Compression failure life prediction and verification of polymethacrylimide foam
-
摘要: 聚甲基丙烯酸酰亚胺(PMI)泡沫因其性能优越,在航空航天领域广泛应用。本文主要针队PMI泡沫在弹筒适配器领域的功能特性开展研究,主要研究了其在常温条件下的压缩蠕变特性。依据使用工况及高分子材料的蠕变特性,采用“时间强化”模型设计实验,分别对密度为0.075 g/cm3和0.110 g/cm3的PMI泡沫进行了为期180天的常温压缩蠕变实验。通过对实验数据分析、拟合,预测了两种不同密度的PMI泡沫常温、1250 N条件下的压缩蠕变寿命,密度0.075 g/cm3 PMI泡沫压缩蠕变失效寿命约为11年;而密度0.110 g/cm3 PMI泡沫约为53年,同时对模型的可靠性进行了验证分析。Abstract: Polymethacrylate imide (PMI) foam is widely used in aerospace field because of its superior performance. This paper mainly studies the functional characteristics of PMI foam in the field of cartridge adapter, and mainly studies its compression creep characteristics at room temperature. According to the working conditions and creep characteristics of polymer materials, the "time strengthening" model was adopted to design experiments, and the PMI foam with densities of 0.075 g/cm3 and 0.110 g/cm3 were respectively tested for 180 days under normal temperature compression creep. By analyzing and fitting the experimental data, the compression creep life of two PMI foam with different densities at room temperature and 1250 N was predicted. The compression creep failure life of PMI foam with density of 0.075 g/cm3 is about 11 years. The density of 0.110 g/cm3 PMI foam is about 53 years, and the reliability of the model is verified and analyzed.
-
Key words:
- PMI foam /
- compression creep /
- creep model /
- constant load /
- life
-
表 1 聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺(PMI)泡沫编号
Table 1. Number of polymethacrylimide (PMI) foams
Specimen number Density/(g·cm−3) Load/N A-1 0.075 937.5 A-2 0.075 1250.0 A-3 0.075 1562.5 A-4 0.075 1875.0 B-1 0.110 937.5 B-2 0.110 1250.0 B-3 0.110 1562.5 B-4 0.110 1875.0 表 2 不同载荷及时间下0.075 g/cm3 PMI泡沫蠕变应变
Table 2. Creep strain of 0.075 g/cm3 PMI foams under different loads and time
Time/h A-1 A-2 A-3 A-4 0 0 0 0 0 168 0.000450 0.000630 0.000985 0.001260 336 0.000845 0.001160 0.001770 0.002330 720 0.001170 0.001580 0.002470 0.002900 1440 0.001480 0.002040 0.003060 0.003670 2160 0.001690 0.002310 0.003460 0.004170 2880 0.001840 0.002510 0.003860 0.004670 3600 0.001980 0.002650 0.004240 0.005060 4320 0.002120 0.002800 0.004450 0.005480 表 3 不同载荷及时间下0.110 g/cm3 PMI泡沫蠕变应变
Table 3. Creep strain of 0.110 g/cm3 PMI foams under different loads and time
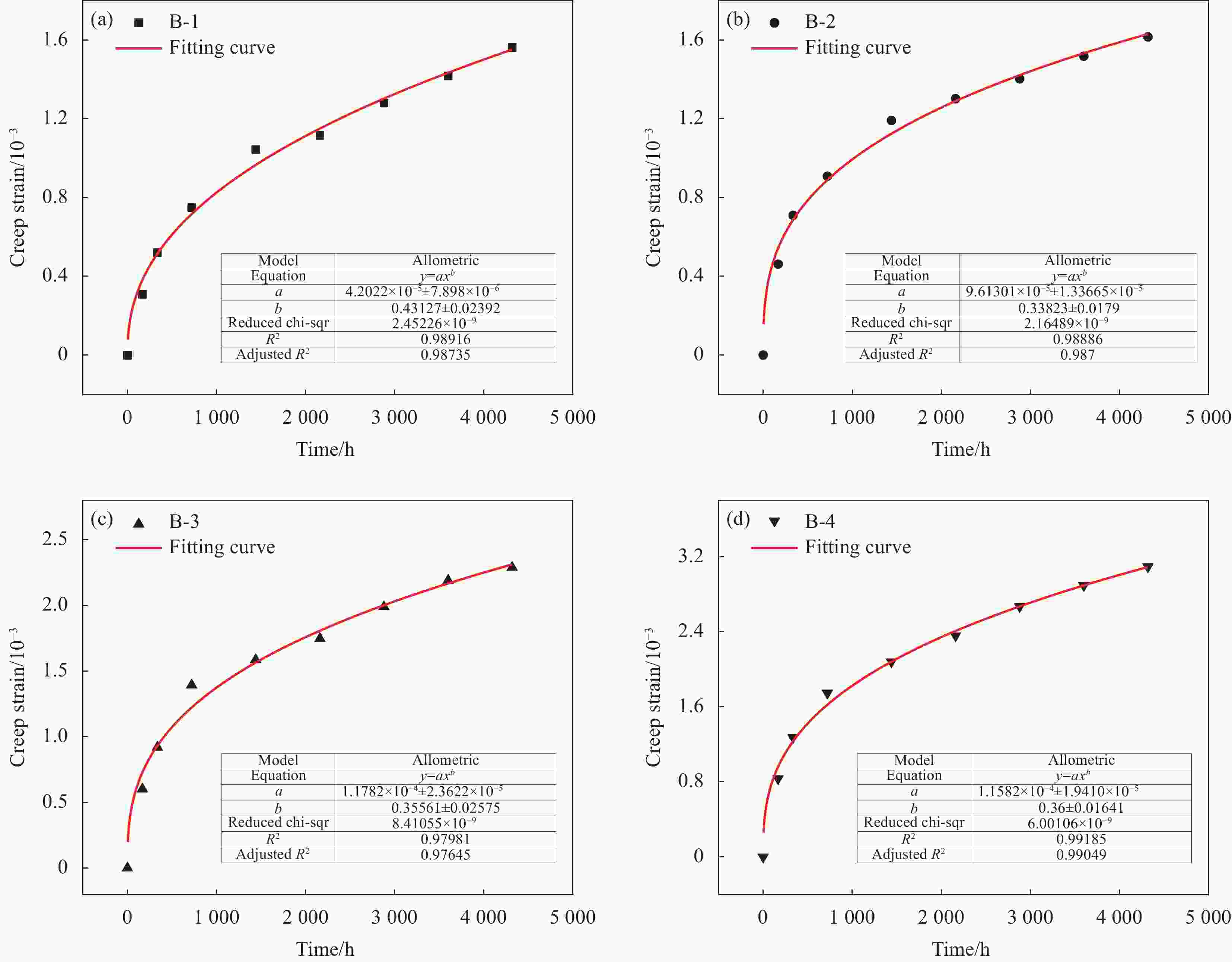
Time/h B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 0 0 0 0 0 168 0.000310 0.000462 0.000602 0.000833 336 0.000523 0.000710 0.000919 0.001273 720 0.000751 0.000908 0.001393 0.001747 1440 0.001046 0.001191 0.001586 0.002079 2160 0.001118 0.001302 0.001747 0.002357 2880 0.001282 0.001402 0.001989 0.002669 3600 0.001420 0.001518 0.002190 0.002893 4320 0.001565 0.001616 0.002290 0.003094 表 4 0.075 g/cm3 PMI泡沫不同载荷下拟合模型参数
Table 4. Fitting model parameters of 0.075 g/cm3 PMI foams under different loads
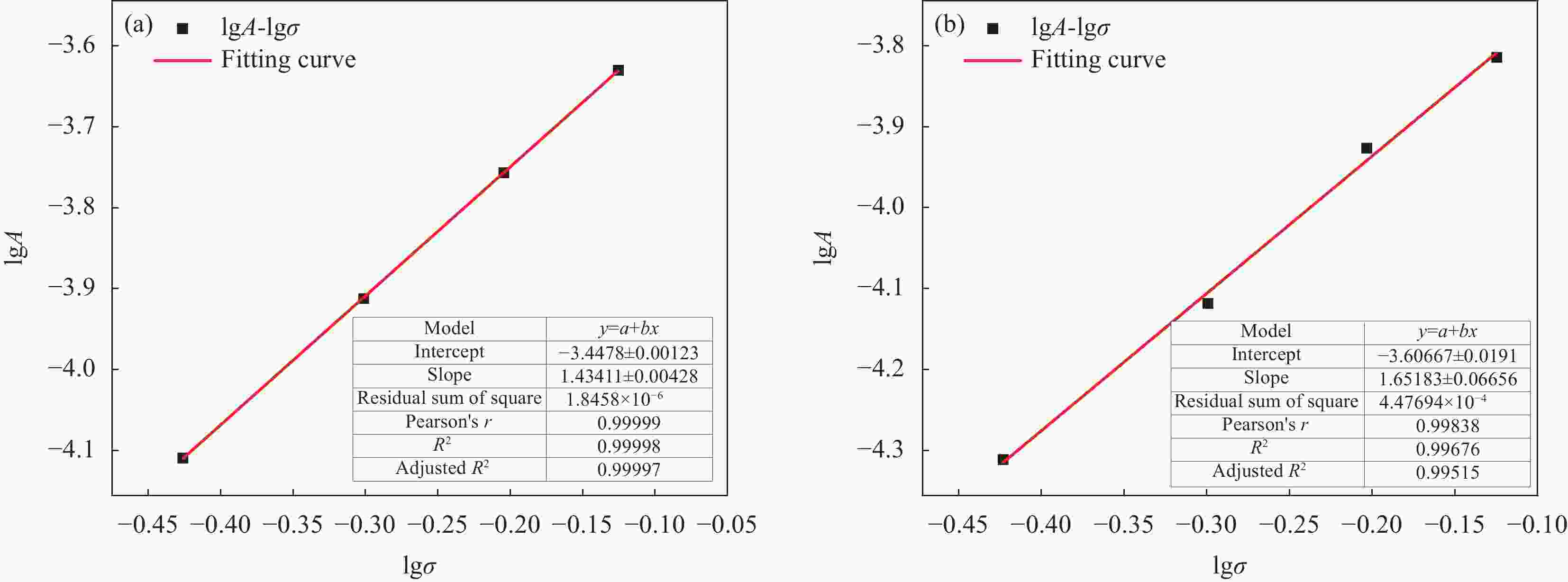
Sample Model parameters A A3 R2 A-1 8.74×10−5 0.38308 0.97667 A-2 1.32×10−4 0.36915 0.98022 A-3 1.82×10−4 0.38437 0.99314 A-4 2.36×10−4 0.37541 0.98273 表 5 0.110 g/cm3 PMI泡沫不同载荷下拟合模型参数
Table 5. Fitting model parameters of 0.110 g/cm3 PMI foams under different loads
Sample Model parameters A A3 R2 B-1 4.20×10−5 0.43127 0.98916 B-2 9.61×10−5 0.33823 0.98860 B-3 1.18×10−4 0.35561 0.97981 B-4 1.52×10−4 0.36000 0.99185 表 6 0.075 g/cm3 PMI泡沫在不同载荷下的剩余载荷
Table 6. Residual load of 0.075 g/cm3 PMI foams under different loads
Sample Initial load/N Average creep/mm Residual load/N Residual stress/MPa A-1 937.5 0.002120 936.864 0.374746 A-2 1250.0 0.002800 1249.160 0.499664 A-3 1562.5 0.004450 1561.165 0.624466 A-4 1875.0 0.005480 1873.356 0.749342 表 7 0.110 g/cm3 PMI泡沫在不同载荷下的剩余载荷
Table 7. Residual load of 0.110 g/cm3 PMI foams under different loads
Sample Initial load/N Average creep/mm Residual load/N Residual stress/MPa B-1 937.5 0.062608 936.952 0.374781 B-2 1250.0 0.064634 1249.434 0.499774 B-3 1562.5 0.091596 1561.699 0.624680 B-4 1875.0 0.123757 1873.917 0.749567 -
[1] 胡培, 陈志东, 薛元德, 等. 泡沫夹层结构的模压共固化成型工艺及参数选定[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2007(8):25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2007.08.007HU Pei, CHEN Zhidong, XUE Yuande, et al. Pressmolding co-curing processing method and specification determination offoamcored sandwich structure[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2007(8):25-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2007.08.007 [2] 刘燕青, 黄安民, 刘婷, 等. 聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺泡沫塑料的制备及研究现状[J]. 塑料科技, 2012(6):86-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3360.2012.06.015LIU Yanqing, HUANG Anmin, LIU Ting, et al. Research situation of polymethacrylimide foam plastics and its preparation[J]. Plastics Science and Technology,2012(6):86-90(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3360.2012.06.015 [3] SEIBERT H F. Applications for PMI foams in aerospace sandwich structures[J]. Reinforced Plastics,2006,50(1):44-48. [4] SERVATY S, GEYER W, RAU N, et al. Method for producing block-shaped polymethacrylimide foamed materials: WO, WO2000063280 A1[P]. 2003-12-30. [5] RAMAKRISHNAN K R, GUERARD S, MAHEO L, et al. A new method for the study of parabolic impact of foam-core sandwich panels[J]. Composites,2019,167:717-727. [6] GUEDES, MIRANDA R. A systematic methodology for creep master curve construction using the stepped isostress method (SSM): A numerical assessment[J]. Mechanics of Time-dependent Materials,2018,22:79-93. [7] ZHONG J, YANG C, MA W, et al. Long-term creep behavior prediction of polymethacrylimide foams using artificial neural networks[J]. Polymer Testing,2020,93:43-53. [8] ZHOU H, LIU R, HU Y, et al. Quasi-static compressive strength of polymethacrylimide foam-filled square carbon fiber reinforced composite honeycombs[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures and Materials,2020,0(0):1-17. [9] 李涛, 陈蔚, 成理, 等. 泡沫夹层结构复合材料的应用与发展[J]. 科技创新导报, 2009(14):9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2009.14.002LI Tao, CHEN Wei, CHENG Li, et al. Development and application of foam sandwich structural composites[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Heral,2009(14):9-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-098X.2009.14.002 [10] SIIVOLA J T, MINAKUCHI S, TAKEDA N. Effect of temperature and humidity conditions on polymethacrylimide (PMI) foam core material and indentation response of its sandwich structures[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2015,17(4):149-155. [11] 陈吉平, 毛敏梁, 郑义珠, 等. 湿热环境下的PMI泡沫材料压缩蠕变特性[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2020, 48(2): 75-80.CHEN Jiping, MAO Minliang, ZHENG Yizhu, et al. Compressive creep properties of PMI foam in hydrothermal condition[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2020,48(2): 75-80(in Chinese). [12] 刘浩, 韩常玉, 董丽松. 闭孔泡沫塑料结构与性能研究进展[J]. 高分子通报, 2008(3):31-44.LIU Hao, HAN Changyu, DONG Lisong. Research progress in structure-properties relationships of closed cell polymer foams[J]. Chinese Polymer Bulletin,2008(3):31-44(in Chinese). [13] 毛敏梁, 彭昆, 郑翻番, 等. 聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺(PMI)泡沫夹芯复合材料的滚筒剥离性能研究[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2017(11):62-65.MAO Minliang, PENG Kun, ZHENG Fanfan, et al. The study of peel strength of PMI foam sandwich structure compo-sites[J]. Composite Science and Engineering,2017(11):62-65(in Chinese). [14] 米星宇, 张广成, 张乐, 等. 硬质泡沫塑料耐热性测试方法研究[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2012, 40(8):74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2012.06.001MI Xingyu, ZHANG Guangcheng, ZHANG Le, et al. Heat resistance testing methods of rigid foam plastics[J]. Engi-neering Plastics Application,2012,40(8):74-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2012.06.001 [15] GNIP I Y, VAITKUS S, KERULIS V, et al. Analytical description of the creep of expanded polystyrene (EPS) under long-term compressive loading[J]. Polymer Testing,2011,30(5):493-500. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2011.03.012 [16] 贾思宜, 王莹, 成艳娜. PMI泡沫真空辅助热成型工艺及其生产应用研究[J]. 科技创新导报, 2020, 17(508):124-126.JIA Siyi, WANG Ying, CHENG Yanna. Research on PMI foam vacuum-assisted thermo forming process and its production application[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald,2020,17(508):124-126(in Chinese). [17] 刘永涛, 杨杰, 刘新东. 夹层结构用泡沫芯材的耐水性能[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2018, 46(4):108-112.LIU Yongtao, YANG Jie, LIU Xindong. Water durability of foam core used in sandwich structure[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2018,46(4):108-112(in Chinese). [18] 曾泽群, 吴锦裕, 向辉, 等. 吸湿行为对PMI泡沫性能及应用的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(11):64-70.ZENG Zequn, WU Jinyu, XIANG Hui, et al. Effect of hygroscopic behavior on properties and applications of PMI foam[J]. China Plasics,2021,35(11):64-70(in Chinese). [19] SEIBERT H F. PMI foam cores find further applications[J]. Reinforced Plastics,2000,44(1):36-38. doi: 10.1016/S0034-3617(00)86485-1 [20] FENG J, CHUHAN Z, GANG W, et al. Creep modeling in excavation analysis of a high rock slope[J]. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering,2003,129(9):849-857. [21] CHEN S M, GAO H L, SUN X H, et al. Superior biomimetic nacreous bulk nanocomposites by a multiscale soft-rigid dual-network interfacial design strategy[J]. Matter, 2019, 1(2): 412-427. [22] BOZORG-HADDAD A, ISKANDER M. Predicting compres-sive creep behavior of virgin HDPE using thermal acceleration[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2011,23(8):1154-1162. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000278 [23] YANG Y, LIU J, XIN L U, et al. Study of manufacturing pressure effect on bonding quality of polymethacrylimide (PMI) foams/high temperature cured carbon fiber sandwich composites structure[J]. Hi-Tech Fiber & Application,2012,37(1):14-21. [24] 王凯, 贺强. 聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺泡沫夹层结构全生命周期的关键技术研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(8): 1805-1822.WANG Kai, HE Qiang. Progress on study of key technologies for polymethacrylimide foam core sandwich lifecycle[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(8): 1805-1822(in Chinese). [25] JADAAN O M, POWERS L M, GYEKENYESI J P. Creep life prediction of ceramic components subjected to transient tensile and compressive stress states[C]//Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. New York: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1997: 235-278. [26] MAHMUD H A, RADUE M S, CHINKANJANAROT S, et al. Multiscale modeling of carbon fiber-graphene nanoplatelet-epoxy hybrid composites using a reactive force field[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 172: 628-635. -





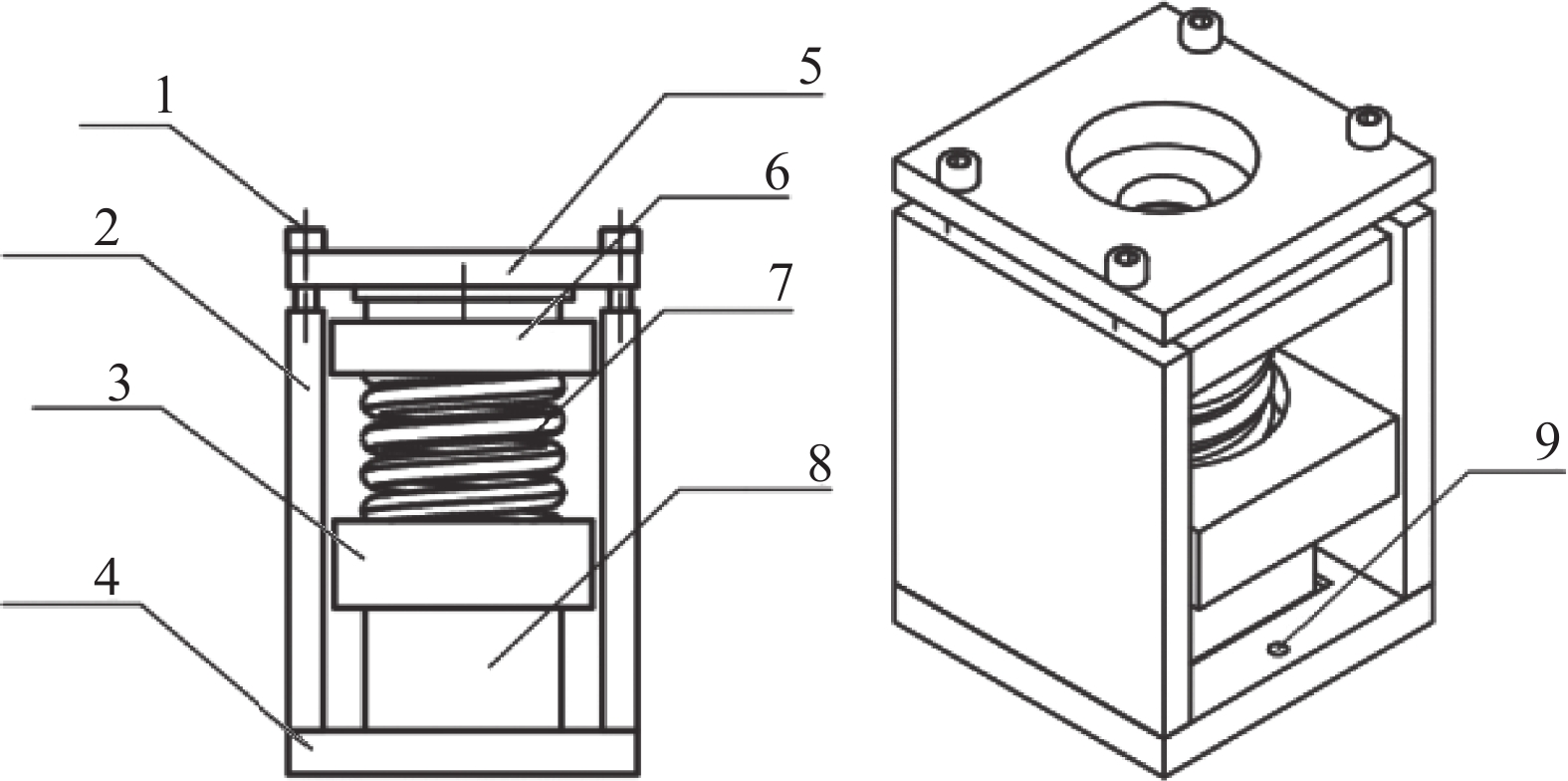
 下载:
下载: