Microstructure and corrosion properties of the laser cladding Al-TiC composite coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy
-
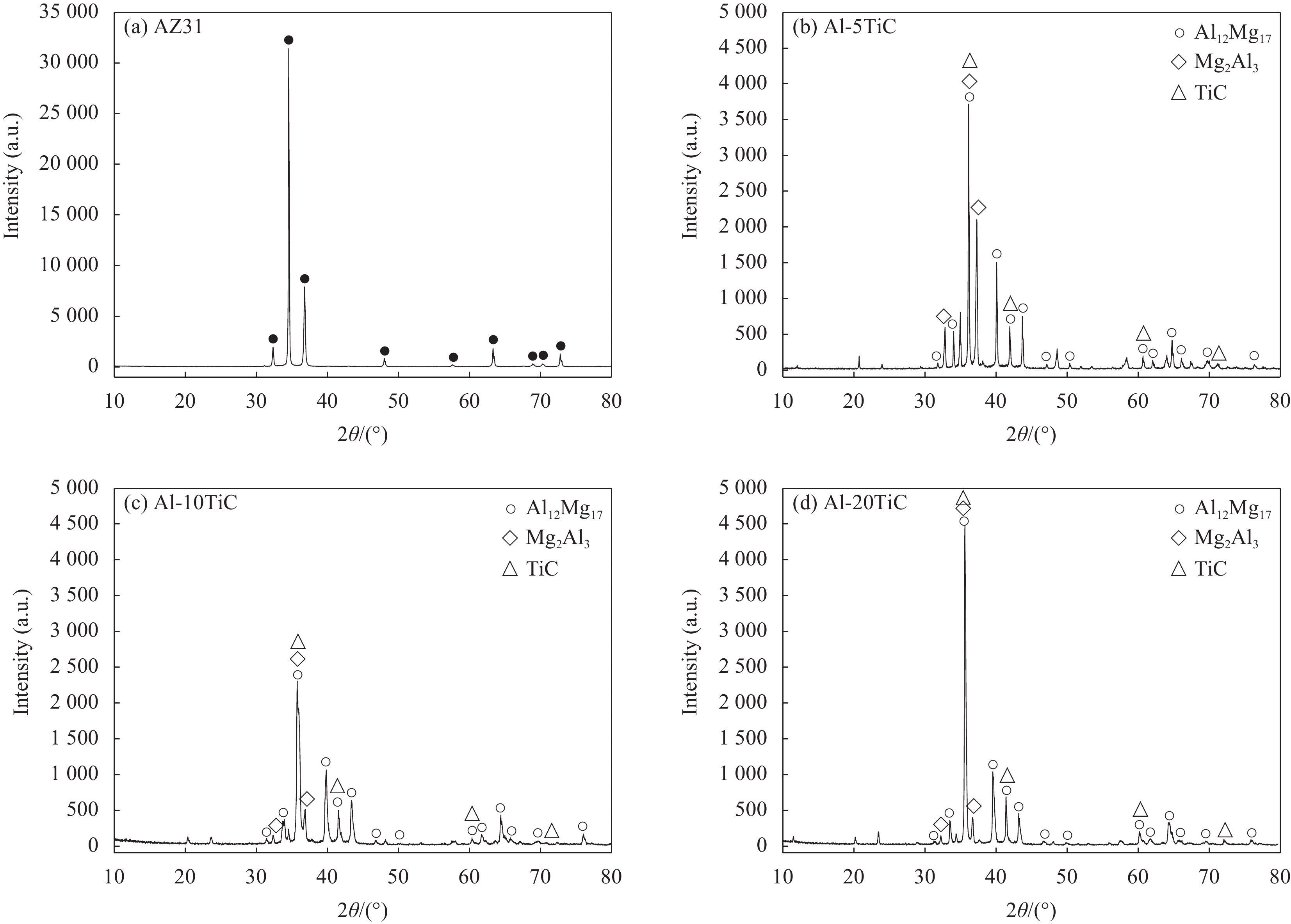
摘要: 为有效改善AZ31镁合金表面的腐蚀性能,本文采用激光熔覆技术在AZ31镁合金表面成功制备了无缺陷的Al-TiC复合涂层。研究了不同成分含量的Al-TiC复合涂层的相组成、微观组织和耐腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明:在Al-TiC复合涂层内形成了大量的Al12Mg17、Mg2Al3和TiC相。复合涂层内微观组织呈现出连续网络状分布特征。随着Al-TiC混合粉末中Al含量的减小,复合涂层中Al12Mg17、Mg2Al3和TiC相的含量呈递增趋势,网络状分布的微观组织结构变得更加均匀连续。复合涂层与AZ31基体之间形成了良好的冶金结合界面。激光熔覆制备的Al-TiC复合涂层耐腐蚀性能较AZ31基体显著提升。自腐蚀电位由基体的−1.563 V提升至−1.144 V,自腐蚀电流由基体的1.55×10−4 A减小至2.63×10−6 A。
-
关键词:
- 激光熔覆 /
- Al-TiC复合涂层 /
- AZ31合金 /
- 微观组织 /
- 耐腐蚀性
Abstract: In order to enhance the surface corrosion resistance of the AZ31 magnesium alloy, the defect-free Al-TiC composite coatings were prepared on AZ31 magnesium alloy using laser cladding technology. The influences of Al-TiC compositions with different contents on the phase composition, microstructure and corrosion resistance of the Al-TiC composite coatings were investigated. The results indicate that a large number of Al12Mg17, Mg2Al3 and TiC phases are produced in the Al-TiC composite coating. The microstructure of the composite coating characterizes as a continuous network distribution. With the decrease of the Al content in the composite powder, the contents of the Al12Mg17, Mg2Al3 and TiC phases in the composite coating gradually increase, and the network-like distribution characteristics of the microstructure in the composite coating become more uniform and continuous. In addition, a sound metallurgical bonding interface is prepared between the composite coating and the AZ31 substrate. The corrosion resistance of the Al-TiC composite coating prepared using the laser cladding technology is significantly enhanced compared to that of the AZ31 substrate. The self-corrosion potential increased from −1.563 V of the AZ31 substrate to −1.144 V of the Al-TiC composite coating, whereas the self-corrosion current decreased from 1.55×10−4 A to 2.63×10−6 A.-
Keywords:
- laser cladding /
- Al-TiC composite coating /
- AZ31 alloy /
- microstructure /
- corrosion resistance
-
碳纤维复合材料层合板因具有优异的力学性能,特别是其最佳的比强度和比刚度,而广泛应用于航空航天等领域[1-2]。这些层合板结构在服役过程中,不可避免会遇到工具坠落或者外物低速冲击。因为多层、非均质和弹性各向异性特点[3],导致其对垂直于铺层方向的冲击载荷较为敏感,即使在低速冲击下,内部也可能产生不可见的冲击损伤[4]。由于结构内部复杂的应力作用,多种损伤机制之间相互耦合,导致损伤不断演变和扩展,结构的强度严重降低甚至失效。为解决这一问题,众多学者通过试验手段,开展大量动态冲击测试,研究层合板损伤机制、设计结构安全系数等。此外,动态原位试验技术也得到了发展[5-6]。结合高速摄像、微观X射线计算机断层扫描技术和深度学习语义分割算法,可以更深入认识试样损伤状态,但也存在内部损伤捕捉不足、实时监测成本高等问题,导致材料渐进损伤行为描述存在局限。因此,开展低速冲击过程的数值模拟研究显得尤为关键。
已有数值模拟研究中,宏观渐进分析方法因考虑了从损伤起始到失效的完整演化过程得到重视[7]。该方法包括损伤起始准则、演化方法和渐进本构关系。损伤起始判定可分与失效模式无关的第一类准则和与失效模式相关的第二类准则。第一类如最大应力准则、Tsai-Hill失效准则和Tsai-Wu准则等,它们是根据局部的应力或应变条件判断层合板整体是否失效,预测结果往往过于保守。第二类准则以试验现象和失效机理为依据,适用于复合材料损伤机理和复杂结构强度的分析,如Chang-Chang[8]、Hou[9]、Hashin[10]和Puck[11]等准则。其中,Chang-Chang、Hou和Hashin准则相对简单,多用于复材的冲击损伤分析[12-14]。然而也因自身存在的劣势,例如,Chang-Chang忽略了面外的剪切作用[12],Hou没有考虑贯穿厚度方向的应力作用[13],Hashin没有考虑压缩载荷下断裂面的影响,导致损伤预测结果有偏差[14]。为了考虑在横向压缩载荷对抗剪强度的增强作用,Puck准则引入了基体损伤断裂面的概念,可精确描述压缩状态下的层合板脆性断裂行为[15]。
损伤发生后,后续的扩展规律遵循特定损伤演化方法[16-19]。合理的演化方法可以解释物理机制,并具有良好的数值收敛性和计算精度[16]。演化方法可分为直接和渐进刚度退化两种。直接退化方法假定弹性模量和泊松比下降到预定值,可用于结构强度的粗略估计[17]。然而,该方法严重依赖于经验知识,其物理机制难以解释。此外,该方法对预测整体结构强度以及内部分层和基体损伤通常过于保守[18]。相比之下,渐进退化方法将损伤扩展描述为一个连续演化的过程。损伤起始后,有较多微裂纹产生并分散在结构内部,在宏观尺度上反映出弹性模量等力学性能降低。随着冲击加载持续,微裂纹逐渐积累并最终升级为宏观裂纹,外在反映出结构的承载能力降低甚至失效[17]。在该方法中,当前损伤程度是通过计算损伤区域附近的应变和位移等力学参数获得损伤状态变量进而确定的。然而,在计算之前,该方法需要预先定义刚度退化的趋势,常用的有线性和指数型两种[12-19]。因此,渐进退化可分为线性/指数型等效应变/位移方法。
针对层合板冲击损伤问题的分析,不同学者将损伤起始准则和演化方法进行了不同的组合[12-22]。早期研究主要是将单一损伤起始准则和单一演化方法相结合作为一种辅助分析手段,重点采用实验方法对纤维增强复合材料层合板以及三明治夹芯结构的损伤机制和剩余压缩强度等问题进行研究[12-20],而不同起始准则、演化方法对损伤预测影响并没有涉及。为此,在新近的研究中对比了不同组合对冲击损伤的预测能力,例如Hashin、Chang-Chang和Puck准则分别结合线性等效应变演化方法(E1)[21]。在此基础上,最大应力、Tsai-Wu及Hou准则结合E1和等效位移(E2)两种线性演化方法对预测能力的影响也得到进一步分析[22]。因为最大应力准则倾向于过度预测复合材料在轴向拉伸下的破坏载荷,而Tsai-Wu准则却低估了它们;且Tsai-Wu准则不是独立方程形式,未能区分基体拉伸、压缩损伤。故而,探讨这两个准则对预测层合板损伤的意义不大。此外,指数型演化方法(E3)的损伤预测结果在报道中更符合实际情况[18]。有学者将E3方法与直接演化方法进行对比,验证了该方法的预测能力[23],但不同起始准则对其预测能力的影响尚未开展研究。因此,为准确揭示渐进损伤行为、解释损伤形成机制,不同损伤起始准则、演化方法对层合板冲击损伤预测的影响仍需进一步探索。相关研究对发展可靠的工程预测方法很有意义。
本文旨在评估Hashin应力、Hashin应变和Puck三种损伤起始准则以及E1、E2和非线性指数型等效位移(E3)三种损伤演化方法对复合材料层合板低速冲击损伤预测的影响。为此,建立了低速冲击损伤三维有限元数值模型,设计了冲击损伤动态渐进行为模拟流程,并将其编码在ABAQUS/Explicit的VUMAT子程序中。提出一种通过损伤状态变量表征损伤面积的方法,为阐释损伤行为提供有力工具。在此基础上,对本文数值模拟进行验证并探讨了不同起始准则和演化方法的损伤预测能力。
1. 复材损伤理论
低速冲击载荷引起层合板损伤有多种模式,可分为在层内发生的纤维/基体拉伸/压缩损伤和在层间发生的分层损伤。针对这多模式的冲击损伤,本文采用基于连续损伤力学理论的渐进分析方法研究损伤的起始判定以及累积和扩展行为。
1.1 层内损伤起始准则
起始准则多以应力作为判定参数。但是,层合板在冲击载荷的作用下,其内部应力会因损伤的产生而导致剧烈变化,而应变参数变化较为连续,故而认为应变形式准则更适合用作损伤预测[19]。因此,本文基于应力的Hashin-Stress和Puck以及应变的Hashin-Strain三种准则为研究对象,探讨其损伤预测性能。
纤维损伤起始准则[24]
拉伸(ε11⩾):
{\xi _{{\mathrm{ft}}}} = {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{11}}}}{{\varepsilon _{11}^{\mathrm{T}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{12}}}}{{\varepsilon _{12}^{\mathrm{G}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{13}}}}{{\varepsilon _{13}^{\mathrm{G}}}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 (1) 压缩( {\varepsilon _{11}} < 0 ):
{\xi _{{\mathrm{fc}}}} = {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{11}}}}{{\varepsilon _{11}^{\mathrm{C}}}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 (2) Hashin-Stress准则,
拉伸( {\sigma _{22}} + {\sigma _{33}} \geqslant 0 ):
\begin{aligned} \xi_{\mathrm{mt}}= & \left(\frac{\sigma_{22}+\sigma_{33}}{Y_{\mathrm{T}}}\right)^2+\frac{1}{S_{23}^2}\left(\sigma_{23}^2-\sigma_{22} \sigma_{33}\right) + \\ &\left(\frac{\sigma_{12}}{S_{12}}\right)^2+\left(\frac{\sigma_{13}}{S_{13}}\right)^2 \geqslant 1 \end{aligned} (3) 压缩( {\sigma _{22}} + {\sigma _{33}} < 0 ):
\begin{array}{l}{\xi }_{{\mathrm{mc}}}={\left(\dfrac{{\sigma }_{22}+{\sigma }_{33}}{2{S}_{23}}\right)}^{2}+\dfrac{{\sigma }_{22}+{\sigma }_{33}}{{Y}_{{\mathrm{C}}}}\left[{\left(\dfrac{{Y}_{{\mathrm{C}}}}{2{S}_{23}}\right)}^{2}-1\right]+\\ \begin{array}{cc}& \end{array}\dfrac{1}{{S}_{23}^{2}}\left({\sigma }_{23}^{2}-{\sigma }_{22}{\sigma }_{33}\right)+{\left(\dfrac{{\sigma }_{12}}{{S}_{12}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\dfrac{{\sigma }_{13}}{{S}_{13}}\right)}^{2}\geqslant1\end{array} (4) Hashin-Strain准则
拉伸( {\varepsilon _{22}} + {\varepsilon _{33}} \geqslant 0 ):
{\xi _{{\mathrm{mt}}}} = {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{22}}}}{{\varepsilon _{22}^{\mathrm{T}}}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 (5) 压缩( {\varepsilon _{22}} + {\varepsilon _{33}} < 0 ):
\begin{gathered} {\xi _{{\mathrm{mc}}}} = \frac{{{{\left( {{\varepsilon _{22}} + {\varepsilon _{33}}} \right)}^2}}}{{\varepsilon _{22}^{\mathrm{C}} \cdot \varepsilon _{33}^{\mathrm{C}}}} + \left( {\frac{{\varepsilon _{22}^{\mathrm{C}}}}{{2 \cdot \varepsilon _{12}^{\mathrm{G}}}} - 1} \right) \cdot \frac{{{\varepsilon _{22}} + {\varepsilon _{33}}}}{{\varepsilon _{22}^{\mathrm{C}}}} \\ \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{} \end{array} - \frac{{{\varepsilon _{22}} \cdot {\varepsilon _{33}}}}{{{{\left( {\varepsilon _{23}^{\mathrm{G}}} \right)}^2}}} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{12}}}}{{\varepsilon _{12}^{\mathrm{G}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{13}}}}{{\varepsilon _{13}^{\mathrm{G}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{23}}}}{{\varepsilon _{23}^{\mathrm{G}}}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 \\ \end{gathered} (6) Puck准则
拉伸( {\sigma _{{\mathrm{nn}}}}(\theta ) \geqslant 0 ):
{\xi _{{\mathrm{mt}}}}(\theta ) = {\left( {\frac{{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nn}}}}(\theta )}}{{{Y_{\mathrm{T}}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nt}}}}(\theta )}}{{S_{23}^{\mathrm{A}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nl}}}}(\theta )}}{{{S_{12}}}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 (7) 压缩( {\sigma _{{\mathrm{nn}}}}(\theta ) < 0 ):
{\xi _{{\mathrm{mc}}}}(\theta ) = {\left( {\frac{{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nt}}}}(\theta )}}{{S_{23}^{\mathrm{A}} - {\mu _{{\mathrm{nt}}}}{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nn}}}}(\theta )}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nl}}}}(\theta )}}{{{S_{12}} - {\mu _{{\mathrm{nl}}}}{\sigma _{{\mathrm{nl}}}}(\theta )}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 (8) 式中,Hashin和Puck是一种独立方程式准则,用于拉、压载荷下纤维和基体不同损伤模式的评估。同时也是一种交互式准则,对于基体损伤,考虑了横向应力和面内剪应力之间的相互关系,提高了损伤分析精度。 \xi 为失效因子,下标ft、fc、mt和mc指纤维拉伸/压缩和基体拉伸/压缩状态,当 \xi \geqslant 1 时,表示层合板产生损伤。下标1、2和3分别指纤维方向、面内横向和面外法向。X、Y为纤维方向和面内横向的强度,其下标T、C代表拉/压状态。S12、S13、S23表示面内、面外抗剪强度。其中,对于Puck准则[11],它认为在层合板中存在一个平行于纤维方向的潜在断裂面,而且在该面上存在沿着法向、纵向剪切和横向剪切方向的特定应力分量,即 {\sigma _{{\mathrm{nn}}}}(\theta ) 、 {\sigma _{{\mathrm{nt}}}}(\theta ) 和 {\sigma _{{\mathrm{nl}}}}(\theta ) ,如图1所示。由于这些应力分量的共同作用,在该断裂面上发生失效的概率最大。单元在三维应力加载情况下,识别和计算断裂面角度是使用该准则的重要前提[16]。鉴于断裂面为基体损伤因子 {\xi _{{\mathrm{mt}}/{\mathrm{c}}}}(\theta ) 最大值对应的角度,本文采用黄金搜索方法对该角度进行求解[15]。此外, S_{23}^{\mathrm{A}} 为断裂面的横向抗剪强度, {\mu _{{\mathrm{nt}}}}(\theta ) 和 {\mu _{{\mathrm{nl}}}}(\theta ) 为摩擦系数,计算如下式所示:
\left\{\begin{array}{l} \varepsilon_{11}^{\mathrm{T}}=\dfrac{X_{\mathrm{T}}}{E_{11}}, \varepsilon_{11}^{\mathrm{C}}=\dfrac{X_{\mathrm{C}}}{E_{11}}, \varepsilon_{22}^{\mathrm{T}}=\dfrac{Y_{\mathrm{T}}}{E_{22}}, \varepsilon_{22}^{\mathrm{C}}=\dfrac{Y_{\mathrm{C}}}{E_{22}} \\ \varepsilon_{33}^{\mathrm{C}}=\dfrac{Z_{\mathrm{C}}}{E_{33}}, \varepsilon_{12}^{\mathrm{G}}=\dfrac{S_{12}}{2 \cdot G_{12}}, \varepsilon_{13}^{\mathrm{G}}=\dfrac{S_{13}}{2 \cdot G_{13}}, \varepsilon_{23}^{\mathrm{G}}=\dfrac{S_{23}}{2 \cdot G_{23}} \end{array}\right. (9) \left\{\begin{aligned} & \sigma_{\mathrm{nn}}(\theta)=\sigma_{22} \cos ^2 \theta+\sigma_{33} \sin ^2 \theta+2 \sigma_{23} \cos \theta \sin \theta \\ & \sigma_{\mathrm{n} 1}(\theta)=\sigma_{12} \cos \theta+\sigma_{13} \sin \theta \\ & \sigma_{\mathrm{nt}}(\theta)=-\sigma_{22} \cos \theta \sin \theta+\sigma_{33} \cos \theta \sin \theta+ \\ &\qquad 2 \sigma_{23}\left(2 \cos ^2 \theta-1\right) \\ & \mu_{\mathrm{n} 1}(\theta)= \tan \left(2 \theta-90^{\circ}\right), \frac{\mu_{\mathrm{nt}}(\theta)}{S_{23}^{\mathrm{A}}}=\frac{\mu_{\mathrm{n} 1}(\theta)}{S_{12}} \\ & S_{23}^{\mathrm{A}}=\frac{Y_{\mathrm{C}}}{2}\left(\frac{1-\sin \phi}{\cos \phi}\right), \phi=2 \theta-90^{\circ} \end{aligned}\right. (10) 1.2 层内损伤演化方法
层合板损伤发生后,后续过程进入演化阶段,即损伤区域内应力下降,宏观力学性能表现为刚度退化。演化方法包括直接和渐进刚度退化两种方法。直接方法依赖经验,缺乏理论支持,且常低估力学性能,而渐进方法考虑了损伤逐渐累积过程,使演化行为得以很好描述。本文主要研究线性和指数型渐进演化方法,如图2所示。
![]() 图 2 渐进演化方法中应力、损伤变量与位移的关系Figure 2. Relationship between stress, damage variables and displacement in progressive evolution methods{\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i} and {\sigma }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i} are equivalent displacement and stress; {\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i}^{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} and {\sigma }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i}^{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} are initiation equivalent displacement and stress. {\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i}^{\mathrm{f}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} is failure equivalent displacement. {d}_{i} is damage state variable. {G}_{i} is fracture energy
图 2 渐进演化方法中应力、损伤变量与位移的关系Figure 2. Relationship between stress, damage variables and displacement in progressive evolution methods{\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i} and {\sigma }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i} are equivalent displacement and stress; {\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i}^{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} and {\sigma }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i}^{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} are initiation equivalent displacement and stress. {\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i}^{\mathrm{f}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} is failure equivalent displacement. {d}_{i} is damage state variable. {G}_{i} is fracture energy1.2.1 线性等效应变方法
基于断裂能的具有线性退化趋势的损伤演化有等效应变(E1)和等效位移(E2)两种方法。本节首先介绍E1演化方法。采用损伤状态变量di定义渐进损伤刚度折减方案,其表达式:
d_i=\frac{\varepsilon_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {final }}}{\varepsilon_{\text {eq }, i}^{\text {final }}-\varepsilon_{\text {eq }, i}^{\text {initial }}} \cdot\left(1-\frac{\varepsilon_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {initial }}}{\varepsilon_{\text {eq }, i}}\right) d_i \in[0,1] (11) 下标i为损伤模式; \varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{} 为等效应变,表示前一增量步结束时输出的单元节点应变; \varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 和 \varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{final}}} 为损伤起始和临界失效的等效应变。当di = 0时,表示单元处于损伤将要产生的临界状态,其与 \xi = 1 相对应;而di = 1表示单元完全失效。
网格单元完全失效所释放的临界断裂能 {G_i} (图2中紫色线所围的三角形面积)可表示为
{G_i} = \frac{1}{2} \cdot \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} \cdot \varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{final}}} \cdot {l^{\mathrm{c}}} (12) 所以 \varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{final}}} 表示:
\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{final}}} = \frac{{2 \cdot {G_i}}}{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} \cdot {l^{\mathrm{c}}}}} (13) 式中, \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 为损伤起始应力,计算中将其等效为材料的强度; {l^{\mathrm{c}}} 为单元特征长度,可正则化断裂能,减轻损伤演化过程中对网格大小的依赖,其值是单元体积的立方根。此外 \varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 表示:
\varepsilon _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} = \frac{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}}}}{{E_j^{}}} (14) E_j^{} 为对应方向的弹性模量。
为保证材料刚度的持续退化,损伤变量 {d_i} 要服从演化过程中的不可逆原则:
\begin{gathered} {d_i}\left( {t + \Delta t} \right) = \max \left\{ {0,\min \left[ {1,{d_i}\left( {t + \Delta t} \right)} \right]} \right\} \\ {d_i}\left( {t + \Delta t} \right) \geqslant {d_i}\left( t \right) \\ \end{gathered} (15) 1.2.2 线性等效位移方法
基于等效位移的损伤变量表达式为
d_i=\frac{\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {inal }}}{\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {inal }}-\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {initial }}} \cdot\left(1-\frac{\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {initial }}}{\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}}\right) (16) \delta _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 和 \delta _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{final}}} 为损伤起始和临界失效的等效位移:
\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {final }}=\frac{2 \cdot G_i}{\sigma_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {initial }}}, \delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}^{\text {initial }}=\frac{\delta_{\mathrm{eq}, i}}{\sqrt{\xi_i}} (17) \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 为起始等效应力:
\sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} = \frac{{\sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{}}}{{\sqrt {{\xi _i}} }} (18) 式中, \delta _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{} 和 \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{} 为等效位移和等效应力,其计算方法如表1所示。
1.2.3 指数型等效位移方法
本节指数型损伤演化方法(E3)是基于等效位移变化而言的。网格单元在外部载荷作用下,其节点等效位移达到损伤起始点 \delta _{{\mathrm{eq}},i}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 之后,则进入演化阶段。随着载荷持续作用,其位移将继续增加,对应的损伤演化将按照指数型方式进行,直至单元完全失效,如图2中绿色曲线所示。该方法损伤变量表达式为
{d_i} = 1 - \frac{1}{{{{\sqrt \xi }_i}}} \cdot \exp\left[ {\frac{{\left( {1 - \sqrt {{\xi _i}} } \right){{\left( {S_j^{}} \right)}^2}{l^{\mathrm{c}}}}}{{E_j^{} \cdot {G_i}}}} \right] (19) 式中,临界失效的等效位移的计算同E2方法。
表 1 不同损伤模式下的等效位移和等效应力Table 1. Equivalent displacement and equivalent stress for different damage modesModes Equivalent displacement Equivalent stress ft \delta _{{\mathrm{eq,ft}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \sqrt {{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{11}}} \right\rangle }^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{12}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{13}}} \right)}^2}} \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq,ft}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \dfrac{{\left\langle {{\sigma _{11}}} \right\rangle \left\langle {{\varepsilon _{11}}} \right\rangle + {\sigma _{12}}{\varepsilon _{12}} + {\sigma _{13}}{\varepsilon _{13}}}}{{\delta _{{\mathrm{eq,ft}}}^{}}} fc \delta _{{\mathrm{eq,fc}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \left\langle { - {\varepsilon _{11}}} \right\rangle \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq,fc}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \dfrac{{\left\langle { - {\sigma _{11}}} \right\rangle \left\langle { - {\varepsilon _{11}}} \right\rangle }}{{\delta _{{\mathrm{eq,fc}}}^{}}} mt \delta _{{\mathrm{eq,mt}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \sqrt {{{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{22}}} \right\rangle }^2} + {{\left\langle {{\varepsilon _{33}}} \right\rangle }^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{12}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{23}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{13}}} \right)}^2}} \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq,mt}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \dfrac{{\left\langle {{\sigma _{22}}} \right\rangle \left\langle {{\varepsilon _{22}}} \right\rangle + \left\langle {{\sigma _{33}}} \right\rangle \left\langle {{\varepsilon _{33}}} \right\rangle + {\sigma _{12}}{\varepsilon _{12}} + {\sigma _{13}}{\varepsilon _{13}} + {\sigma _{23}}{\varepsilon _{23}}}}{{\delta _{{\mathrm{eq,mt}}}^{}}} mc \delta _{{\mathrm{eq,mc}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \sqrt {{{\left\langle { - {\varepsilon _{22}}} \right\rangle }^2} + {{\left\langle { - {\varepsilon _{33}}} \right\rangle }^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{12}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{23}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{\varepsilon _{13}}} \right)}^2}} \sigma _{{\mathrm{eq,mc}}}^{} = {l^{\mathrm{c}}} \cdot \dfrac{{\left\langle { - {\sigma _{22}}} \right\rangle \left\langle { - {\varepsilon _{22}}} \right\rangle + \left\langle { - {\sigma _{33}}} \right\rangle \left\langle { - {\varepsilon _{33}}} \right\rangle + {\sigma _{12}}{\varepsilon _{12}} + {\sigma _{13}}{\varepsilon _{13}} + {\sigma _{23}}{\varepsilon _{23}}}}{{\delta _{{\mathrm{eq,mc}}}^{}}} Notes: < > is Macaulay bracket. {\sigma }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i} and {\delta }_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{q},i} is equivalent stress and displacement, where i= ft, fc, mt and mc damage model. {l}^{\mathrm{c}} is the characteristic length of element. 1.3 层内损伤本构关系
层合板在冲击载荷下的持续作用下,内部损伤不断累积和扩展导致刚度逐渐退化,故而需及时更新材料本构关系。采用方法是将损伤状态变量引入到原始本构方程中,按弹性各向异性进行相应比例的刚度衰减。材料原始本构方程:
{\sigma _{ij}} = {C_{ijkl}} \cdot {\varepsilon _{kl}} (20) 式中, {\sigma _{ij}} 、 {\varepsilon _{kl}} 和 {C_{ijkl}} (i, j, k, l = 1, 2, 3)分别表示工程应力、工程应变和刚度矩阵分量。指数1、2、3分别为纤维方向、面内横向和面外方向。由于层合板中的每一层均可看作是横观各向同性材料,这意味着E22 = E33,ν12 = ν13,G12 = G13。因此独立的工程常数Eij、νij、Gij可以减少为5个。引入损伤变量退化后的刚度矩阵Cd可表示:
{C_d} = \frac{1}{\Delta } \cdot \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {c_{11}^d}&{c_{12}^d}&{c_{13}^d}&{}&{}&{} \\ {}&{c_{22}^d}&{c_{23}^d}&{}&{}&{} \\ {}&{}&{c_{33}^d}&{}&{}&{} \\ {}&{}&{}&{c_{44}^d}&{}&{} \\ {}&{}&{}&{}&{c_{55}^d}&{} \\ {}&{}&{}&{}&{}&{c_{66}^d} \end{array}} \right] (21) \left\{ \begin{gathered} c_{11}^{\rm {d}} = {d_{\rm {f}}}{E_{11}}\left( {1 - {d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{23}}{\upsilon _{32}}} \right) \\ c_{12}^{\rm {d}} = {d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{E_{11}}\left( {{\upsilon _{21}} + {d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{23}}{\upsilon _{31}}} \right) \\ c_{13}^{\rm {d}} = {d_{\rm {f}}}{E_{11}}\left( {{\upsilon _{31}} + {d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{21}}{\upsilon _{32}}} \right) \\ c_{23}^{\rm {d}} = {d_{\rm {m}}}{E_{22}}\left( {{\upsilon _{32}} + {d_{\rm {f}}}{\upsilon _{12}}{\upsilon _{31}}} \right) \\ c_{22}^{\rm {d}} = {d_{\rm {m}}}{E_{22}}\left( {1 - {d_{\rm {f}}}{\upsilon _{13}}{\upsilon _{31}}} \right) \\ c_{33}^{\rm {d}} = \Delta \cdot {d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{G_{23}} \\ c_{44}^{\rm {d}} = {E_{33}}\left( {1 - {d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{12}}{\upsilon _{21}}} \right) \\ c_{55}^{\rm {d}} = \Delta \cdot {d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{G_{23}} \\ c_{66}^{\rm {d}} = \Delta \cdot {d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{G_{13}} \\ {d_{\rm {f}}} = \left( {1 - {d_{ft}}} \right) \cdot \left( {1 - {d_{fc}}} \right) \\ {d_{\rm {m}}} = \left( {1 - {S_{mt}}{d_{mt}}} \right) \cdot \left( {1 - {S_{mc}}{d_{mc}}} \right) \\ \Delta = 1 - {d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{12}}{\upsilon _{21}} - {d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{23}}{\upsilon _{32}} - \\ \qquad {d_{\rm {f}}}{\upsilon _{13}}{\upsilon _{31}} - 2{d_{\rm {f}}}{d_{\rm {m}}}{\upsilon _{21}}{\upsilon _{32}}{\upsilon _{13}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. (22) 式中,Smt和Smc是用来控制基体拉、压损伤引起的剪切刚度损失的相关参数,可避免层合板结构在演化过程中过度软化[26]。本文取值Smt = Smc = 0.965[13]。此外,全局基体损伤变量dm能够减小由于忽略基体塑性变形而导致的偏差。
1.4 层间损伤分析方法
层合板结构层间分层是指相邻层间的界面剥离。本文采用内聚力单元建模方法,在模型中插入具有一定厚度的界面单元。因层间界面总是受到混合载荷模式的作用,其本构关系如图3所示,故而采用二次应力失效准则预测分层损伤起始。采用基于能量的Bengeggagh-Kenane线性演化方法描述分层扩展规律。式中, \delta _{\mathrm{m}}^{{\mathrm{initial}}} 和 \delta _{\mathrm{m}}^{{\mathrm{final}}} 是指混合模式响应下损伤起始和完全失效位移。
![]() 图 3 层间单元混合型双线性牵引-分离本构关系Figure 3. Constitutive relation of the mixed-model bilinear traction-separation for cohesive element{\delta }_{\mathrm{m}}^{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} and {\delta }_{\mathrm{m}}^{\mathrm{f}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} are initiation and failure equivalent displacement. Model Ⅰ, Ⅱ/Ⅲ are the failure model in out-of-plane direction and in-plane transverse direction. N, S and T are the strength in three directions
图 3 层间单元混合型双线性牵引-分离本构关系Figure 3. Constitutive relation of the mixed-model bilinear traction-separation for cohesive element{\delta }_{\mathrm{m}}^{\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} and {\delta }_{\mathrm{m}}^{\mathrm{f}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{l}} are initiation and failure equivalent displacement. Model Ⅰ, Ⅱ/Ⅲ are the failure model in out-of-plane direction and in-plane transverse direction. N, S and T are the strength in three directions2. 有限元数值模拟
复合材料层合板低速冲击损伤的数值模拟包括建立有限元模型和设计模拟流程。
2.1 有限元模型的建立
几何参数、边界条件和接触定义。根据ASTM D7136M-15标准[27]给出的指南,采用网格偏置方法,对材料体系为T700 GC/M21、堆叠顺序为[02, 452, 902, −452]S及几何尺寸为150 × 100 × 4.015 mm3 的层合板进行建模。层内厚度为0.25 mm,胶层厚度为0.001 mm。冲头为刚性材料,直径为16 mm,集总参考质量为2 kg。冲头外表面与层合板上表面设置0 mm距离接触。冲头初速度预设为5 m/s。为模拟实验中的夹紧条件,建立一个全方位约束的刚性支撑板,内部区域为125 × 75 mm2。将层合板放置在支撑板上,并且在四周约束了x、y和z三方向的自由度,如图4所示。面和面之间的接触设置关乎力学响应的准确性和冲头对层合板的穿透性。本文采用面-面接触算法描述冲头外表面和层合板上表面之间的接触行为。其余的面和面之间均采用通用接触算法来模拟。接触属性在切向采用罚法(摩擦系数为0.3),在法向采用硬接触法。
网格策略、单元类型和材料特性。为平衡计算精度和效率之间的矛盾,本文将层合板模型离散分为细网格的中心区域和粗网格的外围区域。其中,中心区域网格单元大小为0.5 × 0.5 mm2。对于单元类型,层内采用降积分八节点实体单元(C3D8R)进行网格划分。本文采用松弛刚度法避免单元发生伪变形,即沙漏现象。层间单元采用八节点三维Cohesive element(COH3D8)的网格属性进行划分。模型中的层内和层间单元均被设置为不允许删除。冲头和支撑板的网格类型为四节点三维双线性刚体四边形(R3D4)。单向板和层间胶层材料参数,汇总至表2中[13,28]。
表 2 T700 GC/M21单向板和界面材料参数Table 2. Material parameters of unidirectional laminate and interlayer for T700 GC/M21 compositeLaminate properties Density/(kg·m−3) 1600 Young’s modulus/GPa E11 = 130; E22 = E33 = 7.7; G12 = G13 = 4.8; G23 = 3.8 Poisson’s ratio ν12 = ν13 = 0.33; ν23 = 0.35 Strength/MPa XT = 2080 ; XC =1250 ; YT = 60; YC =140; S12 = S13 = S23 = 110Fracture energy/(N·mm−1) Gft = 133; Gfc = 40; Gmt = 0.6 N; Gmc = 2.1 Interlayer properties Elastic modulus/GPa E = 5 Strength/MPa N = S = T = 30 Fracture energy/(N·mm−1) GIC = 0.6; GIIC = 2.1 Power exponent η 1.45 2.2 数值模拟流程的设计
将1.1至1.3节的渐进损伤理论公式编码在VUMAT子程序中,然后利用ABAQUS/Explicit平台进行调用和计算,流程设计如图5所示。在计算期间,增量步的控制和迭代是在ABAQUS/Explicit动态求解器中进行。而对于在每个增量步的具体求解,ABAQUS/Explicit则是将当前应变增量传递给子程序并在其中进行。以应力准则为例,通过健康材料本构关系经计算获得单元积分点处的应力值,并分析该值是否满足损伤起始准则。一旦满足,损伤分析则进入演化阶段,紧接着求解损伤变量和更新刚度矩阵。然后基于更新后的刚度矩阵,进一步计算获得损伤单元的应力。最后,将更新后的状态变量返还给ABAQUS/Explicit以推动下一个增量步的进行,直到冲击过程全部结束。对于层间单元损伤,基于2.2节损伤模型理论,在ABAQUS/Explicit中采用相应的内置算法进行模拟求解。本文以冲击力响应降为零作为计算终止的判定条件,经过多次预调,分析步时长为3.7 ms,每一步的物理时长为软件默认设置。
3. 结果和讨论
3.1 低速冲击损伤数值模拟验证
为了验证数值模型的预测能力,本节选用了Hashin-Strain损伤起始准则结合E1演化方法(Hashin-Strain-E1)为代表的数值结果,与Hongkarnjanakul等[29]的测试数据进行比较。图6(a)、6(b)为冲击过程动态力学响应,反映了层合板结构的抗冲击性能,图6(a)为冲击力-时程曲线。从冲头与层合板接触开始,冲击力在短时间内线性、迅速上升。直到当内部出现第一次损伤时,结构刚度发生衰减,冲击力曲线表现出轻微抖动。紧接着在0.75 ms时曲线出现强烈的抖动现象,是因为内部产生较大的损伤导致刚度衰减严重。在冲击力峰值附近,曲线抖动情况明显,可能是由于钢制冲头发生的激振频率和层合板弯曲的振动频率相近而发生共振现象促成的。此外,由于局部材料刚度退化导致历史输出频率与稳定时间增量之间不匹配也有可能是引起抖动的原因。在冲击力峰值之后,曲线缓慢下降但仍然伴随有较为明显抖动。当冲头和层合板分离后,冲击力变为零。图6(b)为冲击力-位移曲线。曲线与和实验吻合较好,尤其在回弹阶段。曲线封闭区间面积表示冲击过程的吸收能量,而回弹曲线与时间轴所围面积表示该过程恢复能量。在冲击过程中,冲头总动能传递给层合板。层合板中少部分能量以弹性势能形式返传递给冲头,其余部分被层合板吸收用于损伤形成、塑性变形以及摩擦耗散的过程中。图6(c)为验证数值模拟正确性的指标参数。对于峰值冲击力指标,预测载荷值为8.84 kN,相比实验结果要多0.19 kN。在最大挠度方面,预测值要比实验值少0.14 mm。此外,冲击时间比实验少0.1 ms,吸收能量多2.97 J。经上述分析,数值预测结果与实验吻合较好,验证了本文有限元模型的建立和模拟流程的设计均是正确的。
冲击载荷作用过程中动态力学响应曲线发生抖动,其本质是层合板内部有损伤产生致使其局部刚度衰减,从而外在反映出冲击力的突变现象。基于ABAQUS结果后处理平台,提出一种通过损伤变量实现损伤面积定量、动态表征的方法。
\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} \begin{gathered} {S_i}(t) = \sum\limits_{n = 1}^{n = N} {{{\left[ {{d_i}(t) \cdot \Delta s} \right]}_n}} \\ {d_i}(t) \geqslant {d_0} \\ \end{gathered} &{} \end{array} (23) 式中, {S_i}(t) 为任意t时刻对应损伤类型i的总损伤面积; {d_i}(t) 为单元网格质心处的损伤状态变量值,基体拉伸和压缩两个损伤变量需通过在VUMAT子程序中定义,分层损伤变量用内置算法“标量刚度退化”表示; \Delta s 为网格单元的面积; {d_0} 为损伤阈值,表示单元将发生严重损伤,极大降低了层合板的刚度甚至失去承载能力;n为单元数量。冲击载荷下层合板内部的分层、基体损伤面积动态表征结果如图7所示。通过分析这些图像,可以跟踪整个冲击过程中的损伤演变情况。
在图6(a)中所示的力学响应曲线中有三次明显抖动现象,这与层合板内部某种或者某几种模式的冲击损伤有关联,本节结合损伤面积动态表征结果对其间的关联性展开分析。对于第“1”次抖动,在大约0.2 ms的时间内分层、基体拉伸损伤和压缩损伤面积分别激增10 cm2 (主要是第6、10和12界面)、3 cm2 (主要是第11、13和15层)和1.5 cm2 (主要是第1、3和5层)。可见,中性层及以下部分界面的分层是导致本次抖动的一种损伤模式。此外,靠近冲击正面的第一层和中性层以下的层发生横向基体开裂是另外一种损伤模式。第一层损伤是由于局部高剪应力而引发,而远侧层则是因为高拉应力而引起的。故而,这次抖动是层合板内部的分层和基体损伤共同作用而导致的,但是分层损伤占据主导地位。层合板产生损伤后其内部结构重新叠加继续抵抗冲击载荷作用,所以冲击力曲线会接连抖动向上,直到在峰值力附近出现第“2”次抖动。这次抖动除了上述解释的共振等原因之外,分层和基体损伤的产生也贡献了作用。然而相对基体损伤而言,分层损伤仍然起主要作用。第“3”次明显抖动是出现在层合板达到最大挠度后的回弹阶段,这说明在此过程中结构内部仍然有新损伤在产生。值得一提的是,本次抖动对应的内在损伤模式不同于前两次,结合图7(b)可发现是由于回弹时局部区域的高压应力造成的。
需要注意的是,本文预测的损伤发生顺序和每种损伤模式在力学响应中起到的作用仅对当前25 J能量有效。改变冲击能量可能会影响各种损伤模式对力学响应的贡献。随着冲击能量的增加,靠近受冲击正面的近侧层由于局部高剪应力以及远侧层由于弯曲拉应力而发生纤维断裂。
3.2 不同起始准则、演化方法损伤预测能力评价
损伤起始准则和损伤演化方法是层合板冲击渐进损伤行为分析的必要组成部分,其严重影响层合板结构外部力学响应和内部损伤状态。本节对Hashin-Stress、Hashin-Strain及Puck起始准则分别结合E1、E2及E3演化方法的数值预测能力进行探讨。力学响应如图8所示,其评价结果被列至表3中。
表 3 预测模型能力指标评价Table 3. Index evaluation for the capability of prediction modelPeak force/kN Max. displacement/mm Impact time/ms Absorbed energy/J Experiment 8.65 5.11 3.60 13.00 Hashin-Stress E1 10.50(+21.4%) 4.72(−7.6%) 3.24(−10% 8.66(−33.4%) Hashin-Strain 8.84(+2.2%) 4.97(−2.7%) 3.70(+2.8%>) 10.03(−22.8%) Puck 11.44(+32.3%) 4.64(−9.2%) 3.11(−13.6%) 8.08(−37.8%) Hashin-Stress E2 8.74(+1.0%) 4.91(−3.9%) 3.70(2.8%) 11.00(−15.4%) Hashin-Strain — — — — Puck 8.62(−0.3%) 4.93(−3.5%) 3.50(−2.8%) 9.44(−27.4%) Hashin-Stress E3 9.40(+8.7%) 4.96(−2.9%) 3.70(+2.8%) 10.60(−18.5%) Hashin-Strain — — — — Puck 7.85(−9.2%) 5.09(−0.4%) 3.70(+2.8%) 9.44(−27.4%) 对于E1演化方法(图8(a)、8(b)),Hashin-Strain准则预测结果和实验吻合最好,其余准则结果与实验误差较大。对于E2和E3演化方法(图8(c)~8(f)))呈现出与E1方法不同的现象,即Puck和Hashin-Stress准则表现出较强的预测能力。而对于Hashin-Strain准则,由于内部刚度严重衰减致使层合板“过软”而出现穿透性损伤(图8(c)、8(e))。在冲击损伤数值模拟过程中,通常会因失效单元变形影响结果收敛性而出现了计算误差,甚至还会遇到过度变形导致计算终止的情况。为防止失效单元的过度变形,应该通过控制失效后最大刚度退化来保持残余刚度。在不同的研究工作中,渐进损伤单元的最大刚度退化值被设定为0.9[30]、0.99[31]、0.999[32],以免遭受过度扭曲。而在本文工作中为了公平比较各个准则的预测能力,将它们设定相同的演化条件,不考虑最大刚度退化情况,故而出现上述现象。此外,E2和E3方法预测的结果有相同的变化趋势,其原因是E3方法是基于等效位移进行演化的,且最终失效位移与E2方法相等。
综上所述,Hashin-Stress准则结合E2方法(Hashin-Stress-E2)、Hashin-Strain准则结合E1方法(Hashin-Strain-E1)和Puck准则结合E3方法(Puck-E3)会表现出更优越的预测能力。
为定量研究不同损伤起始准则和演化方法对损伤累积过程的影响,图9给出了损伤面积动态表征结果。经观察发现不同演化方法预测的分层损伤面积虽有不同,但最终集中分布在22~27 cm2 之间;基体拉伸损伤具有相似的现象,损伤面积集中在3.8~5.2 cm2之间(图9(a))。这说明演化方法对分层和基体拉伸损伤的影响较小。然而,基体压缩损伤对演化方法较为敏感(图9(b))。无论对于Hashin-Stress还是Puck准则,E2和E3方法有相同的变化趋势。然而E2方法预测的损伤扩展速度和最终损伤面积均要大于E3方法,因为E2相比E3方法在后期的演化过程中(0.8~1.5 ms)刚度降低速度更快,产生更多的损伤。下面从起始准则方面展开分析。对于Hashin-Stress准则,因为E1方法中忽略了剪切应变分量,导致冲击点处基体的压缩损伤产生会慢于E2和E3方法。而在整个演化阶段(0.5~1.5 ms),损伤变量从0~1的增加速度要明显大于E2和E3方法,导致最终产生更大的损伤面积。对于Puck准则,却有完全不同的现象,即E1方法相对E2和E3方法表现出最慢的演化速度并得到最小的损伤面积,可能是Puck准则存在横向压缩载荷抑制断裂面上非线性剪切的原因导致的。需要注意的是,E2和E3方法在早期演化阶段(0.5~0.8 ms)演化速度近似相等,因为Puck准则中没有贯穿厚度方向的应力作用,导致两个演化方法差异性不明显。
为研究冲击损伤扩展行为,图10给出了不同起始准则结合E1演化方法的损伤形貌。图10(a)分层形貌。对于中性层上面的界面,分层传播行为相似。这可从层合板的变形破坏机制来解释,因为分层从层合板的底部开始向上扩展,冲击侧的压应力在一定程度上会抑制分层的发展,导致中性层上面损伤区域差异不大。然而,对于中性层下面的界面,分层形貌有明显差异,尤其对于Puck准则的C10界面。原因可能与基体损伤有关联,渐进式分层和基体损伤之间存在复杂的相互作用方式。基体损伤很有可能导致界面处出现较大的横向剪切应力,从而产生较大分层。图10(b)为基体拉伸损伤形貌。各起始准则预测的损伤形貌大致相同,尤其对于受拉程度较小的中性层上面铺层。在中性层下面铺层的损伤面积大于上面铺层,且距离底层越近,损伤面积越大。因为弯曲拉应力导致在冲击背面先产生拉伸损伤并向上逐层传播。Hashin-Stress和Hashin-Strain准则预测的损伤形貌,在其前两层中间出现较小的空心现象。其原因可能是这三个准则使用横向和面外法向应力或应变之和( {\sigma _{22}} + {\sigma _{33}} 或 {\varepsilon _{22}} + {\varepsilon _{33}} )来判定基体损伤的起始。图10(c)为基体压缩损伤形貌。基体压缩损伤主要出现在层合板中性层上面铺层,其原因是压缩损伤由冲击正面产生并逐渐扩展到下层。使用Hashin-Stress和Hashin-Strain两个准则预测的每层损伤形貌相似。而Puck准则预测的损伤形貌偏差较大,预测的损伤程度较轻且损伤仅在层合板前三层出现。因为Puck准则中不存在贯穿厚度方向的面外法向应力( {\sigma _{33}} ),故而导致其预测的损伤主要集中在冲击点附近而不能向下层方向扩展。
上述模型验证是针对正冲击工况而言,在其他工况如重复和倾斜冲击条件下,其预测结果可能会有所不同。前者不同的冲击能量会导致当前冲击下纤维和基体损伤程度不同,进而影响后续冲击,后者可看作面内、外两方向上分冲击的共同作用。因此模型预测结果会和正冲击表现出相同的趋势。因此,本文数值模型经适当改进后能够用于重复冲击和倾斜冲击等工况下的损伤渐进行为研究,有助于深入理解低速冲击下复合材料层合板的损伤演变机制,为工程中开展冲击损伤及性能评估提供参考和借鉴。
4. 结 论
(1)通过提取损伤状态变量对损伤面积进行定量和动态表征。这为解释冲击损伤的渐进行为和形成机制提供一种新的视角。
(2)在本文研究条件下,Hashin-Strain准则结合线性等效应变方法(Hashin-Strain-E1)和Puck准则结合指数型等效位移方法(Puck-E3)最优。然而,当Hashin-Strain准则结合线性或指数型等效位移方法时(Hashin-Strain-E2/E3),会由于严重刚度退化而出现穿透性损伤。
(3)起始准则对分层和基体拉伸损伤影响较小,但损伤之间的耦合作用会导致局部区域出现不同现象。起始准则对基体压缩损伤形貌影响较大,尤其是Puck准则。因为该准则不考虑法向应力,限制了损伤的深层扩展。演化方法对基体压缩损伤影响显著,表现为损伤面积分布更为分散,而对分层和基体拉伸损伤影响较小。
(4)本文研究结果有助于减少与起始准则和演化方法间不同组合设计相关的试验工作量,为在工程应用中获得更好的冲击损伤预测性能提供参考和借鉴。
-
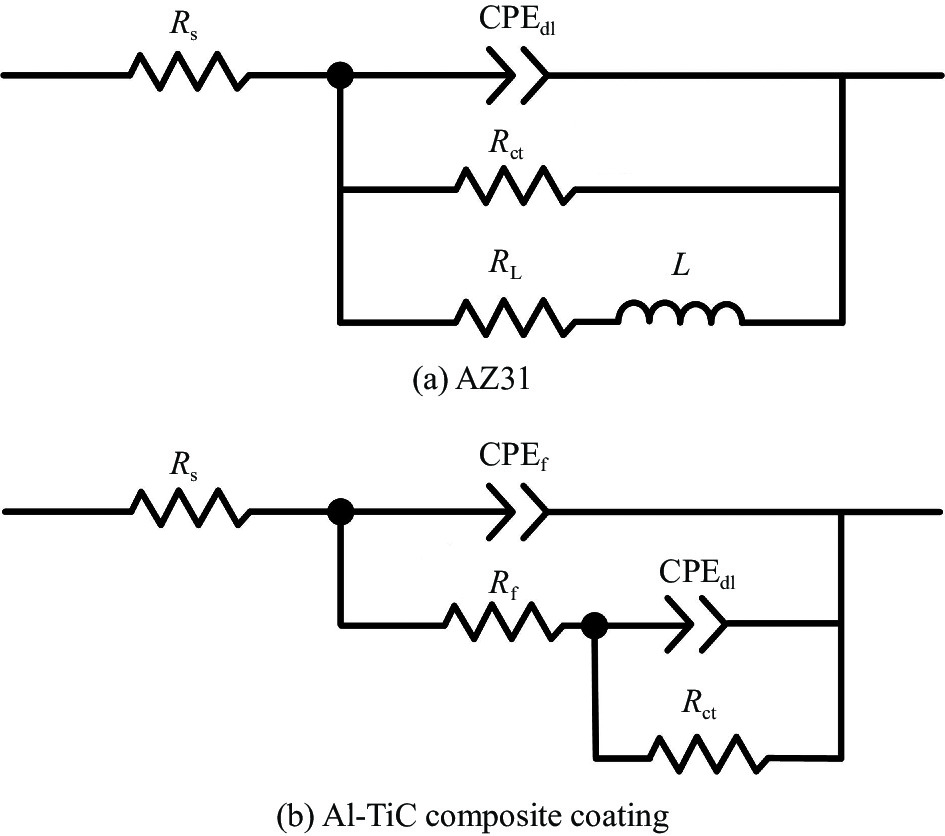
图 10 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的EIS等效电路图
Rs—Solution resistance; CPEf—Al-TiC composite coating capacitance; Rf—Al-TiC composite coating resistance; CPEdl—Electric double layer capacitor; Rct—Charge transfer resistance; L—Inductance; RL—Inductor resistance
Figure 10. EIS equivalent circuit diagram of AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatings
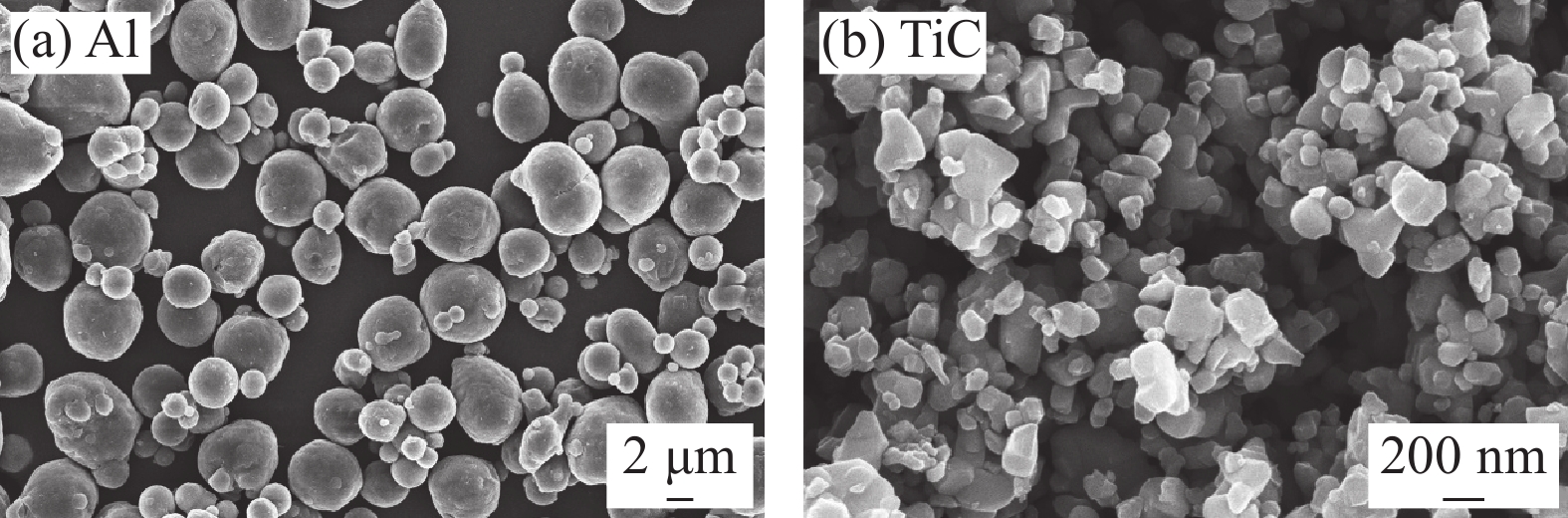
表 1 Al-TiC复合涂层具体粉末配比
Table 1 Specific ratios of the Al-TiC composite coatings
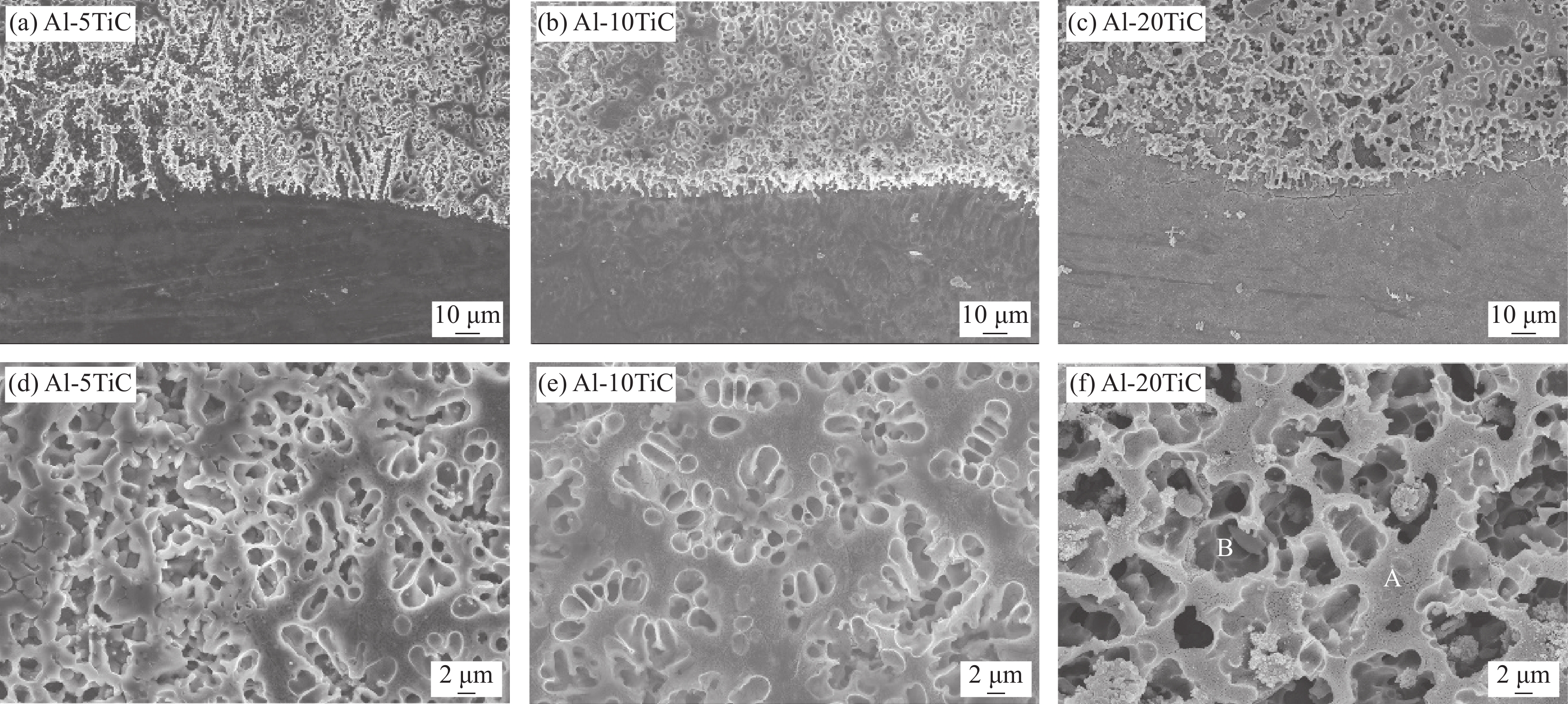
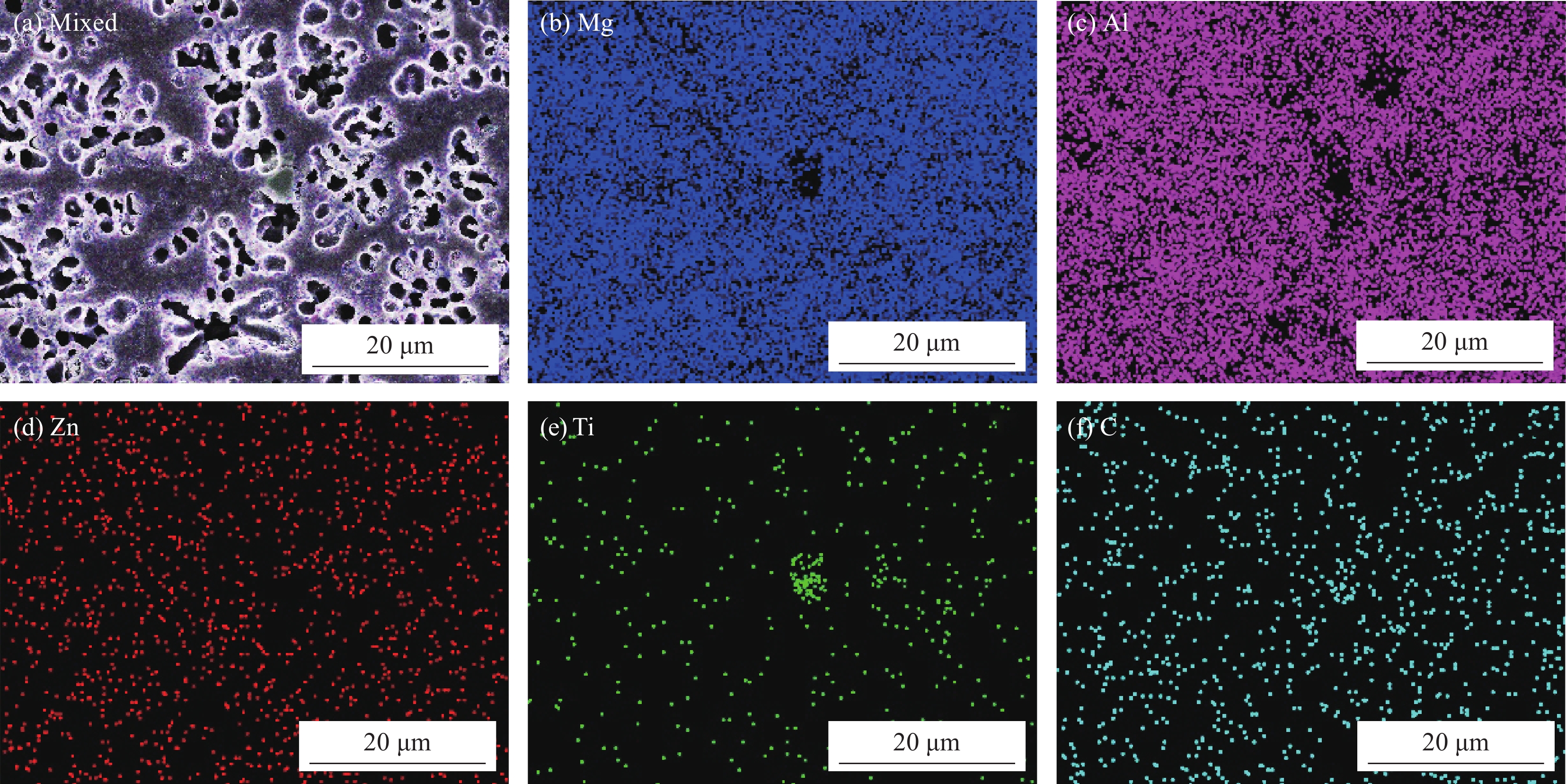
Sample Powders and powder ratio Al/wt% TiC/wt% Al-5TiC 95 5 Al-10TiC 90 10 Al-20TiC 80 20 表 2 A点和B点的EDS测试结果
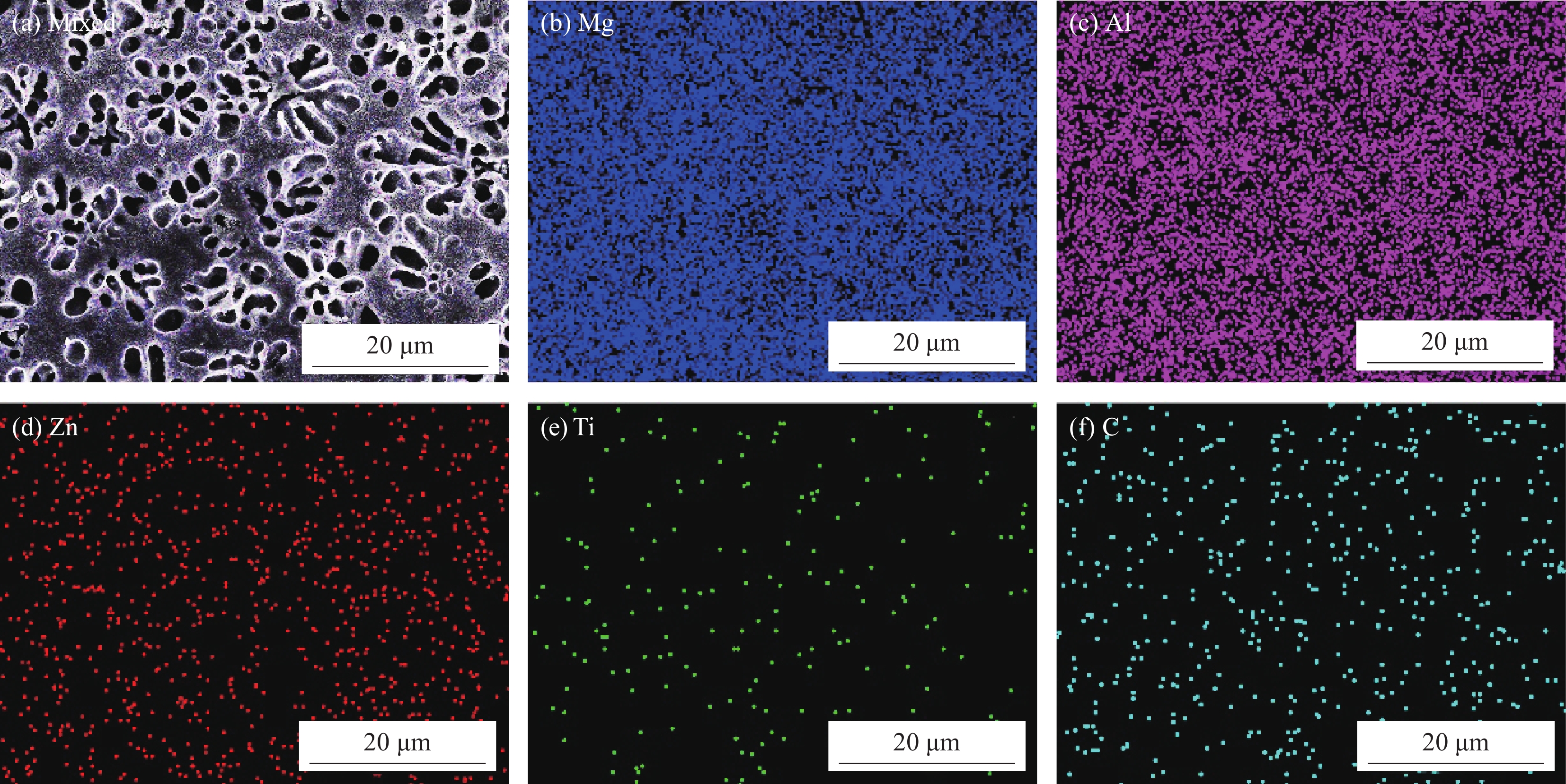
Table 2 EDS analysis of point A and point B
Point Mg/at% Al/at% Zn/at% TiC/at% C/at% A 38.32 32.43 0.80 2.48 25.96 B 47.97 33.04 0.85 0.09 18.05 表 3 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流
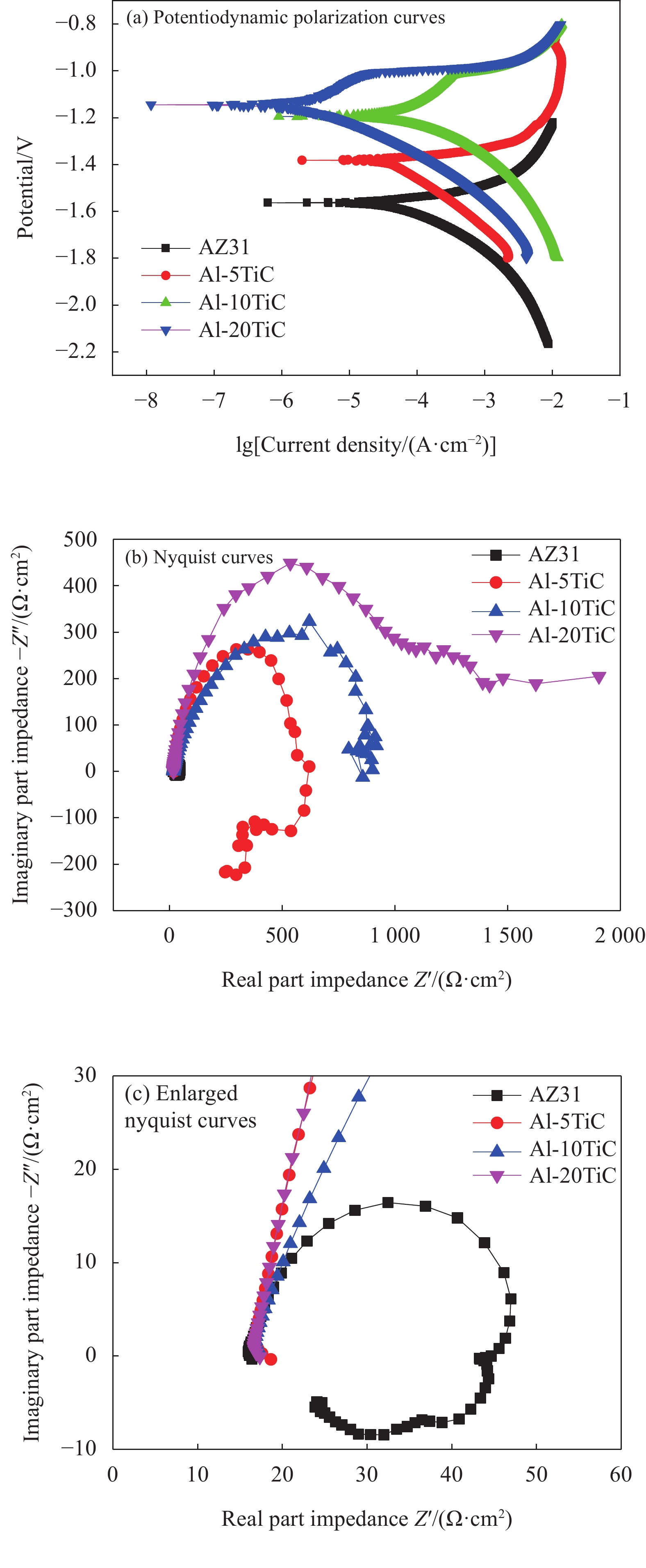
Table 3 Self-corrosion potential and self-corrosion current of the AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatings
Sample Self-corrosion potential/V Self-corrosion current/A AZ31 −1.563 1.55×10−4 Al-5TiC −1.381 2.30×10−4 Al-10TiC −1.195 7.55×10−5 Al-20TiC −1.144 2.63×10−6 表 4 等效电路模型拟合的电化学参数
Table 4 Electrochemical parameters fitted by the equivalent circuit model
Parameter Rs/(Ω·cm2) CPEf/(Ω·cm2·Sn) nf Rf/(Ω·cm2) CPEdl/(Ω·cm2·Sn) ndl Rct/(Ω·cm2) L/(H·cm2) RL/(Ω·cm2) AZ31 16.50 – – – 7.69×10−6 0.91 27.6 13.46 10.29 Al-5TiC 16.99 7.38×10−6 0.95 118.5 4.36×10−6 0.89 452.2 – – Al-10TiC 15.96 3.04×10−5 0.76 506.5 3.22×10−5 0.85 416.3 – – Al-20TiC 16.47 1.83×10−5 0.87 1045.0 1.01×10−4 0.68 774.8 – – Notes: nf—CPEf index; ndl—CPEdl index. -
[1] JOOST W J, KRAJEWSKI P E. Towards magnesium alloys for high-volume automotive applications[J]. Scripta Materialia,2017,128:107-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.07.035
[2] CHEN J X, TAN L L, YU X M, et al. Mechanical properties of magnesium alloys for medical application: A review[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2018,87:68-79. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.07.022
[3] 赵聪铭, 邓坤坤, 聂凯波, 等. 挤压包覆轧制对SiCp增强镁合金(AZ91)复合板显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(1):164-172. ZHAO Congming, DENG Kunkun, NIE Kaibo, et al. Effect of extrusion-cladding rolling on microstructure and mecha-nical property of SiCp reinforced magnesium alloy (AZ91) clad plate[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(1):164-172(in Chinese).
[4] FRIEDRICH H, SCHUMANN S. Research for a new age of magnesium in the automotive industry[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 117: 276-281.
[5] PARDO A, MERINO M C, COY A E, et al. Corrosion behaviour of magnesium/aluminium alloys in 3.5wt%NaCl[J]. Corrosion Science,2008,50(3):823-834. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.11.005
[6] PAITAL S M, BHATTACHARYA A, MONCAYO M, et al. Improved corrosion and wear resistance of Mg alloys via laser surface modification of Al on AZ31 B[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2012,206(8-9):2308-2315. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.10.009
[7] BALAKRISHNAN M, DINAHARAN I, PALANIVEL R, et al. Synthesize of AZ31/TiC magnesium matrix composites using friction stir processing[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys,2015,3:76-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.jma.2014.12.007
[8] NIE X M, SHEN H Y, FU J Z, et al. Effective control of microstructure evolution in AZ91 D magnesium alloy by SiC nanoparticles in laser powder-bed fusion[J]. Materials and Design,2021,206:109787. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109787
[9] LIU F J, LI Y P, SUN Z Y, et al. Corrosion resistance and tribological behavior of particles reinforced AZ31 magnesium matrix composites developed by friction stir processing[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2021,11:1019-1030. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.071
[10] YANG L Q, LI Z Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Al-TiC in situ compo-site coating fabricated by low power pulsed laser cladding on AZ91 D magnesium alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,435:1187-1198. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.240
[11] LIU H X, XU Q, WANG C Q, et al. Corrosion and wear behavior of Ni60 CuMoW coatings fabricated by combination of laser cladding and mechanical vibration processing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2015,621:357-363. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.030
[12] WENG F, YU H J, CHEN C Z, et al. Microstructures and wear properties of laser cladding Co-based composite coatings on Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Materials and Design,2015,80:174-181. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.05.005
[13] 王鑫, 潘希德, 牛强, 等. AZ33 M镁合金激光熔覆制备了Al-Si涂层的组织和性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2021, 46(5):202-206. WANG Xin, PAN Xide, NIU Qiang, et al. Microstructure and properties of laser clad Al-Si coating on AZ33 M magnesium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals,2021,46(5):202-206(in Chinese).
[14] 靳坤, 张英乔, 张涛, 等. AZ91 D镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-Ti-Ni/C涂层的电化学腐蚀行为[J]. 电焊机, 2019, 49(10): 83-87. JIN Kun, ZHANG Yingqiao, ZHANG Tao, et al. Electroche-mical corrosion behavior of laser cladding Al-Ti-Ni/C coating on AZ94 D magnesium alloy[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2019, 49(10): 83-87(in Chinese).
[15] 刘德坤, 张可敏, 刘应瑞. AZ31镁合金表面Al-Ti-TiB2激光熔覆层的组织和性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2018, 42(10):24-28, 33. DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201810005 LIU Dekun, ZHANG Kemin, LIU Yingrui. Microstructure and properties of Al-Ti-TiB2 laser-cladding layer on surface of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy[J]. Materials for Mechani-cal Engineering,2018,42(10):24-28, 33(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201810005
[16] LIN P Y, ZHANG Z H, REN L Q. The mechanical properties and microstructures of AZ91 D magnesium alloy processed by selective laser cladding with Al powder[J]. Optics and Laser Technology,2014,60:61-68. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2013.12.024
[17] AYDIN F, SUN Y, TURAN M E. Influence of TiC content on mechanical, wear and corrosion properties of hot-pressed AZ91/TiC composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2020,54:141-152. DOI: 10.1177/0021998319860570
[18] ZHENG B J, CHEN X M, LIAN J S. Microstructure and wear property of laser cladding Al+SiC powders on AZ91 D magnesium alloy[J]. Optics and Laser Technology,2010,48:526-532. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2010.01.001
[19] MASSALSKI T B, OKAMOTO H, SUBRAMAMIAN P R, et al. Binary alloy phase diagrams[M]. 2nd Edition. Metals Park: ASM International, 1990: 170.
[20] LIU F J, JI Y, MENG Q S, et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of laser cladding and friction stir processing hybrid modification Al-Si coatings on AZ31 B[J]. Vacuum,2016,133:31-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2016.08.010
[21] LIU F J, JI Y, SUN Z Y, et al. Enhancing corrosion resistance of Al-Cu/AZ31 composites synthesized by a laser cladding and FSP hybrid method[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 34: 1458-1466.
[22] 朱红梅, 龚文娟, 易志威. AZ91镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-Cu 合金涂层的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(7):1498-1504. ZHU Hongmei, GONG Wenjuan, YI Zhiwei. Microstructure and property of laser cladding Al-Cu alloy coating on surface of AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2016,26(7):1498-1504(in Chinese).
[23] 孙琪, 李志勇, 张英乔, 等. AZ91 D 镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-TiC涂层组织和性能的研究[J]. 表面技术, 2017, 46(1):40-44. SUN Qi, LI Zhiyong, ZHANG Yingqiao, et al. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding Al-TiC coating on AZ91 D magnesium alloy[J]. Surface Technology,2017,46(1):40-44(in Chinese).
[24] SONG G L, ATRENS A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,1999,1(1):11-33. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1527-2648(199909)1:1<11::AID-ADEM11>3.0.CO;2-N
[25] 刘奋军, 张媛媛, 刘建勃, 等. 镁合金表面高转速搅拌摩擦加工区的微观组织和耐腐蚀性能[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(3):330-337. LIU Fenjun, ZHANG Yuanyuan, LIU Jianbo, et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of high rotating speed friction stir processed zone on magnesium alloy[J]. Surface Technology,2021,50(3):330-337(in Chinese).
[26] 楚志兵, 吕阳阳, 唐宾, 等. 表面渗铝改性镁合金的轧制组织性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(5):1374-1380. CHU Zhibing, LV Yangyang, TANG Bin, et al. Structure and properties on surface of aluminizing-modification magnesium alloy in rolling[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(5):1374-1380(in Chinese).
[27] JALILVAND M N, MAZAHERI Y. Effect of mono and hybrid ceramic reinforcement particles on the tribological behavior of the AZ31 matrix surface composites developed by friction stir processing[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46:20345-20356. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.123
[28] LIU F J, LIU J B, JI Y, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of friction stir welded Mg-Al-Zn alloy thick plate joints[J]. Welding in the World,2021,65:229-241. DOI: 10.1007/s40194-020-01012-z
[29] LIU F J, JI Y, BAI Y X. Influence of multipass high rotating speed friction stir processing on microstructure evolution, corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of stirred zone on AZ31 alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2020,30:3263-3273. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65459-0
[30] BU R, JIN A X, SUN Q, et al. Study on laser cladding and properties of AZ63-Er alloy for automobile engine[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2020,9(3):5154-5160. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.03.032
[31] ARTHANARI S, LI Y H, NIE L, et al. Microstructural evolution and properties analysis of laser surface melted and Al/SiC cladded magnesium-rare earth alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,848:156598. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156598
-





 下载:
下载: