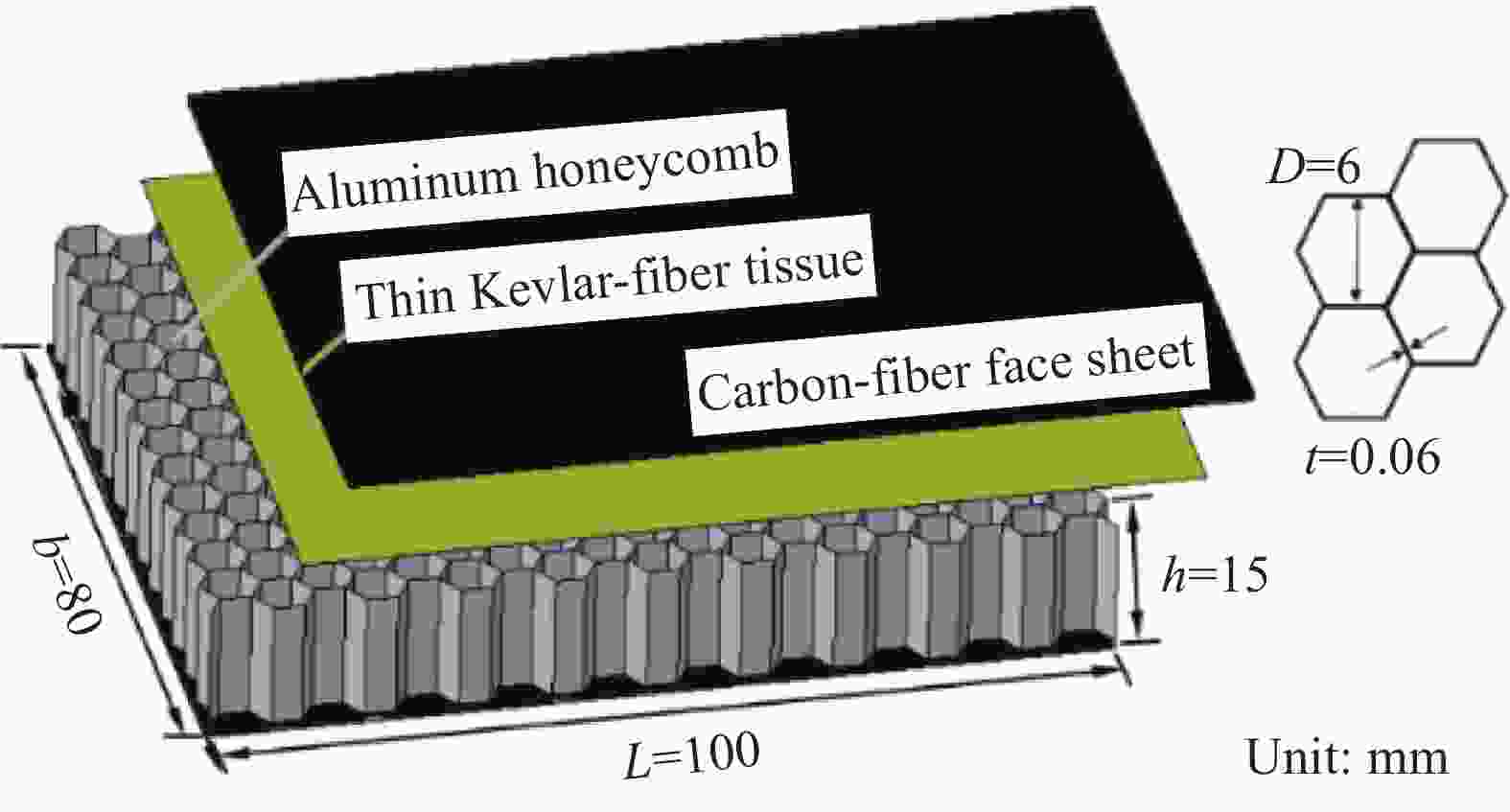
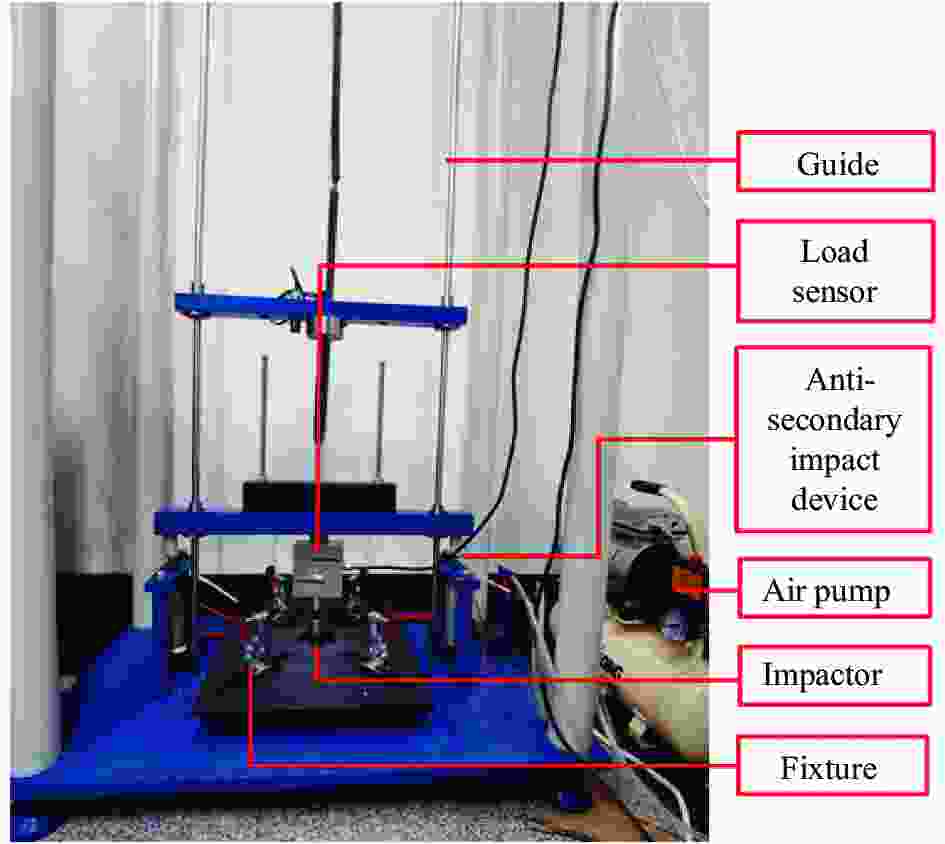
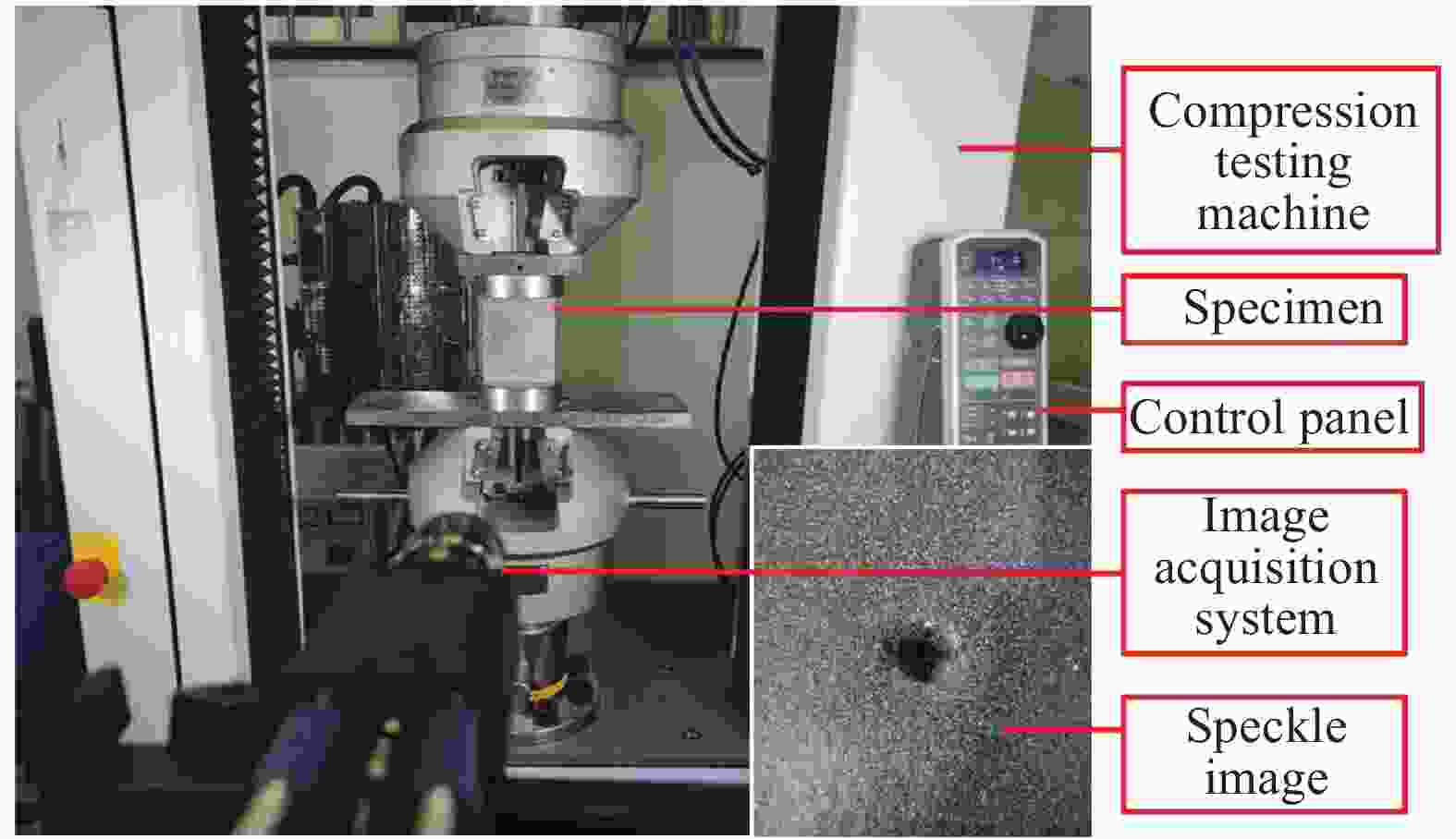
Compression after impact properties of carbon-fiber/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich panels with short-Kevlar-fiber toughening
-
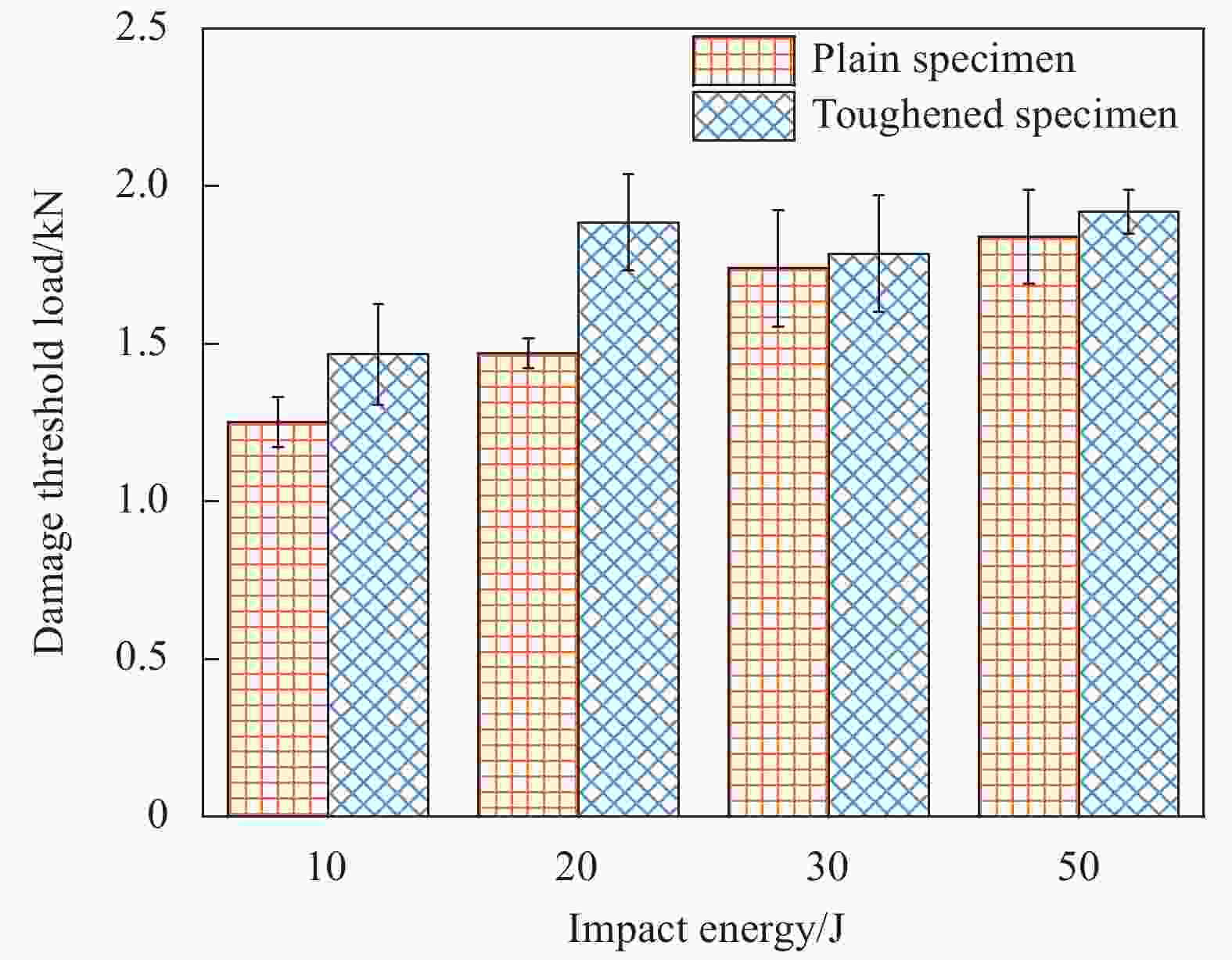
摘要: 碳纤维夹芯板受到冲击载荷后易发生分层损伤,在工程应用中严重影响结构安全。首先对碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板界面进行Kevlar短纤维增韧设计;其次对比研究了Kevlar短纤维界面增韧及未增韧夹芯板的低速冲击行为和冲击后压缩行为,将其冲击后剩余压缩强度、能量吸收及破坏模式进行对比;最后运用数字图像相关技术(DIC)获取增韧及未增韧试件在冲击后压缩过程中的应变云图。结果表明:低速冲击过程中,Kevlar短纤维增韧可以有效提高碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板的冲击损伤阻抗,增韧试件的临界损伤阈值载荷明显高于未增韧试件;相比于未增韧试件,4种冲击能量下增韧试件的冲击后剩余压缩强度(CAI)值分别提高了2.68%、9.24%、4.65%、11.13%,能量吸收分别提高了69.09%、52.88%、55.03%、101.70%;对碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板冲击后压缩过程中的DIC观测,进一步验证了芳纶短纤维对界面的增韧效果,并揭示了增韧界面对结构的增强机制。Abstract: Delamination between face sheets and core is one of the most common damage mode of carbon-fiber sandwich panels under impact loading, which seriously affects structural safety. Firstly, short-Kevlar-fibers were used for toughening the interface of carbon-fiber/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich panel. Secondly, low velocity impact and compression after impact tests were conducted for plain and toughened specimens. The residual compression strength, energy absorption and failure mode were compared. Finally, the strains of plain and toughened specimens during compression after impact test were obtained by digital image correlation (DIC). The results show that short-Kevlar-fiber toughening is capable to effectively increase the impact damage resistance of carbon-fiber/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich panel, and the damage threshold load of toughened specimens is signifi-cantly higher than that of plain specimens. Compared with the plain specimens, the residual compression strength values after impact of toughened specimens are increased by 2.68%, 9.24%, 4.65% and 11.13%, respectively, under four different impact energies. Meanwhile the energy absorption values of toughened specimens are increased by 69.09%, 52.88%, 55.03% and 101.70%, respectively. Furthermore, DIC observations were used to investigate the toughening effects of short-Kevlar-fibers and the strengthening mechanism.
-
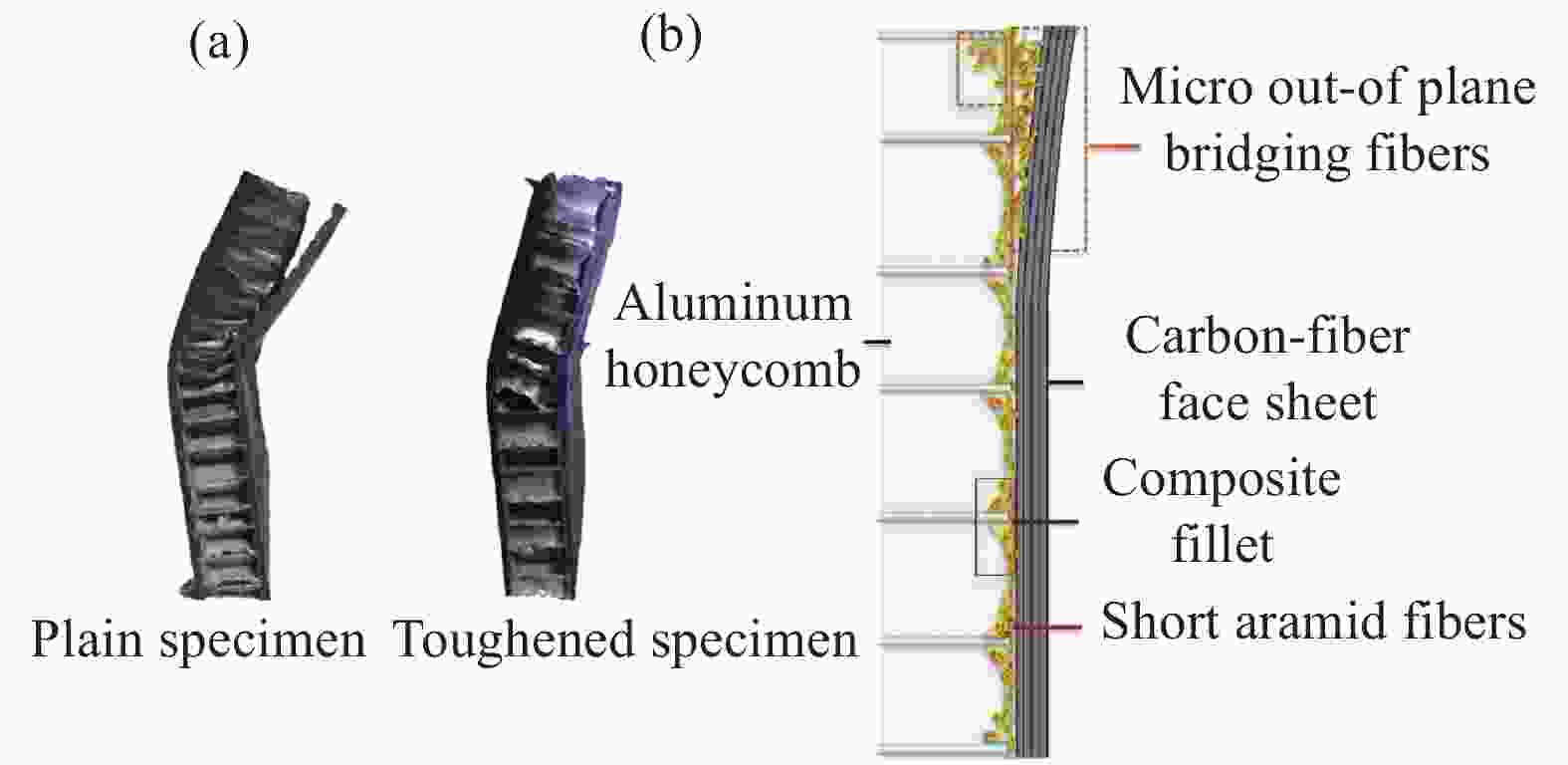
图 9 碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板CAI破坏模式及短纤维增韧示意图:(a) 30 J冲击能量下未增韧和增韧试件CAI破坏模态;(b) Kevlar短纤维界面增韧示意图[25]
Figure 9. Schematic diagram of CAI failure mode of carbon fiber/aluminum honeycomb sandwich panel and sketch of the toughening effects: (a) CAI failure mode of carbon fiber/aluminum honeycomb sandwich panel with and without toughening under the impact energy of 30 J; (b) Sketch of the toughening effects with short Kevlar fibers[25]
表 1 不同冲击能量下Kevlar短纤维界面增韧碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板面板破坏形貌
Table 1. Failure morphologies of carbon-fiber/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich panel with short-Kevlar-fiber toughening under different impact energies
Impact energy/J 10 20 30 50 Top surface 



Bottom surface 



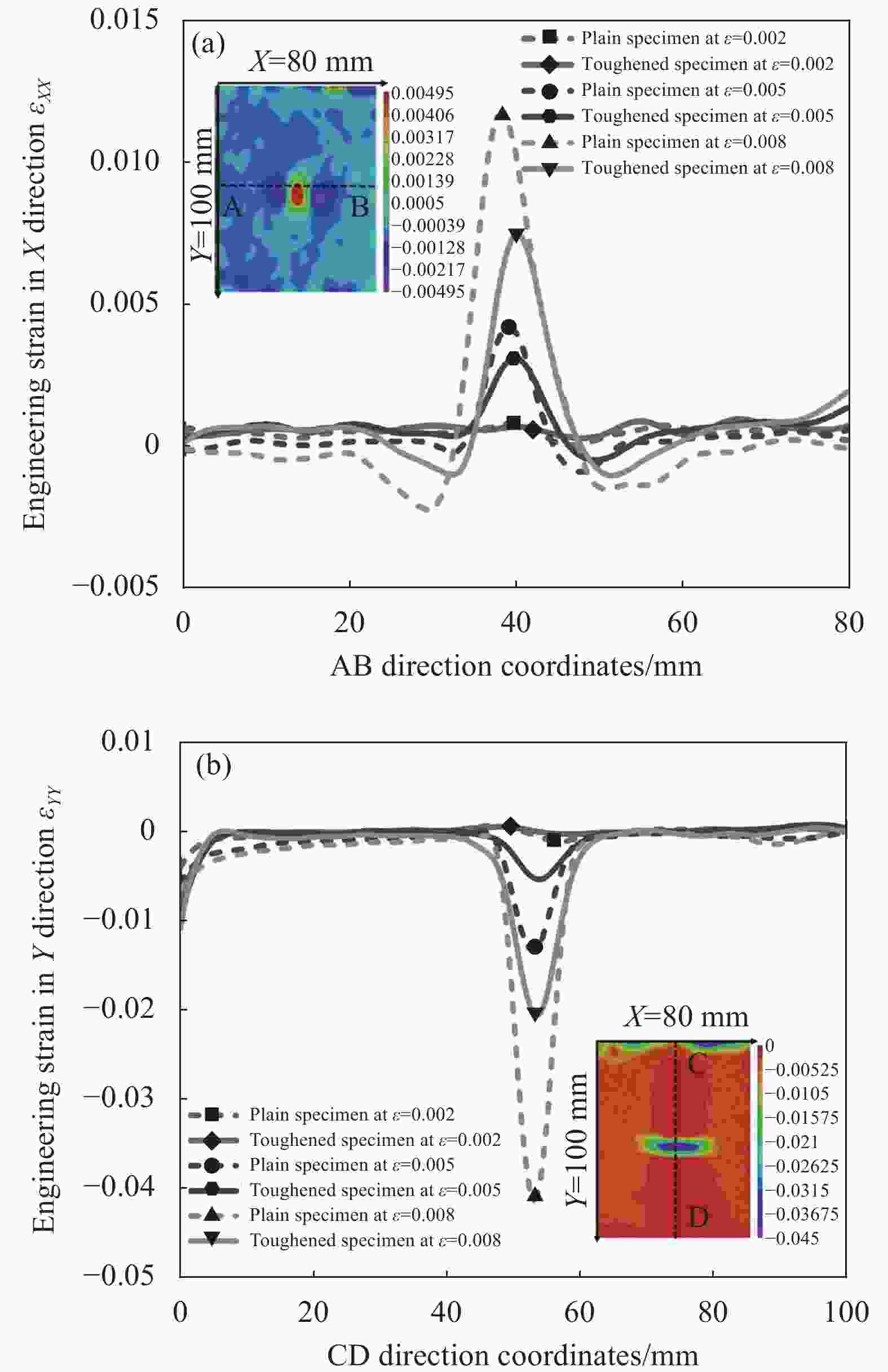
表 2 Kevlar短纤维界面增韧与未增韧碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板在20 J能量冲击后压缩过程中不同压缩应变对应的工程应变云图
Table 2. Engineering strain nephograms of carbon-fiber/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich panels with and without short-Kevlar-fiber toughening at different compression strain under the impact energy of 20 J
Engineering strain Plain specimen Toughened specimen $ \varepsilon $ =0.002 $ \varepsilon $ =0.005 $ \varepsilon $ =0.008 $ \varepsilon $ =0.002 $ \varepsilon $ =0.005 $ \varepsilon $ =0.008 $ {\varepsilon }_{YY} $ 





$ {\varepsilon }_{XX} $ 





$ {\varepsilon }_{XY} $ 





Notes: $ { \varepsilon } $—Average compression strain; $ {\varepsilon }_{YY} $—Engineering strain in Y direction; $ {\varepsilon }_{XX} $—Engineering strain in X direction; $ {\varepsilon }_{XY} $—Shear strain. -
[1] DAS T K, GHOSH P, DAS N C. Preparation, development, outcomes, and application versatility of carbon fiber-based polymer composites: A review[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials,2019,2(2):214-233. doi: 10.1007/s42114-018-0072-z [2] BIRMAN V, KARDOMATEAS G A. Review of current trends in research and applications of sandwich structures[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,142:221-240. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.027 [3] SHIN K B, LEE J Y, CHO S H. An experimental study of low-velocity impact responses of sandwich panels for Korean low floor bus[J]. Composite Structures,2008,84(3):228-240. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.08.002 [4] HE W T, LU S J, YI K, et al. Residual flexural properties of CFRP sandwich structures with aluminum honeycomb cores after low-velocity impact[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2019,161:105026. [5] YANG B, WANG Z Q, ZHOU L M, et al. Study on the low-velocity impact response and CAI behavior of foam-filled sandwich panels with hybrid facesheet[J]. Composite Structures,2015,132:1129-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.07.058 [6] SUN X C, HALLETT S R. Failure mechanisms and damage evolution of laminated composites under compression after impact (CAI): Experimental and numerical study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,104:41-59. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.10.026 [7] BHATTACHARYYA R, BASU P. Multiscale progressive damage analysis of CFRP composites using a mechanics based constitutive relation[J]. Composite Structures,2020,235:111759. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111759 [8] ZHANG D H, JIANG D, FEI Q G, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on indentation and energy absorption of a honeycomb sandwich panel under low-velocity impact[J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design,2016,117-118:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.finel.2016.04.003 [9] LIU J X, HE W T, XIE D, et al. The effect of impactor shape on the low-velocity impact behavior of hybrid corrugated core sandwich structures[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,111:315-331. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.11.060 [10] 齐佳旗, 段玥晨, 铁瑛, 等. 结构参数对CFRP蒙皮-铝蜂窝夹层板低速冲击性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1352-1363.QI Jiaqi, DUAN Yuechen, TIE Ying, et al. Effect of structural parameters on the low-velocity impact performance of aluminum honeycomb sandwich plate with CFRP face sheets[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1352-1363(in Chinese). [11] WANG J, WAAS A M, WANG H. Experimental and numeri-cal study on the low-velocity impact behavior of foam-core sandwich panels[J]. Composite Structures,2013,96:298-311. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.09.002 [12] WU Y H, LIU Q, FU J, et al. Dynamic crash responses of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP panels[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,121:122-133. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.030 [13] ZHANG X Y, XU F, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on damage behavior of honeycomb sandwich panel subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures,2020,236:111882. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.111882 [14] YANG X F, XI X L, PAN Q F, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing of a novel circular-celled honeycomb nested with petal-shaped mesostructure[J]. Composite Structures,2019,226:111219. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111219 [15] 张亚文, 陈秉智, 石姗姗, 等. 格栅-蜂窝混式芯体夹芯结构的低速冲击性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):386-394.ZHANG Yawen, CHEN Bingzhi, SHI Shanshan, et al. Low-velocity impact performance of grid-honeycomb hybrid core sandwich structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):386-394(in Chinese). [16] ZHANG Y W, YAN L L, ZHANG C, et al. Low-velocity impact response of tube-reinforced honeycomb sandwich structure[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2021,158:107188. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107188 [17] 仲越, 徐铭涛, 王萍, 等. 碳纤维-超高分子量聚乙烯纤维混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料低速冲击性能及失效机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3202-3211.ZHONG Yue, XU Mingtao, WANG Ping, et al. Low-velocity impact properties and failure mechanism of carbon fiber-UHMWPE fiber hybrid reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3202-3211(in Chinese). [18] JIANG H Y, CHENG F, HU Y S, et al. Micro-mechanics modeling of compressive strength and elastic modulus enhancements in unidirectional CFRP with aramid pulp micro/nano-fiber interlays[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2021,206(2):108664. [19] SUN Z, CHEN H J, SONG Z W, et al. Three-point bending properties of carbon fiber/honeycomb sandwich panels with short-fiber tissue and carbon-fiber belt interfacial toughening at different loading rate[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2021,143(5):106289. [20] 郑昊, 李岩, 涂昊昀. 短纤维插层碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料层间性能研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8):3674-3683.ZHENG Hao, LI Yan, TU Haoyun. Research on interlayer properties of short fiber intercalated carbon fiber/epoxy composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(8):3674-3683(in Chinese). [21] YUAN B Y, YE M X, HU Y S, et al. Flexure and flexure-after-impact properties of carbon fibre composites interleaved with ultra-thin non-woven aramid fibre veils[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2020,131:1-10. [22] YUAN B Y, TAN B, HU Y S, et al. Improving impact resistance and residual compressive strength of carbon fibre composites using un-bonded non-woven short aramid fibre veil[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,121:105813. [23] SUN Z, HU X Z, CHEN H R. Effects of aramid-fibre toughening on interfacial fracture toughness of epoxy adhesive joint between carbon-fibre face sheet and aluminium substrate[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives,2014,48:288-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2013.09.023 [24] SUN Z, SHI S S, HU X Z, et al. Adhesive joints between carbon fiber and aluminum foam reinforced by surface-treated aramid fibers[J]. Polymer Composites,2015,36(1):192-197. doi: 10.1002/pc.22929 [25] SHI S S, SUN Z, HU X Z, et al. Carbon-fiber and aluminum-honeycomb sandwich composites with and without Kevlar-fiber interfacial toughening[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2014,67:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.08.017 [26] 刘浩洋, 吕超雨, 石姗姗, 等. 芳纶纤维增韧碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料-铝蜂窝夹芯结构界面性能和增韧机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2):567-575.LIU Haoyang, LV Chaoyu, SHI Shanshan, et al. Interfacial toughening and toughening mechanism of aramid staple fiber to carbon fiber/aluminum honeycomb sandwich structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(2):567-575(in Chinese). [27] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for measuring the resistance of a fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/D7136M-2015[S]. West Conshohockens: American Society for Testing and Materials International, 2015. [28] SCHOEPPNER G A, ABRTE S. Delamination threshold loads for low velocity impact on composite laminates[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2000, 31(9): 903-915. [29] 屈天骄, 郑锡涛, 范献银, 等. 复合材料层合板低速冲击损伤影响因素分析[J]. 航空材料学报, 2011, 31(12):81-86.QU Tianjiao, ZHENG Xitao, FAN Xianyin, et al. Exploration of several influence factors of low-velocity impact damage on composite laminates[J]. Journal of Aeronauti-cal Materials,2011,31(12):81-86(in Chinese). [30] 管清宇, 冯剑飞, 夏品奇, 等. 复合材料层压板低速冲击行为及剩余拉伸强度[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(6):1220-1232.GUAN Qingyu, FENG Jianfei, XIA Pinqi, et al. Low velocity impact behavior and residual tensile strength of compo-site laminates[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2021,47(6):1220-1232(in Chinese). [31] SUN Z, JEYARAMAN J, SUN S Y, et al. Carbon-fiber aluminum-foam sandwich with short aramid-fiber interfacial toughening[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(11):2059-2064. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.06.002 [32] 石姗姗, 陈秉智, 陈浩然, 等. Kevlar短纤维增韧碳纤维/铝蜂窝夹芯板三点弯曲与面内压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(9):1953-1959.SHI Shanshan, CHEN Bingzhi, CHEN Haoran, et al. Three-point bending and in-plane compression properties of carbon-fiber/aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels with short-Kevlar-fiber toughening[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(9):1953-1959(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: