Influence of moisture absorption on the mechanical properties of unidirectional flax fibre composites
-
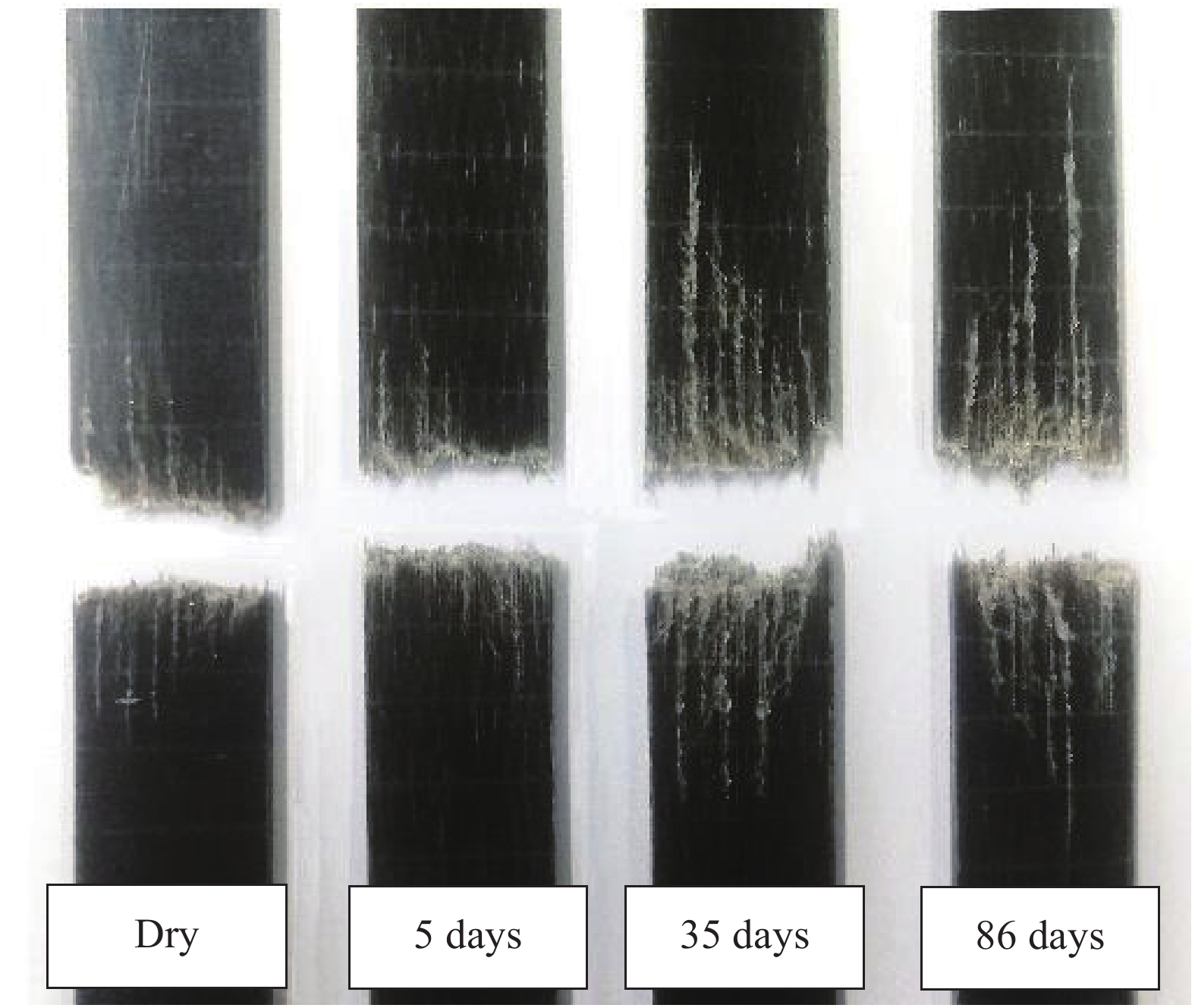
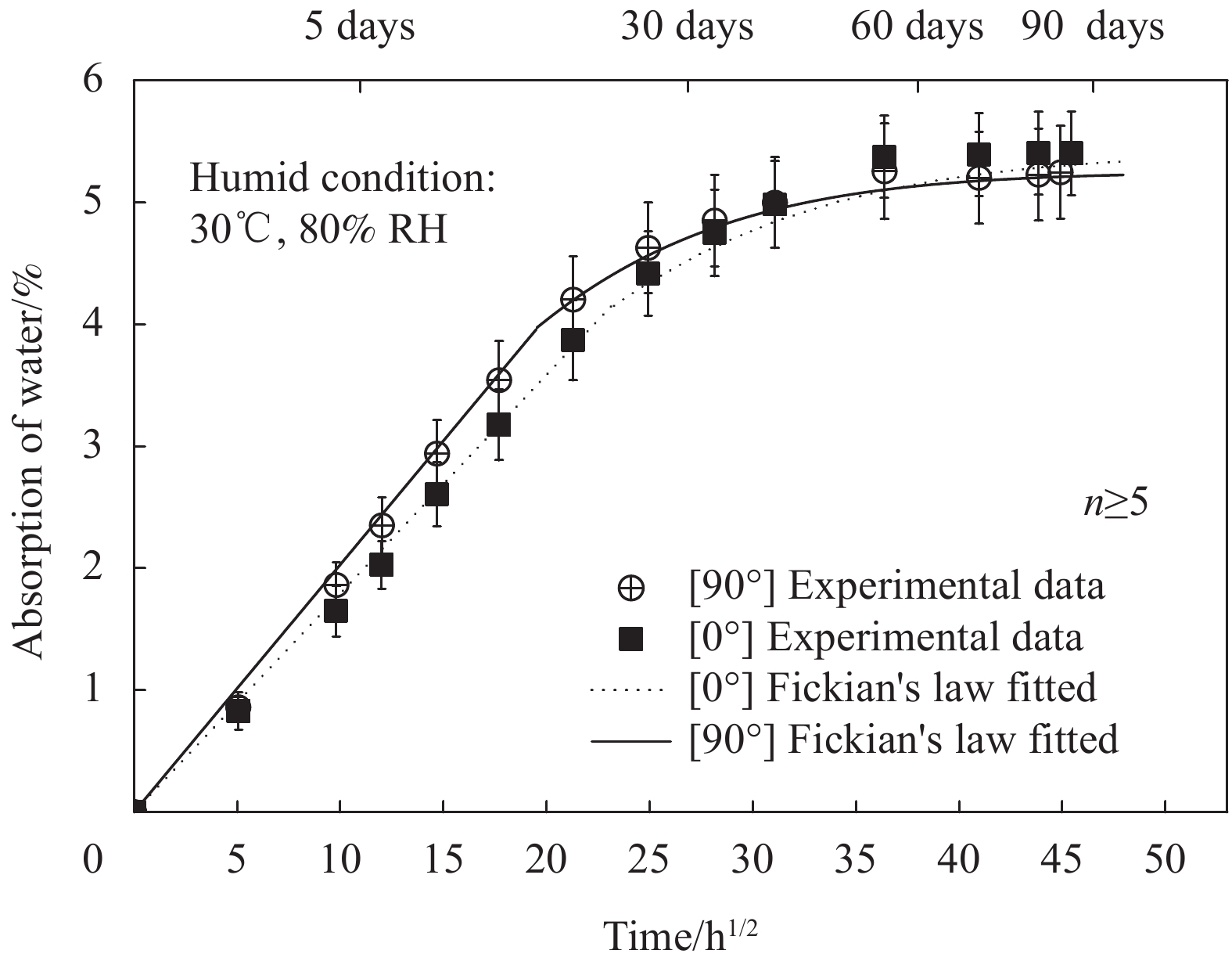
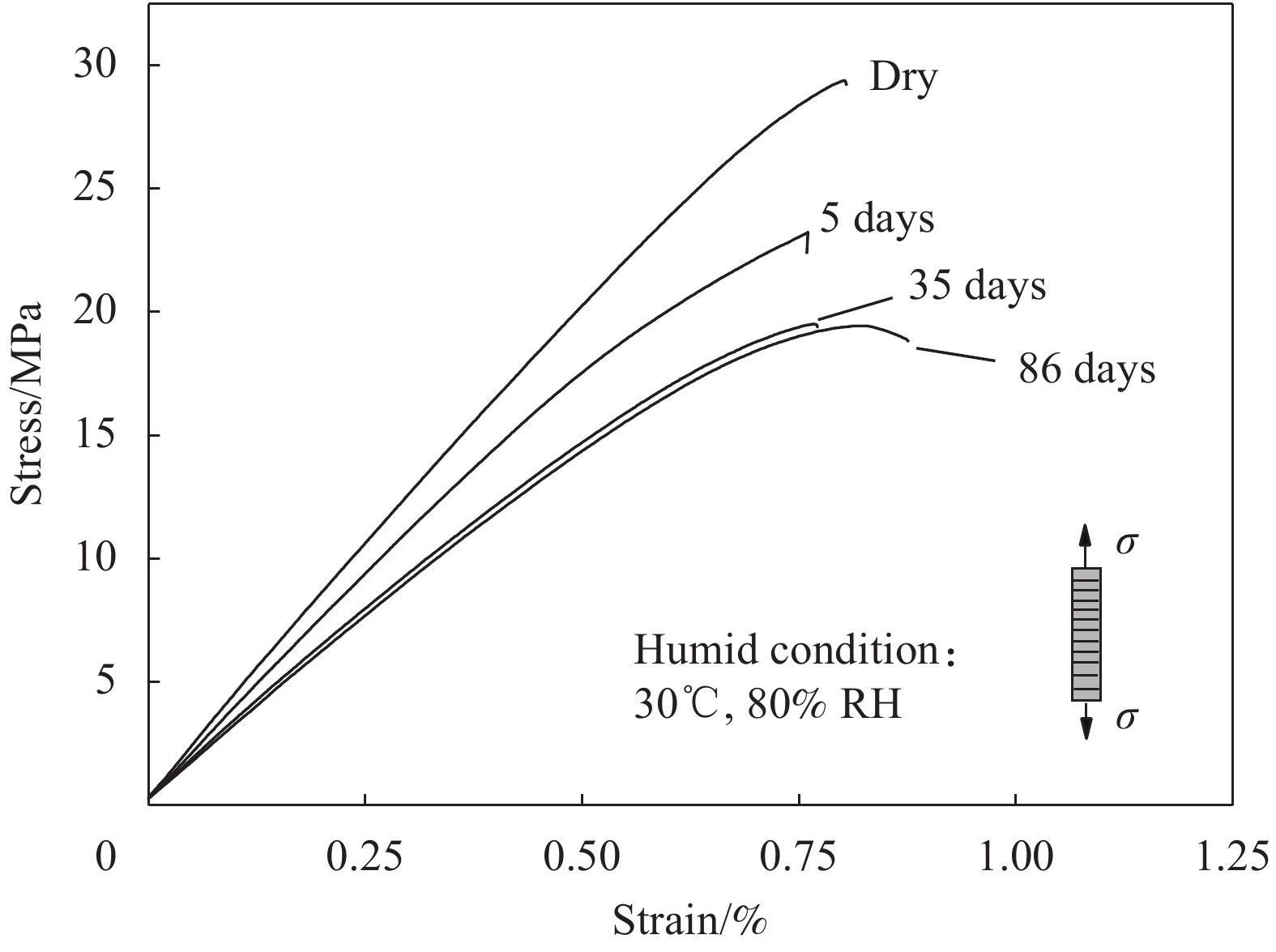
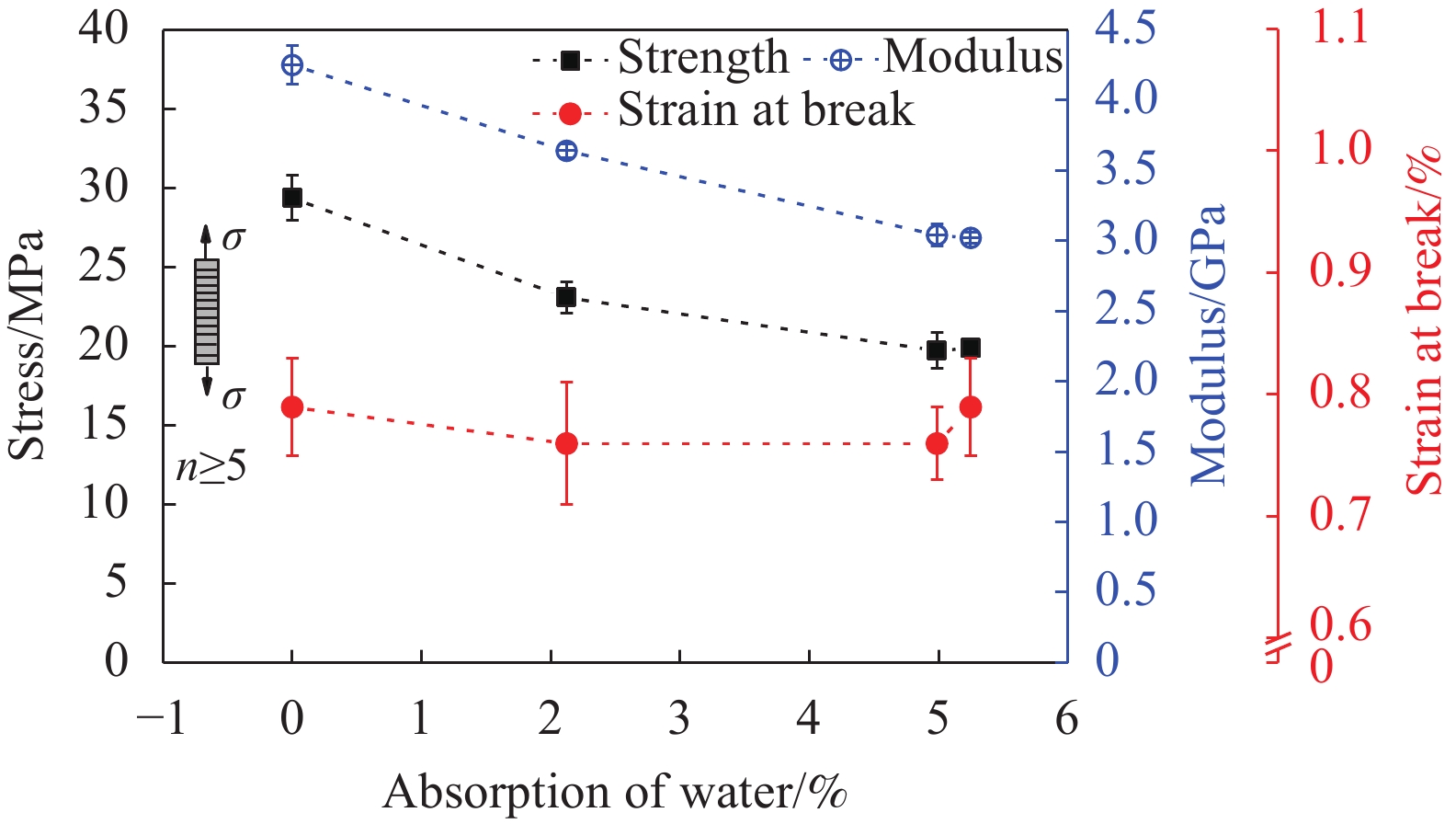
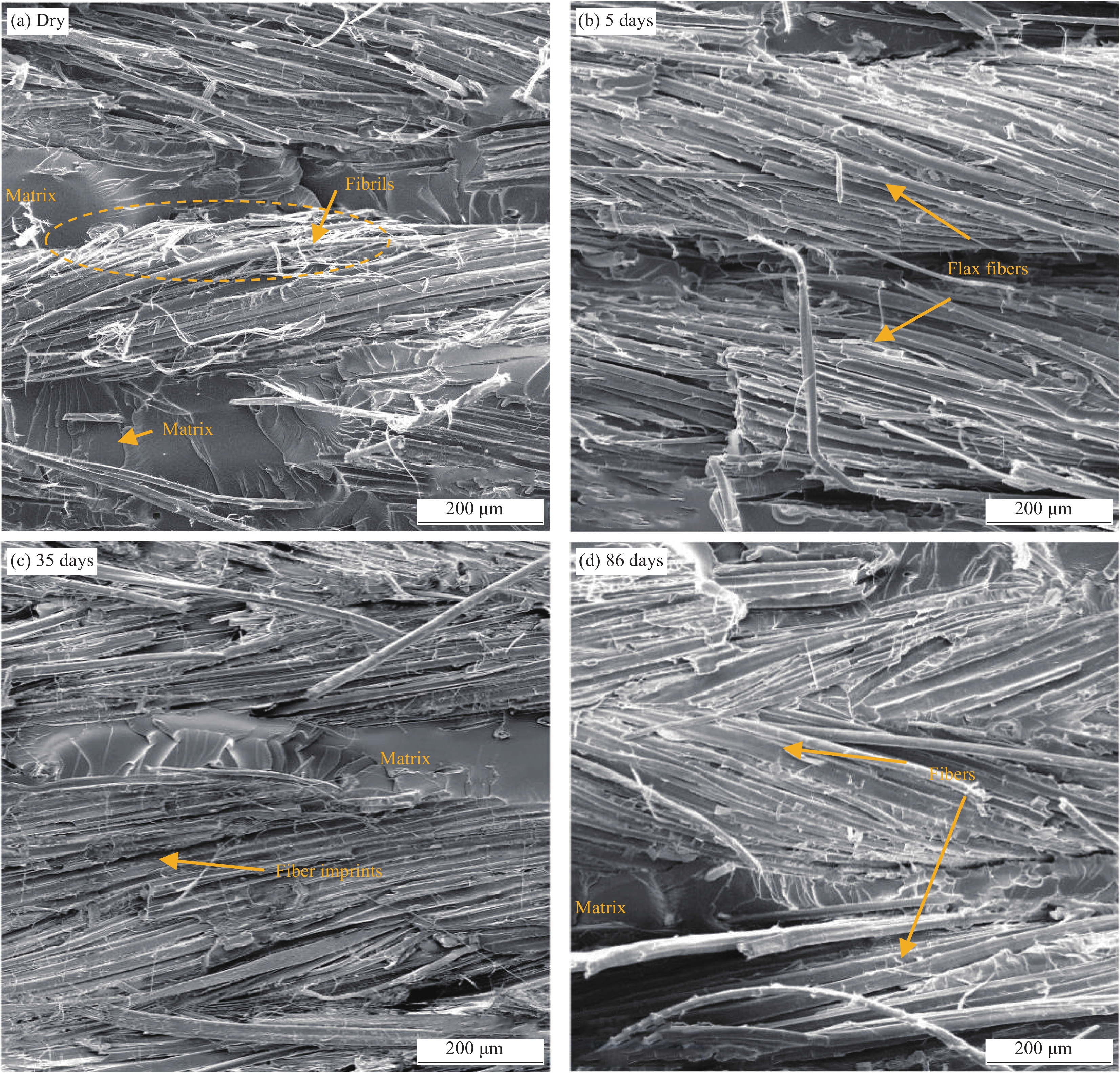
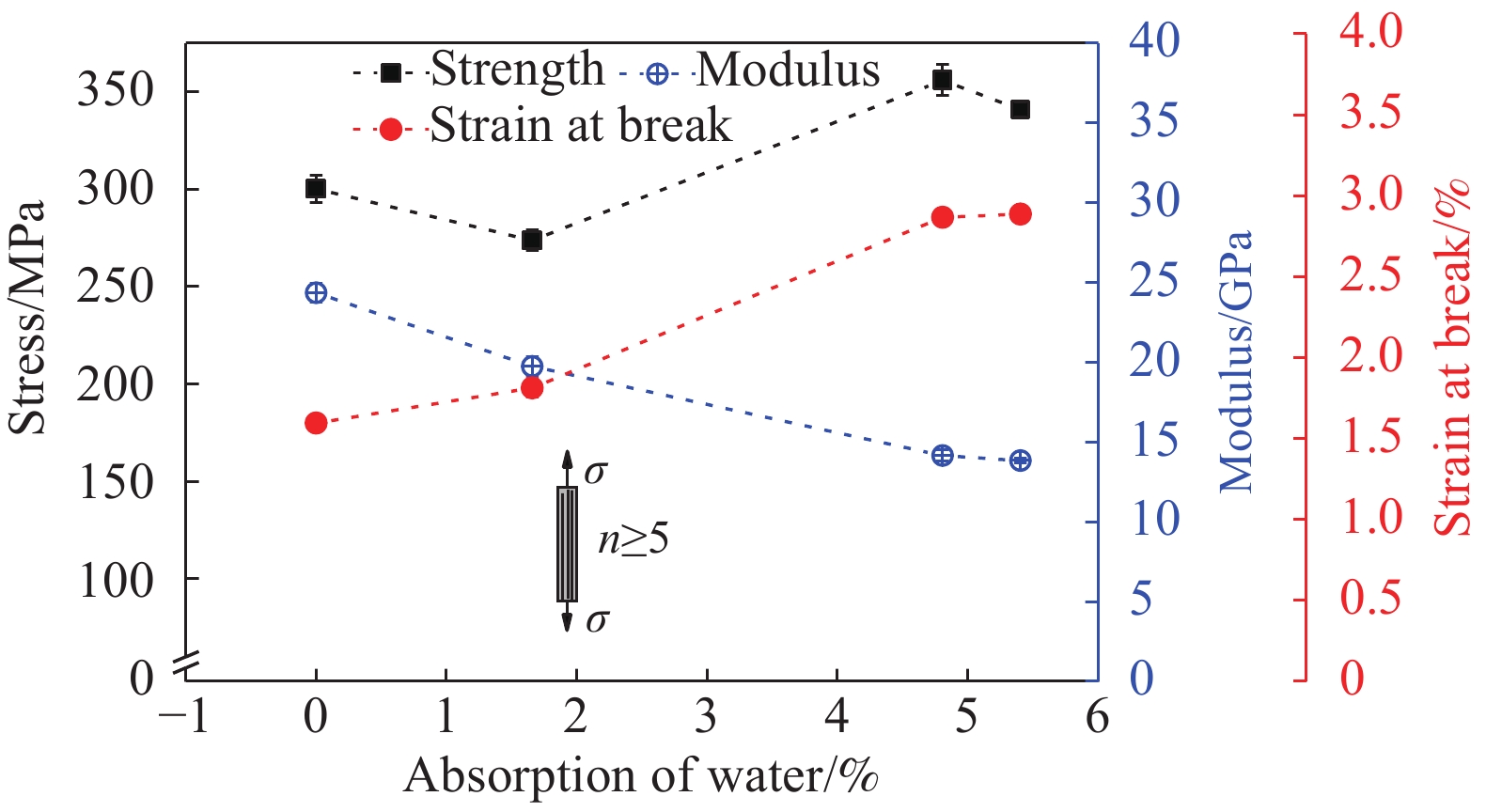
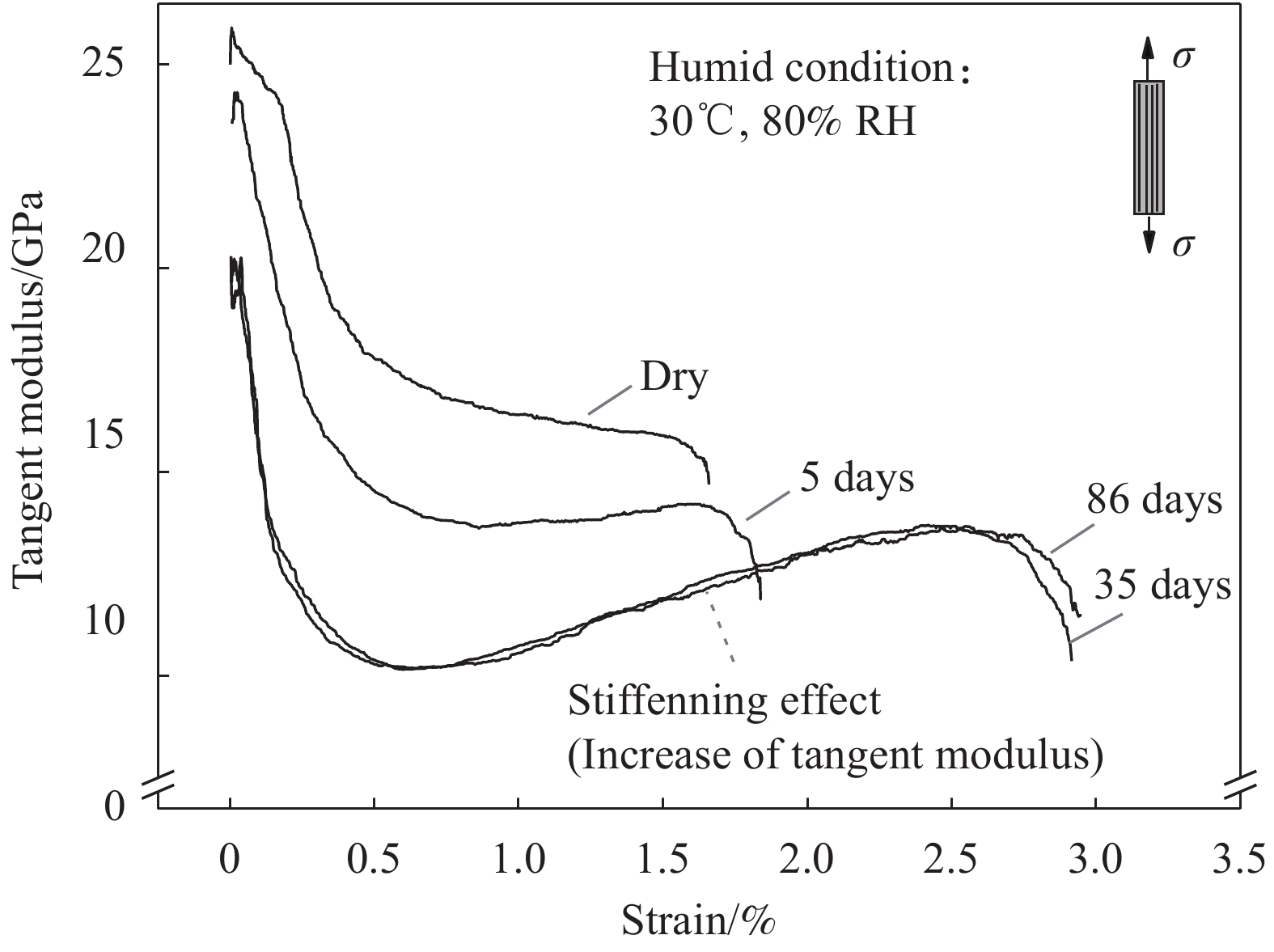
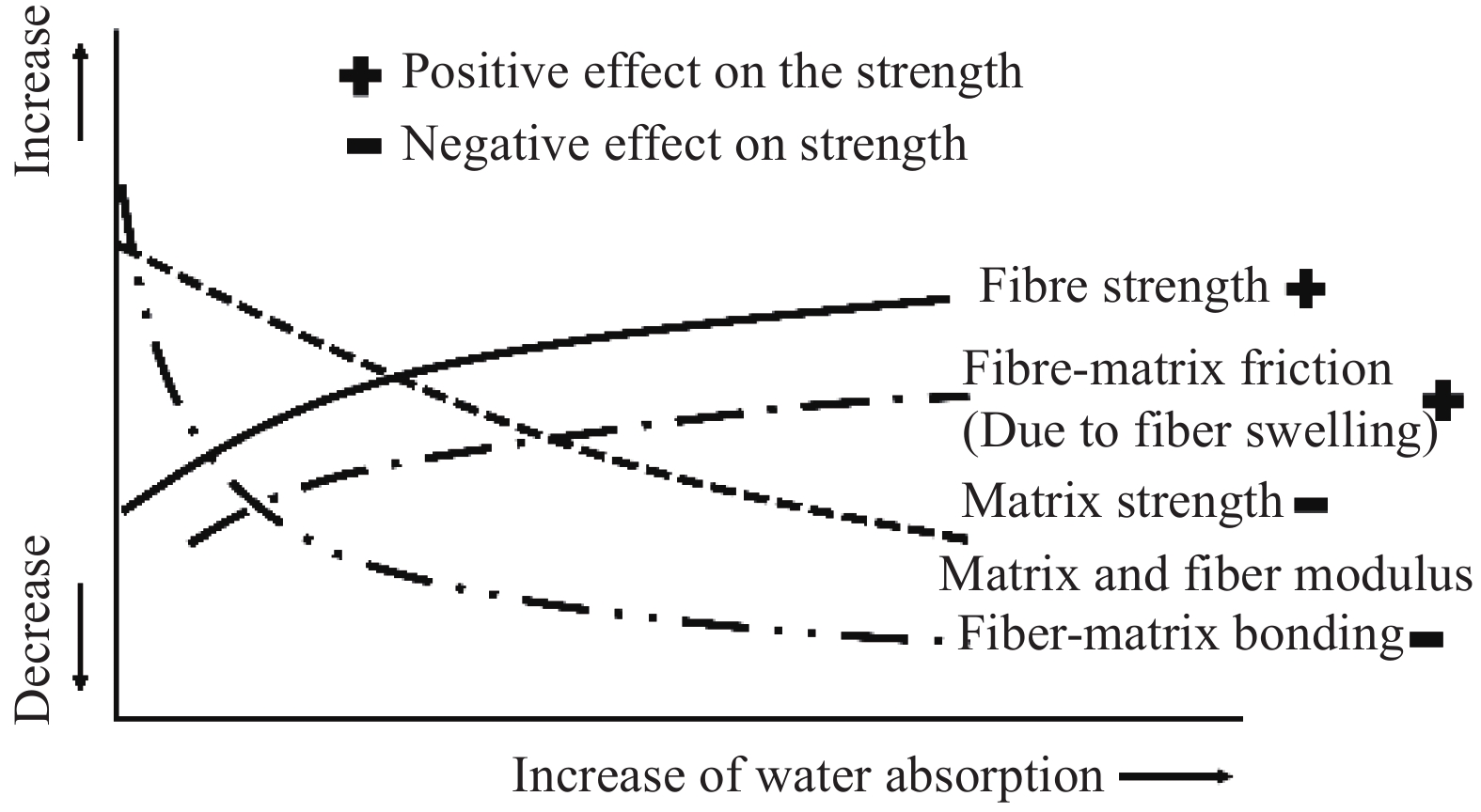
摘要: 为探明亚麻纤维增强树脂复合材料(FFRPs)在长期潮湿环境中的力学性能变化规律,基于真空辅助树脂模塑传递成型(VARTM)手段制备了的干燥状态的单向FFRPs(纤维体积分数为40vol%)。试验研究了 FFRPs在30°C、80%相对湿度(RH)环境中放置5天、35天、86天后拉伸力学性能变化。结果表明,FFRPs在湿热环境中吸水量近似符合一维情况下的Fickian第二定律,饱和吸水量为5.3%左右。FFRPs在垂直于纤维方向上的拉伸强度和模量随吸湿度增加递减,断口微观分析表明吸湿降低了纤维基体界面结合性能。然而,FFRPs在纤维方向上的拉伸强度并未因吸湿降低,反而在吸湿过程呈现出先减小后增加的趋势,此变化规律文献中尚未报道:相比干燥状态,放置5天后拉伸强度下降5.7%;放置35天后拉伸强度增加18.7%;放置86天时样品已处在饱和吸湿状态,拉伸强度略微减小,但仍比干燥状态增加13.7%。FFRPs在纤维取向上拉伸强度变化可解释为多因素共同作用的结果。Abstract: This paper investigated the evolution of mechanical properties of flax fibre reinforced polymer compo-sites (FFRPs) conditioned in humid condition for a long term. Dry unidirectional FFRPs having fibre volume fraction of 40vol% were manufactured via vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding (VARTM). FFRPs were conditioned in 30°C, 80% relative humidity (RH) for different time (5 days, 35 days and 86 days) and their tensile properties were tested and analyzed. The results demonstrate that the moisture absorption of FFRPs fairly follows one dimensional Fickian’s second law. The equilibrated water content is around 5.3%. Tensile strength and modulus perpendicular to fibre direction decrease with moisture absorption. Fracture morphology shows that fibre-matrix bonding strength decreases after moisture absorption. Tensile strength in fibre direction is not degraded by moisture absorption, and exhibits a trend featured by a first drop followed by an increase, which has not been reported in literatures. Tensile strength in fiber direction decreases by 5.7% after being conditioned in humid for 5 days, and increases by 18.7% after 35 days. Further absorption of moisture up to 86 days (already saturated) causes a slight decrease in tensile strength but is still 13.7% higher than that at dry state. The change trend of tensile strength in fibre direction during moisture absorption can be explained as a consequence of averaging effects of several factors.
-
Keywords:
- plant fibre composites /
- flax fibres /
- moisture absorption /
- tensile properties /
- durability
-
-
表 1 [0°]和[90°]FFRPs样品的计算Fickian扩散系数
Table 1 Calculated Fickian diffusion coefficients of [0°] and [90°] FFRPs
1/(10−7 mm2·s−1) 2/(10−7 mm2·s−1) 3/% [0°] 2.40 1.84 5.41 [90°] 3.27 2.74 5.25 Notes: —Diffusion coefficient calculated from experimental data; —Corrected diffusion coefficient; —Absorption of water at saturation. 表 2 亚麻纤维纱线的拉伸性能 (n≥20)
Table 2 Tensile properties of tested flax yarns (n≥20)
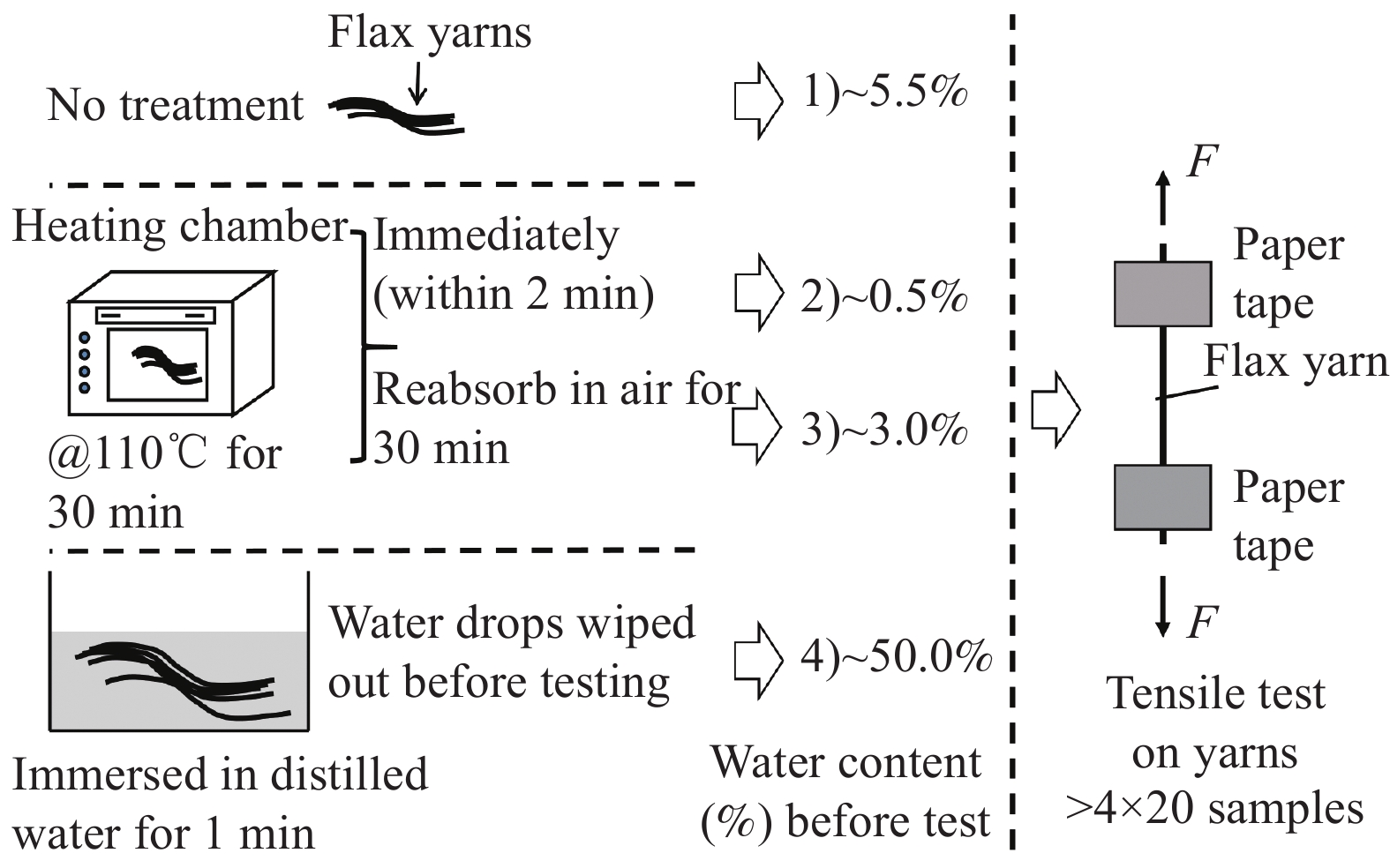
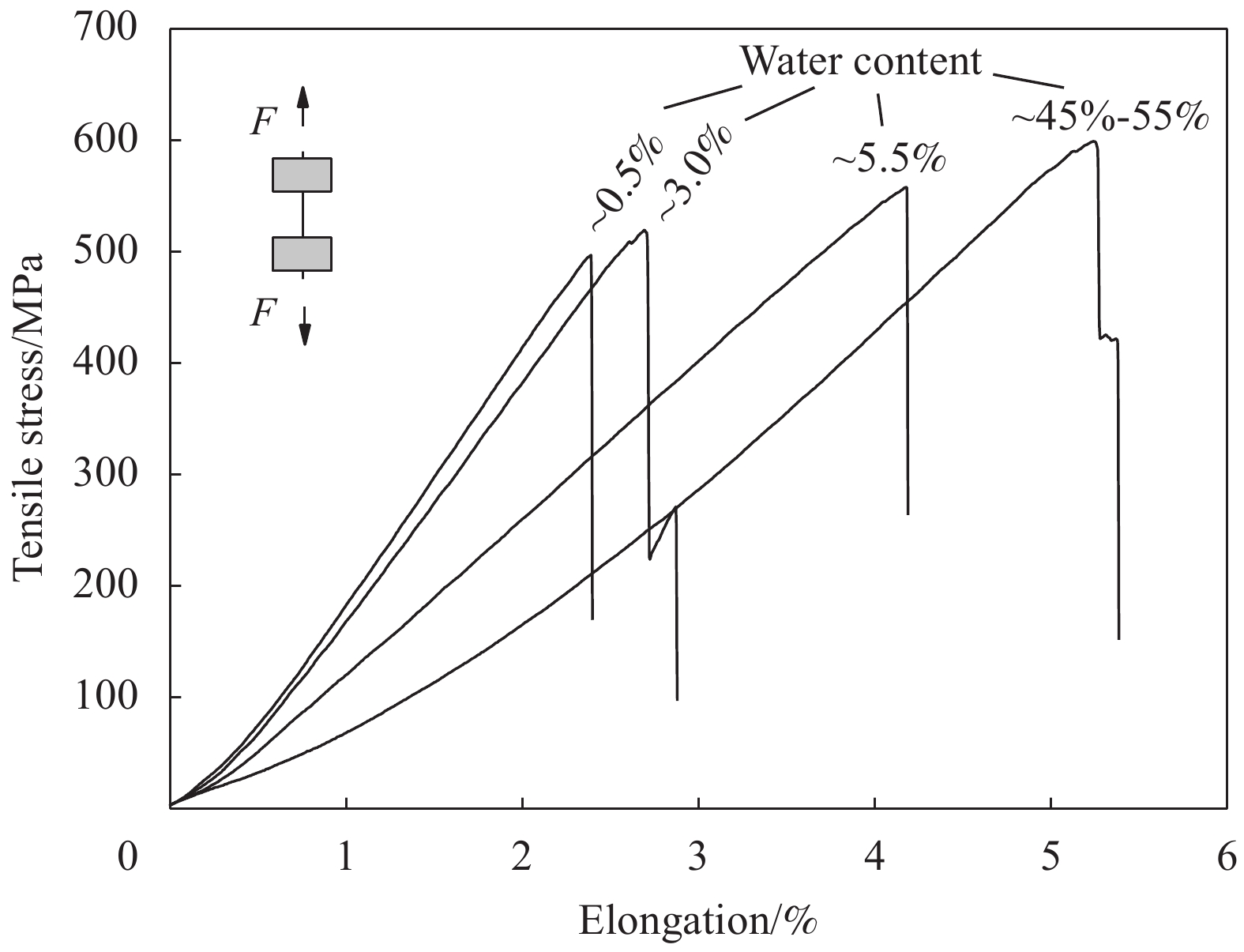
Water content/% Strength/MPa Modulus1/GPa Elongation at break/% ~0.5 486.0±74.9 22.0±2.9 2.5±0.2 ~3.0 517.2±92.2 16.4±2.9 3.4±0.5 ~5.5 544.1±81.2 14.4±1.9 4.1±0.4 ~50.0 598.8±136.4 10.7±0.9 5.6±0.9 Notes: Modulus1 was calculated as the gradient of the regression line between 100 MPa and 200 MPa; n—Sample size of each condition. -
[1] SHEKAR H S, RAMACHANDRA M. Green composites: A review[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2018,5(1):2518-2526. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.034
[2] PICKERING K L, EFENDY M A, LE T M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre composites and their mechanical performance[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2016,83:98-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.038
[3] LIBO YAN, CHOUW N, JAYARAMAN K. Flax fibre and its composites–A review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2014,56:296-317. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.014
[4] IBRAHIM M. Natural-fibre composites: An overview[EB/OL]. [2020-11-04]. .
[5] HALLAK PANZERA T, JEANNIN T, GABRION X, et al. Static, fatigue and impact behaviour of an autoclaved flax fibre reinforced composite for aerospace engineering[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,197:108049. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108049
[6] MOKHOTHU T H, JOHN M J. Review on hygroscopic aging of cellulose fibres and their biocomposites[J]. Carbohydrate polymers,2015,131:337-354. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.027
[7] MOUDOOD A, RAHMAN A, CHSNER A, et al. Flax fiber and its composites: An overview of water and moisture absorption impact on their performance[J]. Journal of Rnforced Plastics and Composites,2018,38(7):1-17.
[8] WANG A, XIAN G, LI H. Effects of fiber surface grafting with nano-clay on the hydrothermal ageing behaviors of flax fiber/epoxy composite plates[J]. Polymers,2019,11(8):1278-1289. DOI: 10.3390/polym11081278
[9] ASSARAR M, SCIDA D, EL MAHI A, et al. Influence of water ageing on mechanical properties and damage events of two reinforced composite materials: Flax-fibres and glass-fibres[J]. Materials & Design,2011,32(2):788-795.
[10] SCIDA D, ASSARAR M, POILÂNE C, et al. Influence of hygrothermal ageing on the damage mechanisms of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy composite[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2013,48:51-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.12.010
[11] LE DUIGOU A, DAVIES P, BALEY C. Exploring durability of interfaces in flax fibre/epoxy micro-composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2013,48:121-128. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.01.010
[12] BERGES M, LÉGER R, PLACET V, et al. Influence of moisture uptake on the static, cyclic and dynamic behaviour of unidirectional flax fibre-reinforced epoxy laminates[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2016,88:165-177. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.05.029
[13] MUNOZ E, GARCÍA-MANRIQUE J A. Water absorption behaviour and its effect on the mechanical properties of flax fibre reinforced bioepoxy composites[J]. International Journal of Polymer Science,2015,6:1-10.
[14] MOUDOOD A, HALL W, ÖCHSNER A, et al. Effect of moisture in flax fibres on the quality of their composites[J]. Journal of Natural Fibers,2019,16(2):209-224. DOI: 10.1080/15440478.2017.1414651
[15] GOUTIANOS S, PEIJS T, NYSTROM B, et al. Development of flax fibre based textile reinforcements for composite applications[J]. Applied Composite Materials,2006,13(4):199-215. DOI: 10.1007/s10443-006-9010-2
[16] ASTM. Standard test method for tensile properties of polymer matrix composite materials: D3039M—17[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2017.
[17] ASTM. Standard test method for moisture absorption properties and equilibrium conditioning of polymer matrix composite materials: D5229M—12[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2012.
[18] 边佳燕, 刘钧, 鲍铮. 聚合物基复合材料吸湿研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(28):340-344. BIAN Jiayan, LIU Jun, BAO Zheng. Research progress in moisture absorption of polymer matrix composites[J]. Materials Reports,2016,30(28):340-344(in Chinese).
[19] SHEN C H, SPRINGER G S. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1976,10(1):2-20. DOI: 10.1177/002199837601000101
[20] MASSETEAU B, MICHAUD F, IRLE M, et al. An evaluation of the effects of moisture content on the modulus of elasticity of a unidirectional flax fiber composite[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2014,60:32-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.01.011
[21] STAMBOULIS A, BAILLIE C A, PEIJS T. Effects of environmental conditions on mechanical and physical properties of flax fibers[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2001,32(8):1105-1115. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-835X(01)00032-X
[22] BALEY C, LE DUIGOU A, BOURMAUD A, et al. Influence of drying on the mechanical behaviour of flax fibres and their unidirectional composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(8):1226-1233. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.03.005
[23] DEBORAH D L. Carbon composites (Second edition)[M]. Netherlands: Elsevier, 2017: 88-160.
[24] LEFEUVRE A, BOURMAUD A, MORVAN C, et al. Elementary flax fibre tensile properties: Correlation between stress-strain behaviour and fibre composition[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2014,52:762-769. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.11.043
[25] LEFEUVRE A, LE DUIGOU A, BOURMAUD A, et al. Analysis of the role of the main constitutive polysaccharides in the flax fibre mechanical behaviour[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2015,76:1039-1048. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.07.062
[26] BALEY C. Analysis of the flax fibres tensile behaviour and analysis of the tensile stiffness increase[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2002,33(7):939-948. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-835X(02)00040-4
[27] PUCCI M F, LIOTIER P J, SEVENO D, et al. Wetting and swelling property modifications of elementary flax fibres and their effects on the liquid composite molding process[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,97:31-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.02.028
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李佥,王添誉,孙西同,陈晓艺,李苗,韩雨擎,曾祥冰,孙芳鸿,李宪臻. 贻贝仿生修饰多孔磁性材料的制备及其在固定化脂肪酶中的应用. 复合材料学报. 2024(11): 6156-6169 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载: