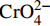Performance and mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by sludge-derived biochar loaded with nanoscale zero-valent iron
-
摘要: 针对电镀、冶金、印染等行业产生的含铬废水所导致的环境污染难题,以城市污泥热解获得的污泥基生物炭(SB)为载体,制备了污泥基生物炭负载纳米零价铁(nZVI-SB)材料用于去除水中的Cr(VI),探究了铁炭质量比、初始pH值、投加量、温度等因素对去除Cr(VI)的影响。通过SEM-EDS、XRD和XPS等手段对nZVI-SB去除Cr(VI)的机制进行分析。结果表明:nZVI-SB对Cr(VI)废水具有较好的去除能力。在投加量0.5 g/L、初始pH=2、温度40℃条件下, Fe与SB质量比为1∶1的nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)吸附量最大为150.60 mg/g。Cr(VI)去除过程可通过Langmuir吸附等温式与准二级动力学方程进行拟合。nZVI-SB对Cr(VI)去除机制主要包括吸附、还原和共沉淀。本文表明污泥基生物炭与纳米零价铁可以协同发挥除Cr(VI)作用。Abstract: Chromium-containing wastewater was generated in electroplating, metallurgy, printing and dyeing industries, which caused environmental pollution. The sludge-derived biochar (SB) was obtained from the pyrolysis of municipal sludge, and then loaded with nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) to prepare sludge-derived biochar loaded with nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI-SB) for the removal of Cr(VI) from water. The effect of the iron to carbon mass ratio, initial pH value, dosage and temperature on the removal of Cr(VI) were explored. SEM-EDS, XRD and XPS were used to characterize the mechanisms of Cr(VI) removal. The results show that nZVI-SB has a desirable removal capacity for Cr(VI). Under the conditions of dosage 0.5 g/L, pH=2 and 40℃, the maximum adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) is 150.60 mg/g by nZVI-SB(1∶1) with a mass ratio of 1∶1 between Fe and SB. The Cr(VI) removal process can be fitted by Langmuir adsorption isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic equations. The removal mechanisms of Cr(VI) mainly include adsorption, reduction and co-precipitation. The present study confirms SB and nZVI can synergically remove Cr(VI).
-
Keywords:
- sludge-derived biochar /
- nanoscale zero-valent iron /
- Cr(VI) /
- adsorption capacity /
- mechanism /
- reduction
-
铬(Cr)作为一种重要的生产原材料被广泛应用于制革、冶金、电镀、纺织印刷、电池等行业中[1- 2],也相应产生了含铬废水,如果处理不当,会对生态环境造成危害[3]。水中的铬(Cr)主要以Cr(VI)和Cr(III)两种形式存在,其中Cr(VI)具有溶解度高、迁移能力强、危害大的特点[4]。目前,含Cr(VI)废水的处理方法有沉淀法、光催化法、吸附还原法、离子交换法等[5],其中吸附还原法运行成本低、操作简单、效率高,受到研究者广泛关注。
纳米零价铁(nZVI)比表面积大、还原性强、表面活性高,对重金属具有良好的去除效果,在环境污染方面受到重视。秦泽敏等[6]对比了还原性铁粉、活性炭及nZVI对Cr(VI)的去除效果,发现nZVI对Cr(VI)的去除率达到了80%以上,远大于还原性铁粉(2%)和活性炭(5%)。然而,由于nZVI粒径小、表面能大及自身磁性,容易产生团聚,导致比表面积和还原能力降低,限制了其在水处理中的应用[7]。为了克服这个缺点,研究人员尝试使用不同的材料作为nZVI载体,以减少颗粒团聚,如膨润土[8]、介孔二氧化硅[9]、活性炭[10]、生物炭[11]等。Shi等[8]采用膨润土作为载体,制备膨润土负载nZVI复合材料,对含Cr(VI)电镀废水的去除率大于90%。Petala等[9]采用介孔二氧化硅负载零价铁纳米,有效地抑制了nZVI的团聚,对Cr(VI)去除能力比nZVI更高。刘剑等[12]通过液相还原法制备了活性炭负载nZVI复合材料,在Cr(VI) 初始浓度50 mg/L、温度40℃、初始pH=2.0、投加量3.0 g/L条件下反应5 min,Cr(VI)去除率为99.4%。生物炭具有较大的比表面积、发达的孔隙结构及丰富的官能团,对重金属具有良好的吸附性能[13-14]。生物炭负载零价纳米铁,能有效降低nZVI的团聚效应[15],而且生物炭良好的导电性,能够增强nZVI的电子转移能力,从而提高nZVI的反应活性[16]。生物炭负载nZVI在重金属废水处理中能发挥协同作用。但目前鲜有通过污泥基生物炭(SB)负载nZVI处理含Cr(VI)废水的报道。
因此,本文以市政污泥为原料制备SB负载nZVI复合材料(nZVI-SB),探讨其对废水中Cr(VI)的去除性能、Cr(VI)去除的机制,为nZVI-SB应用于含Cr(VI)废水处理提供借鉴。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 nZVI-SB的制备
脱水污泥取自湖南某污水处理厂,其含水率为50.83%。脱水污泥经研磨、干燥后,通过0.18 μm筛收集过筛粉末污泥,干燥后的粉末污泥挥发分含量为37.94wt%,灰分含量为61.03wt%[14]。
SB制备:称取一定量干燥的粉末污泥填满坩埚并压实,盖紧坩埚盖,制造一个无氧环境。将坩埚置于450℃的马弗炉中热解2 h,得到黑色固体物质即为SB。
nZVI制备[17]:向装有70 mL超纯水和30 mL乙醇的三颈烧瓶中加入7.4464 g FeSO4·7H2O,在搅拌器上匀速搅拌(150 r/min),直至FeSO4·7H2O完全溶解。然后充入氮气排出空气,持续搅拌,以2.5 mL/min匀速加入适量的硼氢化钠,直至无气泡产生,反应完成。取出沉淀,迅速用超纯水洗涤3次,无水乙醇洗涤2次,得到的黑色固体放入60℃真空干燥箱中干燥8 h,干燥后的黑色固体即为nZVI。
nZVI-SB制备:将适量的SB加入不同量的FeSO4·7H2O溶液中,使nZVI-SB 中Fe∶C的质量比分别为 1∶4、1∶2、1∶1和2∶1。然后按照上述合成nZVI的方法制备nZVI-SB,分别记为nZVI-SB(1∶4)、nZVI-SB(1∶2)、nZVI-SB(1∶1)和nZVI-SB(2∶1),见表1。
表 1 样品名称缩写Table 1. Abbreviation name of samplesSample Fe/wt% SB/wt% nZVI-SB(1∶4) 20.0 80.0 nZVI-SB(1∶2) 33.3 66.7 nZVI-SB(1∶1) 50.0 50.0 nZVI-SB(2∶1) 66.7 33.3 Notes: nZVI—Nanoscale zero-valent iron; SB—Sludge-based biochar. 1.2 重金属含量分析
将1 g污泥和SB分别加入50 mL的逆王水(浓硝酸∶浓盐酸=3∶1)中,在微波消解仪(ETHOS 1,意大利)中消解处理2 h,测定过滤液中重金属浓度。采用电感耦合等离子发射光谱法测定重金属浓度。
1.3 批量吸附实验
1.3.1 Fe∶C质量比的影响
为了研究Fe∶C质量比对Cr(VI)去除效果的影响,将不同质量比(1∶4、1∶2、1∶1和2∶1) nZVI-SB样品0.025 g和50 mL的Cr(VI)溶液(50 mg/L)加入到150 mL锥形瓶中,调节初始pH值为2.0,温度为30℃,在150 r/min的恒温振荡器(IS-RDD3,美国精骐)中反应4 h后取上清液,测量剩余Cr(VI)浓度。
1.3.2 初始pH的影响
反应初始pH设置为2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9,Cr(VI)溶液初始浓度为50 mg/L,温度为30℃,准确吸取50 mL该溶液于150 mL锥形瓶中,加入0.025 g nZVI-SB(1∶1),恒温振荡4 h后取上清液,测量Cr(VI)的浓度,以考察初始pH对Cr(VI)去除效果的影响。
1.3.3 nZVI-SB投加量的影响
配制Cr(VI)溶液初始浓度为50 mg/L,分别准确吸取50 mL该溶液加入一系列150 mL锥形瓶中,再分别加入0.005 g、0.0125 g、0.025 g、0.035 g、0.05 g、0.065 g nZVI-SB(1∶1),以设置nZVI-SB投加量分别为0.1、0.25、0.5、0.7、1.0和1.3 g/L,在初始pH为2、30℃条件下恒温振荡4 h后取上清液,测量Cr(VI)的浓度。
采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法测定溶液中Cr(VI)的吸光度,重复3次计算剩余Cr(VI)的平均值。Cr(VI)的去除率和吸附量计算如下式所示:
R=C0−CeC0×100\% (1) q=(C0−Ce)Vm (2) 式中:R为去除率(%);C0为溶液中初始Cr(VI)质量浓度(mg/L);Ce为反应结束后溶液中Cr(VI)质量浓度(mg/L);q为Cr(VI)的吸附容量(mg/g);V为溶液体积(L);m为nZVI-SB质量(g)。
1.4 吸附模型
将500 mL的Cr(VI)溶液(50 mg/L)加入1000 mL锥形瓶中,调节溶液pH为2,再加入0.5 g/L nZVI-SB(1∶1),在30℃的恒温振荡器中吸附0~720 min,采用准一级动力学模型、准二级动力学模型和颗粒内扩散模型对吸附过程进行拟合,方程式如下式:
ln(qe−qt)=lnqe−K1t (3) tqt=1K2q2e+tqe (4) qt=Kdt12+Ci (5) 式中:qe为平衡吸附量(mg/g);qt为t时刻的吸附量(mg/g);K1为准一级吸附速率常数(min−1);K2为准二级吸附速率常数(g/(mg·min)−1);Kd为颗粒内扩散速率常数(mg/(m·min1/2));Ci为边界层常数。
将不同浓度的Cr(VI)溶液(40~110 mg/L)50 mL分别加入150 mL锥形瓶中,调节初始 pH值为2,加入0.5 g/L nZVI-SB(1∶1),分别在20℃、30℃和 40℃的恒温振荡器中吸附4 h,考察温度对Cr(VI)去除效果的影响,并用Langmuir吸附等温线模型和Freundlich吸附等温线模型进行拟合,方程式如下所示:
Ceqe=Ceqm+1qmKL (6) lnqe=(1/n)lnCe+lnKF (7) 式中:qm为吸附质在单位质量吸附剂的最大吸附容量(mg/g);KL为Langmuir模型的吸附平衡常数;KF为Freundlich模型的吸附平衡常数;1/n为与吸附强度有关的经验参数。
1.5 材料表征
采用SEM (Inspect F50,美国FEI)观察nZVI-SB微观形貌,对比nZVI-SB去除Cr(VI)前后的形态变化;采用TEM (HT7700,日本日立公司)来观察nZVI在生物炭表面的分布情况及是否生成纳米颗粒;同时采用比表面积分析仪(3Flex 5.02,美国麦克)分析nZVI-SB孔隙结构;通过能量色散X射线光谱(EDS) (X-Max,英国牛津)对nZVI-SB表面的元素组成进行分析;使用XRD (Bruker D8,德国布鲁克)分析样品晶型结构及物象组成,XRD数据通过Jade 6.5软件处理;采用XPS (Escalab 250Xi,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific)分析样品元素组成与价态变化,原始数据采用Avantage软件进行分峰拟合。综合表征结果探讨Cr(VI)去除机制。
1.6 nZVI-SB再生试验
过滤、收集与Cr(VI)反应后的nZVI-SB(1∶1),并将其加入到0.2 mol/L的HCl中振荡脱附2 h。之后将溶液过滤,沉淀用去离子水洗涤至中性,60℃真空干燥12 h后重复Cr(VI)去除试验,计算nZVI-SB再生后对Cr(VI)的去除效果。
2. 结果和讨论
2.1 重金属含量分析
污泥和SB消解液中重金属浓度如表2所示,热解制备成生物炭之后Zn、Pb、Cu、Ba和Cd的浓度有一定程度的富集,这与污泥热解过程中有机质不断分解有关。两者的重金属浓度值都远低于《危险废物鉴别标准浸出毒性鉴别》(GB/T 5085.3—2007)规定值(不超过1/6)[18],说明SB中重金属含量符合规范要求。
表 2 污泥及污泥基生物炭(SB)消解液中重金属浓度Table 2. Heavy metal concentrations in digestion solution of sludge and sludge-based biochar (SB)(mg·L−1) Sample Zn Pb Cu Ba Cd Cr Sludge 5.28 0.34 2.37 7.32 0.06 0.14 SB 7.81 0.51 3.01 8.67 0.09 0.13 Specified value
in GB/T
5085.3—2007[18]100.00 5.00 100.00 100.00 1.00 15.00 2.2 材料表征分析
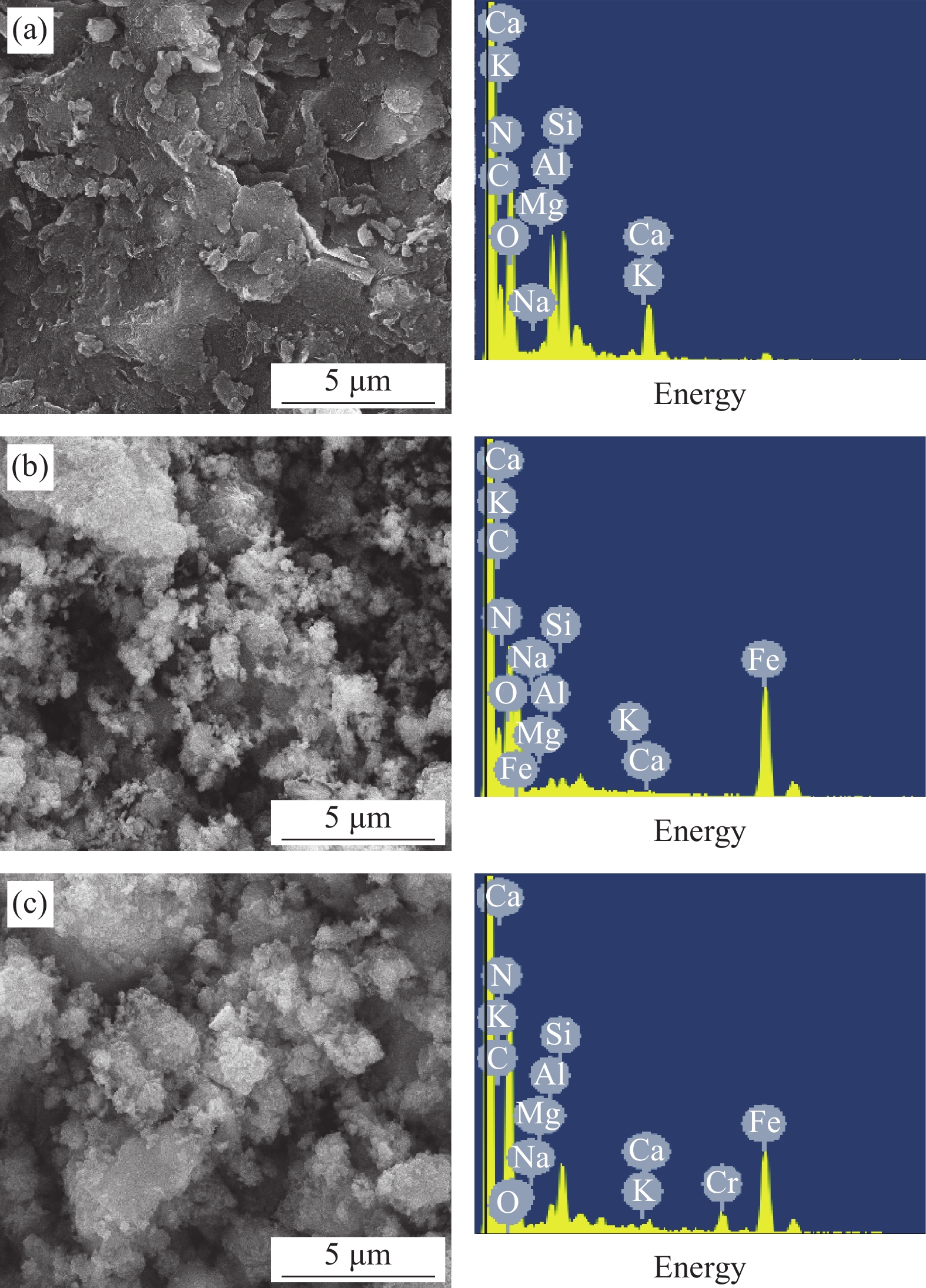
图1为SB和nZVI-SB(1∶1)处理Cr(VI)前、后的SEM-EDS图像。从图1(a)可看出,SB存在大量的块状结构,表面更加光滑。而nZVI-SB(1∶1)(图1(b))的表面存在大量链状聚集的颗粒物[19],这说明零价铁被负载在SB表面。图1(b)的EDS结果显示有Fe峰,进一步验证nZVI-SB复合材料制备成功。吸附Cr(VI)后,SEM变化不大,而EDS出现了Cr元素,证明nZVI-SB(1∶1)成功固定了铬(图1(c))。EDS分析得出nZVI-SB(1∶4)、nZVI-SB(1∶2)、nZVI-SB(1∶1)和nZVI-SB(2∶1)中Fe的质量百分数分别约为19.87wt%、33.31wt%、49.92wt%和66.63wt%(表3),符合预期比例。
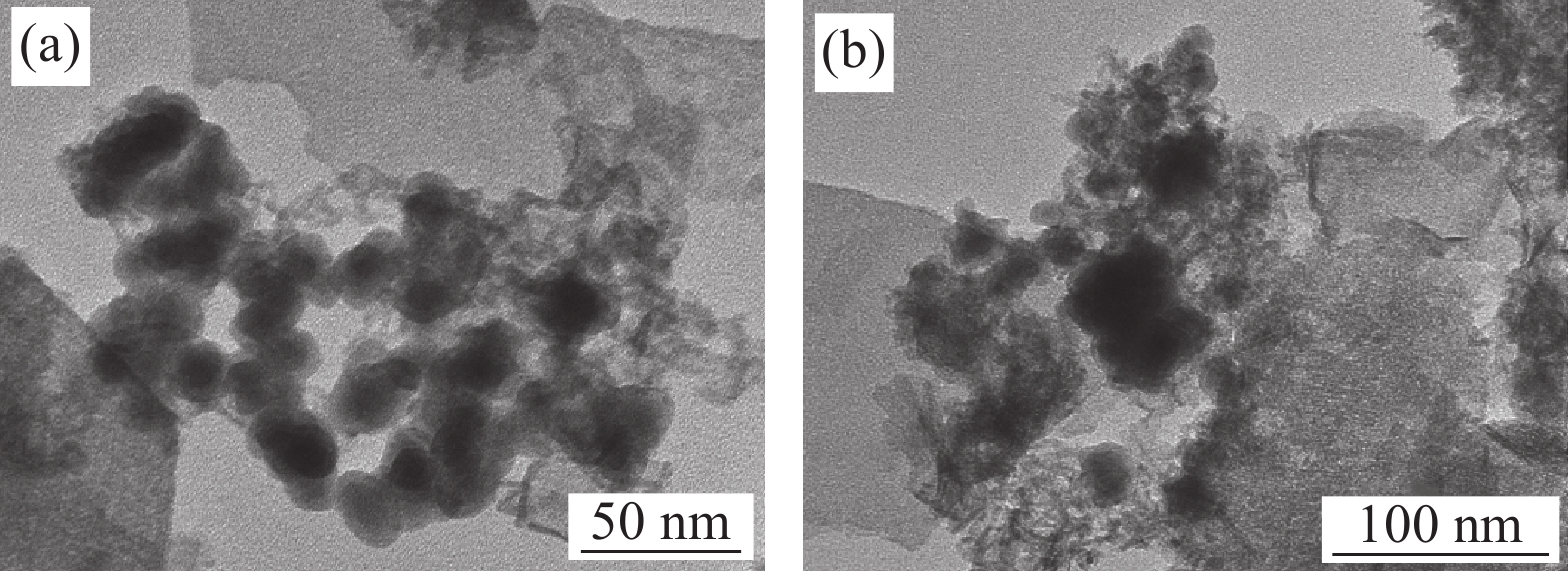
图2为nZVI-SB(1∶1)处理含Cr(VI)废水前、后的TEM图像。处理含Cr(VI)废水前nZVI颗粒均匀分散并固定在SB表面(图2(a))。结果表明,在SB中引入nZVI颗粒提高了nZVI的分散和稳定性,从而增加了nZVI-SB(1∶1)还原或吸附Cr(VI)的活性位点[20]。吸附Cr(VI)后,nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面纳米颗粒减少,且相应的颗粒物变大(图2(b)),推测这可能是生成了Cr(III)-Fe(III)氢氧化物沉淀;结合图1(c)的EDS图中Cr 峰的出现,表明溶液中的Cr(VI)能够被nZVI-SB(1∶1)去除。
表 3 SB和nZVI-SB的元素组成Table 3. Elemental composition of SB and nZVI-SBwt% Sample C N O Na Mg Al Si K Ca Cr Fe SB 40.48 8.46 34.94 0.19 0.39 3.26 6.43 0.88 3.05 0.33 1.59 nZVI-SB(1∶4) 36.63 7.56 33.05 0.22 0.48 0.63 0.76 0.28 0.30 0.22 19.87 nZVI-SB(1∶2) 30.41 6.41 27.55 0.18 0.36 0.51 0.62 0.23 0.24 0.18 33.31 nZVI-SB(1∶1) 23.92 3.11 21.45 0.14 0.27 0.28 0.35 0.19 0.21 0.16 49.92 nZVI-SB(2∶1) 16.48 1.76 14.45 0.06 0.13 0.11 0.16 0.08 0.08 0.06 66.63 通过N2吸脱附比表面积测量仪测定SB及nZVI-SB(1∶1)比表面积和孔径,结果图3所示。SB和nZVI-SB(1∶1)的比表面积分别为47.07 m2/g和116.32 m2/g(图3(a)),孔径分别为14.34 nm和11.56 nm(图3(b))。nZVI-SB(1∶1)的比表面积远远大于SB,说明SB经过nZVI改性后所得的复合材料具有更大的吸附Cr(VI)潜力。nZVI-SB(1∶1)孔径比SB小,是由于SB具有多孔性结构,nZVI颗粒在制备过程中一部分球状颗粒嵌入生物炭的孔隙中[21],造成孔径减小。
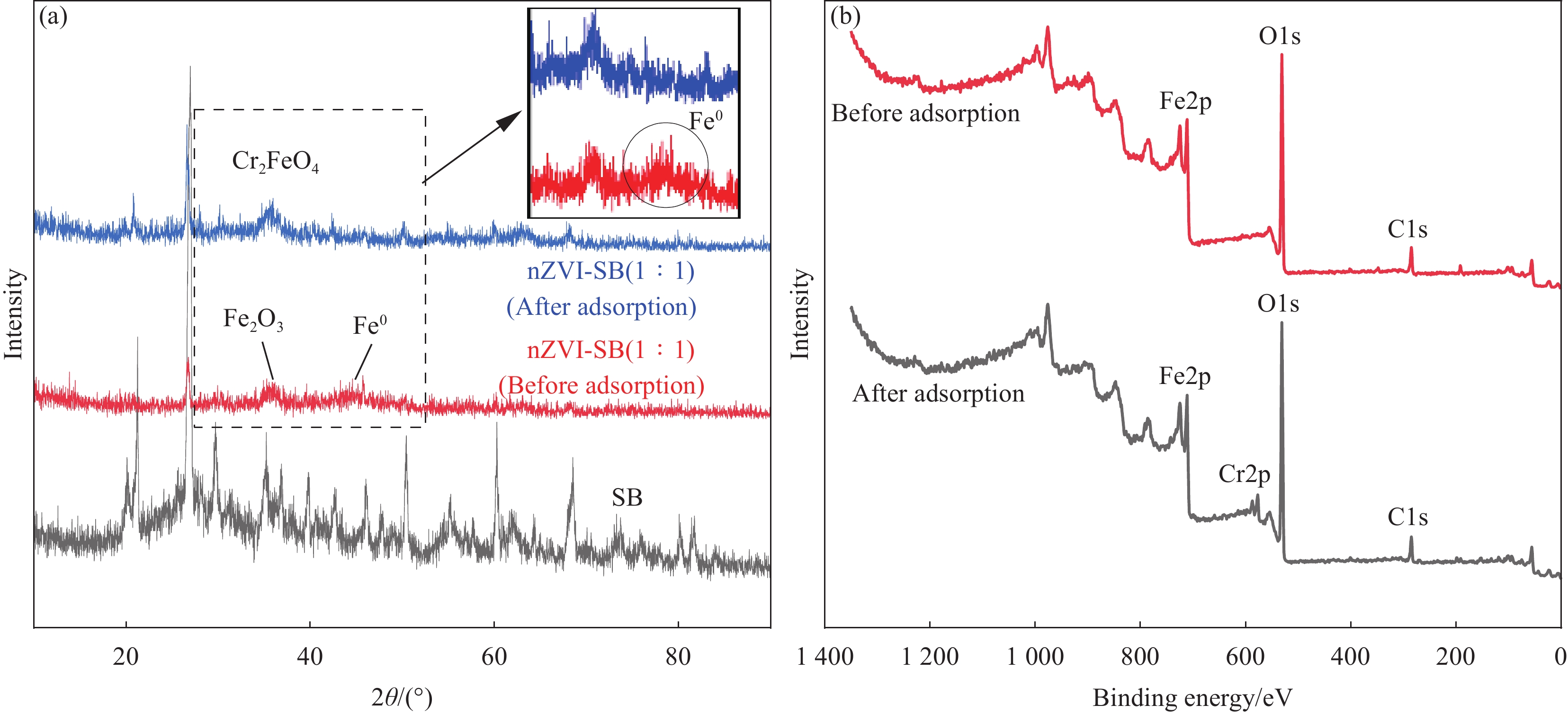
SB和nZVI-SB(1∶1)去除Cr(VI)前、去除Cr(VI)后的XRD图谱如图4(a)所示。SB的XRD图谱中,2θ=20.9°、26.79°、35.01°、50.6°、60.01°及68.62°对应的主要物质为SiO2,而2θ=29.37°、39.4°对应的物质为CaCO3[22]。负载nZVI后,nZVI-SB(1∶1)的XRD特征峰发生变化,SiO2和CaCO3的相关峰减弱,甚至消失,检测到与α-Fe0相关的44.7°的特征峰,证明Fe0的存在[23-24],这表明nZVI在SB上负载成功[15]。2θ=35.65°处为Fe2O3 峰[25],可能是nZVI-SB复合材料制备过程中,部分nZVI被氧化。去除Cr(VI)后,nZVI 峰显著减弱,2θ=35.5°处为Cr2FeO4峰,证明nZVI和Cr(VI)之间发生了氧化还原反应,形成了混合铬铁氧化物Cr2FeO4[26]。图4(b)为nZVI-SB(1∶1)去除Cr(VI)前、去除Cr(VI)后的XPS全谱,处理前没有Cr(VI)的特征峰,去除Cr(VI)后可观察到Cr2p特征峰,表明复合材料可吸附固定Cr(VI)。
2.3 不同Fe∶C质量比对Cr(VI)去除的影响
图5显示了不同吸附剂类型对Cr(VI)的去除效果,SB、nZVI、nZVI-SB(1∶4、1∶2、1∶1、2∶1)对Cr(VI)的平衡吸附量分别为8.13、88.80、50.00、85.33、99.13和91.33 mg/g。SB的吸附量最低,主要是通过吸附作用固定Cr(VI)[13],而nZVI具有很强的还原性,可通过还原、吸附和共沉淀作用去除水中的Cr(VI)[27]。从图5可知,nZVI-SB中的Fe∶C质量比会对去除效果产生明显的影响。随着Fe/C从0.25增加到1.0,吸附量从50.00 mg/g显著增加到99.13 mg/g,进一步证实nZVI的负载增强了SB对Cr(VI)的去除能力。nZVI的去除性能优于nZVI-SB(1∶4)和nZVI-SB(1∶2),这可能是在nZVI-SB(1∶4)和nZVI-SB(1∶2)中,过量的生物炭占据nZVI的表面活性位点[28],从而影响了nZVI与Cr(VI)的反应。另外,与nZVI-SB(1∶1)相比,nZVI-SB(2∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附量出现了降低,这可能是过量的nZVI在SB表面出现团聚,从而导致吸附量的下降。结果表明,Fe∶C质量比为1∶1的nZVI-SB去除Cr(VI)的能力最高。因此,选择nZVI-SB(1∶1)进行后续试验。
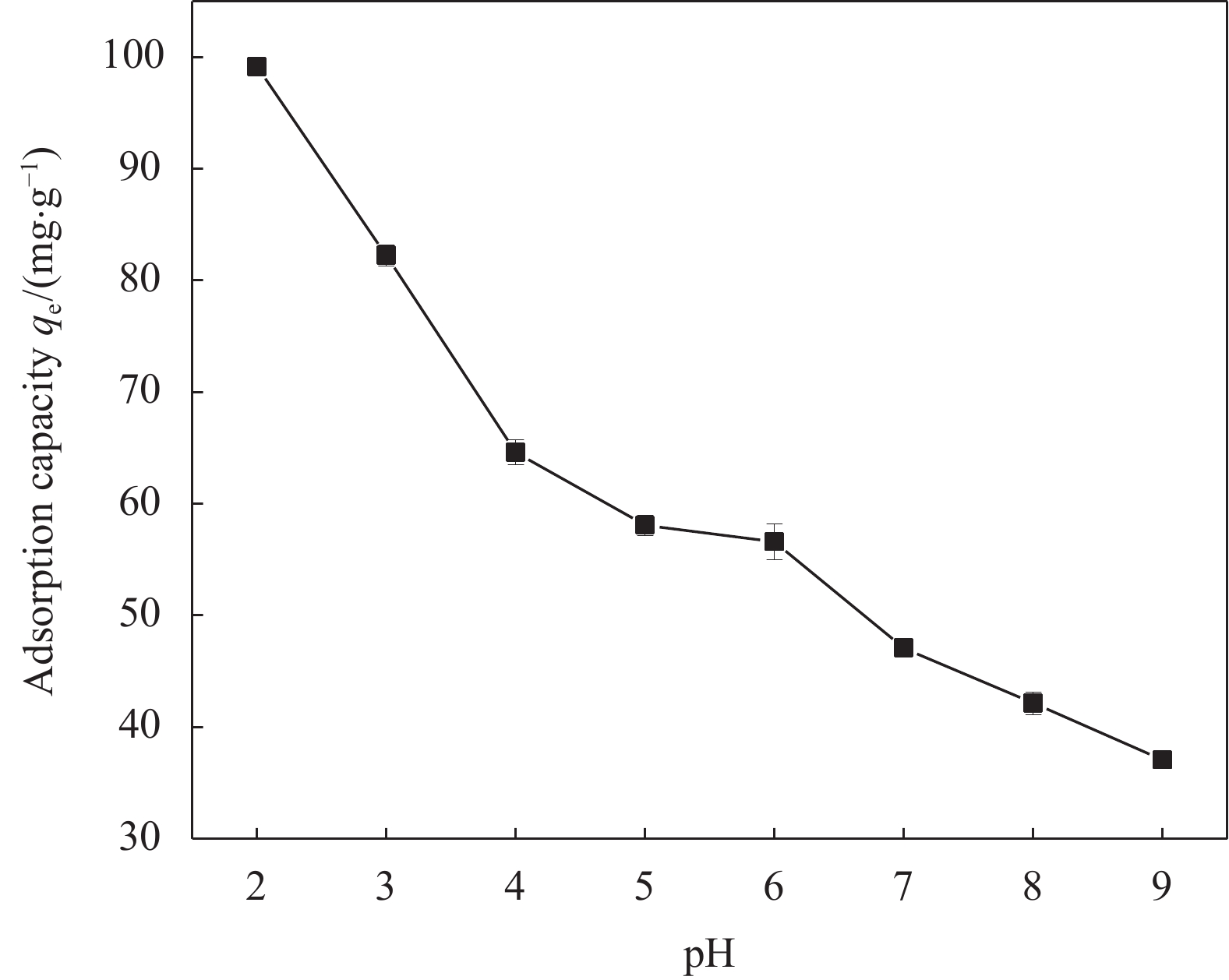
2.4 溶液初始pH对Cr(VI)去除的影响
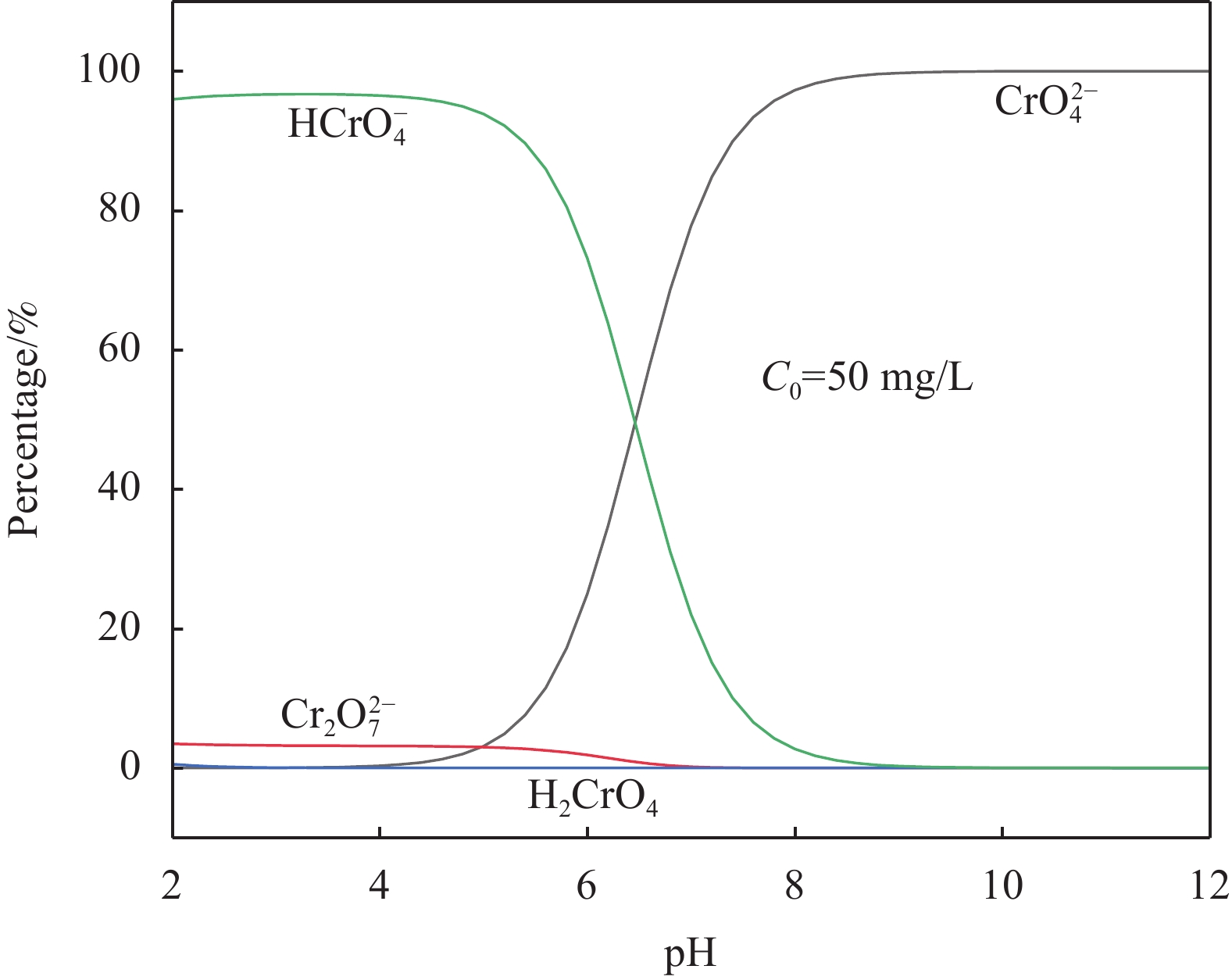
初始pH值对Cr(VI)去除的影响如图6所示。随着溶液pH从2增加到9,nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)吸附量从99.13 mg/g下降至37.07 mg/g,原因可能是在酸性条件下存在大量的H+,促进nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面上氧化铁的溶解,暴露出更多的反应位点[29]。图7是用Visual MINTEQ软件模拟了Cr(VI)在不同pH值(2~12)的存在形态分布曲线图。在高pH值下,复合材料容易去质子化带负电[14, 30],Cr(VI)在溶液中主要以阴离子
CrO2−4 形式存在,两者同性相斥,从而造成吸附量下降。当pH>7时,溶液中存在大量的OH−,这有利于nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面形成Cr(III)-Fe(III)氢氧化物沉淀,阻碍了nZVI内部的电子向外转移[31],妨碍了Cr(VI)与活性位点的接触,从而抑制反应的进行。2.5 投加量对Cr(VI)去除的影响
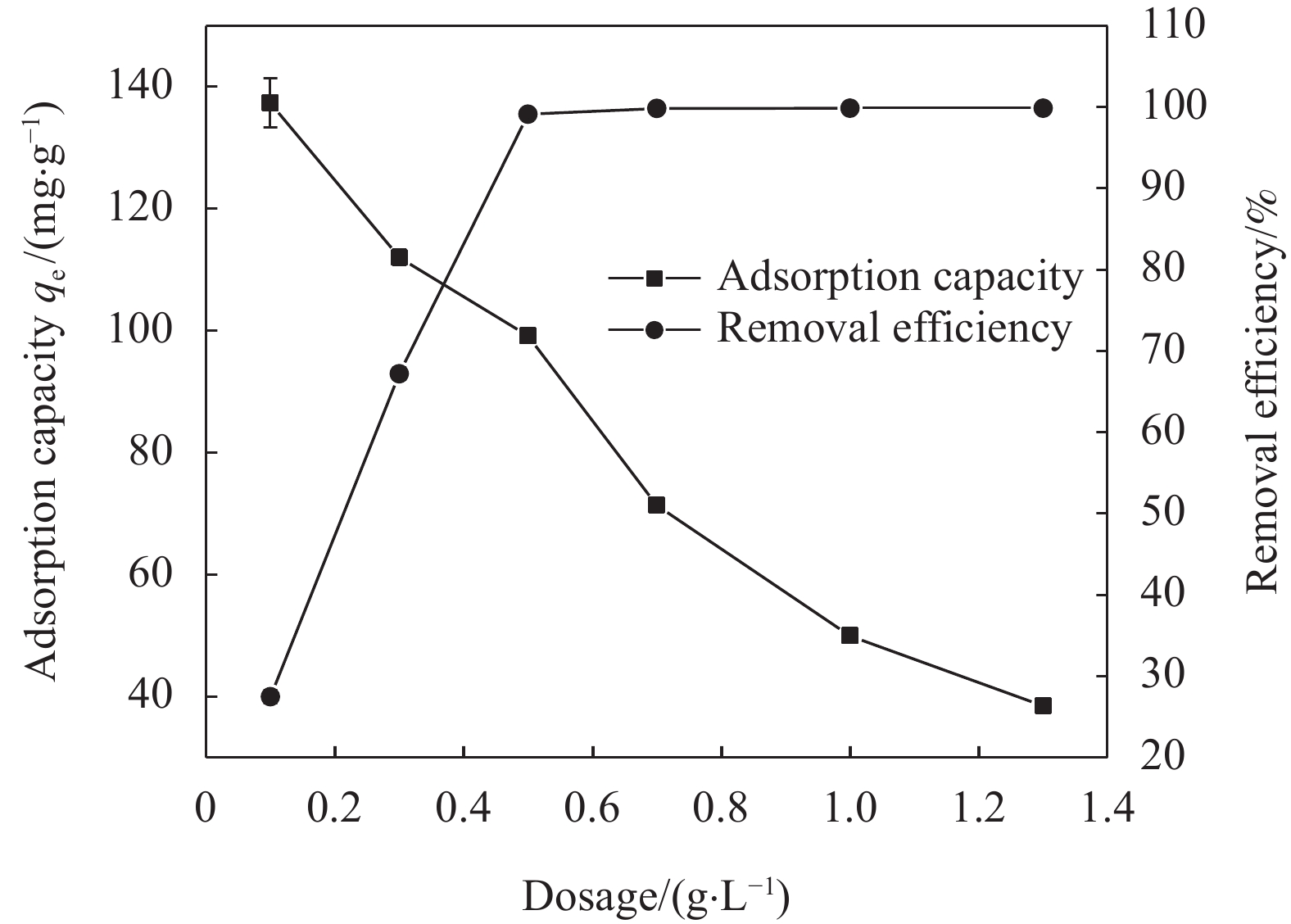
nZVI-SB(1∶1)投加量对Cr(VI)去除效果见图8。当nZVI-SB(1∶1)的投加量从0.1 g/L增加到0.5 g/L时,nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除率从27.48%快速增加到99.13%;当投加量大于0.5 g/L后,去除率基本保持不变。分析原因是,反应初期随着nZVI-SB(1∶1)投加量的增加,活性位点迅速增多[15],导致nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除率迅速增加;但随着投加量的继续增加,而溶液中的Cr(VI)离子有限,对Cr(VI)的去除率增加变缓并趋于稳定。总体上吸附容量随着投加量的增加而减少,从最初的137.33 mg/g减少到38.41 mg/g。原因是随着投加量增加,单位质量nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附量下降[32]。
2.6 吸附动力学
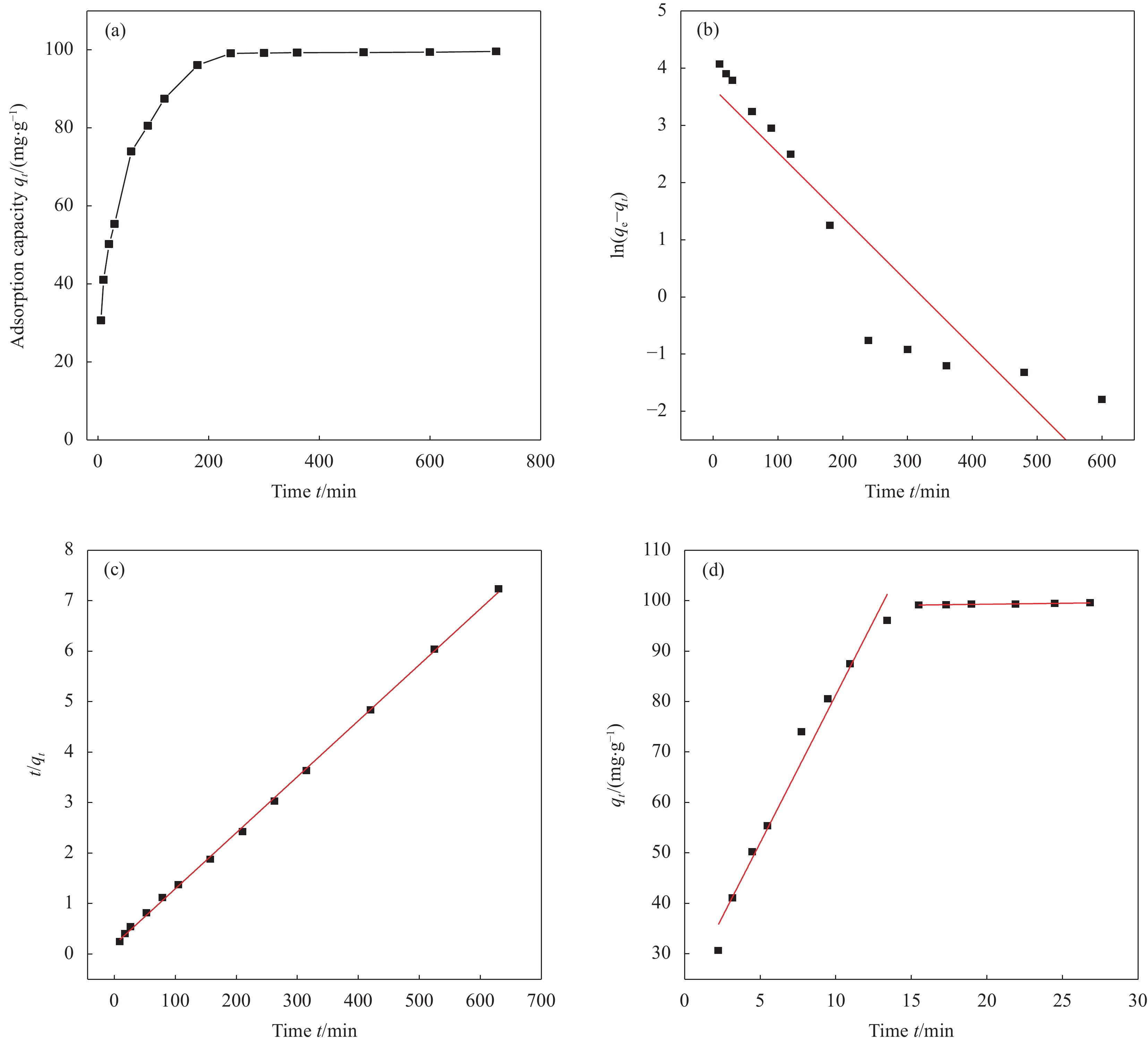
在温度30℃、nZVI-SB(1∶1)投加量为0.5 g/L、Cr(VI)浓度为50 mg/L和溶液初始pH为2的条件下,Cr(VI)在720 min内的去除情况如图9(a)所示。随着反应时间的增加,nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附容量逐渐增加,前5~180 min吸附量增加较快,之后增加较缓慢,在240 min时基本达到吸附平衡。在初始阶段,吸附容量的迅速增加主要是由于有大量的结合位点可供吸附;随着吸附的继续,吸附位点接近饱和状态,吸附速率减慢,直至达到平衡[33]。
为了探究nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附过程和控速步骤,选用准一级动力学模型、准二级动力学模型和颗粒内扩散模型对实验数据进行分析,结果及相应的拟合参数如图9(b)~9(d)和表4所示。结果发现,t/qt与t呈明显的直线关系,准二级吸附动力学方程的线性相关系数(R2=0.999)大于其准一级动力学方程的线性相关系数(R2=0.855)。而准一级动力学模型拟合的qe(38.57 mg/g)与实际吸附量(99.13 mg/g)相差较大,而准二级动力学模型拟合的qe(103.07 mg/g)与实际值相当,说明准二级动力学方程能够更好地描述nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附过程。因此,吸附过程以化学吸附为主[34]。颗粒内扩散模型拟合分析发现,吸附分为吸附剂表面吸附和孔道内缓慢扩散两个阶段。直线都不经过原点,说明孔道内扩散不是控制吸附过程的关键步骤[19]。而粒子扩散常数Kd1>Kd2,表明表面吸附是Cr(VI)吸附去除的限速步骤[25]。
2.7 吸附等温线
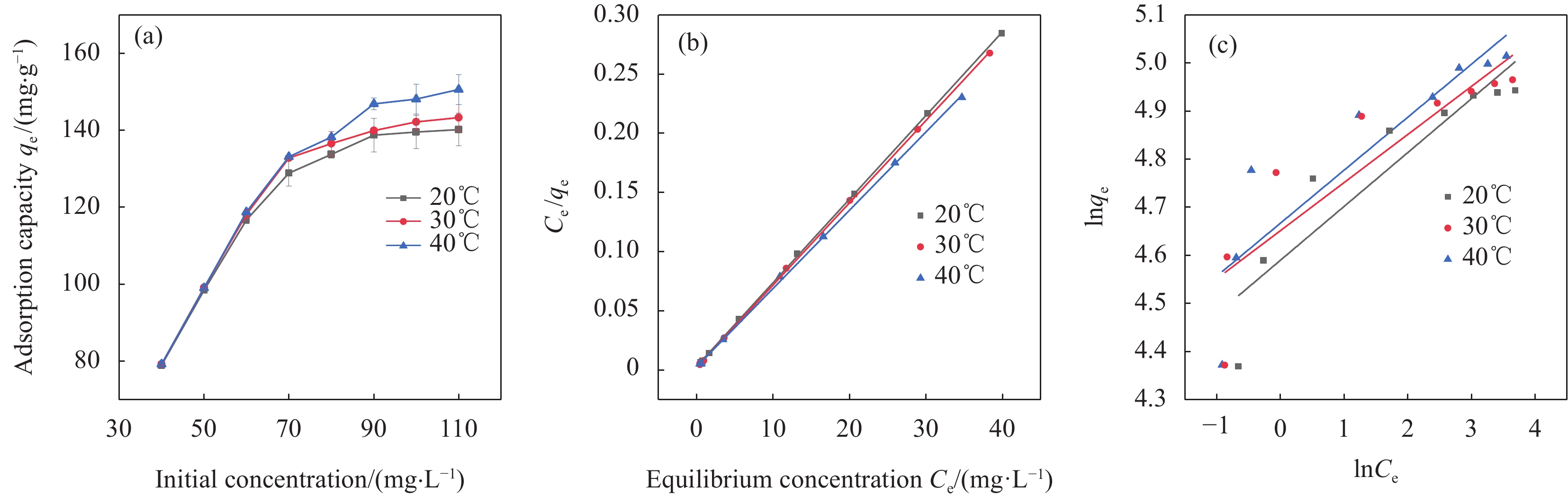
在pH为2、投加量0.5 g/L、吸附时间4 h条件下,探讨Cr(VI)初始质量浓度(40~110 mg/L)和吸附温度(20℃、30℃及40℃)对Cr(VI)去除的影响,结果如图10(a)所示。随着Cr(VI)初始质量浓度的增加,吸附量呈上升趋势,这可能与传质驱动力有关,较高的Cr(VI)浓度使液相和nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面之间的浓度梯度更大,导致更多的Cr(VI)转移到nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面[35]。在相同Cr(VI)初始质量浓度下,40℃下Cr(VI)吸附量最大,说明升高温度能够促进nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除。原因是较高的温度有利于增加金属离子的迁移率,从而增加Cr(VI)与吸附位点的接触概率[36]。
表 4 nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附动力学参数Table 4. Adsorption kinetic parameters of Cr(VI) adsorption by nZVI-SB(1∶1)Intraparticle diffusion model qe/(mg·g−1) K/(min−1) R2 Kd/(mg·(m·min0.5)−1) C R2 Quasi-first order dynamics model 38.57 0.0113 0.855 5.858 22.731 0.971 Quasi-second-stage dynamics model 103.07 0.0005 0.999 0.038 98.551 0.946 Notes: qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity; K—Adsorption rate constant; R2—Linear correlation coefficient; Kd—Particle diffusion constants; C—Constant. 通过Langmuir和Freundlich吸附等温线模型对Cr(VI)去除过程进行拟合,拟合曲线和拟合参数分别如图10(b)、10(c)和表5所示。结果表明,Langmuir方程模拟所得的最大吸附量(151.23 mg/g)和实际吸附容量(150.60 mg/g)相当。Langmuir吸附等温线的相关系数均高于Freundlich吸附等温线的相关系数。这表明Langmuir吸附等温模型更适合描述nZVI-SB去除Cr(VI)的过程,即Cr(VI)在nZVI-SB表面的吸附是均匀的单分子层吸附[16]。与其他吸附剂相比,本文中的nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除性能优于绝大部分吸附剂,见表6。
2.8 机制分析
为了更加深入的了解nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除机制,对处理Cr(VI)前、处理Cr(VI)后的nZVI-SB(1∶1)进行XPS分析,结果如图11和表7所示。图11(a)为nZVI-SB(1∶1) C1s的高分辨精细图谱,吸附前主要峰有C—C(284.64 eV)、C—O(286.06 eV)和C=O(288.54 eV)。与Cr(VI)反应后,这3个峰的面积存在变化,表明这些基团参与了对Cr(VI)的吸附[16]。图11(b)中反应前O1s的主要峰有Fe—O(529.95 eV)、C—O(531.17 eV)和C=O(532.04 eV),吸附后C—O的峰面积增多,C=O的峰面积减少,表明生物炭可以作为电子传递介质,通过表面某些官能团得失电子参与反应[40]。吸附前nZVI-SB(1∶1)的Fe2p光谱中(图11(c)),出现Fe0弱峰(706.70 eV),表明成功合成了nZVI。结合能为724.39 eV 和711.10 eV,对应于Fe(II)的氧化物(FeO);结合能为728.15 eV和714.41 eV对应于Fe(III)的氧化物(Fe2O3),这与XRD的结果一致。吸附后Fe0特征峰消失,Fe(II)峰面积下降,Fe(III)峰面积上升,表明nZVI和Fe(II)被Cr(VI)氧化[41]。图11(d)中580.40 eV和590.28 eV处的峰为Cr(VI)特征峰,说明Cr(VI)被nZVI-SB(1∶1)吸附[42]。577.01 eV和586.85 eV处的峰为Cr(III)特征峰,说明部分Cr(VI)能被nZVI-SB(1∶1)还原生成Cr(III)[25]。其中Cr(III)和Cr(VI)分别占元素Cr含量的84.39%和15.61%(表7),大部分Cr以Cr(III)的形式存在。
表 5 nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附等温线拟合参数Table 5. Adsorption isotherm fitting parameters of Cr(VI) by nZVI-SB(1∶1)Temperature/℃ Langmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) KL R2 KF n R2 20 141.55 0.457 0.999 98.48 8.93 0.821 30 143.84 0.338 0.999 104.73 9.99 0.744 40 151.23 0.433 0.999 106.38 9.07 0.766 Notes: qm—Maximum adsorption capacity; KL—Adsorption equilibrium constant of the Langmuir model; KF—Adsorption equilibrium constant of Freundlich model; n—Constants related to the adsorption intensity. 表 6 nZVI-SB(1∶1)和其他吸附剂对Cr(VI)的吸附能力比较Table 6. Comparison of the adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) by nZVI-SB(1∶1) and other adsorbentsAdsorbent pH Temperature/℃ Adsorption
capacity/(mg·g−1)Ref. Sludge biochar (500℃) 7 25 7.93 [13] Bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (B-nZVI) 5 25 39.48 [23] Ficus carica biosorbent 3 30 19.68 [36] Magnetic nanoparticle-Phosphorene-Titanium nano tubes (MNP-PN-TNT) 9 25 35.00 [2] Nanoscale zero-valent iron grafted on acid-activated attapulgite (A-nZVI) 7 27 4.94 [31] HNO3 modified quinoa biochar 4 — 55.85 [37] ZnO modified hyacinth biochar — 25 43.48 [38] Halloysite nanotubes/ploy composites 2 25 855.66 [39] nZVI-SB(1∶1) 2 40 150.60 This study 综合2.2节SEM、TEM和XRD分析,推测nZVI-SB(1∶1)去除Cr(VI)的主要机制如图12所示。Cr(VI)首先被nZVI-SB(1∶1)吸附固定,此后部分Cr(VI)与nZVI提供的电子接触后被还原为Cr(III),nZVI被氧化为Fe2+,Fe2+仍具有还原性,可将Cr(VI)还原为Cr(III)。生成的Cr(III)、Fe(III)结合成为Cr(III)-Fe(III)氢氧化物沉淀[19],通过C—C、C—O和C=O等官能团吸附在nZVI-SB(1∶1)上,达到去除Cr(VI)的目的。
表 7 nZVI-SB(1∶1)去除Cr(VI)前、去除Cr(VI)后的C1s、O1s、Fe2p和Cr2p XPS光谱的成分和相应的相对百分比Table 7. Composition and relative percents of C1s, O1s, Fe2p and Cr2p XPS spectra before and after Cr(VI) removal by nZVI-SB(1∶1)Components Relative percentage/% Binding energy/eV Before After Before After C1s C—C 58.99 59.78 284.64 284.69 C—O 26.24 24.00 286.06 286.27 C=O 14.77 16.22 288.54 288.72 O1s Fe—O 32.07 30.05 529.95 529.99 C—O 29.94 57.76 531.17 531.40 C=O 37.99 12.19 532.04 532.58 Fe2p Fe0 0.36 0.00 706.70 — Fe(II) 70.31 67.96 711.10/724.39 711.11/724.45 Fe(III) 29.33 32.04 714.41/728.15 714.44/728.55 Cr2p Cr(III) — 84.39 — 577.01/586.85 Cr(VI) — 15.61 — 580.40/590.28 2.9 洗脱再生试验
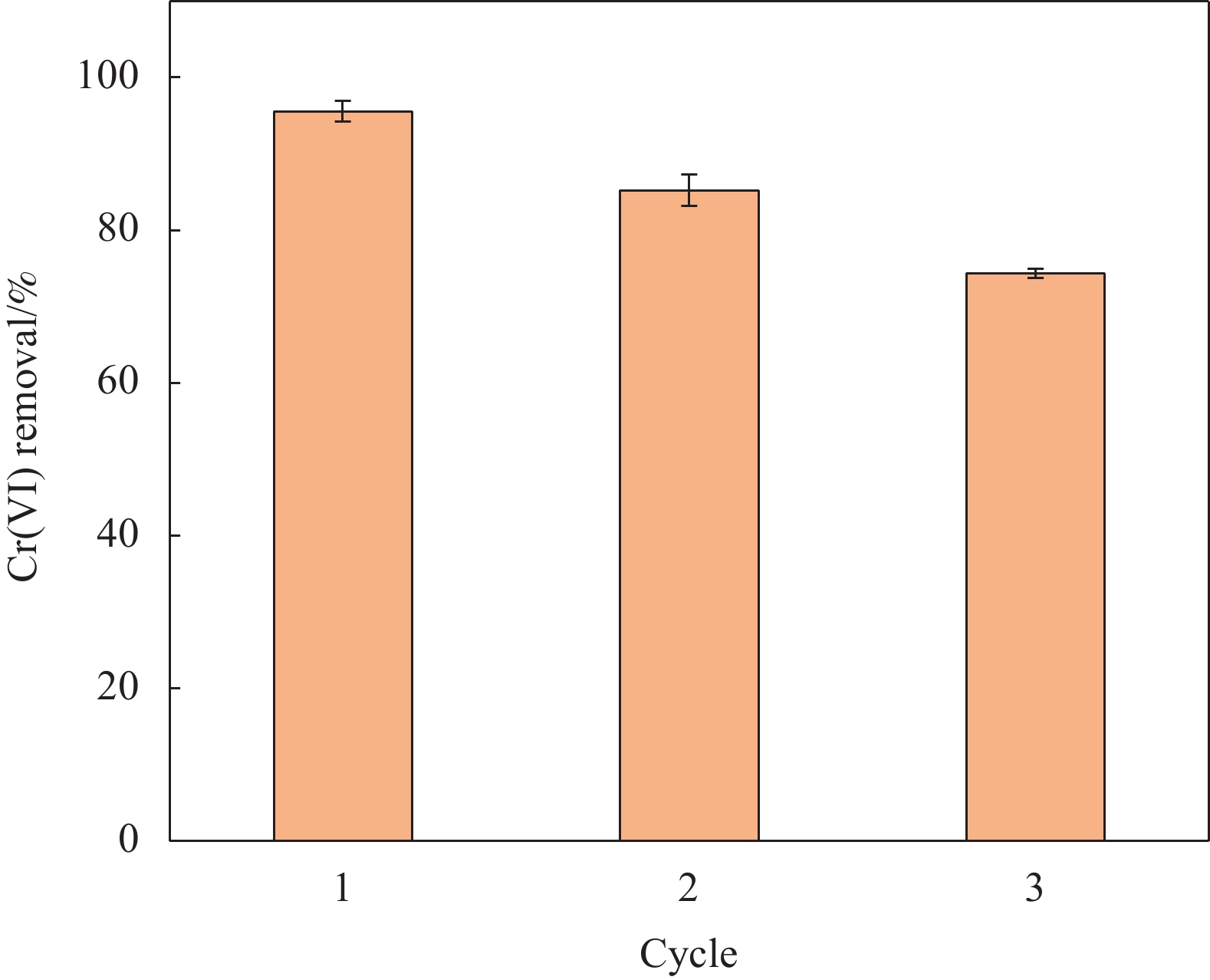
nZVI-SB(1∶1)的洗脱再生试验如图13所示。经过3次循环,nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除率逐次降低,第3次能够保持在74.34%。随着洗脱次数的增加,Cr(VI)去除率逐渐下降。这可能是复合材料上的nZVI被洗脱及nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面上Fe0和Fe2+逐渐消耗造成的[32]。但对于SB而言,成本低廉,可以很容易制备,因此后续nZVI-SB再生主要考虑如何保持nZVI活性方面。
3. 结 论
(1) 以污泥基生物炭(SB)作为载体,通过液相还原法成功制备了纳米零价铁(nZVI)-SB材料,Fe∶C质量比为1∶1时,nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的去除效果最好。
(2) 在初始pH值为2、投加量为0.5 g/L、温度为40℃条件下,nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的最大去除量为150.60 mg/g。Cr(VI)去除过程符合Langmuir吸附等温模型和准二级吸附动力学模型,说明Cr(VI)吸附属于均匀的化学吸附过程。
(3) nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附机制主要为Cr(VI)首先被吸附到nZVI-SB(1∶1)表面,随后大部分与nZVI、Fe(II)反生氧化还原反应,生成Cr(III);最后与Fe(III)形成Cr(III)-Fe(III)氢氧化物沉淀。
(4) 以市政污泥为原料,制备SB负载nZVI,可高效处理含Cr(VI)废水。生物炭有效的解决了nZVI易团聚问题,提高nZVI的活性,生物炭负载nZVI在含Cr(VI)废水处理中能发挥协同作用。
-
表 1 样品名称缩写
Table 1 Abbreviation name of samples
Sample Fe/wt% SB/wt% nZVI-SB(1∶4) 20.0 80.0 nZVI-SB(1∶2) 33.3 66.7 nZVI-SB(1∶1) 50.0 50.0 nZVI-SB(2∶1) 66.7 33.3 Notes: nZVI—Nanoscale zero-valent iron; SB—Sludge-based biochar. 表 2 污泥及污泥基生物炭(SB)消解液中重金属浓度
Table 2 Heavy metal concentrations in digestion solution of sludge and sludge-based biochar (SB)
(mg·L−1) Sample Zn Pb Cu Ba Cd Cr Sludge 5.28 0.34 2.37 7.32 0.06 0.14 SB 7.81 0.51 3.01 8.67 0.09 0.13 Specified value
in GB/T
5085.3—2007[18]100.00 5.00 100.00 100.00 1.00 15.00 表 3 SB和nZVI-SB的元素组成
Table 3 Elemental composition of SB and nZVI-SB
wt% Sample C N O Na Mg Al Si K Ca Cr Fe SB 40.48 8.46 34.94 0.19 0.39 3.26 6.43 0.88 3.05 0.33 1.59 nZVI-SB(1∶4) 36.63 7.56 33.05 0.22 0.48 0.63 0.76 0.28 0.30 0.22 19.87 nZVI-SB(1∶2) 30.41 6.41 27.55 0.18 0.36 0.51 0.62 0.23 0.24 0.18 33.31 nZVI-SB(1∶1) 23.92 3.11 21.45 0.14 0.27 0.28 0.35 0.19 0.21 0.16 49.92 nZVI-SB(2∶1) 16.48 1.76 14.45 0.06 0.13 0.11 0.16 0.08 0.08 0.06 66.63 表 4 nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附动力学参数
Table 4 Adsorption kinetic parameters of Cr(VI) adsorption by nZVI-SB(1∶1)
Intraparticle diffusion model qe/(mg·g−1) K/(min−1) R2 Kd/(mg·(m·min0.5)−1) C R2 Quasi-first order dynamics model 38.57 0.0113 0.855 5.858 22.731 0.971 Quasi-second-stage dynamics model 103.07 0.0005 0.999 0.038 98.551 0.946 Notes: qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity; K—Adsorption rate constant; R2—Linear correlation coefficient; Kd—Particle diffusion constants; C—Constant. 表 5 nZVI-SB(1∶1)对Cr(VI)的吸附等温线拟合参数
Table 5 Adsorption isotherm fitting parameters of Cr(VI) by nZVI-SB(1∶1)
Temperature/℃ Langmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) KL R2 KF n R2 20 141.55 0.457 0.999 98.48 8.93 0.821 30 143.84 0.338 0.999 104.73 9.99 0.744 40 151.23 0.433 0.999 106.38 9.07 0.766 Notes: qm—Maximum adsorption capacity; KL—Adsorption equilibrium constant of the Langmuir model; KF—Adsorption equilibrium constant of Freundlich model; n—Constants related to the adsorption intensity. 表 6 nZVI-SB(1∶1)和其他吸附剂对Cr(VI)的吸附能力比较
Table 6 Comparison of the adsorption capacity of Cr(VI) by nZVI-SB(1∶1) and other adsorbents
Adsorbent pH Temperature/℃ Adsorption
capacity/(mg·g−1)Ref. Sludge biochar (500℃) 7 25 7.93 [13] Bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (B-nZVI) 5 25 39.48 [23] Ficus carica biosorbent 3 30 19.68 [36] Magnetic nanoparticle-Phosphorene-Titanium nano tubes (MNP-PN-TNT) 9 25 35.00 [2] Nanoscale zero-valent iron grafted on acid-activated attapulgite (A-nZVI) 7 27 4.94 [31] HNO3 modified quinoa biochar 4 — 55.85 [37] ZnO modified hyacinth biochar — 25 43.48 [38] Halloysite nanotubes/ploy composites 2 25 855.66 [39] nZVI-SB(1∶1) 2 40 150.60 This study 表 7 nZVI-SB(1∶1)去除Cr(VI)前、去除Cr(VI)后的C1s、O1s、Fe2p和Cr2p XPS光谱的成分和相应的相对百分比
Table 7 Composition and relative percents of C1s, O1s, Fe2p and Cr2p XPS spectra before and after Cr(VI) removal by nZVI-SB(1∶1)
Components Relative percentage/% Binding energy/eV Before After Before After C1s C—C 58.99 59.78 284.64 284.69 C—O 26.24 24.00 286.06 286.27 C=O 14.77 16.22 288.54 288.72 O1s Fe—O 32.07 30.05 529.95 529.99 C—O 29.94 57.76 531.17 531.40 C=O 37.99 12.19 532.04 532.58 Fe2p Fe0 0.36 0.00 706.70 — Fe(II) 70.31 67.96 711.10/724.39 711.11/724.45 Fe(III) 29.33 32.04 714.41/728.15 714.44/728.55 Cr2p Cr(III) — 84.39 — 577.01/586.85 Cr(VI) — 15.61 — 580.40/590.28 -
[1] GAO Q Y, LIN D G, FAN Y J, et al. Visible light induced photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) by self-assembled and amorphous Fe-2MI[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,374:10-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.151
[2] LIN Y J, CHEN J J, CAO W Z, et al. Novel materials for Cr(VI) adsorption by magnetic titanium nanotubes coated phosphorene[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2019,287:110826. DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.04.103
[3] GHADIKOLAEI N F, KOWSARI E, BALOU S, et al. Preparation of porous biomass-derived hydrothermal carbon modified with terminal amino hyperbranched polymer for prominent Cr(VI) removal from water[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,288:121545. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121545
[4] ZHANG W Y, QIAN L B, OUYANG D, et al. Effective remo-val of Cr(VI) by attapulgite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: Enhanced adsorption and crystallization[J]. Chemosphere,2019,221:683-692. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.070
[5] 孙建德. 含铬废水的处理现状[J]. 湖南有色金属, 2013, 29(5):59-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2013.05.017 SUN Jiande. Current situation on the treatment for chromium-containing wastewater[J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals,2013,29(5):59-62(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2013.05.017
[6] 秦泽敏, 董黎明, 刘平, 等. 零价纳米铁吸附去除水中六价铬的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(12):3106-3111. QIN Zemin, DONG Liming, LIU Ping, et al. Removal Cr6+ from water using nanoscale zero-valent iron[J]. China Environmental Science,2014,34(12):3106-3111(in Chinese).
[7] GUAN X H, SUN Y K, QIN H J, et al. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: The development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994-2014)[J]. Water Research,2015,75:224-248. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.034
[8] SHI L N, ZHANG X, CHEN Z L. Removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron[J]. Water Research,2011,45(2):886-892. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.025
[9] PETALA E, DIMOS K, DOUVALIS A, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on mesoporous silica: Characterization and reactivity for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,261:295-306. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.046
[10] ZHU H J, JIA Y F, WU X, et al. Removal of arsenic from water by supported nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,172(2-3):1591-1596. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.031
[11] SU H J, FANG Z Q, TSANG P E, et al. Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by biochar-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2016,318:533-540. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.039
[12] 刘剑, 黄莉, 彭钢, 等. 颗粒活性炭载纳米零价铁去除水中的Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. 过程工程学报, 2019, 19(4):714-720. LIU Jian, HUANG Li, PENG Gang, et al. Removal of Cr(VI) from water by granular activated carbon supported nanoscale zero-valent iron[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2019,19(4):714-720(in Chinese).
[13] 陈林, 平巍, 闫彬, 等. 不同制备温度下污泥生物炭对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附特性[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(8):119-124. CHEN Lin, PING Wei, YAN Bin, et al. Adsorption characteristics of Cr(Ⅵ) by sludge biochar under different pyrolysis temperatures[J]. Environmental Engineering,2020,38(8):119-124(in Chinese).
[14] 莫官海, 谢水波, 曾涛涛, 等. 污泥基生物炭处理酸性含U(VI)废水的效能与机理[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5):2352-2362. MO Guanhai, XIE Shuibo, ZENG Taotao, et al. The efficiency and mechanism of U(VI) removal from acidic wastewater by sewage sludge-derived biochar[J]. CIESC Journal,2020,71(5):2352-2362(in Chinese).
[15] CHEN X, FAN G J, LI H B, et al. Nanoscale zero-valent iron particles supported on sludge-based biochar for the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous system[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,29(3):3853-3863.
[16] ZHOU M, ZHANG C G, YUAN Y F, et al. Pinewood outperformed bamboo as feedstock to prepare biochar-supported zero-valent iron for Cr6+ reduction[J]. Environmental Research,2020,187:109695. DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109695
[17] DIAO Z H, DU J J, JIANG D, et al. Insights into the simultaneous removal of Cr6+ and Pb2+ by a novel sewage sludge-derived biochar immobilized nanoscale zero valent iron: Coexistence effect and mechanism[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,642:505-515. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.093
[18] 国家环境保护总局, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 危险废物鉴别标准浸出毒性鉴别: GB/T 5085.3—2007[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2007. Environmental Protection Administration of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. Identification standards for hazardous wastes identification for extraction toxicity: GB/T 5085.3—2007[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2007(in Chinese).
[19] ZHANG Y T, JIAO X Q, LIU N, et al. Enhanced removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a green synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on oak wood biochar[J]. Chemosphere,2020,245:125542. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125542
[20] MA F F, PHILIPPE B, ZHAO B W, et al. Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium on biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in aqueous solution[J]. Water Science and Technology,2020,82(7):1339-1349. DOI: 10.2166/wst.2020.392
[21] CHOI H, AL-ABED S R, AGARWAL S, et al. Synthesis of reactive nano-Fe/Pd bimetallic system-impregnated activated carbon for the simultaneous adsorption and dechlorination of PCBs[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2008,20(11):3649-3655. DOI: 10.1021/cm8003613
[22] PHOUNGTHONG K, ZHANG H, SHAO L M, et al. Leaching characteristics and phytotoxic effects of sewage sludge biochar[J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2018,20(4):2089-2099. DOI: 10.1007/s10163-018-0763-0
[23] DIAO Z H, XU X R, JIANG D, et al. Bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate system for the simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol from aqueous solutions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,302:213-222. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.062
[24] SHI L N, DU J H, CHEN Z L, et al. Functional kaolinite supported Fe/Ni nanoparticles for simultaneous catalytic remediation of mixed contaminants (lead and nitrate) from wastewater[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2014,428:302-307. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.04.059
[25] YI Y, WANG X Y, MA J, et al. An efficient Egeria najas-derived biochar supported nZVI composite for Cr(VI) removal: Characterization and mechanism investigation based on visual MINTEQ model[J]. Environmental Research,2020,189:109912. DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109912
[26] DONG H R, DENG J M, XIE Y K, et al. Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2017,332:79-86. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002
[27] FANG Y, WU X G, DAI M, et al. The sequestration of aqueous Cr(VI) by zero valent iron-based materials: From synthesis to practical application[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,312:127678. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127678
[28] DONG H R, ZHANG C, HOU K J, et al. Removal of trichloroethylene by biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous solution[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2017,188:188-196. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.033
[29] HUANG L H, ZHOU S J, JIN F, et al. Characterization and mechanism analysis of activated carbon fiber felt-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2014,447:59-66.
[30] CHOI K, LEE W. Enhanced degradation of trichloroethylene in nano-scale zero-valent iron Fenton system with Cu(II)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2012,211:146-153.
[31] QUAN G X, ZHANG J, GUO J, et al. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron grafted on acid-activated attapulgite[J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution,2014,225(6):1979.
[32] QIU Y, ZHANG Q, GAO B, et al. Removal mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by biochar supported nanosized zero-valent iron: Synergy of adsorption, reduction and transformation[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,265:115018. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115018
[33] LIU L H, LIU X, WANG D Q, et al. Removal and reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated wastewater using magnetic biochar prepared by co-pyrolysis of nano-zero-valent iron and sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,257:120562. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120562
[34] WANG H B, CAI J Y, LIAO Z W, et al. Black liquor as biomass feedstock to prepare zero-valent iron embedded biochar with red mud for Cr(VI) removal: Mechanisms insights and engineering practicality[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,311:123553. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123553
[35] AWANG N A, SALLEH W N W, ISMAIL A F, et al. Adsorption behavior of chromium(VI) onto regenerated cellulose membrane[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2019,58(2):720-728.
[36] GUPTA V K, PATHANIA D, AGARWAL S, et al. Removal of Cr(VI) onto Ficus carica biosorbent from water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2013,20(4):2632-2644. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-012-1176-6
[37] IMRAN M, KHAN Z U, IQBAL M M, et al. Effect of biochar modified with magnetite nanoparticles and HNO3 for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from contaminated water: A batch and column scale study[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,261:114231. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114231
[38] YU J D, JIANG C Y, GUAN Q Q, et al. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by supported ZnO nanoparticles on biochar derived from waste water hyacinth[J]. Chemosphere,2018,195:632-640. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.128
[39] 陈泽文, 周子晗, 吴美仪, 等. 埃洛石纳米管/聚间苯二胺复合材料去除Cr(Ⅵ)的性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3):493-503. CHEN Zewen, ZHOU Zihan, WU Meiyi, et al. Adsorption properties of halloysite nanotubes/poly(m-phenylenediamine) composites for Cr(VI)[J]. Acta Materiae Compo-sitae Sinica,2020,37(3):493-503(in Chinese).
[40] 席冬冬, 李晓敏, 熊子璇, 等. 生物炭负载纳米零价铁对污染土壤中铜钴镍铬的协同去除[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(6):58-66. XI Dongdong, LI Xiaomin, XIONG Zixuan, et al. Synergis-tic removal of Cu, Co, Ni and Cr from contaminated soil by biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron[J]. Environmental Engineering,2020,38(6):58-66(in Chinese).
[41] YOON I H, BANG S, CHANG J S, et al. Effects of pH and dissolved oxygen on Cr(VI) removal in Fe(0)/H2O systems[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,186(1):855-862. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.074
[42] WANG Z, CHEN G H, WANG X R, et al. Removal of hexavalent chromium by bentonite supported organosolv lignin-stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles from wastewater[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,267:122009. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122009
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 陈然,贾红斌,李奕莹,李双洋,周建飞,石碧. 胶原生物炭/g-C_3N_4/WO_3复合材料光催化去除水体中Cr(Ⅵ). 皮革科学与工程. 2025(01): 1-7+28 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙志勇,张宇辰,吴喜军. 聚乙烯亚胺交联膨润土对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能与机制. 复合材料学报. 2025(02): 949-960 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 赵啟超,白红娟,韩群英,孙竹梅,刘鹏霄,王子豪,叶宇晗,王瑶. 低温热解磷酸改性花生壳生物炭的制备及对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的去除. 中北大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 503-512 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李然,纪丽丽,何前锐,夏晓月,王亚宁. 贻贝壳负载纳米零价铁去除钒(Ⅴ)的性能与机制. 工业水处理. 2024(09): 127-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张潇宇. 试分析钢铁厂含铬废水污泥处理工艺. 冶金与材料. 2024(11): 71-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 郜飞,董良飞,葛玉龙,唐园园,李芬. 污泥生物炭/凹凸棒土的制备及其吸附性能研究. 无机盐工业. 2023(05): 91-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王阳,高衍浩,孔凡今. 生物炭负载纳米零价铁修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展. 山东化工. 2023(10): 98-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 吴培,刘子璇,雷明婧,余意,刘家豪,聂芳,朱健,王平. 葡萄籽提取液还原制备生物炭负载纳米铁对水中As(Ⅲ)的去除性能及机理. 环境工程学报. 2023(08): 2596-2605 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李佳璇,王平,万斯,陈润华. 高孔隙率生物炭研制及其处理废水中磷酸盐. 复合材料学报. 2023(11): 6395-6406 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 农海杜,毛悦梅,沙海超,谢水波,陈胜兵,曾涛涛. 污泥基生物炭负载纳米零价铁除U(Ⅵ)性能及机理. 环境科学与技术. 2023(11): 195-202 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)
-




 下载:
下载: