester plain woven fabric composite for case 3#
uf=uw/mm Ex=Ey/GPa Ez/GPa Gyz=Gxz/GPa Gxy/GPa vyx vzx=vzy 0.1 34.933 18.531 7.451 7.074 0.122 0.300 0.2 33.230 17.365 6.993 6.716 0.124 0.304 0.3 31.432 16.452 6.531 6.357 0.127 0.303 0.4 29.516 15.552 6.109 5.997 0.130 0.304 0.5 27.534 14.645 5.709 5.637 0.133 0.306 0.6 25.516 13.730 5.324 5.277 0.137 0.308 表 8 相邻纤维束之间间距对E玻璃纤维/乙烯基酯树脂平纹机织复合材料弹性性能影响(案例4#)
Table 8. Effects of the spacing between the adjacent fiber strands on elastic properties of E-glass/vinyl ester plain woven fabric composite for case 4#
gf=gw/mm Ex=Ey/GPa Ez/GPa Gyz=Gxz/GPa Gxy/GPa vyx vzx=vzy 0.1 25.516 13.730 5.324 5.277 0.137 0.308 0.2 22.442 12.271 4.724 4.707 0.142 0.312 0.3 20.108 11.196 4.291 4.289 0.147 0.316 0.4 18.283 10.370 3.964 3.971 0.152 0.320 0.5 16.821 9.714 3.707 3.719 0.157 0.324 0.6 15.623 9.177 3.500 3.515 0.162 0.328 -
[1] 王琦, 蒋秋梅, 杨旭锋, 等. 三维机织复合材料残余应力/应变多尺度分析及工艺参数优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4):1167-1176.WANG Qi, JIANG Qiumei, YANG Xufeng, et al. Multiscale analysis and process parameters optimization of residual stress/strain of 3D woven composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(4):1167-1176(in Chinese). [2] 张超, 许希武, 许晓静. 三维多向编织复合材料宏细观力学性能有限元分析研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(5):1241-1251.ZHANG Chao, XU Xiwu, XU Xiaojing. Research progress in finite element analysis on macro-meso mechanical properties of 3D multi-directional braided composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(5):1241-1251(in Chinese). [3] 陈利, 焦伟, 王心淼, 等. 三维机织复合材料力学性能研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(8):62-72. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000210CHEN Li, JIAO Wei, WANG Xinmiao, et al. Research progress on mechanical properties of 3D woven composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2020,48(8):62-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000210 [4] 李明, 陈秀华, 汪海. 二维平纹机织复合材料弹性性能预测的域分解方法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(6):197-205.LI Ming, CHEN Xiuhua, WANG Hai. Evaluating the mechanical behavior of 2D woven fabric composite by domain decomposition method[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(6):197-205(in Chinese). [5] 卢子兴, 徐强, 王伯平, 等. 含缺陷平纹机织复合材料拉伸力学行为数值模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(6):200-207.LU Zixing, XU Qiang, WANG Boping, et al. Numerical simulation of plain weave composites with defects under unidirectional tension[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2011,28(6):200-207(in Chinese). [6] 徐焜, 许希武, 汪海. 三维四向编织复合材料的几何建模及刚度预报[J]. 复合材料学报, 2005, 22(1):133-138. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2005.01.024XU Kun, XU Xiwu, WANG Hai. On geometrical model and stiffness prediction of 3D 4-directional braided compo-sites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2005,22(1):133-138(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2005.01.024 [7] 燕瑛, 楼畅, 成传贤, 等. 机织复合材料力学性能的细观分析与实验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2001, 18(2):109-113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2001.02.025YAN Ying, LOU Chang, CHENG Chuanxian, et al. Micromechanical analysis and experimental evaluation of the property of woven composite materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2001,18(2):109-113(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2001.02.025 [8] TINA O, ABBAS S. A highly interpretable materials informatics approach for predicting microstructure-property relationship in fabric composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2022,217:109080. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.109080 [9] 高旭东, 马贵春, 姚君. 三维机织复合材料力学性能研究[J]. 机械工程与自动化, 2013(2):220-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6413.2013.03.093GAO Xudong, MA Guichun, YAO Jun. Study on mechanical properties of 3D woven composites[J]. Mechanical Engi-neering & Automation,2013(2):220-221(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6413.2013.03.093 [10] ZHOU C W. Micro mechanical model of 3D woven compo-sites[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2005,18(1):40-46. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(11)60280-X [11] LI D S, DANG M G, JIANG L. Elevated temperature effect on tension fatigue behavior and failure mechanism of carbon/epoxy 3D angle-interlock woven composites[J]. Composite Structures,2021,268:113897. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113897 [12] SCIDA D, ABOURA Z, BENZEGGAGH M L, et al. Prediction of the elastic behaviour of hybrid and non-hybrid woven composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1998,57(12):1727-1740. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(97)00105-X [13] SCIDA D, ABOURA Z, BENZEGGAGH M L, et al. A micromechanics model for 3D elasticity and failure of woven-fibre composite materials[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1999,59(4):505-517. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(98)00096-7 [14] LEISCHNER U, JONHSON A F. Micromechanics analysis of hybrid woven fabric composites under tensile and compression load[J]. Composite Material Technology,1994,4:397-405. [15] DONADON M V, FALZON B G, IANNUCCI L, et al. A 3D micromechanical model for predicting the elastic behaviour of woven laminates[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2007,67:2467-2477. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.12.019 [16] 陈继刚, 薛亚红, 闫世程. 二维机织复合材料弹性常数的有限元法预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(8):1702-1709.CHEN Jigang, XUE Yahong, YAN Shicheng. Finite element prediction of elastic constants for 2D woven fabric compo-site[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(8):1702-1709(in Chinese). [17] 易洪雷, 丁辛. 三维机织复合材料的弹性性能预报模型[J]. 力学学报, 2003, 35(5):569-577. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2003.05.008YI Honglei, DING Xin. A model to predict elastic properties of 3D woven composites[J]. Acta Mechanic Sinica,2003,35(5):569-577(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2003.05.008 [18] 王立朋, 燕瑛. 编织复合材料弹性性能的细观分析及试验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2004, 21(4):152-156. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2004.04.030WANG Lipeng, YAN Ying. Micro analysis and experimental study of the elastic properties of braided composites structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2004,21(4):152-156(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2004.04.030 [19] ZHOU Guangming, ZHOU Chuwei, WANG Xinfeng. Micro mechanical analysis of 3D woven composites[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics,2004,21(3):163-167. [20] 余育苗, 王肖钧, 李永池, 等. 三维正交机织复合材料的单胞模型及应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2009, 26(4):181-185. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2009.04.032YU Yumiao, WANG Xiaojun, LI Yongchi, et al. Cell model of 3D orthogonal woven composite and its application[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2009,26(4):181-185(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2009.04.032 [21] 郑君, 温卫东, 崔海涛, 等. 2.5维机织结构复合材料的几何模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(2):143-148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.024ZHENG Jun, WEN Weidong, CUI Haitao, et al. Geometric model of 2.5 dimensional woven structures[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2008,25(2):143-148(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.024 [22] 梁仕飞, 矫桂琼, 王波. 三维机织C/C-SiC复合材料弹性性能预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(1):138-142.LIANG Shifei, JIAO Guiqiong, WANG Bo. Prediction of elastic properties of three dimensional woven C/C-SiC composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2011,28(1):138-142(in Chinese). [23] 顾卫平, 徐斌, 张雪雯. 基于均匀化方法的三维正交机织复合材料弹性性能预测[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2013, 32(12):1785-1788.GU Weiping, XU Bin, ZHANG Xuewen. Prediction of the elastic property of 3D woven composites based on the homogenization method[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering,2013,32(12):1785-1788(in Chinese). [24] 边天涯, 关志东, 刘发齐, 等. 含孔隙基体缎纹编织复合材料面内压缩弹性性能预报[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(5):1016-1024.BIAN Tianya, GUAN Zhidong, LIU Faqi, et al. Prediction on in-plane compression elastic properties of satin weave composites with pore matrix[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2016,42(5):1016-1024(in Chinese). [25] LI Z G, LI D S, ZHU H, et al. Mechanical properties prediction of 3D angle-interlock woven composites by finite element modeling method[J]. Materials Today Communications,2020,22:100769. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100769 [26] ZHAO C Q, LI D S, GE T Q, et al. Experimental study on the compression properties and failure mechanism of 3D integrated woven spacer composites[J]. Materials & Design,2014,56:50-59. [27] LI S, ZHOU C, YU H, et al. Formulation of a unit cell of a reduced size for plain weave textile composites[J]. Computational Materials Science,2011,50(5):1770-1780. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2011.01.013 [28] NAIK N K, SHEMBEKAR P S. Elastic behavior of woven fabric composites: I—Lamina analysis[J]. Journal of Compo-site Materials,1992,26(15):2196-2225. doi: 10.1177/002199839202601502 [29] 沈观林, 胡更开. 复合材料力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 86-91.SHEN Guanlin, HU Gengkai. Mechanics of composite materials[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006: 86-91(in Chinese). [30] 朱俊, 郭万涛, 李想, 等. 含面内波纹缺陷的复合材料层合板刚度性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(4):793-803.ZHU Jun, GUO Wantao, LI Xiang, et al. Stiffness of compo-site laminates with in-plane waviness defect[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(4):793-803(in Chinese). [31] LI S. General unit cells for micromechanical analyses of unidirectional composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2001,32(6):815-826. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00182-2 -





 下载:
下载: