Preparation and thermally conductive properties of functionalized boron nitride nanosheets/polyurethane composites with double heat-conduction networks
-
摘要: 研发低填充且高导热的聚合物基导热复合材料是目前亟需解决的瓶颈问题。基于层层氢键组装,以聚氨酯(PU)开孔泡沫为模板,以聚多巴胺功能化改性氮化硼纳米片(BNNS@PDA)为导热填料,采用浸涂-热压成型法制得低填充、高导热BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料。深入研究了BNNS@PDA和BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的微观结构、导热性能和热稳定性等。结果表明,通过聚多巴胺(PDA)对BNNS进行表面功能化改性能够使其良好地负载于PU开孔泡沫的三维骨架表面。通过热压成型形成以PU骨架为主要导热网络、以PU骨架表面包覆的BNNS@PDA为次级导热网络的高效双重三维导热网络结构,从而降低导热复合材料的界面热阻。当BNNS@PDA填充量为16.3wt%时,双导热网络BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率达到0.783 W/(m·K),与单导热网络PU的热导率(0.387 W/(m·K))相比提高了102.3%。Abstract: The development of polymer-based thermally conductive composites with low filling and high thermally conductivity remains a bottleneck problem that needs to be solved. Based on the layer-by-layer hydrogen-bond assembly, the low filling and high thermally conductive BNNS@PDA/PU composites are prepared by the dip coating-hot pressing method, using the porous polyurethane (PU) foams as template, and polydopamine functionalized nitride boron nanosheets (BNNS@PDA) as thermally conductive fillers. The microstructures, thermal conductive properties and thermal stability of BNNS@PDA and BNNS@PDA/PU composites were investigated in detail. The results show that the surface functionalization of BNNS by PDA can make it coat well on the three-dimensional skeleton of porous PU foams. After hot pressing, the highly effective double heat-conduction networks with the PU skeleton as the main heat-conduction network and BNNS@PDA on the surface of PU skeleton as the secondary heat-conduction network are constructed, leading to the decreased interfacial thermal resistance of the thermally conductive composites. When the filling amount of BNNS@PDA is 16.3wt%, the thermal conductivity of BNNS@PDA/PU composites with double heat-conduction networks reaches 0.783 W/(m·K), which is 102.3% higher than that of PU with single heat-conduction network (0.387 W/(m·K)).
-
随着航空航天、5G通信和人工智能等领域高集成化、多功能化和智能化技术的迅猛发展,电路传输功耗和发热量急剧增大,引起严重的材料失效问题,因此需要高效导热耗散热量保障设备的正常工作温度并延长工作寿命。聚合物导热材料由于良好的可加工性、耐腐蚀性和电绝缘性在热管理领域备受关注[1-3]。常见的聚合物导热材料主要包括两种:本征型聚合物导热材料和填充型聚合物导热材料。本征型聚合物导热材料的制备工艺繁琐、成本高昂,在工业应用上不具备优势,而填充型聚合物导热材料制备流程简便、可控程度高,适用于大规模工业生产与应用[4]。但是填充型聚合物导热材料通常需要较高的填充量以达到理想的热导率,严重影响聚合物导热材料的力学性能和可加工性。因此,如何通过结构/功能一体化设计构筑高效导热网络,获得低填充且高导热的聚合物导热材料是目前亟需解决的难题。
二维纳米材料如氮化硼纳米片(BNNS)、还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)和多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)等被广泛用作高导热填料[5-10]。其中,BNNS具有与石墨烯类似的二维片层结构,热导率达到1700~2000 W/(m·K)。Wang等[11]以三聚氰胺泡沫(MF)为三维骨架,通过逐层组装将BNNS包覆其上,并使用环氧树脂(EP)浸渍封装制得MF@BNNS/EP复合材料。当BNNS填充量为1.1vol%时,复合材料的热导率为0.6 W/(m·K)。与纯EP相比,其热导率提高了123%。聚氨酯(PU)开孔泡沫是由聚醚/聚酯多羟基醇与含有氨基的多元异氰酸酯反应并发泡所制得的多孔材料,具有高孔隙率和高弹性,泡棱表面含有大量的极性官能团(如羰基),且制作工艺成熟、成本低、环保可降解,是一种理想的聚合物多孔材料模板[12-16]。Yang等[17]首先将BNNS和碳纳米管(CNTs)包覆于PU开孔泡沫骨架,然后采用牺牲模板法将复合材料在380℃下热解1 h得到三维BNNS/CNT复合材料,并使用EP浸渍封装制得三维BNNS/CNT/EP复合材料。当BNNS/CNT填充量为5wt%时,其热导率为0.33 W/(m·K)。Zeng等[18]使用冰模板法制得BNNS气凝胶,再通过EP封装得到低填充高导热复合材料。上述研究尽管构筑了连续的导热网络,但通过树脂封装后增大了界面热阻,并未充分发挥连续导热网络的优势。
本文首先通过超声剥离法制备BNNS,并对其进行聚多巴胺(PDA)功能化改性得到BNNS@PDA,然后通过层层氢键组装将BNNS@PDA包覆于PU开孔泡沫的三维骨架表面,再经热压成型制得具有以PU骨架为主要导热网络、以PU骨架表面包覆的BNNS@PDA为次级导热网络的双导热网络BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料。重点研究了导热复合材料的微观结构、导热性能和热稳定性。该方法制备工艺简便,为大规模制备低填充、高导热聚合物导热材料提供了新的思路和方法。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
氮化硼(BN)、盐酸多巴胺(DA)和三(羟甲基)氨基甲烷盐酸盐(Tris),萨恩化学技术(上海)有限公司;异丙醇(IPA),天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;PU开孔泡沫,江西鸿司远特种泡沫材料有限公司。
1.2 BNNS的制备与功能化改性
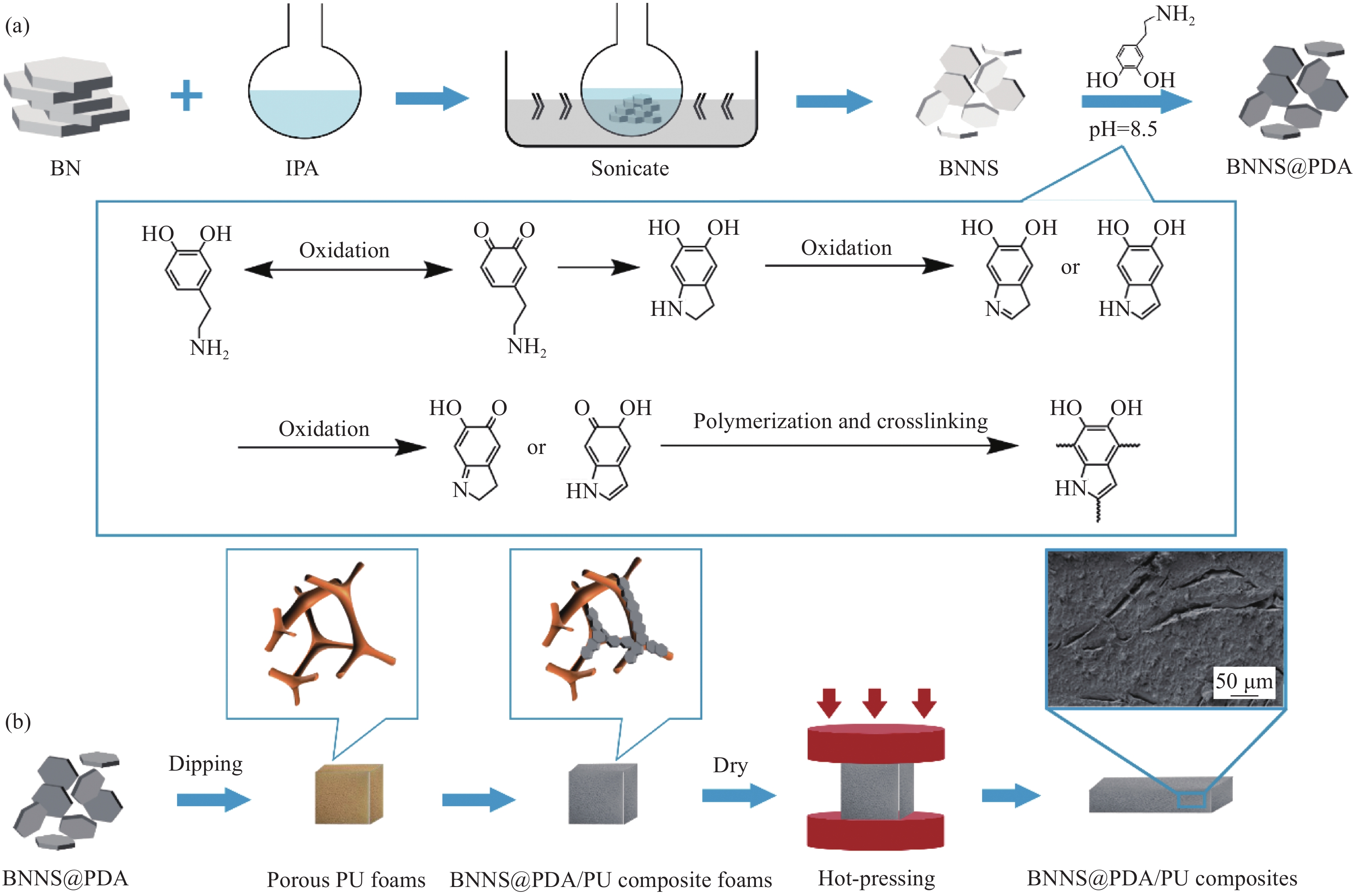
BNNS@PDA的制备与功能化改性过程如图1(a)所示。取2 g BN粉末加入单口烧瓶,加入200 mL IPA溶液,在20 kHz、200 W条件下超声搅拌6 h得到乳白色BN和BNNS混合分散液,静置一段时间后以2000 r/min转速离心20 min使BNNS和BN分层,将上层清液真空辅助抽滤后,置于70℃烘箱中干燥4 h得到BNNS。取0.2 g BNNS置于单口烧瓶中,加入200 mL Tris缓冲溶液(pH=8.5),在20 kHz、200 W条件下超声搅拌1 h使BNNS分散均匀,再加入0.6 g DA于60℃水浴条件下搅拌6 h,使DA自聚得到PDA并接枝到BNNS表面,得到棕黑色分散液,静置冷却至室温,使用去离子水多次抽滤洗涤,置于70℃烘箱内干燥,得到BNNS@PDA。
1.3 BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的制备
BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的制备如图1(b)所示。将BNNS@PDA分散于去离子水中配制成2 mg/mL分散液,将PU开孔泡沫逐次在分散液中浸涂并干燥,重复1~5次,使BNNS@PDA负载于PU开孔泡沫的三维骨架表面,得到不同BNNS@PDA填充量的BNNS@PDA/PU复合泡沫,然后将其置于厚0.5 mm的模具中,在175℃、10 MPa条件下热压10 min,冷却至室温取出得到双导热网络BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料。将未浸涂BNNS@PDA的PU开孔泡沫在相同模具和工艺条件下进行热压得到具有单导热网络PU材料。
1.4 分析与表征
使用德国布鲁克公司红外光谱仪(VECTOR-22)对BNNS和BNNS@PDA的化学结构进行表征。通过日本岛津公司X射线光电子能谱仪(AXIS SUPRA)检测BNNS和BNNS@PDA表面元素的变化。使用德国布鲁克公司的X射线衍射仪(D8 QUEST)对BNNS和BNNS@PDA晶格结构进行表征。使用日本日立公司热重分析仪(STA7200RV)对BNNS、BNNS@PDA和BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料进行热重分析。使用美国FEI公司的高分辨场发射扫描电镜(FEI Verios 460)观察BNNS、BNNS@PDA和BNNS@PDA/PU的微观形貌。采用西安夏溪电子科技公司的导热系数仪(TC3000)对复合材料的热导率进行测试。使用红外热成像仪(Fluke Ti300)分析BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料在65℃热台上的表面温度分布变化。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 BNNS与BNNS@PDA的化学结构
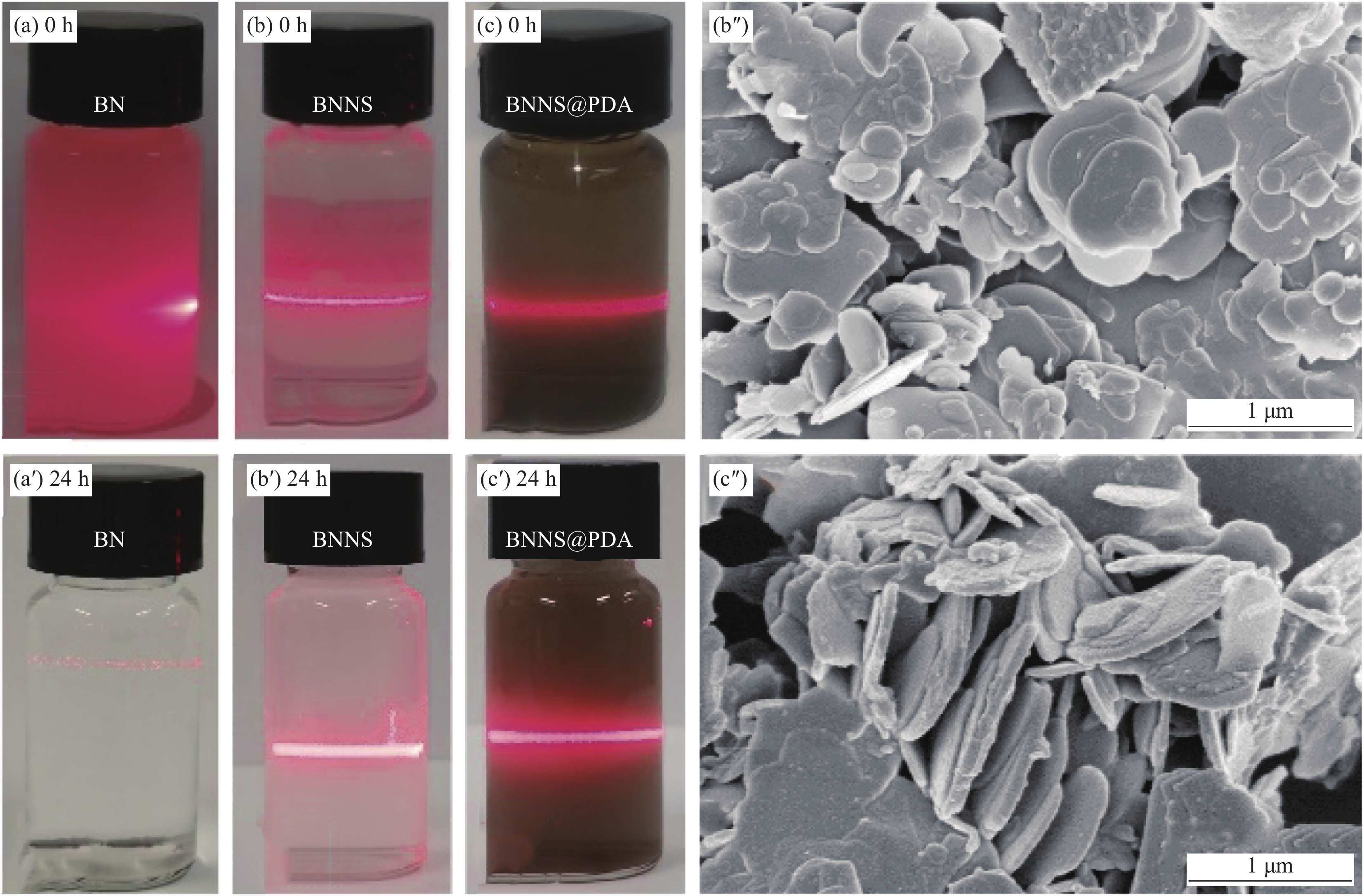
图2(a)~2(c)分别是BN、BNNS和BNNS@PDA的水分散液数码照片,使用激光笔照射分散液,可以观察到在BNNS和BNNS@PDA分散液中有明显的光路,产生了丁达尔效应,说明BNNS和BNNS@PDA在去离子水中具有良好的分散性。图2(a')~2(c')是静置24 h后的数码照片,BN分散液出现明显沉淀,而BNNS和BNNS@PDA分散液无明显沉淀,且光路清晰。这是由于通过超声剥离和功能化改性得到的BNNS和BNNS@PDA表面存在大量羟基和氨基,使其亲水性增加,能够在去离子水中保持稳定的分散状态。图2(b'')和2(c'')分别是BNNS和BNNS@PDA的SEM图像。可以看出,剥离后的BNNS和BNNS@PDA表现出纳米片层结构,并且形貌完整。BNNS@PDA表面较粗糙,说明PDA已成功接枝于BNNS表面[17-19]。
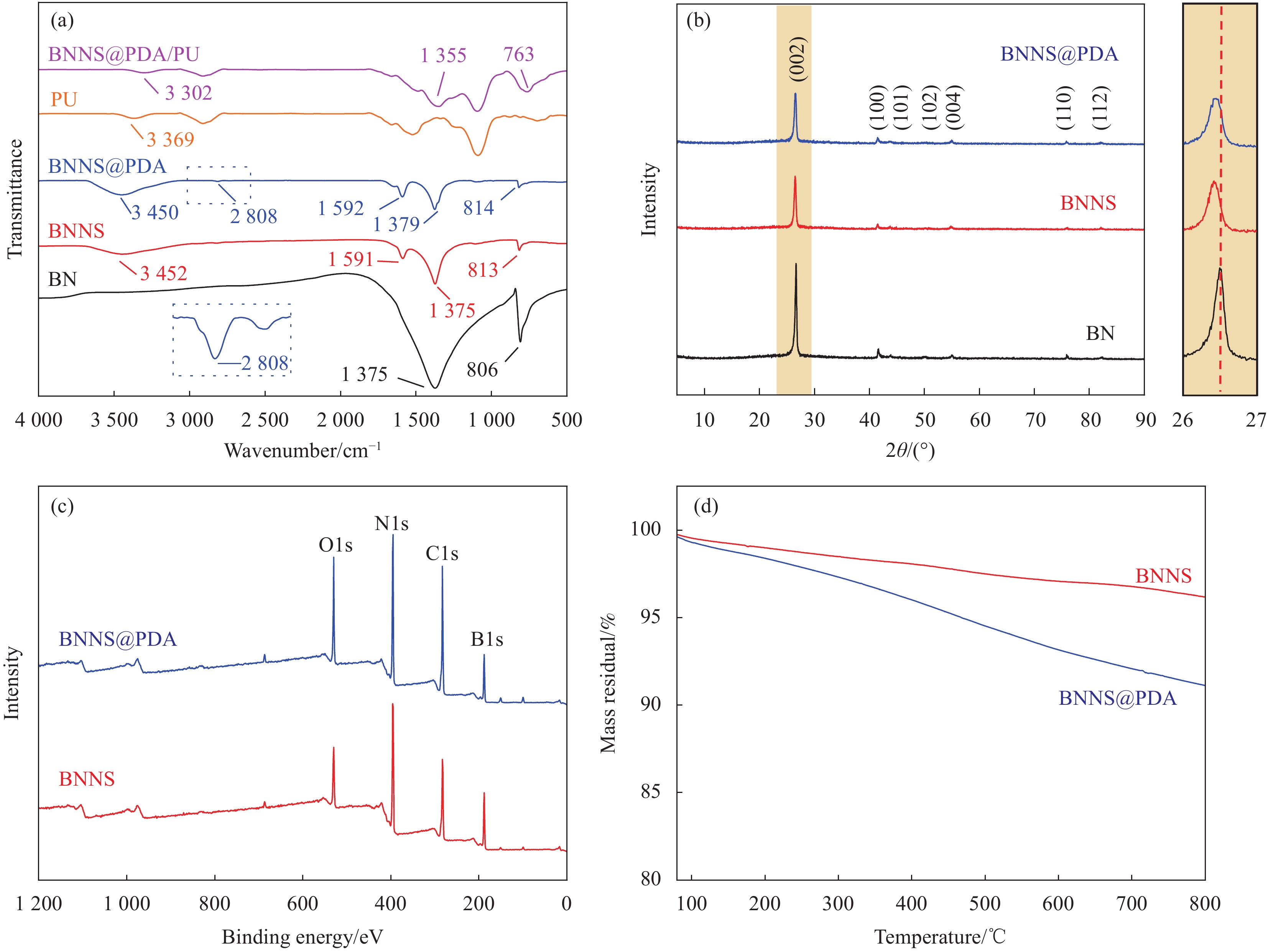
图3(a)是BN、BNNS、BNNS@PDA、PU开孔泡沫和BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的红外图谱。BNNS在3452 cm−1、1591 cm−1、1375 cm−1和813 cm−1处的特征峰分别是—OH、N—H键的面内弯曲振动及B—N键的面内拉伸振动和面外弯曲振动,这是由于经剥离后得到的BNNS表面形成了—OH。BNNS@PDA在2808 cm−1处产生了亚甲基面内弯曲振动的特征峰,说明DA发生自聚并接枝在BNNS表面[20]。BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料在3302 cm−1、1355 cm−1和763 cm−1处的特征峰分别是酰胺基团中N—H键的面内弯曲振动及N—B键的面内拉伸振动和面外弯曲振动。其中N—H键的特征峰位置较PU开孔泡沫中N—H键的特征峰(3369 cm−1)发生红移,这是由于BNNS@PDA表面的—OH与PU中的N—H形成氢键。因此BNNS@PDA可通过层层氢键组装包覆于PU开孔泡沫的三维骨架表面。
![]() 图 3 (a) BN、BNNS、BNNS@PDA、PU开孔泡沫和BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的FTIR图谱;(b) BN、BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XRD图谱;BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XPS图谱 (c) 和TGA曲线 (d)Figure 3. (a) FTIR spectras of BN, BNNS, BNNS@PDA, porous PU foams and BNNS@PDA/PU composites; (b) XRD patterns of BN, BNNS and BNNS@PDA; XPS spectras (c) and TGA curves (d) of BNNS and BNNS@PDA
图 3 (a) BN、BNNS、BNNS@PDA、PU开孔泡沫和BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的FTIR图谱;(b) BN、BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XRD图谱;BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XPS图谱 (c) 和TGA曲线 (d)Figure 3. (a) FTIR spectras of BN, BNNS, BNNS@PDA, porous PU foams and BNNS@PDA/PU composites; (b) XRD patterns of BN, BNNS and BNNS@PDA; XPS spectras (c) and TGA curves (d) of BNNS and BNNS@PDA图3(b)是BN、BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XRD图谱。图中的衍射峰从左到右分别对应(002)、(100)、(101)、(102)、(004)、(110)和(112)晶面衍射峰(JCPDS:01-073-2095)。剥离后得到的BNNS与BN有相似的衍射特征峰,并且BNNS的(002)晶面对应的衍射峰位置发生左移。这是由于BNNS晶面间距增大,衍射角减小,说明从BN上成功剥离出BNNS且并未破坏BNNS的晶面结构。BNNS@PDA的晶面衍射峰位置与BNNS相近,说明功能化改性未破坏BNNS的晶面结构,且未明显改变晶面间距。
图3(c)是BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XPS图谱。BNNS@PDA的O1s、N1s和C1s的峰值强度比BNNS有所增加,表明PDA成功接枝在BNNS表面。图3(d)是BNNS和BNNS@PDA的热失重(TGA)曲线。在800℃时,BNNS质量下降3.8%,BNNS@PDA质量下降8.9%。这是由于BNNS表面官能团较少,在800℃时仅有少量分解。BNNS@PDA的表面接枝了PDA,因其氧化和降解导致质量下降。再次证明PDA成功接枝于BNNS表面。
2.2 BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的微观结构
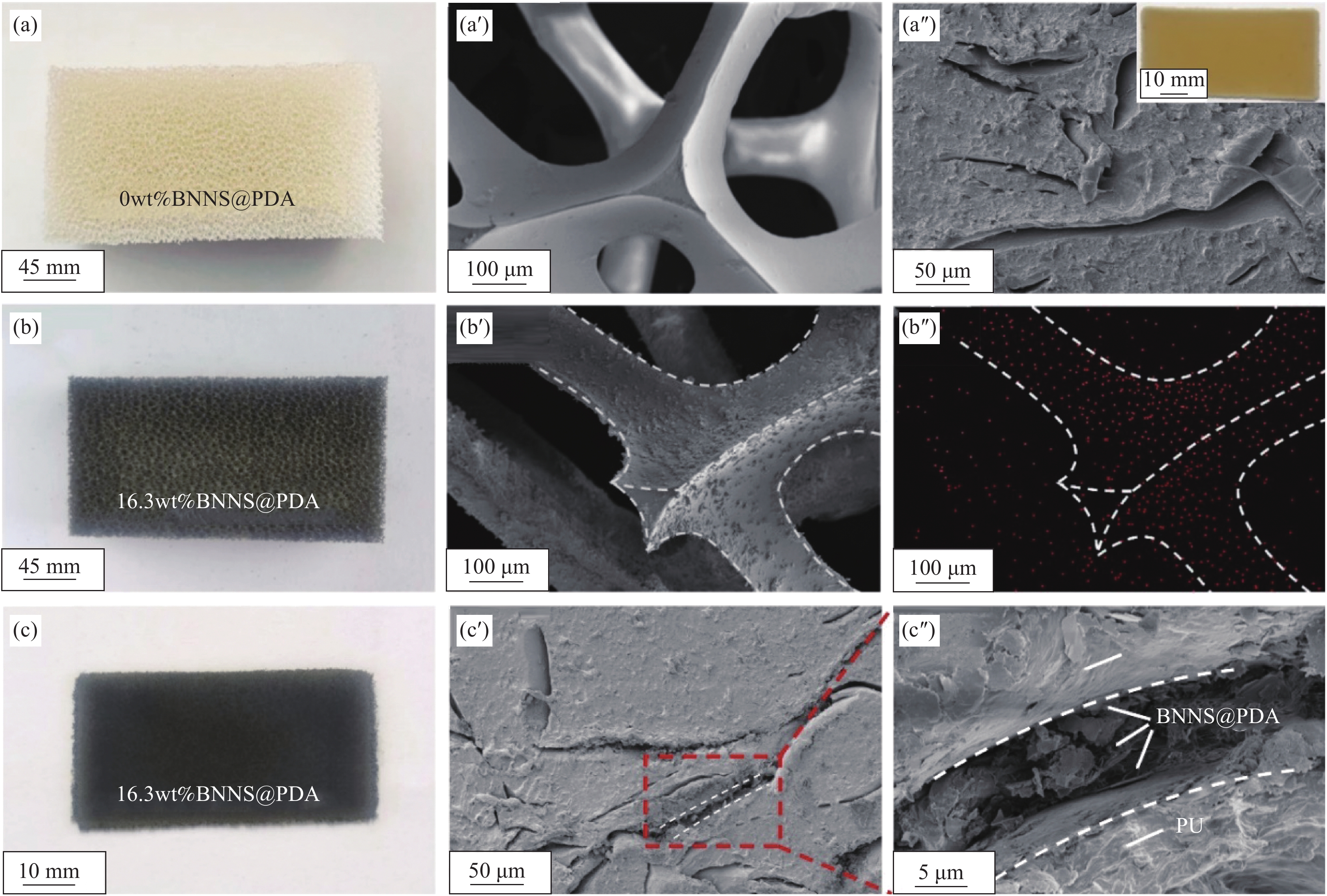
图4(a)~4(a'')分别是PU开孔泡沫的数码照片、SEM图像及单导热网络PU材料的断面SEM图像。可以看到,PU开孔泡沫骨架表面光滑平整,经过热压得到的单导热网络PU材料依然保留了泡沫的三维网络结构,该结构可作为主导热通路进行热量的传递。图4(b)~4(b'')是BNNS@PDA含量为16.3wt%的BNNS@PDA/PU复合泡沫的数码照片、SEM图像和B元素的EDS分布图像。可以看出,BNNS@PDA通过层层氢键组装均匀包覆于PU开孔泡沫骨架上。包覆在PU泡沫骨架上的BNNS@PDA紧密排列并在骨架上相互连接形成次级三维连续导热网络结构。图4(c)~4(c'')是BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的数码照片和断面SEM图像。所得复合材料既可以通过连续三维PU骨架进行热量的传递,也能通过BNNS@PDA连续网络进行热量的传递,具有双导热网络结构。
![]() 图 4 PU开孔泡沫的数码照片 (a) 和SEM图像 (a') 及单导热网络PU材料的SEM图像 (a'');BNNS@PDA/PU复合泡沫数码照片 (b)、SEM图像 (b') 和B元素EDS分布图像 (b'');BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料数码照片 (c) 和断面SEM图像 ((c'), (c''))Figure 4. Digital photo (a) and SEM image of porous PU foams (a') and SEM image of PU with single heat-conduction network (a''); Digital photo (b), SEM image (b') and EDS mapping image of B (b'') of BNNS@PDA/PU composite foams; Digital photo (c), SEM images ((c'), (c'')) of BNNS@PDA/PU composites
图 4 PU开孔泡沫的数码照片 (a) 和SEM图像 (a') 及单导热网络PU材料的SEM图像 (a'');BNNS@PDA/PU复合泡沫数码照片 (b)、SEM图像 (b') 和B元素EDS分布图像 (b'');BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料数码照片 (c) 和断面SEM图像 ((c'), (c''))Figure 4. Digital photo (a) and SEM image of porous PU foams (a') and SEM image of PU with single heat-conduction network (a''); Digital photo (b), SEM image (b') and EDS mapping image of B (b'') of BNNS@PDA/PU composite foams; Digital photo (c), SEM images ((c'), (c'')) of BNNS@PDA/PU composites2.3 BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率及导热机制
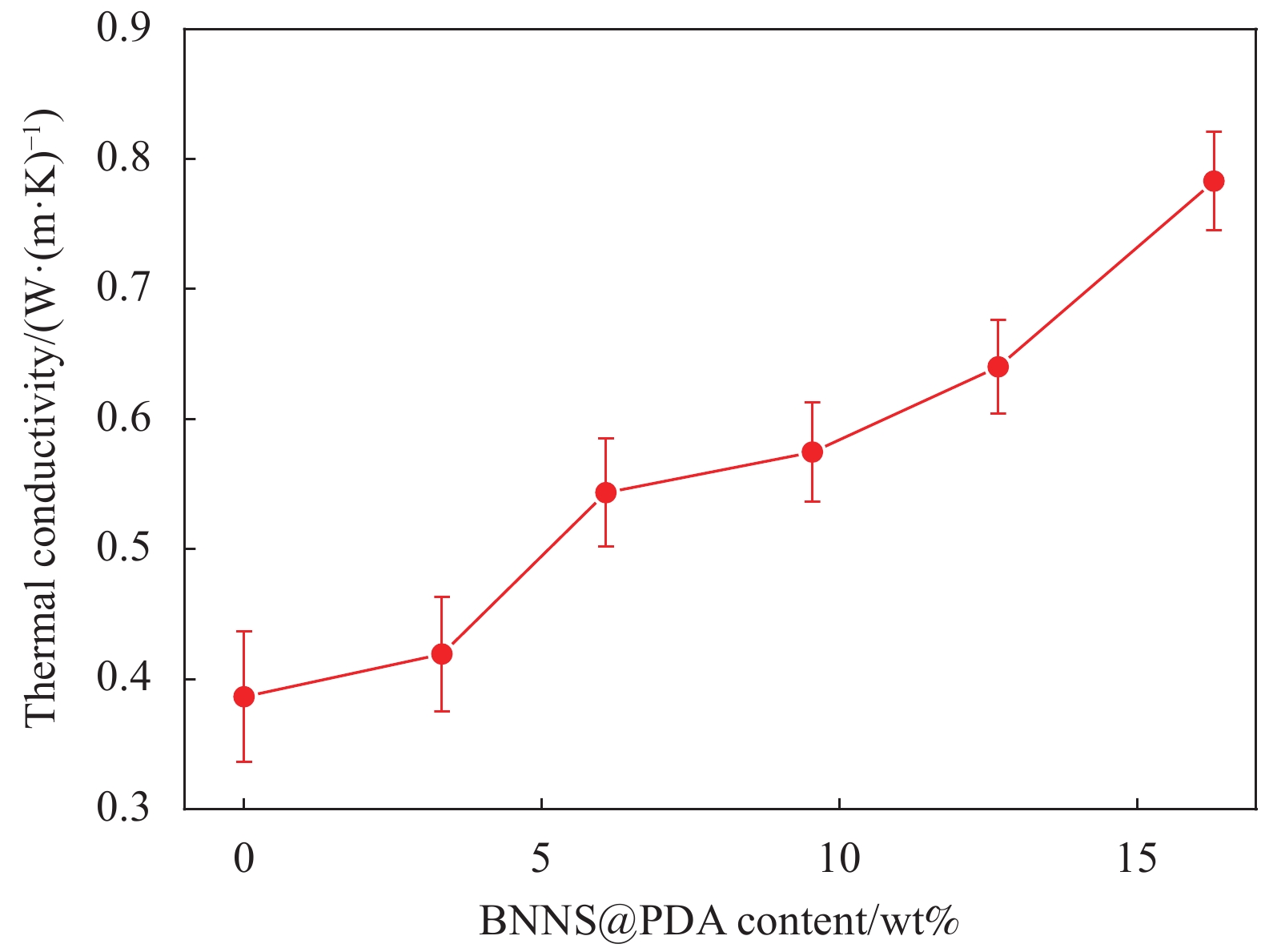
图5为不同BNNS@PDA含量的BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率。可以看出,BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率随着BNNS@PDA含量的增加而增大,其中单导热网络PU材料的热导率为0.387 W/(m·K),与纯PU(0.21 W/(m·K))相比提高了45.7%[21]。当BNNS@PDA的含量为16.3wt%时,复合材料的热导率达到0.783 W/(m·K),与单导热网络PU材料相比提高了102.3%。这是由于引入BNNS@PDA后,包覆在PU开孔泡沫三维骨架表面的BNNS@PDA形成连续导热网络,与PU三维骨架共同形成双导热网络进行热量的传输,进一步提高了BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率。
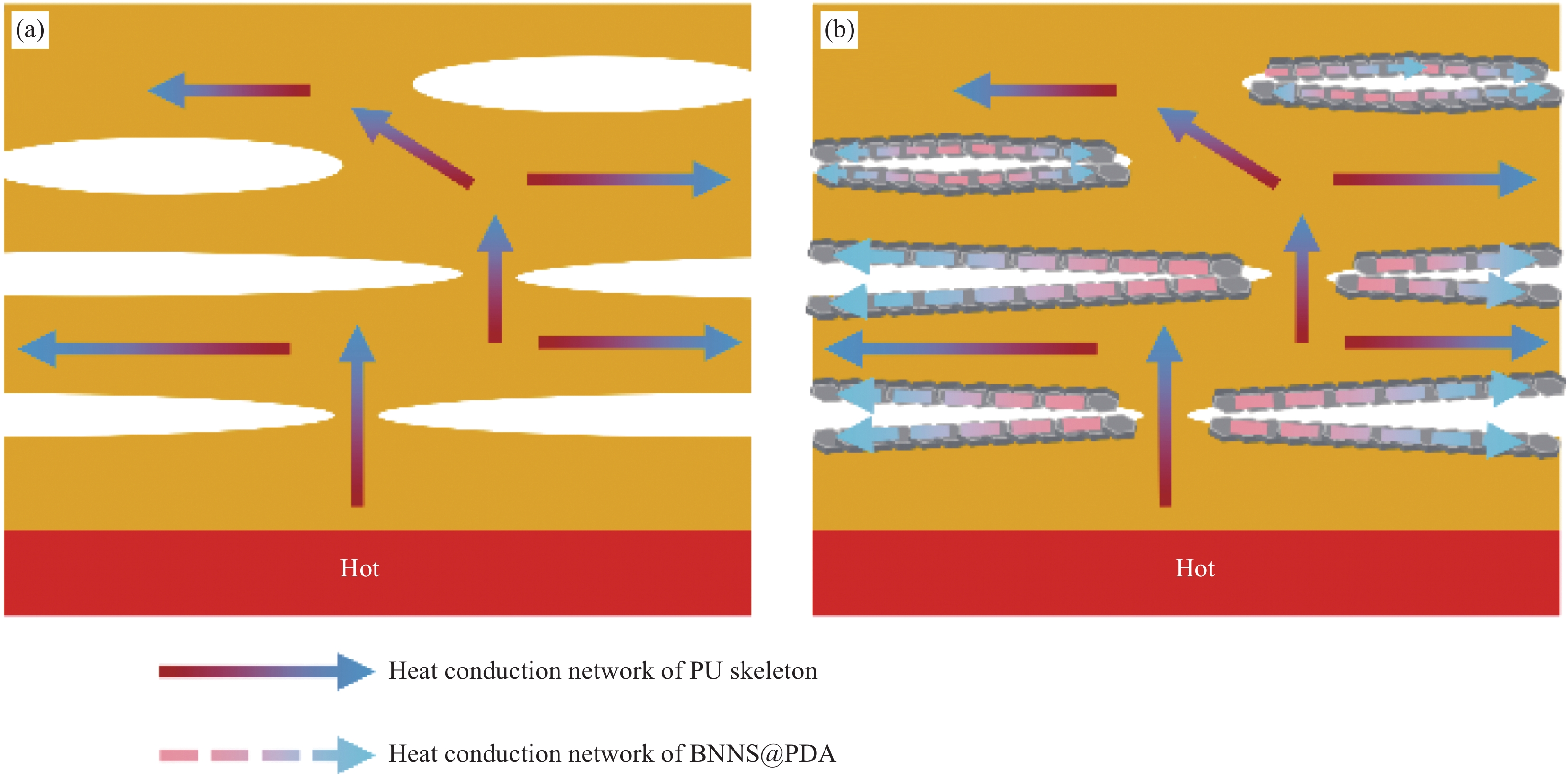
BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的导热机制通过图6进行阐述。图6(a)是单导热网络PU材料的导热机制。PU在发泡时泡棱延长受到局部拉伸应力,诱导分子链沿泡棱方向发生取向,从而增强热量在PU骨架上的传递[22]。PU开孔泡沫经热压后仍保留了原三维骨架中的有序取向结构,可作为主导热网络进行热量的传输。图6(b)是BNNS@PDA通过氢键作用层层组装在PU三维骨架上的导热机制,通过热压使复合材料内部形成“PU三维骨架—BNNS@PDA”双重导热网络结构,PU三维骨架上紧密包覆的BNNS@PDA作为次级导热网络进一步增强热量在复合材料内部的传输能力,从而使复合材料的热导率提高。
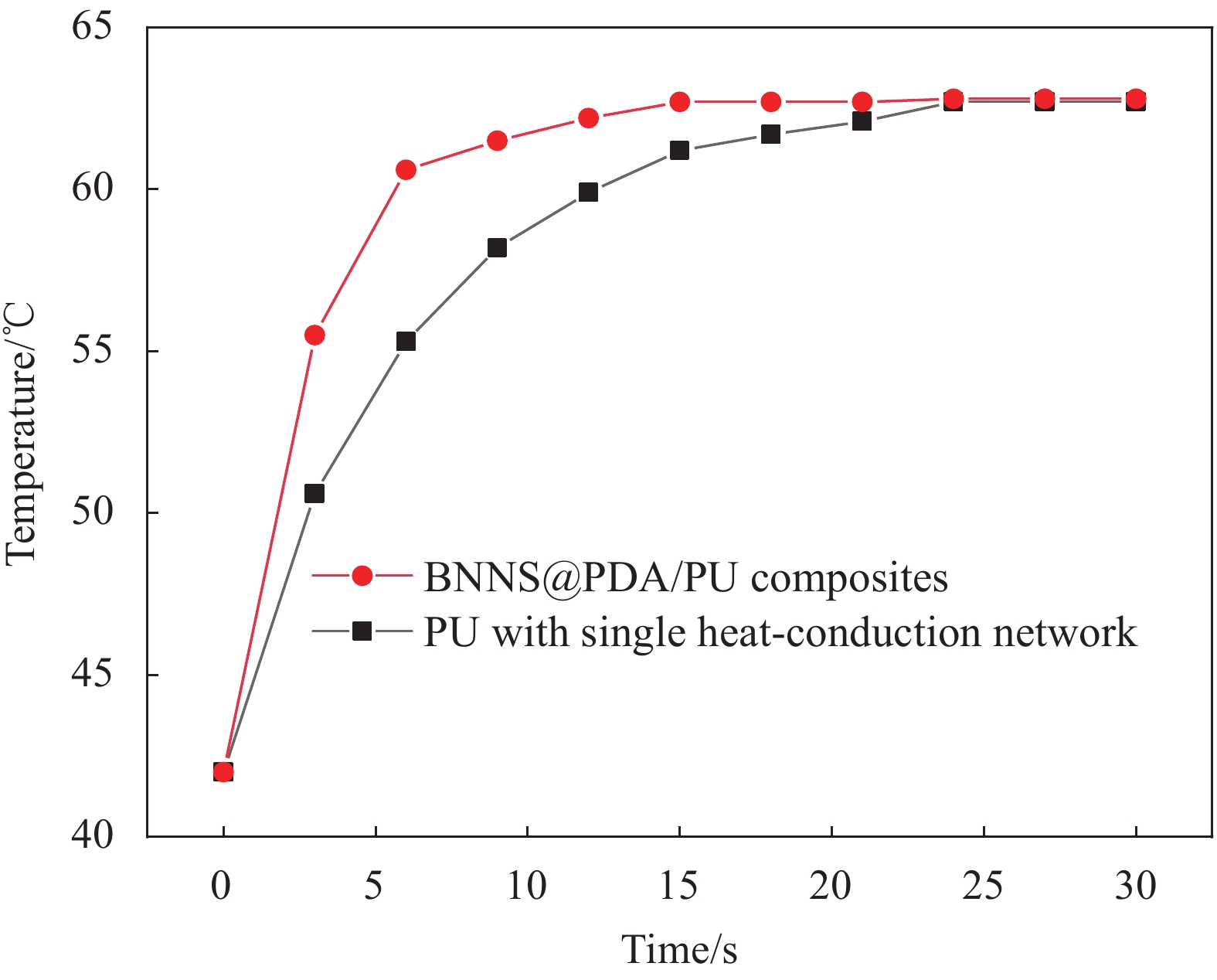
图7为BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料在65℃热板上受热升温的红外热成像图像。从图7(a)中可以看到单导热网络PU材料受热6 s后,表面温度从42℃上升到55.3℃。图7(b)中BNNS@PDA含量为16.3wt%的BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料受热6 s后,表面温度从42℃上升到60.6℃。图8为BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料受热温度变化曲线,与单导热网络PU材料相比,BNNS@PDA含量为16.3wt%的BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料在初始阶段升温速率更快,并且迅速达到热稳定状态,说明引入BNNS@PDA后,复合材料热响应时间更快,导热能力更强,能够将热板的温度快速传递到复合材料表面。
2.4 BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热稳定性
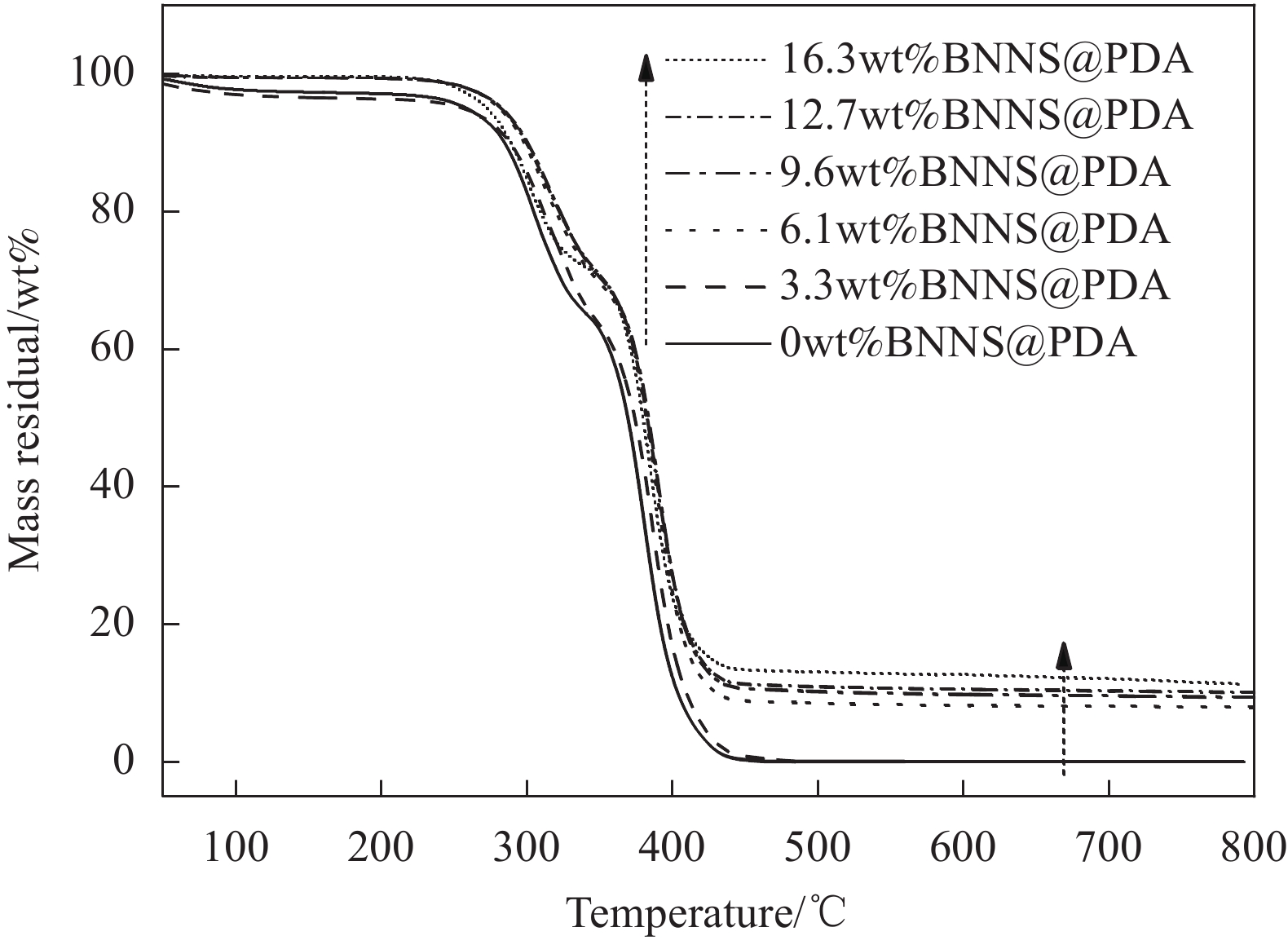
图9为BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的TGA曲线。可知,BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热失重温度达到近300℃,引入BNNS@PDA并未降低复合材料的热降解温度,表明所制备的BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料具有良好的热稳定性。复合材料的残余质量与BNNS@PDA含量有关,随着BNNS@PDA含量增大而增大。
3. 结 论
(1) 基于层层氢键组装,以聚氨酯(PU)开孔泡沫为模板,以聚多巴胺功能化改性氮化硼纳米片(BNNS@PDA)为导热填料,采用浸涂-热压成型法制得低填充、高导热BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料。
(2) 通过多巴胺对BNNS进行表面功能化改性能够使其良好地负载于PU开孔泡沫的三维骨架表面,并通过热压成型形成以PU骨架为主要导热网络、以PU骨架表面包覆的BNNS@PDA为次级导热网络的高效双重三维导热网络结构,从而降低导热复合材料的界面热阻。
(3) BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率随着BNNS@PDA含量增加而增大。当BNNS@PDA含量为16.3wt%时,BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的热导率达到0.783 W/(m·K),与单导热网络PU的热导率(0.387 W/(m·K))相比提高了102.3%。
-
图 3 (a) BN、BNNS、BNNS@PDA、PU开孔泡沫和BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料的FTIR图谱;(b) BN、BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XRD图谱;BNNS和BNNS@PDA的XPS图谱 (c) 和TGA曲线 (d)
Figure 3. (a) FTIR spectras of BN, BNNS, BNNS@PDA, porous PU foams and BNNS@PDA/PU composites; (b) XRD patterns of BN, BNNS and BNNS@PDA; XPS spectras (c) and TGA curves (d) of BNNS and BNNS@PDA
图 4 PU开孔泡沫的数码照片 (a) 和SEM图像 (a') 及单导热网络PU材料的SEM图像 (a'');BNNS@PDA/PU复合泡沫数码照片 (b)、SEM图像 (b') 和B元素EDS分布图像 (b'');BNNS@PDA/PU复合材料数码照片 (c) 和断面SEM图像 ((c'), (c''))
Figure 4. Digital photo (a) and SEM image of porous PU foams (a') and SEM image of PU with single heat-conduction network (a''); Digital photo (b), SEM image (b') and EDS mapping image of B (b'') of BNNS@PDA/PU composite foams; Digital photo (c), SEM images ((c'), (c'')) of BNNS@PDA/PU composites
-
[1] SONG Y, JIANG F, SONG N, et al. Multilayered structural design of fexible flms for smart thermal management[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2021,141:106222. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.106222
[2] CHEN J, HUANG X Y, ZHU Y K, et al. Cellulose nanofiber supported 3D interconnected BN nanosheets for epoxy nanocomposites with ultrahigh thermal managementcapability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2017,27(5):1604754. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201604754
[3] ZENG X L, SUN J L, YAO Y M, et al. A combination of boron nitride nanotubes and cellulose nanofibers for the preparation of a nanocomposite with high thermal conductivity[J]. ACS Nano,2017,11(5):5167-5178. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.7b02359
[4] GU J W, RUAN K P. Breaking through bottlenecks for thermally conductive polymer composites: A perspective for intrinsic thermal conductivity, interfacial thermal resistance and theoretics[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2021,13:110. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-021-00640-4
[5] ZHENG D W, PAUL P, MEZIANI M J, et al. Dispersion of high-quality boron nitride nanosheets in polyethylene for nanocomposites of superior thermal transport properties[J]. Nanoscale Advances,2020,2(6):2507-2513. DOI: 10.1039/D0NA00190B
[6] TESSEMA A, DAN Z, MOLL J, et al. Effect of filler loading, geometry, dispersion and temperature on thermal conductivity of polymer nanocomposites[J]. Polymer Testing,2016,57:101-106.
[7] CHO H B, TOKOI Y, TANAKA S, et al. Modification of BN nanosheets and their thermal conducting properties in nanocomposite film with polysiloxane according to the orientation of BN[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2011,71(8):1046-1052. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.03.002
[8] FU L, WANG T, YU J H, et al. An high-performance heat spreader fabricated with boron nitride nanosheets[J]. 2D Materials,2017,4:025047. DOI: 10.1088/2053-1583/aa636e
[9] YU C, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Enhanced through-plane thermal conductivity of boron nitride/epoxy composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 98: 25-31.
[10] CHEN X, LIM J, YAN W, et al. Salt template assisted BN scaffold fabrication towards highly thermal conductive epoxy composites[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(14):16987-16996.
[11] WANG X W, WU P Y. Melamine foam-supported 3D interconnected boron nitride nanosheets network encapsulated in epoxy to achieve significant thermal conductivity enhancement at an ultralow filler loading[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,348:723-731. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.196
[12] ZHU Q, CHU Y, WANG Z, et al. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2013,1(17):5386-5393. DOI: 10.1039/c3ta00125c
[13] SU B, WANG S, SONG Y, et al. Utilizing super hydrophilic materials to manipulate oil droplets arbitrarily in water[J]. Soft Matter,2011,7(11):5144-5149. DOI: 10.1039/c0sm01480j
[14] ADEBAJO M O, FROST R L, KLOPROGGE J T, et al. Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: A review of synthesis and absorbing properties[J]. Journal of Porous Materials,2003,10:159-170. DOI: 10.1023/A:1027484117065
[15] ZHANG X, ZHOU L, LIU K, et al. Bioinspired multifunctional foam with self-cleaning and oil/water separation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2013,23(22):2881-2886. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201202662
[16] 杨振生, 张阳阳, 李春利, 等. 疏水聚氨酯海绵吸油材料研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(8):34-38. YANG Zhensheng, ZHANG Yangyang, LI Chunli, et al. Progress of hydrophobic polyurethane sponge used as oil sorbent material[J]. New Chemical Materials,2019,47(8):34-38(in Chinese).
[17] YANG W, WANG Y F, LI Y, et al. Three-dimensional skeleton assembled by carbon nanotubes/boron nitride as filler in epoxy for thermal management materials with high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2021,224:109168. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109168
[18] ZENG X, YAO Y, GONG Z, et al. Ice-templated assembly strategy to construct 3D boron nitride nanosheet networks in polymer composites for thermal conductivity improvement[J]. Small,2015,11(46):6205-6213. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201502173
[19] MA T B, ZHAO Y S, RUAN K P, et al. Highly thermal conductivities, excellent mechanical robustness and flexibility, and outstanding thermal stabilities of aramid nano-fiber composite papers with nacre-mimetic layered structures[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(1):1677-1686.
[20] LIU Y L, AI K L, LU L H. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields[J]. Chemical Reviews,2014,114(9):5057-5115. DOI: 10.1021/cr400407a
[21] 余翠平. 有序排列氮化硼/聚合物复合材料的可控制备与导热性能研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2018. YU Cuiping. Study on controllable preparation and thermal conductivity of aligned boron nitride/polymer composites[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2018(in Chinese).
[22] 张军, 郑昌仁, 冯今明. 高聚物的热传导性质[J]. 高分子通报, 2001(6):54-59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3726.2001.06.007 ZHANG Jun, ZHENG Changren, FENG Jinming. Survey of thermal conductivity property of polymer[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2001(6):54-59(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3726.2001.06.007
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 耿乾浩,徐晓云,李冰晶. 矿用聚氨酯注浆材料反应热控制技术研究进展. 化工进展. 2025(01): 319-328 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吴连锋,朱洪宇,申小松,朱艳吉,汪怀远. 1, 5-萘二酚改性环氧树脂及其氮化硼复合材料的制备与导热性能. 中国表面工程. 2024(01): 110-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨承伟,王玉斌,傅伟强,王煦. 纳米材料改性聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯的研究进展. 塑料科技. 2024(01): 112-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王世民,温变英. 模压氮化硼/聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯复合材料的导热机制与散热效果. 复合材料学报. 2023(01): 160-170 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 石贤斌,张帅,陈超,聂向导,班露露,赵亚星,刘仁,桑欣欣. 氮化硼纳米片的绿色制备及其在导热复合材料中的应用. 复合材料学报. 2023(08): 4558-4567 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 郑舒方,王玉印,郭兰迪,靳玉岭. 具有三维连续网络结构的聚合物基导热复合材料研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2023(12): 6528-6544 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(8)
-




 下载:
下载: