Graphene-enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of FeSiAl-MoS2/PLA composites
-
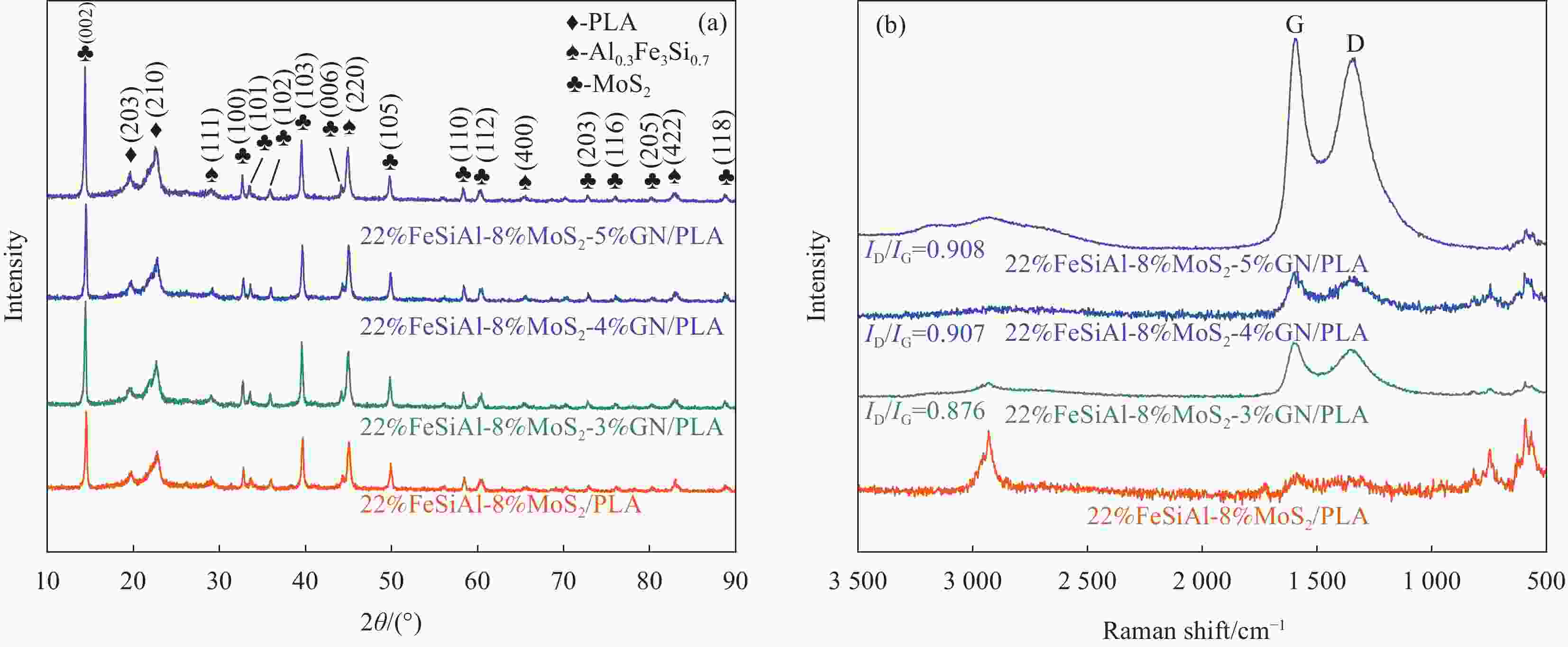
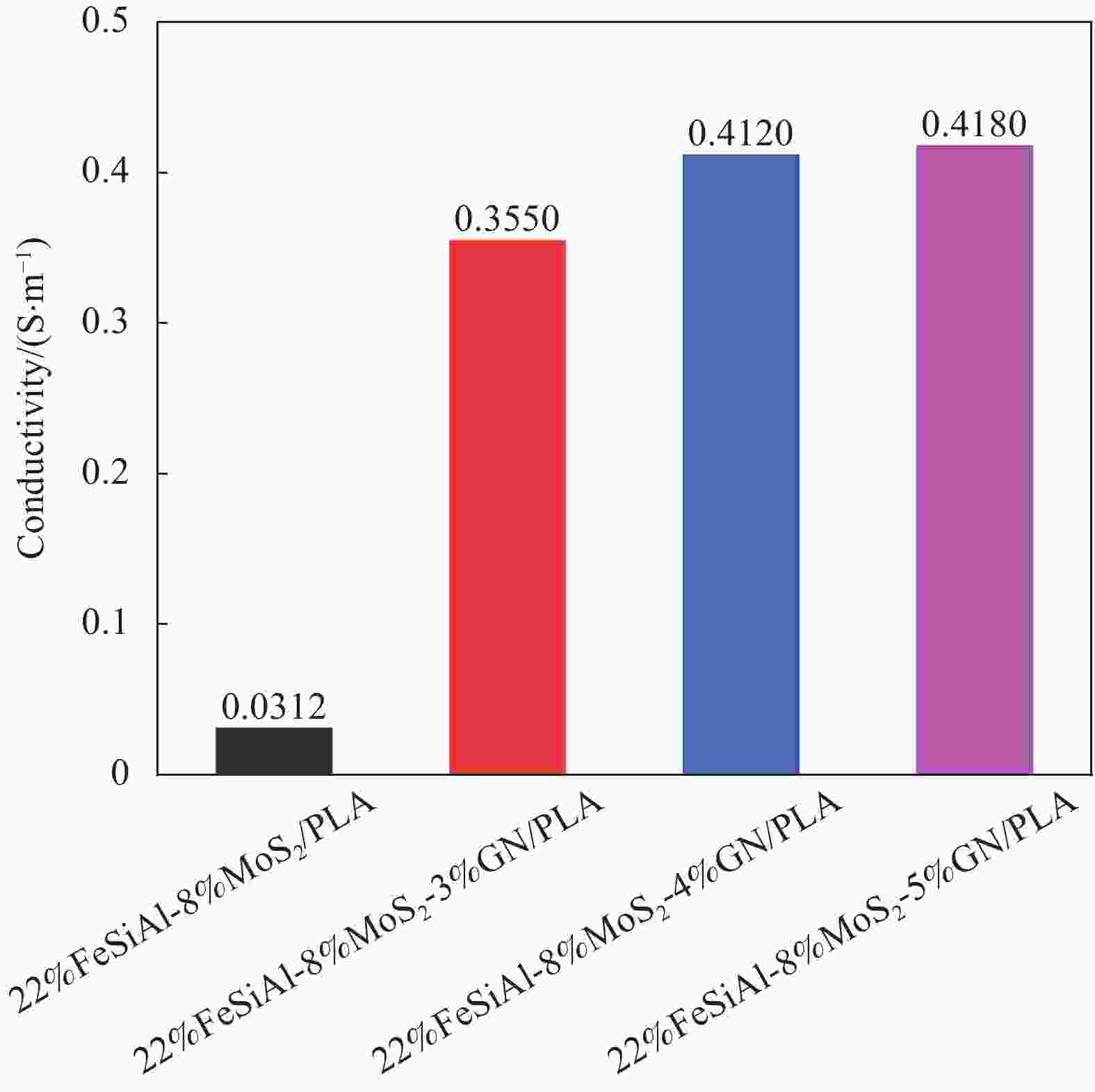
摘要: 多元材料复合是制备轻质、宽频和强吸收吸波材料的有效方法。以聚乳酸(PLA)为基体,FeSiAl、MoS2和石墨烯(GN)为填料,通过球磨和熔融挤出两步法制备了可用于熔融沉积成形(FDM)的FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA复合材料。采用XRD、拉曼光谱、SEM和矢量网络分析仪分别对复合材料的物相结构、微观形貌和电磁特性进行了表征,并研究了石墨烯含量对复合材料吸波性能的影响。研究表明:石墨烯、FeSiAl和MoS2随机分散在PLA基体中,形成了复杂的导电网络;多元材料复合构筑了丰富的介电/磁异质界面,有利于促进界面极化;当石墨烯含量增加时,复合材料的吸波性能随之增强,当石墨烯含量为5wt%时,复合材料的吸波性能最佳,在厚度为1.7 mm时最小反射损耗为−27.90 dB,在厚度为1.9 mm时有效吸收带宽为4.96 GHz(12.64~17.60 GHz)。其优异的吸波性能归因于良好的阻抗匹配及介电损耗和磁损耗之间的协同作用。Abstract: Multi-material composite is an effective method to prepare light-weight, broadband and strong absorbing materials. In this paper, polylactic acid (PLA) was used as the matrix material, and FeSiAl, MoS2 and graphene (GN) were used as fillers. FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA composites, which were used for fused deposition modeling (FDM), prepared by the two-step process of ball milling and melt extrusion. The phase structure, microscopic morphology and electromagnetic properties of composites were characterized by XRD, Raman spectroscopy, SEM and vector network analyzer, respectively. And the effect of graphene content on the electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of composites was also investigated. The research shows that graphene, FeSiAl and MoS2 are randomly dispersed in the PLA matrix and form a complex conductive network; Multi-material composites build rich dielectric/magnetic heterointerfaces, which are beneficial to promote interface polarization; The higher the graphene content, the stronger the electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of composites; When the graphene content is 5wt%, the minimum reflection loss is −27.90 dB at a thickness of 1.7 mm, and the effective absorption bandwidth is 4.96 GHz (12.64-17.60 GHz) at a thickness of 1.9 mm. Its excellent absorbing properties are attributed to the perfect impedance matching and the synergy between dielectric and magnetic losses.
-
Key words:
- composites /
- FeSiAl /
- MoS2 /
- graphene /
- impedance matching /
- electromagnetic wave absorbing pro-perties
-
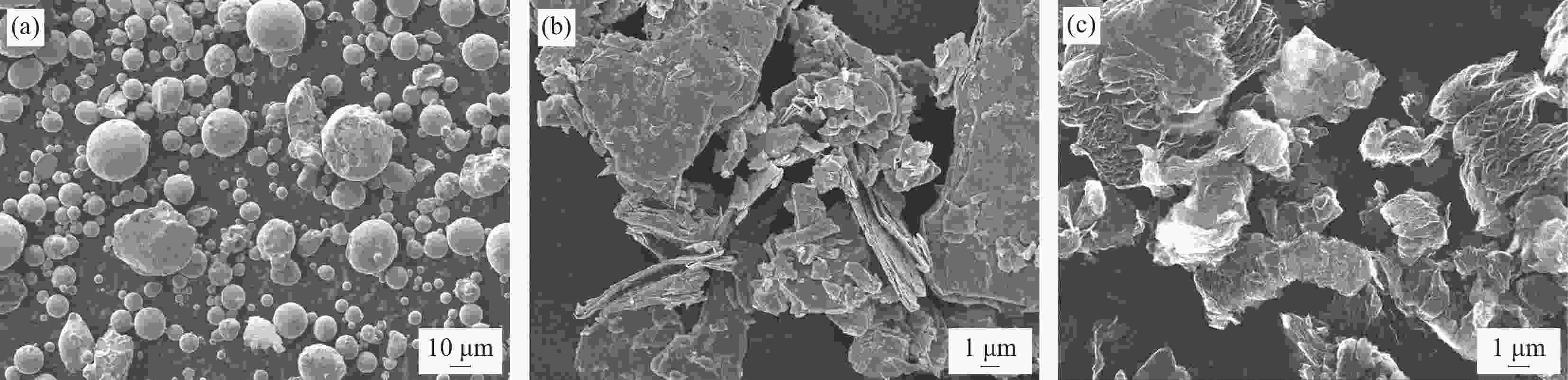
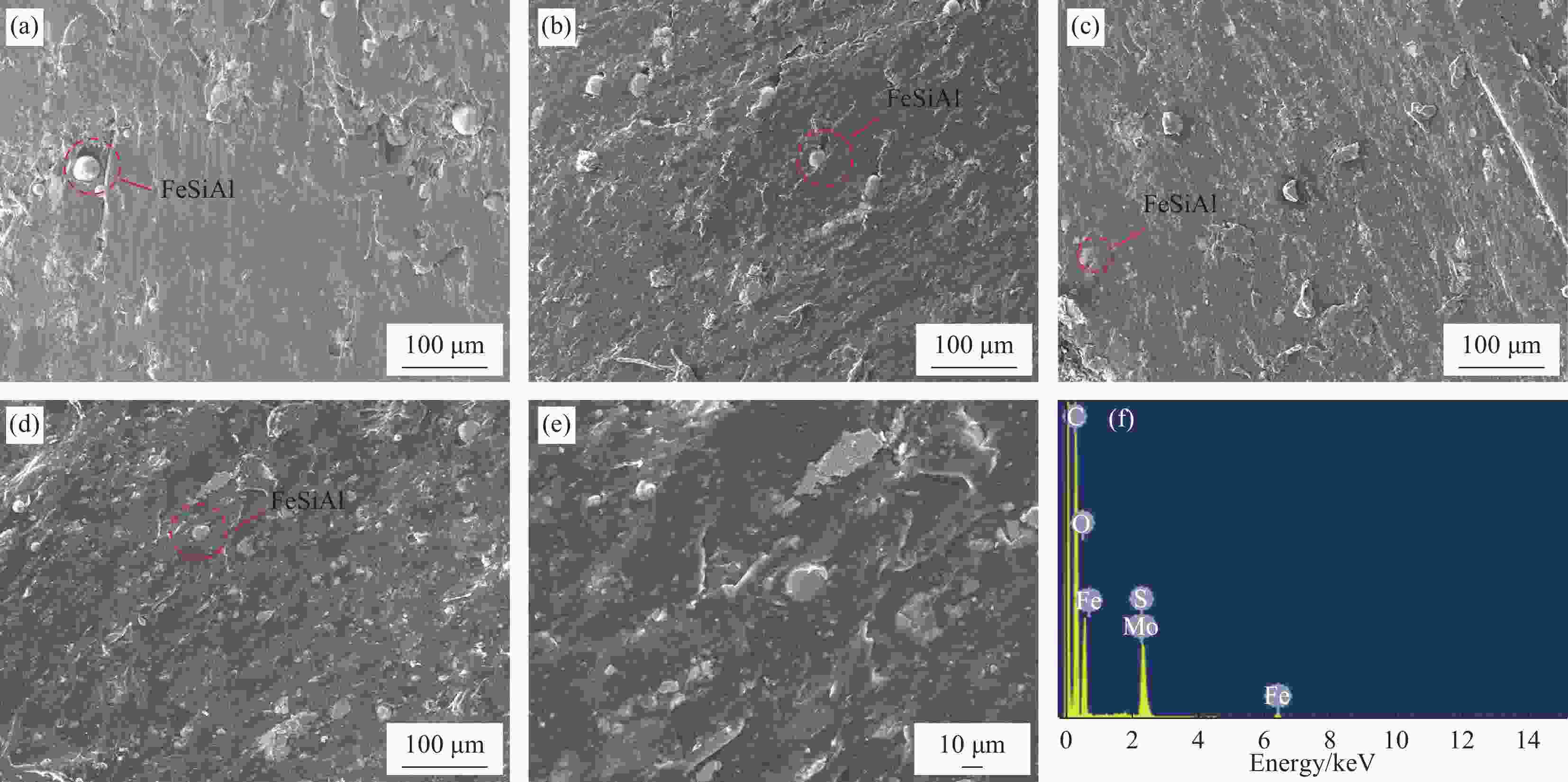
图 7 FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA复合材料的SEM图像:(a) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA;(b) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA;(c) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA;(d) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA;((e), (f)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA的EDS图谱
Figure 7. SEM images of FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA composites: (a) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA; (b) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA; (c) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA; (d) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA; ((e), (f)) EDS mapping of 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA
图 8 FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA复合材料的电磁参数:(a)复介电常数实部;(b)复介电常数虚部;(c)介电损耗角正切;(d)复磁导率实部;(e)复磁导率虚部;(f)磁损耗角正切
Figure 8. Electromagnetic parameters of FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA composites: (a) Real part of complex permittivity; (b) Imaginary part of complex permittivity; (c) Dielectric loss tangent; (d) Real part of complex permeability; (e) Imaginary part of complex permeability; (f) Magnetic loss tangent
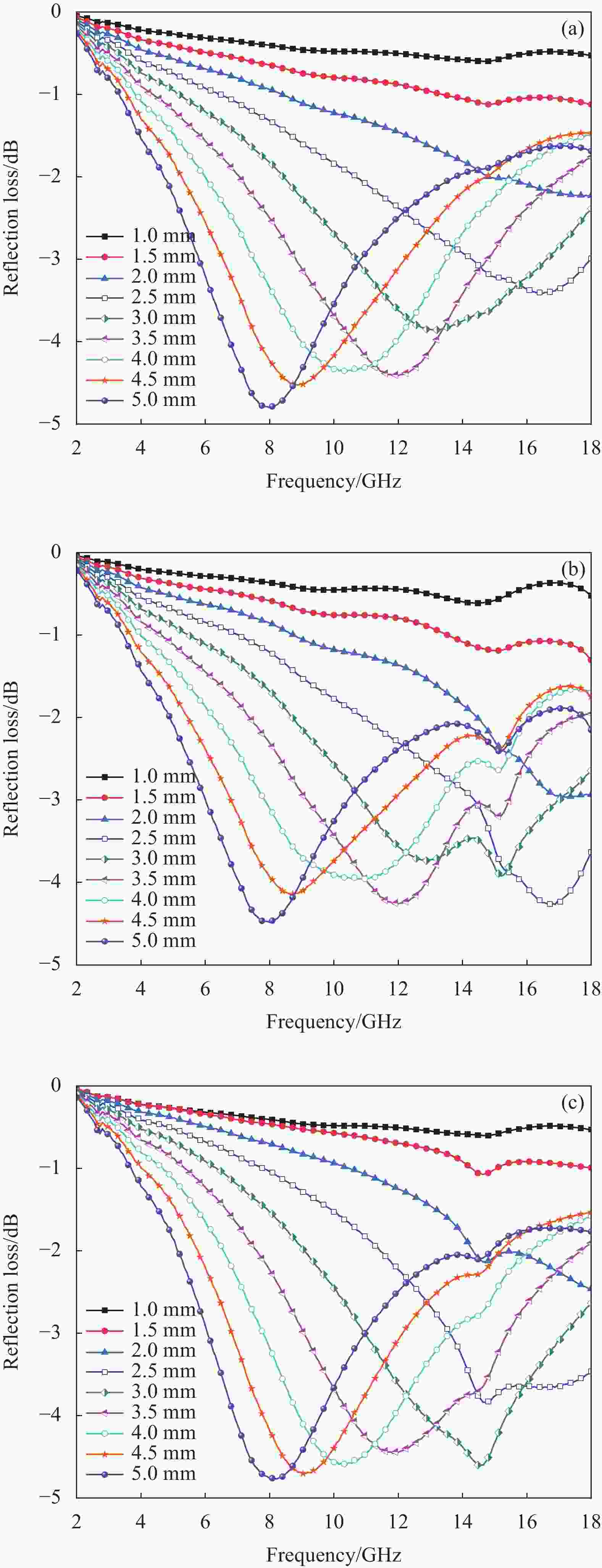
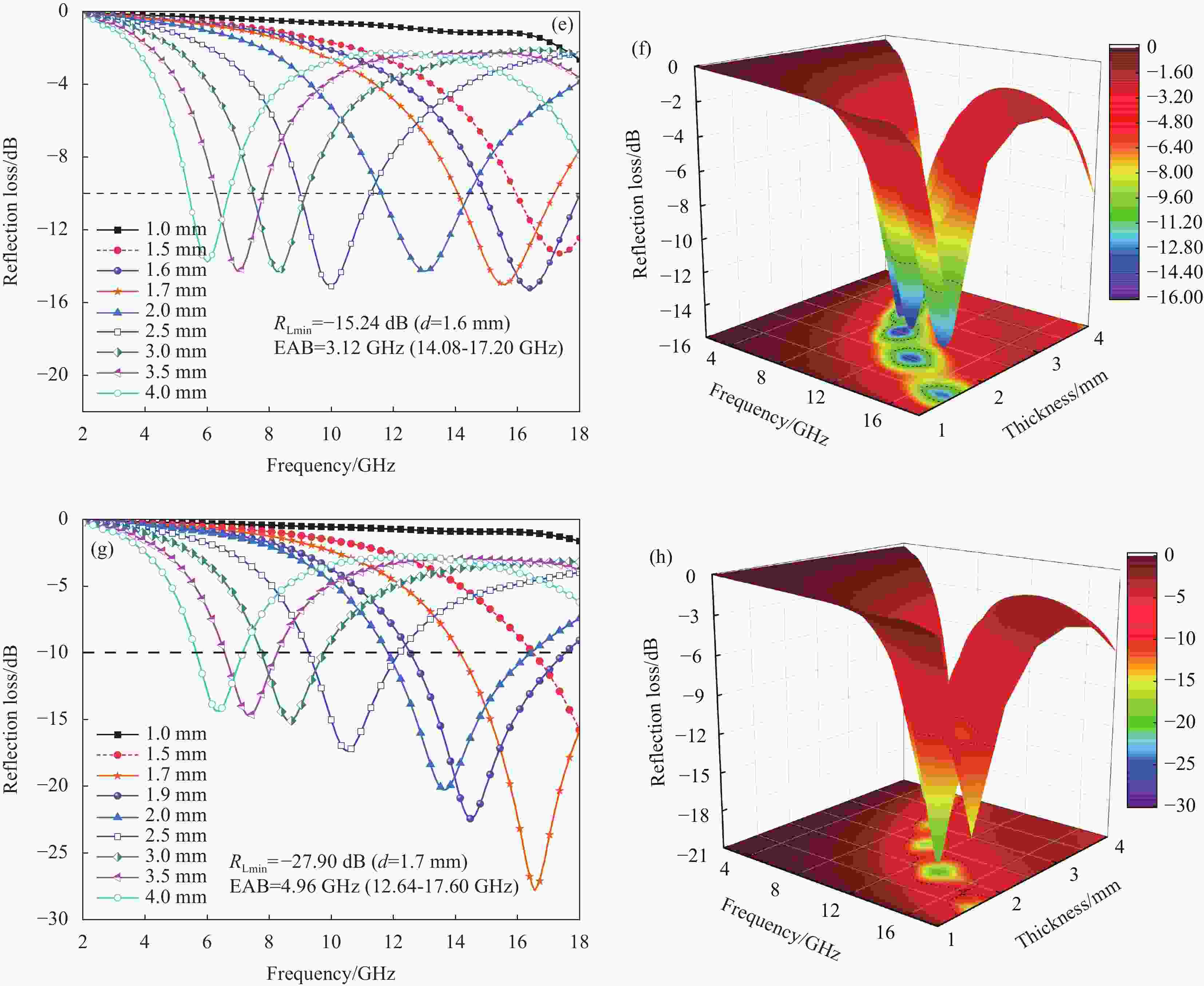
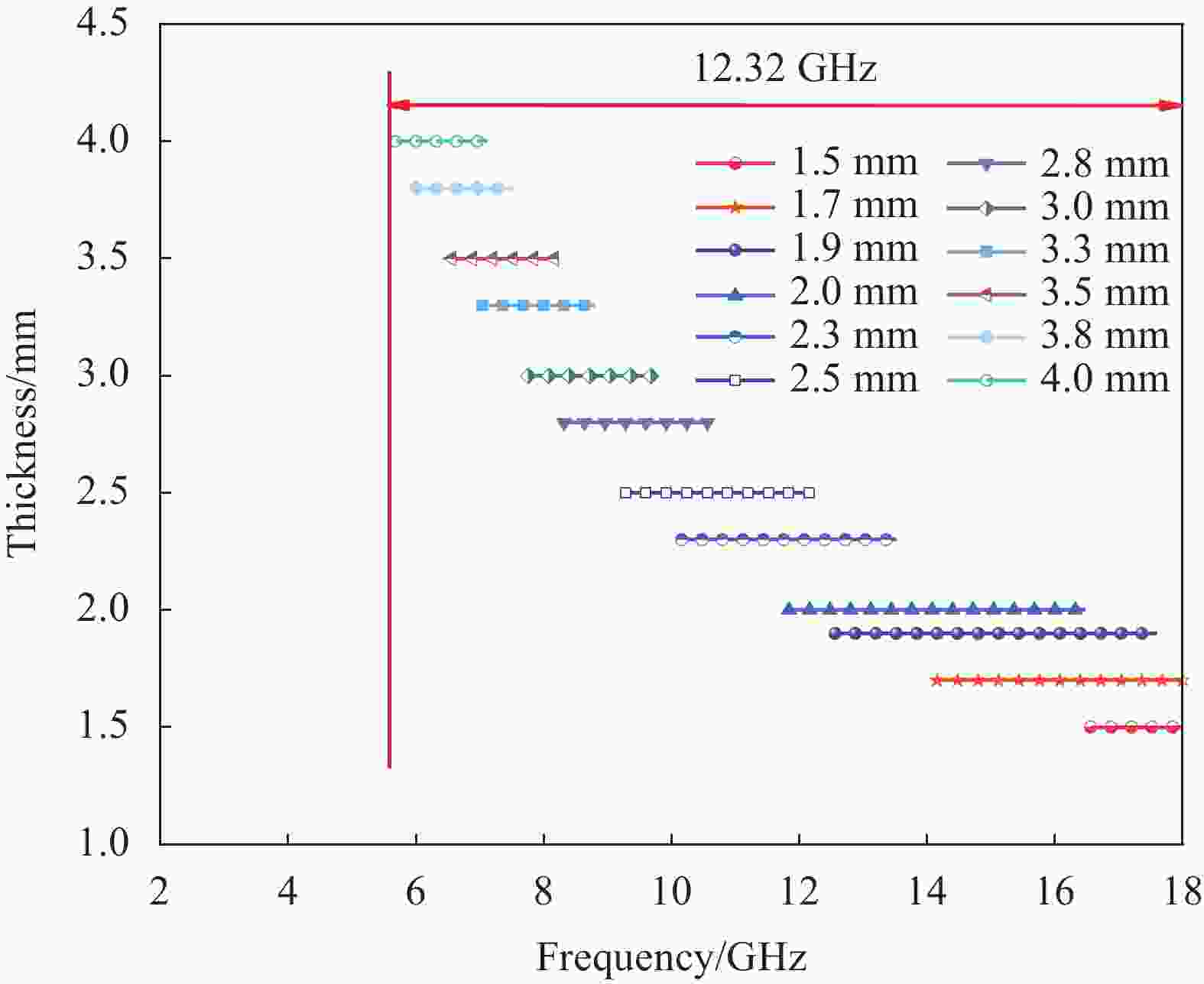
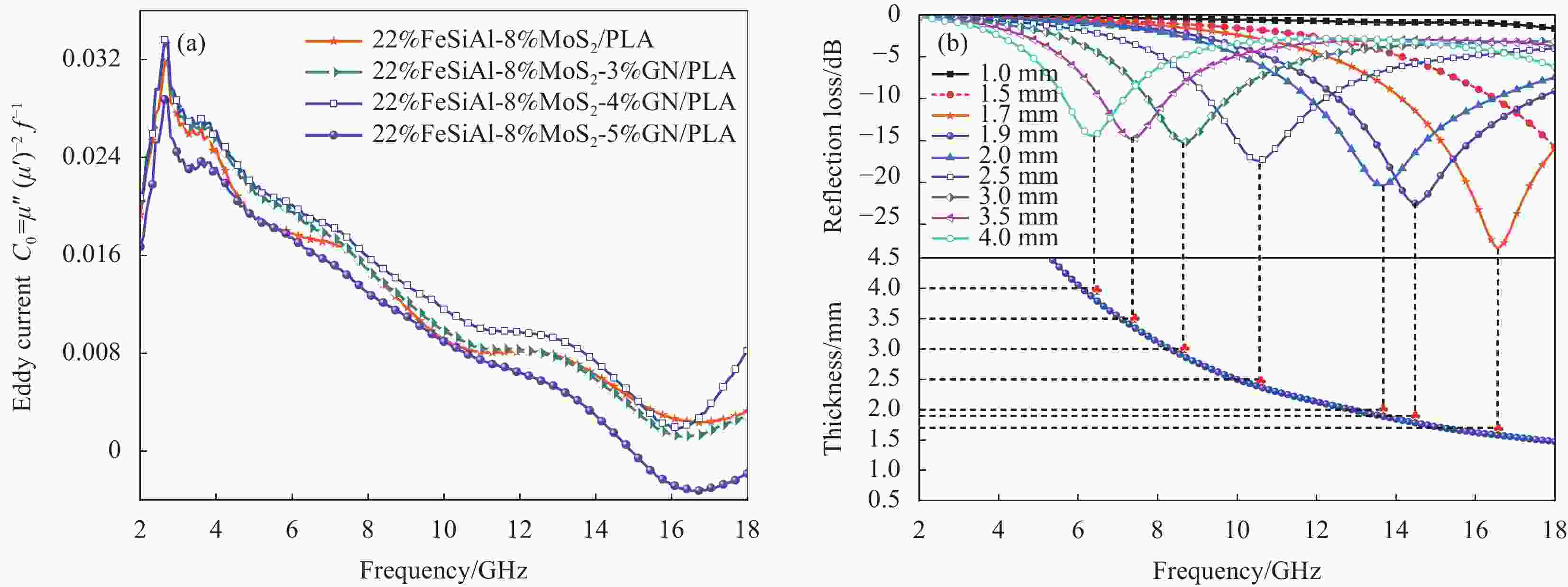
图 9 FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA复合材料的反射损耗曲线图与3D颜色映射曲面图:((a), (b)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA;((c), (d)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA;((e), (f)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA;((g), (h)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA
RLmin—Minimum reflection loss; EAB—Effective absorption bandwidth; d—Thickness
Figure 9. Reflection loss curves and 3D color mapping surfaces of FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA composites: ((a), (b)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA; ((c), (d)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA; ((e), (f)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA; ((g), (h)) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA
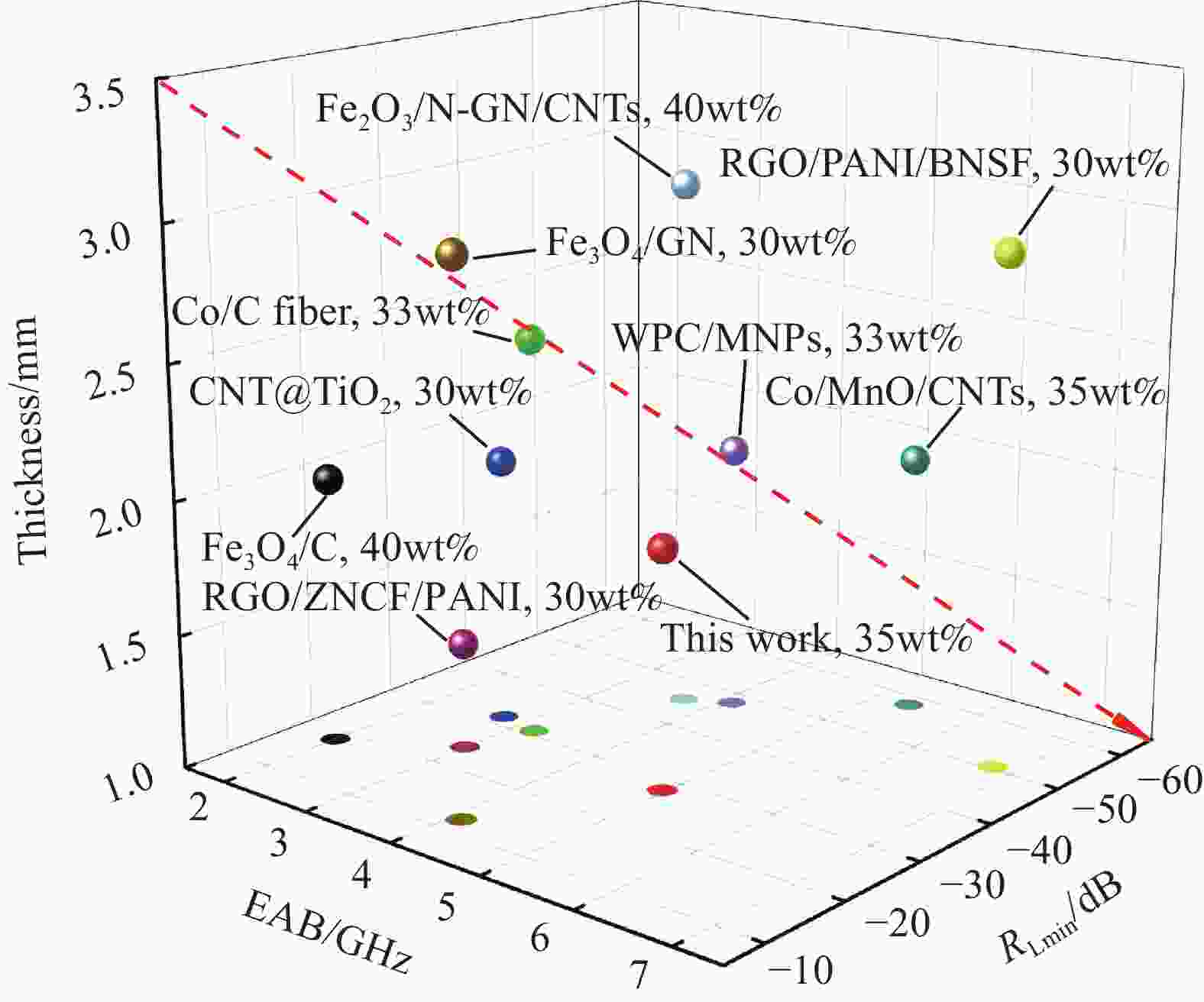
图 11 本文中吸波材料与文献中填充量相近的吸波材料吸波性能对比[40-48]
Figure 11. Comparison of the absorbing properties of the absorbing material in this paper with the absorbing materials with similar filling amount in other literatures[40-48]
RGO—Reduced graphene oxide; BNSF—BaNd0.2Sm0.2Fe11.6O19; ZNCF—Co-doped ZnNi ferrite; PANI—Polyaniline; CNT—Carbon nanotubes; WPC/MNPs—Porous carbon/magnetic nanoparticles composite
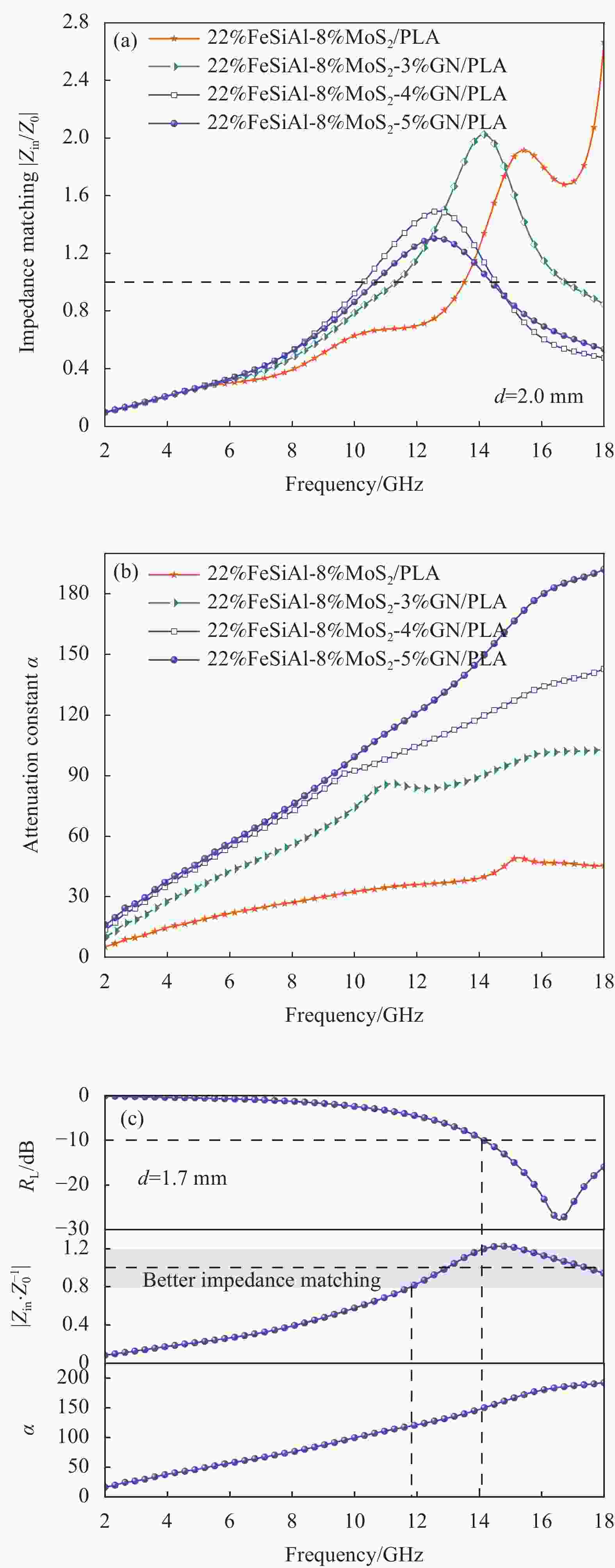
图 12 FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA复合材料厚度为2.0 mm时的阻抗匹配特性(a)和衰减常数(b);(c) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA复合材料的反射损耗、阻抗匹配和衰减常数的对应关系图
Figure 12. Impedance matching characteristics in the 2.0 mm (a) and attenuation constants (b) of FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA composites; (c) Correspondence diagram of reflection loss, impedance matching and attenuation constant of 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA composite
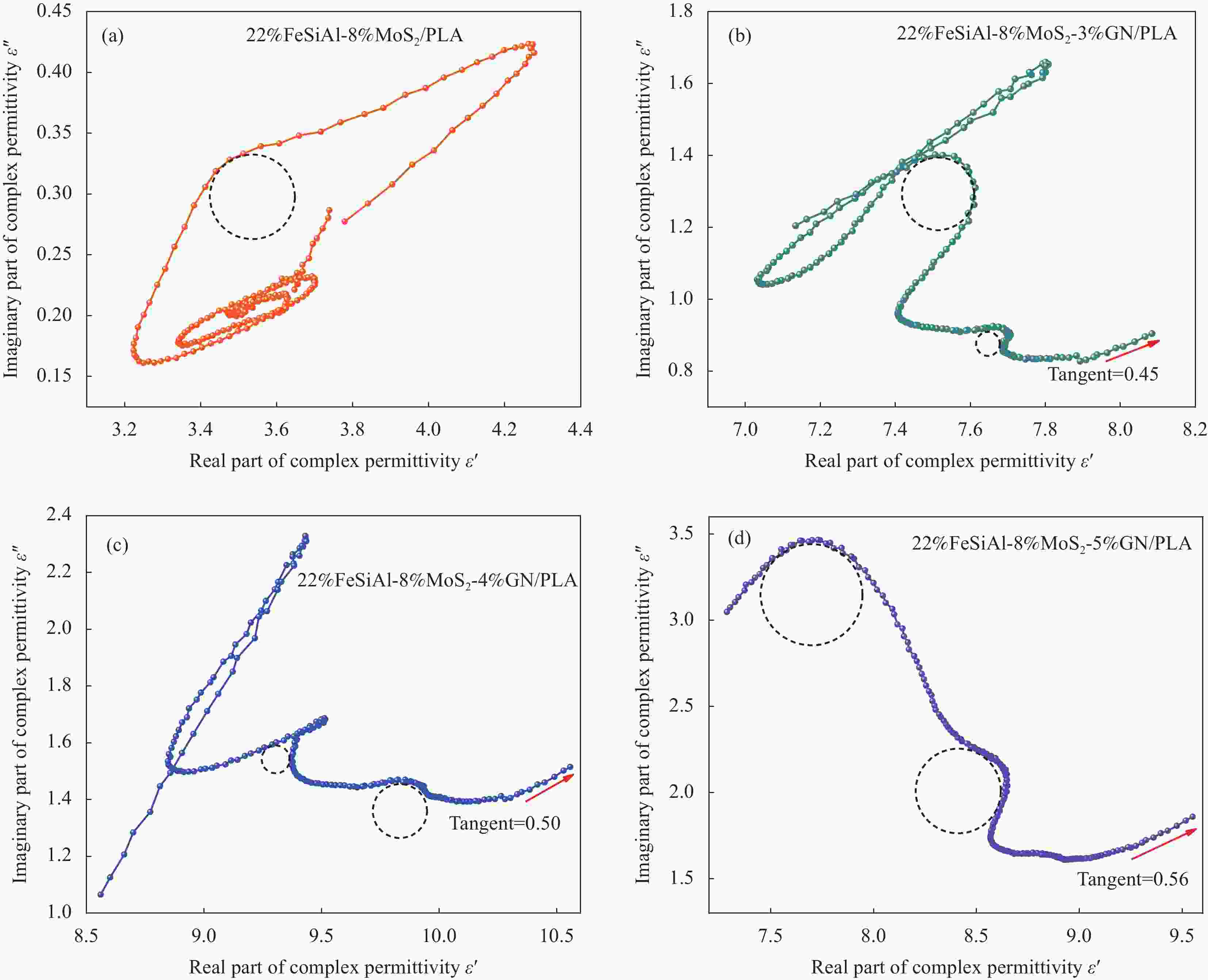
图 13 FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA复合材料的Cole-Cole曲线:(a) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA;(b) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA;(c) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA;(d) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA
Figure 13. Cole-Cole curves of FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/PLA composites: (a) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA; (b) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA; (c) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA; (d) 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA
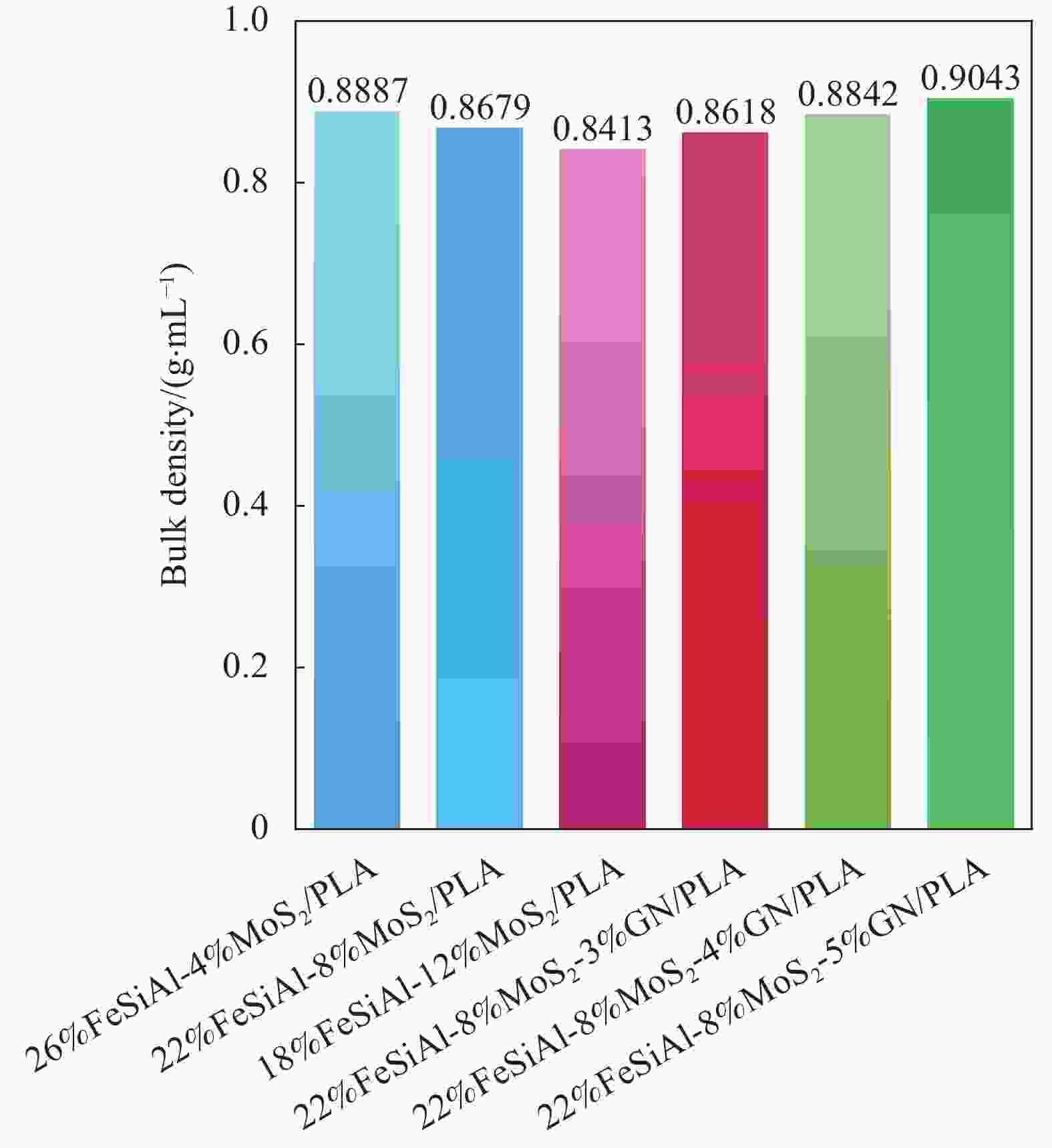
表 1 FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/聚乳酸(PLA)复合材料的成分
Table 1. Ingredients of FeSiAl-MoS2-GN/polylactic acid (PLA) composites
Sample Mass fraction/wt% GN FeSiAl MoS2 PLA 26%FeSiAl-4%MoS2/PLA 0 26 4 70 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2/PLA 0 22 8 70 18%FeSiAl-12%MoS2/PLA 0 18 12 70 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-3%GN/PLA 3 22 8 67 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA 4 22 8 66 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA 5 22 8 65 Note: GN—Graphene. 表 2 近五年文献中报道的FeSiAl复合材料与本文制备的复合材料吸波性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of the absorbing properties of FeSiAl composites reported in the literature in the past five years and the composites prepared in this paper
Materials Loading/wt% Matrix RLmin (Thickness) EAB/GHz Ref. FeSiAl/nitrides 50 Paraffin −34.50 dB (2.50 mm) 8.11 [5] FeSiAl/MgO 80 Paraffin −33.00 dB (1.50 mm) 4.93 [6] FeSiAl@SiO2 80 Paraffin −21.40 dB (2.10 mm) 3.80 [7] FeSiAl@SiO2@C 80 Paraffin −46.75 dB (3.50 mm) 7.73 [9] FeSiAl hollow microspheres 60 Paraffin −22.10 dB (5.00 mm) 3.30 [30] FeSiAl@C 50 Paraffin −15.68 dB (4.00 mm) 2.00 [31] FeSiAl/rGO/Al2O3 5 Al2O3 −35.42 dB (1.40 mm) 1.12 [32] FeSiAl/MnZnFe2O4 80 Paraffin −16.50 dB (1.50 mm) 4.60 [33] Flaky FeSiAl/MnZnFe2O4 80 Paraffin −24.30 dB (1.50 mm) 3.60 [34] Flakey FeSiAl/NiZnFe2O4 60 Paraffin −29.20 dB (2.50 mm) 4.00 [35] FeSiAl/ZnO/epoxy resin 55 Epoxy −40.50 dB (2.20 mm) 3.50 [36] FeSiAl@ZnO2@Al2O3 80 Paraffin −50.60 dB (3.72 mm) 1.50 [37] FeSiAl@SiO2@PUA 80 Paraffin −49.00 dB (4.50 mm) 7.80 [38] FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 80 Paraffin −46.29 dB (2.50 mm) 7.33 [39] 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-4%GN/PLA 34 PLA −15.24 dB (1.60 mm) 3.12 This work 22%FeSiAl-8%MoS2-5%GN/PLA 35 PLA −27.90 dB (1.70 mm) 4.96 This work Notes: EAB—Effective absorption bandwidth (RL≤–10 dB); PUA—Polyurethane-acrylic; GN—Graphene, rGO—Reduced graphene oxide. -
[1] CHENG J Y, ZHANG H B, XIONG Y F, et al. Construction of multiple interfaces and dielectric/magnetic heterostructures in electromagnetic wave absorbers with enhanced absorption performance: A review[J]. Journal of Materiomics,2021,7(6):1233-1263. doi: 10.1016/j.jmat.2021.02.017 [2] RUSAKOVA A, NOSACHEV I, LYSENKO V, et al. Impact of high strength electromagnetic fields generated by Tesla transformer on plant cell ultrastructure[J]. Information Processing in Agriculture,2017,4(3):253-258. doi: 10.1016/j.inpa.2017.05.002 [3] TAO J Q, ZHOU J T, YAO Z J, et al. Multi-shell hollow porous carbon nanoparticles with excellent microwave absorption properties[J]. Carbon,2021,172:542-555. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.10.062 [4] ZENG X J, CHENG X Y, YU R H, et al. Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers[J]. Carbon,2020,168:606-623. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.07.028 [5] LIU D, ZHANG Y, ZHOU C, et al. A facile strategy for the core-shell FeSiAl composites with high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,818:152861. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152861 [6] ZHANG Y, ZHOU T D. Structure and electromagnetic pro-perties of FeSiAl particles coated by MgO[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2017,426:680-684. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.10.144 [7] ZHOU L, XU H, SU G X, et al. Tunable electromagnetic and broadband microwave absorption of SiO2-coated FeSiAl absorbents[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,861:157966. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157966 [8] LEI C L, GE C N, GE X, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption of flaky FeSiAl/ZnO composites fabricated via precipitation[J]. Materials Science & Engineering B,2022,275:115502. [9] TIAN W, ZHANG X Z, GUO Y, et al. Hybrid silica-carbon bilayers anchoring on FeSiAl surface with bifunctions of enhanced anti-corrosion and microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2021,173:185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.002 [10] 贾琨, 王东红, 李克训, 等. 石墨烯复合吸波材料的研究进展及未来发展方向[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(5):805-811. doi: 10.11896/cldb.201905012JIA Kun, WANG Donghong, LI Kexun, et al. Progress and future developments of graphene composites serving as microwave absorbing materials[J]. Materials Reports,2019,33(5):805-811(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.201905012 [11] 谢文瀚, 耿浩然, 柳扬, 等. MoS2/生物质碳复合材料的制备与吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5): 2211-2221.XIE Wenhan, GENG Haoran, LIU Yang, et al. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of MoS2/biomass carbon composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sincia, 2022, 39(5): 2211-2221(in Chinese). [12] SONG Q, YE F, KONG L, et al. Graphene and MXene nanomaterials: Toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption in gigahertz band range[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(31):2000475. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000475 [13] WANG Y, CHEN D, YIN X, et al. Hybrid of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide: A lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7:26226-26234. [14] WANG J N, WANG Q J, WANG W, et al, Hollow Ni/C microsphere@graphene foam with dual-spatial and porous structure on the microwave absorbing performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 873: 159811. [15] LI M, CAO X, ZHENG S, et al. Ternary composites RGO/MoS2@Fe3O4: Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics,2017,28(22):16802-16812. doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-7595-x [16] ZHANG H X, SHI C, JIA Z R, et al. FeNi nanoparticles embedded reduced graphene/nitrogen-doped carbon composites towards the ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,584:382-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.122 [17] 吴海华, 胡正浪, 李雨恬, 等. 铁镍合金/聚乳酸复合材料的熔融沉积成形制备及其电磁吸收性能和力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):158-168.WU Haihua, HU Zhenglang, LI Yutian, et al. Electromagnetic absorption properties and mechanical properties of Fe-Ni alloy/polylactic acid composites fabricated by fused deposition modeling[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):158-168(in Chinese). [18] 叶喜葱, 欧阳宾, 杨超, 等. 石墨烯-羰基铁粉线材的制备及其吸波性能分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3292-3302.YE Xicong, OUYANG Bin, YANG Chao, et al. Preparation of graphene carbonyl iron powder wire and analysis of its wave absorption performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3292-3302(in Chinese). [19] 胡正浪, 吴海华, 杨增辉, 等. 石墨烯-铁镍合金-聚乳酸复合材料的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3303-3316.HU Zhenglang, WU Haihua, YANG Zenghui, et al. Preparation of graphene-iron-nickel alloy-polylactic acid compo-sites and their microwave absorption properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3303-3316(in Chinese). [20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料拉伸性能的测定: GB/T 1040—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics: Determination of tensile properties: GB/T 1040—2006[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2006(in Chinese). [21] ZHANG M, QIAN X, ZENG Q W, et al. Hollow microspheres of polypyrrole/magnetite/carbon nanotubes by spray-dry as an electromagnetic synergistic microwave absorber[J]. Carbon,2021,175:499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.01.013 [22] XIANG Z, HUANG C, SONG Y M, et al. Rational construction of hierarchical accordion-like Ni@porous carbon nanocomposites derived from metal-organic frameworks with enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2020, 167:364-377. [23] YANG K, CUI Y H, LIU Z H, et al. Design of core-shell structure NC@MoS2 hierarchical nanotubes as high-perfor-mance electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Chemical Engi-neering Journal,2021,426(1):131308. [24] SHU R W, WAN Z L, ZHANG J B, et al. Synergistically assembled nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite aerogels with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2021,210:108818. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108818 [25] DI X C, WANG Y, LU Z, et al. Heterostructure design of Ni/C/porous carbon nanosheet composite for enhancing the electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2021,179:566-578. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.04.050 [26] GAO J, DING Q, YAN P, et al. Highly improved microwave absorbing and mechanical properties in cold sintered ZnO by incorporating graphene oxide[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2022,42(3):993-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.10.053 [27] YAN F, ZHANG S, ZHANG X, et al. Growth of CoFe2O4 hollow nanoparticles on graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2018,6(47):12781-12787. doi: 10.1039/C8TC04222E [28] XU Z, DU Y, LIU D, et al. Pea-like Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles embedded in nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with tunable dielectric/magnetic loss and efficient electromagnetic absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(14):4268-4277. [29] 朱晓宇, 邱红芳, 陈平. Co@CNT复合电磁波吸收剂的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2021, 35(11):811-819.ZHU Xiaoyu, QIU Hongfang, CHEN Ping. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of composites of cobalt coated graphitic carbon nitride Co@CNTs[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research,2021,35(11):811-819(in Chinese). [30] 王建江, 蔡旭东, 温晋华, 等. FeSiAl软磁合金空心微珠的微观结构控制及其低频吸波性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2018, 47(10):3072-3079.WANG Jianjiang, CAI Xudong, WEN Jinhua, et al. Microstructure control of FeSiAl magnetically soft alloy hollow microspheres and their microwave absorption properties at low frequency[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2018,47(10):3072-3079(in Chinese). [31] ZHANG X Z, GUO Y, RASHAD A, et al. Bifunctional carbon-encapsulated FeSiAl hybrid flakes for enhanced microwave absorption properties and analysis of corrosion resistance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,828:154079. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154079 [32] 黄巨龙. 热压烧结FeSiAl/碳系吸收剂/Al2O3复合材料的制备及其电磁性能研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019.HUANG Julong. Study on preparation and electromagnetic properties of hot pressed sintered FeSiAl/carbon-based absorbent/Al2O3 composites[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2019(in Chinese). [33] ZHOU T D, XUE J, LIU W B, et al. Microstructural and magnetic evolution of MnZn/FeSiAl composites synthesized by mechanochemistry[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(2):1784-1792. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.153 [34] YAN H Y, ZHOUG L, TANG J L, et al. Decreasing the complex permittivity to enhance microwave absorption properties of flaky FeSiAl/MnZn ferrites composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2021,32:18371-18380. doi: 10.1007/s10854-021-06380-w [35] LEI C, DU Y. Tunable dielectric loss to enhance microwave absorption properties of flakey FeSiAl/ferrite composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,822:153674. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153674 [36] ZHOU L, HUANG J L, WANG H B, et al. FeSiAl/ZnO-filled resin composite coatings with enhanced dielectric and microwave absorption properties[J]. Springer US,2019,30(2):1896-1906. [37] TIAN W, LI J Y, LIU Y F, et al. Atomic-scale layer-by-layer deposition of FeSiAl@ZnO@Al2O3 hybrid with threshold anti-corrosion and ultra-high microwave absorption pro-perties in low-frequency bands[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2021,13(10):308-321. doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00678-4 [38] PAN Y, LI J Y, LIU Z Y, et al. Inorganic/organic bilayer of silica/acrylic polyurethane decorating FeSiAl for enhanced anti-corrosive microwave absorption[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,567:150829. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150829 [39] GUO Y, JIAN X, ZHANG L, et al. Plasma-induced FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 core-shell structure for exceptional microwave absorption and anti-oxidation at high temperature[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,384:123371. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123371 [40] YANG C, DAI S L, ZHANG X Y, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption property of graphene with Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2016,16:1483-1490. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2016.10707 [41] ZHANG K, LUO J H, YU N, et al. Synthesis and excellent electromagnetic absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide/PANI/BaNd0.2Sm0.2Fe11.6O19 nanocompo-sites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,779:270-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.284 [42] LEI Y M, YAO Z J, LIN H Y, et al. Synthesis and high-performance microwave absorption of reduced graphene oxide/Co-doped ZnNi ferrite/polyaniline composites[J]. Materials Letters,2019,236:456-459. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.10.158 [43] LI W X, QI H X, GUO F, et al. Co nanoparticles supported on cotton-based carbon fibers: A novel broadband microwave absorbent[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,772:760-769. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.075 [44] ZHOU N, AN Q D, XIAO Z Y, at el. Solvothermal synthesis of three-dimensional, Fe2O3 NPs-embedded CNT/N-doped graphene composites with excellent microwave absorption performance[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7:45156-45169. doi: 10.1039/C7RA06751H [45] XUE W, YANG G, BI S, et al. Construction of caterpillar-like hierarchically structured Co/MnO/CNTs derived from MnO2/ZIF-8@ZIF-67 for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2021,173(48):521-527. [46] MO Z C, YANG R L, LU D W, et al. Lightweight, three-dimensional carbon nanotube@TiO2 sponge with enhanced microwave absorption performance[J]. Carbon,2019,144:433-439. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.12.064 [47] ZOU C W, YAO Y D, WEI N D, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of mesoporous Fe3O4/C nanocomposites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2015,77:209-214. [48] FANG J Y, LIU T, CHEN Z, et al. A wormhole-like porous carbon/magnetic particles composite as an efficient broadband electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Nanoscale,2016, 16:8899-8909. [49] WANG J W, WANG B B, FENG A L, et al. Design of morphology-controlled and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance of sheet-shaped ZnCo2O4 with a special arrangement[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,834:155092. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155092 [50] CUI Y, XU K Z, ZHU B, et al. Synthesis of niobium nitride porous nanofibers with excellent microwave absorption properties via reduction nitridation of electrospinning precursor nanofibers with ammonia gas[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,907:164453. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164453 [51] ZHANG W D, ZHANG X, ZHU Q, et al. High-efficiency and wide-bandwidth microwave absorbers based on MoS2-coated carbon fiber[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,586:457-468. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.109 [52] SUN Z H, YAN Z Q, YUE K C, et al. Multi-scale structural nitrogen-doped rGO@CNTs composites with ultra-low loading towards microwave absorption[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,538:14793. [53] XU J, CUI Y H, WANG J Q, et al. Fabrication of wrinkled carbon microspheres and the effect of surface roughness on the microwave absorbing properties[J]. Chemical Engi-neering Journal,2020,401:126027. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126027 [54] WANG H Y, SUN X B, YANG S H, et al. 3D ultralight hollow NiCo compound@MX high-efficient microwave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2021,13(12):330-344. [55] DONG Y Y, ZHU X J, PAN F, et al. Fire-retardant and thermal insulating honeycomb-like NiS2/SnS2 nanosheets@3D porous carbon hybrids for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,426:131272. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131272 -





 下载:
下载: