Microstructure and corrosion properties of the laser cladding Al-TiC composite coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy
-
摘要: 为有效改善AZ31镁合金表面的腐蚀性能,本文采用激光熔覆技术在AZ31镁合金表面成功制备了无缺陷的Al-TiC复合涂层。研究了不同成分含量的Al-TiC复合涂层的相组成、微观组织和耐腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明:在Al-TiC复合涂层内形成了大量的Al12Mg17、Mg2Al3和TiC相。复合涂层内微观组织呈现出连续网络状分布特征。随着Al-TiC混合粉末中Al含量的减小,复合涂层中Al12Mg17、Mg2Al3和TiC相的含量呈递增趋势,网络状分布的微观组织结构变得更加均匀连续。复合涂层与AZ31基体之间形成了良好的冶金结合界面。激光熔覆制备的Al-TiC复合涂层耐腐蚀性能较AZ31基体显著提升。自腐蚀电位由基体的−1.563 V提升至−1.144 V,自腐蚀电流由基体的1.55×10−4 A减小至2.63×10−6 A。
-
关键词:
- 激光熔覆 /
- Al-TiC复合涂层 /
- AZ31合金 /
- 微观组织 /
- 耐腐蚀性
Abstract: In order to enhance the surface corrosion resistance of the AZ31 magnesium alloy, the defect-free Al-TiC composite coatings were prepared on AZ31 magnesium alloy using laser cladding technology. The influences of Al-TiC compositions with different contents on the phase composition, microstructure and corrosion resistance of the Al-TiC composite coatings were investigated. The results indicate that a large number of Al12Mg17, Mg2Al3 and TiC phases are produced in the Al-TiC composite coating. The microstructure of the composite coating characterizes as a continuous network distribution. With the decrease of the Al content in the composite powder, the contents of the Al12Mg17, Mg2Al3 and TiC phases in the composite coating gradually increase, and the network-like distribution characteristics of the microstructure in the composite coating become more uniform and continuous. In addition, a sound metallurgical bonding interface is prepared between the composite coating and the AZ31 substrate. The corrosion resistance of the Al-TiC composite coating prepared using the laser cladding technology is significantly enhanced compared to that of the AZ31 substrate. The self-corrosion potential increased from −1.563 V of the AZ31 substrate to −1.144 V of the Al-TiC composite coating, whereas the self-corrosion current decreased from 1.55×10−4 A to 2.63×10−6 A.-
Keywords:
- laser cladding /
- Al-TiC composite coating /
- AZ31 alloy /
- microstructure /
- corrosion resistance
-
镁合金因密度小、比强度和比刚度高、电磁屏蔽和减震吸冲性能好、可回收再利用率高等特征,被寄希望能够替代铝合金和钢铁等金属材料而广泛应用到交通运输和航空航天等领域[1-3]。作为最轻的金属材料之一,镁合金被誉为“21世纪绿色工程材料”[4]。作为结构材料应用时,镁合金将不可避免地暴露于潮湿的空气中形成疏松多孔的氢氧化物薄膜,薄膜在碱性或中性环境中较稳定,在含有氯离子的酸性环境中将被破坏而形成氯化物,进而进一步侵蚀镁合金基体而被腐蚀破坏[5]。耐腐蚀性差已经严重制约了镁合金的广泛应用。
通过在镁合金表面添加合金元素或制备一层复合涂层来提升镁合金的耐腐蚀性能,不仅有效保留了镁合金的优异性能,还明显改善了镁合金的表面性能。通常添加的合金元素以高纯Al粉为主[6],陶瓷粉末(如TiC[7]和SiC[8]等)为微量调节元素,来细化组织[9]和制备化合物相[10]。激光熔覆技术作为一种先进的表面改性技术,因其具有能量密度高、基体与涂层冶金结合性能好、熔覆层微观组织均匀和生产效率高等优点,已被广泛应用于镁基复合涂层的制备[11-12]。王鑫等[13]利用激光熔覆技术在AZ33 M镁合金表面制备了Al-Si涂层,凭借第二相强化和细晶强化,制备的Al-Si涂层相比镁合金基体具有更高的硬度和更强的耐腐蚀性。靳坤等[14]对AZ91 D镁合金进行了激光熔覆Al-Ti-Ni/C涂层,熔覆层的腐蚀电位相比基体提高了167 mV,腐蚀电流略有下降。刘德坤等[15]采用不同功率的高能激光在AZ31镁合金表面熔覆了质量比分别为1.0∶3.0∶0.5的铝、钛和TiB2混合粉,显著提高镁合金的耐腐蚀性能。采用激光熔覆在AZ31镁合金表面制备的Al涂层,因其表面形成了大量网络状分布特征的Al12Mg17相,大幅提升了镁合金的耐腐蚀性能[16]。采用热压成型技术在AZ91镁合金中添加TiC陶瓷粉末制备的TiC/AZ91镁基复合材料,耐腐蚀性能随着TiC含量的增加而变差[17]。通过腐蚀行为分析发现,随着TiC含量的增加,增强体与基体之间的电化学反应加剧,致使镁基复合涂层的耐腐蚀性能下降。采用激光熔覆技术在AZ91镁合金表面制备Al-TiC复合涂层时,可在复合涂层内形成大量的Al12Mg17和TiC相,显著提升了AZ91镁合金的耐腐蚀性能。然而,改善AZ91镁合金耐腐蚀性能的主要影响因素为Al12Mg17相还是TiC相,文中并未阐明。基于已有的研究结果可知,在合金表面添加Al粉、TiC粉或Al-TiC复合粉末对镁合金表面耐腐蚀性能影响显著。本文拟通过添加纯Al粉来制备大量的Al12Mg17相,添加纳米陶瓷TiC粉末来增加形核质点,采用激光熔覆技术在AZ31镁合金表面制备Al-TiC复合涂层,使Al-TiC复合涂层呈现出连续网络状分布的细化组织,改善AZ31镁合金的耐腐蚀性能。
1. 实验材料与过程
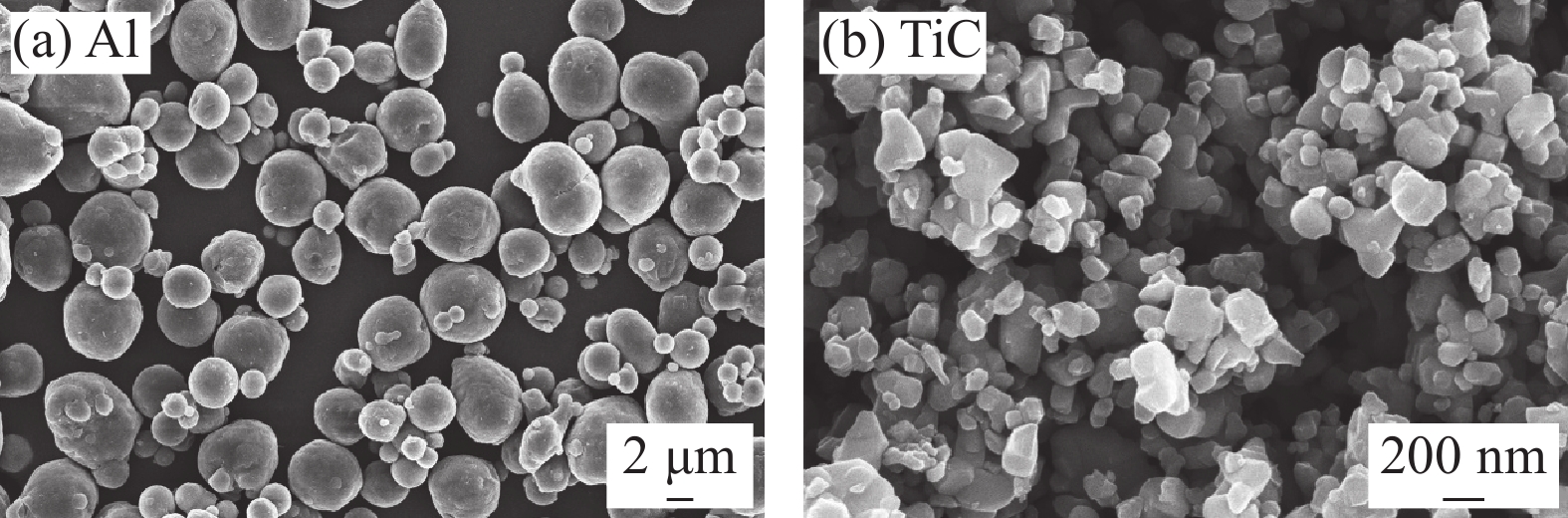
本实验选用商用AZ31镁合金板材为基体,尺寸为300 mm×300 mm×10 mm。所选用Al粉和TiC粉的纯度均为99.95%,粒径分别为1~6 μm和60~300 nm,如图1所示。具体的粉末配比和对应编号见表1。首先将配制好的不同成分配比的Al-TiC混合粉末按照约1:3的球料比分别放入球磨罐中并安装在天津日晟久源仪器设备有限公司生产的型号为QF-WL-4 L全方位行星式球磨机中进行均匀化球磨。球磨珠直径为4 mm,球磨转速为300 r/min,时长为1 h。采用喷砂设备对AZ31镁合金待熔覆表面进行喷砂处理,去除表面氧化物,增加表面粗糙度,便于铺放混合粉末。然后依次用丙酮、酒精和去离子水清洗,并用吹风机快速吹干待用。将搅拌均匀的Al-TiC混合粉末均匀铺在AZ31镁合金已处理表面上,厚度约为0.5 mm。采用Laserline公司的SISTAN3000型半导体激光器进行熔覆处理,波长为960 nm,光斑直径为15 mm,熔敷功率为1.2 kW,熔敷速率为300 mm/min,相邻两道的搭接率为40%。高纯氩气作为保护气体。
表 1 Al-TiC复合涂层具体粉末配比Table 1. Specific ratios of the Al-TiC composite coatingsSample Powders and powder ratio Al/wt% TiC/wt% Al-5TiC 95 5 Al-10TiC 90 10 Al-20TiC 80 20 采用线切割设备沿垂直于激光熔覆方向截取微观组织观察试样和腐蚀性能测试试样。采用典型的金相制样方法对微观组织观察试样进行磨抛制备,并采用成分为1 mL硝酸+1 g草酸+150 mL去离子水的腐蚀剂进行腐蚀,时长15~20 s。采用型号为ZEISS Sigma 300的扫描电子显微镜(SEM)及自带的X-ray 20型能谱探测仪(EDS)对复合材料横截面微观组织特征及元素分布进行观察与测试。采用型号为Bruker S8 TIGER的X射线衍射仪(XRD)对复合材料表层进行物相确定,扫描角度为10°~80°,扫描速率为0.1°/s,扫描电压40 kV,扫描电流40 mA。采用普林斯顿电化学工作站V-400在质量分数为3.5wt%的NaCl水溶液中对AZ31基体和Al-TiC复合涂层进行耐腐蚀性能测试。测试体系为常规三电极系统,其中试样为工作电极,测试面积为1 cm2,铂电极为辅助电极,铂片尺寸为10 mm×15 mm×0.2 mm,饱和甘汞电极为参比电极,扫描速率为1 mV/s。电化学阻抗测试的频率为10−2~105 Hz,电位振幅为10 mV。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 Al-TiC复合涂层的物相分析
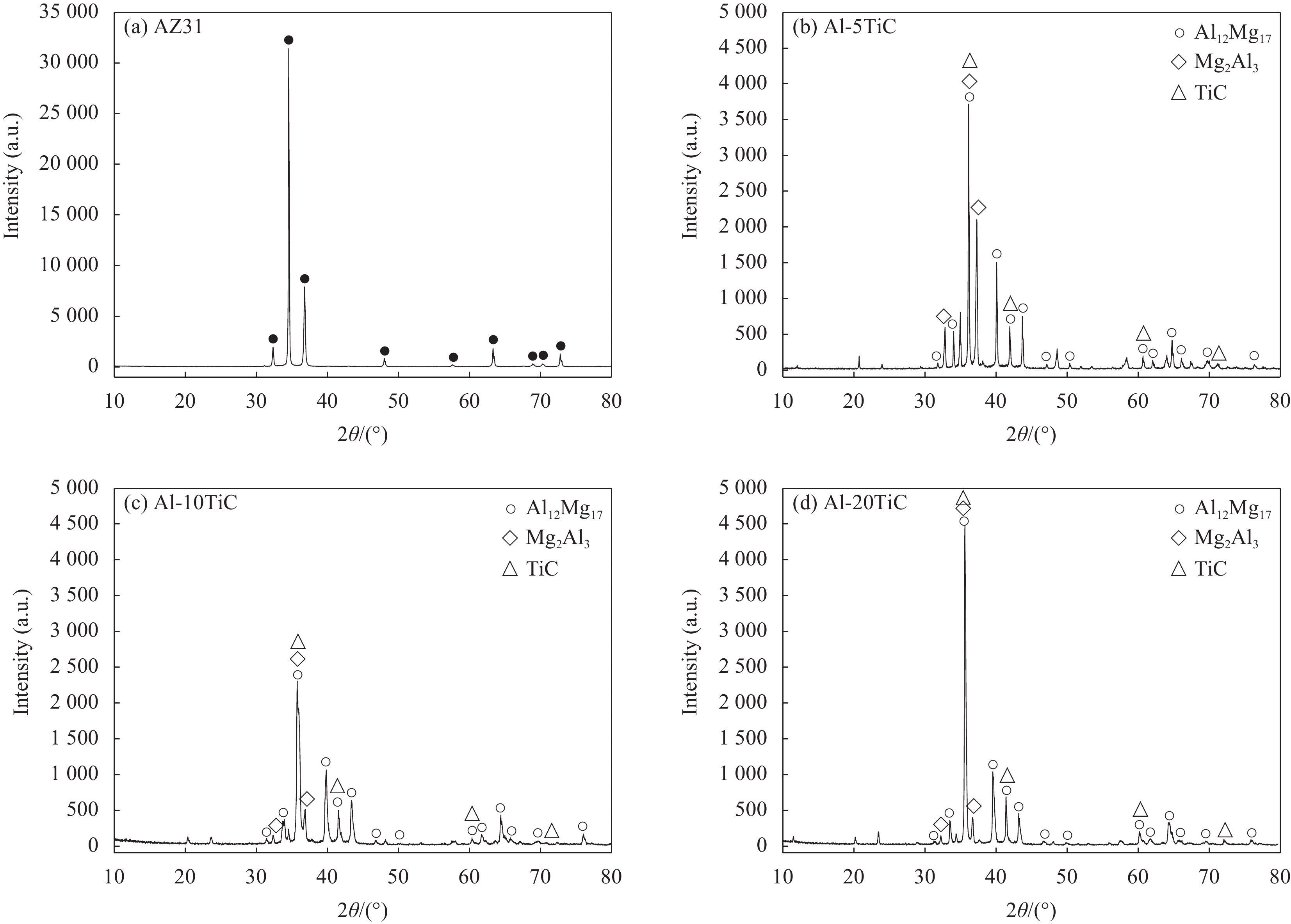
图2为AZ31镁合金基体和Al-TiC复合涂层表面的XRD图谱。基体主要由α-Mg(PDF卡片号:35-0821)固溶体相组成,峰值最大强度高达31427,如图2(a)所示。在AZ31基体中未检测到Al12Mg17相,这主要是由于α-Mg固溶体相含量多,峰值强度过大,致使Al12Mg17衍射峰被显著压缩而未显现。Al-TiC复合涂层主要由Al12Mg17(PDF卡片号:01-1128)、Mg2Al3(PDF卡片号:40-0903)和TiC(PDF卡片号:32-1383)相组成。随着复合涂层中Al含量的减少或TiC含量的增加,最强衍射峰值强度由Al-5TiC试样的3711减小至Al-10TiC试样的2301,然后又增加至Al-20TiC试样的4469,如图2(b)~2(d)所示。这就说明化合物相含量随Al含量减小或TiC含量增加呈先减小后增加现象。Al-20TiC试样的衍射峰值强度最大,表明化合物相含量最多;Al-10TiC试样的衍射峰值强度最小,表明化合物相含量最少。
激光熔覆过程中,当激光照射在Al-TiC复合涂层表面时,光子能量迅速转化成热量,并通过热传导扩散至Al-TiC复合涂层与基体之间的接触界面处积聚。当累积热量温度达到基体或Al的熔点时,在结合界面处的局部区域出现熔池,随着热量的不断累加与积聚,液态熔池逐渐增大直至接触界面全部形成。此时,在接触界面就形成了固-液和液-液扩散体系[6,18]。基体材料和固态Al-TiC复合涂层不断熔融至液态熔池,液态熔池内的Mg、Al、TiC又不断扩散。而且,根据Mg-Al二元平衡相图及先前的研究结果可知[19-21],Al在α-Mg固溶体中的最大固溶度为12.7%,随着Al含量的增加,Mg-Al液相体系逐渐向Al12Mg17和Mg2Al3相区域移动,这将有助于在复合涂层内形成大量的Al12Mg17和Mg2Al3化合物相。在本实验中,Al-TiC复合涂层中Al的最小含量高达80%,远远大于12.7%,这就使激光熔覆过程中形成的Mg-Al液相体系趋向于Al12Mg17和Mg2Al3化合物相区。在随后的冷却过程中,发生冶金反应而形成Al12Mg17和Mg2Al3新相。再加上复合涂层中已添加的TiC陶瓷相,在Al-TiC复合涂层表面形成了Al12Mg17、Mg2Al3和TiC相共存的复合涂层。
2.2 Al-TiC复合涂层的宏观成型与微观组织
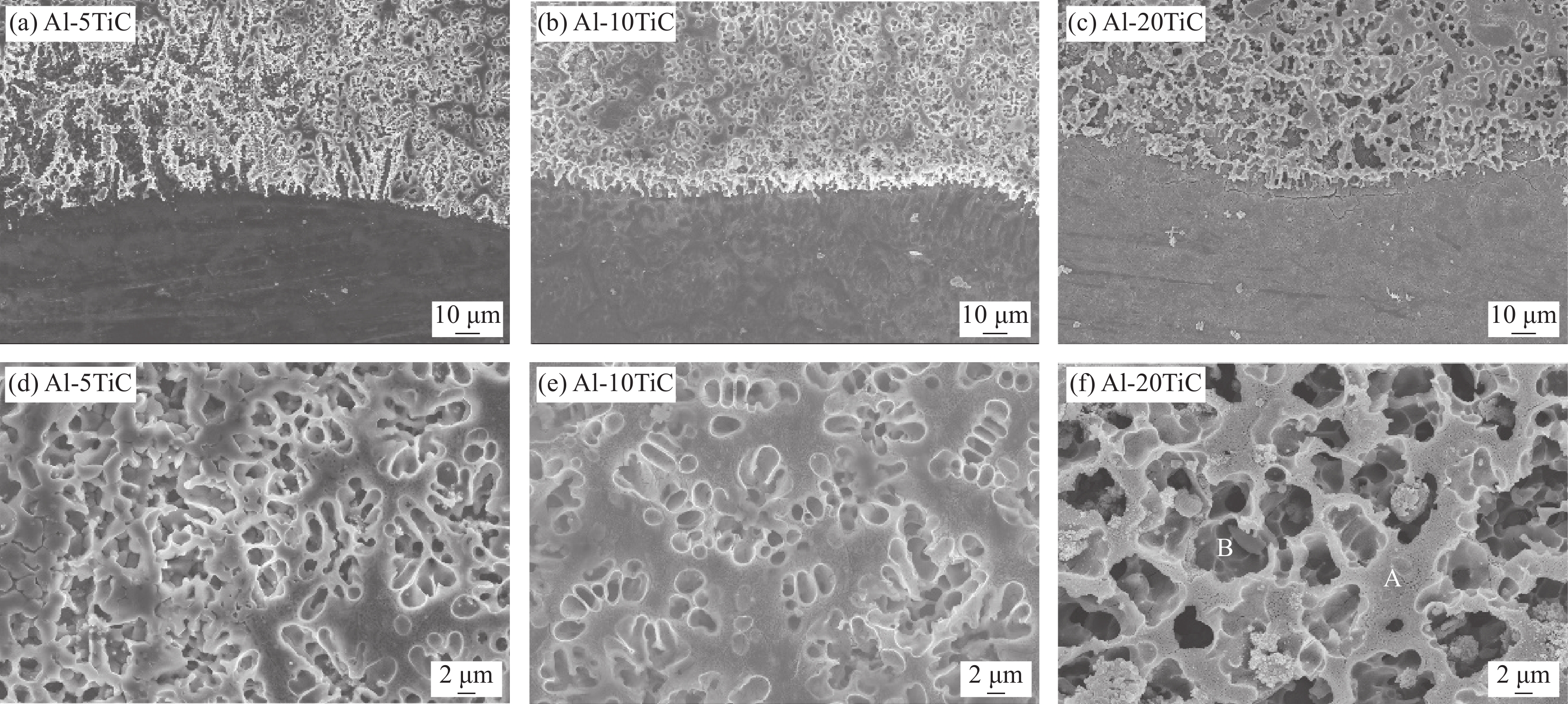
图3所示为Al-TiC复合涂层表面与横截面宏观成型。采用激光熔覆制备的Al-TiC复合涂层表面成型良好,除了在Al-5TiC和Al-20TiC试样表面观察到少量的飞溅之外,表面未观察到孔洞和裂纹等缺陷,如图3(a)~3(c)所示。对Al-TiC复合涂层横截面观察发现,在复合涂层内和结合界面处均未观察到裂纹和气孔等缺陷,如图3(d)~3(f)所示。这就表明本实验所选用的激光熔覆功率和速率合适,有助于制备出宏观成型良好的Al-TiC复合涂层。
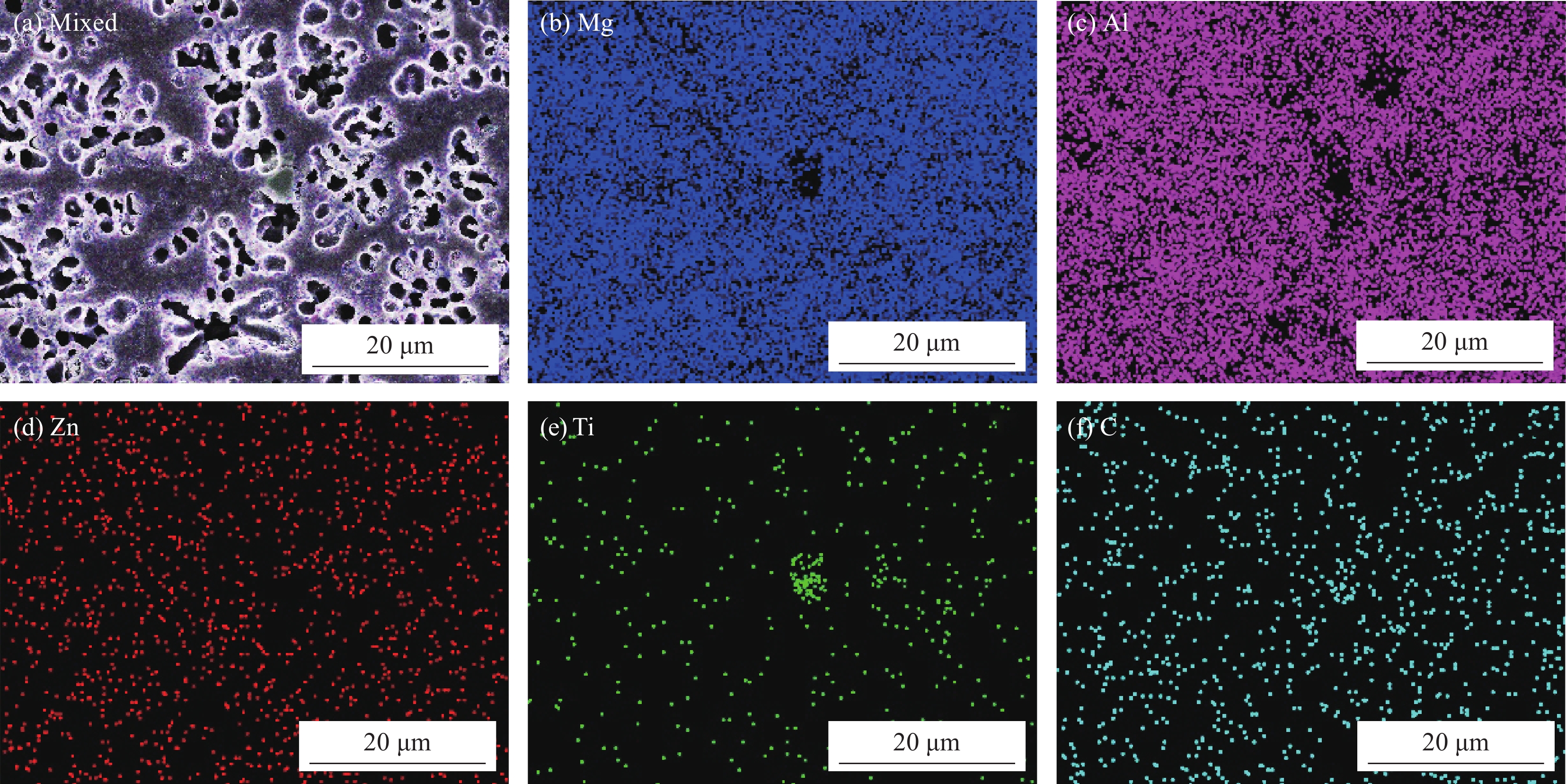
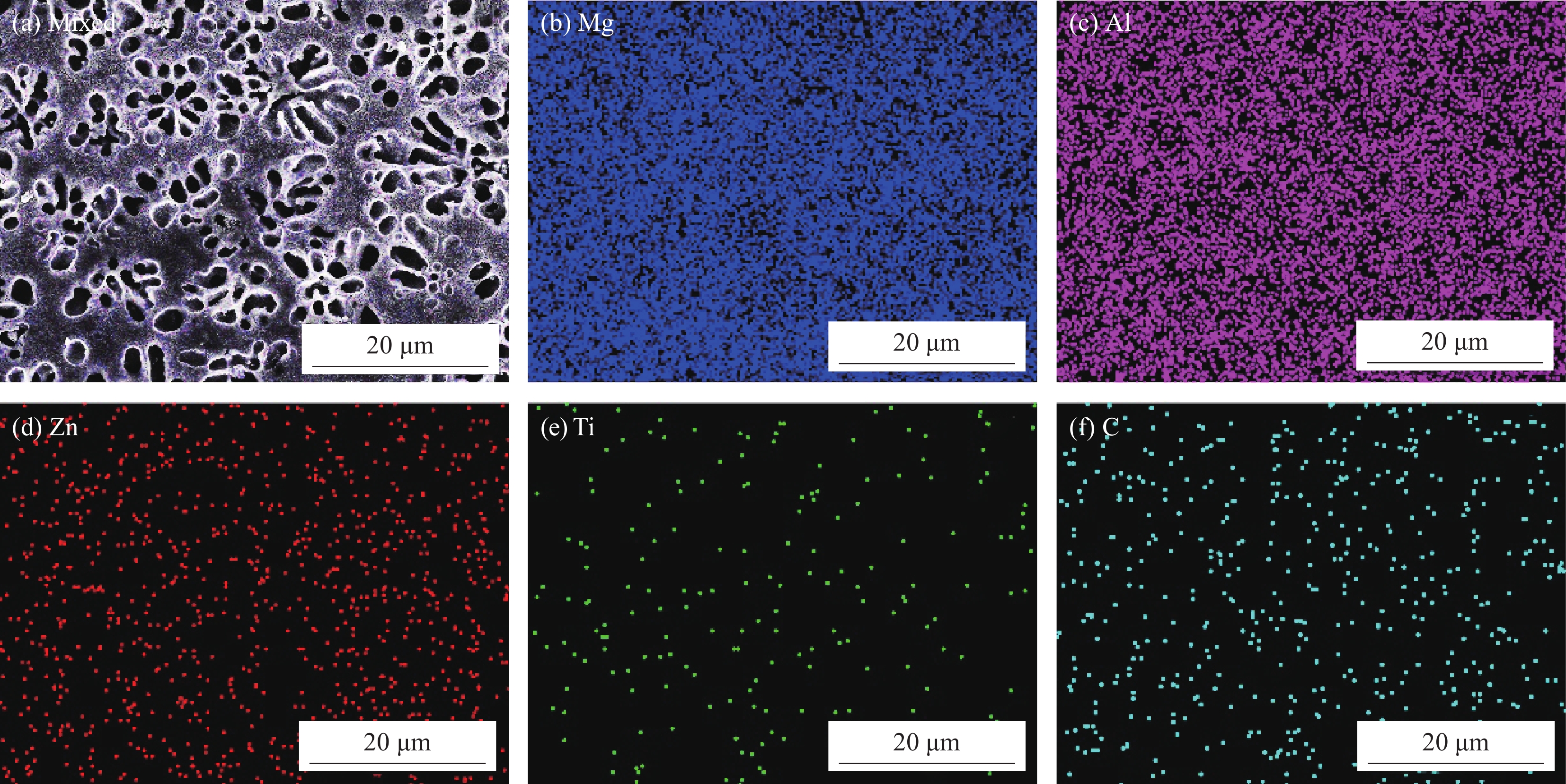
对Al-TiC复合涂层结合界面和复合涂层进一步深入分析发现,复合涂层与基体之间的结合界面为典型的树枝晶组织,呈锯齿状咬合结构,结合界面处未观察到气孔和裂纹,表明在复合涂层和基体之间形成了良好的冶金结合界面,如图4(a)~4(c)所示。复合涂层内也未观察到气孔和裂纹,且由连续网状分布的外凸深灰色相和点式胞状分布的内凹浅灰色相组成,如图4(d)~4(f)所示。Al-5TiC试样复合涂层中外凸深灰色相的连续网络状分布骨骼较细小,大量点式胞状分布的内凹浅灰色相较均匀地分布在外凸深灰色相网络中,如图4(d)所示。Al-10TiC试样复合涂层中外凸深灰色相的连续网络状分布骨骼较粗大,点式胞状分布的内凹浅灰色相被连续网络状分布的外凸深灰色相阻隔,分布均匀性较差,如图4(e)所示。Al-20TiC试样复合涂层中连续网络状分布的外凸深灰色相骨骼更加细小,点式胞状分布的内凹浅灰色相尺寸明显增大,分布更加均匀,如图4(f)所示。对外凸深灰色相和内凹浅灰色相进行EDS成分测试可知,深灰色相(点A)和浅灰色相(点B)均为富Mg、Al和C相,Ti和Zn的含量较少,尤其是Ti的含量在内凹浅灰色相中的含量更少,在外凸深灰色相中的含量较内凹浅灰色相明显增多,如表2所示。结合EDS成分测试和XRD物相分析结果可以推断,连续网络状分布的外凸深灰色相和点式胞状分布的内凹浅灰色相为Mg-Al化合物相,即为Al12Mg17和Mg2Al3混合物相。对复合涂层微观组织进一步放大观察发现,在连续网络状分布的外凸深灰色相骨骼中分布着细小的颗粒,其尺寸大小与形貌和TiC粉末较一致,如图5所示。然而,在外凸深灰色相和内凹浅灰色相中检测出的C含量相对较多,Ti含量较C含量明显较少。基于此,对复合涂层进行EDS面扫描测试,如图6~图8所示。Ti和C元素在复合涂层内的分布均匀性较差,分布特征与连续网络状分布外凸深灰色相的分布骨骼特征极其相似,证明连续网络状分布的外凸深灰色相骨骼中分布的细小颗粒为TiC相。此外,还可知复合涂层主要由Mg和Al元素组成,Mg和Al在复涂合层中的分布较均匀,这与EDS成分测试结果相吻合,连续网络状分布的外凸深灰色相和点式胞状分布的内凹浅灰色相为富Mg和Al相。
表 2 A点和B点的EDS测试结果Table 2. EDS analysis of point A and point BPoint Mg/at% Al/at% Zn/at% TiC/at% C/at% A 38.32 32.43 0.80 2.48 25.96 B 47.97 33.04 0.85 0.09 18.05 激光熔覆过程中,激光辐射的热量从Al-TiC复合涂层表面经热传导扩散至Al-TiC复合涂层与AZ31镁合金基体的结合界面处并积聚,最终在结合界面处的低熔点AZ31镁合金基体首先熔化形成局部熔池,通过固-液和液-液扩散,Al-TiC复合涂层中的Al和TiC元素及AZ31基体不断被熔蚀到熔池中,再加上热量的不断积聚,熔池铺满整个Al-TiC和AZ31镁合金基体的接触界面。在随后的冷却凝固过程中,由于AZ31镁合金基体紧贴钢垫板且导热性较好,熔池温度可通过AZ31镁合金基体和钢垫板的热传导而快速散热而明显降低,在紧邻AZ31镁合金基体的熔池底部温度相对较低,熔池顶部温度相对较高,在熔池底部和顶部形成温度梯度,促使凝固界面存在温度梯度而在AZ31镁合金基体和Al-TiC复合涂层结合界面处有利于枝晶生长而形成树枝晶结构[18,22]。最终,在AZ31镁合金基体和Al-TiC复合涂层之间形成了锯齿状咬合的宏观结合界面特征。在Al-TiC复合涂层内,随着树枝晶由结合界面逐渐向熔池内部生长,熔池内部温度较高,抑制了树枝晶生长,导致凝固方式由枝晶生长逐渐转变为平面生长[23]。因此,Al-TiC复合涂层内的晶粒以平面晶外延生长而形成连续网络状分布特征。此外,由于TiC陶瓷相的熔点较高,在凝固过程中充当了形核质点,主要分布在连续网络状分布相的骨骼中。
2.3 Al-TiC复合涂层的耐腐蚀性能
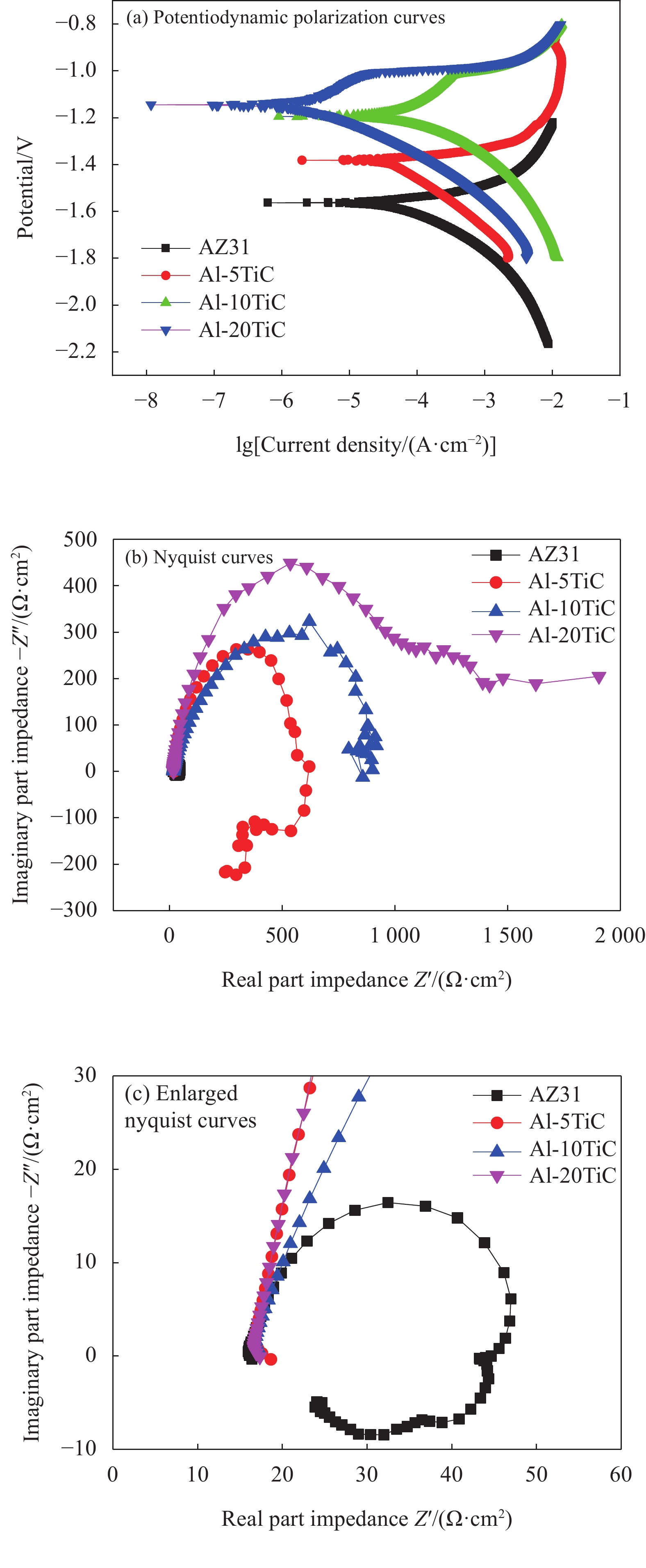
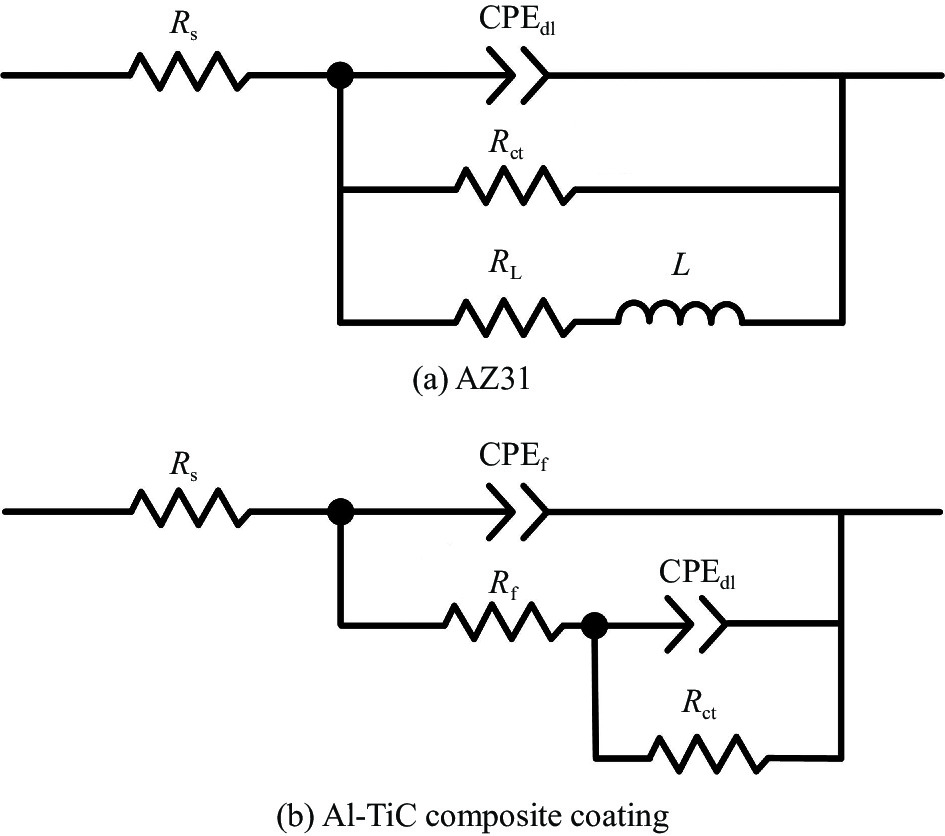
图9为AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的动电位极化曲线和奈奎斯特曲线。根据Tafel阴极区域直线外推法计算所得的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流见表3。可以看出,Al-TiC复合涂层的动电位极化曲线均向上移动,Al-20TiC试样的动电位极化曲线更是明显向左移动。动电位极化曲线向上移动,表明自腐蚀电位增大,耐腐蚀性能增强;动电位极化曲线向左移动,表明自腐蚀电流减小,耐腐蚀性能增大。由此可知,Al-20TiC试样展示出最优的耐腐蚀性能。结合表3中的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流可知,AZ31的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流分别为−1.563 V和1.55×10−4 A。复合涂层的自腐蚀电位由Al-5TiC试样的−1.381 V增加至Al-20TiC试样的−1.144 V,自腐蚀电位均高于AZ31基体,耐腐蚀性能获得显著提升。复合涂层的自腐蚀电流由Al-5TiC试样的2.30×10−4 A减小至Al-20TiC试样的2.63×10−6 A,自腐蚀电流除了Al-5TiC试样与基体相当之外,Al-10TiC和Al-20TiC试样的自腐蚀电流均小于AZ31基体,耐腐蚀性能获得明显提升。奈奎斯特曲线图谱也表明,Al-TiC复合涂层的电容回路直径明显大于AZ31基体,表明Al-TiC复合涂层的耐腐蚀性能较AZ31基体获得明显提升,如图9(b)所示。电容回路直径由Al-20TiC试样至Al-5TiC试样逐渐减小,表明Al-20TiC试样具有最优的耐腐蚀性能。根据电化学阻抗谱测试结果拟合的AZ31和Al-TiC涂层的等效电路模型,如图10所示。相应的拟合电化学参数,见表4。Rs代表溶液电阻,CPE为常相位角元件,可以用来代表非理想状态下的电容行为,CPEf和Rf分别代表Al-TiC涂层的电容和电阻,CPEdl和Rct分别代表双电层电容和电荷转移电阻,L和RL分别代表电感和电感电阻,Rf和Rct之和可以反应材料整体的腐蚀阻抗。结合表4的结果可知,AZ31镁合金的腐蚀阻抗最小,Al-TiC复合涂层的腐蚀阻抗随着TiC含量增加而逐渐提升,耐腐蚀性能逐渐提高。腐蚀试样表面腐蚀形貌观察表明,AZ31基体的表面腐蚀破坏最严重,腐蚀沿晶界扩展,如图11(a)所示。Al-5TiC试样的表面腐蚀破坏较AZ31基体轻微,在局部区域腐蚀形成的腐蚀坑较浅小,腐蚀裂纹也较细小,如图11(b)所示。Al-10TiC试样表面的腐蚀破坏行为较Al-5TiC试样轻微,腐蚀坑更加浅小,腐蚀裂纹更加细小,在局部区域形成了较浅的腐蚀带条,如图11(c)所示。Al-20TiC试样的表面腐蚀破坏行为最轻,表面未观察到明显的腐蚀破坏宏观区域,仅在局部区域形成极其浅小的腐蚀坑,见图11(d)。
镁合金暴露在含有Cl–的潮湿空气中时,与空气中水分经化学反应生成的氢氧化镁将与Cl–发生新的化学反应而生成氯化镁,对镁合金基体失去保护作用[24]。镁合金的耐腐蚀性能很大程度取决于Al12Mg17相的含量、尺寸大小和分布特征[25-28]。Al12Mg17相含量越多,尺寸越细小,分布越均匀且呈连续网络状特征,镁合金耐腐蚀性能越好[29]。此外,当镁合金表面制备成复合涂层时,其耐腐蚀性能除了受Al12Mg17影响之外,还受其他化合物相的含量、尺寸大小和分布特征影响[10,17,30-31]。化合物相之间的电势差越小,其含量越大、越细小,耐腐蚀性能越好;化合物相之间的电势差越大,化合物相之间又将形成新的电化学反应,耐腐蚀性能受含量、尺寸和分布特征的影响越明显,越不利于镁合金耐腐蚀性能的改善[12]。
表 3 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流Table 3. Self-corrosion potential and self-corrosion current of the AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatingsSample Self-corrosion potential/V Self-corrosion current/A AZ31 −1.563 1.55×10−4 Al-5TiC −1.381 2.30×10−4 Al-10TiC −1.195 7.55×10−5 Al-20TiC −1.144 2.63×10−6 ![]() 图 10 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的EIS等效电路图Rs—Solution resistance; CPEf—Al-TiC composite coating capacitance; Rf—Al-TiC composite coating resistance; CPEdl—Electric double layer capacitor; Rct—Charge transfer resistance; L—Inductance; RL—Inductor resistanceFigure 10. EIS equivalent circuit diagram of AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatings表 4 等效电路模型拟合的电化学参数Table 4. Electrochemical parameters fitted by the equivalent circuit model
图 10 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的EIS等效电路图Rs—Solution resistance; CPEf—Al-TiC composite coating capacitance; Rf—Al-TiC composite coating resistance; CPEdl—Electric double layer capacitor; Rct—Charge transfer resistance; L—Inductance; RL—Inductor resistanceFigure 10. EIS equivalent circuit diagram of AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatings表 4 等效电路模型拟合的电化学参数Table 4. Electrochemical parameters fitted by the equivalent circuit modelParameter Rs/(Ω·cm2) CPEf/(Ω·cm2·Sn) nf Rf/(Ω·cm2) CPEdl/(Ω·cm2·Sn) ndl Rct/(Ω·cm2) L/(H·cm2) RL/(Ω·cm2) AZ31 16.50 – – – 7.69×10−6 0.91 27.6 13.46 10.29 Al-5TiC 16.99 7.38×10−6 0.95 118.5 4.36×10−6 0.89 452.2 – – Al-10TiC 15.96 3.04×10−5 0.76 506.5 3.22×10−5 0.85 416.3 – – Al-20TiC 16.47 1.83×10−5 0.87 1045.0 1.01×10−4 0.68 774.8 – – Notes: nf—CPEf index; ndl—CPEdl index. 在本实验中,Al12Mg17相呈现出连续网络状骨骼分布特征,表现出良好的耐腐蚀性能。弥散分布在Al12Mg17网络状骨骼中的TiC作为陶瓷相,自腐蚀电位高,整体提升了Al-TiC复合涂层的自腐蚀电位。但涂层中真正形成大量电偶腐蚀接触的相是Al12Mg17与α-Mg固溶体。同时TiC与Al12Mg17之间还会形成电偶腐蚀,一定程度上降低了复合涂层的耐腐蚀性。Aydin等[17]在研究不同TiC含量对AZ91/TiC复合材料耐腐蚀性能的影响中,发现随着TiC含量增加,促进了TiC和α-Mg之间的电化学反应,加快了腐蚀速率,降低了腐蚀性能。因此,在Al-TiC复合涂层中真正提高腐蚀性能的相是Al12Mg17。在本实验中,Al-20TiC试样耐腐蚀性能最优正是由于其具有最多的Al12Mg17相,该相的连续网络状分布更加均匀,提高了复合涂层的耐腐蚀性。
3. 结 论
(1) 采用激光熔覆技术在AZ31镁合金表面成功制备了表面成型美观的Al-TiC复合涂层。复合涂层中形成了大量的Al12Mg17、Mg2Al3和TiC相。
(2) 激光熔覆制备的Al-TiC复合涂层微观组织呈连续网络状均匀分布特征,且在复合涂层与基体之间形成了无缺陷的冶金界面。
(3) 激光熔覆制备的Al-20TiC(80wt%Al+20wt%TiC)复合涂层展示出优异的耐腐蚀性能,自腐蚀电位由基体的−1.563 V提升至−1.144 V,自腐蚀电流由基体的1.55×10−4 A减小至2.63×10−6 A。Al12Mg17相含量和分布特征是影响Al-TiC复合涂层耐腐蚀性能的主要因素。激光熔覆制备无缺陷Al-TiC复合涂层用以改善AZ31镁合金表面腐蚀性是一种既简单又高效的方法。
-
图 10 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的EIS等效电路图
Rs—Solution resistance; CPEf—Al-TiC composite coating capacitance; Rf—Al-TiC composite coating resistance; CPEdl—Electric double layer capacitor; Rct—Charge transfer resistance; L—Inductance; RL—Inductor resistance
Figure 10. EIS equivalent circuit diagram of AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatings
表 1 Al-TiC复合涂层具体粉末配比
Table 1 Specific ratios of the Al-TiC composite coatings
Sample Powders and powder ratio Al/wt% TiC/wt% Al-5TiC 95 5 Al-10TiC 90 10 Al-20TiC 80 20 表 2 A点和B点的EDS测试结果
Table 2 EDS analysis of point A and point B
Point Mg/at% Al/at% Zn/at% TiC/at% C/at% A 38.32 32.43 0.80 2.48 25.96 B 47.97 33.04 0.85 0.09 18.05 表 3 AZ31和Al-TiC复合涂层的自腐蚀电位和自腐蚀电流
Table 3 Self-corrosion potential and self-corrosion current of the AZ31 and Al-TiC composite coatings
Sample Self-corrosion potential/V Self-corrosion current/A AZ31 −1.563 1.55×10−4 Al-5TiC −1.381 2.30×10−4 Al-10TiC −1.195 7.55×10−5 Al-20TiC −1.144 2.63×10−6 表 4 等效电路模型拟合的电化学参数
Table 4 Electrochemical parameters fitted by the equivalent circuit model
Parameter Rs/(Ω·cm2) CPEf/(Ω·cm2·Sn) nf Rf/(Ω·cm2) CPEdl/(Ω·cm2·Sn) ndl Rct/(Ω·cm2) L/(H·cm2) RL/(Ω·cm2) AZ31 16.50 – – – 7.69×10−6 0.91 27.6 13.46 10.29 Al-5TiC 16.99 7.38×10−6 0.95 118.5 4.36×10−6 0.89 452.2 – – Al-10TiC 15.96 3.04×10−5 0.76 506.5 3.22×10−5 0.85 416.3 – – Al-20TiC 16.47 1.83×10−5 0.87 1045.0 1.01×10−4 0.68 774.8 – – Notes: nf—CPEf index; ndl—CPEdl index. -
[1] JOOST W J, KRAJEWSKI P E. Towards magnesium alloys for high-volume automotive applications[J]. Scripta Materialia,2017,128:107-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.07.035
[2] CHEN J X, TAN L L, YU X M, et al. Mechanical properties of magnesium alloys for medical application: A review[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2018,87:68-79. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.07.022
[3] 赵聪铭, 邓坤坤, 聂凯波, 等. 挤压包覆轧制对SiCp增强镁合金(AZ91)复合板显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(1):164-172. ZHAO Congming, DENG Kunkun, NIE Kaibo, et al. Effect of extrusion-cladding rolling on microstructure and mecha-nical property of SiCp reinforced magnesium alloy (AZ91) clad plate[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(1):164-172(in Chinese).
[4] FRIEDRICH H, SCHUMANN S. Research for a new age of magnesium in the automotive industry[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2001, 117: 276-281.
[5] PARDO A, MERINO M C, COY A E, et al. Corrosion behaviour of magnesium/aluminium alloys in 3.5wt%NaCl[J]. Corrosion Science,2008,50(3):823-834. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.11.005
[6] PAITAL S M, BHATTACHARYA A, MONCAYO M, et al. Improved corrosion and wear resistance of Mg alloys via laser surface modification of Al on AZ31 B[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2012,206(8-9):2308-2315. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.10.009
[7] BALAKRISHNAN M, DINAHARAN I, PALANIVEL R, et al. Synthesize of AZ31/TiC magnesium matrix composites using friction stir processing[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys,2015,3:76-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.jma.2014.12.007
[8] NIE X M, SHEN H Y, FU J Z, et al. Effective control of microstructure evolution in AZ91 D magnesium alloy by SiC nanoparticles in laser powder-bed fusion[J]. Materials and Design,2021,206:109787. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109787
[9] LIU F J, LI Y P, SUN Z Y, et al. Corrosion resistance and tribological behavior of particles reinforced AZ31 magnesium matrix composites developed by friction stir processing[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2021,11:1019-1030. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.01.071
[10] YANG L Q, LI Z Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Al-TiC in situ compo-site coating fabricated by low power pulsed laser cladding on AZ91 D magnesium alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,435:1187-1198. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.240
[11] LIU H X, XU Q, WANG C Q, et al. Corrosion and wear behavior of Ni60 CuMoW coatings fabricated by combination of laser cladding and mechanical vibration processing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2015,621:357-363. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.030
[12] WENG F, YU H J, CHEN C Z, et al. Microstructures and wear properties of laser cladding Co-based composite coatings on Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Materials and Design,2015,80:174-181. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.05.005
[13] 王鑫, 潘希德, 牛强, 等. AZ33 M镁合金激光熔覆制备了Al-Si涂层的组织和性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2021, 46(5):202-206. WANG Xin, PAN Xide, NIU Qiang, et al. Microstructure and properties of laser clad Al-Si coating on AZ33 M magnesium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals,2021,46(5):202-206(in Chinese).
[14] 靳坤, 张英乔, 张涛, 等. AZ91 D镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-Ti-Ni/C涂层的电化学腐蚀行为[J]. 电焊机, 2019, 49(10): 83-87. JIN Kun, ZHANG Yingqiao, ZHANG Tao, et al. Electroche-mical corrosion behavior of laser cladding Al-Ti-Ni/C coating on AZ94 D magnesium alloy[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2019, 49(10): 83-87(in Chinese).
[15] 刘德坤, 张可敏, 刘应瑞. AZ31镁合金表面Al-Ti-TiB2激光熔覆层的组织和性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2018, 42(10):24-28, 33. DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201810005 LIU Dekun, ZHANG Kemin, LIU Yingrui. Microstructure and properties of Al-Ti-TiB2 laser-cladding layer on surface of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy[J]. Materials for Mechani-cal Engineering,2018,42(10):24-28, 33(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201810005
[16] LIN P Y, ZHANG Z H, REN L Q. The mechanical properties and microstructures of AZ91 D magnesium alloy processed by selective laser cladding with Al powder[J]. Optics and Laser Technology,2014,60:61-68. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2013.12.024
[17] AYDIN F, SUN Y, TURAN M E. Influence of TiC content on mechanical, wear and corrosion properties of hot-pressed AZ91/TiC composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2020,54:141-152. DOI: 10.1177/0021998319860570
[18] ZHENG B J, CHEN X M, LIAN J S. Microstructure and wear property of laser cladding Al+SiC powders on AZ91 D magnesium alloy[J]. Optics and Laser Technology,2010,48:526-532. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2010.01.001
[19] MASSALSKI T B, OKAMOTO H, SUBRAMAMIAN P R, et al. Binary alloy phase diagrams[M]. 2nd Edition. Metals Park: ASM International, 1990: 170.
[20] LIU F J, JI Y, MENG Q S, et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of laser cladding and friction stir processing hybrid modification Al-Si coatings on AZ31 B[J]. Vacuum,2016,133:31-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2016.08.010
[21] LIU F J, JI Y, SUN Z Y, et al. Enhancing corrosion resistance of Al-Cu/AZ31 composites synthesized by a laser cladding and FSP hybrid method[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 34: 1458-1466.
[22] 朱红梅, 龚文娟, 易志威. AZ91镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-Cu 合金涂层的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(7):1498-1504. ZHU Hongmei, GONG Wenjuan, YI Zhiwei. Microstructure and property of laser cladding Al-Cu alloy coating on surface of AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2016,26(7):1498-1504(in Chinese).
[23] 孙琪, 李志勇, 张英乔, 等. AZ91 D 镁合金表面激光熔覆Al-TiC涂层组织和性能的研究[J]. 表面技术, 2017, 46(1):40-44. SUN Qi, LI Zhiyong, ZHANG Yingqiao, et al. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding Al-TiC coating on AZ91 D magnesium alloy[J]. Surface Technology,2017,46(1):40-44(in Chinese).
[24] SONG G L, ATRENS A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,1999,1(1):11-33. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1527-2648(199909)1:1<11::AID-ADEM11>3.0.CO;2-N
[25] 刘奋军, 张媛媛, 刘建勃, 等. 镁合金表面高转速搅拌摩擦加工区的微观组织和耐腐蚀性能[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(3):330-337. LIU Fenjun, ZHANG Yuanyuan, LIU Jianbo, et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of high rotating speed friction stir processed zone on magnesium alloy[J]. Surface Technology,2021,50(3):330-337(in Chinese).
[26] 楚志兵, 吕阳阳, 唐宾, 等. 表面渗铝改性镁合金的轧制组织性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(5):1374-1380. CHU Zhibing, LV Yangyang, TANG Bin, et al. Structure and properties on surface of aluminizing-modification magnesium alloy in rolling[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(5):1374-1380(in Chinese).
[27] JALILVAND M N, MAZAHERI Y. Effect of mono and hybrid ceramic reinforcement particles on the tribological behavior of the AZ31 matrix surface composites developed by friction stir processing[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46:20345-20356. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.123
[28] LIU F J, LIU J B, JI Y, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of friction stir welded Mg-Al-Zn alloy thick plate joints[J]. Welding in the World,2021,65:229-241. DOI: 10.1007/s40194-020-01012-z
[29] LIU F J, JI Y, BAI Y X. Influence of multipass high rotating speed friction stir processing on microstructure evolution, corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of stirred zone on AZ31 alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2020,30:3263-3273. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65459-0
[30] BU R, JIN A X, SUN Q, et al. Study on laser cladding and properties of AZ63-Er alloy for automobile engine[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2020,9(3):5154-5160. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.03.032
[31] ARTHANARI S, LI Y H, NIE L, et al. Microstructural evolution and properties analysis of laser surface melted and Al/SiC cladded magnesium-rare earth alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,848:156598. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156598
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 柯俊,李志虎,秦玉林. 金属主簧-复合材料副簧复合刚度计算模型. 汽车实用技术. 2021(05): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾婷,王咏莉,尹忠旺,苏婷慧,师志峰,饶猛. 端面凸轮下压机构支承轴承冲击失效分析及优化(英文). 机床与液压. 2017(24): 37-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-




 下载:
下载: