Effects of dispersible graphene in water on the electrical conductivity, heat generation and thermoelectric properties of cement slurry
-
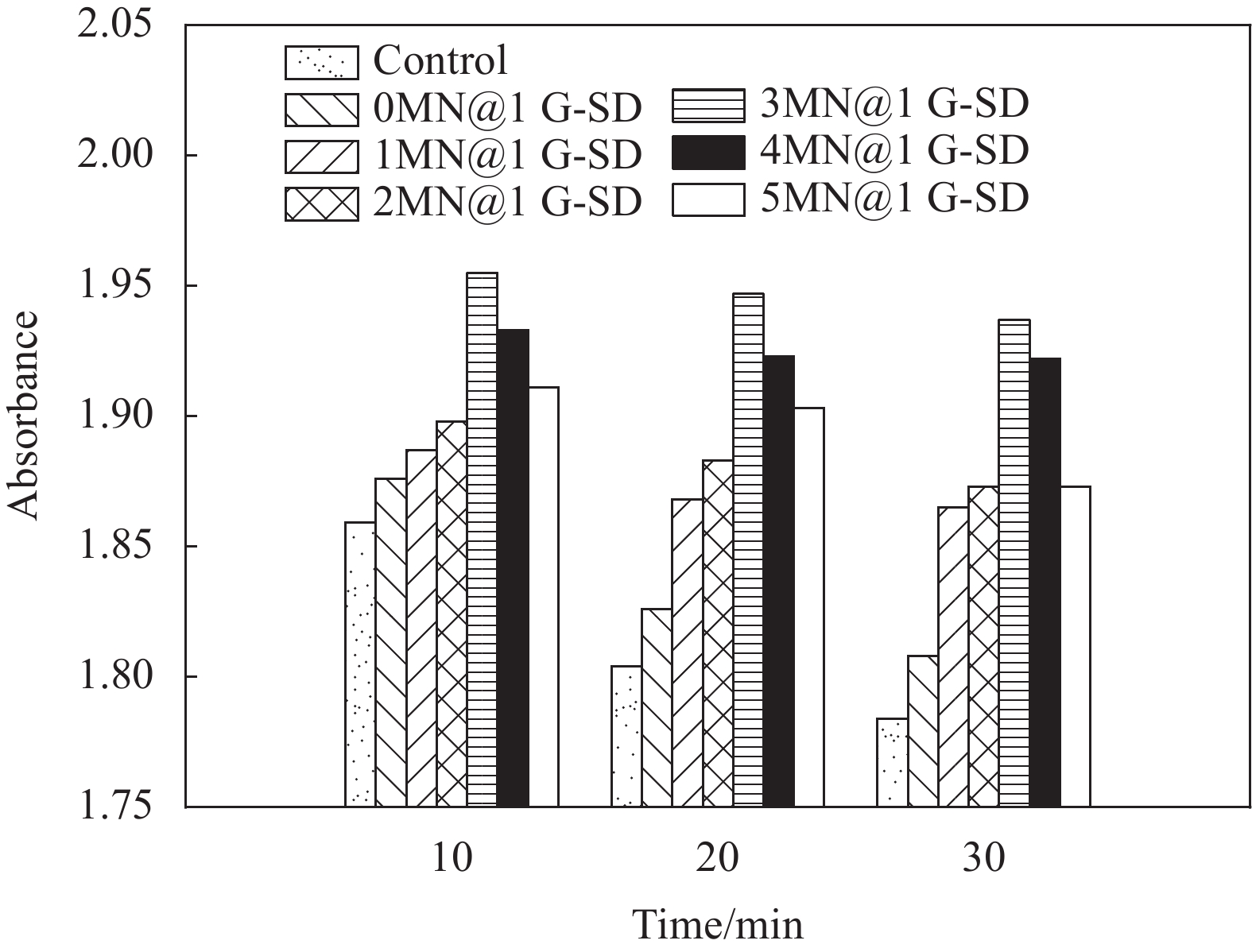
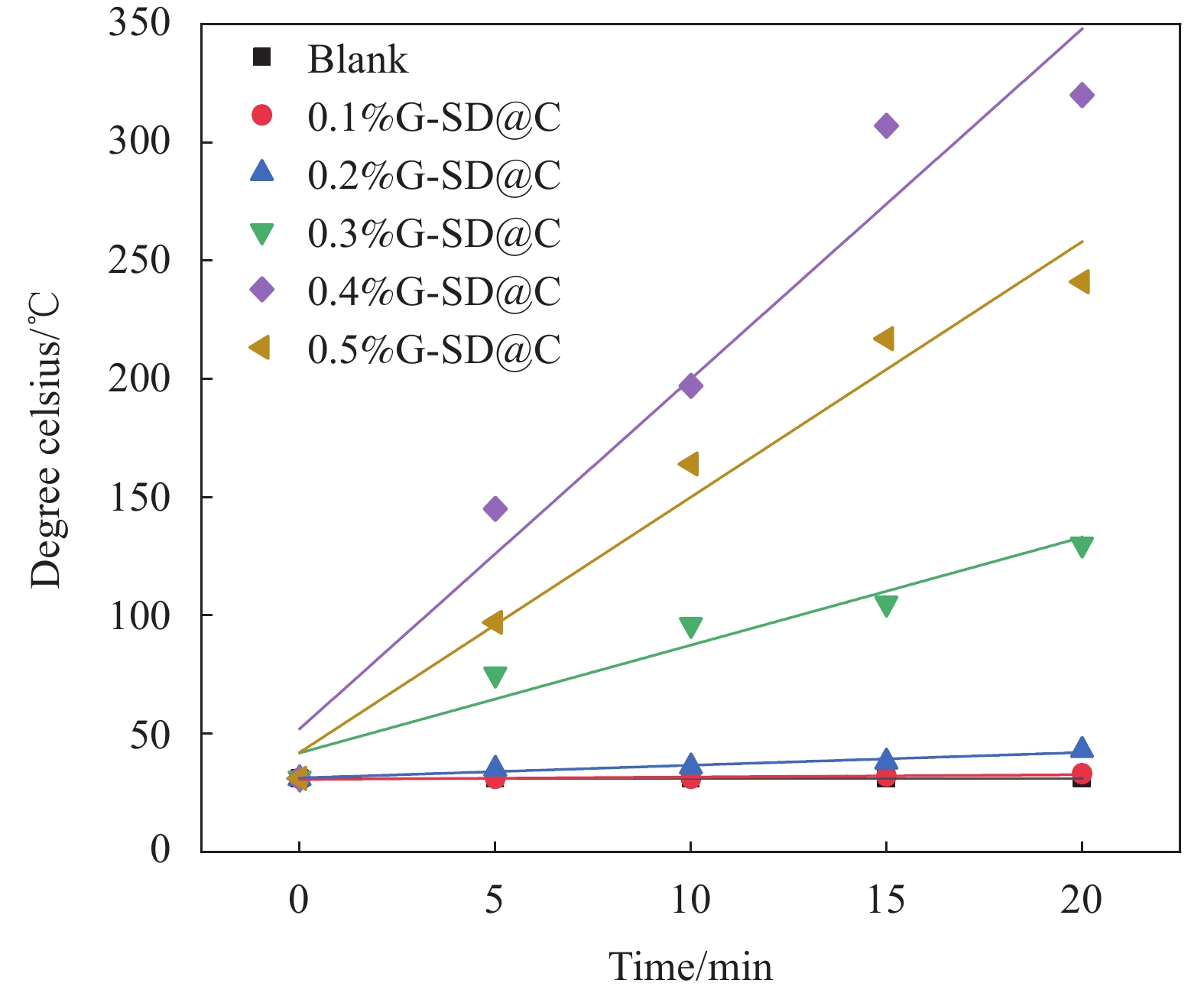
摘要: 为解决石墨烯(G)在水泥浆中均匀分散及其功能化水泥基材料时掺量过高的难题,选择一种兼顾高导电性与水溶性的石墨烯(G-SD)作为导电填料,研究了聚羧酸减水剂(PCE)存在时,木质素磺酸钠(MN)对G-SD在模拟水泥水化孔隙液的饱和氢氧化钙溶液(CH)中分散能力的影响及其对水泥净浆的导电性能、电热性能、融雪化冰和热电性能的影响。吸光度测试表明,当MN与G-SD质量比为3∶1时,G-SD的分散性最佳。电学性能测试发现,石墨烯水泥基材料的渗滤阀值为0.4%,阀值下试件的电热性能良好,在外加30 V电压下通电20 min,试件温度可达320℃,40 min内可将4 cm厚冰层完全融化,具有优异的融雪化冰潜力。热电性能研究表明,当G-SD掺量为0.1% 时,试件的Seebeck系数为154.4 μV/K。以上研究表明,G-SD能在极低掺量下赋予水泥基材料优异的电、热及热电等功能特性。Abstract: In order to solve the problem that graphene (G) is uniformly dispersed in cement slurry and its dosage is too high when it is functionalized into cement-based materials, a graphene (G-SD) with both high conductivity and water solubility was selected as a conductive filler. The effect of sodium lignosulfonate (MN) on the dispersion ability of G-SD in saturated calcium hydroxide solution (CH) used for simulated cement pore solution in the presence of polycarboxylate superplasticizer (PCE) and the effects of G-SD on the resistivity, electrothermal properties, snow melting and deciding, and thermoelectric properties of cement paste were investigated. The absorbance test shows that when the mass ratio of MN to G-SD is 3∶1, the dispersion of G-SD reaches the best. The electrical performance test shows that percolation threshold of graphene cement-based materials is 0.4%. What's more, good electrothermal performance are shown under the threshold, the temperature of cement paste specimen can be increased by 320℃ for 20 min with 30 V voltage, and 4 cm thick ice layer can be basically melted within25 min, so it possesses good potential for deicing and snow-melting. The thermoelectric properties shows that Seebeck coefficient of cement paste specimen is 154.4 μV/K when the content of G-SD is 0.1% by the cement mass. The above studies show that G-SD can endow cement-based materials with excellent electrical, thermal and thermoelectric functional properties at very low dosage.
-
目前我国土木工程领域已经进入新建和加固并重的新时期。碳纤维增强树脂复合材料(Carbon fiber reinforced polymer,CFRP)具有耐腐蚀、轻质高强及耐久性好等优点,且外贴CFRP片材加固有可操作性高、经济效益高等优点。因此外贴CFRP片材来加固既有混凝土结构引起了广泛关注。但采用CFRP片材加固后的混凝土结构易遭受二次腐蚀,混凝土表面裂缝的出现导致应力集中,易发生CFRP片材与混凝土界面的过早剥离破坏,会大大降低CFRP片材的利用率和结构的安全性能[1]。外贴CFRP片材和既有混凝土结构之间能否保证有效粘结从而有效传递应力是决定加固效果的关键[2-3]。
工程水泥基复合材料(Engineered cementitious composites,ECC)因其多裂缝开裂、耐久性好等特性在加固既有混凝土结构领域引起了学者广泛关注。结构用ECC加固后耐久性能提升明显,但其极限承载力提高有限[4-5]。在CFRP片材和混凝土之间设置ECC层,ECC良好的耐久性可减少外界环境对混凝土结构的侵蚀,细密裂缝的特性则可以延缓CFRP片材的剥离,有效地传递界面剪应力,从而更好地发挥CFRP片材高抗拉强度的优点。葛文杰等[6]和Wu等[7]的研究表明:混凝土结构用CFRP布和ECC复合加固后其综合性能得到明显改善,大大提高了加固效益。
学者们用纤维增强树脂复合材料(FRP)对受弯梁进行抗弯加固进行了大量研究[8-12],结果表明:若用FRP材料对混凝土结构进行加固,其综合性能会得到明显改善。而对于ECC作为过渡层来研究FRP加固的界面粘结性能方面的研究较少,试验数据有限导致影响变量尚不明确。因此ECC与CFRP片材的结合使用时两者界面粘结性能需进一步研究。Sui等[13]研究了常规环境下FRP-ECC-混凝土单面剪切试件的性能,结果表明随着ECC的加入,极限滑移、耗能能力及FRP的有效利用率均显著提高。
本文通过单面剪切试验对CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土复合界面抗剪性能进行研究,设计变量为混凝土/ECC强度、和ECC厚度,研究其对复合界面承载力、应变分布规律、粘结滑移曲线规律等的影响。
1. 试验概况
1.1 材料性能
试验所用CFRP片材厚度为1.2 mm,其拉伸强度、弹性模量分别为2451 MPa和167 GPa,极限延伸率可达到1.41%。CFRP-A/B胶作为CFRP片材-ECC复合界面的结构胶结剂,按2∶1的质量进行配比使用。粘结胶的抗拉强度为38.2 MPa,弹性模量为2530 MPa,极限延伸率为1.72%,胶层刚度Ka
为5 MPa左右。 采用C30和C50两种强度的ECC,其配合比见表1。水泥为P42.5普通硅酸盐水泥,粉煤灰采用I级粉煤灰,石英砂采用74~106 μm石英砂,所用减水剂的减水率在25%以上。聚乙烯醇(PVA)纤维材料性能指标见表2。
表 1 工程水泥基复合材料(ECC)配合比Table 1. Proportion of engineered cementitious composites (ECC)ECC Cement Fly ash Silica fume Quartz sand Water PVA Water reducer Thickener C30 1 3.0 0.3 0.4 1.37 2.00% 0.2% 0.08% C50 1 2.0 0.3 0.4 0.92 2.00% 0.2% 0.05% Notes: Fly ash, silica fume, quartz sand, water—Relative mass ratios to cement; PVA, water reducer, thickener—Relative volume ratios to ECC; PVA—Polyvinyl alcohol. 表 2 聚乙烯醇(PVA)纤维的材料性能Table 2. Material properties of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibersDiameter/μm Length/mm Tensile strength/MPa Young’s modulus/GPa Density/(g·cm−3) 40 12 1560 41 1.3 ECC基本拉伸力学性通过狗骨状试件拉伸试验进行,加载装置如图1(a)所示,加载速率设定为0.5 mm/min。ECC拉伸应力-应变曲线见图1(b),其主要分为3个阶段:(1) 弹性阶段:应力应变线性增长且没有裂缝产生;(2) 屈服阶段:试件出现多条细密裂纹,曲线斜率下降,没有出现应力集中的现象,为ECC的应变硬化阶段;(3) 下降阶段:试件上某条裂缝宽度增大,出现应力集中,直至最终破坏。C30和C50强度ECC极限抗拉强度分别为5.5 MPa和6.3 MPa。
采用C30和C50两种强度的混凝土且配合比见表3。水泥为P42.5普通硅酸盐水泥,细骨料为细度模数为2.3~3.0的Ⅱ区河砂,粗骨料为粒径为5~20 mm的碎石。C30和C50强度混凝土28天平均立方体抗压强度分别为38.3 MPa和59.1 MPa。
表 3 混凝土配合比Table 3. Proportion of concretekg/m3 Concrete Water Cement Fly ash Sand Gravel C30 165 281 70 678 1206 C50 165 376 95 565 1199 1.2 试件设计
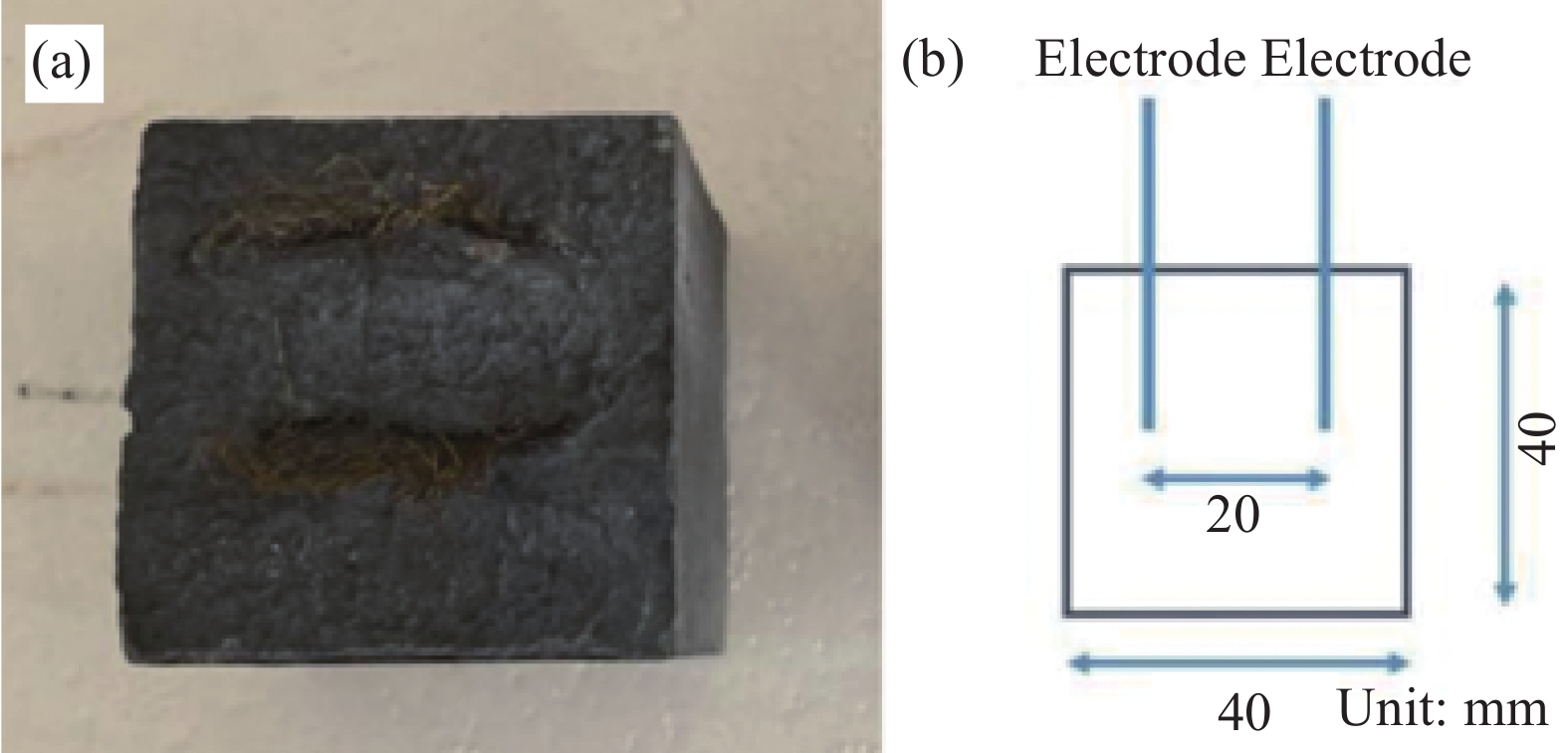
试件尺寸为300 mm×150 mm×150 mm。ECC尺寸为260 mm×120 mm,设置10 mm、20 mm、30 mm三种厚度。CFRP片材厚度为1.2 mm,宽度为50 mm,在ECC上的粘贴长度为200 mm。在加载端有30 mm的非粘结区以避免加载过程中出现应力集中现象。试件示意图如图2(a)所示。将混凝土/ECC强度(混凝土和ECC强度一致)、ECC厚度作为试验变量,单面剪切试件共7组21个试件。其中1组为不设置ECC层的对照组,其混凝土强度为C30。每组包含3个试件以提高结果可靠性。具体试件设计见表4。C30和C50为混凝土/ECC强度等级,E10/E20/E30为ECC层厚度,试件序号为最后一个数字。为防止混凝土和ECC界面发生剥离破坏,提高CFRP片材利用率,使用高压水射法对混凝土表面进行处理从而提高其粗糙度,处理后的界面如图3所示。
表 4 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土试件设计Table 4. Design of CFRP plate-ECC-concrete specimensSpecimen Concrete/ECC strength/MPa ECC thickness/mm C30-E10 30 10 C30-E20 30 20 C30-E30 30 30 C50-E10 50 10 C50-E20 50 20 C50-E30 50 30 C30 30 – 1.3 加载装置
试件尺寸及加载示意图如图2所示。该试验用1对量程为10 T的液压千斤顶手动施加荷载。加载时调整加载端垫板的高度使千斤顶、力传感器及CFRP片材三者的中心在同一水平面上。然后用螺栓把加载端CFRP片材固定防止在加载过程中脱落。在CFRP片材表面每隔30 mm粘贴1个120-5AA应变片以测量加载过程中CFRP片材的应变变化和分布。
2. CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土试验破坏现象
设置ECC层的试件破坏模式均为CFRP片材-ECC复合界面的剥离破坏,如图4所示,这是希望出现的破坏模式,表明高压水枪喷射法处理混凝土表面可保证混凝土和ECC界面的有效粘结。初加荷载时,界面粘结应力主要集中在加载端,CFRP片材通过胶层与ECC粘结在一起,试件处于线弹性阶段,各部分变形协调。随着荷载的增加,参与受力的CFRP片材的长度增加,试件开始发出断断续续“噔”的声音,此时CFRP片材-ECC复合界面粘结应力开始从加载端逐渐向自由端传递。荷载达加到极限承载力的80%左右时,加载端ECC达到其抗拉强度,CFRP片材-ECC复合界面在加载端开始出现明显剥离,胶层与ECC的接触面开始出现裂缝,试件持续发出“噔”的声音。当参与受力的CFRP片材长度达到有效锚固长度后,荷载基本不再增加,但CFRP片材应变持续增大,最大剪应力处向自由端发展。复合界面剥离达到极限状态时,伴着较大的一声“砰”的声响,CFRP片材从ECC表面剥离,试件最终破坏。
不设置ECC层的试件破坏模式均为CFRP片材与混凝土界面的剥离。加载初期,混凝土和CFRP片材界面间无明显滑移。随着荷载的增加,可以听见轻微剥离声。荷载达到极限承载力的80%左右时,相对滑移明显增加,试件持续发出剥离的声音。伴随一声“砰”的声响,CFRP片材完全剥离,试件发生脆性破坏。
试件破坏后,有不同厚度的ECC被CFRP片材粘下,如图5所示。当ECC厚度为10 mm时,剥离表面可以清晰的看到PVA纤维,被粘下的ECC较薄。ECC厚度增加到20 mm时,约3~4 mm的ECC附着在CFRP片材上。当ECC厚度为30 mm时,约5 mm厚ECC被剥离,且ECC表面被拔出纤维更加明显。
3. 试验结果分析
3.1 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土极限承载力
单面剪切试件极限承载力分布汇总见图6和表5,复合界面极限承载力随着ECC厚度及混凝土/ECC强度的增加而增加,但厚度越大增长的速率反而呈下降的趋势。设置3种不同ECC层厚度的单面剪切试件相比于无ECC层试件C30的极限承载力增加了27.3%~59.6%。对于混凝土/ECC强度为C30的试件,随着ECC厚度的增加最大承载力与未设置ECC层试件相比分别提高27.3%、49.5%和59.6%。当混凝土/ECC强度为C50,ECC厚度为20 mm、30 mm时,相比于ECC厚度为10 mm的试件极限承载力分别增加25%、27.4%。厚度为30 mm时相比20 mm厚度的ECC强度增加有限,表明单面剪切试件受力时,CFRP片材-ECC复合界面粘结应力无法传递到20 mm厚度以上的ECC或传递的力较小,因此不能仅靠提高ECC厚度来在增强极限承载力,否则无法发挥材料的最佳性能。对于ECC层厚度为10 mm、20 mm和30 mm的单面剪切试件,混凝土/ECC强度为C50时试件其极限承载力比强度为C30的试件分别提高了30.2%、38.5%和32.3%。由此可知:ECC厚度为30 mm时,随着混凝土强度提高极限承载力提高率不增反降,表明在ECC厚度较大时提高混凝土强度不是提高极限承载力有效方法。
表 5 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土试验结果汇总Table 5. Summary of test results of CFRP plate-ECC-concrete specimensSpecimen Ultimate load/kN Average/kN Theoretical/kN E/T YANG yongxin et al[14] Neubauer et al[15] LU xinzheng et al[16] C30-1 9.2 C30-2 9.6 9.9 – – 12.5 20.8 15.4 C30-3 10.8 C30-E10-1 12.3 0.88 C30-E10-2 12.4 12.6 13.9 0.89 27.9 42.3 28.2 C30-E10-3 13.0 0.94 C30-E20-1 14.8 0.89 C30-E20-2 14.6 14.8 16.6 0.88 27.9 42.3 28.2 C30-E20-3 14.9 0.90 C30-E30-1 15.3 0.86 C30-E30-2 15.8 15.8 18.3 0.84 27.9 42.3 28.2 C30-E30-3 16.2 0.89 C50-E10-1 15.9 1.14 C50-E10-2 16.8 16.4 13.9 1.20 30.3 45.2 29.2 C50-E10-3 16.4 1.17 C50-E20-1 20.4 1.22 C50-E20-2 21.5 20.5 16.6 1.19 30.3 45.2 29.2 C50-E20-3 19.6 1.18 C50-E30-1 22.3 1.21 C50-E30-2 20.5 20.9 18.3 1.12 30.3 45.2 29.2 C50-E30-3 20.0 1.09 Notes: E—Experimental value; T—Theoretical value. 3.2 CFRP片材应变分布
典型试件的CFRP片材沿长度方向应变分布见图7。在加载初期,CFRP片材应变近似呈线性分布,且此时应变均较小。应变随着荷载的增加而增加,且近似呈二次分布,相邻区域应变差值逐渐增大,CFRP片材-ECC复合界面剪应力也逐渐增大,且粘结应力从加载端逐渐向自由端传递。随着荷载的增加,加载端ECC逐渐达到其极限抗拉强度,CFRP片材-ECC界面在加载端开始出现明显剥离,胶层与ECC的接触面开始出现裂缝,此时在加载端处ECC传递至CFRP片材上的应力有限,相对应的CFRP片材的应变也相对较小。传递应力最大处转移至未开裂的远离加载端的CFRP-ECC界面,因此应变峰值点也转移至未出现剥离的远离加载端的部位。CFRP片材应变表现为先增大后减小的趋势。这与试件破坏规律相对应,此时CFRP片材应变为典型的“S”形应变分布直到失效。对于具有ECC层的试件,试件破坏时距加载端160 mm以上时也存在应变,覆盖整个粘合区域,对于无ECC层试件则始终为零,这证实了ECC的裂缝控制能力可以有效地传递界面剪切应力,延缓CFRP板的剥离。试件C50-E30-3极限承载力达到20.0 kN,CFRP片材极限微应变可达到17.23×10−4,表明混凝土/ECC强度以及ECC厚度的增加有利于发挥CFRP片材性能。而对比组试件C30-3材料未充分利用,试件极限承载力和CFRP片材极限微应变均最小分别为10.8 kN和10.24×10−4。
4. CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土复合界面承载力计算模型
试件极限承载力与ECC厚度关系拟合曲线如图8所示,混凝土/ECC强度对极限承载力影响较大,因此区分不同的强度分别进行拟合。当混凝土/ECC强度为C30和C50时,曲线拟合相关系数R2分别达到0.925和0.763,表明ECC厚度与试件极限承载力间有良好的线性相关性。
国内外学者经过大量试验及理论分析,提出多个极限承载力计算模型。可以得出:模型考虑因素越多,计算结果越为精准。经典承载力模型如下:
杨勇新等[14]的模型,考虑了混凝土强度、有效锚固长度及FRP片材刚度的影响:
τu=0.5ft (1a) Le=100mm (1b) Pu=(0.5+0.08√Eftf100ft)bfLeτu (1c) Neubauer等[15]的模型,考虑了混凝土强度、有效锚固长度、FRP片材刚度及宽度比的影响:
βw=√1.1252−bf/bc1+bf/400 (2a) Le=√Eftf2ft (2b) {Pu=0.64βwbf√EftfftL⩾ (2c) Lu等[16]综合诸多模型后对承载力计算模型提出简化:
{P_{\rm{u}}} = {\beta _{\rm{l}}}{b_{\rm{f}}}\sqrt {2{E_{\rm{f}}}{t_{\rm{f}}}{G_{\rm{f}}}} (3a) {G_{\rm{f}}} = 0.308\sqrt {{f_{\rm{t}}}} \beta _{_{\rm{w}}}^2 (3b) {\beta _{\rm{w}}} = \sqrt {\frac{{2.25 - {b_{\rm{f}}}/{b_{\rm{c}}}}}{{1.25 + {b_{\rm{f}}}/{b_{\rm{c}}}}}} (3c) {\beta _{\rm{l}}} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {\dfrac{L}{{{L_{\rm{e}}}}}(2 - \dfrac{L}{{{L_{\rm{e}}}}})\;L < {L_{\rm{e}}}{\rm{ }}}\\ {1\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;L \geqslant {L_{\rm{e}}}{\rm{ }}} \end{array}} \right.{L_{\rm{e}}} = 1.33\dfrac{{\sqrt {{E_{\rm{f}}}{t_{\rm{f}}}} }}{{{f_{\rm{t}}}}} (3d) 式中:τu为平均粘结应力;Pu为剥离承载力;Gf为界面破坏能;ft为混凝土抗拉强度;βw和βl分别为尺寸影响系数;Ef、tf和bf分别为CFRP片材的弹性模量、厚度和宽度;L和Le分别为粘结长度和有效粘结长度;bc为混凝土块体的宽度;Gf为破坏能。
以上3种模型计算所得结果见表5。模型计算值均与试验值有所偏差,主要原因可能是以往研究的是FRP与混凝土界面的剥离承载力,而混凝土的厚度远高于比本文所用ECC厚度且没有考虑在计算模型中[17]。而本文所用ECC厚度较小,复合界面剪应力可能传递到普通混凝土,因此在对本文单面剪切试件进行复合界面承载力计算时,不可忽略ECC厚度的影响。本文在Lu等[16]的模型基础上考虑ECC厚度对界面承载力的影响,对公式进一步改进:
{P_{\rm{u}}} = \frac{{{\beta _{\rm{l}}}{b_{\rm{f}}}\sqrt {2{E_{\rm{f}}}{t_{\rm{f}}}{G_{\rm{f}}}\sqrt {{t_{\rm{E}}}} } }}{{3.6}} (4) 式中,tE为ECC厚度。按照此极限承载力计算模型计算结果见表5。计算结果表明:本文考虑ECC厚度影响的承载力计算模型理论值与试验值吻合较好,优于Lu等[16]提出的模型。
5. CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土粘结-滑移模型
粘结-滑移关系反映了界面局部剪应力和相对滑移的发展规律,对采用理论和数值方法分析CFRP片材加固混凝土结构的性能非常重要。粘结-滑移关系决定了界面的受力过程、CFRP片材应变分布等指标。因此,为了更好地研究CFRP片材-混凝土界面性能,需更深入分析复合界面的粘结-滑移关系,其应力和变形分布如图9所示。
![]() 图 9 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土复合界面应力分布示意图Figure 9. Schematic diagram of interface stress distribution between CFRP plate-ECC-concrete compositeP—External force applied; εf—Strain of CFRP plate; σf(x), σc(x)—Stresses of CFRP plate and ECC, respectively; xi—Bonding position for strain gauges of CFRP plate; τ(x)—Interfacial shear stress
图 9 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土复合界面应力分布示意图Figure 9. Schematic diagram of interface stress distribution between CFRP plate-ECC-concrete compositeP—External force applied; εf—Strain of CFRP plate; σf(x), σc(x)—Stresses of CFRP plate and ECC, respectively; xi—Bonding position for strain gauges of CFRP plate; τ(x)—Interfacial shear stress由图9中受力平衡可得:
\tau (x){\rm{d}}x = {t_{\rm{f}}}{\rm{d}}{\sigma _{\rm{f}}}(x) (5) 进一步可得相邻两应变测点间界面剪应力:
{\tau _{i + 1/2}} = {E_{\rm{f}}}{t_{\rm{f}}}\frac{{{\rm{d}}{\varepsilon _{\rm{f}}}}}{{{\rm{d}}x}} = {E_{\rm{f}}}{t_{\rm{f}}}\frac{{{\varepsilon _i} - {\varepsilon _{i + 1}}}}{{\Delta l}} (6) 局部滑移可按照下式计算:
{s_i} = {s_{i + 1}} + \frac{{{\varepsilon _{{\rm{f}},i}} - {\varepsilon _{{\rm{f}},i + 1}}}}{2}\Delta l + {\varepsilon _{{\rm{f}},i + 1}}\Delta l{\kern 1pt} (7) 式中:
{\tau _{i + 1/2}} 和\Delta l 分别为i和i+1点间的剪应力和中心间距;{\varepsilon _i} 为第i个应变测点的值,i=1、2、…、6。选取典型试件的粘结-滑移曲线如图10所示。由式(6)和式(7)计算得到的是相邻应变测点间的平均剪应力和相对滑移值。剪应力基本符合随滑移值的增大先增大后减小的规律。从施加荷载直到剪应力峰值前,曲线近似为直线,试件处于线弹性阶段;随着荷载的增加,参与受力的CFRP片材的长度增加,此时CFRP片材-ECC复合界面进一步出现损伤,表现为达到峰值剪应力后曲线开始下降。以试件C50-E30-1为例,剪应力下降到1 MPa左右时,滑移量迅速增加。此时CFRP片材-ECC复合界面正在发生较大的剥离。滑移值达到0.1 mm左右时,大部分剪应力值已为0,但由于ECC特殊的应变硬化作用,小部分CFRP片材-ECC复合界面在滑移较大时仍能传递一定的剪应力。当剪应力降低直至于0时,CFRP片材从ECC表面剥离。
![]() 图 11 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土试件粘结-滑移数据拟合曲线Figure 11. Bond-slip data fitting curves of CFRP plate-ECC-concrete specimensτ—Corresponding shear stress when the slip is S(Sp); τmax, \bar \tau—Peak shear stress; S_0 , \bar S —Slip corresponding to τmax; Sp—Slip; Su, Sf—Maximum slip; fc, ft—Compressive strength, tensile strength of concrete; βw, Gf—Size influence coefficient and fracture energy; Ef, tf—Elastic modulus and thickness of CFRP plate; bf, bc—Width of CFRP plate and concrete; Ga, ta—Shear modulus and thickness of the adhesive; n—Coefficient
图 11 CFRP片材-ECC-混凝土试件粘结-滑移数据拟合曲线Figure 11. Bond-slip data fitting curves of CFRP plate-ECC-concrete specimensτ—Corresponding shear stress when the slip is S(Sp); τmax, \bar \tau—Peak shear stress; S_0 , \bar S —Slip corresponding to τmax; Sp—Slip; Su, Sf—Maximum slip; fc, ft—Compressive strength, tensile strength of concrete; βw, Gf—Size influence coefficient and fracture energy; Ef, tf—Elastic modulus and thickness of CFRP plate; bf, bc—Width of CFRP plate and concrete; Ga, ta—Shear modulus and thickness of the adhesive; n—Coefficient采用几种典型的FRP-混凝土界面粘结-滑移本构关系,对试件C50-E30-1的粘结-滑移数据进行拟合分析以得到一般性规律,如图11所示。图中:
\tau 为滑移为s 时对应的粘结剪应力;{\tau _{\max }} 、\overline \tau 为峰值剪应力;n为系数;{S_0} 、\overline S 为{\tau _{\max }} 对应的滑移;{S_{\rm{u}}} 、{S_{\rm{f}}} 为最大滑移;fc为混凝土抗压强度;Ga/ta=Ka,Ga和ta分别为胶层剪切模量和厚度。Ferracuti等[18]的模型相比于其他3种模型,在下降段显示了更柔软的响应,考虑的影响因素较全面(混凝土强度、FRP片材刚度、有效锚固长度及宽度比等均考虑),模型的计算结果与试验数据拟合较好。Dai等[19]的模型是基于较小的胶层刚度(Ka<1 MPa)的试验结果,对于有普通胶层刚度(本文Ka为5 MPa左右)的粘结-滑移数据拟合结果滑移量明显偏大。Lu等[20]模型对Gf和τmax的预测值均偏小,低估了界面的抗剪承载力,与试验数据也有一定的偏差。陆新征[21]的模型在粘结-滑移曲线上升段拟合较好,但在下降段没有考虑材料应变硬化特性和界面软化的影响,下降段拟合结果不理想。用Ferracuti等[18]模型拟合典型试件的曲线见图12。设置ECC层的单面剪切试件在达到最大剪切应力时的滑移量均比无ECC层的对照试件大,且最大剪切应力均有增加。由于ECC多缝开裂及应变硬化特性,有ECC层的试件的初始刚度均比无ECC层的对比试件小。大部分试件拟合值与试验结果吻合较好,相关系数可达到0.8以上。
6. 结 论
(1) 采用碳纤维增强树脂复合材料(CFRP)片材-工程水泥基复合材料(ECC)复合界面可有效延缓CFRP片材的剥离,可以更有效地传递界面剪应力。研究表明,复合界面的抗剪性能明显优于纤维增强树脂复合材料(FRP)-混凝土界面的抗剪性能。
(2) 设置ECC层的单面剪切试件破坏模式均为CFRP片材-ECC复合界面的剥离破坏。ECC厚度增加为20 mm以上时,试件破坏后CFRP片材上附着的ECC厚度为3~5 mm,表明ECC厚度的增加有利于提高复合界面抗剪承载力。
(3) 设置ECC层的试件相比于无ECC层试件的极限承载力增加了27.3%~59.6%。ECC厚度由20 mm增加到30 mm时,强度提高率有限,表明不能仅靠提高ECC厚度来在增强极限承载力。
(4) 本文提出的考虑ECC厚度的极限承载力计算模型计算值与试验结果吻合较好。不同的粘结滑移本构关系中,考虑下降段曲线软化的模型与本文试验结果相吻合。
-
表 1 水泥物理性能
Table 1 Physical properties of the cement
Water requirement
of normal
consistency/%Specific surface
area/(m2·kg−1)Density/
(g·cm−3)Setting time/min Flexural strength/MPa Compression strength/MPa Initial Final 3 d 28 d 3 d 28 d 27.8 351 3.15 136 244 5.1 6.3 25.6 43.4 表 2 用于吸光度和Zeta电位测试的水中可分散型石墨烯(G-SD)溶液组成
Table 2 Composition of dispersible graphene in water (G-SD) solution for absorbance and Zeta potential test
Sample Water/mL Ca(OH)2/g G-SD/mL PCE/mL MN① Control 90 0.16 10 0.00 0 0MN@1 G-SD 90 0.16 10 0.05 0 1MN@1 G-SD 90 0.16 10 0.05 1∶1 2MN@1 G-SD 90 0.16 10 0.05 2∶1 3MN@1 G-SD 90 0.16 10 0.05 3∶1 4MN@1 G-SD 90 0.16 10 0.05 4∶1 5MN@1 G-SD 90 0.16 10 0.05 5∶1 Notes: ① Content of MN is its mass ratio to G-SD; PCE—Polycarboxylate; MN—Sodium lignosulfonate. 表 3 不同G-SD掺量的水泥净浆配合比
Table 3 Mix ratios of cement paste with different contents of G-SD
Sample Cement/g PCE/g Water/g G-SD①/% MN①/% Blank 450 1.35 170 0.0 0.00 0.1%G-SD@C 450 1.35 170 0.1 0.03 0.2%G-SD@C 450 1.35 170 0.2 0.06 0.3%G-SD@C 450 1.35 170 0.3 0.09 0.4%G-SD@C 450 1.35 170 0.4 0.12 0.5%G-SD@C 450 1.35 170 0.5 0.15 Notes: ① Mass ratio to cement; C—Cement. 表 4 文献中碳纳米材料的分散方法
Table 4 Dispersion methods of carbon nanomaterials in literature
Reference Conductive fillers Dispersant Dispersion mode and parameter This paper Graphene MN Wet mix method, ultrasonic, 30 min [30] Graphene nanosheets SP Wet mix method, ultrasonic, 1 h [31] Nickel nanowires PCE Wet mix method, ultrasonic, 15 min [32] Carbon nanotubes SP Wet mix method, ultrasonic, – [33] Carbon nanotubes
/nano carbon black3310E Wet mix method, mechanical stirring, 4 min [27] Multiwalled carbon nanotubes MN Wet mix method, ultrasonic, 30 min Notes: SP—Polycarboxylate superplasticizer; 3310 E—3310 E polycarboxylate superplasticizer. 表 5 石墨烯水泥基复合材料的渗滤阀值
Table 5 Percolation threshold of graphene cement-based composites
表 6 各组水泥净浆试件拟合曲线的拟合参数
Table 6 Parameters of fitted curves of each group of cement paste specimen
Parameter A B R2 Blank 0.04 30.8 — 0.1%G-SD@C 0.10 30.6 0.708 0.2%G-SD@C 0.62 30.8 0.925 0.3%G-SD@C 4.56 41.8 0.919 0.4%G-SD@C 14.80 52.0 0.937 0.5%G-SD@C 10.80 42.0 0.965 表 7 不同导电相复合材料的升温情况
Table 7 Temperature rises of cement-based composites with different conductive fillers
表 8 不同导电相复合材料的Seebeck系数
Table 8 Seebeck coefficient of composites with different conductive phases
-
[1] 徐鹏, 张轩翰, 明高林, 等. 纳米改性水泥基材料功能化研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(16): 119-128. XU Peng, ZHANG Xuanhan, MING Gaolin, et al. Research progress on functionalized nano-modified cement-based materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(16): 119-128(in Chinese).
[2] 樊宇澄, 冯闯. 热电水泥基复合材料研究现状及展望[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(17): 145-166. FAN Yucheng, FENG Chuang. Current status and prospect of the research of thermoelectric cement-based composites[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(17): 145-166(in Chinese).
[3] 方思怡, 巴明芳, 许浩锋, 等. HEC分散剂和纤维掺量对短切碳纤维水泥基材料压敏性的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(15): 265-303. FANG Siyi, BA Mingfang, XU Haofeng, et al. Effects of HEC dispersant and fiber content on compression-sensitivity of short carbon fiber cement-based materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(15): 265-303.
[4] DONG S F, LI L W, ASHOUR A, et al. Self-assembled 0D/2D nano carbon materials engineered smart and multifunctional cement-based composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,272:121632. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121632
[5] GHOSH S, HARISH S, OHTAKI M, et al. Thermoelectric figure of merit enhancement in cement composites with graphene and transition metal oxides[J]. Materials Today Energy,2020,18:100492. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100492
[6] 吴磊, 吕生华, 李泽雄, 等. 超低掺量氧化石墨烯的分散行为及其对水泥基材料结构与性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4): 2296-2307. WU Lei, LYU Shenghua, LI Zexiong, et al. Dispersion behavior of ultra-low dosage graphene oxide and its effect on structure and performances of cement-based materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(4): 2296-2307(in Chinese).
[7] 吕骄阳, 李思李, 田波, 等. 石墨烯在水泥净浆中的分散特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4746-4756. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211214.002 LYU Jiaoyang, LI Sili, TIAN Bo, et al. Dispersion characteristics of graphene in cement paste[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4746-4756(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211214.002
[8] 王悦, 王琴, 郑海宇, 等. 分散剂对石墨烯水泥基复合材料压敏性能的影响研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(8):2515-2526. DOI: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2021.08.003 WANG Yue, WANG Qin, ZHENG Haiyu, et al. Influence of dispersant on pressure-sensitive properties of graphene cement-based composites[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(8):2515-2526(in Chinese). DOI: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2021.08.003
[9] 袁小亚, 张维福, 曹潘磊, 等. 复掺石墨烯/氧化石墨烯改性砂浆电学与融雪化冰性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(12):12100-12109. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.12.017 YUAN Xiaoya, ZHANG Weifu, CAO Panlei, et al. Research on electrical properties and performance of deicing and snow-melting of the modified mortar blended with graphene/graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2021,52(12):12100-12109(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.12.017
[10] 钱锋, 刘宪昌. 石墨烯增强水泥基复合材料的制备及热电性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2020, 51(10):10152-10156. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2020.10.023 QIAN Feng, LIU Xianchang. Preparation and thermoelectric properties of graphene-reinforced cement-based composites[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2020,51(10):10152-10156(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2020.10.023
[11] YANG S, JIA W, WANG Y, et al. Hydroxylated graphene: A promising reinforcing nanofiller for nanoengineered cement composites[J]. ACS Omega,2021,6(45):30465-30477. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c03844
[12] RAHMANI S, SHARIF A, HABIBNEJAD K A. Dispersion stability of chitosan grafted graphene oxide nanosheets in cementitious environments and their effects on the fluidity of cement mortar nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2022,139(19):52095. DOI: 10.1002/app.52095
[13] HU M M, LIU M, LI P P, et al. Effects of triethanolamine modified graphene oxide on calcium silicate hydrate in synthesized system and cement composite[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,602:125037. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125037
[14] 陈操, 翟文涛, 郑文革, 等. 水溶性石墨烯及其高导电率薄膜的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(7):707-710. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2011.00707 CHEN Cao, ZHAI Wentao, ZHENG Wen'ge, et al. Preparation and characterization of water-soluble graphene and highly conducting films[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2011,26(7):707-710(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2011.00707
[15] TAO R, LI F, LU X, et al. High-conductivity-dispersibility graphene made by catalytic exfoliation of graphite for lithium-ion battery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(6):2007630. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202007630
[16] 袁小亚. 一种水溶导电型石墨烯及其制备方法: 中国, CN202310595561.X[P]. 2023-10-13 YUAN Xiaoya. A water-soluble conductive graphene and its preparation method: China Patent, CN202310595561. X[P]. 2023-10-13(in Chinese).
[17] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法): GB/T 17671−2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. China National Standardization Management Committee. Strength test method of cement mortar (ISO method): GB/T 17671−2021[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2021(in Chinese).
[18] LIEBSCHER M, TZOUNIS L, JUNGER D, et al. Electrical joule heating of cementitious nanocomposites filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes: Role of filler concentration, water content, and cement age[J]. Smart Materials and Structures,2020,29(12):125019. DOI: 10.1088/1361-665X/abc23b
[19] 余东升, 付芳, 贾铁昆, 等. 亲水型功能化石墨烯的分散性及其对水泥基复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(2):622-629. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200710.002 YU Dongsheng, FU Fang, JIA Tiekun, et al. Dispersity of hydrophilic functional graphene and its impact on mechanical properties of cement based composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(2):622-629(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200710.002
[20] 陈宽, 田建华, 崔兰, 等. 石墨烯和铂/石墨烯的合成及其表征[J]. 无机化学学报, 2012, 28(8):1541-1546. CHEN Kuan, TIAN Jianhua, CUI Lan, et al. Preparation and characterization of graphene and platinum/graphene[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2012,28(8):1541-1546(in Chinese).
[21] 姜晓琳, 李君, 刘臻, 等. 石墨烯炭材料的结构表征方法研究[J/OL]. 洁净煤技术, 2022: 1-13. [2023-02-08]. . JIANG Xiaolin, LI Jun, LIU Zhen, et al. Graphene carbon materials and their characterization methods research[J/OL]. Clean Coal Technology, 2022: 1-13. [2023-02-08]. (in Chinese).
[22] 胡圣飞, 魏文闵, 刘清亭, 等. 超临界流体剥离制备石墨烯研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2017, 45(3):28-34. DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2015.001011 HU Shengfei, WEI Wenmin, LIU Qingting, et al. Research progress on preparation of graphene by supercritical fluid exfoliation[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2017,45(3):28-34(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2015.001011
[23] DRESSELHAUS M S, DRESSELHAUS G F, HOFMANN M. Raman spectroscopy as a probe of graphene and carbon nanotubes[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,2008,366(1863):231-236. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2007.2155
[24] WALL M. The Raman spectroscopy of graphene and the determination of layer thickness[J]. Thermal Science, 2011, 5: 1-5.
[25] 彭黎琼, 谢金花, 郭超, 等. 石墨烯的表征方法[J]. 功能材料, 2013, 44(21):3055-3059. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2013.21.001 PENG Liqiong, XIE Jinhua, GUO Chao, et al. Review of characterization methods of graphene[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2013,44(21):3055-3059(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2013.21.001
[26] 盛况, 杨森, 毕俊峰, 等. 有机染料辅助分散氧化石墨烯及其对水泥砂浆强度和耐久性的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(11):5486-5498. SHENG Kuang, YANG Sen, BI Junfeng, et al. Effect of organic dye assisted dispersion of graphene oxide on mechanical properties and durability of cement mortar[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(11):5486-5498(in Chinese).
[27] 杨森, 王远贵, 齐孟, 等. 氧化石墨烯对多壁碳纳米管掺配水泥砂浆强度、压敏性能与微观结构的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5):2340-2355. YANG Sen, WANG Yuangui, QI Meng, et al. Effect of graphene oxide on mechanical properties, piezoresistivity and microstructure of cement mortar blended with multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(5):2340-2355(in Chinese).
[28] 王晓楠, 冯德成. 纳米碳/水泥基复合材料研究进展[J/OL]. 材料导报, 2023(21): 1-29[2023-11-03]. WANG Xiaonan, FENG Decheng. Research progress on carbon nanomaterials modified cementitious composites[J/OL]. Materials Reports, 2023(21): 1-29[2023-11-03].
[29] 刘金涛, 黄存旺, 杨杨, 等. 三维石墨烯-碳纳米管/水泥净浆的压敏性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):313-321. LIU Jintao, HUANG Cunwang, YANG Yang, et al. Piezoresistivity of three dimensional graphene-carbon nanotubes/cement paste[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):313-321(in Chinese).
[30] DU H J, PANG S D. Dispersion and stability of graphene nanoplatelet in water and its influence on cement composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,167:403-413. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.046
[31] 曹亚龙, 徐金霞, 蒋林华, 等. 自感知镍纳米线/水泥基复合材料的制备及压敏性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(4):957-963. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170622.001 CAO Yalong, XU Jinxia, JIANG Linhua, et al. Fabrication and piezoresistivity of self-sensing Ni nanowire/cement composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(4):957-963(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170622.001
[32] YOO D Y, YOU I, ZI G, et al. Effects of carbon nanomaterial type and amount on self-sensing capacity of cement paste[J]. Measurement,2019,134:750-761. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.11.024
[33] DING S Q, RUAN Y F, YU X, et al. Self-monitoring of smart concrete column incorporating CNT/NCB composite fillers modified cementitious sensors[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,201:127-137. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.203
[34] 赵昕, 黄存旺, 傅佳丽, 等. 石墨烯水泥基复合材料的电学性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(1):8-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2022.01.002 ZHAO Xin, HUANG Cunwang, FU Jiali, et al. Electrical properties of graphene cement based composites[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2022,25(1):8-15(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2022.01.002
[35] ZHANG N, SHE W, DU F Y, et al. Experimental study on mechanical and functional properties of reduced graphene oxide/cement composites[J]. Materials,2020,13(13):3015-3033. DOI: 10.3390/ma13133015
[36] 蒋林华, 白舒雅, 金鸣, 等. 石墨烯水泥基复合材料的电导率研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2018, 39(3):601-606. DOI: 10.11990/jheu.201610043 JIANG Linhua, BAI Shuya, JIN Ming, et al. Electrical conductivity of the graphene/cement composites[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2018,39(3):601-606(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11990/jheu.201610043
[37] BAI S Y, JIANG L H, JIANG Y, et al. Research on electrical conductivity of graphene/cement composites[J]. Advances in Cement Research,2020,32(2):45-52. DOI: 10.1680/jadcr.16.00170
[38] HUANG Y, LI N, MA Y F, et al. The influence of single-walled carbon nanotube structure on the electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency of its epoxy composites[J]. Carbon,2007,45(8):1614-1621. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2007.04.016
[39] 魏建强. 低温下碳纤维混凝土电热效应实验[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2018, 38(3):473-478. DOI: 10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2018.0318 WEI Jianqiang. Effect of thermoelectricity on carbon fiber reinforced concrete under low temperatures[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology,2018,38(3):473-478(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2018.0318
[40] GOMIS J, GALAO O, GOMIS V, et al. Self-heating and deicing conductive cement: Experimental study and modeling[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2015,75:442-449. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.11.042
[41] WEI J, JIA Z Y, WANG Y, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of low carbon cement-based composites by reduced graphene oxide[J]. Energy and Buildings,2021,250:111279. DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111279
[42] TZOUNIS L, LIEBSCHER M, FUGE R, et al. p- and n-type thermoelectric cement composites with CVD grown p- and n-doped carbon nanotubes: Demonstration of a structural thermoelectric generator[J]. Energy and Buildings,2019,191:151-163. DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2019.03.027
[43] WEI J, FAN Y, ZHAO L L, et al. Thermoelectric properties of carbon nanotube reinforced cement-based composites fabricated by compression shear[J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(6):5829-5833. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.074
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 房恩惠,杨树桐,庞瑞阳,孙忠科,兰天. 树脂预浸技术提升CFRP-混凝土界面力学性能研究. 复合材料科学与工程. 2025(02): 117-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丛龙宇,张方,钱永久. 外部粘贴CFRP-ECC粘结性能的影响因素试验. 复合材料学报. 2025(03): 1538-1554 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 温小栋,王俊豪,殷光吉,邵璟璟,冯蕾. 海水与腐蚀电流耦合作用下铝合金与混凝土界面黏结性能. 建筑结构学报. 2024(04): 237-246 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱红兵,付正昊,王烨,陈经毅. 界面剂对全轻陶粒混凝土与普通混凝土粘结界面力学性能的影响. 复合材料学报. 2024(06): 3154-3167 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 叶华勇. 界面处理方式对CFRP-ECC复合加固混凝土梁受弯性能影响研究. 福建建筑. 2024(11): 49-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 姜天华,万聪聪,颜斌. BFRP筋与钢-PVA混杂ECC粘结性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(06): 3499-3512 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 昝鹏,陈燕萍. 水利工程混凝土复合材料的制备与力学性能分析. 塑料助剂. 2023(03): 30-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)
-
目的
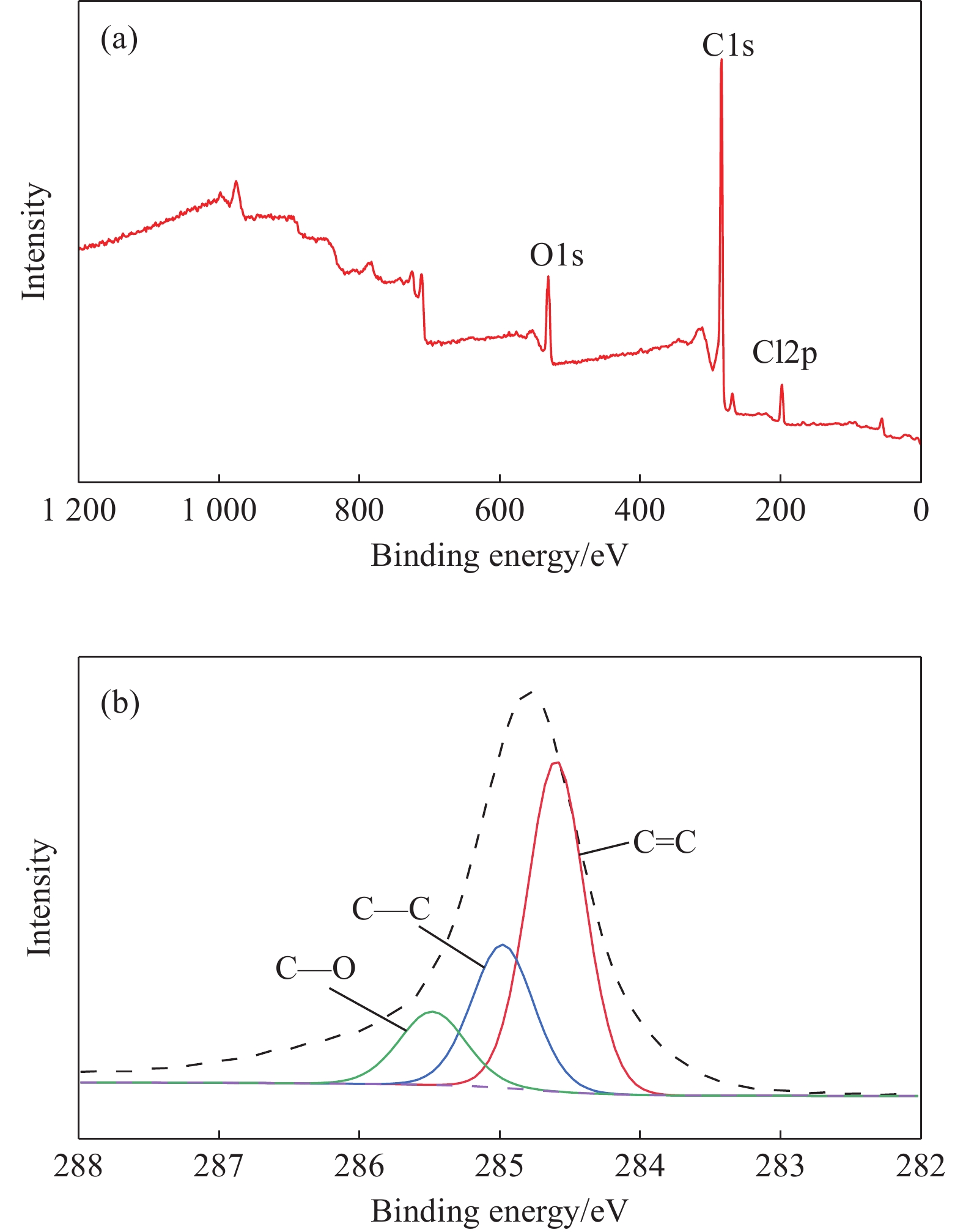
为解决石墨烯(G)在水泥浆中均匀分散及其功能化水泥基材料时掺量过高的难题,选择一种兼顾高导电性与水溶性的石墨烯(G-SD)作为导电填料。智能及功能化水泥基材料是当前研究热点,但由于G层间存在很强的π-π堆叠作用和较强的范德华力,导致其极易团聚而难以均匀分散在水泥基材料中,进而使得功能化水泥基材料的掺量过高。各种共价化学改性的G虽然能很好的分散在水泥基材料中,但较低的电导率导致其不能用作导电填料。因此,需要选择一种分散性与导电性俱佳的G作为功能化水泥基材料的导电填料。
方法首先,对水中可分散石墨烯(G-SD)进行微观结构表征并将其配置成水溶液静置,观察其聚沉情况。其次,采用紫外可见分光光度法和Zeta电位研究了聚羧酸减水剂(PCE)存在时,木质素磺酸钠(MN)对G-SD在模拟水泥水化孔隙液的饱和氢氧化钙溶液 (CH)中分散能力的影响,由此确定MN助分散G-SD的最佳比例。然后,参照《水泥胶砂强度检验
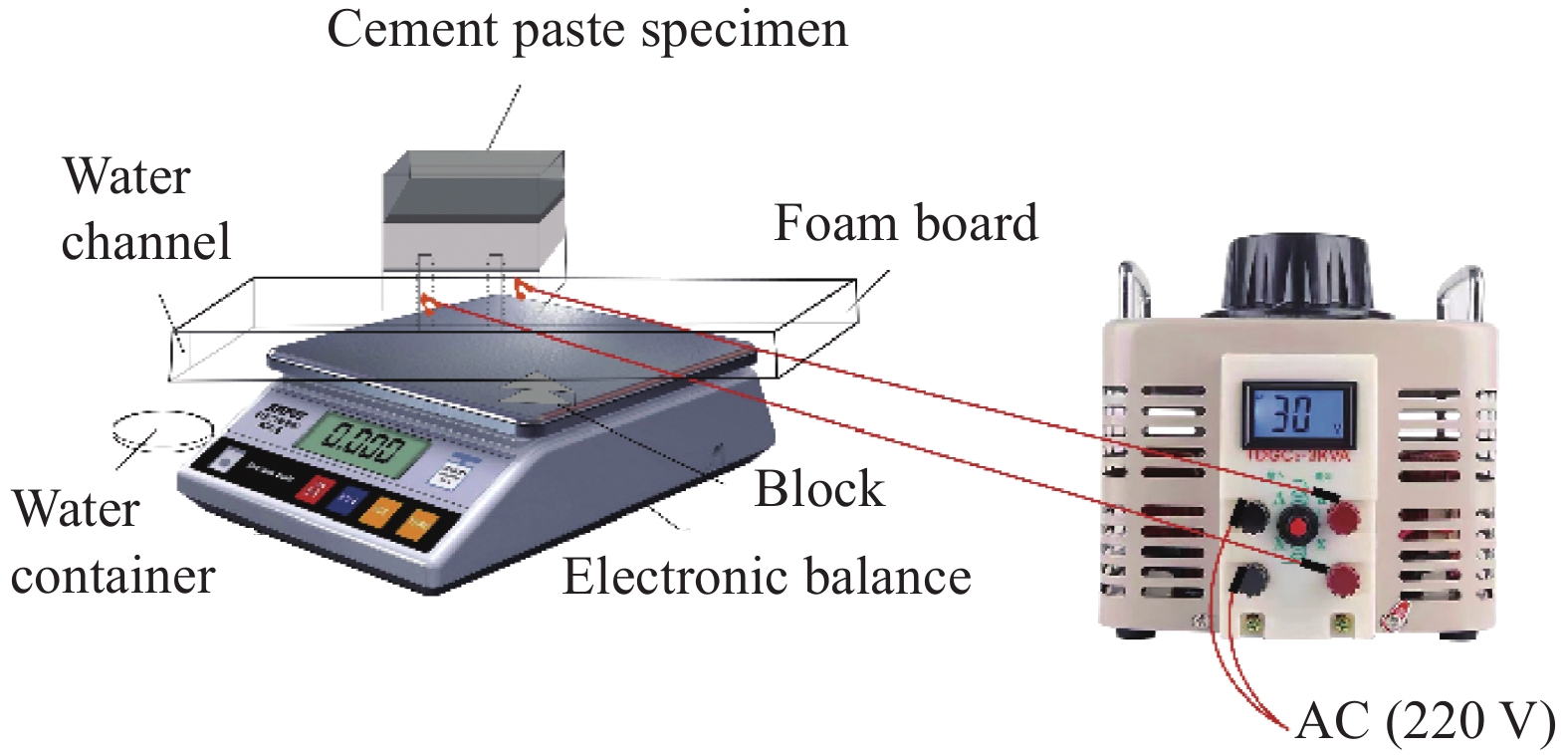
方法(ISO法)》 (GB/T 17671) 标准制作不同G-SD掺量(0.1~0.5 wt%)的水泥净浆试件。最后,采用直流二电极法研究了G-SD改性水泥净浆试件的电阻率及其温度对电阻率的影响;采用自制装置研究了G-SD改性水泥净浆试件的电热性能、融冰化雪性能与热电效应。
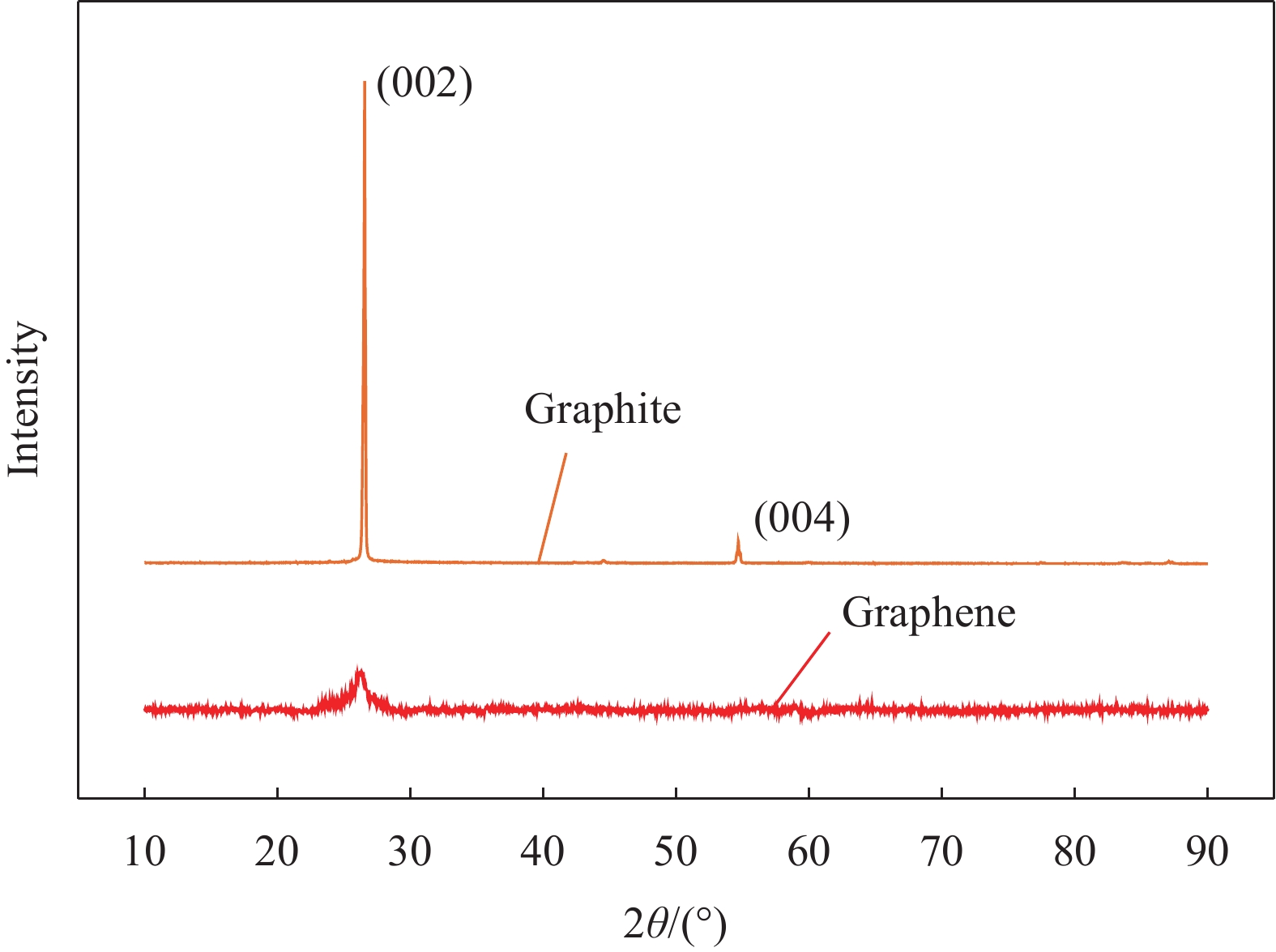
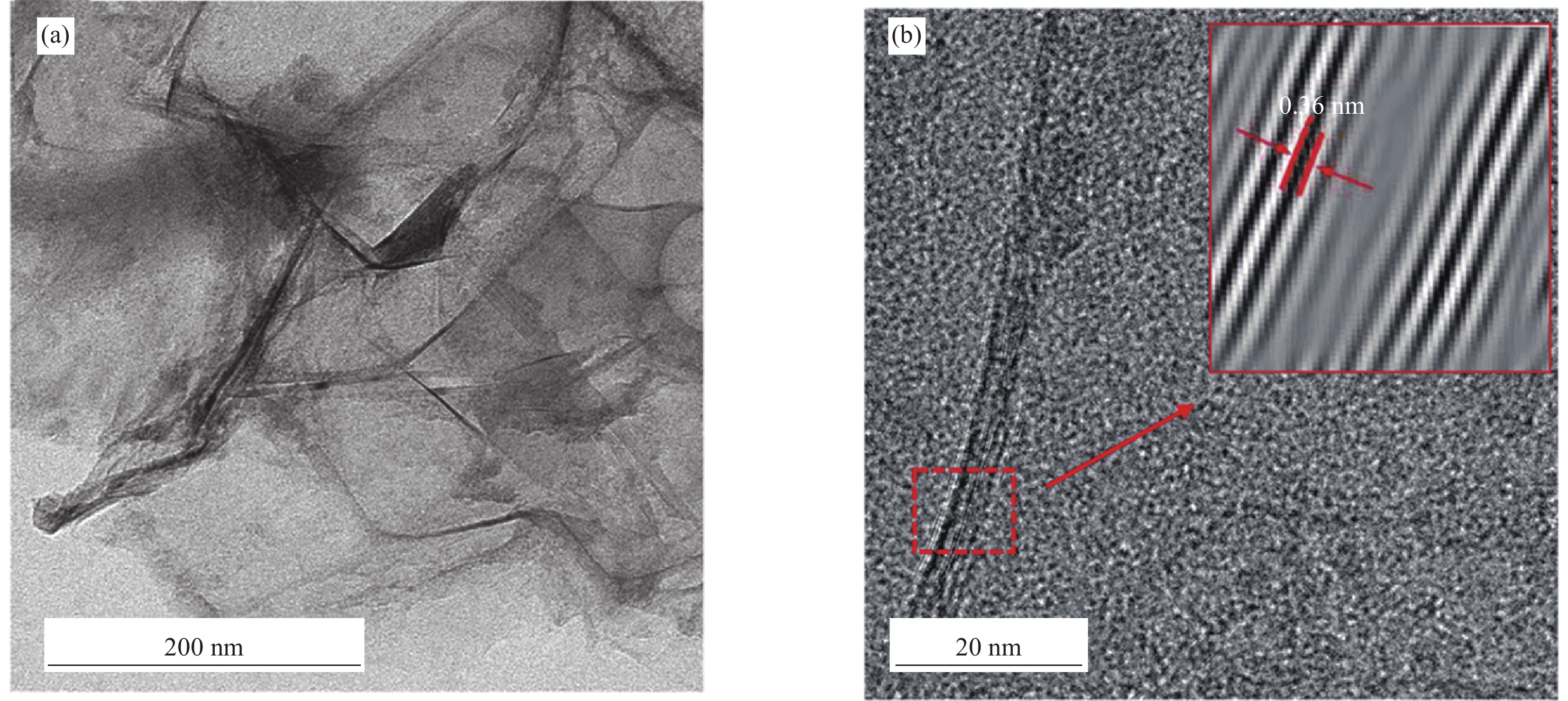
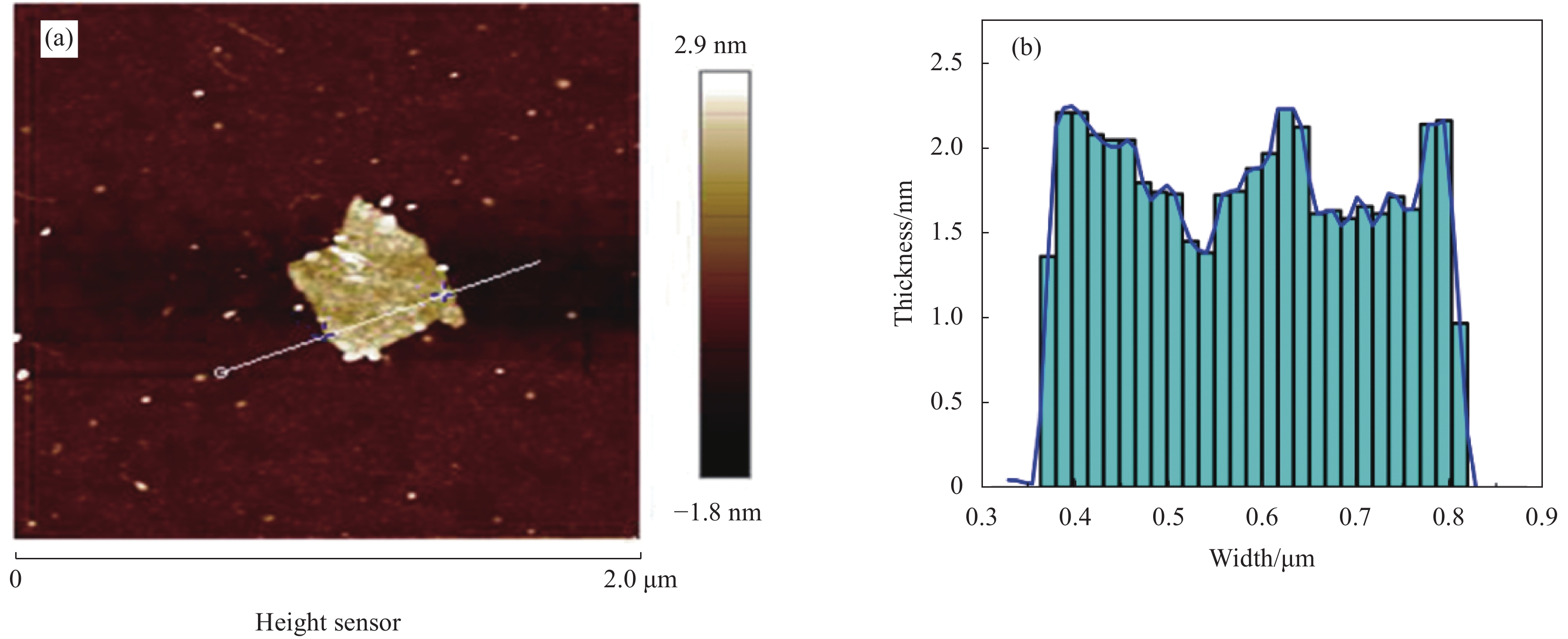
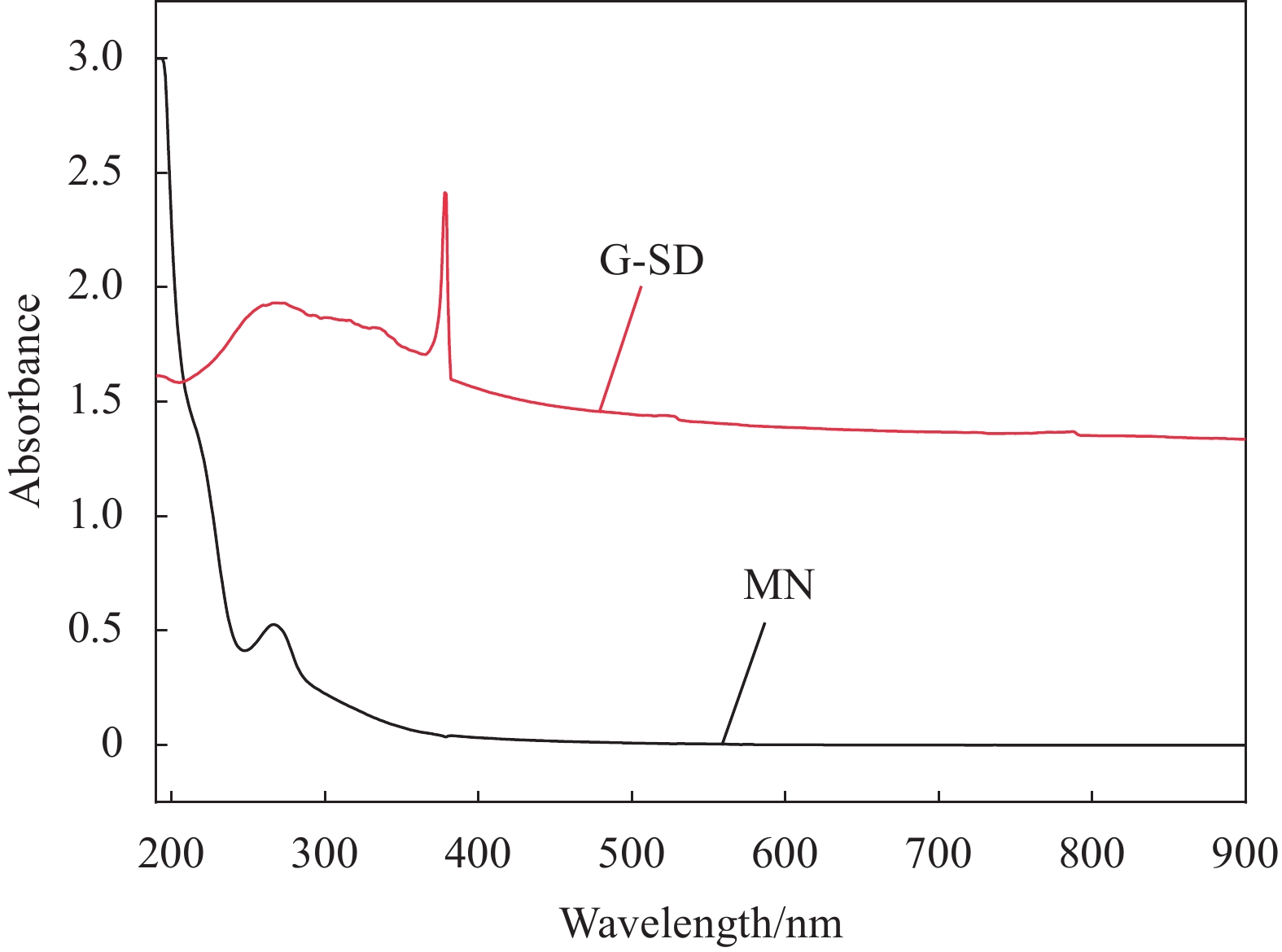
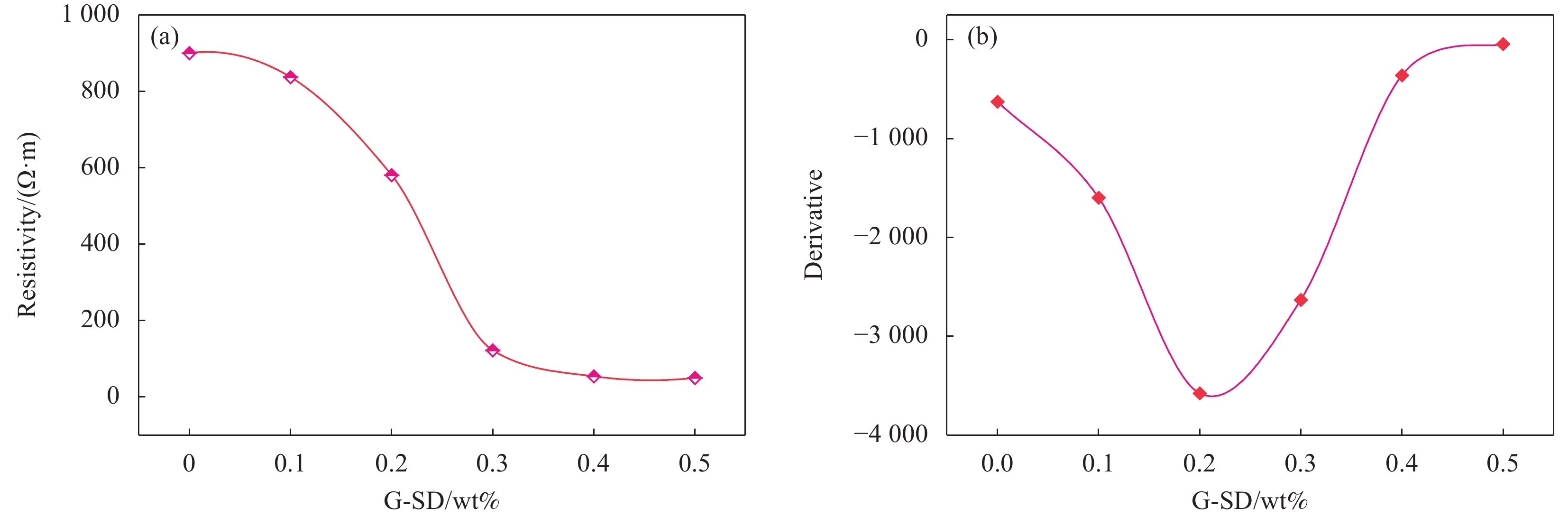
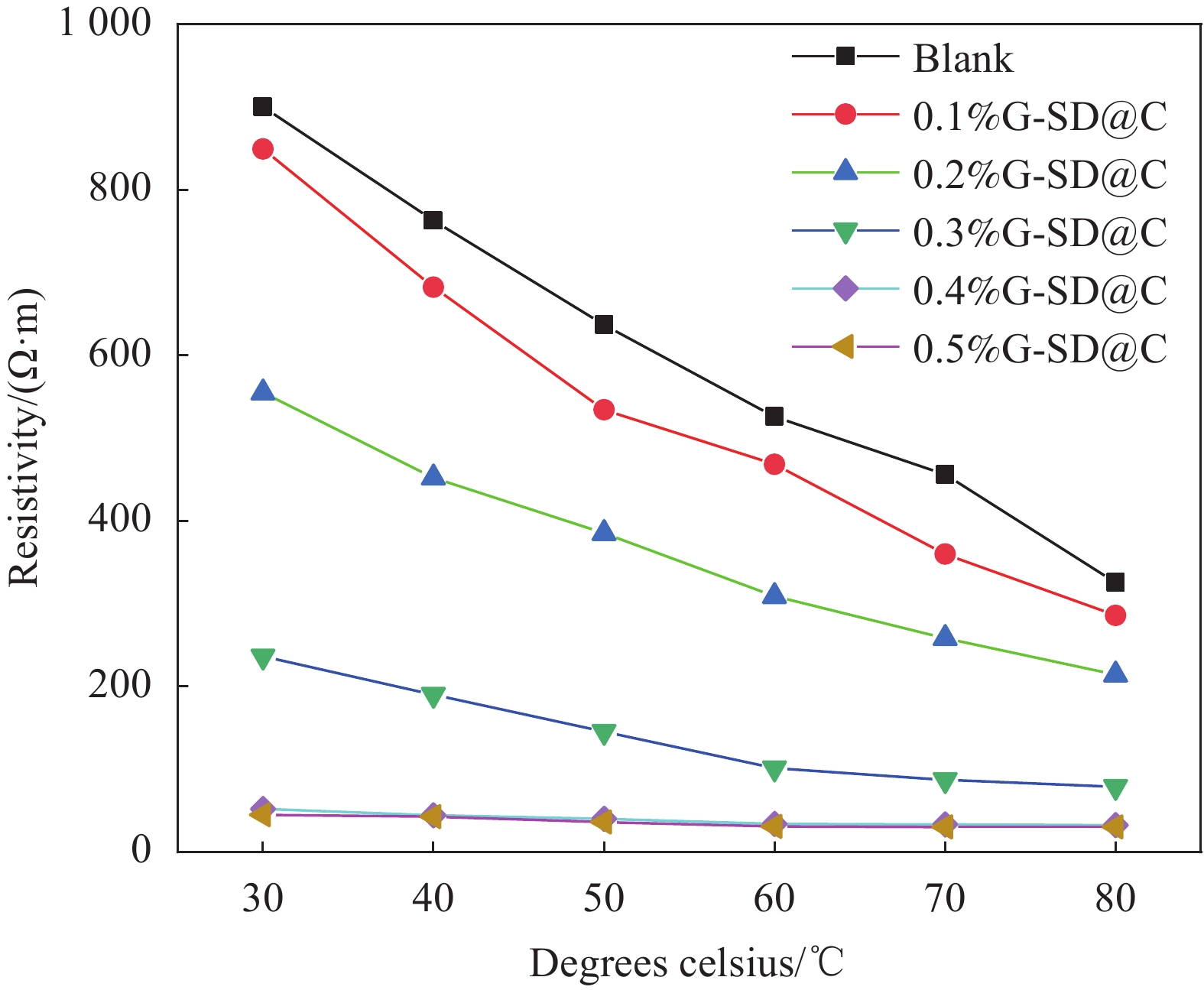
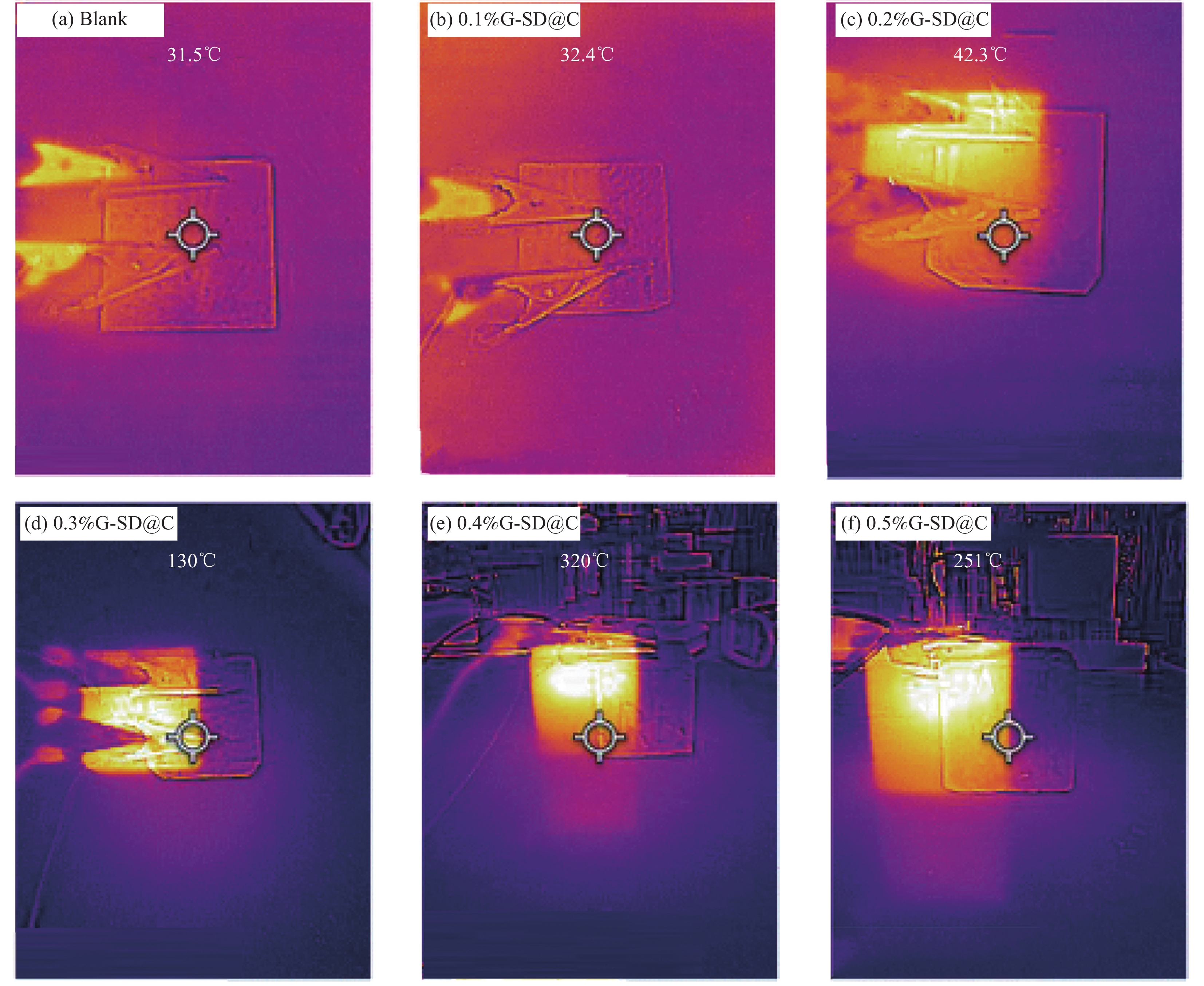
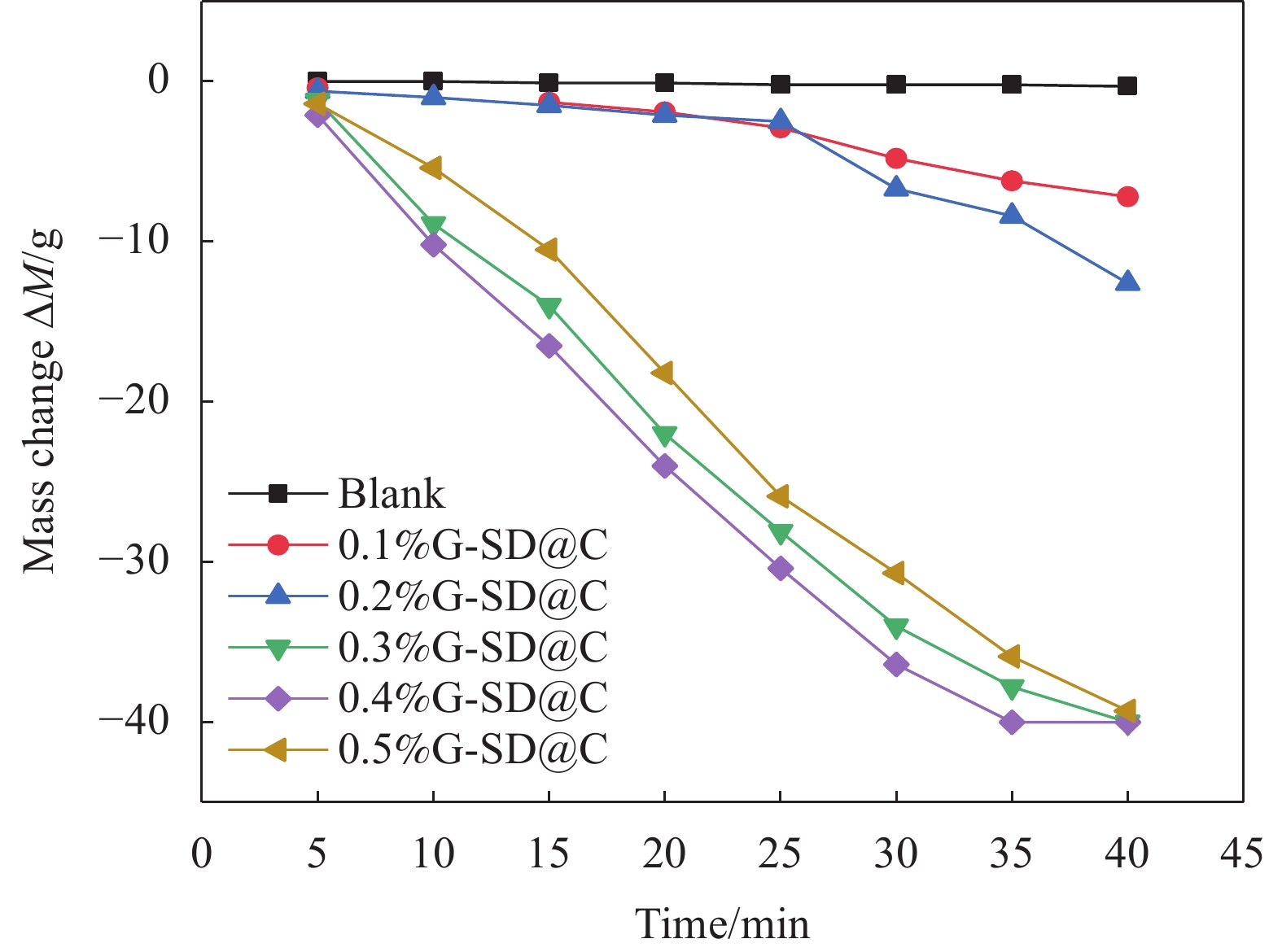
结果微观表征与静置试验表明,G-SD层数较少(4~6),呈半透明薄纱状,边缘含有羟基、环氧基等亲水官能团,薄膜的电导率为300S/cm;G-SD水溶液静置5d后,未出现团聚沉没现象,说明其具有优良的水溶性。吸光度测试表明,当MN与G-SD质量比为3:1时,G-SD的分散性最佳。因此,在制作水泥净浆试件时,选择 MN∶G-SD质量比为 3∶1进行配合比设计。直流二电极法测试发现,当分别掺入0.1wt%、0.2wt%、0.3wt%、0.4wt%和0.5wt%G-SD后,试件0.1%G-SD@C、0.2%G-SD@C、0.3%G-SD@C、0.4%G-SD@C、0.5%G-SD@C的电阻率均呈下降趋势,相比Blank组(900Ω·m)分别降低了7.0%、35.5%、86.5%、94.0%、94.5%,说明G-SD的掺入能显著降低水泥净浆的电阻率,提高其导电性。由水泥净浆电阻率曲线的一阶偏导数求得该体系下水泥净浆复合材料的渗滤阀值为0.4wt%,相比已有文献,其渗滤阀值大幅降低,说明G-SD自身的高导电性和优良的水溶性,保证了其在水泥浆体中的均匀分散,使得其能在极低掺量时形成空间导电网络,从而赋予G-SD改性水泥净浆复合材料具有低掺量、高导电的特性。电学性能测试发现阀值下水泥净浆试件的电热性能良好,在外加30 V电压下通电20 min,试件温度可达320 ℃,40 min内可将4 cm厚冰层完全融化,具有优异的融雪化冰潜力。热电性能研究表明,当G-SD掺量为0.1 wt% 时,试件的Seebeck系数为154.4 μV/K。
结论G-SD优异的水溶性和导电性克服了G的高导电性与水溶性不兼容的难题,将其用作智能与功能化水泥基材料的导电填料时,保证了G-SD在水泥浆体中的均匀分散并能在极低掺量下相互搭接形成空间导电网络,大幅降低了功能化水泥基材料的渗滤阀值,在该渗滤阀值下,水泥净浆试件表现出优异的电热性能和融冰化雪能力,对冬季道路除冰有积极意义。
-
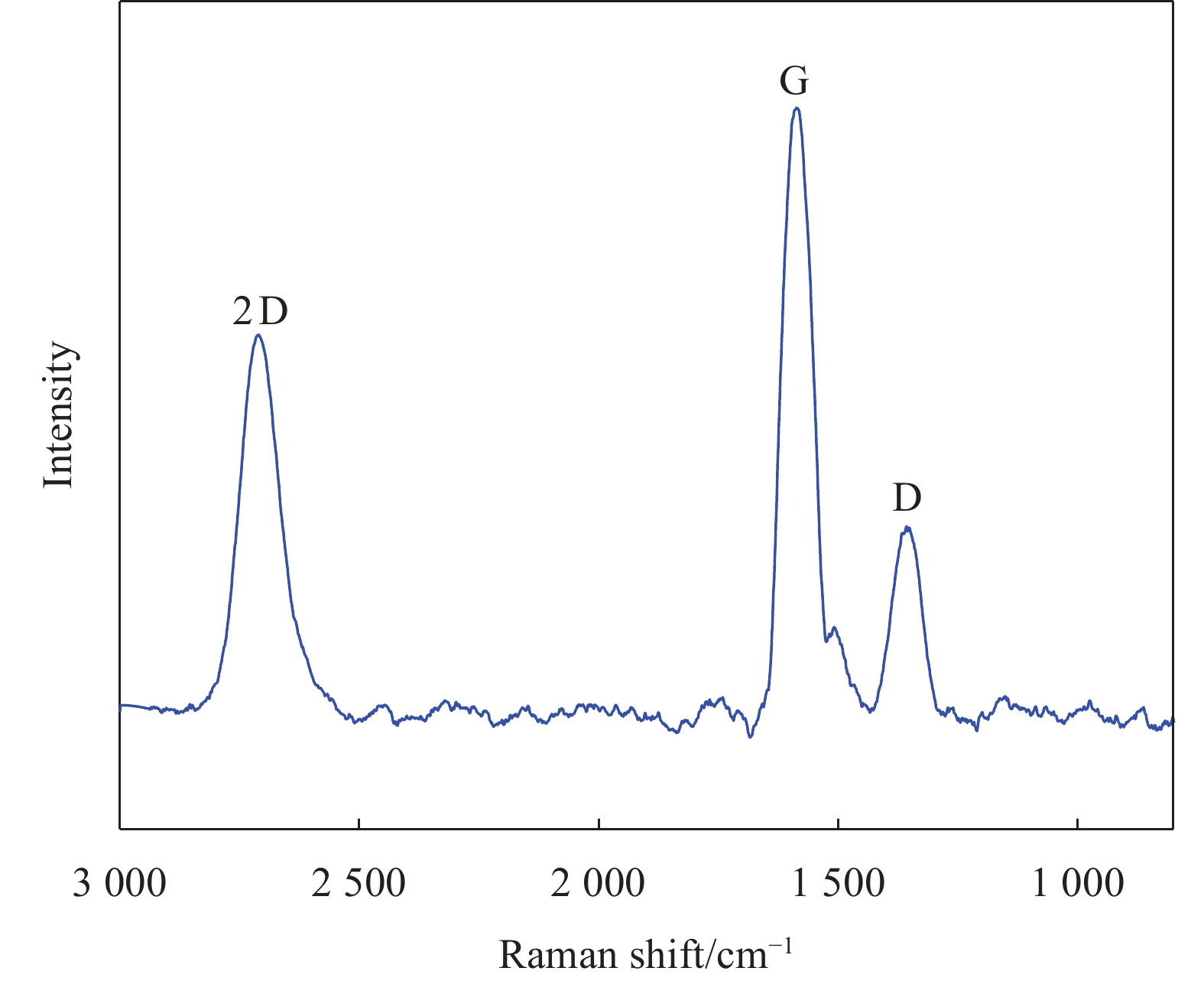
石墨烯(G)具有优异的导电性和二维平面结构,是功能化水泥基材料的理想填料。近年来,基于G改性的智能和功能化水泥基材料成为该领域的研究热点。但目前G功能化水泥基材料面临的难题是G在水泥浆体中的分散不均匀及其导致的功能化水泥基材料时掺量过高。
本文参照国家发明专利(申请号202211299955.2)制备一个兼顾高导电性和水溶性的石墨烯(G-SD),其薄膜电导率为300S/cm,在水溶液中的最大浓度为5.4g/L,在最大浓度下静置5d仍能稳定均匀分散,具有优异的导电性与水溶性,克服了G的高导电性与水溶性不兼容的难题。G-SD优良的导电性与水溶性,保证了其均匀分散在水泥浆体中,并将G功能化水泥基材料的渗滤阀值从1.6wt%降至0.4wt%。在该渗滤阀值下,G-SD改性水泥净浆复合材料的电阻率下降了94.0%;电热性能表现最佳,试件表面温度从31℃上升到320℃,平均升温速率为14.8℃/min,并能在40min内将4cm厚冰层完全融化,这表明G-SD改性水泥净浆复合材料有不错的融冰化雪潜力,对冬季道路除冰有积极意义。

Thermal imaging of G-SD specimens with different content at 20min




 下载:
下载: