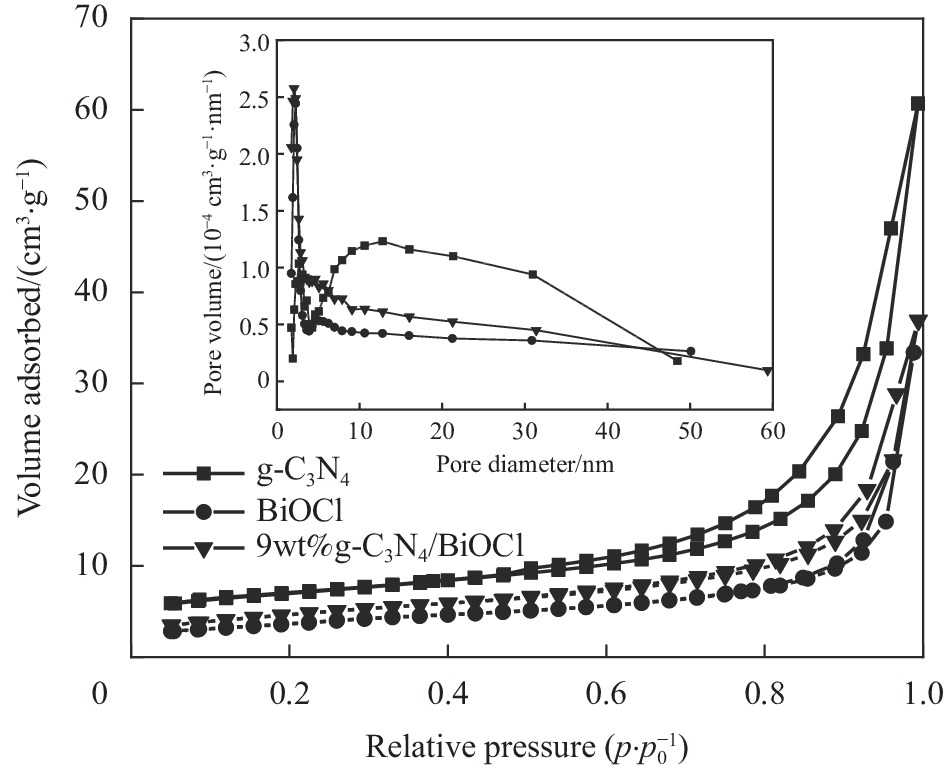
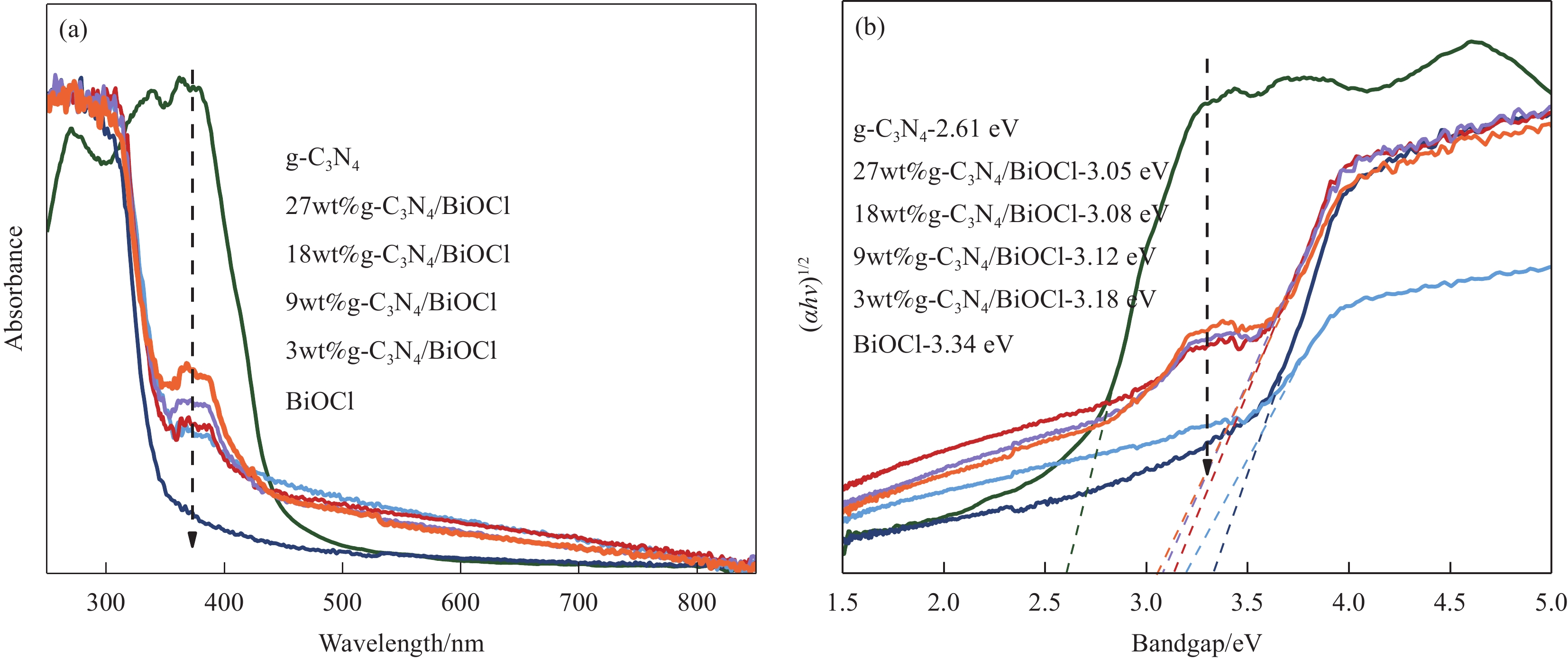
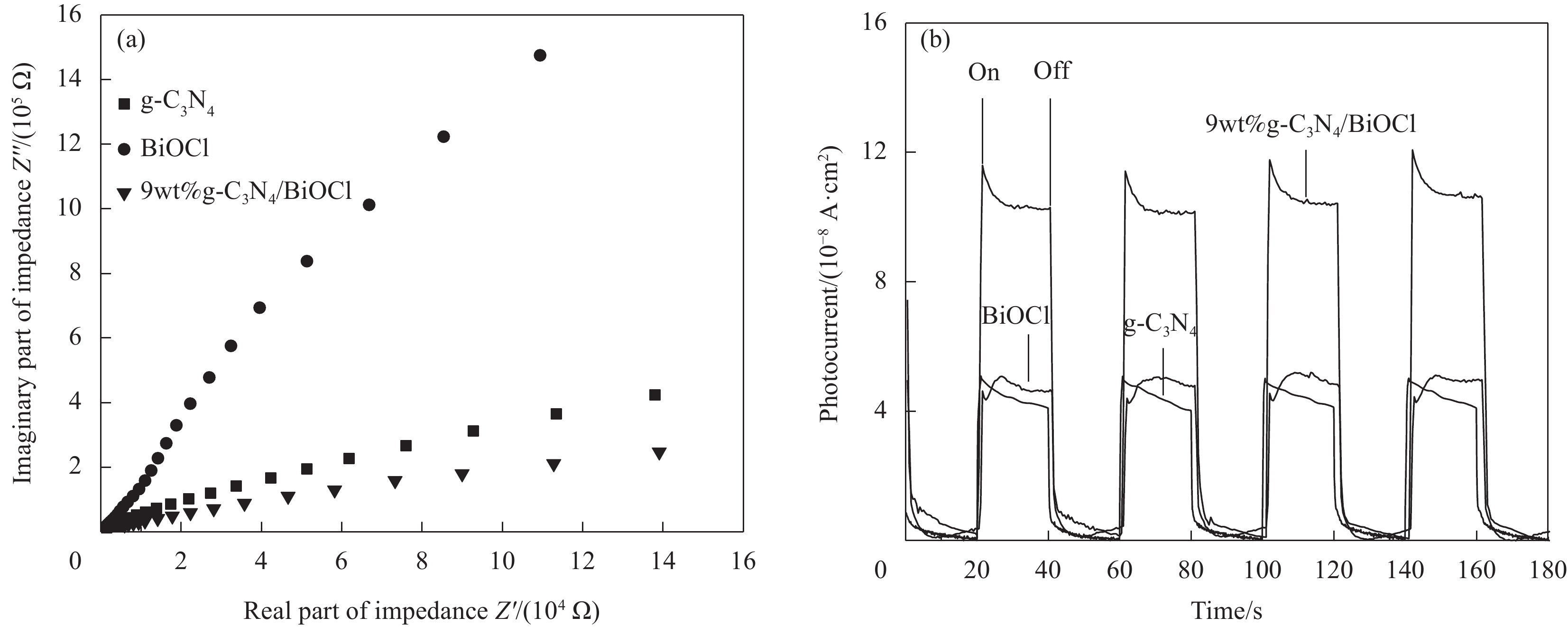
g-C3N4/BiOCl composite photocatalyst used as 2D/2D heterojunction for photocatalytic degradation of dyes
-
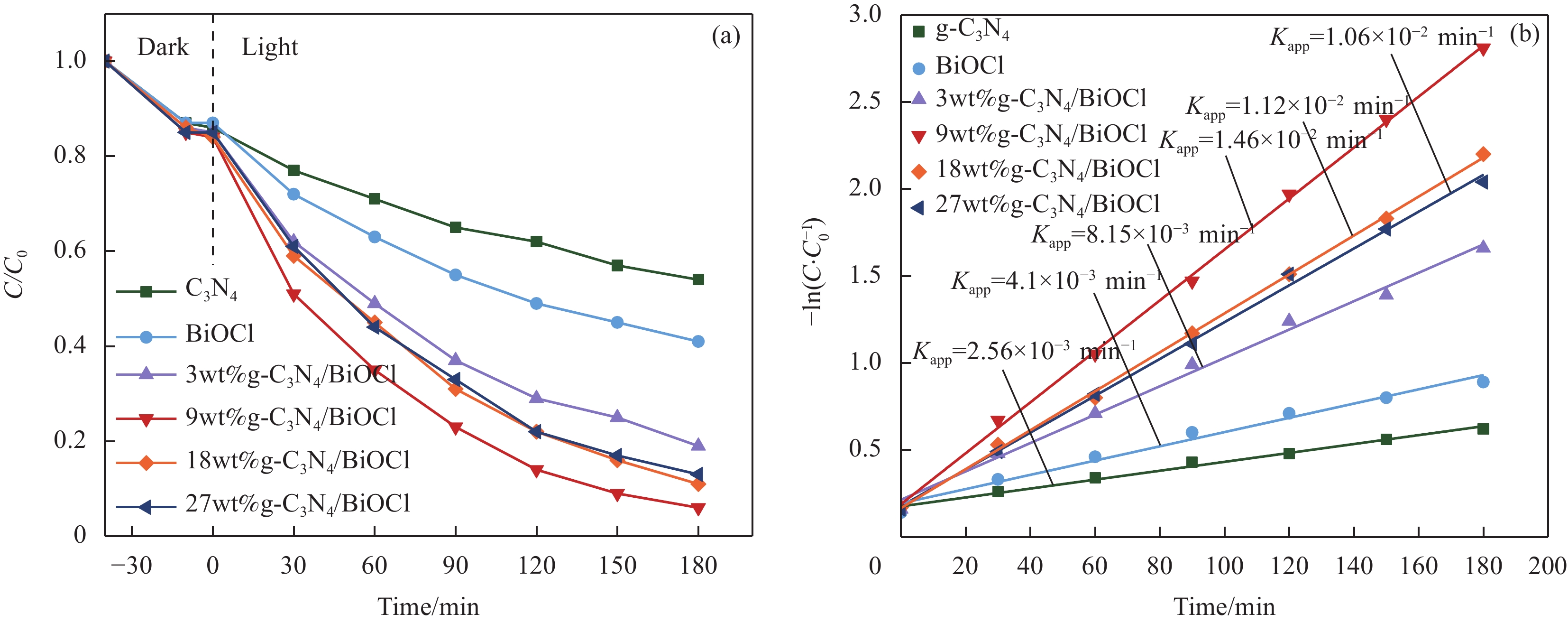
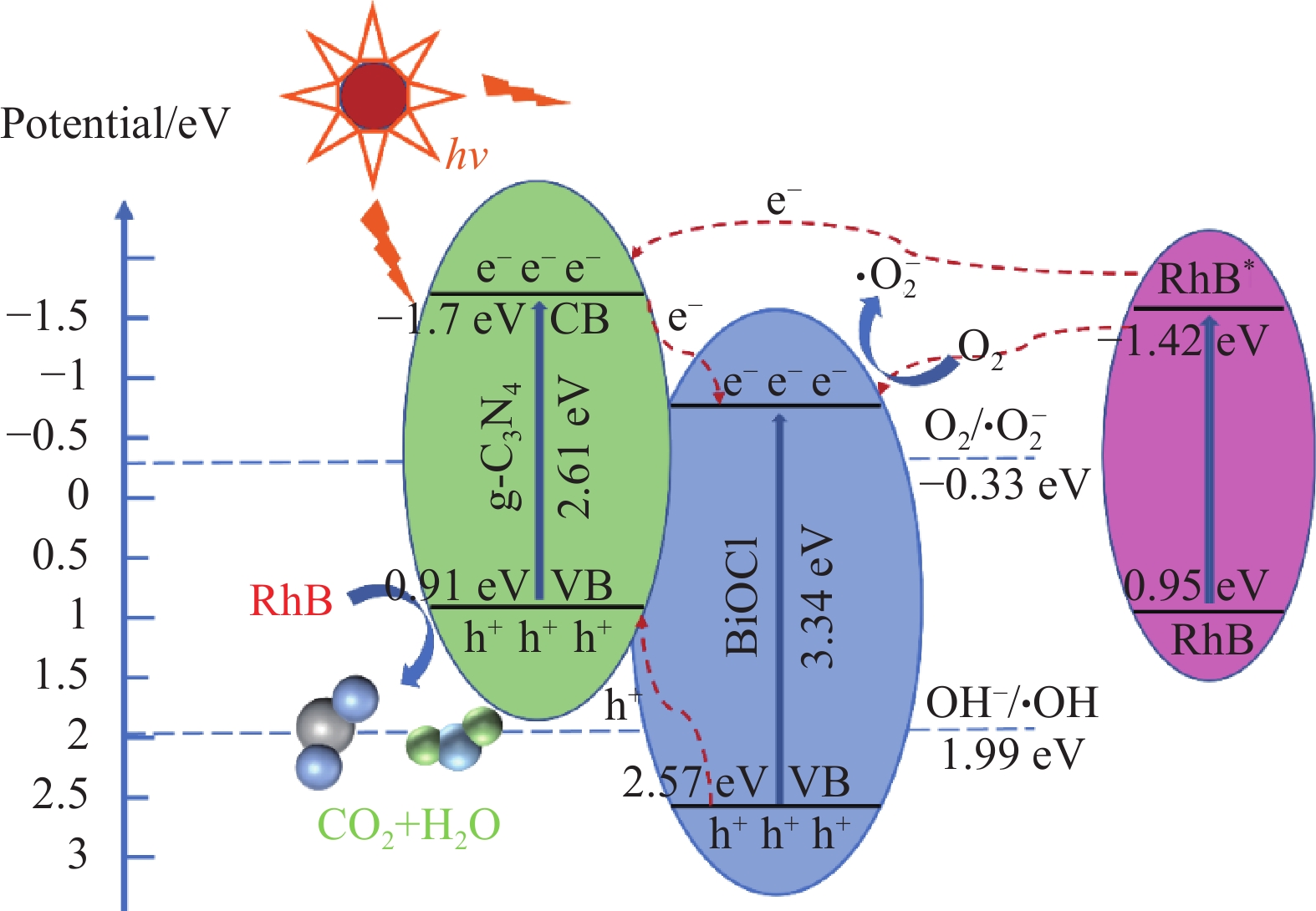
摘要: 为扩大BiOCl的太阳光吸收范围,获得更高效的光催化剂,本文通过水热法制备了石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)/BiOCl (2D/2D)复合光催化剂并对其进行详细表征。结构与形貌表征结果显示BiOCl纳米片沉积在层状g-C3N4表面,形成了2D/2D面-面复合结构;光电化学性质分析表明形成的异质结构能有效扩展光吸收频率范围,促进光生载流子分离和迁移,从而有利于光催化性能的提高。以500 W氙灯模拟太阳光源,光催化降解罗丹明B(RhB)的结果表明g-C3N4/BiOCl异质结的光催化降解活性远高于单纯的g-C3N4和BiOCl。其中9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl表现出了最优越的光催化活性,在180 min内对RhB的降解率为94%,其表观速率常数Kapp值为g-C3N4和BiOCl的5.7和3.6倍。同时对g-C3N4/BiOCl异质结的光催化机制展开研究,结合复合催化剂电子结构和自由基捕获实验提出了在染料敏化作用下RhB的光催化降解机制。Abstract: In order to expand the sunlight absorption range of BiOCl and obtain more efficient photocatalyst, Graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4)/BiOCl (2D/2D) composite photocatalyst was prepared by hydrothermal method and characterized in detail. The results of structural and morphology characterization show that BiOCl nanosheets are deposited on the layered g-C3N4 surface to form 2D/2D face-face composite structure. The analysis of photoelectric chemical properties shows that the formation of heterostructure can effectively expand the frequency range of light absorption and promote the separation and migration of photocarriers, which is conducive to the improvement of photocatalytic performance. The results of photocatalytic degradation of RhB by xenon lamp (500 W) show that the photocatalytic degradation activity of g-C3N4/BiOCl heterojunction is much higher than that of g-C3N4 and BiOCl alone. Among them, 9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl shows the most superior photocatalytic activity, and the degradation rate of RhB is 94% within 180 min, and the apparent rate constant Kapp value of 9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl is 5.7 and 3.6 times that of g-C3N4 and BiOCl. At the same time, the photocatalytic mechanism of g-C3N4/BiOCl heterojunction was studied, and the photocatalytic degradation mechanism of RhB under dye sensitization was proposed by combining the electronic structure of the composite catalyst and free radical capture experiment.
-
飞行器高速跨越大气层飞行时,会面临严峻的气动加热环境[1],高速热流的冲刷剥蚀导致飞行器面临结构破坏和信号中断等问题。为了保证飞行器在极端恶劣的环境中安全服役,确保天线设备系统在通讯导航和远程控制方面平稳运行,对热防护材料的性能提出了更高的要求,即在高温等苛刻的条件下保持结构的完整性和高频电磁波的透波性[2-3]。
可陶瓷化聚合物基复合材料作为一类新型的热防护材料[4],常温下与普通聚合物基复合材料性质相近,在高温环境下可以形成具有一定强度的致密陶瓷层,隔绝材料内部结构与外界热氧的接触,使复合材料保持良好的热稳定性[5-6]。其不仅具有传统的聚合物基复合材料密度低、制备工艺简单高效、可设计制造大面积异型产品等优点,还具备更加优良的耐高温性能,如低烧蚀率和高维形性[7-9]。Yang等[10]将MoSi2引入硼酚醛树脂复合材料中,大幅提高了复合材料的耐烧蚀性能,1400℃下处理20 min后弯曲强度较未添加 MoSi2的复合材料提高了2倍以上。董闯等[11]制备并研究了石榴石微粉改性硼酚醛树脂复合材料的耐高温性能,当石榴石微粉含量为50wt%时,其线烧蚀率和质量烧蚀率与纯硼酚醛树脂相比分别降低了44.05%和43.6%,明显提高了复合材料的耐烧蚀性能。
目前对于可陶瓷化聚合物基复合材料的研究,主要聚焦在耐烧蚀、防隔热等方面,很少应用在高温微波传输领域,因此有必要对其进行相关设计,满足多功能热防护材料的需求。酚醛树脂具有良好的耐热性、力学性能和在各种环境中的耐候性。改性酚醛树脂可用于对材料耐热性要求更高的环境中去。如采用石英纤维增强烯丙基化酚醛树脂与双马树脂预聚得到的耐高温树脂,能够满足飞行器300℃以上短时间高温使用的需求[12]。国内纤维增强SiO2复合材料的研究也比较广泛,先后研制和发展了正交三向石英、高硅氧穿刺等耐热透波复合材料,并已得到应用。宋麦丽等[13]以低残炭率甲基硅树脂为基体,引入金属氧化物和无机氧化物作为除碳剂和介电性能改善剂,结果表明,在 800℃和 1200℃高温处理后,采用电磁波频率 9.30 GHz测试,介电常数小于3.5,介电常数随温度的升高变化不明显。Si3N4基陶瓷材料是综合性能最好的结构陶瓷之一,不仅具有优异的力学性能和良好的热稳定性,而且具有较低的介电常数,广泛应用于高温透波领域。王思青等[14]对颗粒和纤维增强氮化硅基透波复合材料均作了大量研究。采用反应烧结法制备氮化硅基复相陶瓷材料,其弯曲强度和断裂韧性分别为96.7 MPa 和1.80 MPa·m1/2,相对介电常数为3.8~3.9。采用先驱体浸渍裂解工艺制备的石英纤维增强氮化硅基复合材料力学性能和高温介电性能均十分优异[15]。
为了满足高超声速飞行器对热防护材料的防热、承载、透波等性能需求,本文采用低烧蚀、低密度、高温形貌稳定的硼酚醛树脂为基体,耐高温、抗氧化、耐烧蚀的Si3N4陶瓷颗粒作为主要的防热功能体(兼具透波功能),低熔点玻璃料为助熔剂,利用预浸料-层压工艺制备高硅氧纤维增强可陶瓷化复合材料,探究玻璃料对复合材料的耐热性能、耐烧蚀性能及介电性能的影响,并研究了不同温度处理后复合材料的残留物相及微观形貌的变化。
1. 实验材料及表征方法
1.1 原材料
硼酚醛树脂,型号THC-400,陕西太航阻火聚合物有限公司;无水乙醇(分析纯),国药集团化学试剂有限公司;高硅氧玻璃纤维平纹布,SiO2含量为97%,面密度248.3 g/m2,厚度0.2 mm,陕西华特新材料有限公司;β-Si3N4陶瓷颗粒,纯度99.9%,粒径1 μm,密度3.187 g/cm3,上海卜微应用材料技术有限公司;低熔点玻璃料(GF),硅酸盐系,贵州威顿晶磷电子材料股份有限公司,软化点(450±20)℃,主要成分如表1所示。
表 1 低熔点玻璃料(GF)主要成分及含量Table 1. Main components and contents of low melting point glass frit (GF)wt% SiO2 K2O Na2O ZnO Al2O3 BaO TiO2 Bi2O3 P2O5 Fe2O3 52.04 16.26 8.43 5.68 0.44 4.33 9.24 2.96 0.13 0.10 1.2 复合材料制备
将硼酚醛树脂粉末按质量比1∶1溶于无水乙醇中,充分溶解得到硼酚醛树脂溶液,按照表2的配方将Si3N4颗粒和GF依次加入到树脂胶液中,磁力搅拌60 min,得到可陶瓷化树脂,然后将可陶瓷化树脂均匀地刮涂在裁剪好的高硅氧玻璃纤维平纹布上,晾至2~3天,使溶剂充分挥发,得到可陶瓷化预浸料,将裁剪好的预浸料单向层叠16层之后放入厚度为4 mm的模具中进行热压固化,升温速率为2℃/min,固化制度为120℃(30 min,0 MPa)、150℃(60 min,10 MPa)、180℃(120 min,10 MPa)、200℃(60 min,10 MPa);热压固化结束,自然冷却至室温,脱模即可得到可陶瓷化复合材料。
表 2 GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料配方Table 2. GF-Si3N4/BPR composite formulationsSample Mass ratio BPR Si3N4 GF BPR 100 0 0 Si3N4/BPR 100 30 0 5GF-Si3N4/BPR 100 30 5 10GF-Si3N4/BPR 100 30 10 15GF-Si3N4/BPR 100 30 15 20GF-Si3N4/BPR 100 30 20 Note: BPR—Boron phenolic resin. 1.3 试样高温处理
将制备的可陶瓷化复合材料试样切割成尺寸为80 mm×15 mm×4 mm的样条,采用上海光明实验电炉厂生产的LD-1700 STN型管式炉在空气气氛下对复合材料试样进行高温处理,升温速率为10℃/min,在不同温度下(800℃、1000℃、1200℃、1400℃)处理20 min,取出试样冷却测试。
1.4 测试与表征
采用德国耐驰公司生产的STA2500型TG-DTA同步热分析仪对可陶瓷化复合材料进行热稳定性分析(空气气氛,升温速率为10℃/min,室温到1500℃)。采用日本理学株式会社生产的D/MAX-RB型X射线衍射仪对复合材料试样进行物相分析,扫描速率为10°/min。采用捷克TESCAN公司生产的TESCAN MIRA4型场发射扫描电子显微镜对复合材料试样进行微观形貌观察。采用深圳瑞格尔公司生产的RGM4100型电子万能试验机对复合材料试样进行弯曲强度测试,测试标准为GB/T 1449—2005[16]。采用氧乙炔火焰对复合材料试样进行烧蚀测试,测试标准为GJB 323 A—1996[17]。采用波导法,使用美国AGILENT公司生产的PNA-N5244 A型矢量网络分析仪对不同配方的复合材料试样进行介电性能测试,测试频率为8.2 GHz。采用美国AGILENT公司生产的安捷伦4339 b型电阻率测试仪对复合材料试样进行电阻率/电导率测试,采用法国H.J.Y公司生产的LabRam ARAMIS型高分辨拉曼光谱仪对复合材料试样进行拉曼光谱测试,激光器类型 514 nm,扫描范围为 750~2150 cm−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料热稳定性能的影响
图1为 GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料的TG和DTG曲线,表3为各温度区间复合材料的热分解特性。分析可知复合材料的裂解大致分为4个阶段。室温到400℃,复合材料的热失重率比较低,400℃时复合材料的残重率分别为90.63%、92.41%、93.42%、93.30%、94.33%和93.28%,失重的主要原因是复合材料中水分的蒸发及交联副产物、未反应的低聚物和一些小基团的损失[18];400~600℃第二次裂解过程中,复合材料裂解速率最大,热失重率也最大,600℃残重率分别为54.32%、69.73%、70.21%、71.05%、75.14%和73.73%,该温度区间内,复合材料剧烈裂解产生大量H2O、CO和小分子碳氢化合物[19]。由图1(a)可知,600℃前后Si3N4颗粒非常稳定,因此该温度区间复合材料的热失重主要是硼酚醛树脂的裂解;800~1200℃,树脂进一步裂解,1200℃时残重率分别为52.15%、68.98%、69.33%、71.56%、75.40%和74.78%,除BPR之外,复合材料的残重率略有增加,结合其XRD分析,可能是GF成分促进Si3N4颗粒少量氧化生成SiO2增重及与树脂裂解产物的相互作用,使其转化为以Na2Si2O5为主要成分的玻璃相,提高了裂解产物的热稳定性。在1200~1400℃时,残重率略有降低,1400℃下,裂解残留物进一步氧化,复合材料裂解产物中已经不再有金属Bi和其他裂解过程中生成的玻璃相,可能是随着温度的升高逐渐挥发。
表 3 GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料的热分解特性Table 3. Thermal decomposition properties of GF-Si3N4/BPR compositesSample Tmax/℃ Residue yield/% 400℃ 600℃ 800℃ 1200℃ 1400℃ BPR 495.9 90.63 54.32 52.88 52.15 51.54 Si3N4/BPR 494.2 92.41 69.73 69.14 68.98 68.87 5GF-Si3N4/BPR 501.3 93.42 70.21 69.24 69.33 68.75 10GF-Si3N4/BPR 481.8 93.30 71.05 71.40 71.56 70.54 15GF-Si3N4/BPR 500.9 94.33 75.14 75.31 75.40 73.91 20GF-Si3N4/BPR 495.7 93.28 73.73 74.36 74.78 73.61 Note: Tmax—Temperature at which the thermal mass loss rate is the maximum. 2.2 GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料弯曲强度的影响
图2是不同温度处理后GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料的弯曲强度,总体上不同配方复合材料的弯曲强度随着热处理温度的升高而降低,这是由于随着温度的升高,基体裂解及裂解炭的氧化程度加剧,基体与纤维之间的界面结合越来越差造成的(图3)。常温下,BPR、Si3N4/BPR的弯曲强度分别为133.5 MPa和179.5 MPa,Si3N4/BPR相较于BPR弯曲强度提高了34.5%,主要是由于添加的β-Si3N4颗粒是短柱状,可以嵌入在树脂和纤维之间,提高复合材料的抗弯强度;而引入GF之后,总的填料含量太高,树脂与纤维之间界面结合性能变差,故而常温下复合材料的弯曲强度随玻璃料含量的增加而下降。另外,添加GF后,不同温度处理之后的复合材料弯曲强度均随着玻璃料含量的增加呈先增加后降低的趋势,当GF含量为10wt%时,10GF-Si3N4/BPR的弯曲强度最高。这是由于GF在高温下熔融、填充、愈合基体裂解及裂解炭氧化形成的孔洞裂纹等缺陷,促进复合材料的陶瓷化过程,进而增加复合材料的致密度[20](图3(e))。但是,当GF含量过高时,复合材料界面结合变差,因此会导致力学性能变差。1200℃高温处理后,BPR的弯曲强度为12.3 MPa,Si3N4/BPR、10GF-Si3N4/BPR的弯曲强度分别是19.4 MPa和22.3 MPa,相较于BPR提高了58.5%和81.6%。此外, 1200℃处理后的10GF-Si3N4/BPR比1000℃和1400℃处理后的更高,这是由于1200℃下,GF的流动性更强,能更有效地愈合孔隙,复合材料的致密度相较1000℃处理后的更高,而1000℃下,基体裂解的速率加快,产生的挥发性小分子数量增大,Si3N4颗粒的贯穿桥接作用减弱,影响了复合材料的弯曲强度。当温度升高至1400℃,GF部分挥发,对裂解炭的保护程度下降,复合材料的致密度也会降低,此外,高硅氧纤维中的SiO2在高温下结晶[21],强度衰减,从而导致复合材料弯曲强度进一步下降。
![]() 图 3 1200℃处理后GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料表面和断面微观形貌:((a), (c), (e)) BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR的表面;((b), (d), (f)) BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR的断面Figure 3. Surface and cross-section micro-morphologies of GF-Si3N4/BPR composites treated at 1200℃: ((a), (c), (e)) Surfaces of BPR, Si3N4/BPR and 10GF-Si3N4/BPR; ((b), (d), (f)) Cross-sections of BPR, Si3N4/BPR and 10GF-Si3N4/BPR
图 3 1200℃处理后GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料表面和断面微观形貌:((a), (c), (e)) BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR的表面;((b), (d), (f)) BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR的断面Figure 3. Surface and cross-section micro-morphologies of GF-Si3N4/BPR composites treated at 1200℃: ((a), (c), (e)) Surfaces of BPR, Si3N4/BPR and 10GF-Si3N4/BPR; ((b), (d), (f)) Cross-sections of BPR, Si3N4/BPR and 10GF-Si3N4/BPR2.3 GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料裂解物相及表面形貌的影响
为了探究GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料在不同温度下裂解产物物相和形貌的影响,对Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR在不同温度下的裂解产物进行了XRD分析和SEM表面形貌分析。图4(a)和图4(b)为Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR在不同温度下于空气气氛中裂解20 min后残留物的物相图谱;图5为Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR在1200℃下裂解20 min后表面微观形貌图及特定元素分布的EDS分析。
由图4(a)可以看出,从室温到1200℃,Si3N4/BPR的XRD衍射峰基本重合,说明1200℃以下,添加的Si3N4颗粒非常稳定;图4(b)中,800℃下GF中的Bi2O3被酚醛树脂裂解产生的CO还原产生金属Bi,同时玻璃料中的一些氧化物和树脂裂解产物互相反应生成以Na2Si2O5为主要成分的玻璃相;1200℃处理后,通过其相应的元素EDS映射分布图可以看出,10GF-Si3N4/BPR的O元素分布密度明显大于Si3N4/BPR,且10GF-Si3N4/BPR的Si元素分布比较均匀,说明复合材料经高温处理后,10GF-Si3N4/BPR的液相明显增多,同时Si3N4颗粒氧化,表面形成熔体膜,抑制了Si3N4颗粒的进一步氧化[22];由图4(b)可知,1400℃下,10GF-Si3N4/BPR裂解产物中已经不再有金属Bi和其他化合物,这可能是Bi和其他裂解过程中生成的化合物随着温度的升高逐渐挥发所致,裂解过程涉及的化学反应如下:
BPR→C(s)+CO(g)+CH4(g) (g) Bi2O3(s)+3CO(g)=2Bi(s)+3CO2(g) (1) Si3N4(s)+3O2(g)=3SiO2(s)+2N2(g) (2) Na2O(s)+2SiO2(s)=Na2Si2O5(s) (3) 2.4 GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料烧蚀性能的影响
为了探究GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料耐烧蚀性能的影响,对BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR进行了氧乙炔烧蚀测试(图6和图7),并对烧蚀后的材料表面进行微观形貌观察及物相分析(图8和图9)。
从图7可以看出,BPR的线烧蚀率和质量烧蚀率明显大于Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR试样,这是由于BPR在氧乙炔高温热流冲刷下,中间出现凹坑,形成凹坑的主要原因是氧-乙炔火焰中心温度将高硅氧纤维熔化,形成液态SiO2 ,然后从火焰喷射中心被吹走,在试样四周温度较低的部位凝固成透明熔滴[23]及树脂裂解残碳的氧化生成气体逸出所致。10GF-Si3N4/BPR中添加的GF在高温热流的冲刷下,熔融产生液相,部分液相被热流冲刷消散,剩下的熔融相的GF迅速向树脂裂解产生的孔洞渗透填充,再者,Si3N4高温下氧化反应生成SiO2,反应增重,抵消了部分质量损失;因此10GF-Si3N4/BPR的线烧蚀率大于Si3N4/BPR,而质量烧蚀率却相对于Si3N4/BPR较小。Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料表面陶瓷相的微观形貌及EDS分析如图8所示,氧乙炔烧蚀之后,复合材料产生了不同致密程度的陶瓷层,10GF-Si3N4/BPR的陶瓷相较Si3N4/BPR更致密,可能是添加的GF成分促进了Si3N4颗粒氧化及与树脂裂解产物的相互作用,反应生成了以Si3N4和SiC为主要成分的陶瓷层,提高了复合材料的耐烧蚀性能。
2.5 GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料介电性能的影响
为了探究低熔点GF对GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料介电性能的影响,对BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR在不同温度下的介电常数ε和介电损耗角正切值tanδ(测试频率为8.2 GHz)及复合材料电导率进行测试分析。图10为复合材料介电常数和损耗角正切值随温度的变化情况,表4为不同温度处理后的复合材料电导率。
表 4 不同温度处理后的GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料电导率Table 4. Conductivity of GF-Si3N4/BPR composites treated at different temperaturesSample Conductivity/(10−10 S·m–1) RT 800℃ 1000℃ 1200℃ 1400℃ BPR 0.222 113 93.5 162 358 Si3N4/BPR 0.125 149 142 80 188 10GF-Si3N4/BPR 0.111 87 150 65.8 128 由图10(a)可以看出,在室温~600℃时,BPR、Si3N4/BPR和10GF-Si3N4/BPR 3种材料的介电常数没有明显变化,介电常数均小于3.5;从800~1400℃,复合材料的介电常数发生了明显变化,600~1000℃材料的介电常数出现激增,主要是硼酚醛树脂分子中含有大量极性基团,随着温度的升高使其介电常数和介电损耗明显增大;随着树脂充分裂解,产生的碳杂质在基体中聚集形成碳层或弥散分布,对电磁波有很大的屏蔽或衰减作用,从而影响复合材料的介电性能,同时伴随大量的H2O、CO、CH4等气体和挥发性小分子物质,在复合材料内部和表面留下大量孔洞、裂纹等缺陷,当电磁波入射至材料表面时,会发生多次反射和折射,空隙影响了电磁波在介质中的传播,在一定程度上会吸收电磁波[23]。由此可见,高温作用使材料表面化学成分发生变化,从而导致复合材料介电常数和损耗角正切值发生变化。而且在这个温度区间内,10GF-Si3N4/BPR添加的GF中Bi2O3被还原成金属Bi,Bi和树脂裂解残留物可能形成导电通道,同时添加GF时引入的微量杂质随温度的升高开始电离并产生离子电导,导致复合材料的介电常数和介电损耗大幅提升[24]。1200℃处理后,GF中的氧化物会促进Si3N4氧化,形成SiO2熔体膜,提高复合材料的致密度,从而改善复合材料的介电性能。
1400℃下复合材料的介电常数和介电损耗大幅增加,根据图11和表5的拉曼光谱测试数据分析可能是该温度下复合材料的裂解玻璃碳石墨化程度加深导致。在无序碳中,除了 1580 cm −1处有G峰外,在低波数1350 cm −1处也有D峰 [25] 。D和G峰的存在和位置、D带与G带的强度比ID/IG可以反映无序碳石墨化程度[26] 。从表5可以看出,从800℃到1400℃,ID/IG的值逐渐变小,这说明,随裂解温度的升高,玻璃碳中石墨微晶的数量逐渐增多,其石墨化程度逐渐加深,对电磁波有明显的吸收作用,从表4中1400℃处理后的复合材料电导率的增大也可以证实这一点。
表 5 GF-Si3N4/BPR复合材料裂解玻璃碳的ID/IG值Table 5. ID/IG values of pyrolyzed glassy carbon of GF-Si3N4/BPR compositesSample ID/IG 800℃ 1400℃ BPR 2.717 2.403 Si3N4/BPR 3.236 2.364 10GF-Si3N4/BPR 3.663 2.326 Note: ID/IG—Intensity ratio of the D band to the G band. 3. 结论
(1) 玻璃料(GF)的添加,提高了复合材料高温下的致密性和完整性。复合材料在高温下生成Na2Si2O5等化合物,与Si3N4氧化生成的SiO2熔体膜形成致密的陶瓷层,抑制了氧气对复合材料内部的进一步侵蚀,提高了复合材料的热稳定性。
(2) GF的添加,提高了复合材料高温下的力学性能和耐烧蚀性能。1200℃处理后,其弯曲强度为22.3 MPa,与纯树脂试样相比,提高了81.3%,与未添加GF的试样相比,提高了14.9%;其质量烧蚀率为0.022 g/s,分别降低了73.1%和55.1%。
(3) GF的添加,改善了复合材料的介电性能。800℃以上,树脂充分裂解,产生了吸收电磁波的游离碳和衰减电磁波的孔洞、裂纹,导致其介电常数和损耗角正切值逐渐增大,而复合材料表面生成的致密玻璃相有效遏制了这种不利影响。
-
图 2 (a) g-C3N4、BiOCl和9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl的XPS全谱;((b)~(d)) BiOCl和9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl的Bi4f、O1s, Cl2p高分辨XPS光谱;((e)、(f)) g-C3N4和9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl的C1s、N1s高分辨XPS光谱
Figure 2. (a) XPS survey spectra of g-C3N4, BiOCl and 9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl; ((b)-(d)) Bi4f, O1s and Cl2p high-resolution XPS spectra of BiOCl and 9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl, respectively; ((e), (f)) C1s, N1s high-resolution XPS spectra of g-C3N4 and 9wt%g-C3N4/BiOCl
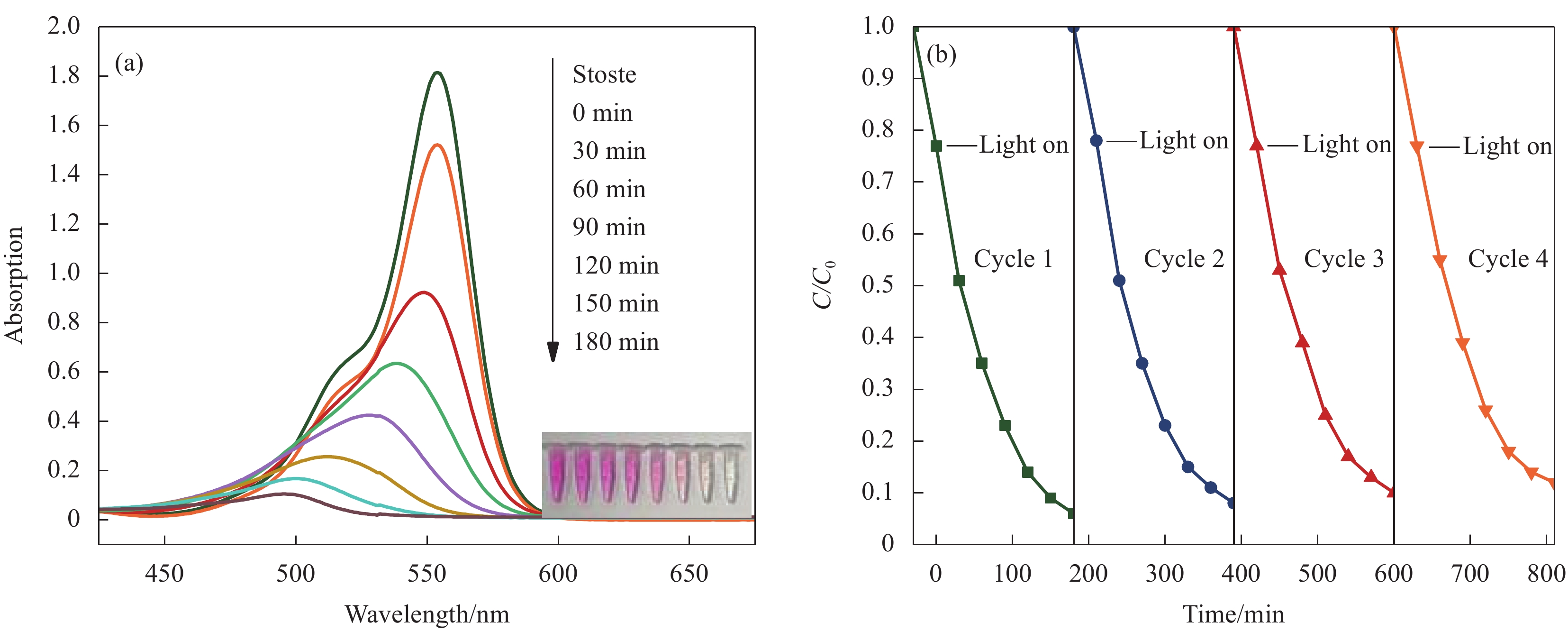
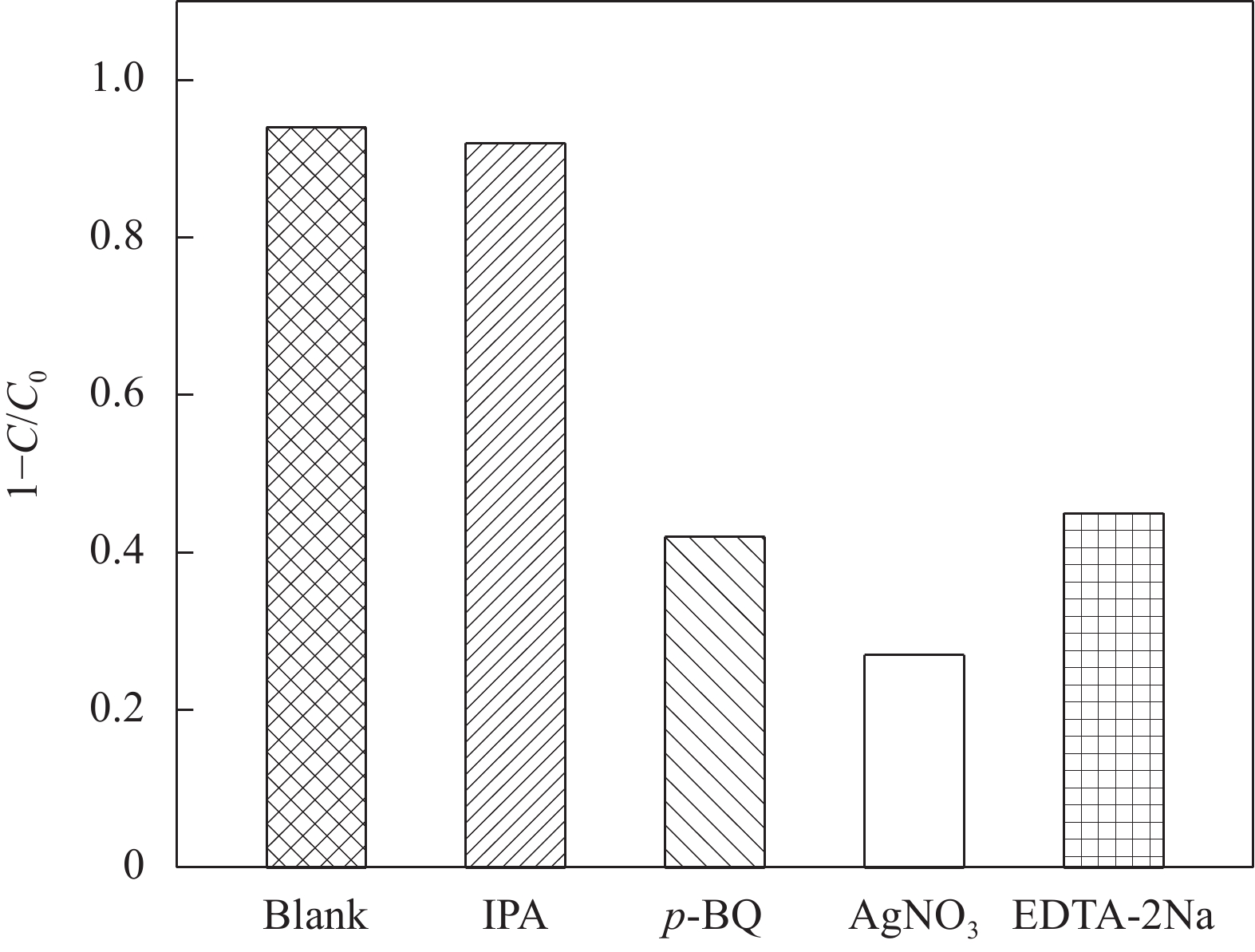
图 8 (a) g-C3N4、BiOCl及g-C3N4/BiOCl异质结对罗丹明B (RhB)的降解率;(b) g-C3N4、BiOCl及g-C3N4/BiOCl异质结对 RhB的降解反应动力学
Figure 8. (a) Degradation rate of rhodamine B (RhB) by g-C3N4, BiOCl and g-C3N4/BiOCl heterojunction; (b) Kinetics of RhB degradation over g-C3N4, BiOCl and g-C3N4/BiOCl heterojunction
C/C0—Ratio of the concentration of the organic pollutant solution after a certain period of time to the concentration of the organic pollutant solution before the photocatalytic reaction; Kapp—Apparent rate constant of photocatalyst degradation of organic pollutants
-
[1] LI M L, ZHANG L X, WU M Y, et al. Mesostructured CeO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposites: Remarkably enhanced photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction by mutual component activations[J]. Nano Energy,2016,19:145-155. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.11.010
[2] CHEN C S, MEI W, WANG C, et al. Synthesis of a flower-like SnO/ZnO nanostructure with high catalytic activity and stability under natural sunlight[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,826:154122. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154122
[3] CHEN L J, SHI L, WU J B, et al. N-SrTiO3 nanoparticle/BiOBr nanosheet as 0D/2D heterojunctions for enhanced visible light photocatalytic dye degradation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B,2020,261:114667. DOI: 10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114667
[4] MENG X C, ZHANG Z S. Bismuth-based photocatalytic semiconductors: Introduction, challenges and possible approaches[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical,2016,423:533-549. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2016.07.030
[5] WANG Q Z, HUI J, HUANG T J, et al. The preparation of BiOCl photocatalyst and its performance of photodegradation on dyes[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2014,17:87-93. DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2013.08.018
[6] ZHANG X, WANG X B, WANG L W, et al. Synthesis of a highly efficient BiOCl single-crystal nanodisk photocatalyst with exposing {001} facets[J]. Applied Materials and Interfaces,2014,6(10):7766-7772. DOI: 10.1021/am5010392
[7] CHEN H B, YU X, ZHU Y, et al. Controlled synthesis of {001} facets-dominated dye-sensitized BiOCl with high photocatalytic efficiency under visible-light irradiation[J]. Journal of Nanoparticl Research,2016,18:225. DOI: 10.1007/s11051-016-3529-4
[8] CHEN F, LIU H Q, BAGWASI S, et al. Photocatalytic study of BiOCl for degradation of organic pollutants under UV irradiation[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,2010,215(1):76-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2010.07.026
[9] LI B X, SHAO L Z, WANG R S, et al. Interfacial synergism of Pd-decorated BiOCl ultrathin nanosheets for selective oxidation of aromatic alcohols[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6(15):6344-6355. DOI: 10.1039/C8TA00449H
[10] YU C L, HE H B, LIU X Q, et al. Novel SiO2 nanoparticle-decorated BiOCl nanosheets exhibiting high photocatalytic performances for the removal of organic pollutants[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2019,40(8):1212-1221. DOI: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63359-0
[11] PAN J B, LIU J J, ZUO S L, et al. Synthesis of cuboid BiOCl nanosheets coupled with CdS quantum dots by region-selective deposition process with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2018,103:216-224. DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.03.043
[12] PAN J B, LIU J J, ZUO S L, et al. Structure of Z-scheme CdS/CQDs/BiOCl heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity for environmental pollutant elimination[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,444:177-186. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.189
[13] WANG Q, LI P J, ZHANG Z, et al. Kinetics and mechanism insights into the photodegradation of tetracycline hydrochloride and ofloxacin mixed antibiotics with the flower-like BiOCl/TiO2 heterojunction[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,2019,378:114-124. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.04.028
[14] ZHAO S, ZHANG Y W, ZHOU Y M, et al. Reactable polyelectrolyte-assisted synthesis of BiOCl with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering,2017,5(2):1416-1424. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01987
[15] HU J L, FAN W J, UE W Q, et al. Insights into the photosensitivity activity of BiOCl under visible light irradiation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2014,158-159:182-189. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.019
[16] ONG W J. 2D/2D graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) heterojunction nanocomposites for photocatalysis: Why does face-to-face interface matter[J]. Frontiers in Materials,2017,4:11. DOI: 10.3389/fmats.2017.00011
[17] TIAN N, ZHANG Y H, LI X W, et al. Precursor-reforming protocol to 3D mesoporous g-C3N4 established by ultrathin self-doped nanosheets for superior hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Energy,2017,38:72-81. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.05.038
[18] ZHANG Y, LIN L H, WANG B, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride polymers toward sustainable photoredox catalysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2015,54(44):12868-12884. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201501788
[19] LI J Y, CUI W, SUN Y J, et al. Directional electrons delivery via vertical channel between g-C3N4 layers promoting the photocatalysis efficiency[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(19):9358-9364. DOI: 10.1039/C7TA02183F
[20] CHEN Y, WANG X C. Template-free synthesis of hollow g-C3N4 polymer with vesicle structure for enhanced photocatalytic water splitting[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry,2018,122(7):3786-3793. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12496
[21] LIANG D, HUANG Y L, WU F, et al. In situ synthesis of g-C3N4/TiO2 with {001} and {101} facets coexposed for water remediation[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,487:322-334. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.088
[22] ZHU X, WANG Y T, GUO Y, et al. Environmental-friendly synthesis of heterojunction photocatalysts g-C3N4/BiPO4 with enhanced photocatalytic performance[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,544:148872. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148872
[23] ZHAN S, ZHOU F, HUANG N B, et al. g-C3N4/ZnWO4 films: Preparation and its enhanced photocatalytic decomposition of phenol in UV[J]. Applied Surface Science,2015,358:328-335. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.180
[24] ZHANG L, NIU C G, ZHAO X F, et al. Ultrathin BiOCl single-crystalline nanosheets with large reactive facets area and high electron mobility efficiency: A superior candidate for high-performance dye self-photosensitization photocatalytic fuel cell[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,2018,10(46):39723-39734. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b14227
[25] ZOU Y J, SHI J W, MA D D, et al. In situ synthesis of C-doped TiO2@g-C3N4 core-shell hollow nanospheres with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for H2 evolution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,322:435-444. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.056
[26] HUANG Z F, SONG J J, PAN L, et al. Carbon nitride with simultaneous porous network and O-doping for efficient solar-energy-driven hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Energy,2015,12:646-656. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.01.043
[27] SHE X J, WU J J, ZHONG J, et al. Oxygenated monolayer carbon nitride for excellent photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and external quantum efficiency[J]. Nano Energy,2016,27:138-146. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.06.042
[28] MA D M, ZHONG J B, LI J Z, rt al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of BiOCl by C70 modification and mechanism insight[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,443:497-505. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.018
[29] HU T P, YANG Y, DAI K, et al. A novel Z-scheme Bi2MoO6/BiOBr photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,456:473-481. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.186
[30] CHANG F, WU F Y, YAN W J, et al. Oxygen-rich bismuth oxychloride Bi12O17Cl2 materials: Construction, characterization, and sonocatalytic degradation performance[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2019,50:105-113. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.09.005
[31] LIU C, ZHOU J L, SU J Z, et al. Turning the unwanted surface bismuth enrichment to favourable BiVO4/BiOCl heterojunction for enhanced photoelectrochemical performance[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2019,241:506-513. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.060
[32] GAO J C, GAO Y, SUI Z Y, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of BiOBr/FeWO4 composite photocatalysts and their photocatalytic degradation of doxycycline[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,732:43-51. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.092
[33] ZHU M Y, LIU Q, CHEN W, et al. Boosting the visible-light photoactivity of BiOCl/BiVO4/N-GQD ternary heterojunctions based on internal Z-scheme charge transfer of N-GQDs: Simultaneous band gap narrowing and carrier lifetime prolonging[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,2017,9(44):38832-38841. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b14412
[34] ZHANG G G, HUANG C J, WANG X C. Dispersing molecular cobalt in graphitic carbon nitride frameworks for photocatalytic water oxidation[J]. Small,2015,11(9-10):1215-1221. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201402636
[35] JIN X Y, GUAN Q M, TIAN T, et al. In2O3/boron doped g-C3N4 heterojunction catalysts with remarkably enhanced visible-light photocatalytic efficiencies[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,504:144241. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144241
[36] TAO R, LI X H, LI X W, et al. TiO2/SrTiO3/g-C3N4 ternary heterojunction nanofibers: Gradient energy band, cascade charge transfer, enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution, and nitrogen fixation[J]. Nanoscale,2020,12(15):8320-8329. DOI: 10.1039/D0NR00219D
[37] GAO X Y, PENG W, TANG G B, et al. Highly efficient and visible-light-driven BiOCl for photocatalytic degradation of carbamazepine[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,757:455-465. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.081
[38] XIAO Y, PENG Z Y, ZHANG S, et al. Z-scheme CdIn2S4/BiOCl nanosheet face-to-face heterostructure: In-situ synthesis and enhanced interfacial charge transfer for high-efficient photocatalytic performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2019,54:9573-9590. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-019-03401-2
[39] GUO L A, YOU Y, HUANG H W, et al. Z-scheme g-C3N4/Bi2O2[BO2(OH)] heterojunction for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2020,568:139-147. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.02.025
[40] DENG C H, HU H M, YU H, et al. Facile microwave-assisted fabrication of CdS/BiOCl nanostructures with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2021,56:2994-3010. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-020-05427-3
[41] GUO S E, DENG Z P, LI M X, et al. Phosphorus-doped carbon nitride tubes with a layered micronanostructure for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Angewandte Chemie,2016,128(5):1862-1866. DOI: 10.1002/ange.201508505
[42] RAN J R, MA T Y, GAO G P, et al. Porous P-doped graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for synergistically enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Energy and Environmental Science,2015,8(12):3708-3717. DOI: 10.1039/C5EE02650D
[43] PENG B Y, ZHANG S S, YANG S Y, et al. Synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4/Cu2O composite catalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2014,56:19-24. DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.04.042
[44] BING X M, JIAN X Y, CHU J H, et al. Hierarchically porous BiOBr/ZnAl1.8Fe0.2O4 and its excellent adsorption and photocatalysis activity[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2019,110:1-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.10.006
[45] ZHENG J H, ZHANG L. Incorporation of CoO nanoparticles in 3D marigoldflower-like hierarchical architecture MnCo2O4 for highly boosting solar light photo-oxidation and reduction ability[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2018,237:1-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.060
[46] WANG J L, YU Y, ZHANG L Z. Highly efficient photocatalytic removal of sodium pentachlorophenate with Bi3O4Br under visible light[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2013,136-137:112-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.02.009
[47] CHEN C C, MA W H, ZHAO J C. Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutans under visible-light irradiation[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2010,39(11):4206-4219. DOI: 10.1039/b921692h
[48] FUJISHIMA A, ZHANG X T. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis: Present situation and future approaches[J]. Comptes Rendus Chimie,2006,9(5-6):750-760. DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2005.02.055
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张恒,张保平,肖煜坤,王尹. 氨基硫脲/季铵木质素对铂的吸附. 复合材料学报. 2022(10): 4674-4684 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 狄婧,刘海霞,姜永强,郭金鑫,赵国虎. 聚吡咯/壳聚糖复合膜的制备及其对Cu(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)吸附机制. 复合材料学报. 2021(01): 221-231 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 苏凯,廖明旭,张胜利,贺玉龙. 蒙脱石-纤维素复合膜对Cd(Ⅱ)吸附性能研究. 矿物岩石. 2020(04): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-




 下载:
下载: