Preparation and properties of jackfruit seeds starch biodegradable composite film
-
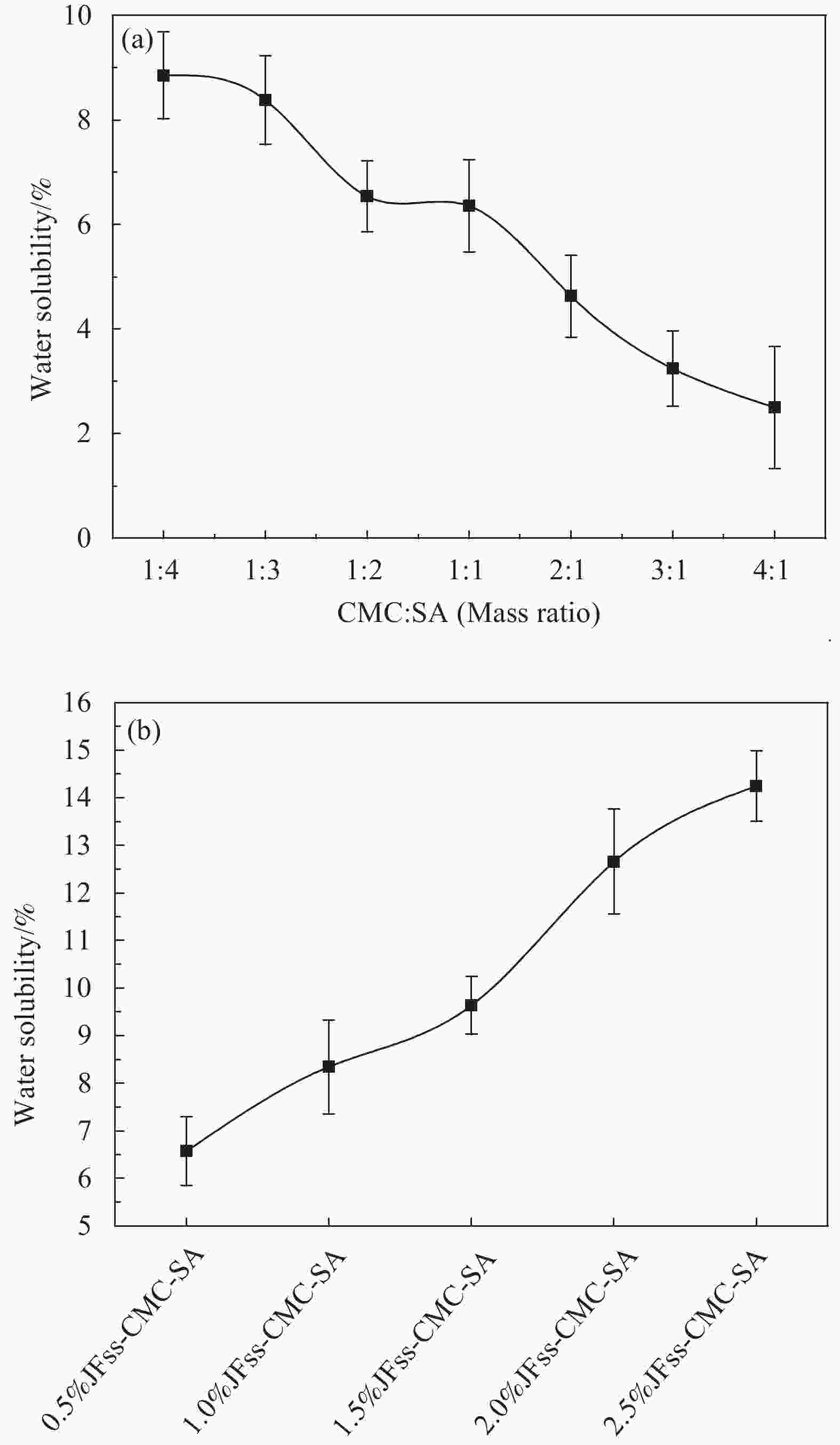
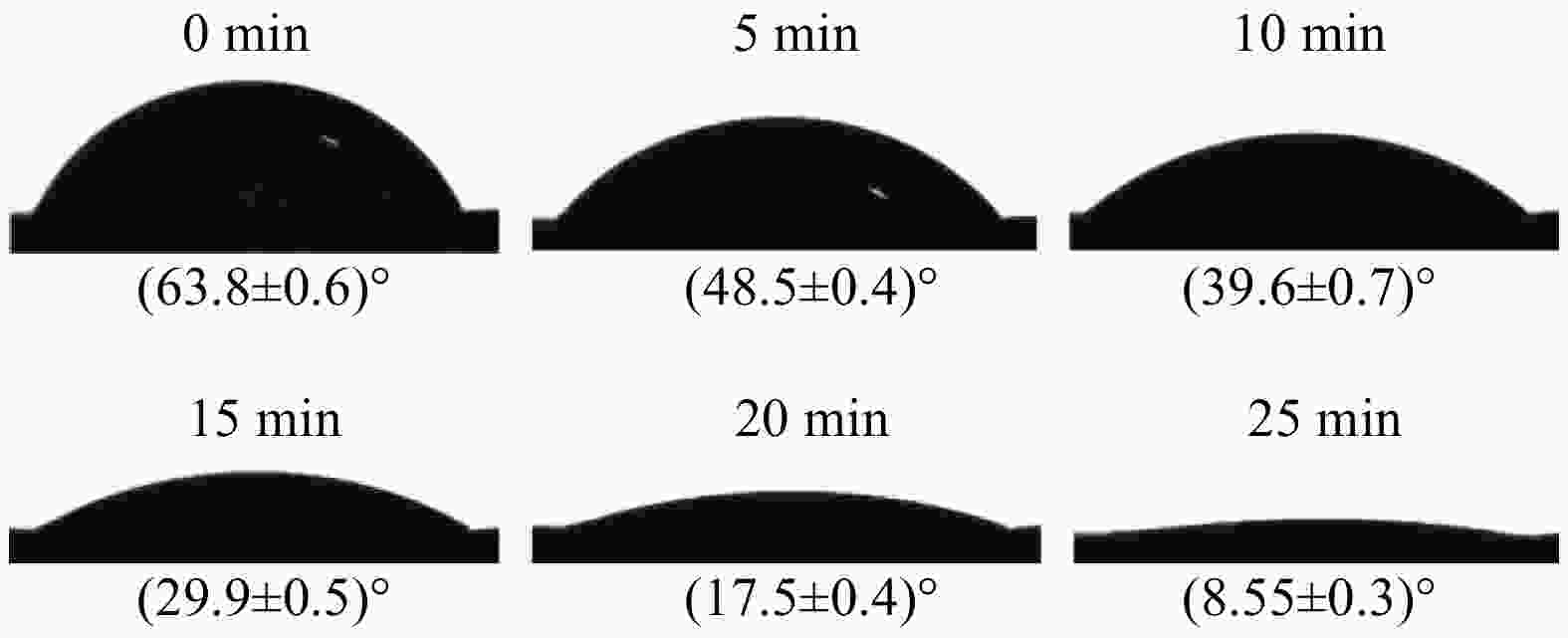
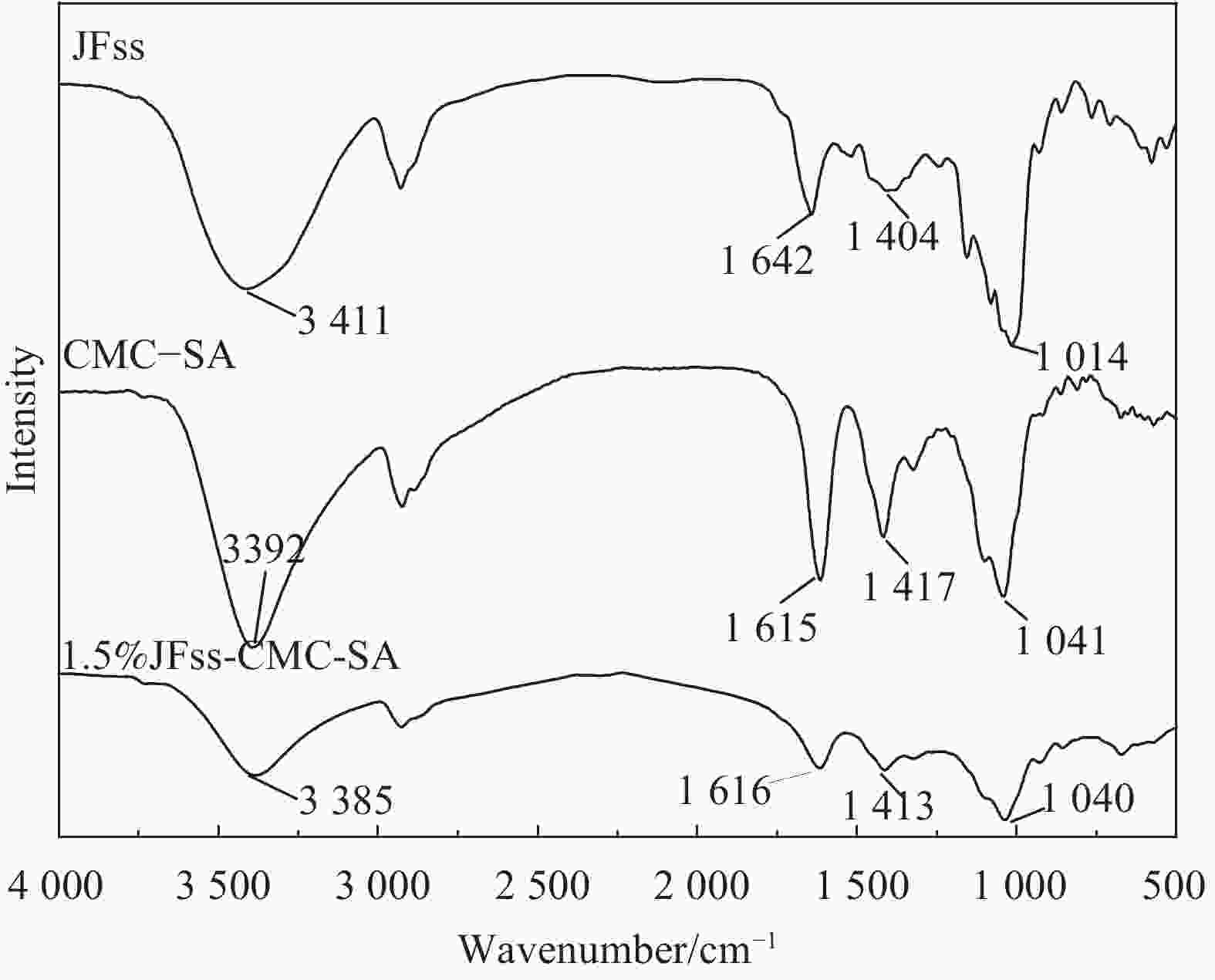
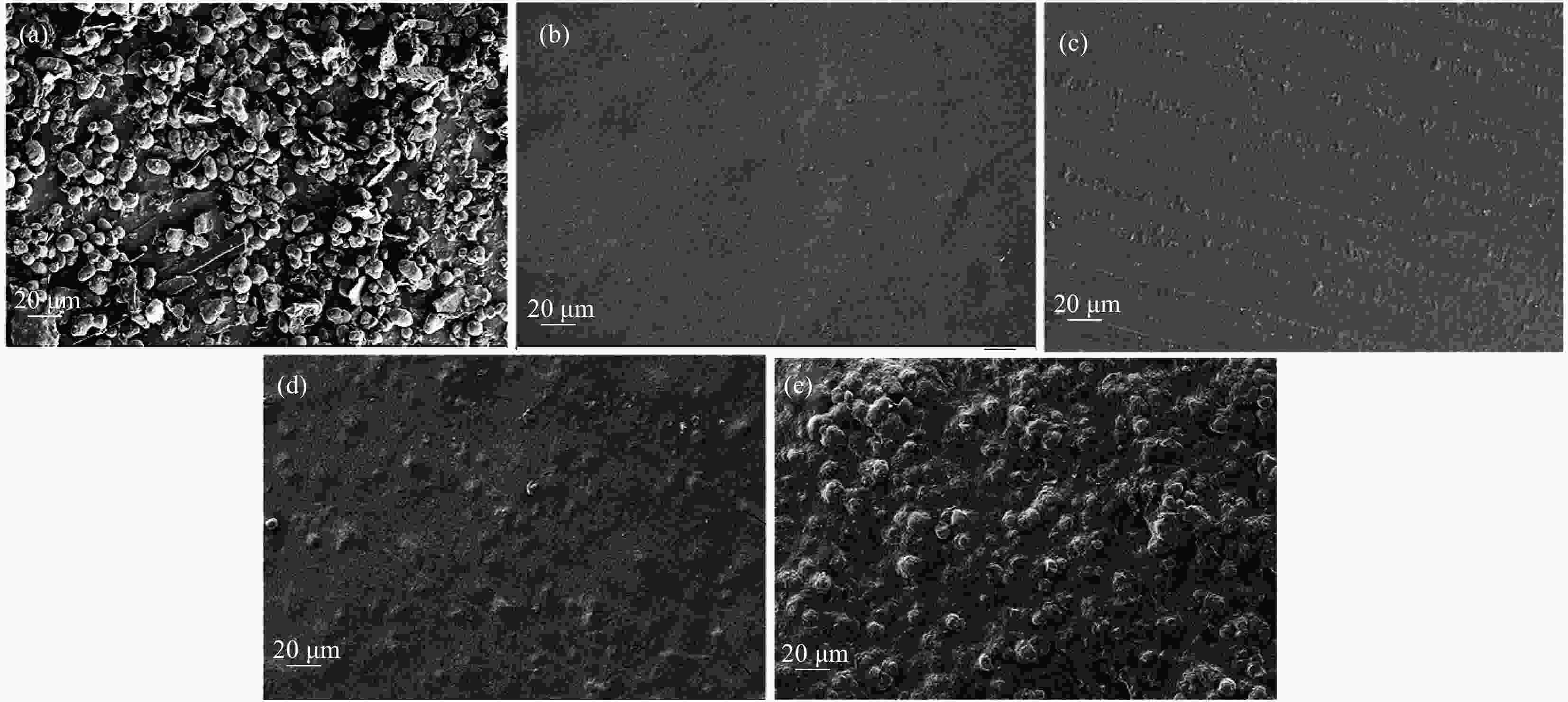
摘要: 针对传统塑料制品难降解、污染环境等问题,选用环境友好、可降解菠萝蜜种子淀粉(JFss)、羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC)和海藻酸钠(SA)为原料,采用涂膜工艺制备了一种可生物降解复合膜。研究JFss的用量对复合膜力学性能、耐水性、水溶性、透湿性的影响及复合膜润湿性随着时间变化规律,并对复合膜进行土埋降解性测试。采用SEM、FITR、XRD和TGA对复合膜形貌、结构和热稳定性表征。结果表明,JFss的添加使复合膜拉伸强度提高35.8%,耐水性提高4.16%,水溶性提高7.8%,水蒸汽阻隔性提高153.7%,且具有良好的润湿性、保湿性和生物降解性。另外,复合膜中CMC、SA、JFss各组分形成分子间氢键,具有良好的相容性和热稳定性。本方法复合膜制备的原料廉价、制备简单,可大规模生产,在生物降解材料领域具有潜在的应用价值。Abstract: Aiming at the problems of traditional plastic products which are difficult to degrade and pollute the environment, this work selects environmentally friendly and degradable Jackfruit seeds starch (JFss), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and sodium alginate (SA) as raw materials and prepares a biodegradable composite film by a coating process. The effects of the amount of JFss on the mechanical properties, water resistance, water solubility and moisture permeability of the composite membrane were investigated, as well as the changes of the wettability of the composite membrane with time, and the composite membrane was tested for soil burial degradability. SEM, FITR, XRD and TGA were used to characterize the morphology, structure and thermal stability of the composite films. The results show that the addition of JFss increases the tensile strength of the composite film by 35.8%, water resistance by 4.16%, water solubility by 7.8%, water vapor barrier by 153.7%, and has good wettability, moisture retention and biodegradability. In addition, each component of CMC, SA and JFss in the composite film forms intermolecular hydrogen bonds, which have good compatibility and thermal stability. The raw materials for the preparation of composite film by this method are inexpensive, simple to prepare, and can be produced on a large scale, which have potential applications in the field of biodegradable materials.
-
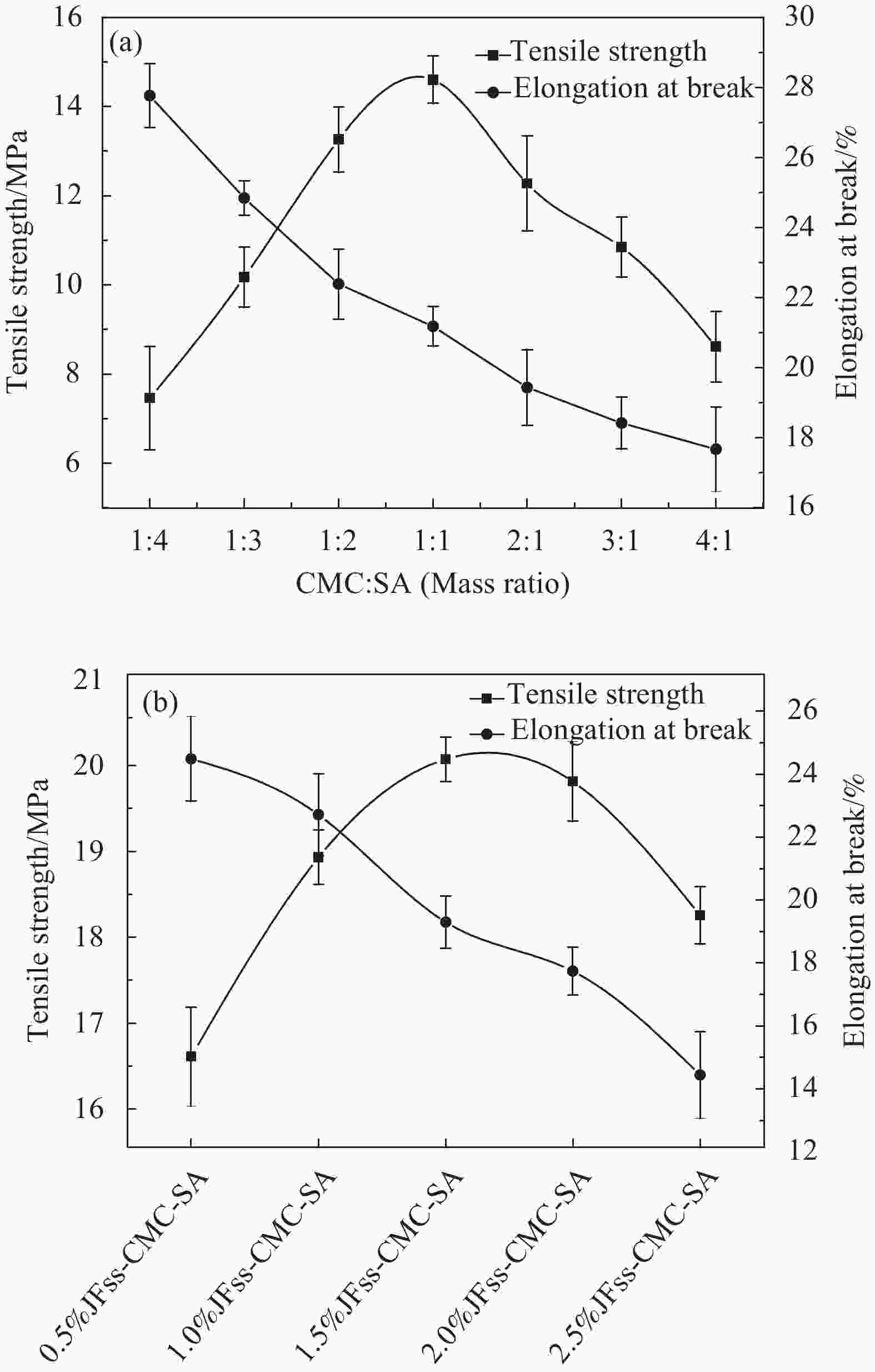
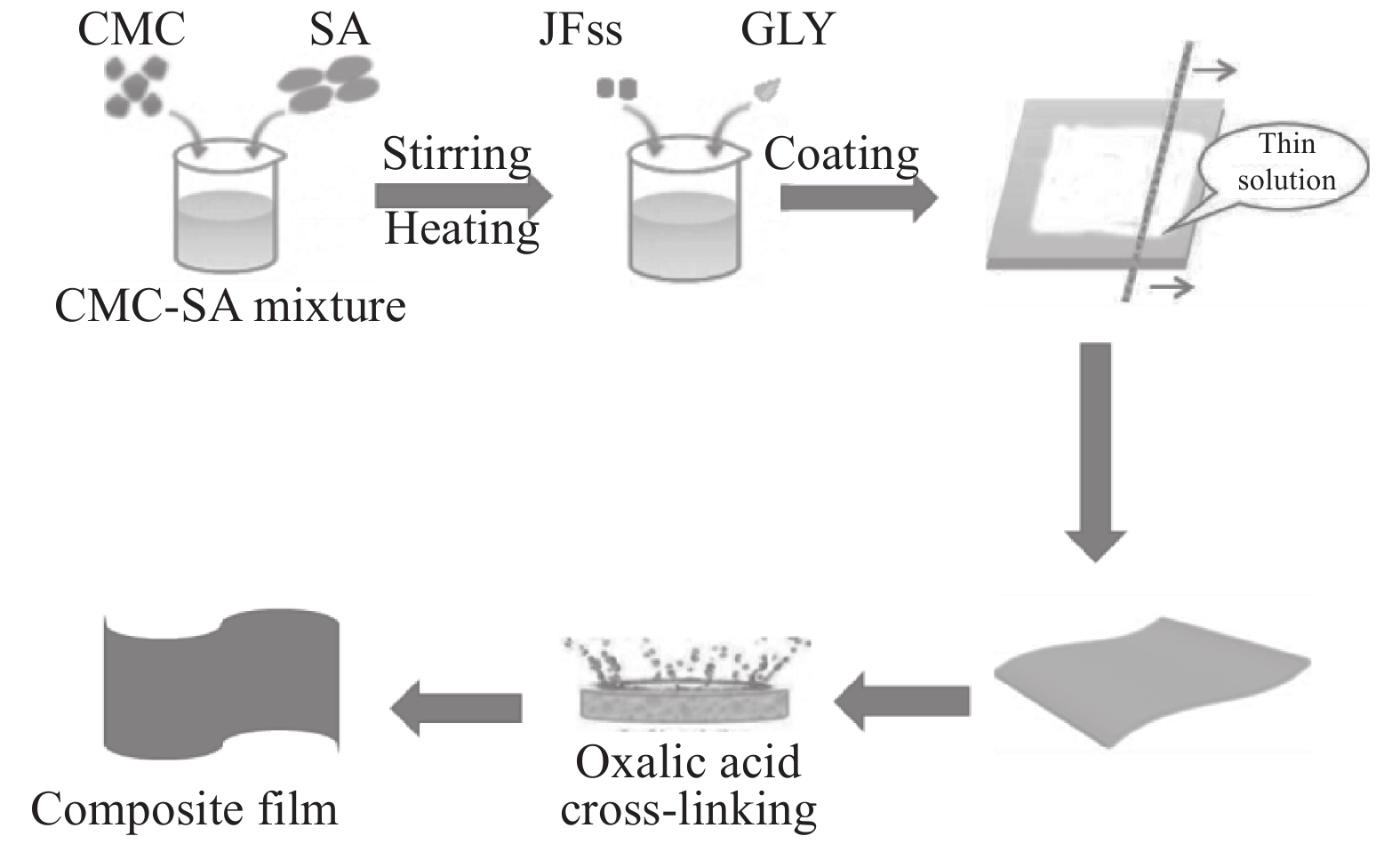
表 1 羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC)-海藻酸钠(SA)复合膜各组分配比
Table 1. Proportions of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)-sodium alginate (SA) composite films
Number CMC/
gSA/
gDW/
mLGLY/
mLCMC∶SA
(Mass ratio)1 0.24 0.96 40 0.6 1∶4 2 0.3 0.9 40 0.6 1∶3 3 0.4 0.8 40 0.6 1∶2 4 0.6 0.6 40 0.6 1∶1 5 0.8 0.4 40 0.6 2∶1 6 0.9 0.3 40 0.6 3∶1 7 0.96 0.24 40 0.6 4∶1 Notes: DW—Deionized water; GLY—Glycerin. 表 2 菠萝蜜种子淀粉(JFss)-CMC-SA复合膜各组分配比
Table 2. Proportions of jackfruit seed starch (JFss)-CMC-SA composite films
Sample JFss/g CMC/g SA/g 0.5%JFss-CMC-SA 0.006 0.6 0.6 1.0%JFss-CMC-SA 0.012 0.6 0.6 1.5%JFss-CMC-SA 0.018 0.6 0.6 2.0%JFss-CMC-SA 0.024 0.6 0.6 2.5%JFss-CMC-SA 0.03 0.6 0.6 -
[1] RAI P, MEHROTRA S, PRIYA S, et al. Recent advances in the sustainable design and applications of biodegradable polymers[J]. Bioresource Technology,2021,325(1):124739. [2] SHRIVASTAVA A, DONDAPATI S. Biodegradable compo-sites based on biopolymers and natural bast fibres: A review[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2021,2:652. [3] ZHANG Y J, LI B, ZHANG Y T, et al. Effect of degree of polymerization of amylopectin on the gelatinization properties of Jackfruit seed starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,107(11):268-283. [4] 钟旋, 简秀梅, 蒋恩臣, 等. 稻壳生物炭/醋酸酯淀粉-尿素复合膜的结构和性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(7):1746-1752.ZHONG Xuan, JIAN Xiumei, JIANG Enchen, et al. Structure and properties of rice husk biochar/acetate starch-ureastarch composite films[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(7):1746-1752(in Chinese). [5] ABID U, GILL Y Q, IRFAN M S, et al. Potential applications of polycarbohydrates, lignin, proteins, polyacids, and other renewable materials for the formulation of green elastomers[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,181:1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.057 [6] LIU D, ZHAO K Y, QI M, et al. Preparation of protein molecular-imprinted polysiloxane membrane using calcium alginate film as matrix and its application for cell culture[J]. Polymers (Basel),2018,10:170. doi: 10.3390/polym10020170 [7] GALIANO F, BRICENO K, MARINOA T, et al. Advances in biopolymer-based membrane preparation and applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2018,564(5):562-586. [8] ZHANG Y J, ZHANG Y T, XU F, et al. Structural characterization of starches from chinese Jackfruit seeds (artocarpus heterophyllus lam)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,80:141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.015 [9] ZHANG Y T, ZHANG Y J, LI B, et al. In vitro hydrolysis and estimated glycemic index of Jackfruit seed starch prepared by improved extrusion cooking technology[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:1109-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.075 [10] SURYADEVARA V, LANKAPALLI S R, DANDSA L H, et al. Studies on Jackfruit seed starch as a novel natural superdisintegrant for the design and evaluation of irbesartan fast dissolving tablets[J]. Integrative Medicine Research,2017,6:280. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2017.04.001 [11] ZHANG Y J, HU M J, ZHU K X, et al. Functional properties and utilization of Artocarpus Heterophyllus Lam seed starch from new species in China[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,107:1395-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.001 [12] ZHANG Y T, LI B, ZHANG Y J, et al. Effect of degree of polymerization of amylopectin on the gelatinization properties of Jackfruit seed starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,289(3):152-159. [13] ZHU H M, ZHANG Y J, TIAN J W, et al. Effect of a new shell material-Jackfruit seed starch on novel flavor microcapsules containing vanilla oil[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2018,112(7):47-52. [14] ZHANG Y J, ZUO H Y, XU F, et al. The digestion mechanism of Jackfruit seed starch using improved extrusion cooking technology[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,110(6):106154. [15] JIANG T Y, DUAN Q F, ZHU J, et al. Starch-based biodegradable materials: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research,2020,3(1):8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.aiepr.2019.11.003 [16] BONOMO R C F, SANTOS T A, SANTOS L S, et al. Effect of the incorporation of lysozyme on the properties of Jackfruit starch films[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2018,26:508. doi: 10.1007/s10924-016-0902-4 [17] SANTANA R F, BONOMO R C F, GANDOLFI O R R, et al. Characterization of starch-based bioplastics from Jackfruit seed plasticized with glycerol[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,55:278. [18] WANG R J, LI X J, REN Z Y, et al. Characterization and antibacterial properties of biodegradable films based on CMC, mucilage from dioscorea opposita Thunb. and Ag nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,163:2189-2198. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.115 [19] 陈港, 胡稳, 朱朋辉, 等. 高透明羧甲基纤维素/纤维素纤维复合薄膜的制备及其力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(6):1574-1581.CHEN Gang, HU Wen, ZHU Penghui, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of highly transparent carboxymethyl cellulose/cellulose fiber composite films[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(6):1574-1581(in Chinese). [20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 塑料拉伸性能的测定: GB/T 1040—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.General Administration of Quality Supervision, In section and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics-Determination of tensile properties: GB/T 1040—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006(in Chinese) [21] 国家技术监督局. 漆膜耐水性测定法: GB/T 1733—93[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993.The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Determination of resistance to water of films: GB 1733—93[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 1993(in Chinese). [22] ASTM. Standard test methods for water vapor transmission of materials: ASTM E96/E96M—05[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials, 2005. [23] KONG W J, LI Q, LI X D, et al. A biodegradable biomass-based polymeric composite for slow release andwater retention[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2019,230:190-198. [24] JAYARAMUDU J, REDDY G S M, VARAPRASAD K, et al. Preparation and properties of biodegradable films from sterculia urens short fiber/cellulose green composites[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,93:622. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.032 [25] CHEN Q F, SHI Y H, CHEN G X, et al. Enhanced mechanical and hydrophobic properties of composite cassava starch films with stearic acid modified MCC (microcrystalline cellulose)/NCC (nanocellulose) as strength agent[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,142:846-854. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.024 [26] BADIGER H, SHUKLA S, KALYANI S, et al. Thin film composite sodium alginate membranes for dehydration of acetic acid and isobutanol[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2014,131(6):131. [27] NGUYEN VU H P, LUMDUBWONG N. Starch behaviors and mechanical properties of starch blend films with different plasticizers[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,154:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.034 [28] SIFUENTES-NIEVES I, FLORES-SILVA P C, GALLARDO-VEGA C, et al. Films made from plasma-modified corn starch: chemical, mechanical and barrier properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,237(2):116103. [29] MARAN J P, SIVAKUMAR V, THIRUGNANASAMBANDHAM K, et al. Modeling and analysis of film composition on mechanical properties of maize starch based edible films[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,62:565. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.09.027 [30] CHENG S, LIU X M, ZHEN J H, et al. Preparation of superabsorbent resin with fast water absorption rate based on hydroxymethyl cellulose sodium and its application[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,225(8):115214. [31] WANG Q Q, ZHANG G Q, ZHANG L, et al. Mechanical properties and water absorption of alginate/hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose blend membranes with semi-interpenetrating network[J]. Fibers Polymers,2020,21:1403. doi: 10.1007/s12221-020-9854-3 [32] FLORENCIAl V, LOPEZ O V, GARCIA M A,. Exploitation of by-products from cassava and ahipa starch extraction as filler of thermoplastic corn starch[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,182:107653. [33] XU C J, CHEN C, WU D F. The starch nanocrystal filled biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone) composite membrane with highly improved properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,182:115. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.001 [34] BAHREMAND A H, MOUSAVI S M, AHMADPOUR A, et al. Biodegradable blend membranes of poly (butylene succinate)/cellulose acetate/dextran: Preparation, characterization and performance[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,173:497. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.010 [35] SINTIM H Y, BARY A I, HAYES D G, et al. In situ degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in compost and agricultural soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,727:138668. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138668 [36] 郑霞, 李新功, 吴义强, 等. 竹纤维/聚乳酸可生物降解复合材料自然降解性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(2):363-367.ZHENG Xia, LI Xingong, WU Yiqiang, et al. Natural degradation properties of bamboo fibers/polylactic acid biodegradable composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(2):363-367(in Chinese). [37] VONON BORRIE-MEDRANOS E, JAIME-FONSECA M R, AGUILAR-MENDEZ M A, et al. Starch-guar gum extrudates: microstructure, physicochemical properties and in-vitro digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:891. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.085 [38] ANDREUCCETTI C, CARVALHO R A, GALICIA-GARCÍA T, et al. Effect of surfactants on the functional properties of gelatin-based edible films[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2011,103:129. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.10.007 [39] LAN W T, ZHANG R, JI T T, et al. Improving nisin production by encapsulated lactococcus lactis with starch/carboxymethyl cellulose edible films[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,251:117062. [40] ZHANG Y J, ZHU K X, HE S Z, et al. Characterizations of high purity starches isolated from five different Jackfruit Cultivars[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,52:785. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.07.037 [41] WANG Z Y, QIAO X Y, SUN K. Rice straw cellulose nanofibrils reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) composite films[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,197(4):442-450. [42] TAVARES K M, CAMPOS A D, MITSUYUKI M C, et al. Corn and cassava starch with carboxymethyl cellulose films and its mechanical and hydrophobic properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,223(6):115055. [43] TAVARES K M, CAMPOS A D, LUCHESI B R, et al. Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose concentration on mechanical and water vapor barrier properties of corn starch films[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,246(2):116521. -





 下载:
下载: