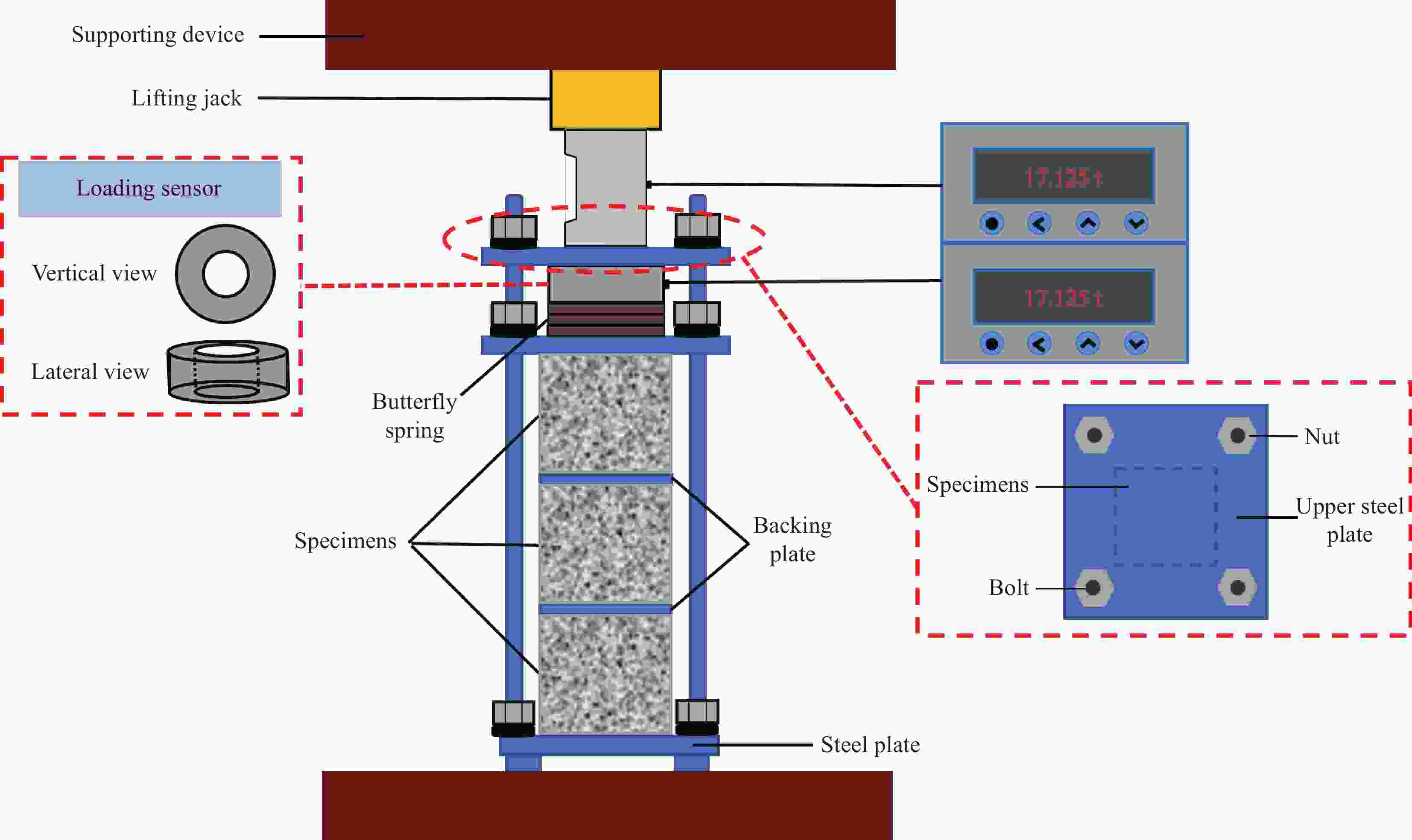
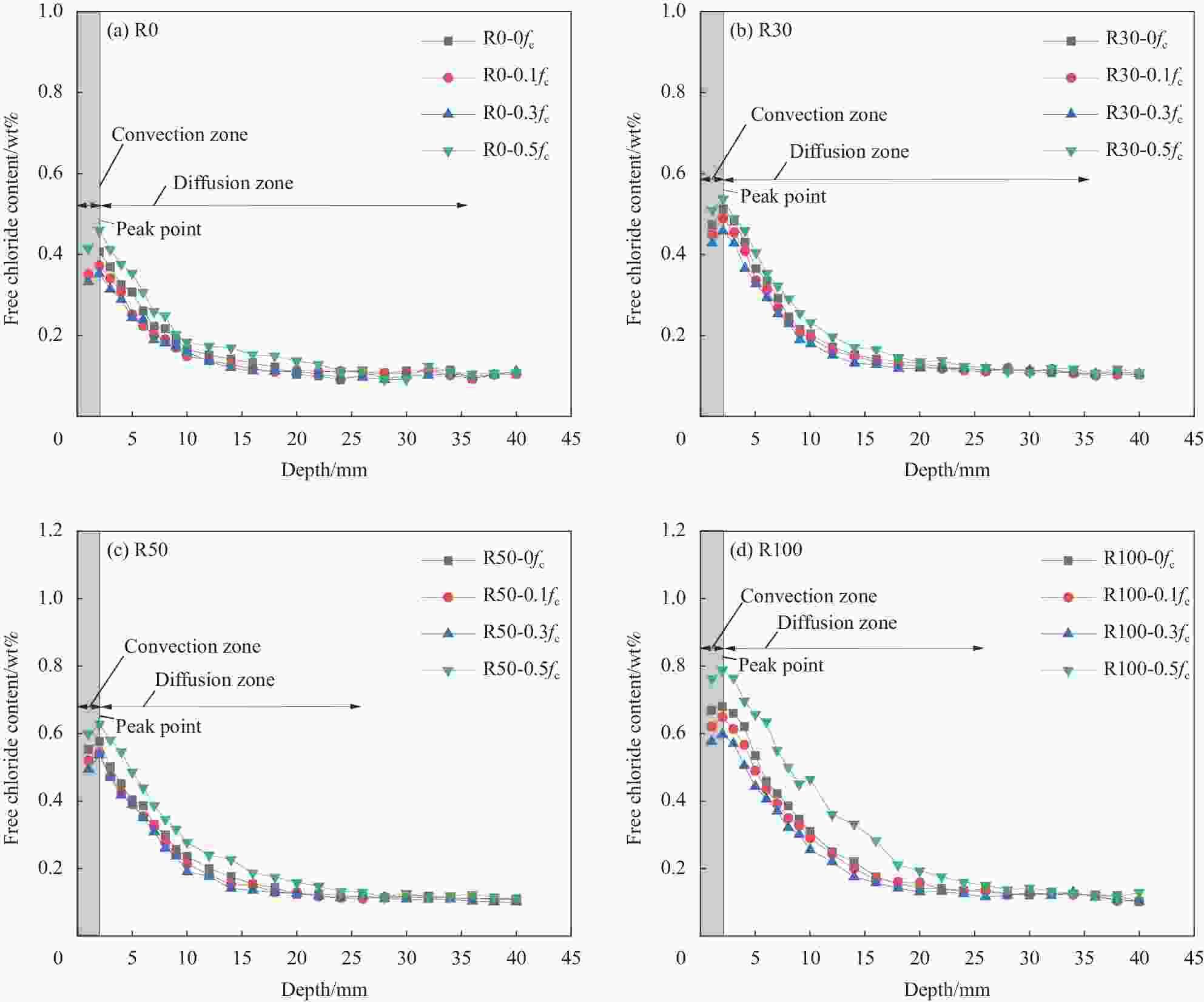
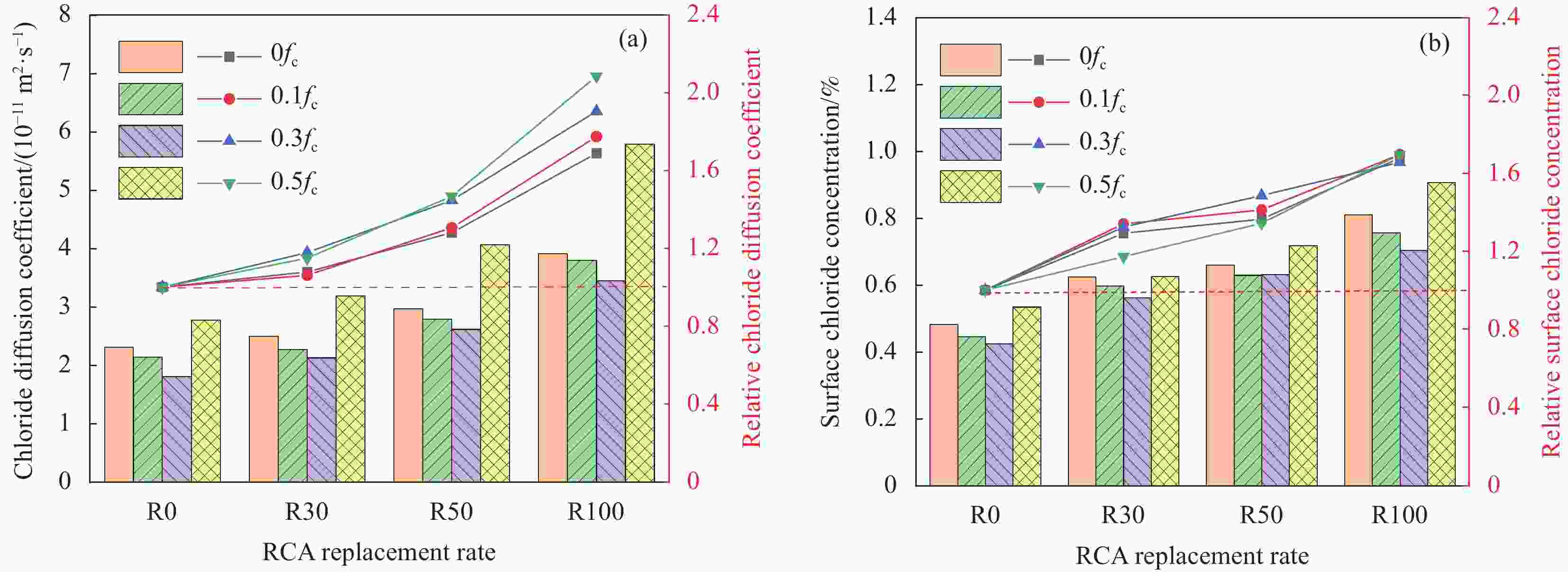
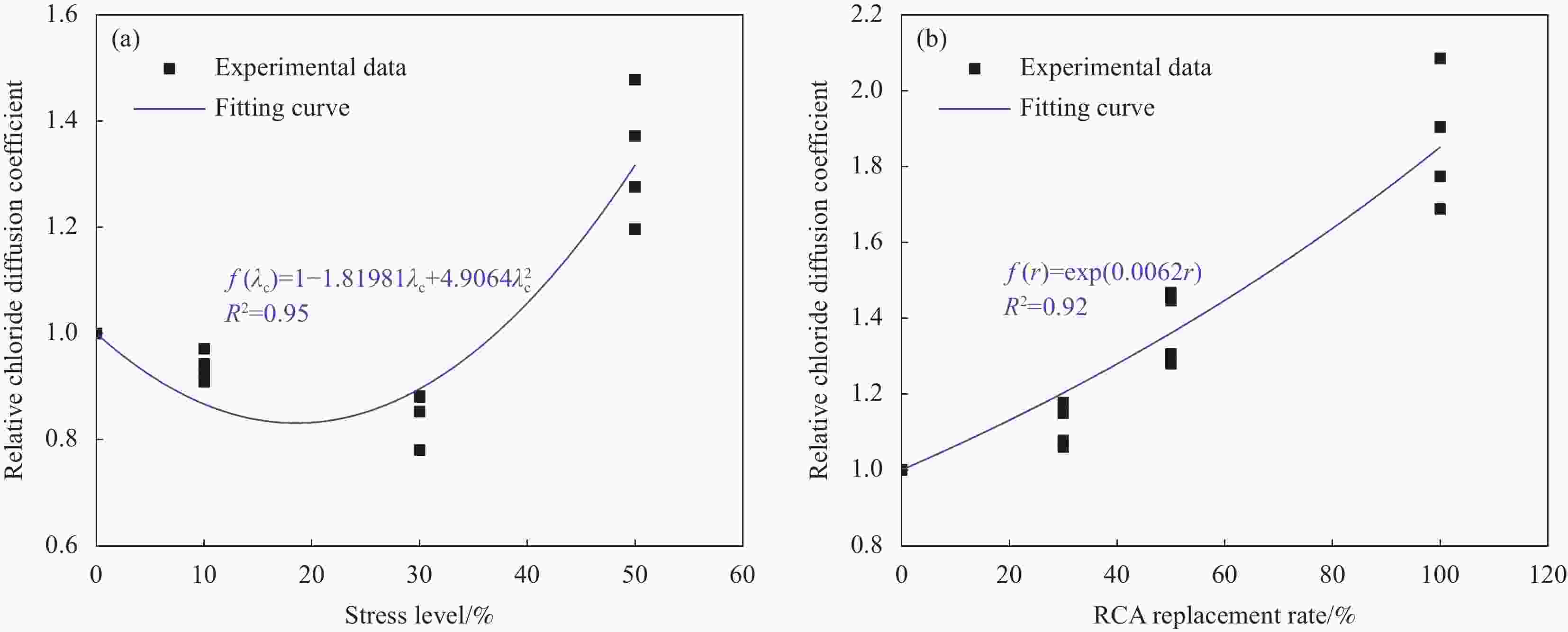
Chloride ingress behavior of recycled aggregate concrete subjected to sustained compressive loading and drying-wetting cycles
-
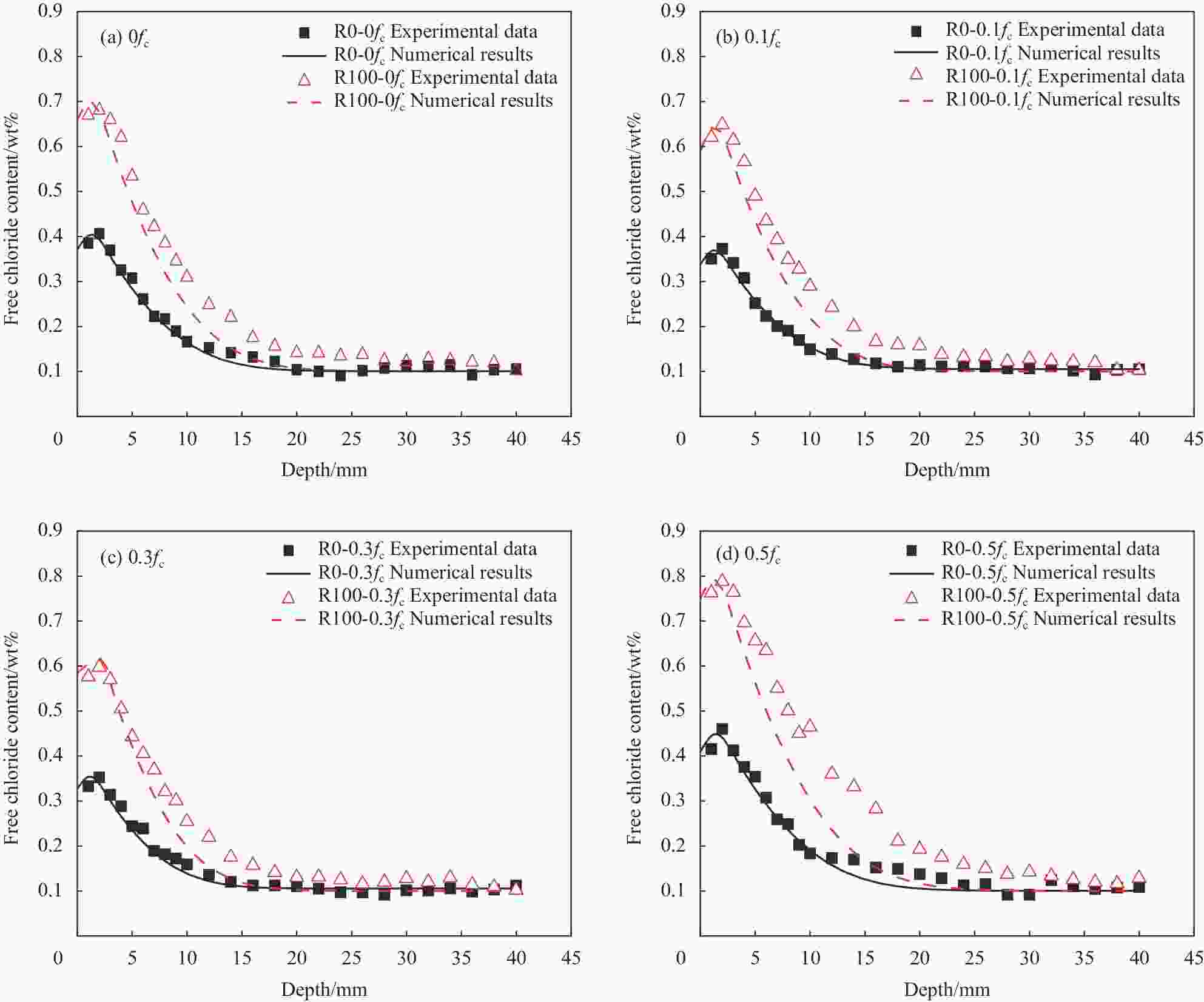
摘要: 采用干湿比为3∶1和质量分数为5wt%的NaCl溶液,开展了持压荷载与干湿循环共同作用下不同再生粗骨料取代率(r=0%、30%、50%、100%)混凝土的氯离子传输试验,分析了持压应力水平(λc=0.1、0.3、0.5)对氯盐侵蚀性能的影响。基于非饱和混凝土的氯离子对流-扩散模型,提出了考虑应力水平和再生骨料取代率影响的水分和氯离子扩散系数模型,并验证了该模型的有效性。结果表明:相同再生粗骨料取代率的混凝土内自由氯离子含量、氯离子扩散系数和表面氯离子浓度均随应力水平的增加呈先减小后增大的趋势,同一应力水平下与再生粗骨料取代率呈正相关,再生粗骨料取代率为100%的试件承受0.1fc、0.3fc、0.5fc (fc为再生混凝土(RAC)立方体抗压强度值)应力作用的氯离子扩散系数分别是无应力状态的0.97、0.88和1.48倍;所建立的持压荷载与干湿循环作用下RAC氯离子传输模型,为再生混凝土耐久性分析提供理论依据。Abstract: The chloride attack environment with cyclic drying-wetting ratio of 3 : 1 and 5wt% mass fraction of NaCl solution was simulated to conduct the chloride ingress test of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) with diffe-rent replacement rates (r=0%, 30%, 50%, 100%) subjected to sustained compressive loading and drying-wetting cycles. Effect of different sustained compressive stress levels (λc=0.1, 0.3, 0.5) the chloride ingress performance of RAC was studied. Based on the chloride convection-diffusion model of unsaturated concrete, the models of water diffusivity and chloride diffusion coefficient considering the effects of recycled coarse aggregate replacement rate and stress level were proposed and validated. The results indicate that at the same replacement rate of recycled coarse aggregates, the free chloride content, chloride diffusion coefficient and surface chloride concentration in RAC decrease first and then increase with the increase of sustained compressive stress level. Under the same stress level, they are positively correlated with the replacement rate of recycled coarse aggregates. The chloride diffusion coefficients of specimens with the replacement rate of 100% subjected to 0.1fc, 0.3fc and 0.5fc (fc means the cubic comprssive strength of RAC) are 0.97, 0.88 and 1.48 times than that of unstressed state, respectively. The established model of the chloride ingress in RAC under sustained compressive loading and drying-wetting cycles can partly provide the theoretical basis for the durability of RAC.
-
表 1 粗骨料物理指标
Table 1. Physical index of coarse aggregate
Coarse aggregate Water absorption
/%Moisture content
/%Crushing index
/%Apparent density
/(kg·m−3)NCA 1.5 0.4 11.2 2590.5 RAC 7.5 3.4 19.1 2534.7 表 2 再生混凝土(RAC)配合比
Table 2. Mix proportion of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC)
kg/m3 Type C S RCA W AW NCA SP R0 380 627 0.0 152 0.0 1269.0 2.3 R30 380 627 380.7 152 15.6 888.3 2.3 R50 380 627 634.5 152 26.0 634.5 2.3 R100 380 627 1269.0 152 52.0 0.0 2.3 Notes: R0, R30, R50 and R100—Recycled aggregate concrete with the replacement ratio of 0%, 30%, 50% and 100%, respectively; C—Cement; S—Sand; W—Water; AW—Additional water; SP—Superplasticizer. -
[1] 肖建庄. 再生混凝土[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008.XIAO Jianzhuang. Recycled concrete[M]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2008(in Chinese). [2] PEDRO D, DE BRITO J, EVANGELISTA L. Durability performance of high-performance concrete made with recycled aggregates, fly ash and densified silica fume[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2018,93:63-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.07.002 [3] 宋鲁光. 荷载干湿交替作用下氯离子在混凝土中的传输性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015.SONG Luguang. Transport of chloride in concrete subjected to coupling flexural load and wetting-drying cycles[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015(in Chinese). [4] CAO T, ZHANG L, SUN G, et al. Simulation of chloride ion transport in concrete under the coupled effects a bending load and drying-wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,241:118045. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118045 [5] WANG J, BASHEER P, NANUKUTTAN S, et al. Influence of service loading and the resulting micro-cracks on chloride resistance of concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,108:56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.01.005 [6] 张伟平, 张庆章, 顾祥林, 等. 环境条件和应力水平对混凝土中氯离子传输的影响[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 34(1):101-106.ZHANG Weiping, ZHANG Qingzhang, GU Xianglin, et al. Effects of environmental conditions and stress level on chloride ion transport in concrete[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition),2013,34(1):101-106(in Chinese). [7] XU J, LI F, ZHAO J, et al. Model of time-dependent and stress-dependent chloride penetration of concrete under sustained axial pressure in the marine environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,170:207-216. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.077 [8] WU J, LI H, WANG Z, et al. Transport model of chloride ions in concrete under loads and drying-wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,112:733-738. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.167 [9] 欧阳璋, 陈幼佳. 重复压应力作用后再生混凝土中氯离子渗透性研究[J]. 混凝土, 2017(1):31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2017.01.009OUYANG Zhang, CHEN Youjia. Study on chloride permeability of recycled concrete after repeated compressive stress[J]. Concrete,2017(1):31-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2017.01.009 [10] 鲍玖文, 李树国, 张鹏, 等. 轴压重复荷载作用后再生混凝土毛细吸水性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(1):71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.01.010BAO Jiuwen, LI Shuguo, ZHANG Peng, et al. Capillary water absorption of recycled aggregate concrete after repeated axial compressive loading[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2021,24(1):71-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.01.010 [11] 王玉建. 加载对再生骨料混凝土渗透性的影响[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2010.WANG Yujian. Effect of loading on permeability of recycled aggregate concrete[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2010(in Chinese). [12] QI B, GAO J, CHEN F, et al. Chloride penetration into recycled aggregate concrete subjected to wetting-drying cycles and flexural loading[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,174:130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.122 [13] WU Y, XIAO J. The effect of microscopic cracks on chloride diffusivity of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,170:326-346. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.045 [14] JIN L, YU H, WANG Z, et al. Effect of crack and damaged zone on chloride penetration in recycled aggregate concrete: A seven-phase mesoscale numerical method[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,291:123383. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123383 [15] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 混凝土用再生粗骨料: GB/T 25177—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Recycled coarse aggregate for concrete: GB/T 25177—2010[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2010(in Chinese). [16] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 建筑用卵石、碎石: GB/T 14685—2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Pebbie and crushed stone for building: GB/T 14685—2011[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011(in Chinese). [17] 郭远新, 李秋义, 单体庆, 等. 再生粗骨料混凝土配合比简易设计方法[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2017(6):75-84.GUO Yuanxin, LI Qiuyi, SHAN Tiqing, et al. Simplified design method for mix proportion of recycled coarse aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science),2017(6):75-84(in Chinese). [18] XIAO J, LI J, ZHANG C. Mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete under uniaxial loading[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2005,35(6):1187-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.09.020 [19] MA Z, LIU M, TANG Q, et al. Chloride permeability of recycled aggregate concrete under the coupling effect of freezing-thawing, elevated temperature or mechanical damage[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,237:117648. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117648 [20] 吴相豪, 岳鹏君. 再生混凝土中氯离子渗透性能试验研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2011, 14(3):381-384, 417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2011.03.018WU Xianghao, YUE Pengjun. Experimental study on chloride ion penetration into recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2011,14(3):381-384, 417(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2011.03.018 [21] 肖建庄, 李标, 杨钱荣, 等. 复合改性再生混凝土抗氯离子渗透性能[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2019, 282(10):1-5.XIAO Jianzhuang, LI Biao, YANG Qianrong, et al. Study on chloride penetration resistance of compound modified recycled concrete[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products,2019,282(10):1-5(in Chinese). [22] WANG W, WU J, WANG Z, et al. Chloride diffusion coefficient of recycled aggregate concrete under compressive loading[J]. Materials and Structures,2016,49(11):4729-4736. doi: 10.1617/s11527-016-0820-x [23] 鲍玖文, 王立成. 干湿交替下水分及氯离子在混凝土中传输的细观数值模拟[J]. 海洋工程, 2014, 32(1):68-74, 83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2014.01.009BAO Jiuwen, WANG Licheng. Mesoscale simulation of water and chloride transport in concrete subjected to drying-wetting cycles[J]. The Ocean Engineering,2014,32(1):68-74, 83(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2014.01.009 [24] 曹卫群. 干湿交替环境下混凝土的氯离子侵蚀与耐久性防护[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2013.CAO Weiqun. Chloride transport and cover protection of concrete under drying-wetting cycles[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [25] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 水运工程混凝土试验检测技术规范: JTS/T 236—2019[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2019.Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China. Technical specification for concrete testing of port and waterway engineering: JTS/T 236—2019[S]. Beijing: China Communication Press, 2019(in Chinese). [26] 高延红, 赵静, 郑盈盈, 等. 模拟自然潮差环境混凝土氯离子侵蚀对流区深度的相似性与随机性[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2018, 27(5):63-69.GAO Yanhong, ZHAO Jing, ZHENG Yingying, et al. Similarity and randomness of convection zone depth of chloride in concrete under simulated tidal environment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2018,27(5):63-69(in Chinese). [27] BAO J, LI S, ZHANG P, et al. Influence of the incorporation of recycled coarse aggregate on water absorption and chloride penetration into concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,239:117845. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117845 [28] WANG J, ZHANG J, CAO D. Pore characteristics of recycled aggregate concrete and its relationship with durability under complex environmental factors[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,272:121642. [29] CHEN D, YANG K, HU D, et al. A meso-stochastic research on the chloride transport in unsaturated concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,273:121986. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121986 [30] 庄智杰. 实海暴露和人工摸拟潮汐区水泥基材料氯离子侵蚀机理研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2021.ZHUANG Zhijie. Study on mechanism of chloride ion erosion on cement-based materials in real sea exposure and artificial tidal zone[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [31] 康天蓓, 刘昱, 周静海, 等. 干湿循环下废弃纤维再生混凝土氯离子传输性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(4): 389-394.KANG Tianbei, LIU Yu, ZHOU Jinghai, et al. Chloride transport performance of waste fiber recycled concrete under wet-dry cycles[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2022, 25(4): 389-394(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: