Preparation and antibacterial properties of porous polyacrylonitrile composite fiber membrane loaded with silver/copper nanoparticles
-
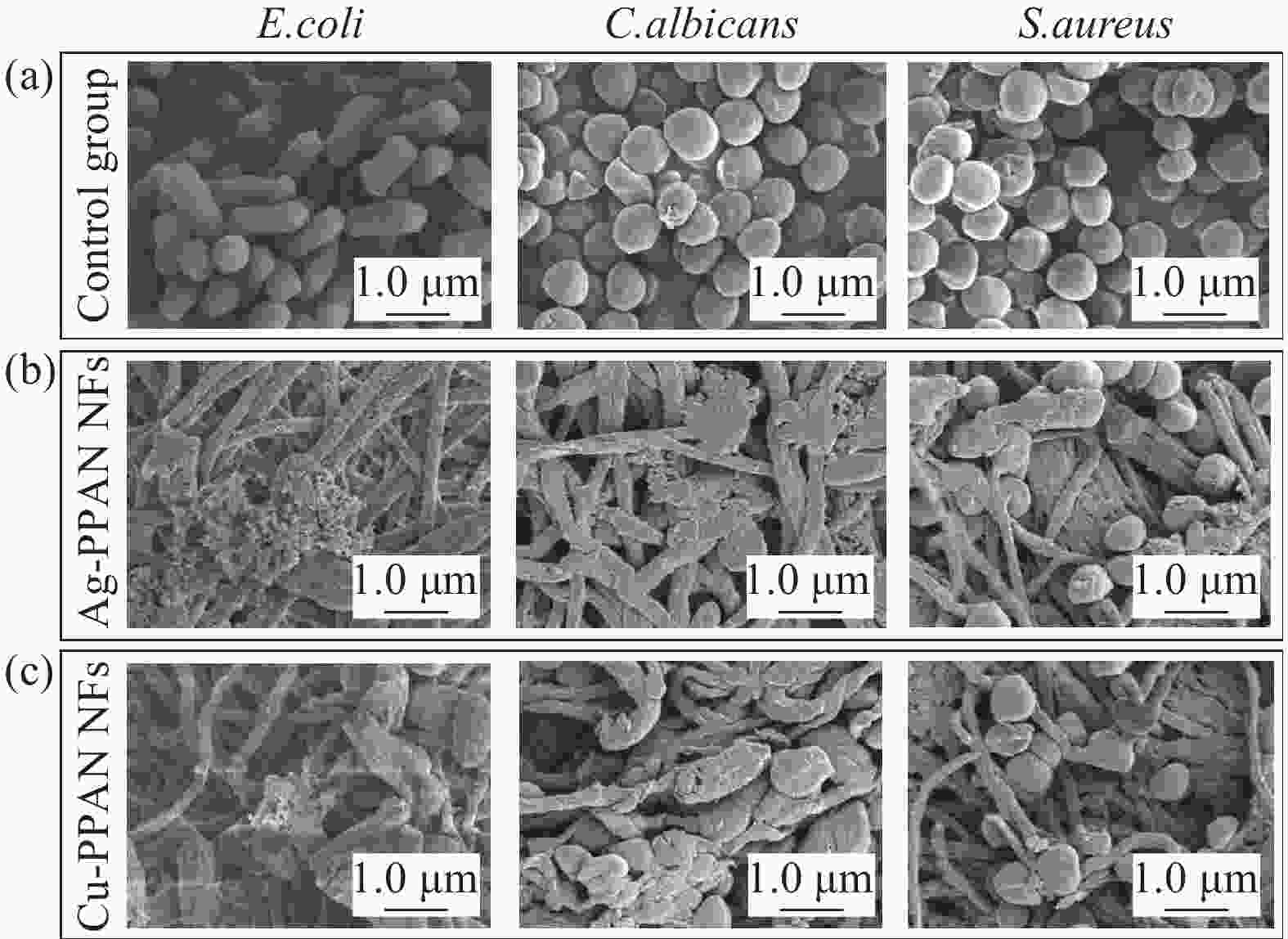
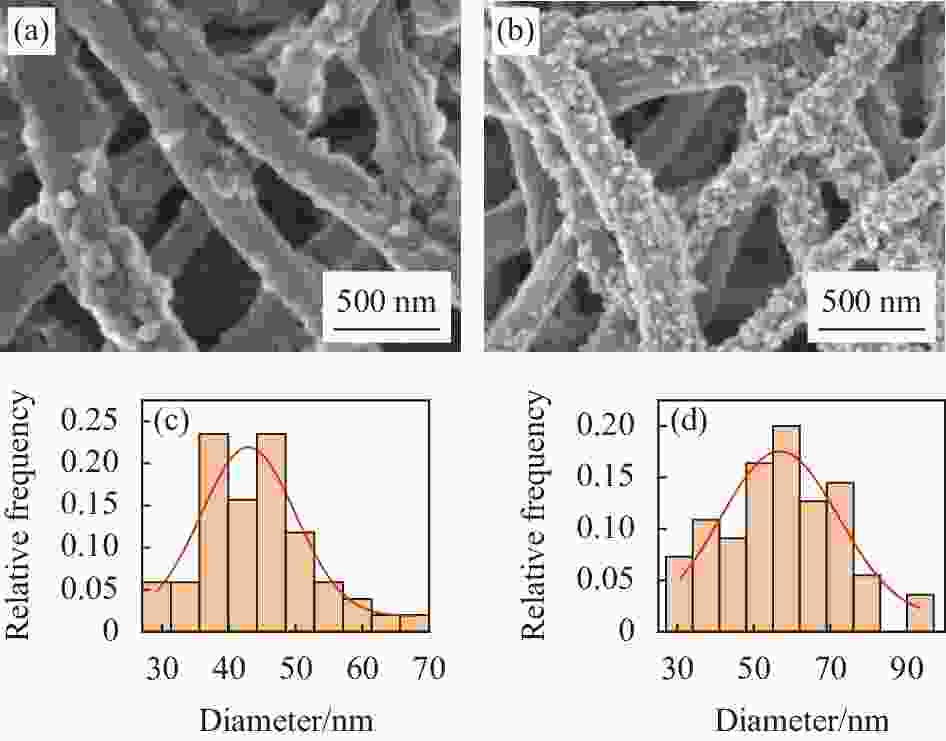
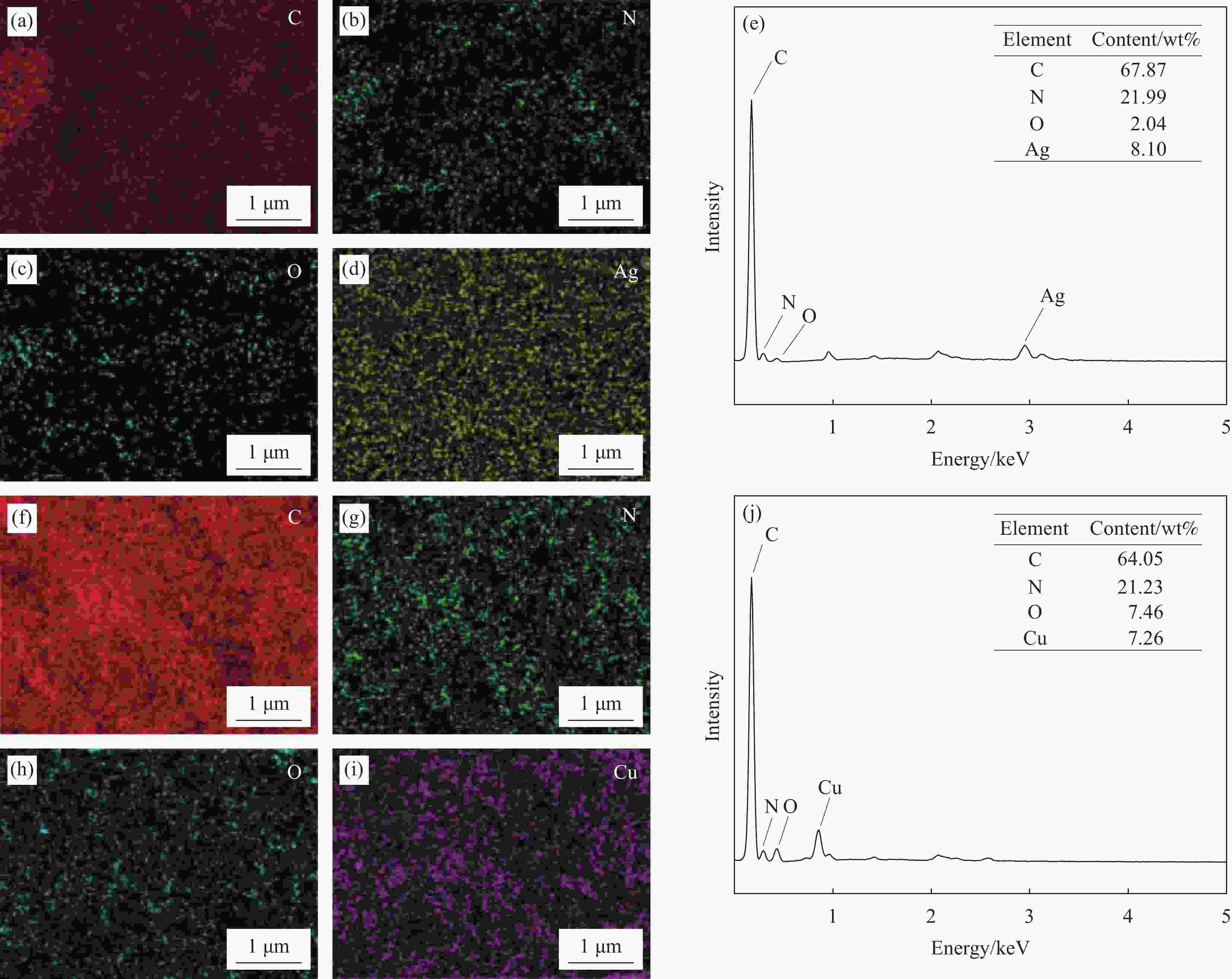
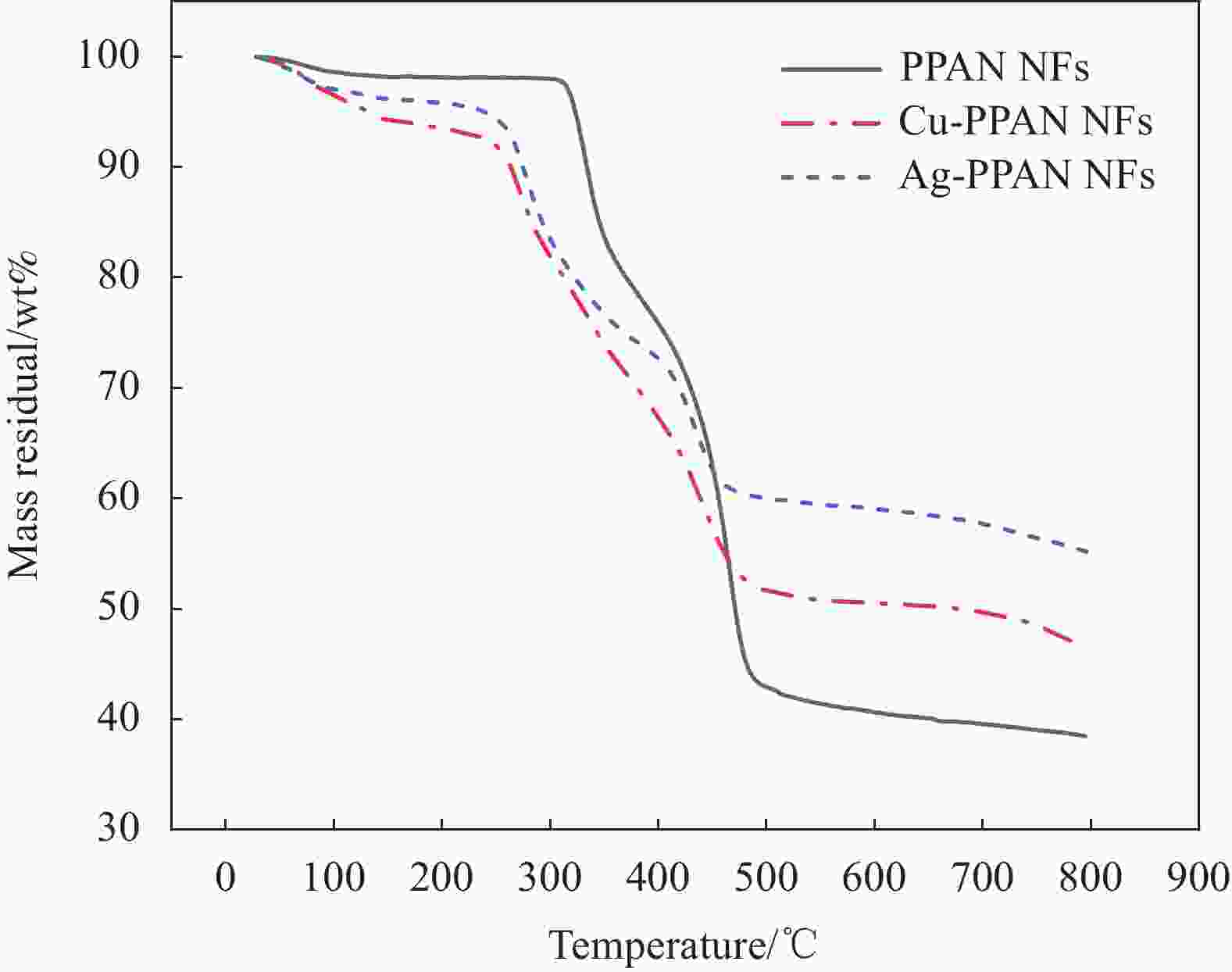
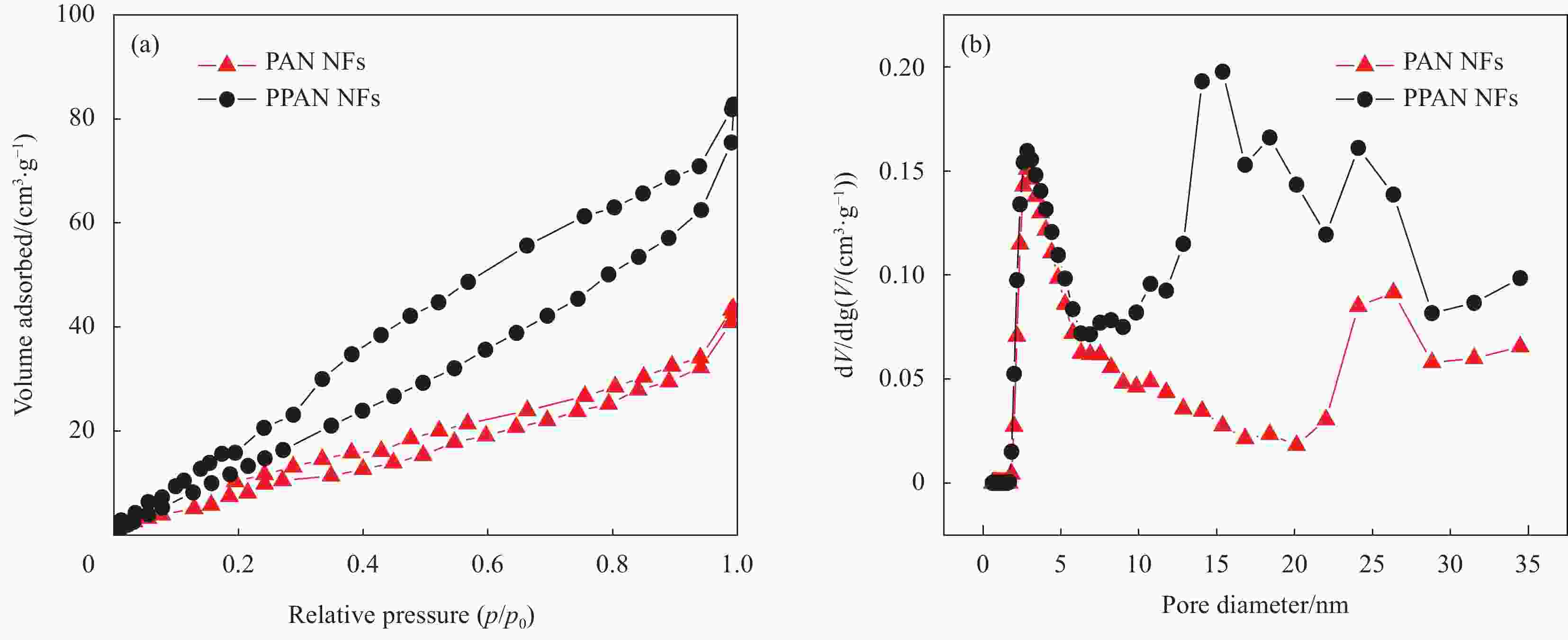
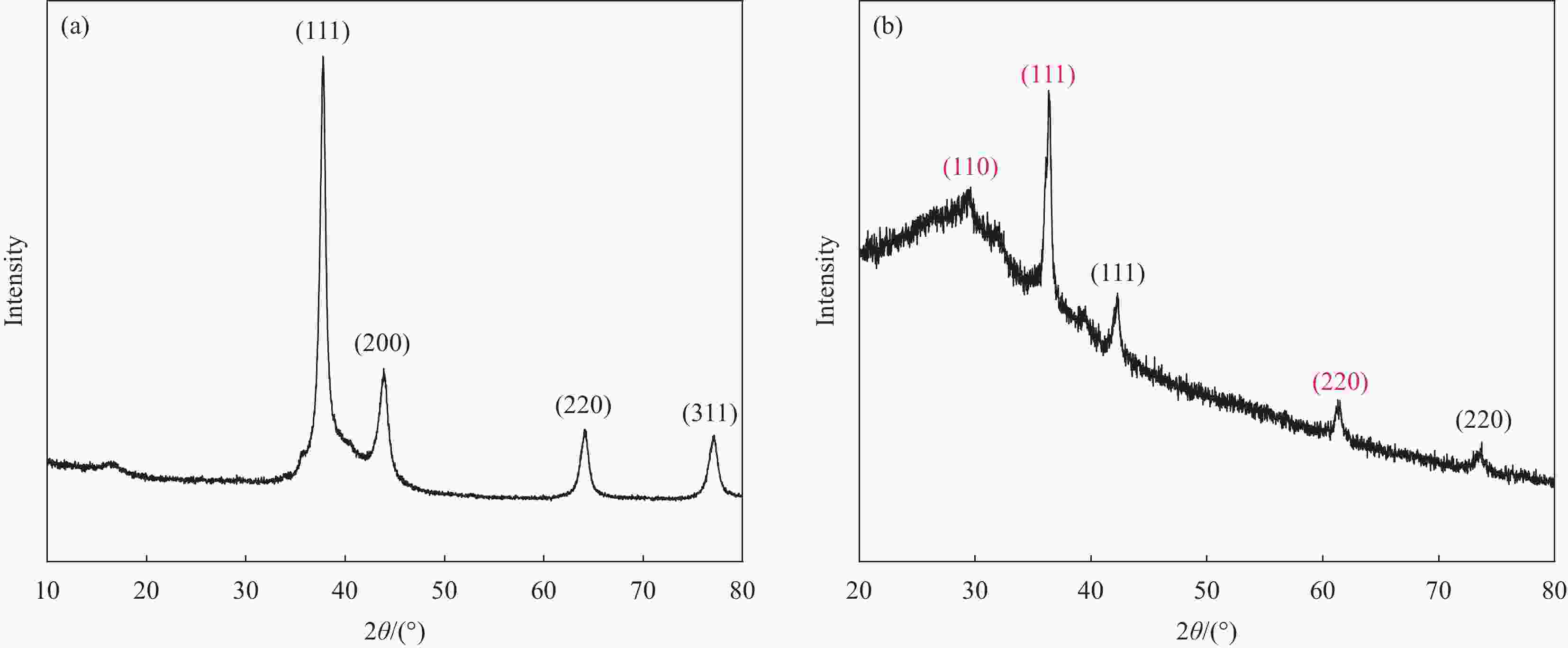
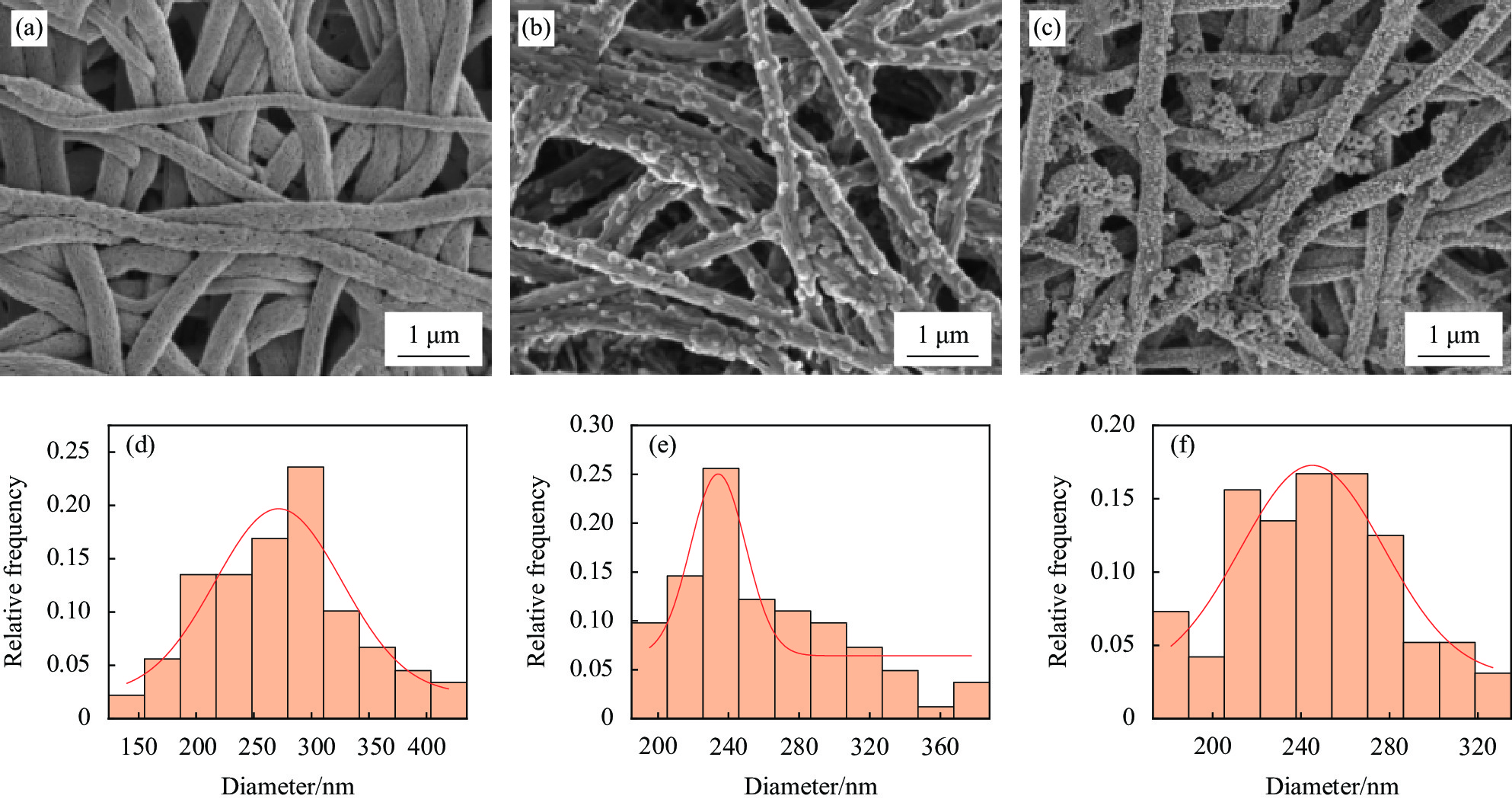
摘要: 金属纳米粒子因其独特的物理化学性能,在催化、抑菌、水污染处理和生物医学等领域表现出巨大的应用前景。但是金属纳米粒子在制备和使用过程中容易发生团聚而影响其性能。因此,提高金属纳米粒子的稳定性,对提升其应用性能具有重大意义。本文在以聚丙烯腈(PAN)为基体,聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)为致孔剂,基于静电纺丝技术制得多孔聚丙烯腈纳米纤维(PPAN NFs)的基础上,通过浸渍沉积法分别制备出负载银纳米粒子(Ag NPs)复合纳米纤维(Ag-PPAN NFs)和负载铜纳米粒子(Cu NPs)复合纳米纤维(Cu-PPAN NFs)。在利用FESEM、EDS、XRD等方法对制备纤维膜的形貌和结构进行表征的基础上,通过抑菌圈法和FESEM观察经复合纳米纤维处理前后的细菌形貌来研究Ag-PPAN NFs和Cu-PPAN NFs对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和白色念球菌的抑菌性能。研究结果发现:PPAN NFs可有效解决Ag NPs和Cu NPs在制备和使用过程中易于聚集的问题,制得的复合纳米纤维对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和白色念球菌具有一定的抗菌活性,可成为一种新型的抗菌纤维材料。Abstract: Metal nanoparticles show great application on prospect in catalysis, bacteriostasis, water pollution treatment and biomedicine, because of their unique physical and chemical properties. Metal nanoparticles tend to agglomerate in the processes of preparation and use. Therefore, improving the stability of nanoparticles is of great significance to improve their application performance. In this study, porous polyacrylonitrile nanofibers (PPAN NFs) were prepared by electrostatic spinning using polyacrylonitrile (PAN) as substrate and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as the pore-making agent. On this basis, Ag-PPAN NFs and Cu-PPAN NFs were prepared by in-situ loading of silver and copper nanoparticles on the surface of PPAN NFs by impregnation deposition. The morphologies and structures of the prepared nanofibers were characterized by FESEM, EDS and XRD, and the antibacterial properties of Ag-PPAN NFs and Cu-PPAN NFs against E. coli, S. aureus and C. albicans were studied by bacteriostatic zone method and FESEM observation. The results show that PPAN NFs provide a rich mesoporous structure for loading of Ag NPs and Cu NPs and inhibited the aggregation of nanoparticles. The prepared Ag-PPAN NFs and Cu-PPAN NFs show good antibacterial activities against E. coli, S. aureus and C. albicans, and which could be used as a new kind of antibacterial fiber material.
-
Key words:
- silver nanoparticles /
- copper nanoparticles /
- porous /
- nanofibers /
- electrospinning /
- antibacterial
-
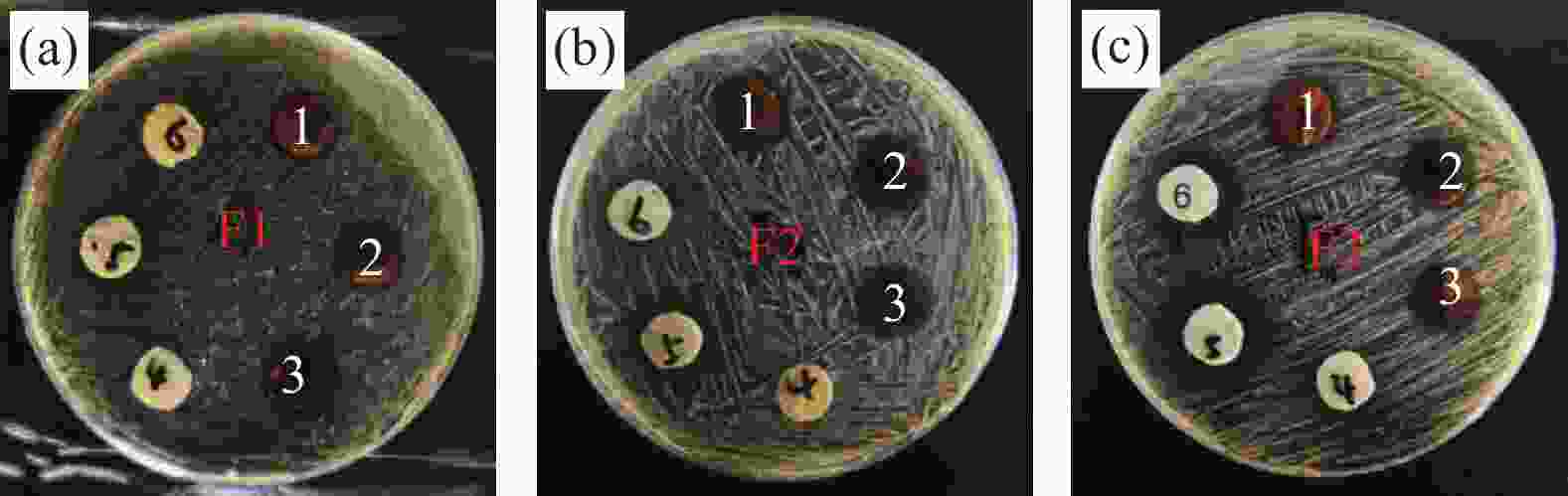
表 1 多孔复合纳米纤维的抗菌抑制区直径
Table 1. Diameter of antibacterial inhibition zone of the porous composite nanofibers
Samples
NumberE. coli/
mmC. albicans/
mmS. aureus/
mmAg-PPAN
NFs (1)1 13.5 14.5 13.5 Ag-PPAN
NFs (2)2 14.5 15.0 14.0 Ag-PPAN
NFs (3)3 15.0 16.0 14.0 Cu-PPAN
NFs (1)4 Not obvious Not obvious 12.0 Cu-PPAN
NFs (2)5 Not obvious Not obvious 19.0 Cu-PPAN
NFs (3)6 Not obvious Not obvious 20.0 -
[1] BEHRAVAN M, PANAHI A H, NAGHIZADEH A, et al. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,124:148-154. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.101 [2] TAO Y, JU E G, REN J S, et al. Bifunctionalized mesoporous silica-supported gold nanoparticles: Intrinsic oxidase and peroxidase catalytic activities for antibacterial applications[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27(6):1097-1104. doi: 10.1002/adma.201405105 [3] PATTANAYAK D S, MALLICK N, THAKUR C, et al. Plant mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial application: Present status[J]. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society,2020,97(7):1108-1114. [4] SHAIKH S, NAZAM N, RIZVI S M D, et al. Mechanistic insights into the antimicrobial actions of metallic nanoparticles and their implications for multidrug resistance[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(10):2468. [5] MUBARAKALI D, THAJUDDIN N, JEGANATHAN K, et al. Plant extract mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2011,85(2):360-365. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.03.009 [6] DURAN N, DURAN M, DE JESUS M B, et al. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity[J]. Nanomedicine-Nanotechnology and Medicine,2016,12(3):789-799. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.11.016 [7] SHU Z, ZHANG Y, YANG Q, et al. Halloysite nanotubes supported Ag and ZnO nanoparticles with synergistically enhanced antibacterial activity[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters,2017,12(1):1-7. doi: 10.1186/s11671-017-1859-5 [8] ANANDALAKSHMI K, VENUGOBAL J, RAMASAMY V. Characterization of silver nanoparticles by green synthesis method using Pedalium murex leaf extract and their antibacterial activity[J]. Applied Nanoscience,2016,6(3):399-408. doi: 10.1007/s13204-015-0449-z [9] CHEN Y F, ZHANG Y T, LIU J D, et al. Preparation and antibacterial property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration hybrid membrane containing halloysite nanotubes loaded with copper ions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,210:298-308. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.100 [10] 刘亚飞, 李梦, 赵欣, 等. 浅谈纳米银粒子的制备及其在抗菌涂料中的应用[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(2):37-41.LIU Yafei, LI Meng, ZHAO Xin, et al. Discussion on preparation of silver nanoparticles and its application in antibactrial coating[J]. New Chemical Materials,2019,47(2):37-41(in Chinese). [11] HAN D L, HAN Y J, LI J, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity and photothermal effects of Cu-doped metal-organic frameworks for rapid treatment of bacteria-infected wounds[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2020,261:118248. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118248 [12] WANG L L, HU C, SHAO L Q, et al. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine,2017,12:1227-1249. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S121956 [13] SANCHEZ-LOPEZ E, GOMES D, ESTERUELAS G, et al. Metal-based nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: An overview[J]. Nanomaterials,2020,10(2):292. [14] KHATRI O P, ICHII T, MURASE K, et al. Covalent assembly of silver nanoparticles on hydrogen-terminated silicon surface[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2012,382:22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2012.06.001 [15] DAI H, CHEN Y L, LIN Y Y, et al. A new metal electrocatalysts supported matrix: Palladium nanoparticles supported silicon carbide nanoparticles and its application for alcohol electrooxidation[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2012,85:644-649. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2012.08.109 [16] ZHANG P, SHAO C L, ZHANG Z Y, et al. In situ assembly of well-dispersed Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) on electrospun carbon nanofibers (CNFs) for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol[J]. Nanoscale,2011,3(8):3357-3363. doi: 10.1039/c1nr10405e [17] 李甫, 康卫民, 程博闻, 等. 负载银中空纳米碳纤维的制备及电化学性能[J]. 材料工程, 2016, 44(11):56-60. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.11.009LI Fu, KANG Weimin, CHENG Bowen, et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of silver doped hollow carbon nanofibers[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2016,44(11):56-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.11.009 [18] DE FARIA A F, MARTINEZ D S T, MEIRA S M M, et al. Anti-adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2014,113:115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.006 [19] XIANG J, LI J L, ZHANG X H, et al. Magnetic carbon nano-fibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(40):16905-16914. doi: 10.1039/C4TA03732D [20] 向军, 张雄辉, 褚艳秋, 等. Fe-Ni合金/Ni铁氧体复合纳米纤维的制备、表征与磁性能研究[J]. 化学学报, 2012, 70:2265-2272. doi: 10.6023/A12080587XIANG Jun, ZHANG Xionghui, CHU Yanqiu, et al. Preparation, characterization and magnetic properties of Fe-Ni alloy/Ni-ferrite composite nanofibers[J]. Acta Chemica Sinica,,2012,70:2265-2272(in Chinese). doi: 10.6023/A12080587 [21] WANG F Y, SUN Y Q, SUN Y Q, et al. Microwave absorption properties of 3D cross-linked Fe/C porous nanofibers prepared by electrospinning[J]. Carbon,2018,134:264-273. [22] ZHAO W X, CI S Q, HU X, et al. Highly dispersed ultrasmall NiS2 nanoparticles in porous carbon nanofiber anodes for sodium ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale,2019,11(11):4688-4695. doi: 10.1039/C9NR00160C [23] WANG M Q, YE C, LIU H, et al. General synthesis of nano-metal phosphides embedded N-doped porous carbon nanofibers for enhanced hydrogen evolution at all pH values[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2017,10(57):150. [24] SONG Z M, LIU X F, SUN X, et al. Alginate-templated synthesis of CoFe/carbon fiber composite and the effect of hierarchically porous structure on electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Carbon,2019,151:36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.05.025 [25] FU Y, YU H Y, JIANG C, et al. NiCo alloy nanoparticles decorated on N-doped carbon nanofibers as highly active and durable oxygen electrocatalyst[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(9):1705094. [26] 孔祥前, 豆彩霞, 柴源涛, 等. 银缓释载银杀菌活性炭的低温水热炭化法制备[J]. 功能材料, 2016, 1(47):1203-1206.KONG Xiangqian, DOU Caixia, CHAI Yuantao, et al. Acti-vated carbon with silver control release and antibacterial behavior by low temperature hydrothermal method[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2016,1(47):1203-1206(in Chinese). [27] 兰小林, 段正康, 王永胜, 等. 不同晶相结构ZrO2负载铜基催化剂用于二乙醇胺脱氢反应[J]. 精细化工, 2019, 36(12):2438-2445.LAN Xiaolin, DUAN Zhengkang, WANG Yongsheng, et al. ZrO2 with different crystal structure supported Cu catalysts for the dehydrogenation of diethanolamine[J]. Fine Chemicals,2019,36(12):2438-2445(in Chinese). [28] 罗凤凤, 王日昕, 廖先金, 等. 葡萄糖还原制备Cu2O及其形貌表征[J]. 化工新型材料, 2020, 48:48-50.LUO Fengfeng, WANG Rixin, LIAO Xianjin, et al. Preparation and morphology characterization of Cu2O by glucose reducing[J]. New Chemical Materials,2020,48:48-50(in Chinese). [29] CHEN Y Q, WU W, XU Z Q, et al. Photothermal-assisted antibacterial application of graphene oxide-Ag nanocomposites against clinically isolated multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2020, 7(7): 192019. [30] CHATTERJEE A K, CHAKRABORTY R, BASU T. Mechanism of antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticles[J]. Nanotechnology, 2014, 25(13): 13501. [31] WANG H L, HAO L L, WANG P, et al. Release kinetics and antibacterial activity of curcumin loaded zein fibers[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,63:437-446. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.09.028 -





 下载:
下载: