Friction and wear properties of TC4 titanium alloy with high-speed nitriding treatment
-
摘要: 为了改善TC4钛合金表面硬度、耐磨性较差的缺点,本文提出了基于超快高温烧结(UHS)工艺的快速渗氮处理(HSNT)表面处理方法。对TC4钛合金表面进行HSNT,利用X射线衍射仪和扫描电子显微镜研究试样的微观组织,采用维氏显微硬度计和摩擦磨损试验装置对试样进行力学性能测试。2 min即可在TC4钛合金表面形成改性层,改性层由两部分组成,最表层为氮化物层,厚度10 μm,平均显微硬度为 HV0.1 973.55,主要成分为TiN;次表层为渗氮层,厚度10 μm,平均显微硬度为HV0.1 774.53 ,截面显微硬度整体呈现出阶梯分布的趋势。摩擦磨损试验发现,在20 N载荷下,经过HSNT的TC4的摩擦系数为0.406,降低了24.4%,经过HSNT的TC4的磨损体积为0.302 mm3,降低了86.7%。不同载荷下经过HSNT的TC4的摩擦系数和磨损体积始终小于TC4钛合金,且均随着载荷的增加而增大。在20 N载荷下,TC4的磨损机制主要表现为磨粒磨损和氧化磨损,经过HSNT的TC4的磨损机制主要表现为粘着磨损和氧化磨损。经过HSNT的TC4钛合金的性能得到了明显的改善,弥补了TC4硬度低、耐磨性差的缺点。Abstract: In order to improve the surface hardness and wear resistance of TC4 titanium alloy, a high-speed nitriding treatment (HSNT) based on ultrafast high-temperature sintering (UHS) process was proposed. HSNT was applied to the surface of TC4 titanium alloy, and the microstructure of the sample was studied by X-ray diffractometer and scanning electron microscope. The mechanical properties of the sample were tested by Vickers microhardness tester and friction and wear test device. The modified layer can be formed on the surface of TC4 titanium alloy in 2 min. The modified layer consists of two parts. The outermost layer is the nitride layer, the thickness is about 10 μm, the average microhardness is HV0.1 973.55, and the main component is TiN. The sub-surface layer is nitriding layer, the thickness is also about 10 μm, the average microhardness is HV0.1 774.53, the cross-section microhardness overall shows a trend of ladder distribution. The friction and wear test shows that under 20 N load, the friction coefficient of TC4 with HSNT is 0.406, which is reduced by 24.4%, and the wear volume of TC4 with HSNT is 0.302 mm3, which is reduced by 86.7%. The friction coefficient and wear volume of TC4 with HSNT under different loads are always smaller than that of TC4 titanium alloy, and all increase with the increase of load. Under 20 N load, the wear mechanism of TC4 is mainly abrasive wear and oxidative wear, while the wear mechanism of TC4 with HSNT is mainly adhesive wear and oxidative wear. The performance of TC4 titanium alloy with HSNT has been significantly improved, making up for the shortcomings of low hardness and poor wear resistance of TC4.
-
-
表 1 TC4钛合金的元素成分(wt%)
Table 1 Elemental compositions of TC4 titanium alloy (wt%)
Ti Alloying element Impurity element Al V Fe Si C N H O Balance 5.5-6.8 3.5-4.5 ≤0.30 ≤0.10 ≤0.10 ≤0.05 <0.015 <0.015 表 2 摩擦磨损试验参数
Table 2 Parameters of frictional wear test
Load/N Friction pair Temperature/℃ Rotate speed/(r·min−1) Time/min Radius/mm 5
20Si3N4 20 500 30 2 -
[1] FENG X, ZHAO Y, NING W. Application of the titanium alloy in civil aviation[J]. Baosteel Technical Research, 2011, 5(4): 25-35.
[2] DING R, GUO Z X. Microstructural evolution of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during β-phase processing: Experimental and simulative investigations[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 365(2): 172-179.
[3] 应扬, 李磊, 赵彬, 等. 钛合金的摩擦磨损性能及其改善方法[J]. 有色金属材料与工程, 2019, 40(3): 49-54. YING Yang, LI Lei, ZHAO Bin, et al. Friction and wear properties of titanium alloys and the improving methods[J]. Nonferrous Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 40(3): 49-54(in Chinese).
[4] 衣晓红, 樊占国, 张景垒, 等. TC4钛合金的固体渗硼[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(9): 1631-1635. YI Xiaohong, FAN Zhanguo, ZHANG Jinglei, et al. Solid-state pack boronizing of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(9): 1631-1635(in Chinese).
[5] ZUO S, MIAO Q, LIANG W, et al. Effects of pretreatment on borocarburized of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(5): 056505. DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab0070
[6] MENG Y G, BAI J, JIANG X J, et al. Effect of Zr on isothermal oxidation behavior of TC4 alloy at 600℃[J]. Vacuum, 2023, 213: 112112. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2023.112112
[7] RASTKAR A R, SHOKRI B, BELL T. Structural and mechanical evaluation of the effect of oxygen boost diffusion on a gamma based titanium aluminide of Ti-45Al-2Nb-2Mn-1B[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2008, 202(24): 6038-6048. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.07.001
[8] ÜSTEL F, ZEYTIN S. Growth morphology and phase analysis of titanium-based coating produced by thermochemical method[J]. Vacuum, 2006, 81(3): 360-365. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2006.06.011
[9] 谭金花, 孙荣禄, 牛伟, 等. TC4合金激光熔覆材料的研究现状[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(15): 15132-15137. TAN Jinhua, SUN Ronglu, NIU Wei, et al. Research status of TC4 alloy laser cladding materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(15): 15132-15137(in Chinese).
[10] KANYANE L R, ADESINA O S, POPOOLA A P, et al. Microstructural evolution and corrosion properties of laser clad Ti-Ni on titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V)[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 35: 1267-1272. DOI: 10.1016/j.promfg.2019.06.086
[11] FENG J, WANG J, YANG K, et al. Microstructure and performance of YTaO4 coating deposited by atmospheric plasma spraying on TC4 titanium alloy surface[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 431: 128004. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.128004
[12] WANG X, WANG X, SUN X, et al. Microstructure and properties evolution of plasma sprayed Al2O3-Y2O3 composite coatings during high temperature and thermal shock treatment[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2021, 39(6): 718-727. DOI: 10.1016/j.jre.2020.09.008
[13] LIN B, CHEN X, CHEN J, et al. Facile synthesis of homogeneously dispersed carbon nanotubes on TC4 alloy powder by in-situ CVD and its growth behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 24: 9928-9938. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.05.127
[14] SHI H, WANG Z, REN H, et al. The research on tool wear of high speed milling titanium alloy TC4[C]// Seventh International Conference on Electronics and Information Engineering. Nanjing: SPIE, 2017: 10322: 882-888.
[15] 杨闯, 刘静, 马亚芹, 等. TC4钛合金表面低压渗氮层的显微组织与耐磨性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2016, 40(6): 98-101. DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201606021 YANG Chuang, LIU Jing, MA Yaqin, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of low pressure nitrided layer on TC4 titanium alloy surface[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 40(6): 98-101(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201606021
[16] ZHU X S, FU Y D, LI Z F, et al. Wear resistance of TC4 by deformation accelerated plasma nitriding at 400℃[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(11): 2771-2776. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-016-3339-y
[17] YANG Y L, ZHAO G J, ZHANG D, et al. Improving the surface property of TC4 alloy by laser nitriding and its mechanism[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 19(2): 151-156.
[18] WEN K, ZHANG C, GAO Y. Influence of gas pressure on the low-temperature plasma nitriding of surface-nanocrystallined TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 436: 128327. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128327
[19] LIU G, LENG K, HE X, et al. Microstructure evolution of Ti-6Al-4V under cold rolling + low temperature nitriding process[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2022, 32(4): 424-432. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2022.06.004
[20] WANG C, PING W, BAI Q, et al. A general method to synthesize and sinter bulk ceramics in seconds[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6490): 521-526. DOI: 10.1126/science.aaz7681
[21] DONG J, POUCHLY V, BIESUZ M, et al. Thermally-insulated ultra-fast high temperature sintering (UHS) of zirconia: A master sintering curve analysis[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2021, 203: 114076. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114076
[22] BIESUZ M, GALOTTA A, MOTTA A, et al. Speedy bioceramics: Rapid densification of tricalcium phosphate by ultrafast high-temperature sintering[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2021, 127: 112246. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112246
[23] GUO R F, MAO H R, ZHAO Z T, et al. Ultrafast high-temperature sintering of bulk oxides[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2021, 193: 103-107. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.045
[24] LI L H, CHEN Y. Atomically thin boron nitride: Unique properties and applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(16): 2594-2608. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201504606
[25] 王培, 叶源盛. 钛合金表面激光熔覆h-BN固体润滑涂层[J]. 表面技术, 2015, 44(8): 44-48. WANG Pei, YE Yuansheng. Solid self-lubricating coatings on TC4 titanium alloy by laser cladding with h-BN[J]. Surface Technology, 2015, 44(8): 44-48(in Chinese).
[26] 杨闯, 彭晓东, 刘静, 等. TC4钛合金低压真空渗氮处理[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2014, 34(11): 1146-1149. YANG Chuang, PENG Xiaodong, LIU Jing, et al. Surface modification of TC4 titanium alloy by low pressure nitriding[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2014, 34(11): 1146-1149(in Chinese).
[27] 胡林泉, 缪强, 梁文萍, 等. 载荷对经氧-氮共渗的TC4钛合金摩擦学性能的影响[J]. 热处理, 2019, 34(3): 1-10. HU Linquan, MIAO Qiang, LIANG Wenping, et al. Effect of loads on tribological characteristics of oxynitrided TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment, 2019, 34(3): 1-10(in Chinese).
[28] LEE H, KANG H, KIM J, et al. Inward diffusion of Al and Ti3Al compound formation in the Ti-6Al-4V alloy during high temperature gas nitriding[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2014, 240: 221-225. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.12.027
[29] AICH S, RAVI CHANDRAN K S. TiB whisker coating on titanium surfaces by solid-state diffusion: Synthesis, microstructure, and mechanical properties[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33: 3489-3498. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-002-0336-6
[30] ZHANG H, CUI H, MAN C, et al. The tribocorrosion resistance of TiN+TiB/TC4 composite coatings and the synergistic strengthening effects of multi-level reinforcements[J]. Corrosion Science, 2023, 219: 111224. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2023.111224
[31] XIAO H, LIU X, LU Q, et al. Promoted low-temperature plasma nitriding for improving wear performance of arc-deposited ceramic coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy via shot peening pretreatment[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022, 19: 2981-2990. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.06.067
[32] 李景阳, 王文波, 秦林, 等. TD3钛合金离子渗氮层的摩擦磨损性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2021, 46(9): 258-261. LI Jingyang, WANG Wenbo, QIN Lin, et al. Friction and wear properties of nitrided layer of TD3 titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021, 46(9): 258-261(in Chinese).
[33] CHEN W, ZHENG J, LIN Y, et al. Comparison of AlCrN and AlCrTiSiN coatings deposited on the surface of plasma nitrocarburized high carbon steels[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 332: 525-532. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.212
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李佥,王添誉,孙西同,陈晓艺,李苗,韩雨擎,曾祥冰,孙芳鸿,李宪臻. 贻贝仿生修饰多孔磁性材料的制备及其在固定化脂肪酶中的应用. 复合材料学报. 2024(11): 6156-6169 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)
-
目的
TC4钛合金(Ti-6Al-4V)具有良好的耐腐蚀性、优异的热稳定性、轻质等优点,普遍应用于航空航天、交通运输、生物医学等重要领域。但是TC4钛合金的表面硬度低、耐磨性较差,限制了钛合金的使用性能和应用范畴。表面渗氮技术能在钛合金表面形成氮化钛硬化层,具有硬度高、耐磨性好、化学稳定性好的特点,能够改善钛合金的硬度低、耐磨性差的缺点,但是目前的表面渗氮技术需要的时间较长,需要10 h乃至以上。于是本文提出了一种High-speed Nitriding Treatment(HSNT)快速渗氮处理的工艺,2 min便可在TC4钛合金表面形成改性层,大大缩短了形成改性层的时间,降低了成本。
方法采用Ultrafast high-temperature sintering(UHS)超快高温快速烧结工艺所用的热源装置替代现有设备中的热源装置,热源装置的核心部件仅由石墨毡与直流电源组成,当石墨毡通直流电时,便会以大约10~10℃/min的速度快速升温,其核心区域的温度可高达3000℃,在其附近可以形成一个高温温度场,断电后石墨毡也会以10 ℃/min的冷却速度快速冷却。实验材料为TC4钛合金棒材,渗氮材料选择的粒径为5~10 μm的h-BN粉末。HSNT工艺流程主要包括涂层浆料制备、冷涂覆以及HSNT三部分。实验后采用采用D8 ADVANCE X射线衍射仪(XRD)对改性层进行物相分析, 采用JSM-7800型场发射扫描电镜(FE-SEM)对改性层的表面形貌、组织形态进行观察,同时采用扫描电镜自带的能谱仪(EDS)分析改性层表面及截面的元素及分布。采用HXS-1000TAC型号维氏显微硬度计测定改性层的硬度。采用HT-1000型常规球盘磨损试验装置研究室温干摩擦条件下改性层的摩擦磨损行为,并采用VK-X200型激光显微镜和JSM-7800型场发射扫描电镜观察分析磨痕形貌。
结果经过HSNT的TC4钛合金的改性层主要由两部分组成,最表层为氮化物层,主要成分为TiN和少量的TiO,有部分孔洞,厚度10 μm,次表层为渗氮层,主要成分为钛-氮固溶体,组织致密,无孔洞和裂纹,厚度10 μm,次表层的N元素含量明显低于最表层。改性层各层之间有明显的界限,与基体结合良好,界面过渡连续。经过HSNT的TC4钛合金表面显微硬度为1018.3 HV,约为原材料的3.1倍。显微硬度整体呈现出阶梯分布的趋势,改性层的显微硬度从表层逐渐下降,直到趋近TC4钛合金的显微硬度。氮化物层平均显微硬度为973.55HV,渗氮层平均显微硬度为774.53 HV。在5 N载荷下,TC4钛合金的平均摩擦系数为0.322,经过HSNT的TC4平均摩擦系数约为0.284,降低了11.8%;在20 N载荷下,TC4钛合金的平均摩擦系数为0.537,经过HSNT的TC4平均摩擦系数约为0.406,降低了24.4%。TC4钛合金的磨损体积约为1.036 mm(5 N),2.268 mm(20 N),经过HSNT的TC4钛合金的磨损体积为0.074 mm(5 N),0.302 mm(20 N),分别降低了92.8%和86.7%。
结论经过HSNT的TC4钛合金的氮化物层形成了硬度较高的TiN相,并且在渗氮层中形成钛-氮固溶体,钛的晶格发生畸变,阻碍了位错运动,提高了硬度。在不同的载荷条件下进行干摩擦试验时,改性层的摩擦系数始终小于TC4钛合金, HSNT前后的TC4钛合金的摩擦系数均随着载荷的增加而增大。在20 N载荷下,TC4钛合金的磨损机制主要表现为磨粒磨损和氧化磨损,经过HSNT的TC4钛合金的磨损机制主要表现为粘着磨损和氧化磨损。
-
TC4钛合金(Ti-6Al-4V)具有良好的耐腐蚀性、优异的热稳定性、轻质等优点,普遍应用于航空航天、交通运输、生物医学等重要领域。但是TC4钛合金的表面硬度低、耐磨性较差,限制了钛合金的使用性能和应用范畴。表面渗氮技术能在钛合金表面形成氮化钛硬化层,具有硬度高、耐磨性好、化学稳定性好的特点,能够改善钛合金的硬度低、耐磨性差的缺点,但是目前的表面渗氮技术需要的时间较长,需要10 h乃至以上。
本文提出了基于超快高温烧结(UHS)工艺的快速渗氮处理(HSNT)表面处理方法。整个渗氮过程在氮气气氛中进行,将石墨毡通直流电,所产生的焦耳热使石墨毡快速升温并在其周围形成一个高温温度场,该温度场可以在2 min内实现材料的渗氮处理,在材料表面形成改性层。改性层由两部分组成,最表层为氮化物层,厚度10 μm,平均显微硬度为973.55 HV0.1,主要成分为TiN;次表层为渗氮层,厚度10 μm,平均显微硬度为774.53 HV0.1,截面显微硬度整体呈现出阶梯分布的趋势。摩擦磨损试验发现,在20 N载荷下,经过HSNT的TC4的摩擦系数为0.406,降低了24.4%,经过HSNT的TC4的磨损体积为0.302 mm3,降低了86.7%。
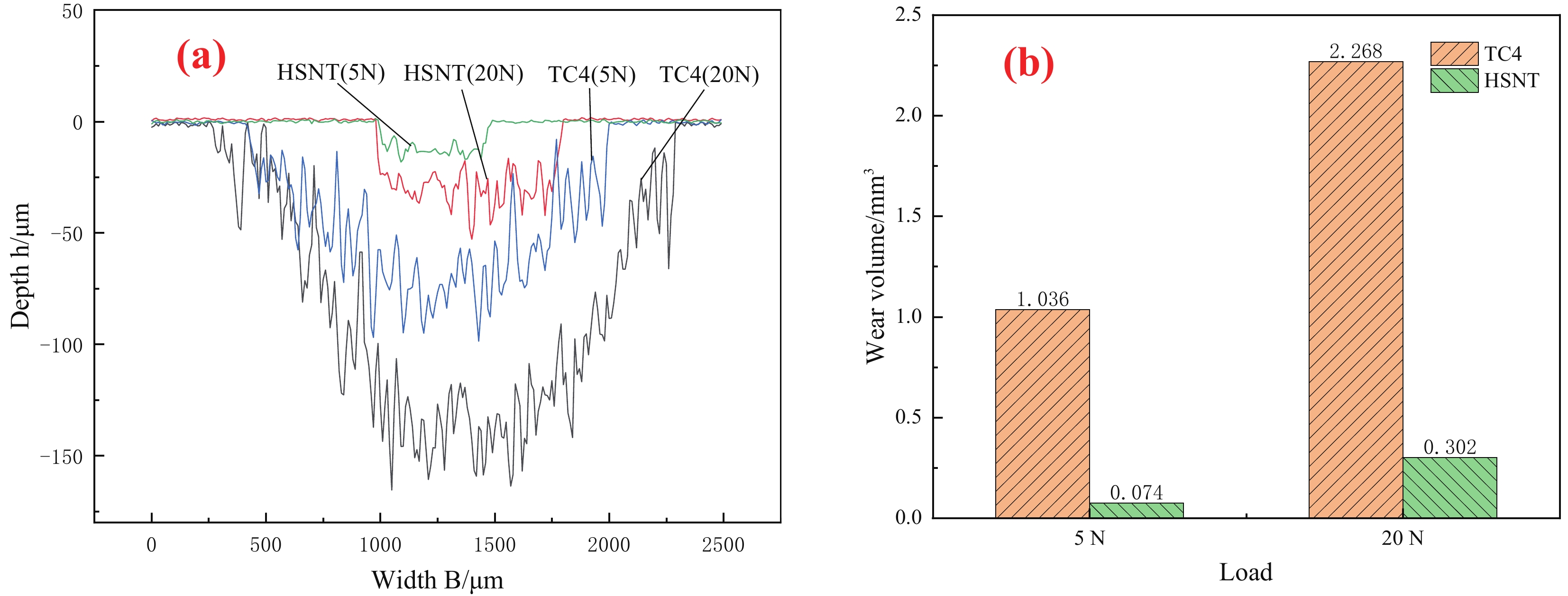
快速渗氮处理前后的TC4钛合金在(a)5 N、20 N载荷下的磨痕截面及(b)磨损体积





 下载:
下载:









