Impact resistance and damage mechanism of low modulus polyester fiber/cement matrix composites
-
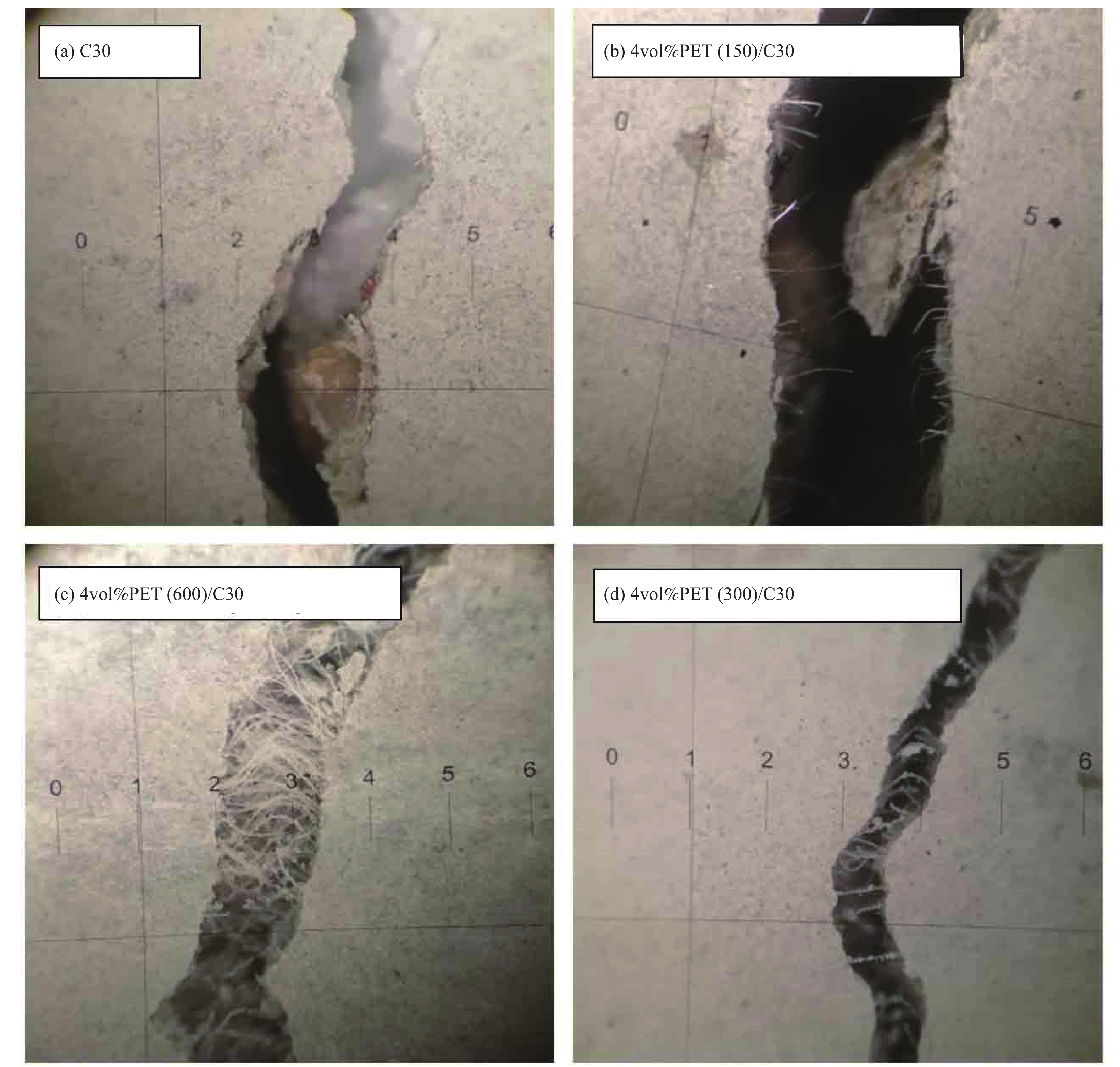
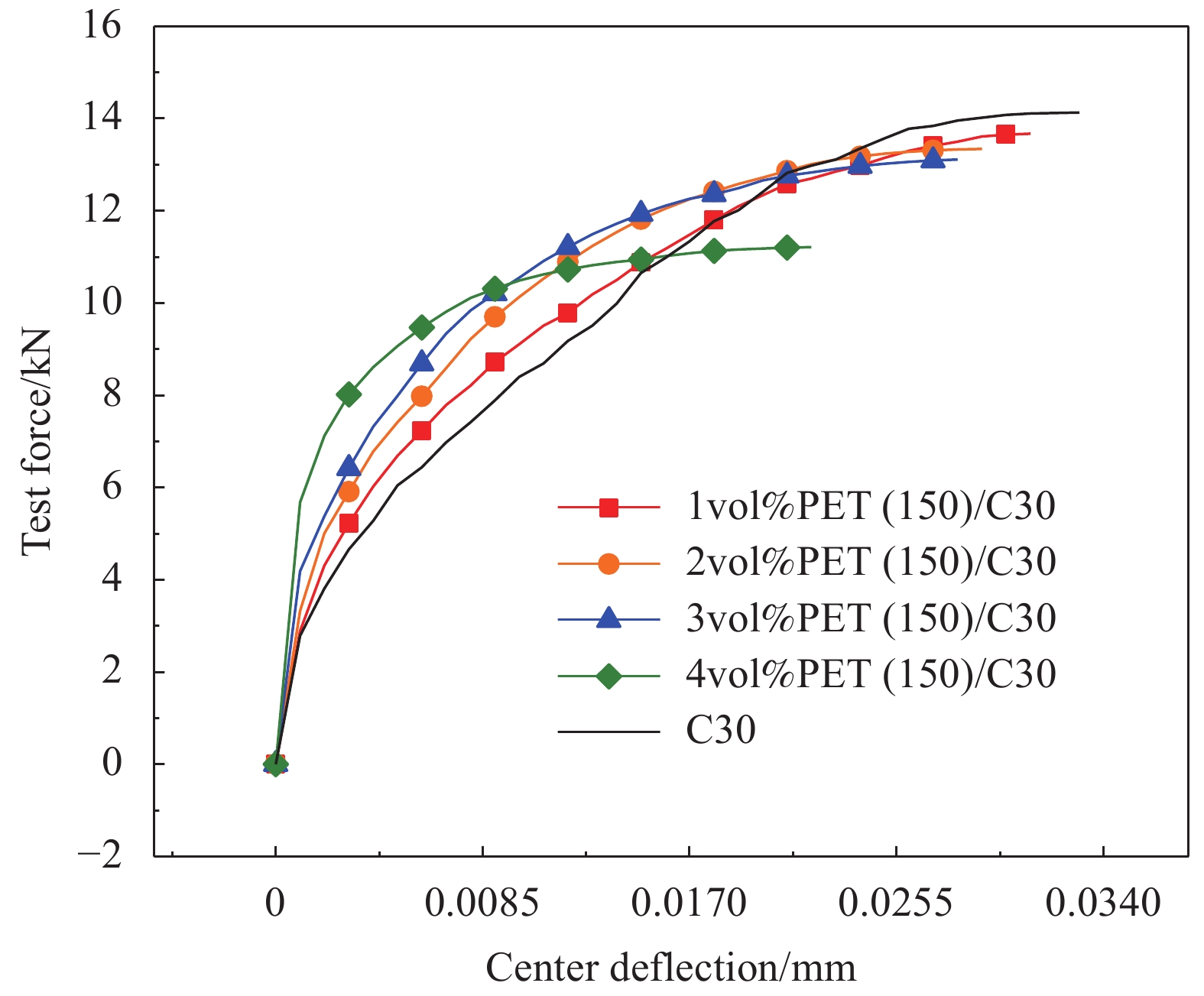
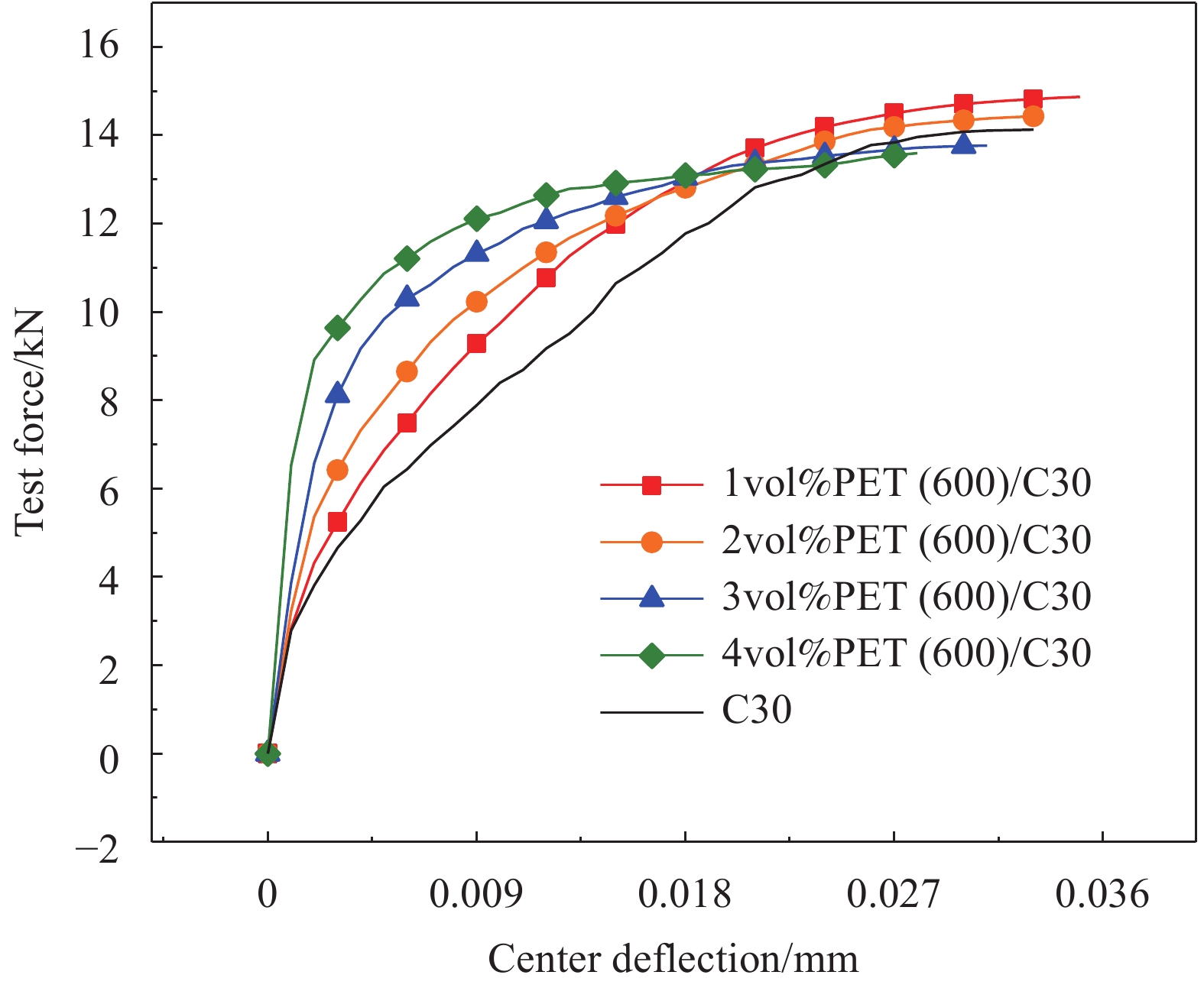
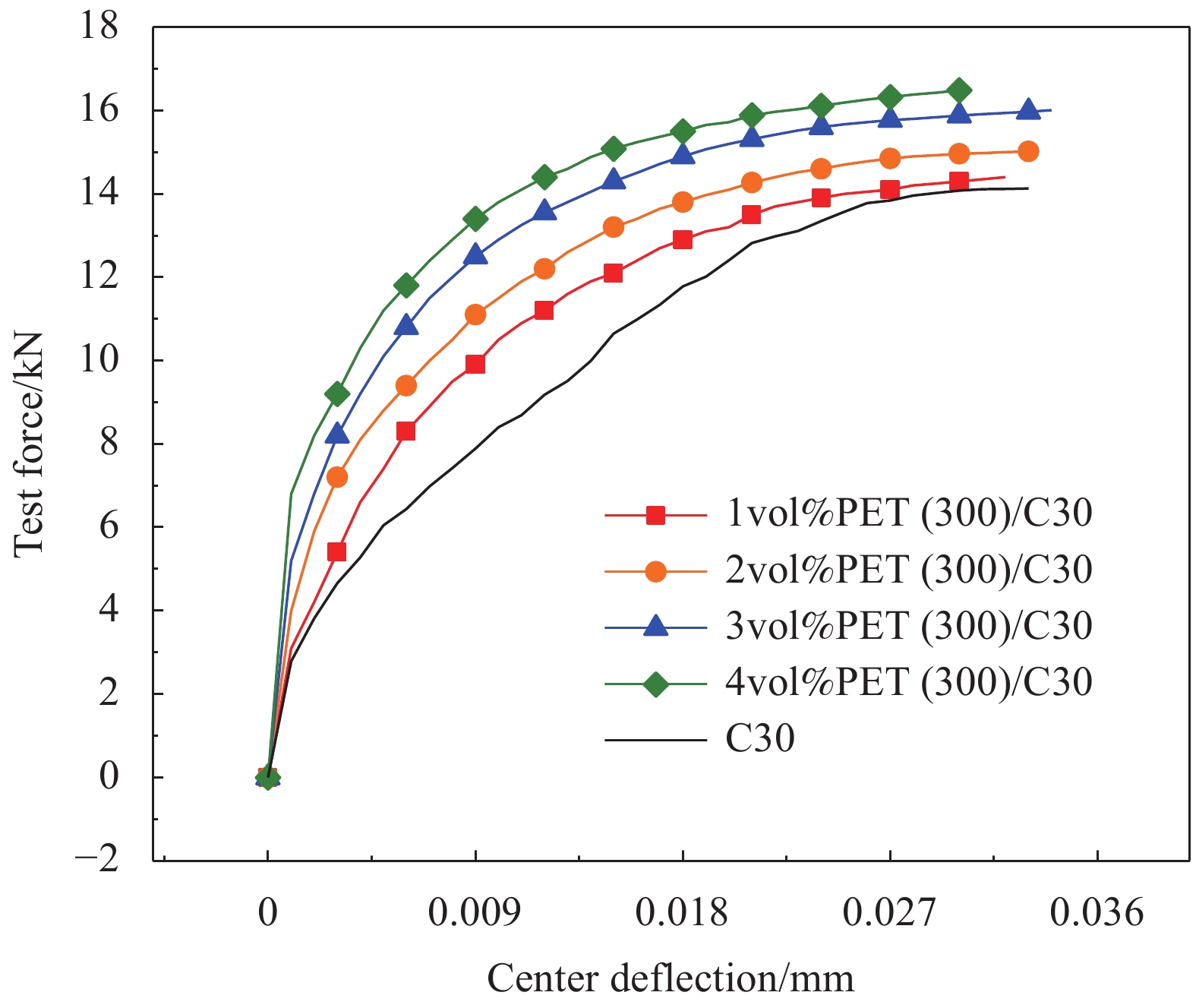
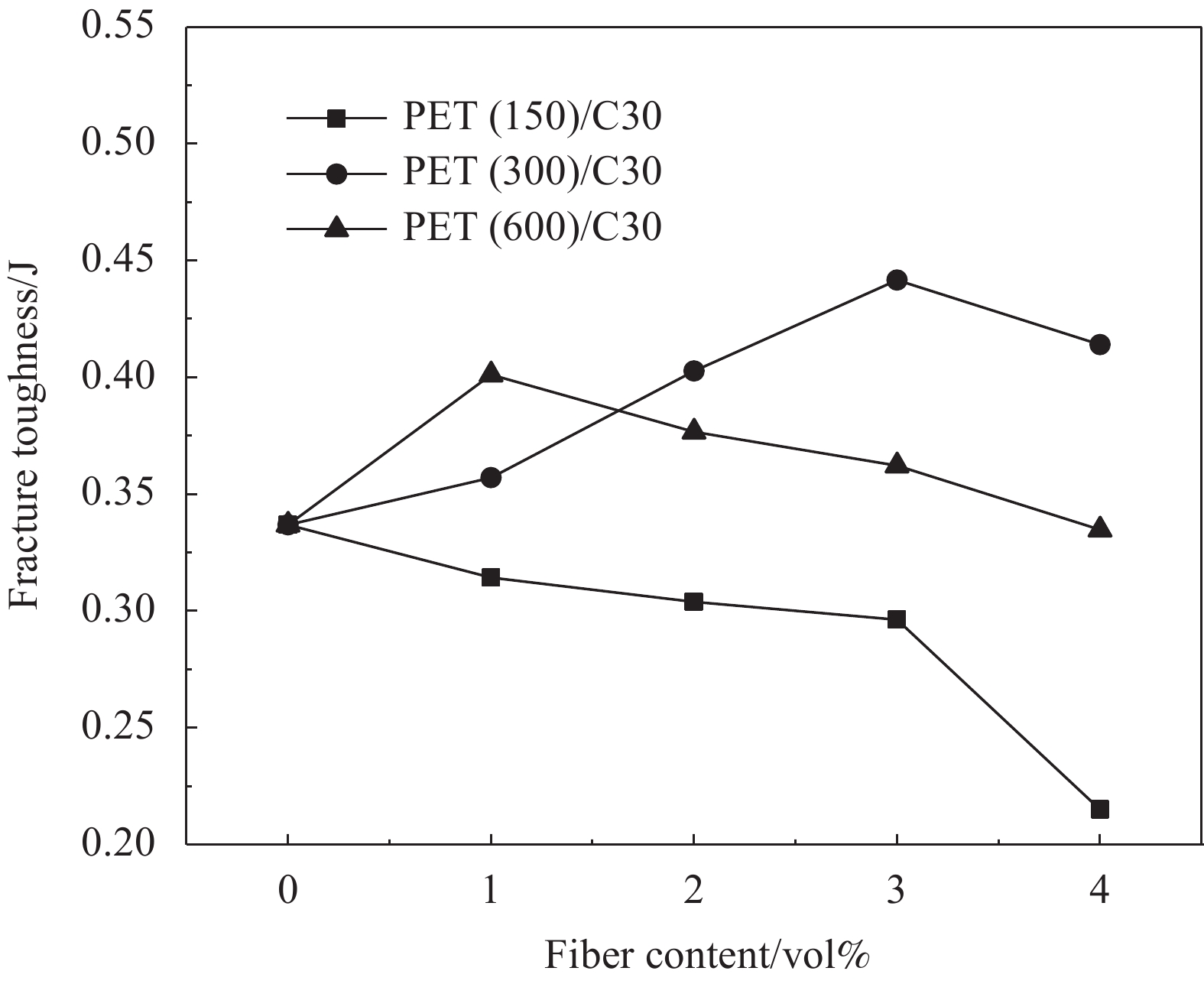
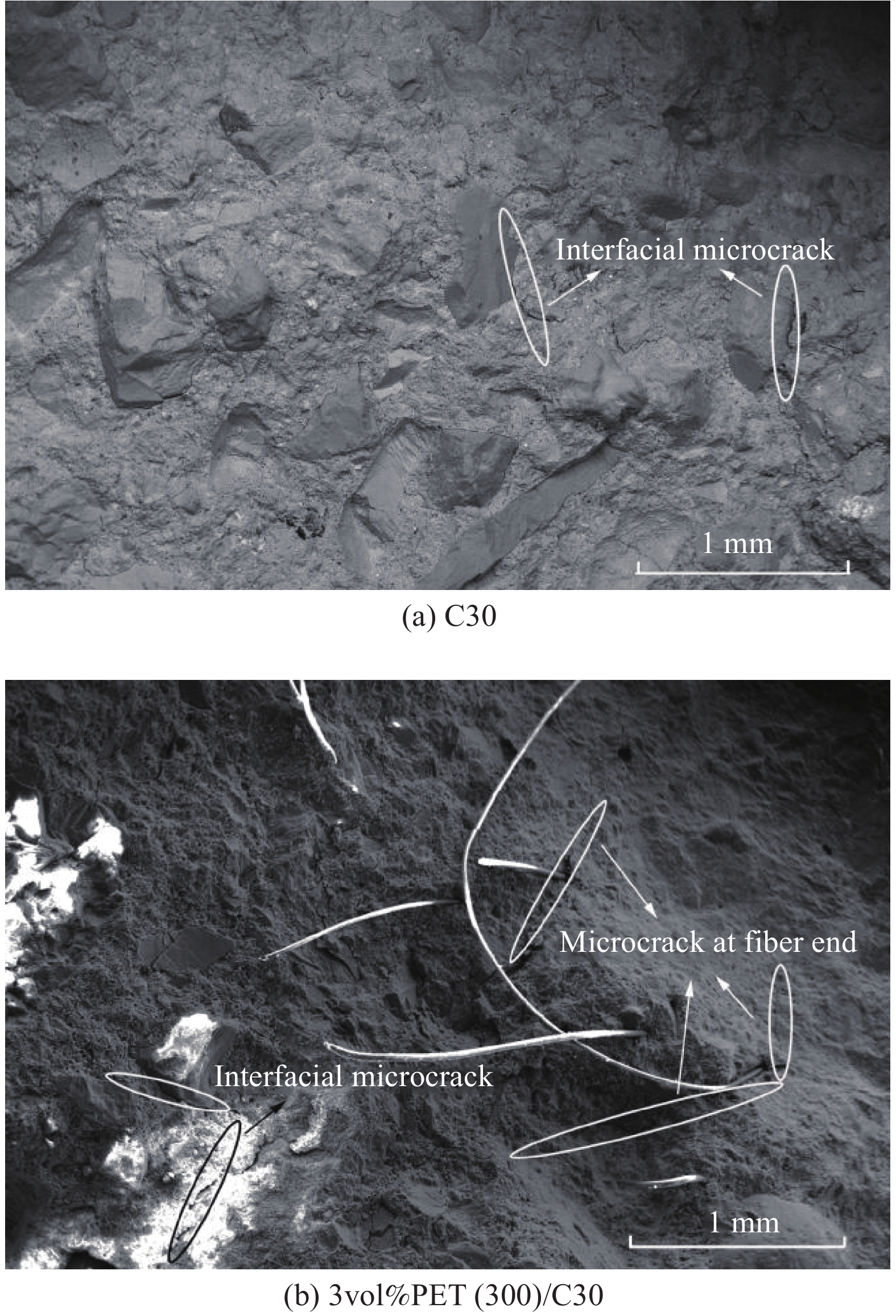
摘要: 研究聚酯纤维长径比、掺量对混凝土抗压强度、抗折强度、劈裂抗拉强度、断裂韧性及冲击荷载等力学性能的影响;运用复合材料理论和纤维间距理论对聚酯纤维/混凝土增韧阻裂机制进行研究,结合SEM观察微观形貌分析纤维长径比与掺量对增韧阻裂机制的影响;采用正交试验设计方法及激光扫描共聚焦显微镜(LSCM)研究冲击高度、试件厚度、长径比及掺量对纤维/混凝土抗冲击性能的影响。结果表明,长径比为300与600的聚酯纤维会降低混凝土抗压强度,低掺量长径比为150的聚酯纤维通过提高混凝土致密程度使混凝土抗压强度有所提升;在抗拉强度方面长径比为150的聚酯纤维主要以缺陷形式存在,长径比为300的聚酯纤维对改善混凝土内部拉结作用最显著,3%(与胶凝材料体积比)掺量聚酯纤维对提高混凝土抗折强度最显著;对于混凝土断裂韧性,长径比为300与600的聚酯纤维/混凝土断裂韧性提高明显,通过SEM微观形貌发现纤维拉结作用产生的微裂纹会提高混凝土耗能能力,从而提高混凝土极限荷载与破坏时中心挠度,长径比为300的聚酯纤维/混凝土抗拉强度变化规律与复合材料理论和纤维间距理论分析结果较吻合;冲击高度为影响冲击荷载大小的主要因素,纤维长径比较纤维掺量影响较大,通过LSCM三维损伤形貌分析得出长径比为150的聚酯纤维对混凝土材料损伤改善效果较显著,同等掺量下长径比为150的聚酯纤维间距较小导致混凝土局部力学性能提高,从而提高混凝土抗冲击性能。Abstract: The effects of length to diameter ratio and mixing amount of polyester fiber on the mechanical properties of concrete, such as compressive strength, flexural strength, splitting tensile strength, fracture toughness and impact load, were studied. The mechanism of toughening and cracking resistance of polyester fiber concrete was studied by composite material theory and fiber spacing theory. The microscopic morphology observed by SEM was used to analyze the influence of fiber length-diameter ratio and content on the mechanism of toughening and cracking resistance. Orthogonal experimental design method and laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM) were used to study the influence of impact height, specimen thickness, aspect ratio and content on the impact resistance of fiber/concrete. The results show that the polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 300 and ratio of length to diameter of 600 would reduce the compressive strength of concrete, the low content of polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 150 increases the compressive strength of concrete by increasing the density of concrete. In terms of tensile strength, the polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 150 mainly exist in the form of defects, the polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 150 have the most significant effect on improving the concrete internal pulling, the addition of 3% (volume ratio to cementitious materials) polyester fiber is the most significant to improve the flexbility of concrete. For the fracture toughness of concrete, the fracture toughness of polyester fiber/concrete with ratio of length to diameter of 300 and 600 is significantly improved. According to the SEM microscopic morphology, it is found that the micro-cracks generated by fiber pulling action would improve the energy dissipation capacity of concrete, thus increasing the ultimate load and central deflection of concrete during failure, and the variation of tensile strength of polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 300 reinforced concrete is in good agreement with the composite material theory and fiber spacing theory. Impact height is the main factor affecting the impact load, and the fiber length and diameter have greater influence than fiber content. Through LSCM analysis of three-dimensional damage morphology, it is concluded that the damage improvement effect of polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 150 on concrete material is relatively significant, and at the same dosage, the small spacing of polyester fibers with ratio of length to diameter of 150 results in the improvement of local mechanical properties of concrete, thus improving the impact resistance of concrete.
-
-
表 1 聚酯(PET)纤维物理性能参数
Table 1 Physical performance parameters of polyester (PET) fiber
Diameter/mm Density/(g·cm−3) Tensile strength/MPa Elastic modulus/MPa Elongation at break/% 2×10−2 1.36 600 8000 15 表 2 试件编号及配合比
Table 2 Specimen number and mix ratio
Specimen number Cement/kg Fine aggregate/kg Coarse aggregate/kg Water/kg Fiber content/(kg·m−3) C30 390 645 1148 218 0 1vol%PET(150)/C30 390 645 1148 218.0 1.986 2vol%PET(150)/C30 390 645 1148 219.0 3.972 3vol%PET(150)/C30 390 645 1148 220.0 5.958 4vol%PET(150)/C30 390 645 1148 221.0 7.944 1vol%PET(300)/C30 390 645 1148 222.0 1.986 2vol%PET(300)/C30 390 645 1148 219.6 3.972 3vol%PET(300)/C30 390 645 1148 221.2 5.958 4vol%PET(300)/C30 390 645 1148 222.8 7.944 1vol%PET(600)/C30 390 645 1148 224.4 1.986 2vol%PET(600)/C30 390 645 1148 220.6 3.972 3vol%PET(600)/C30 390 645 1148 223.2 5.958 4vol%PET(600)/C30 390 645 1148 225.8 7.944 Notes: Use C30 ordinary concrete as reference concrete; In nvol%PET(m)/C30, PET stands for PET fiber; nvol%—Fiber content; m—Fiber aspect ratio of 150, 300, 600, respectively. 表 3 正交试验因素及水平情况
Table 3 Orthogonal test factors and levels
Factor level Impact height/cm Specimen thickness/cm Ratio of length to diameter Fiber content/vol% 1 40 1 150 2 2 38 3 300 3 3 36 5 600 4 4 34 - - - 5 32 - - - 6 30 - - - 表 4 PET纤维/混凝土试样计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of different PET fiber/concrete samples
Specimen
numberFiber content/
(kg·m−3)Tensile
strength1vol%PET(150)/C30 1.986 σ=5.155+0.219ηlτ 2vol%PET(150)/C30 3.972 σ=5.148+0.438ηlτ 3vol%PET(150)/C30 5.958 σ=5.140+0.657ηlτ 4vol%PET(150)/C30 7.944 σ=5.132+0.876ηlτ 1vol%PET(300)/C30 1.986 σ=5.155+0.438ηlτ 2vol%PET(300)/C30 3.972 σ=5.148+0.876ηlτ 3vol%PET(300)/C30 5.958 σ=5.140+1.314ηlτ 4vol%PET(300)/C30 7.944 σ=5.132+1.752ηlτ 1vol%PET(600)/C30 1.986 σ=5.155+0.876ηlτ 2vol%PET(600)/C30 3.972 σ=5.148+1.752ηlτ 3vol%PET(600)/C30 5.958 σ=5.140+2.628ηlτ 4vol%PET(600)/C30 7.944 σ=5.132+3.504ηlτ Notes: σ—Tensile strength; ηl—Effective bond length coefficient; τ—Average bond stress. 表 5 PET纤维/混凝土承受冲击荷载极差分析
Table 5 Analysis of extreme difference of PET fiber/concrete under impact load
Factor Impact height H Specimen thickness S Ratio of length to diameter Lf/df Fiber content T K1/kN 5880.10 3199.51 4180.04 3816.96 K2/kN 4649.30 4386.32 3637.98 3911.55 K3/kN 4017.02 4027.79 3795.59 3885.11 K4/kN 3163.89 - - - K5/kN 2812.53 - - - K6/kN 2704.39 - - - R 3175.71 1186.81 542.06 94.59 Notes: Ki—Sum of the corresponding test results when the level number on any column is i (i=1-6); R—Range. -
[1] 杨娟, 朋改非, 税国双. 再生钢纤维增韧超高性能混凝土的力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8):1949-1956. YANG Juan, PENG Gaifei, SHUI Guoshuang. The mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete toughened by recycled steel fiber[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(8):1949-1956(in Chinese).
[2] 邓宗才, 陈海龙. 集束型玻璃纤维混凝土轴拉、弯曲和断裂性能[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2019, 40(5):993-999. DENG Zongcai, CHEN Hailong. Axial tension, bending and fracture properties of clustered glass fiber concrete[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2019,40(5):993-999(in Chinese).
[3] LI L, GAO D Y, LI Z L, et al. Effect of high temperature on morphologies of fibers and mechanical properties of multi-scale fiber reinforced cement-based composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,261:120487.
[4] AL-HADITHI A I, NOAMAN A T, MOSLEH W K. Mechanical properties and impact behavior of PET fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete (SCC)[J]. Composite Structures,2019,224:111021.
[5] NARAGANTI S R, PANNEM R, PUTTA J. Impact resistance of hybrid fibre reinforced concrete containing sisal fibres[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal,2019,10(2):297-305. DOI: 10.1016/j.asej.2018.12.004
[6] ALSHAIKH I, BAKAR B H, AKIL H M, et al. Impact resistance of plain and rubberized concrete containing steel and polypropylene hybrid fiber[J]. Materials Today Communications,2020,25:101640.
[7] GHASEMI M, GHASEMI M R, MOUSAVI S R. Studying the fracture parameters and size effect of steel fiber-reinforced self- compacting concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,201:447-460.
[8] 马恺泽, 刘亮, 刘超, 等. 高强混合钢纤维混凝土的力学性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2017, 20(2):261-265. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.02.018 MA Kaize, LIU Liang, LIU Chao, et al. The mechanical properties of high-strength steel fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2017,20(2):261-265(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.02.018
[9] SAFIUDDIN M D, YAKHLAF M, SOUDKI K A. Soudki, Key mechanical properties and microstructure of carbon fibre reinforced self-consolidating concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,164:477-488. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.172
[10] 梁宁慧, 钟杨, 刘新荣. 多尺寸聚丙烯纤维混凝土抗弯韧性试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(10):2783-2789. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.10.032 LIANG Ninghui, ZHONG Yang, LIU Xinrong. Experimental study on flexural toughness of multi-size polypropylene fiber concrete[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition),2017,48(10):2783-2789(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.10.032
[11] DING Yining, WANG Qingxuan, PACHECO-TORGAL F, et al. Hybrid effect of basalt fiber textile and macro polypropylene fiber on flexural load-bearing capacity and toughness of two-way concrete slabs[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,261:119881.
[12] 罗洪林, 杨鼎宜, 周兴宇等. 不同长径比聚丙烯纤维增强混凝土的力学特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8):1935-1948. LUO Honglin, YANG Dingyi, ZHOU Xingyu, et al. Mechanical properties of polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete with different length-to-diameter ratios[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(8):1935-1948(in Chinese).
[13] 高丹盈, 赵亮平, 冯虎, 等. 钢纤维混凝土弯曲韧性及其评价方法[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2014, 17(5):783-789. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2014.05.006 GAO Danying, ZHAO Liangping, FENG Hu, et al. Bending toughness of steel fiber concrete and its evaluation method[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2014,17(5):783-789(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2014.05.006
[14] LIU Gaojie, BAI Erlei, XU Jinyu, et al. Dynamic compressive mechanical properties of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer concrete with different polymer-cement ratios at high strain rates[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,261(7):119995.
[15] 安静. 聚酯纤维改性沥青混合料路用性能研究[J]. 公路工程, 2015, 40(6):247-251. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2015.06.054 AN Jing. Study on road performance of polyester fiber modified asphalt mixture[J]. Highway Engineering,2015,40(6):247-251(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0610.2015.06.054
[16] HONG R B, WU J R, CAI H B. Low-temperature crack resistance of coal gangue powder and polyester fibre asphalt mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,238:117678.
[17] BUI N K, SATOMI T, TAKAHASHI H. Recycling woven plastic sack waste and PET bottle waste as fiber in recycled aggregate concrete: An experimental study[J]. Waste Management,2018,78(1):79-93.
[18] 魏艳红, 刘新金, 谢春萍, 等. 几种差别化聚酯纤维的结构与性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2019, 40(11):13-19. WEI Yanhong, LIU Xinjin, XIE Chunping, et al. Structure and properties of several differentiated polyester fibers[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2019,40(11):13-19(in Chinese).
[19] ANTHONY R. Bunsell, handbook of properties of textile and technical fibres (Second edition)[M]. Sawston: Woodhead Publishing, 2018.
[20] PEREIRA E L, LUIS D O J A, FINEZA A G. Optimization of mechanical properties in concrete reinforced with fibers from solid urban wastes (PET bottles) for the production of ecological concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,149(15):837-848.
[21] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土配合比设计规程: JGJ 55—2011[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Design specification for ordinary concrete mix ratio: JGJ 55—2011[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2011(in Chinese).
[22] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of physical and mechanical properties of concrete: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2019(in Chinese).
[23] ASTM. Standard test method for flexural toughness and first-crack strength of fiber-reinforced concrete(using beam with third-point loading): ASTM C 1018[S]. West Conshohocken: American Socicty for Testing and Materials Press, 1997: 544 -551.
[24] 杜任远, 陈宝春, 沈秀将. 不同方法测试的超高性能混凝土抗拉强度[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(S2):483-486, 520. DU Renyuan, CHEN Baochun, SHEN Xiujiang. Ultra-high performance concrete tensile strength tested by different methods[J]. Materials Guide,2016,30(S2):483-486, 520(in Chinese).
[25] 黄承逵. 纤维混凝土结构[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004. HUANG Chengkui. Fiber-reinforced concrete structure[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2004(in Chinese).
[26] 李艺, 赵文. 混杂纤维混凝土阻裂增韧及耐久性能[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. LI Yi, ZHAO Wen. Crack resistance and toughness and durability of hybrid fiber concrete[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[27] ROMUALDI J P, BATSON G B. Mechanics of crack arrest in concrete[J]. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division,1963,89(3):147-168.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李滋阳,王思佳,邓文举. 陶瓷颗粒增强金属基复合材料研究进展. 轻工科技. 2021(04): 41-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈亚楠,金云学,牛牧野,陈洪美,杜文栋. Ni_3Al(Cr)合金室温干滑动摩擦磨损性能研究. 江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(05): 18-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-





 下载:
下载: