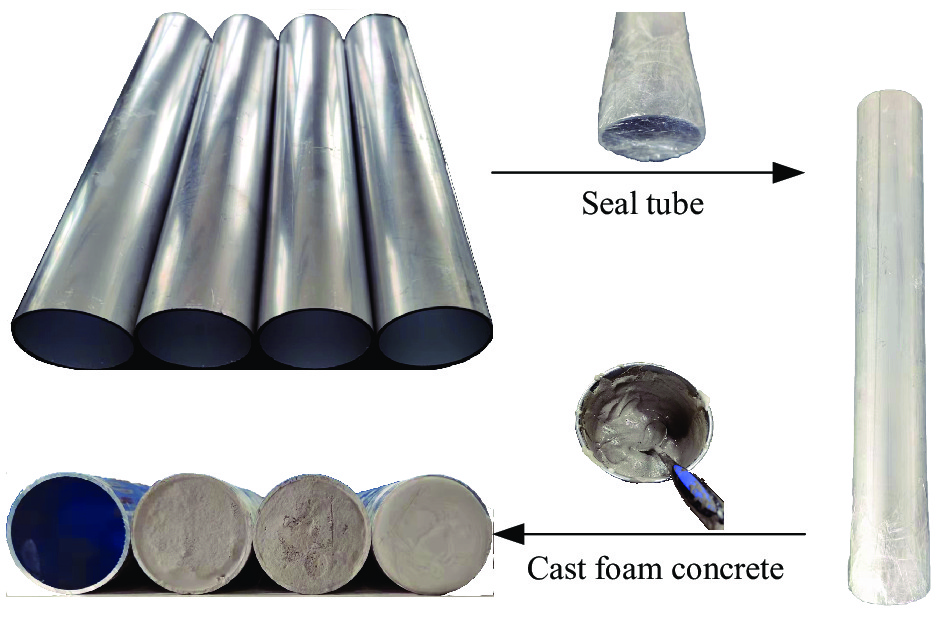
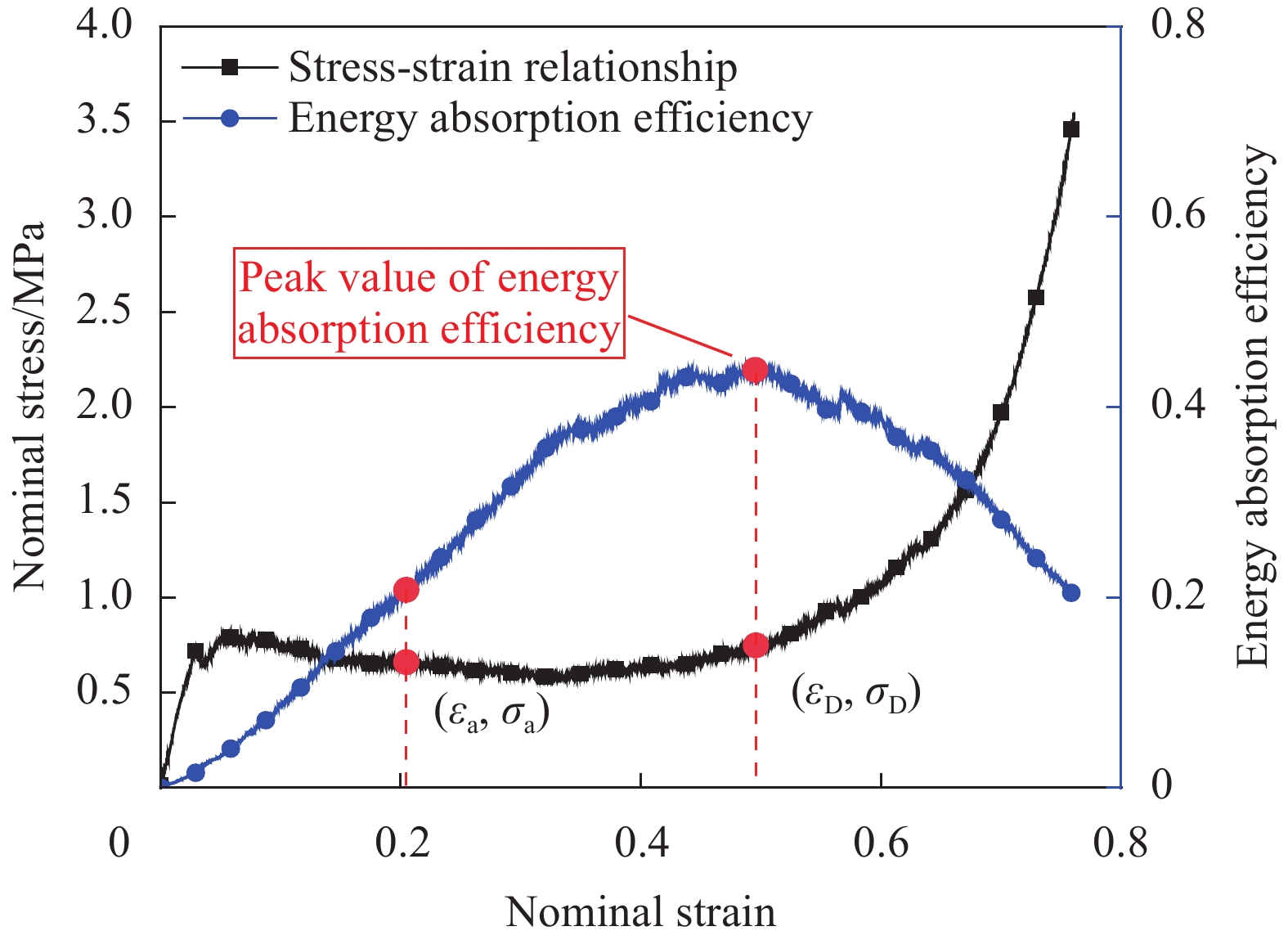
Energy absorption of foam concrete filled aluminum tube composite cladding
-
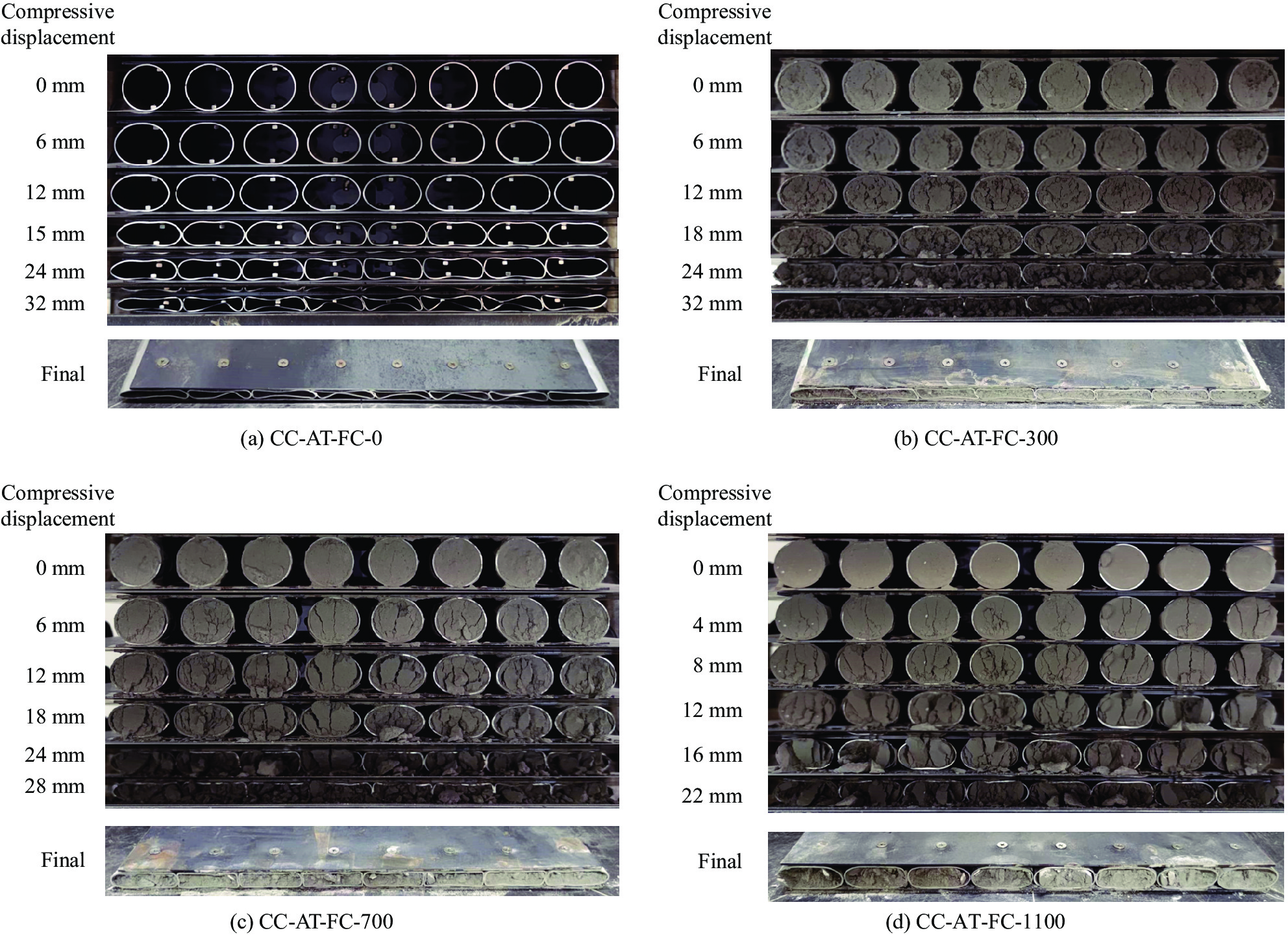
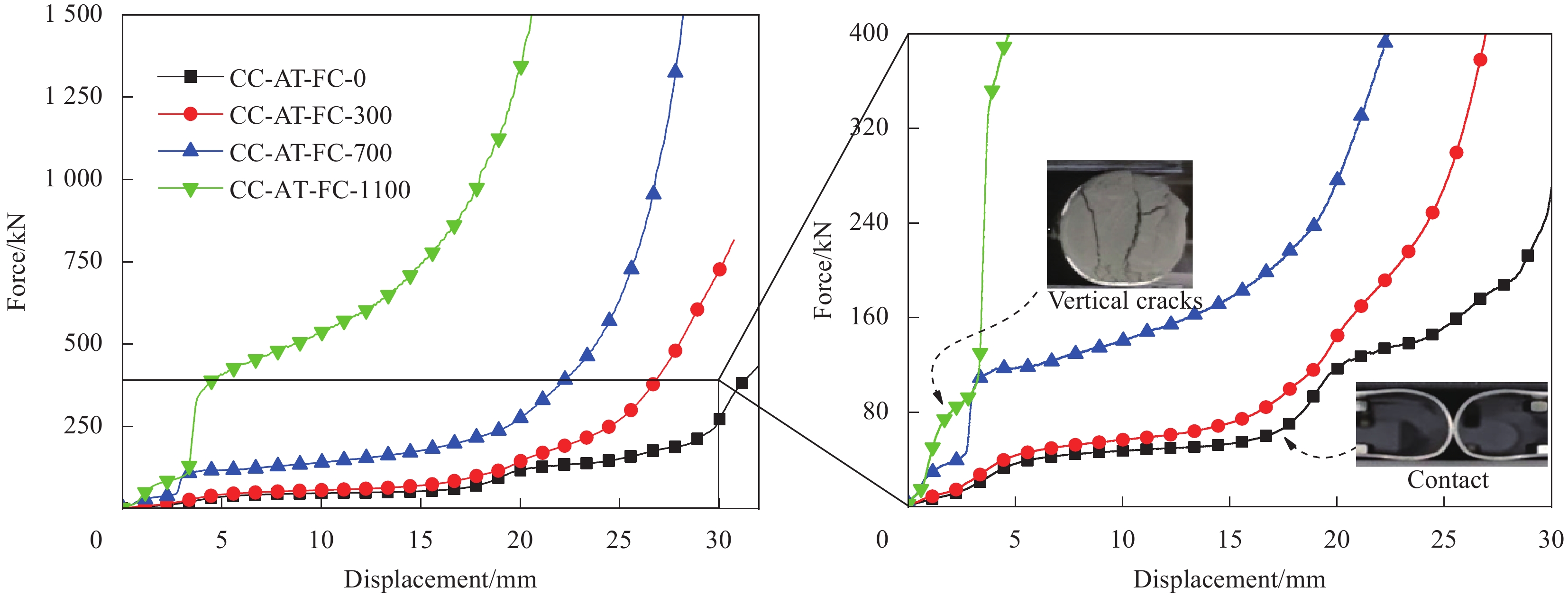
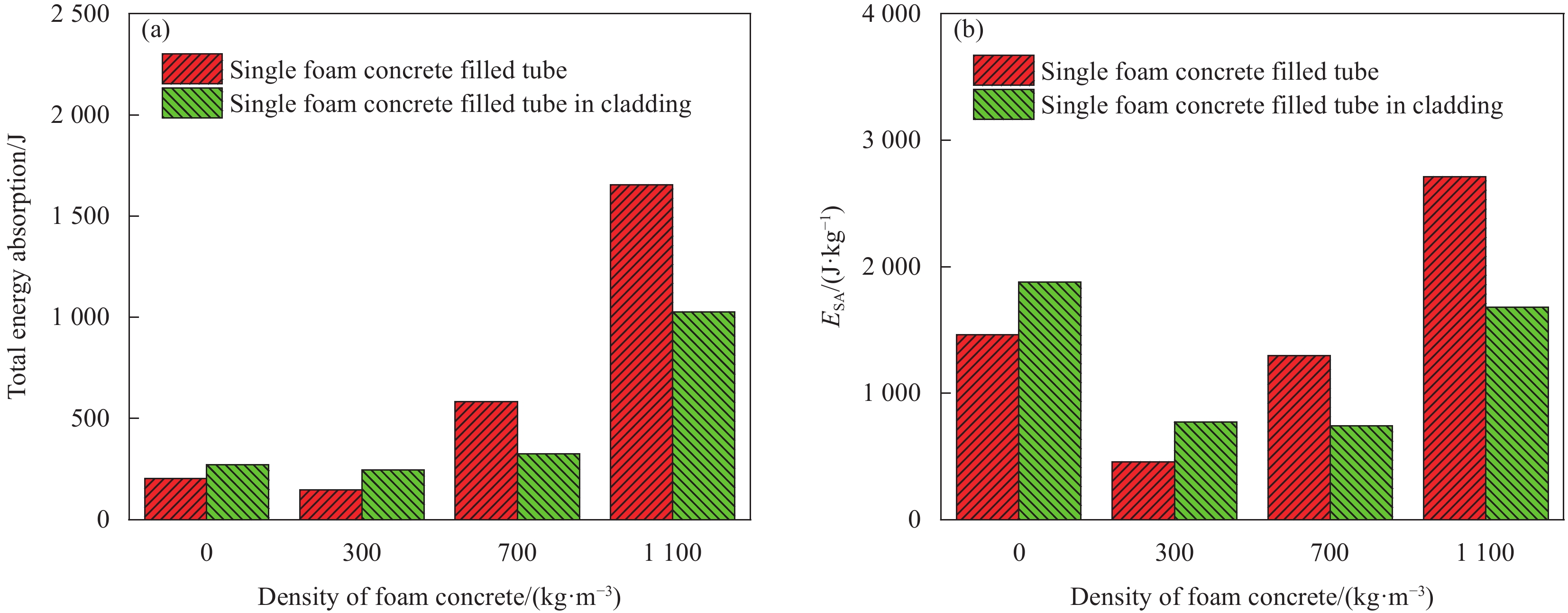
摘要: 为提高金属圆管组合挂板的吸能性能,提出一种填充泡沫混凝土铝管组合挂板。在铝管中分别填充不同密度(300 kg/m3、700 kg/m3、1100 kg/m3)的泡沫混凝土,并对单根填充泡沫混凝土铝管和填充泡沫混凝土铝管组合挂板在准静态压缩下的变形模式、力学性能和吸能性能进行试验研究。结果表明:与单根空铝管相比,填充300 kg/m3泡沫混凝土会小幅降低填充铝管的吸能性能,随着填充物密度增加至700 kg/m3和1100 kg/m3,填充铝管的吸能性能大幅提升,能量吸收总量分别提高286%和815%;与单根铝管压缩相比,组合挂板中填充铝管产生的挤压作用会大幅提升空铝管和填充300 kg/m3泡沫混凝土铝管组合挂板的比吸能,分别提升28.6%和68.9%,而降低填充700 kg/m3和1100 kg/m3泡沫混凝土铝管组合挂板的比吸能,分别降低42.7%和38.1%。因此,考虑组合挂板实际应用,当泡沫混凝土填充物密度较小时,建议选择较小铝管间距;当泡沫混凝土填充物密度较大时,建议选择较大铝管间距防止芯层铝管发生挤压。Abstract: To improve the energy absorption performance of metal circular tube composite cladding, foam concrete filled aluminum tube composite cladding was proposed in the present study. With consideration of different foam concrete densities of 300 kg/m3, 700 kg/m3 and 1100 kg/m3, the deformation mode, mechanical properties and energy absorption performance of single foam concrete filled aluminum tube, as well as foam concrete filled aluminum tube composite cladding under quasi-static compression, were experimentally investigated. The results show that the energy absorption of the aluminum tube filled with 300 kg/m3 foam concrete is slightly inferior to that of the hollow aluminum tube. With increasing the foam concrete density to 700 kg/m3 and 1100 kg/m3, the energy absorption performance of the filled aluminum tube is significantly improved with the increased total energy absorption by 286% and 815%, respectively. Compared to the single aluminum tube, the mutual extrusion among tubes would greatly improve the specific energy absorption of the hollow aluminum tube and 300 kg/m3 foam concrete filled composite claddings, which are increased by 28.6% and 68.9%, respectively. Nevertheless, the specific energy absorptions of 700 kg/m3 and 1100 kg/m3 foam concrete filled aluminum tube composite cladding decrease by 42.7% and 38.1% due to the mutual extrusion effect of aluminum tubes. Therefore, from the point view of the practical application of the proposed foam concrete filled aluminum tube composite cladding, a small aluminum tube spacing is suggested with the low density of foam concrete filler, meanwhile, a large aluminum tube spacing is recommended to prevent the extrusion of aluminum tube with the high density of foam concrete filler.
-
Keywords:
- foam concrete /
- aluminum tube /
- composite cladding /
- deformation model /
- energy absorption
-
纤维增强复合材料具有比强度高、比模量大等优点,已被广泛应用于航空航天等工业领域[1]。但复合材料对冲击敏感性较高,内部受低速冲击后会产生不可见损伤,造成安全隐患。碳纤维-玻璃纤维混杂复合材料是将碳纤维及玻璃纤维在同一种基体内成型的复合材料,可有效提高复合材料的力学性能[2-3]。目前对混杂复合材料低速冲击性能的研究主要集中在混杂结构和纤维种类上[4-5]。Swolfs等[6]研究发现,将低伸长率纤维放在层合板中间位置,可有效提高抗侵彻性能。Hung等[7]分析了碳纤维-玻璃纤维层间混杂复合材料低速冲击性能,发现将碳纤维置于冲击面时抗冲击性能更强。Manikandan等[8]研究发现,将韧性纤维置于复合材料背面可吸收更多冲击能量,原因是由于下部韧性层可为上部脆性层提供更大的变形。Sarasini等[9]对玻璃纤维-玄武岩纤维混杂复合材料进行低速冲击研究表明,玄武岩纤维为芯层的夹芯混杂结构吸收冲击能量更多,玻璃纤维为芯层时弯曲性能较好。有限元分析是分析低速冲击的有效手段,Liu等[10]对比了Puck、Hashin及Chang-Chang失效准则对低速冲击预测的区别,结果表明,三种准则在低速冲击响应和能量耗散方面的预测结果基本一致,在基体和分层损伤的预测上有所不同。Hou等[11]基于连续介质损伤力学(CDM)建立了含修补区域的复合材料低速冲击模型,采用基于断裂韧性的损伤变量,研究了修补区厚度及铺层结构对低速冲击性能的影响。Ebina等[12]对不同铺层结构的碳纤维复合材料进行低速冲击模拟,面内损伤采用增强连续介质力学(ECDM)模型,纤维损伤采用裂缝模型(SCM),层间采用界面单元(CZM),模拟结果与实验数据拟合度较高。Chen等[13]建立了碳纤维-玻璃纤维-玄武岩纤维复合材料低速冲击损伤模型,定义指数型损伤变量,研究发现,碳纤维为芯层的夹芯结构抗冲击性能较好,玄武岩-碳纤维混杂结构与碳纤维-玻璃纤维混杂结构的冲击响应类似。Wu等[14]建立了纱线尺度的三维正交碳纤维-玻璃纤维混杂复合材料低速冲击模型,采用代表性体积单元(RUC)计算复合材料层合板宏观力学参数,研究发现,冲击面为碳纤维时抗冲击性能更好,破坏主要为冲击面碳纤维断裂和上层纤维-基体分层损伤,冲击面为玻璃纤维时破坏主要为复合材料层合板背部分层损伤。由于冲击速度较低,应变率效应不明显,大多数复合材料低速冲击研究会忽略应变率效应[15-16]。部分低速冲击数值模拟研究考虑了应变率效应,Wang等[17]建立了应变率相关的碳纤维复合材料低速冲击三维损伤模型,采用修正的复合材料应力-应变关系及考虑应变率效应的层内层间损伤模型,模拟结果与实验数据拟合程度较好。
本文以碳纤维-玻璃纤维混杂复合材料为研究对象,分析混杂结构和冲击面纤维种类对低速冲击性能的影响。采用商业有限元软件ABAQUS建立了层间和层内两类混杂复合材料低速冲击模型,层内混杂复合材料采用纱线尺度模型。编写VUMAT子程序定义指数型渐进损伤因子及刚度退化方案,考虑纤维断裂、基体开裂、分层等损伤,通过分析实验数据及损伤形貌,揭示了碳纤维-玻璃纤维混杂复合材料低速冲击损伤破坏机制。
1. 实验及仿真方法
1.1 原材料及试样制备
单向经编织物(NCF)采用碳纤维(CF,TORAY T620SC-24K-50C)和玻璃纤维(GF,CPIC ECT469L-2400)制成,包括纯CF和纯GF的NCF织物及两种层内混杂织物,织物规格如表1所示,其中CF-GF和CF-CF-GF-GF为层内混杂织物,织物结构示意图如图1所示。环氧树脂,型号为2511-1A/BS风电叶片真空灌注专用树脂,主剂与固化剂质量比为100∶30,上纬(天津)公司。
表 1 碳纤维-玻璃纤维(CF-GF)单向经编织物(NCF)规格Table 1. Specifications of carbon fiber-glass fiber (CF-GF) non-crimp fabric (NCF)Fabric type Areal density/(g·m−2) Mass ratio of CF to GF CF GF CF 728.3 0 1∶0 GF 0 944.9 0∶1 CF-GF 364.2 472.4 1∶1 CF-CF-GF-GF 364.2 472.4 1∶1 本文设计层间和层内两类混杂结构,层内混杂层合板由CF-GF和CF-CF-GF-GF两种层内混杂织物铺层而成。各层合板的CF-GF混杂比均为1∶1,铺层方式为(0°/90°)4S,共8层,根据混杂结构及冲击面纤维种类进行命名,如表2所示,其中S-C和S-G采用夹芯式层间铺层形式。采用真空辅助树脂传递模塑(VARTM)工艺成型,固化条件为80℃、8 h。
表 2 CF-GF混杂复合材料层合板铺层结构Table 2. Stacking configurations of CF-GF hybrid composite laminatesHybrid structure Stacking sequence Nomenclature Non-hybrid (CFCFCFCF)2s C (GFGFGFGF)2s G Interply-hybrid (CFGFCFGF)2s I-C (GFCFGFCF)2s I-G Sandwich-hybrid (CFCFGFGF)2s S-C (GFGFCFCF)2s S-G Intralayer-hybrid (CF-GF) fabric CN-1 (CF-CF-GF-GF) fabric CN-2 1.2 性能测试
按照ASTM D7136M—05[18],采用INSTRON-9250HV落锤试验机进行低速冲击实验,通过改变冲击速度控制冲击能量,设置两个冲击能量分别为30 J和50 J,试样尺寸为100 mm×150 mm×6 mm,每组测试5个试样。利用NAUT21空气耦合式超声波C扫监测复合材料冲击后分层损伤,采用Bruker SkyScan1072进行Micro-CT测试,观察内部损伤形貌。
1.3 有限元模型
1.3.1 复合材料损伤准则
Hashin失效准则被广泛应用于分析预测复合材料损伤破坏[19],但复合材料在损伤过程中冲击点附近的应力变化剧烈,应力形式的Hashin失效准则无法准确描述材料破坏过程,而应变在冲击过程中的变化较为平缓,更适合作为复合材料的失效判据。因此,本文采用基于应变形式的Hashin失效准则[20],具体表达式如下:
纤维拉伸断裂 (
ε11⩾ ):{e}_{\rm{f}}^{\rm{t}}={\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{11}}{{\varepsilon }_{11}^{\rm{T}}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{12}}{{\tau }_{12}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{13}}{{\tau }_{13}}\right)}^{2}\geqslant 1 (1) 纤维压缩断裂 (
{\varepsilon }_{11}\leqslant 0 ):{e}_{\rm{f}}^{\rm{c}}={\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{11}}{{\varepsilon }_{11}^{\rm{C}}}\right)}^{2}\geqslant 1 (2) 基体拉伸断裂(
{\varepsilon }_{22}\geqslant 0 ):{e}_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{t}}={\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{22}}{{\varepsilon }_{22}^{\rm{T}}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{12}}{{\tau }_{12}}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\frac{{\varepsilon }_{23}}{{\tau }_{23}}\right)}^{2}\geqslant 1 (3) 基体压缩断裂(
{\varepsilon }_{22}\leqslant 0 ):\begin{split} e_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{c}} = &{\left( {\frac{{{E_{22}}{\varepsilon _{22}}}}{{2{G_{12}}{\gamma _{12}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{22}}}}{{\varepsilon _{22}^{\rm{T}}}}} \right)^2}\left[ {\left( {{{\left( {\frac{{{E_{22}}\varepsilon _{22}^{\rm{C}}}}{{2{G_{12}}{\tau _{12}}}}} \right)}^2} - 1} \right)} \right] + \\& {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{12}}}}{{{\tau _{12}}}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\frac{{{\varepsilon _{13}}}}{{{\tau _{13}}}}} \right)^2} \geqslant 1 \end{split} (4) 式中:E和G分别为材料的杨氏模量和剪切模量;
{\varepsilon }_{11} 和{\varepsilon }_{22} 为单元材料主方向的应变分量;{\varepsilon }_{12} 、{\varepsilon }_{13} 和{\varepsilon }_{23} 为单元材料主方向的剪切应变分量;{\varepsilon }_{{{i}}{{i}}}^{\rm{T}} 和{\varepsilon }_{{{i}}{{i}}}^{\rm{C}} 分别为i 方向对应的拉伸和压缩强度的失效应变;{\tau }_{{{i}}{{j}}} 为单元剪切强度对应的剪切失效应变。当某单元内应变分量满足上述某一条件时,即认为该单元发生损伤。失效应变与材料强度之间的关系如下:\begin{split} &{X_{\rm{T}}} = {E_{11}}\varepsilon _{11}^{\rm{T}},{X_{\rm{C}}} = {E_{11}}\varepsilon _{11}^{\rm{C}},{Y_{\rm{T}}} = {E_{22}}\varepsilon _{22}^{\rm{T}},\\ &{Y_{\rm{C}}} = {E_{22}}\varepsilon _{22}^{\rm{C}},{Z_{\rm{T}}} = {E_{33}}\varepsilon _{33}^{\rm{T}},{S_{12}} = {G_{12}}{\tau _{12}},\\ &{S_{13}} = {G_{13}}{\tau _{13}},{S_{23}} = {G_{23}}{\tau _{23}} \end{split} (5) 式中,
{X}_{\rm{T}} 、X_{\rm{C}} 、Y_{\rm{T}} 、Y_{\rm{C}} 、{S}_{{{i}}{{j}}} 分别为层合板轴向拉伸、轴向压缩、横向拉伸、横向压缩和各方向的剪切强度。相关材料属性如表3和表4所示。表 3 用于数值模拟的CF/2511-1A/BS环氧树脂复合材料和GF/2511-1A/BS环氧树脂复合材料弹性参数Table 3. Elastic parameters of CF/2511-1A/BS epoxy composites and GF/2511-1A/BS epoxy composites used in numerical simulationMaterial E11/GPa E22=E33/GPa G12=G13/GPa G23/GPa {\mu }_{12} {\mu }_{13} {\mu }_{23} {G}_{{\rm{f}}}/(kJ·m−2) {G}_{{\rm{m}}}/(kJ·m−2) CF/epoxy 110 8.3 4.6 3.4 0.303 0.303 0.38 80 1 GF/epoxy 40 8.4 4.3 3.2 0.315 0.315 0.39 65 1 Notes: E11, E22, E33—Elastic modulus (direction 11, 22, 33); G12, G13, G23—Shear modulus (direction 12, 13, 23); {\mu }_{12} , {\mu }_{13} , {\mu }_{23} —Poisson’s ratio (direction 12, 13 and 23). 表 4 用于数值模拟的CF/2511-1A/BS环氧树脂复合材料和GF/2511-1A/BS环氧树脂复合材料的强度参数Table 4. Strength parameters of CF/2511-1A/BS epoxy composites and GF/2511-1A/BS epoxy composites used in numerical simulationMPa Material XT XC YT=ZT YC=ZC S12=S13 S23 CF/epoxy 1600 640 48 150 80 60 GF/epoxy 860 550 48 140 65 60 单元产生损伤后需进行材料性能退化,即刚度折减,本文引入指数形式的损伤状态变量d定义渐进损伤刚度折减方案。相比于参数型损伤变量将材料宏观属性直接折减,指数型损伤变量更接近实际情况且损伤过程连续[21]。将Hashin准则中的失效因子(
{e}_{\rm{f}} 、{e}_{\rm{m}} )与损伤变量({d}_{\rm{f}} 、{d}_{\rm{m}} )相关联,具体形式如下:[22],\begin{array}{l} {d_{\rm{f}}} = 1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{e_{\rm{f}}}} }}{{\rm{e}}^{\left( { - {E_{11}}{{\left( {\varepsilon _{11}^{{{{\rm{f}}i}}}} \right)}^2}\left( {\sqrt {{e_{\rm{f}}}} - 1} \right){L^{\rm{c}}}/{G_{\rm{f}}}} \right)}}\\ {d_{\rm{m}}} = 1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {{e_{\rm{m}}}} }}{{\rm{e}}^{\left( { - {E_{22}}{{\left( {\varepsilon _{22}^{{{{\rm{m}}i}}}} \right)}^2}\left( {\sqrt {{e_{\rm{m}}}} - 1} \right){L^{\rm{c}}}/{G_{\rm{f}}}} \right)}} \end{array} (6) 式中:
{G}_{\rm{f}} 和{G}_{\rm{m}} 分别为材料纤维纵向和横向断裂韧性;{L}^{\rm{c}} 为单元特征长度,加入{L}^{\rm{c}} 可降低网格密度对结果精度的影响;i 根据单元受拉或受压分别赋值为T 或C 。本文采用的刚度退化方案如下:\begin{split} &{C}_{11}^{{\rm{d}}}=\left(1-{d}_{\rm{f}}\right){C}_{11} \\ &{C}_{22}^{{\rm{d}}}=\left(1-{d}_{\rm{f}}\right){\left(1-{d}_{\rm{m}}\right)C}_{22} \\ &{C}_{33}^{{\rm{d}}}=\left(1-{d}_{\rm{f}}\right){\left(1-{d}_{\rm{m}}\right)C}_{33} \\ &{C}_{12}^{{\rm{d}}}=\left(1-{d}_{\rm{f}}\right){\left(1-{d}_{\rm{m}}\right)C}_{12} \\ &{C}_{23}^{{\rm{d}}}=\left(1-{d}_{\rm{f}}\right){\left(1-{d}_{\rm{m}}\right)C}_{23} \\ &{C}_{13}^{{\rm{d}}}=\left(1-{d}_{\rm{f}}\right){\left(1-{d}_{\rm{m}}\right)C}_{13} \end{split} (7) 采用双线性内聚力单元(Cohesive element)模拟相邻子层界面的分层损伤[23]。采用二次应力损伤准则(Quads)定义损伤起始,损伤演化采用B-K (Benzeggaph-Kenane)准则,分别如下:
{\left(\frac{{t}_{{\rm{n}}}}{N}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\frac{{t}_{{\rm{s}}}}{S}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\frac{{t}_{\rm{t}}}{T}\right)}^{2}=1 (8) {G}^{\rm{C}}\geqslant {G}_{{\rm{n}}}^{\rm{C}}+\left({G}_{{\rm{S}}}^{\rm{C}}-{G}_{{\rm{n}}}^{\rm{C}}\right){\left(\frac{{G}_{{\rm{s}}}}{{G}_{\rm{T}}}\right)}^{\eta } (9) 式中:
{t}_{{\rm{n}}} 、{t}_{{\rm{s}}} 、{t}_{\rm{t}} 分别为界面法向应力和两个剪切应力;N、S、T对应界面法向和两个剪切强度;{G}_{{\rm{n}}}^{\rm{C}} 和{G}_{{\rm{S}}}^{\rm{C}} 分别为法向和切向临界应变能释放率;{G}_{{\rm{s}}} 和{G}_{{\rm{n}}} 分别为{t}_{{\rm{s}}} 、{t}_{{\rm{n}}} 对应的能量释放率。相关材料属性如表5所示。表 5 CF/2511-1A/BS环氧树脂复合材料和GF/2511-1A/BS环氧树脂复合材料的层间界面参数Table 5. Material properties of interface cohesive elements for CF/2511-1A/BS epoxy composites and GF/2511-1A/BS epoxy compositesρ/(kg·m−3) kN/(GPa·mm−1) kS=kT/(GPa·mm−1) N/MPa S=T/MPa G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·m−2) G_{\rm{S}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·m−2) η 1200 15 1.2 30 60 0.28 0.8 1.5 1.3.2 层间/层内数值模拟模型
图2为层间及夹芯混杂复合材料低速冲击模型,层合板采用沙漏增强模式的减缩积分单元C3D8R,共8层,单层尺寸为150 mm×100 mm×0.75 mm,定义X轴为纤维方向,Y轴为基体方向,通过改变每层材料属性实现相应的混杂结构。界面为0厚度的COH3D8内聚力单元,共7层。夹具是内径为120 mm、宽为10 mm的圆环,冲头是直径为12.6 mm的半球形锤头,夹具和冲头定义为刚体,采用R3D4单元。细化层合板冲击区域网格,提高模拟精准度。
层内混杂复合材料采用纱线尺度模型,层合板、夹具和冲头尺寸与层间模型一致,如图3(a)所示。模型假设树脂对纤维完全浸润,复合材料中纱线系统以纤维束增强树脂的复合形式存在,纤维与树脂为一整体[24],单根纱线横截面尺寸为5 mm×0.75 mm,如图3(b)所示,通过改变每根纤维束材料属性,实现CN-1及CN-2混杂结构,复合材料的基体部分由布尔运算得到,如图3(c)所示。采用金相显微镜观察纤维分布情况如图4(a)和图4(b)所示,测得CF体积分数为68vol%,GF体积分数为70vol%,在ABAQUS中建立四边形RUC (Representative unit cell)单元[25],如图4(c)所示,计算纤维束增强树脂弹性参数,相关属性如表6和表7所示。
表 6 CF-GF层内混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料模型中CF、GF和2511-1A/BS环氧树脂的材料参数Table 6. Material paramenters of CF, GF and 2511-1A/BS epoxy for CF-GF intralayer hybrid reinforced epoxy composite modelMaterial E11/GPa E22=E33/GPa G12=G13/GPa G23/GPa {\mu }_{12} {\mu }_{13} {\mu }_{23} \rho /(kg·m−3) CF 234 20 9.2 7.4 0.3 0.3 0.34 1.77 GF 78.7 7 4.0 2.5 0.3 0.3 0.4 2.54 2511-1A/BS epoxy 3.1 — — — 0.3 — — 1.13 表 7 CF-GF层内混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料模型中CF和GF纤维束的力学性能Table 7. Mechanical properties of CF and GF fiber bundle for CF-GF intralayer hybrid reinforced epoxy composite modelMaterial E11/GPa E22=E33/GPa G12=G13/GPa G23/GPa μ12 μ13 μ23 CF fiber bundle 153 8.70 3.60 3.20 0.3 0.3 0.36 GF fiber bundle 52 5.27 2.48 1.88 0.3 0.3 0.40 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料低速冲击实验结果
极限载荷和吸收能量是表征低速冲击性能的主要数据。图5为CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料的极限载荷和吸收能量。可以发现,不同能量下CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料的极限载荷不同,CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料50 J冲击能量的极限载荷较30 J冲击能量下更高,这是由于在同样配比下,较大的冲击能量对应更快的冲击速度,撞击时的应变率效应更明显[26]。其中,G结构抗冲击性能最弱,S-C结构吸收能量较大,I-C和CN-1结构极限载荷较高。随着能量的增加,极限载荷和吸收能量均增大,混杂结构可提高极限载荷和吸收能量。冲击面为CF时,极限载荷和吸收能量均较高。I-C结构极限载荷最高,相较于G结构提高了24%。I-G和S-G结构的极限载荷相差不大,均较小。两种层内混杂结构呈现出较高的极限载荷,相较于G结构提高了20%左右。冲击面纤维种类相同时,夹芯(S-C和S-G)结构的吸收能量大于层间混杂(I-C和I-G)结构。相同混杂结构中,冲击面为CF时吸收能量较大,S-C结构的吸收能量较C结构和G结构分别提高了10%和16%。CN-2结构的吸收能量大于CN-1结构,与面内混杂界面的分布有关系[27]。
2.2 CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料低速冲击有限元结果
2.2.1 实验与数值模拟结果对比
图6为30 J能量冲击下C结构、I-C结构、S-G结构和CN-1结构的CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料时间-载荷和时间-能量曲线。可知,极限载荷模拟结果略大于实验值,能量模拟数据略低。实验曲线随时间变化趋势与模拟曲线结果拟合度较高。
2.2.2 低速冲击损伤形态及破坏机制
图7为50 J能量冲击后CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料C扫描及分层失效模拟(SDEG)结果。图8为50 J能量冲击后CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料的分层损伤面积。图9为CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料目视及模拟冲击面纤维损伤结果(SDV1)。图10为CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料冲击背面基体目视损伤及数值模拟结果(SDV2)。可知,模拟结果与实验损伤形貌较一致,冲击面为CF (C、I-C、S-C)时,分层面积为菱形,纤维损伤沿Y方向,I-C结构背部基体损伤较少,S-C结构背部基体损伤区域较大且分层面积最大。冲击面为GF (G、I-G、S-G)时,分层面积接近椭圆形,纤维损伤集中于冲击点下方,冲击面损伤呈圆圈状,冲击背面表现为菱形损伤,I-G结构与S-G结构背面基体破坏形貌类似,I-G结构分层面积最小。层内混杂结构的冲击面纤维损伤形貌与C结构类似,但面内损伤传播连续性较低,CF纤维束内SDV1损伤较GF纤维束集中,且沿X轴有横向扩散,在远离冲击点处仍可观察到部分CF纤维束内SDV1失效,而相邻GF纤维束未出现破坏。SDV2损伤由冲击点正下方向四周扩散,经混杂界面后损伤程度明显降低,大多数损伤发生在CF纤维束内,说明CF纤维束对相邻的GF纤维束有保护作用。CN-1结构的纤维损伤较CN-2结构低,纤维束内基体损伤较CN-2高,混杂界面对面内损伤的抑制作用在CN-1结构中更明显。层内混杂结构的树脂损伤由冲击点向下扩展,应力分布呈菱形,底部断裂沿Y方向。30 J能量冲击后损伤形貌与其类似,不再赘述。
前期已对30 J能量冲击下C结构、G结构、I-C结构和S-C结构的CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料内部损伤进行了分析[28]。图11为30 J能量冲击后I-G、S-G、CN-1、CN-2的CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料Micro-CT扫描横截面损伤。可知,冲击方向沿Z轴向下,白色区域为GF层,黑色区域为CF层。I-G结构和S-G结构冲击区域形变不明显,这是由于GF韧性大,变形恢复性好。I-G结构冲击点附近及内部GF层出现纤维断裂损伤,CF层未观察到破坏。S-G结构上部及内部界面有分层损伤,冲击面GF纵向脆断明显,内部CF层损伤较少。CN-1结构中纤维损伤由冲击点向下传播,底部有少量分层。CN-2结构中冲击面GF受剪切力,损伤范围广,复合材料底部观察到分层损伤。
图12为不同时刻I-C和CN-1的CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料纤维损伤(SDV1)情况。图13为不同时刻I-C和CN-1的CF-GF混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料基体损伤(SDV2)情况。可知,I-C结构显示横截面损伤,CN-1结构显示冲击面纤维损伤及冲击背面基体损伤。纤维损伤程度小于基体损伤,基体损伤首先出现在冲击点周围及复合材料背部,冲头达到最低位置时,底部界面有明显分层破坏。I-C结构的失效过程与CN-1结构有区别,I-C结构中纤维损伤主要集中在冲击面CF层及内部GF层,CN-1结构中CF束首先出现破坏,损伤方向沿Y轴,大多数损伤被限制在混杂界面之间。随着冲头下移,纤维损伤沿X轴增加,且GF纤维束内开始出现纤维破坏,CF纤维束中基体破坏呈三角形,沿X轴损伤严重,GF纤维束内损伤较少,部分CF纤维束在远离冲击点区域仍有损伤,而临近的GF纤维束内基体损伤较少。
3. 结 论
(1)相同混杂比条件下,碳纤维-玻璃纤维层间混杂增强环氧树脂复合材料抗冲击性能较好,I-C结构极限载荷较大,S-C结构吸收能量较多。I-G结构和S-G结构对冲击响应区别不明显,抗冲击性能差别不大。CN-1结构比CN-2结构具有更高的极限载荷,CN-2结构的损伤容限较高。
(2)混杂结构可有效降低冲击损伤,I-C结构和CN-1结构内部的纤维及基体损伤程度较其他混杂结构低,夹芯(S-C、S-G)结构表现出明显的分层损伤,其中S-C结构和CN-2结构分层损伤面积较大。CN-1结构的冲击面纤维损伤较CN-2结构轻,冲击背面基体损伤较CN-2结构严重。
(3)层间混杂结构抗冲击性能受混杂界面数量影响,其中玻璃纤维层形变恢复性高而损伤较大,碳纤维层形变量小且损伤较低。层内混杂结构面内损伤具有取向性,面内混杂界面对抑制损伤传播具有积极作用,损伤扩展连续性较层间混杂结构低,应力在碳纤维束内传播速度快且广,碳纤维束承担了大部分冲击损伤,临近玻璃纤维束内损伤较小。
-
表 1 水泥基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of cement
Cement Specific surface area/(m2·kg−1) Setting time/min Flexural strength/MPa Compressive strength/MPa Initial Final 1 d 3 d 1 d 3 d R.SAC 42.5 40 10 15 6.1 6.5 37.2 45.1 表 2 不同密度的泡沫混凝土配合比
Table 2 Mix proportion of foam concrete with different densities
Foam concrete density/(kg·m−3) Mix proportion/(kg·m−3) Water-cement ratio Cement Water Water reducer Foam 300 159.92 79.96 0.48 60.12 0.5 700 438.04 219.02 1.31 42.95 0.5 1100 716.16 358.08 2.15 25.77 0.5 1700 1133.33 566.67 3.40 0 0.5 表 3 泡沫混凝土和填充泡沫混凝土铝管试件汇总
Table 3 Summary of foam concrete and aluminum tubes filled with foam concrete
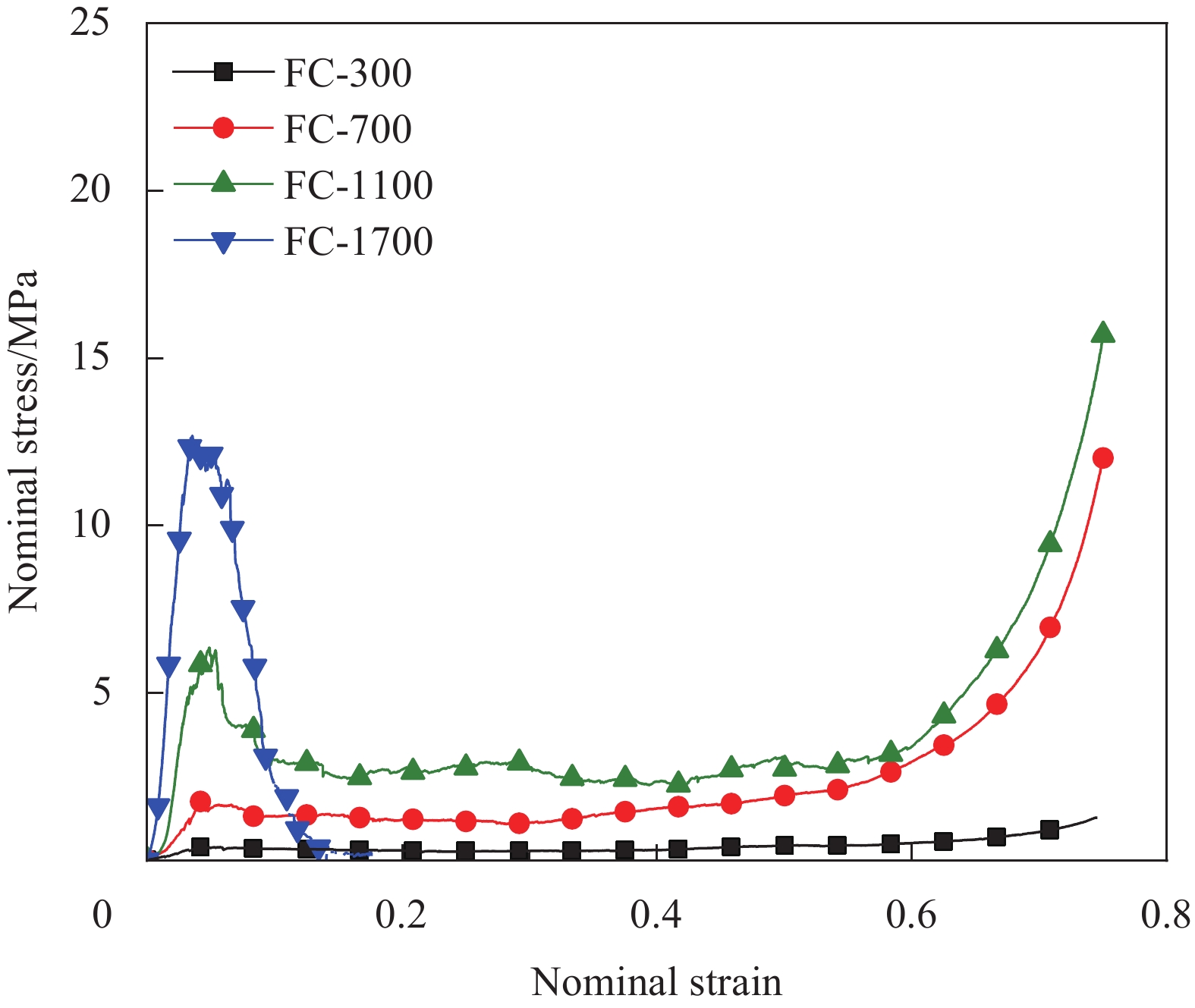
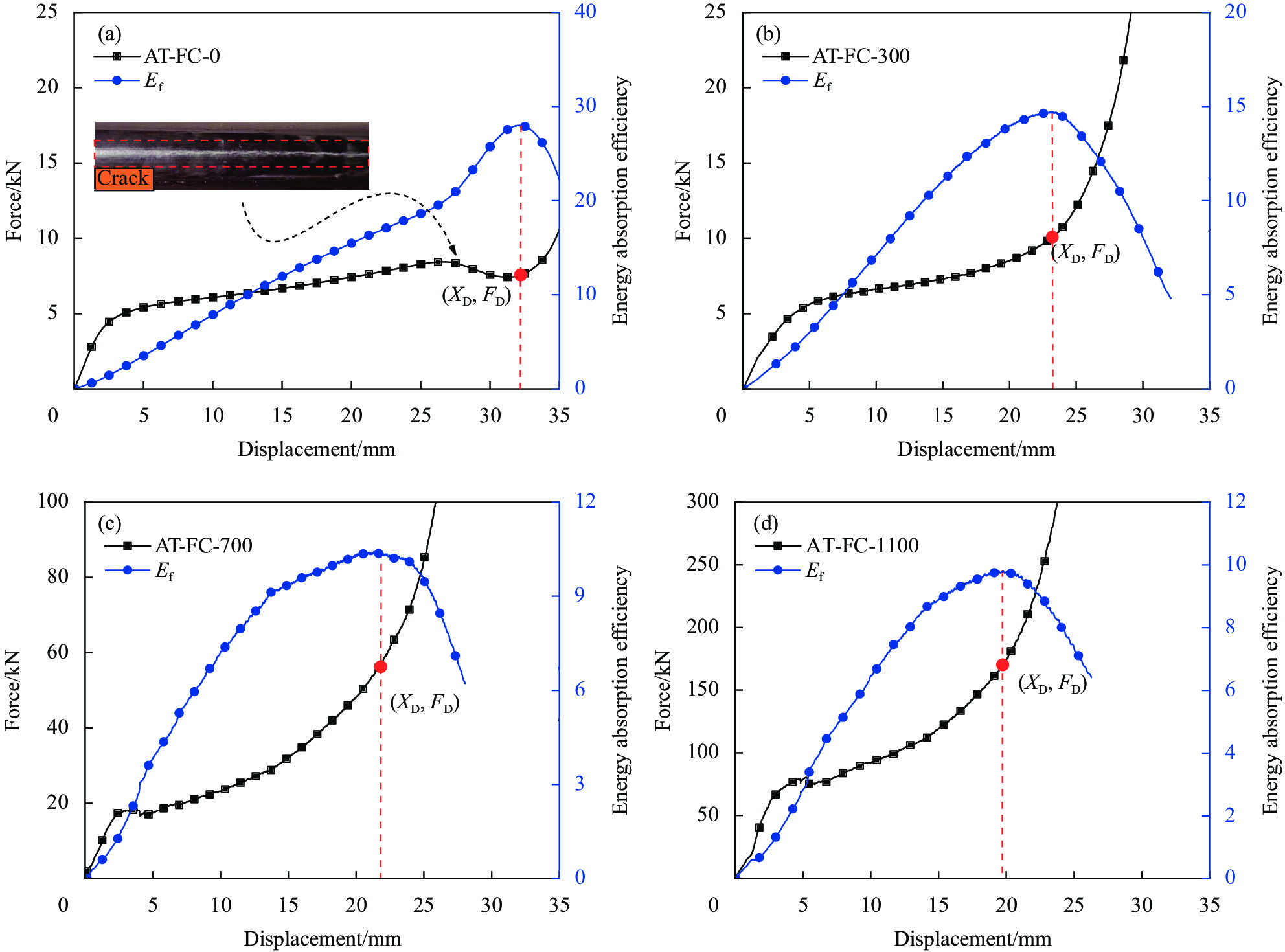
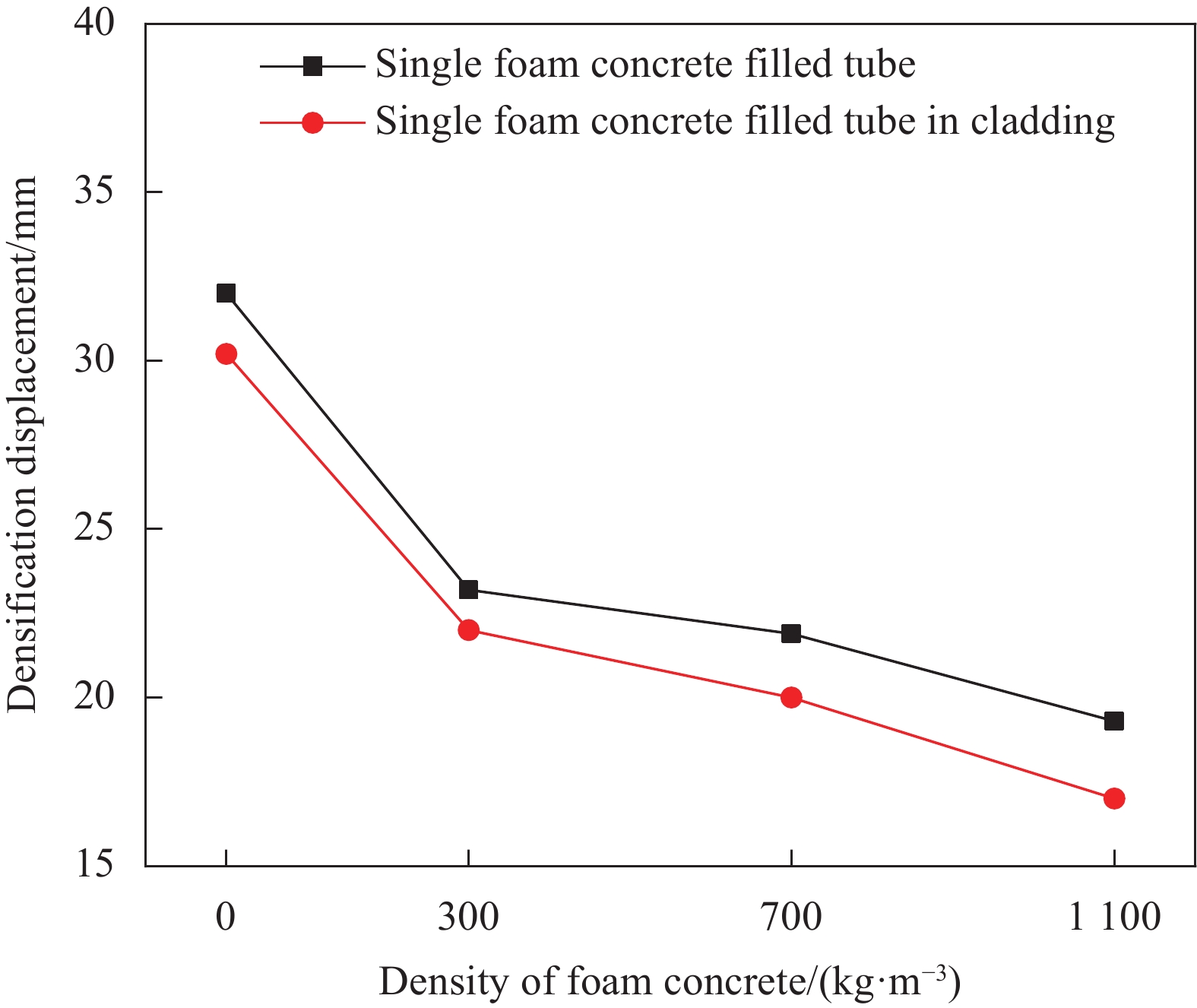
Specimen Foam concrete density/(kg·m−3) Specimen Foam concrete density/(kg·m−3) FC-300 345 AT-FC-0 0 FC-700 713 AT-FC-300 313 FC-1100 1126 AT-FC-700 689 FC-1700 1784 AT-FC-1100 1098 Notes: FC—Foam concrete; AT-FC—Aluminum tubes filled with foam concrete. 表 4 泡沫混凝土填充铝管的吸能性能
Table 4 Energy absorption of the foam concrete filled aluminum tube
Specimen Densification displacement/mm Total energy absorption/J Specific energy
absorption/(J·kg−1)Aluminum tube Foam concrete filler Foam concrete filled
aluminum tubeAT-FC-0 32.3 203.1 − 203.1 1460.9 AT-FC-300 22.6 133.0 13.9 146.9 457.8 AT-FC-700 21.4 124.7 458.0 582.7 1294.8 AT-FC-1100 17.7 68.6 1586.4 1655.0 2713.1 -
[1] 杜善义. 先进复合材料与航空航天[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(1):1-12. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001 DU Shanyi. Advanced composite materials and aerospace engineering[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(1):1-12(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001
[2] WANG Z, ZHOU Y, WANG X, et al. Multi-objective optimization design of a multi-layer honeycomb sandwich structure under blast loading[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering,2017,231(10):1449-1458. DOI: 10.1177/0954407016672606
[3] 周昊, 郭锐, 刘荣忠, 等. 碳纤维增强聚合物复合材料方形蜂窝夹层结构水下爆炸动态响应数值模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(5):1226-1234. ZHOU Hao, GUO Rui, LIU Rongzhong, et al. Simulations on dynamic responses of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite sandwich plates with square honeycomb cores subjected to water blast[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(5):1226-1234(in Chinese).
[4] ZHANG J, ZHOU R, WANG M, et al. Dynamic response of double-layer rectangular sandwich plates with metal foam cores subjected to blast loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2018,122:265-275. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.016
[5] 薛启超, 邹广平, 何建, 等. 聚氨酯弹性体隔板夹层结构的等效参数计算[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(3):564-573. XUE Qichao, ZOU Guangping, HE Jian, et al. Equivalent parameters calculation for sandwich plate with polyurethane elastomer core reinforced by crossing walls[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(3):564-573(in Chinese).
[6] 宋延泽, 王志华, 赵隆茂, 等. 撞击载荷下泡沫铝夹层板的动力响应[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(3):301-307. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)03-0301-07 SONG Yanze, WANG Zhihua, ZHAO Longmao, et al. Dynamic response of foam sandwich plates subjected to impact loading[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves,2010,30(3):301-307(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)03-0301-07
[7] 周宏元, 贾昆程, 王小娟, 等. 负泊松比三明治结构填充泡沫混凝土的面内压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(8):2005-2014. ZHOU Hongyuan, JIA Kuncheng, WANG Xiaojuan, et al. In-plane compression properties of negative Poisson's ratio sandwich structure filled with foam concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(8):2005-2014(in Chinese).
[8] 柯力, 王自力, 王哲, 等. 空中爆炸冲击载荷下折叠式夹层板塑性动力响应研究[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020, 41(6):797-804. DOI: 10.11990/jheu.201901039 KE Li, WANG Zili, WANG Zhe, et al. Plastic dynamic response of folded sandwich panels under air-blast loading[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2020,41(6):797-804(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11990/jheu.201901039
[9] ZHOU H Y, ZHANG X J, WANG X J, et al. Response of foam concrete-filled aluminum honeycombs subject to quasi-static and dynamic compression[J]. Composite Structures,2020,239:112025. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112025
[10] XU F X, ZHANG X, ZHANG H. A review on functionally graded structures and materials for energy absorption[J]. Engineering Structures,2018,171:309-325. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.05.094
[11] BAROUTAJI A, ARJUNAN A, STANFORD M, et al. Deformation and energy absorption of additively manufactured functionally graded thickness thin-walled circular tubes under lateral crushing[J]. Engineering Structures,2021,226:111324. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.111324
[12] 刘伟明, 程和法, 黄笑梅, 等. 开孔泡沫铝填充圆管的准静态压缩行为[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2009, 29(6):654-658. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2009.06.017 LIU Weiming, CHENG Hefa, HUANG Xiaomei, et al. Quasi-static compression behaviors of cylindrical tubes filled with open-cell aluminum foam[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves,2009,29(6):654-658(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2009.06.017
[13] 张光成, 郭超群, 闫治坤, 等. 泡沫钢填充管的准静态压缩变形模式、力学性能及吸能特性[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(24):24158-24163. DOI: 10.11896/cldb.20080301 ZHANG Guangcheng, GUO Chaoqun, YAN Zhikun, et al. Quasi-static compression deformation mode, mechanical property and energy absorption performance of steel foam filled tube[J]. Materials Reports,2021,35(24):24158-24163(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11896/cldb.20080301
[14] YUEN S C K, CUNLIFFE G, DU PLESSIS M C. Blast response of cladding sandwich panels with tubular cores[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2017,110:266-278. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.04.016
[15] WANG C, XU B, YUEN S C K. Numerical analysis of cladding sandwich panels with tubular cores subjected to uniform blast load[J]. International Journal of Impact Engi-neering,2019,133:103345. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103345
[16] RAMAMURTHY K, NAMBIAR E K K, RANJANI G I S. A classification of studies on properties of foam concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2009,31(6):388-396. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2009.04.006
[17] CRANE B, GOODWORTH A D, LIQUORI M, et al. Multidisciplinary testing of floor pads on stability, energy absorption, and ease of hospital use for enhanced patient safety[J]. Journal of Patient Safety,2016,12(3):132-139. DOI: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000079
[18] 宋强, 张鹏, 鲍玖文, 等. 泡沫混凝土的研究进展与应用[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(2):398-410. DOI: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20200316 SONG Qiang, ZHANG Peng, BAO Jiuwen, et al. Research progress and application of foam concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,49(2):398-410(in Chinese). DOI: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20200316
[19] 周明杰, 王娜娜, 赵晓艳, 等. 泡沫混凝土的研究和应用最新进展[J]. 混凝土, 2009(4):104-107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2009.04.031 ZHOU Mingjie, WANG Nana, ZHAO Xiaoyan, et al. Latest development of research and application on foam concrete[J]. Concrete,2009(4):104-107(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2009.04.031
[20] 支旭东, 郭梦慧, 王臣, 等. 泡沫混凝土填充圆钢管的轴压力学性能[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2019, 53(10):1927-1935, 1945. DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2019.10.010 ZHI Xudong, GUO Menghui, WANG Chen, et al. Mechani-cal properties of circular steel tube filled with foam concrete under axial loads[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2019,53(10):1927-1935, 1945(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2019.10.010
[21] 李方贤, 李建新, 肖民, 等. 轻钢龙骨-泡沫混凝土复合墙板的抗冲击性能[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2022, 41(1):68-75. DOI: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.20211123.002 LI Fangxian, LI Jianxin, XIAO Min, et al. Impact resistance of lightweight steel-framed foamed concrete composite wall panels[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2022,41(1):68-75(in Chinese). DOI: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.20211123.002
[22] ZHOU H Y, ZHANG X J, WANG X J, et al. Improving energy absorption capacity of foam concrete with gradient and layered architecture[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,319:126140. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.126140
[23] ZHOU H Y, JIA K C, WANG X J, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of low velocity impact response of foam concrete filled auxetic honeycombs[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2020,154:106898. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106898
[24] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 泡沫混凝土应用技术规程: JGJ/T 341—2014[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Technical specification for application of foamed concrete: JGJ/T 341—2014[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2014(in Chinese).
[25] MILTZ J, GRUENBAUM G. Evaluation of cushioning pro-perties of plastic foams from compressive measurements[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science,1981,21(15):1010-1014.
[26] BAO R H, YU T X. Impact and rebound of an elastic-plastic ring on a rigid target[J]. International Journal of Mechani-cal Sciences,2015,91:55-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.03.031
[27] SHEN J H, LU G X, RUAN D, et al. Lateral plastic collapse of sandwich tubes with metal foam core[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2015,91:99-109. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.11.016
-




 下载:
下载: