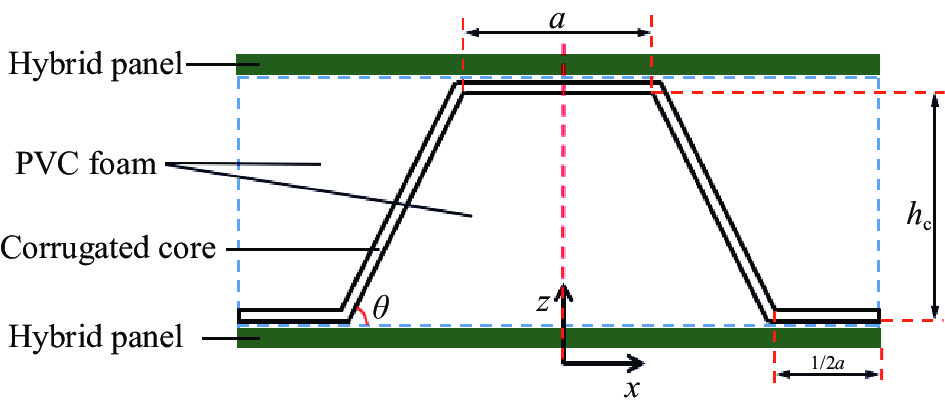
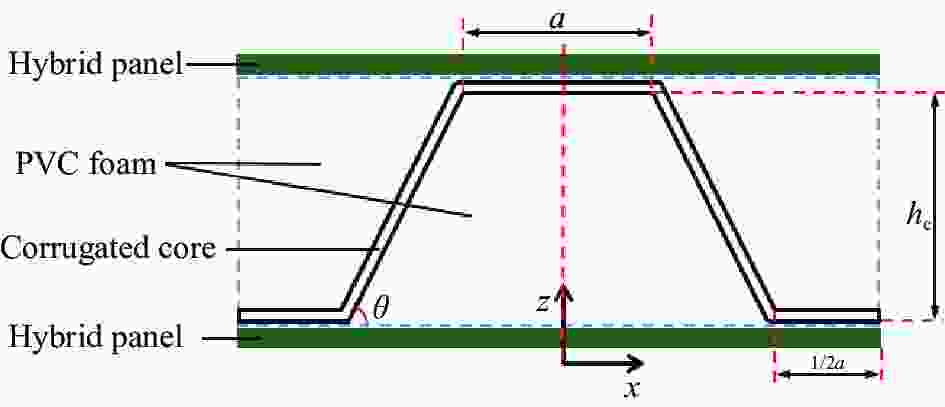
Low-velocity impact properties of carbon/aramid hybrid fiber reinforced corrugated sandwich structure
-
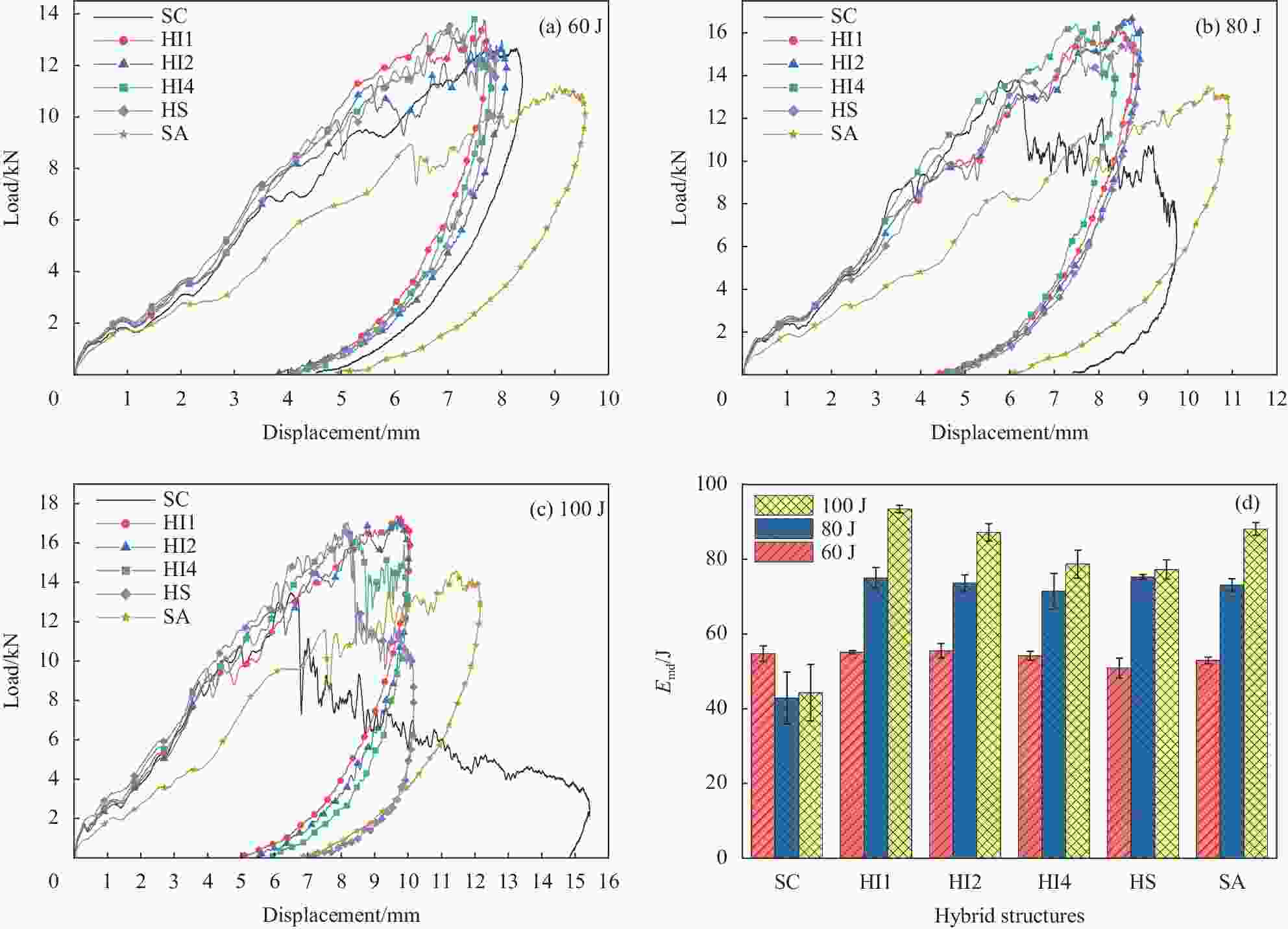
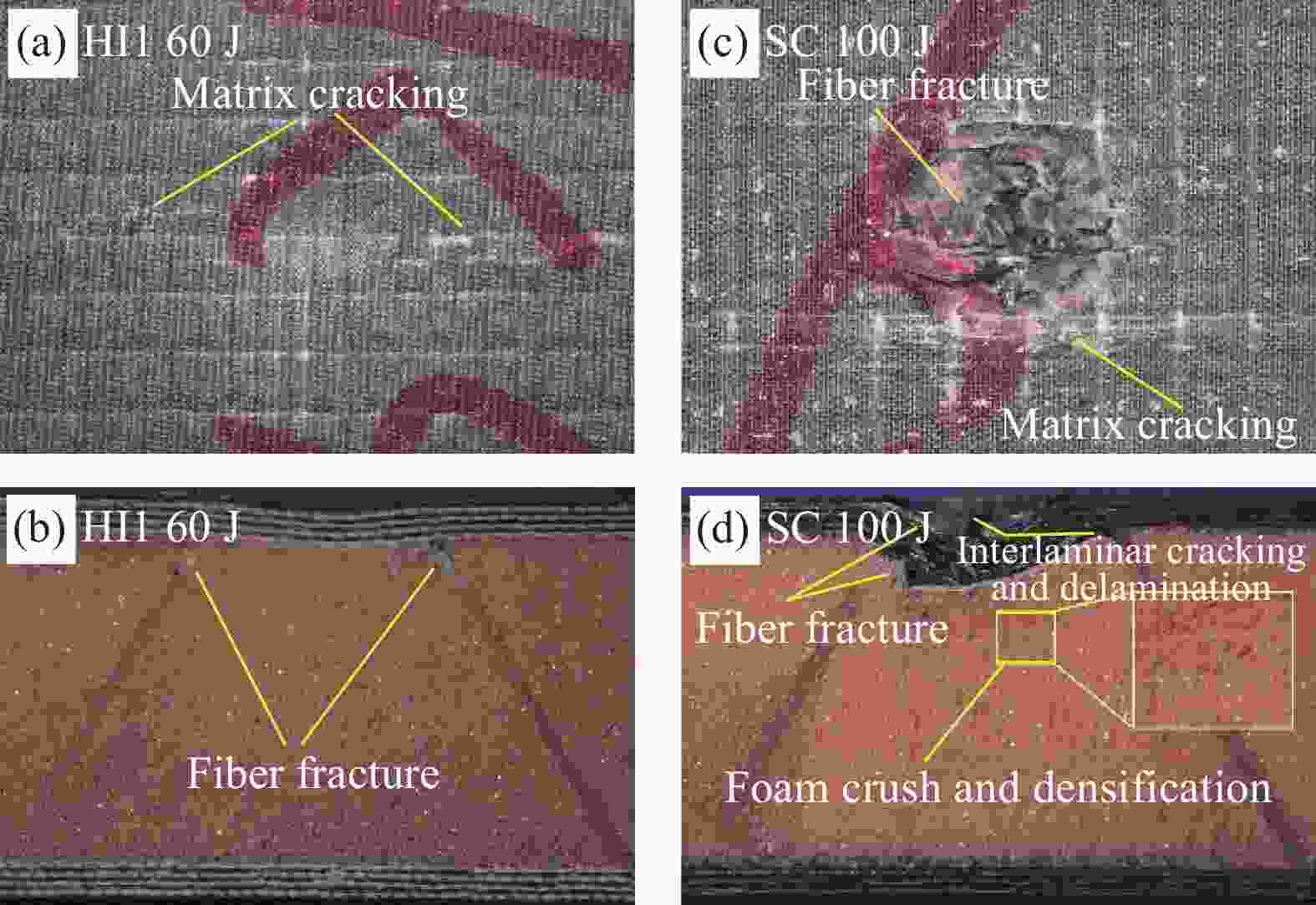
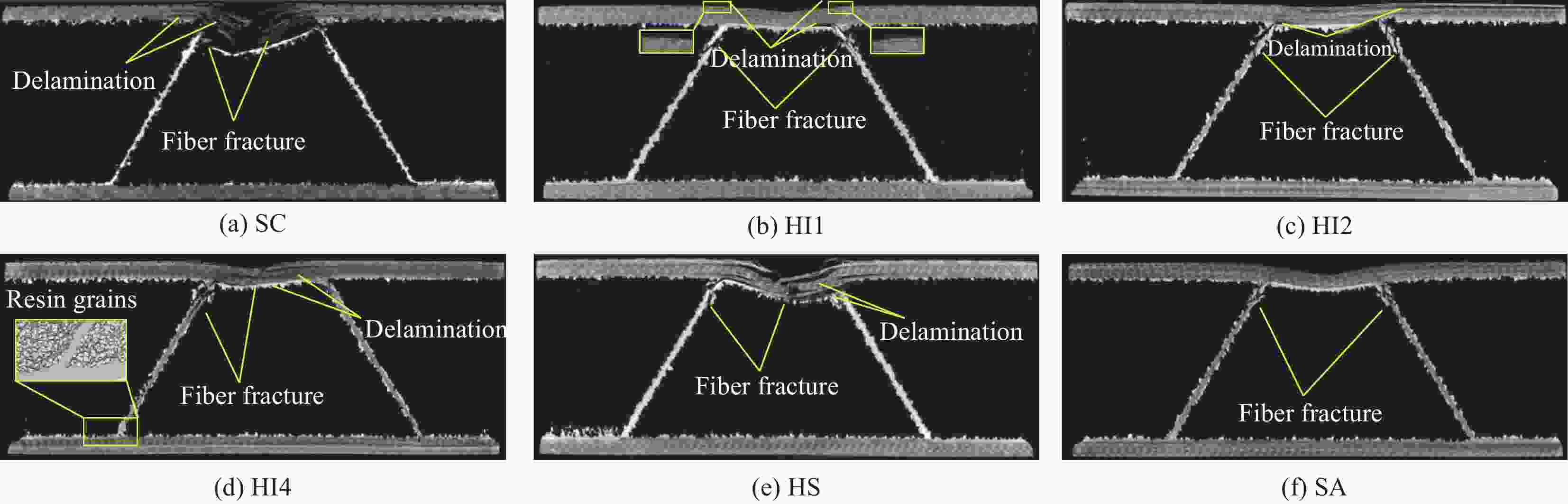
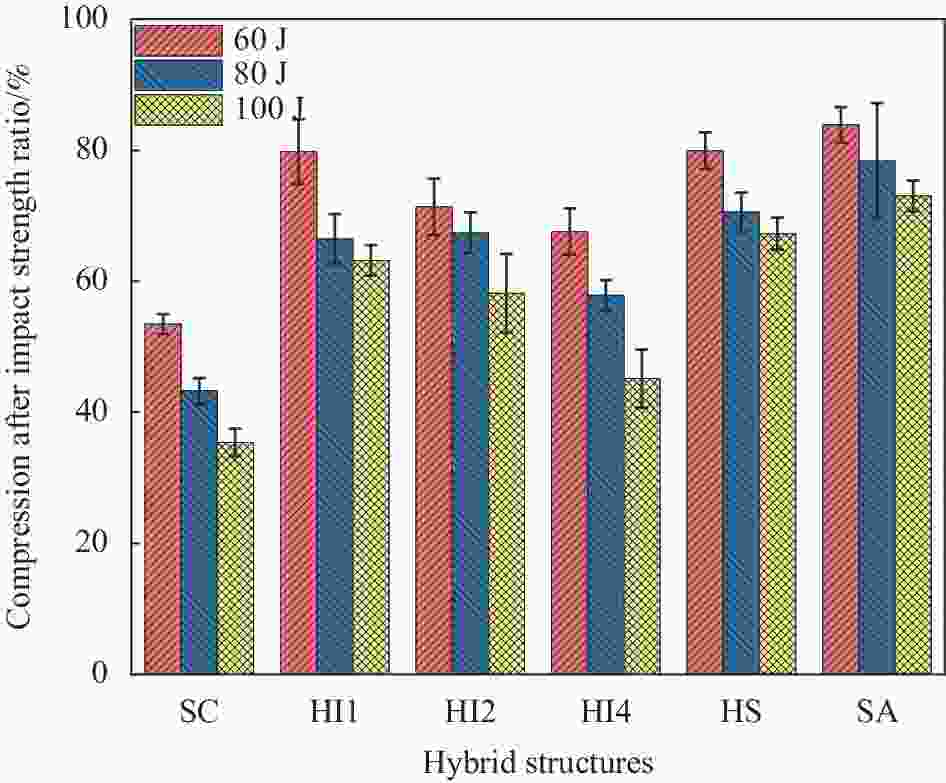
摘要: 采用碳纤维和芳纶纤维增强复合材料对波纹夹芯结构的面板进行层间混杂铺层设计,通过真空辅助树脂灌注(VARI)成型工艺制备混杂波纹夹芯结构。在60 J、80 J和100 J三种不同冲击能量下,研究了面板混杂铺层方式对波纹夹芯结构低速冲击性能及冲击后压缩强度的影响,并利用超声C扫和工业CT断层成像两种无损检测技术对波纹夹芯结构的冲击损伤机制进行了分析。结果表明:冲击能量较低时,波纹夹芯结构的吸收能量基本不受面板的混杂铺层方式影响,而凹坑深度随表层碳纤维层数增加而减少。冲击能量较高时,面板为分层式混杂(碳/芳纶纤维单层交替铺层)的波纹夹芯结构的抗冲击性能最好,纤维断裂损伤和层间分层主要发生在试样表层,但损伤面积较大;面板为夹层式混杂(以碳纤维为蒙皮、芳纶纤维为芯材)的波纹夹芯结构具有较高的吸收能量,整个上面板的纤维都发生了断裂破坏,但损伤面积较小。碳/芳纶混杂波纹夹芯结构的面板采用分层式和夹层式的混杂铺层设计时,具有较高的冲击后压缩强度。Abstract: The carbon/aramid hybrid fiber reinforced composite laminates were used here as skins to design corrugated sandwich structures, which were fabricated by vacuum assisted resin infusion (VARI) process. Low-speed impact tests were conducted by three levels of energy, 60 J, 80 J and 100 J, and compression after impact tests were then carried out on these structures. Later, non-destructive testing techniques, including ultrasonic C-scan and industrial CT tomography, were applied to analyze the damage mechanism. The effects of hybrid modes on the low-speed impact properties and post-impact residual compression strength of the structures were investigated. The results show that at lower impact energy, the energy absorption of the corrugated sandwich structures is basically not affected by the fiber stacking sequence of the skins, but the dent depth decreases with the increase of carbon-fiber layers on the surface. By increasing the impact energy, the corrugated sandwich structure with inter-layer hybrid skins exhibits better impact performance because fiber fracture and interlayer delamination mainly occur between the external layers but larger damage area. On the other hand, the corrugated sandwich structure with sandwich-like hybrid skins can absorb more energy by penetration of the skins in small area. In conclusion, better post-impact compression capacity can be achieved for carbon/aramid hybrid fiber reinforced corrugated sandwich structures by the adoption of inter-layer or sandwich-like hybrid skin designs.
-
表 1 波纹夹芯结构面板铺层方案
Table 1. Panel stacking schemes of corrugated sandwich structures
Alternative Hybrid structure Stacking sequence Thickness/mm SC Non-hybrid [C6/core/C6] 35.81 SA [A8/core/A8] 35.96 HI1 Inter-layer hybrid [CACACACA/core/ACACACAC] 36.32 HI2 [C2A2C2A2/core/A2C2A2C2] 36.34 HI4 Overlay hybrid [C4A4/core/A4C4] 36.38 HS Sandwich-like hybrid [C2A4C2/core/C2A4C2] 36.36 Notes: C, A and core—Carbon fabric, aramid fabric and corrugated core, respectively; SC—Pure carbon fiber structure; SA—Pure aramid fiber structure; HI1—Single layer alternately lay-up structure; H12—Every two layers alternately lay-up stucture; H14—Every four layers alternately lay-up stucture; HS—Sandwich structure. 表 2 不同冲击能量下波纹夹芯结构凹坑深度和损伤面积
Table 2. Dent depth and damage area of corrugated sandwich structures at different impact energies
Impact energy/J Dent depth/mm Damage area/mm2 SC HI1 HI2 HI4 HS SA SC HI1 HI2 HI4 HS SA 60 0.69 0.74 0.62 0.49 0.66 1.07 1026.4 1264.6 1370.5 1541.0 1459.1 — 80 2.79 1.03 0.89 0.80 0.82 1.38 933.0 1413.6 1465.6 1602.7 1863.0 — 100 7.10 1.17 0.92 1.37 2.77 1.55 924.6 2141.9 1805.6 1629.0 1656.4 — 表 3 波纹夹芯结构在不同冲击能量下的压缩强度
Table 3. Compress strength of corrugated sandwich plates at different impact energies
Impact energy/J Compress strength/MPa SC HI1 HI2 HI4 HS SA 0 39.54 26.13 23.00 27.04 22.81 11.60 60 21.15 20.85 16.41 18.28 18.23 9.73 80 17.12 17.36 15.51 15.65 16.10 9.10 100 14.03 16.51 13.38 12.21 15.34 8.47 -
[1] 朱子旭, 朱锡, 李永清, 等. 复合材料夹芯结构研究现状及其在船舶工程的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2018, 40(3):1-7. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2018.03.001ZHU Zixu, ZHU Xi, LI Yongqing, et al. Present researches about sandwich composite structures and its applies in ship industry[J]. Ship Science and Technology,2018,40(3):1-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2018.03.001 [2] XIA F, WU X Q. Study on impact properties of through-thickness stitched foam sandwich composites[J]. Compo-site Structures,2010,92(2):412-421. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.08.016 [3] ZHENG Y Y, XIAO J, DUAN M F, et al. Experimental study of partially-cured Z-pins reinforced foam core composites: K-cor sandwich structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2014,27(1):153-159. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2013.07.016 [4] WANG H, LI S S, LIU Y, et al. Foam-filling techniques to enhance mechanical behaviors of woven lattice truss sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2021,40:102383. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102383 [5] 周磊, 姚凯, 李会民, 等. 复合材料双向波纹夹层结构力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(11):3661-3671.ZHOU Lei, YAO Kai, LI Huimin, et al. Mechanical properties of composite bi-directional corrugated sandwich structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(11):3661-3671(in Chinese). [6] 于渤, 韩宾, 倪长也, 等. 空心及PMI泡沫填充铝波纹夹芯梁冲击性能实验研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2015, 49(1):86-91.YU Bo, HAN Bin, NI Changye, et al. Experimental investigation on impact response of aluminum corrugated sandwich beams with empty and PMI foam filling[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University,2015,49(1):86-91(in Chinese). [7] LIU Y, ZHOU C Y, CEN B, et al. Compression property of a novel lattice sandwich structure[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,117:130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.02.036 [8] DAYYANI I, SHAW A D, FLORES E L S, et al. The mecha-nics of composite corrugated structures: A review with applications in morphing aircraft[J]. Composite Structures,2015,133:358-380. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.07.099 [9] SAFRI S N A, SULTAN M T H, JAWAID M, et al. Impact behaviour of hybrid composites for structural applications: A review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,133:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.09.008 [10] SARASINI F, TIRILLO J, FERRANTE L, et al. Drop-weight impact behaviour of woven hybrid basalt-carbon/epoxy composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2014,59:204-220. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.12.006 [11] 马欢, 张国利, 朱有欣, 等. 复合材料头盔壳体用超薄层合板冲击后的压缩性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2018, 32(5):348-356. doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2017.285MA Huan, ZHANG Guoli, ZHU Youxin, et al. Compression performance after being subjected to impact of ultra-thin composite laminates for helmet[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research,2018,32(5):348-356(in Chinese). doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2017.285 [12] SUN Y, TANG M Y, RONG Z J, et al. An experimental investigation on the low-velocity impact response of carbon-aramid/epoxy hybrid composite laminates[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2017,36(6):422-434. doi: 10.1177/0731684416680893 [13] TORRE L, KENNY J M. Impact testing and simulation of composite sandwich structures for civil transportation[J]. Composite Structures,2000,50(3):257-267. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(00)00101-X [14] PANG Y Z, YAN X J, QU J, et al. Dynamic response of polyurethane foam and fiber orthogonal corrugated sandwich structure subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures,2022,282:114994. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114994 [15] YANG J S, ZHANG W M, YANG F, et al. Low velocity impact behavior of carbon fiber composite curved corrugated sandwich shells[J]. Composite Structures,2020,238:112027. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112027 [16] ZHAO T, JIANG Y B, ZHU Y X, et al. An experimental investigation on low-velocity impact response of a novel corrugated sandwiched composite structure[J]. Compo-site Structures,2020,252:112676. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112676 [17] LIU J X, HE W T, XIE D, et al. The effect of impactor shape on the low-velocity impact behavior of hybrid corrugated core sandwich structures[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,111:315-331. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.11.060 [18] RONG Y, LIU J X, LUO W, et al. Effects of geometric configurations of corrugated cores on the local impact and planar compression of sandwich panels[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,152:324-335. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.08.130 [19] 石昌, 王继辉, 朱俊, 等. 梯形格栅结构增强泡沫夹芯复合材料平压性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2):598-608.SHI Chang, WANG Jihui, ZHU Jun, et al. Flatwise compression properties of trapezoidal lattice-web reinforced foam core sandwich composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(2):598-608(in Chinese). [20] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/7136M[S]. West Conshohocken: International American Society for Testing and Materials, 2007. [21] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for compressive residual strength properties of damaged polymer matrix composite plates: ASTM D7137/D7137M-12[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials, 2012. [22] 杨斌, 章继峰, 周利民. 玻璃纤维-碳纤维混杂增强PCBT复合材料层合板的制备及低速冲击性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(2):435-443.YANG Bin, ZHANG Jifeng, ZHOU Limin. Preparation and low-velocity impact of glass fiber-carbon fiber hybrid reinforced PCBT composite laminate[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(2):435-443(in Chinese). [23] YANG F J, HASSAN M Z, CANTWELL W J, et al. Scaling effects in the low velocity impact response of sandwich structures[J]. Composite Structures,2013,99:97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.11.011 [24] 赵金华, 曹海琳, 晏义伍, 等. 泡沫铝夹层结构复合材料低速冲击性能[J]. 材料工程, 2018, 46(1):92-98. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2015.001295ZHAO Jinhua, CAO Hailin, YAN Yiwu, et al. Low velocity impact properties of aluminum foam sandwich structural composite[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2018,46(1):92-98(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2015.001295 [25] ZHANG C X, HUANG J, LI X, et al. Numerical study of the damage behavior of carbon fiber/glass fiber hybrid composite laminates under low-velocity impact[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2020,21(12):2873-2887. doi: 10.1007/s12221-020-0026-2 [26] WANG M L, PAN Z X, WU Z Y, et al. Effect of carbon/Kevlar asymmetric hybridization ratio on the low-velocity impact response of plain woven laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2021,276:114574. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114574 [27] 段友社, 郭书良, 吴刚, 等. Z向增强泡沫夹芯复合材料冲击损伤及冲击后压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(2):180-185.DUAN Youshe, GUO Shuliang, WU Gang, et al. Impact damage characteristics and post-impact compressive properties of Z-reinforcement foam core sandwich composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(2):180-185(in Chinese). [28] 吴盼, 阎建华, 俞建勇, 等. 碳纤/环氧复合材料层合板低速冲击损伤机理研究[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2016(3):31-37.WU Pan, YAN Jianhua, YU Jianyong, et al. Low-velocity impact damage mechanism of carbon/expoxy composite laminates[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites,2016(3):31-37(in Chinese). [29] MA F W, YANG M, WANG G W, et al. Response of carbon-basalt hybrid fiber reinforced polymer under low velocity impact load[J]. Materials Research Express,2019,6(9):095311. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab2e5f -





 下载:
下载: