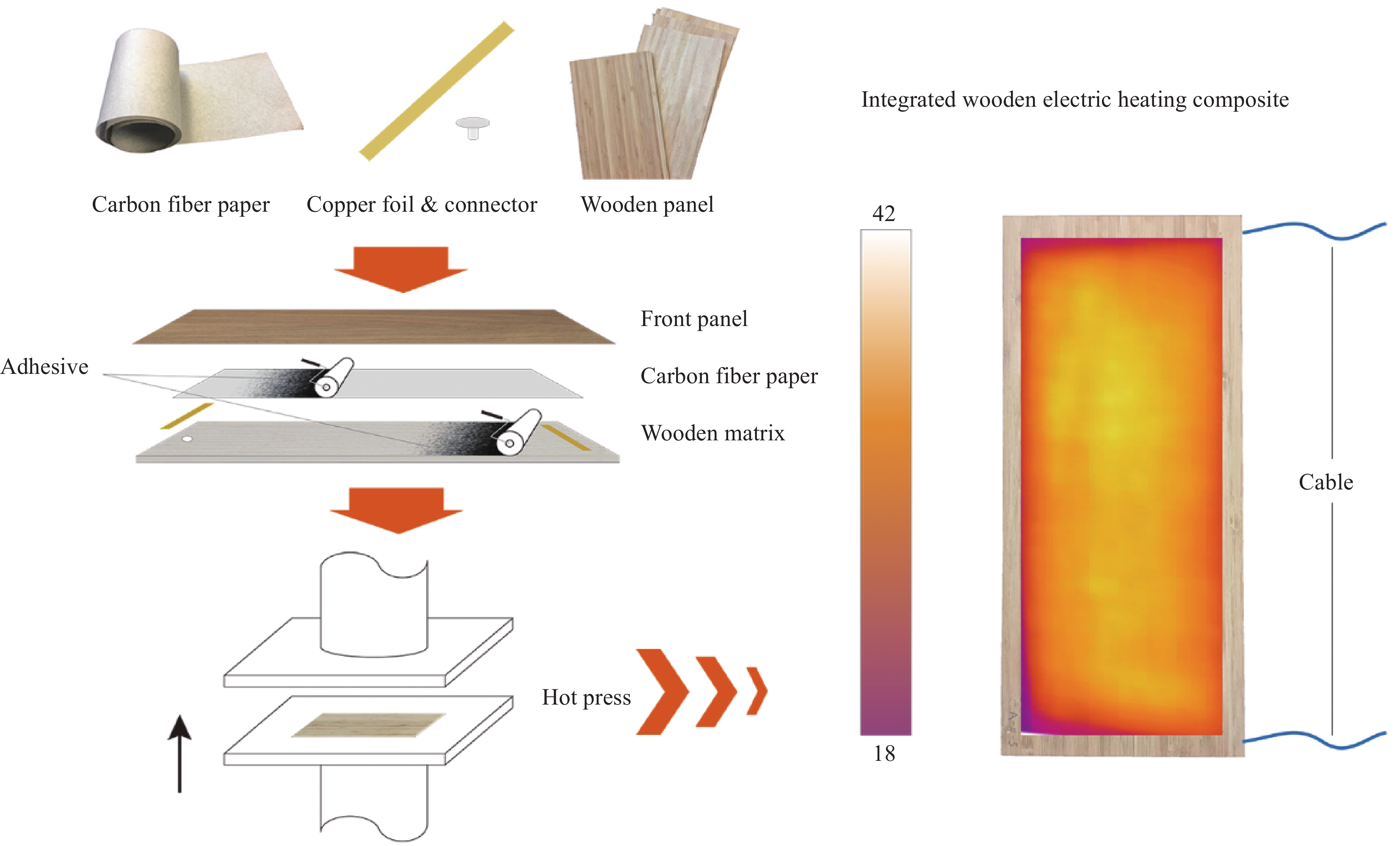
Longitudinal scale effect of electro-thermal effectiveness of front panel of the integrated wooden electric heating composite based on carbon fiber paper
-
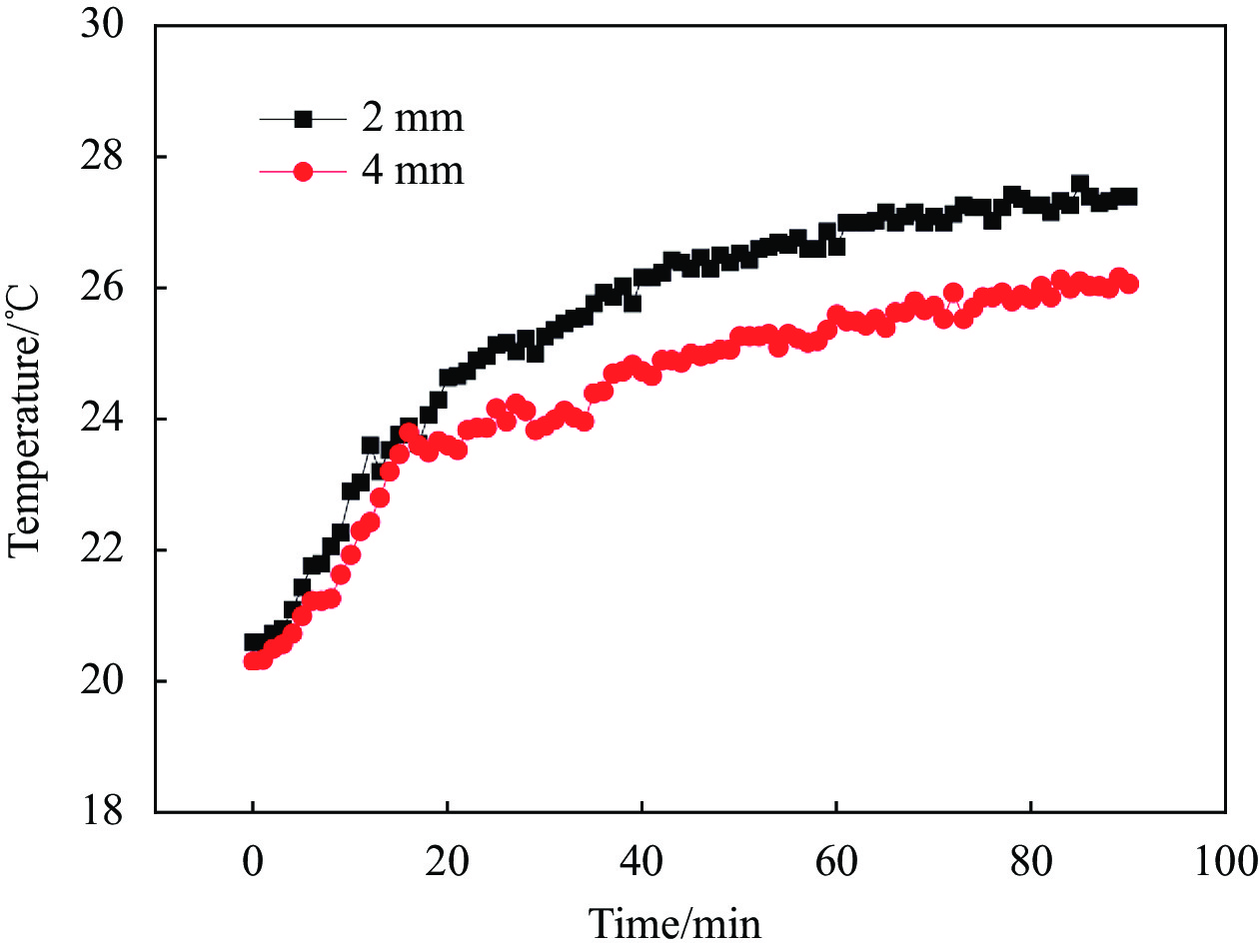
摘要: 根据热力学能量守恒定律和傅里叶(Fourier)定律,利用一维传热理论推导基于碳纤维纸(CFP)的木质电热复合材料的结构特征与其表面空气温度效果之间的理论关系式,对其关系进行了定性分析,研究木质电热复合材料面层电热效果的纵向尺寸效应,分析表明面层板厚度与表面空气温度呈反比例关系。对面层板厚度分别为2 mm和4 mm的木质复合材料开展了温度测试试验,以验证理论计算结果正确性。结果显示,通过理论计算,得出基于CFP的木质电热复合材料面层厚度与表面空气温度之间呈反比关系;通过实验验证,对比两种不同面层材料厚度的电热复合材料表面空气温度,发现厚度为2 mm的电热复合材料表面空气温度高于厚度为4 mm的,与理论计算结果一致。在采暖领域,相对于面层板较厚的木质电热复合材料,面层板较薄的更能充分利用能源。Abstract: Based on laws of thermodynamics: law of conservation of energy and Fourier law, the theoretical relationship between the structure property and the environment temperature above the surface of the integrated wooden electric heating composites based on carbon fiber paper (CFP) was derived with the solution for one-dimensional heat transfer problem, and then qualitatively analyzed to study the longitudinal scale effect of the front panel of the integrated wooden electric heating composites. The derived relational expression shows an inversely proportional relationship between the structure property and the environment temperature. In order to verify the theoretical calculation results, the temperature tests were conducted on the integrated wooden electric heating composites with 2 mm and 4 mm thickness front panel respectively. The results show that the relationship between the thickness of the front panel and the air temperature above the surface of the composites based on CFP presents inversely proportion based on the mathematical calculation. Compared with the air temperature above the surface of composites with 4 mm thickness front panel, the air temperature of the composites with 2 mm thickness front panel turns out to be higher through experimental validation, which is consistent with the theoretical calculation. Hence, the integrated wooden electric heating composites with thinner front panel have an advantage of utilization of energy.
-
随着科学技术的高速发展,现代工程对工件材料的性能要求越来越高,在一些特殊的服役环境下,单一金属材料已经不能满足实际的生产需求。钛合金被誉为“二十一世纪的金属”,是由于其具有良好的耐腐蚀性、较高的强度和良好的耐热性等特点[1]。但其生产成本较高,因此,主要用于航空航天、核电军工、医疗及深海等高科技领域。铝合金具有较好的延展性、低密度及加工成形性能良好等特点[2],在工业制造领域得到了广泛的应用。因此,结合钛合金和铝合金的优势,Ti/Al层状复合材料有效规避了二者的不足,兼具了轻量化、高强度、耐腐蚀及价格低廉的优势,极具应用前景。
目前,Ti/Al层状复合板的制备方法有轧制复合法、爆炸复合法、热压复合法等。其中,热压复合法[3]是在真空环境下,利用高压塑性变形和高温扩散使界面处形成良好的冶金结合。其装置简单,加工效率高,便于批量化生产,同时,制备的层状复合板具有良好的界面结合强度。
层状复合板的常用焊接方法有搅拌摩擦焊(Fricition stir welding,FSW)、激光焊(Laser beam welding,LBW)、真空电子束焊(Electron beam welding,EBW)等。其中,EBW[4]作为一种真空环境下的焊接方法,可以有效避免焊接过程中空气对焊接接头的污染,并且,焊接接头成形性能良好。与传统的焊接方式相比,不受材料导电的影响,EBW技术已广泛应用于复合材料焊接、C纳米管焊接及绝缘体焊接等领域[5]。范林好[6]对Re/GH3128复合材料进行EBW焊接,其中,Re和GH3128均为航空发动机中重要的热交换零部件材料,且二者均属于耐高温材料。为防止Re氧化,获得性能优异的焊接接头,因此,采用EBW实现Re和GH3128的有效连接。
在层状复合板焊接过程中,不同于单一金属材料,接头组织复杂,容易产生脆性的金属间化合物(Intermetallic compounds,IMCs),影响焊接接头的力学性能。曲树平[7]采用铝合金在上、钛合金在下的方式进行电子束搭接焊,分析焊接缺陷产生的原因,探究不同热输入量与界面处元素扩散行为的关系。赵啸等[8]采用FSW对铝/铜复合板进行焊接技术研究,探究热力耦合作用对铜复层流动行为的影响,铝基层在上的焊接接头容易产生明显的隧道缺陷;铜复层在上时得到的焊接接头成形性能良好,平均抗拉强度为85.2 MPa,达到母材强度的62.7%。
为减少或消除IMCs的生成,研究人员进行了大量研究。李福山[9]采用EBW技术对铝/铜复合板进行焊接,为了提高焊接接头的力学性能,提出采用熔池分离的双面焊技术。研究发现,双面焊可以实现铝/铜复合板的焊接,焊接接头的抗拉强度最高可达117.0 MPa,达到母材的92.9%,双面焊可以有效抑制接头中脆性IMCs的形成。因此,为获得力学性能优异的焊接接头,EBW焊接Ti/Al复合板也可采取以上方法。
本文通过真空热压的方法制备Ti/Al层状复合板,采用EBW对Ti/Al层状复合板进行焊接,对比分析了单面焊和双面焊在不同焊接工艺条件下对焊接接头微观组织与力学性能的影响,探究了焊接接头不同区域的微观组织、界面处元素扩散机制及IMCs的形成机制。对焊接接头的力学性能进行测试分析,结合焊接接头的断口形貌,对Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头的断裂机制进行分析。
1. 原材料及方法
本文选用Ti6Al4V (TC4)钛合金、6061铝合金为原始板材,合金板材的规格均为200 mm×100 mm×3 mm,化学成分分别如表1和表2所示。
表 1 TC4钛合金化学成分Table 1. Chemical composition of TC4 titanium alloywt% Ti Al V Fe O C N H Balance 6.2 4.0 0.25 0.15 0.098 0.01 0.004 表 2 6061铝合金化学成分Table 2. Chemical composition of 6061 aluminum alloywt% Al Mg Ti Si Zn Fe Cu Mn Cr Balance 1.05 0.1 0.62 0.18 0.41 0.2 0.12 0.17 对原始板材进行表面预处理:(1) 采用400#和1000#的砂纸对钛、铝预结合面进行打磨;(2) 采用10vol%NaOH熔液对铝合金板预结合面碱洗,10vol%HF熔液对钛合金板预结合面酸洗;(3) 采用无水乙醇对钛合金、铝合金板预结合面清洗,烘干后备用。将组对的Ti/Al层状复合板坯置于真空热压炉(ZDRY-557-200,维科科技有限公司)内,进行真空热压,热压温度550℃,压强20 MPa,保温2 h后随炉冷却,工艺流程示意图如图1(a)所示。
将热压后的Ti/Al层状复合材料(Laminar composites,LMCs)进行EBW,焊接工艺参数如表3所示。其中,Ti层加速电压为50 kV,Al层为40 kV,焊接工作距离均为300 mm,焊接速度均为1000 mm/min。分别进行Ti层在上单面焊接(Type A)、先Ti后Al双面焊接(Type B)和先Al后Ti双面焊接(Type C) 3种方式焊接,对不同方式下的焊接接头成形性能进行分析。EBW设备原理及焊接方式示意图如图1(b)和图1(c)所示。
采用金相显微镜(OM,CX40M,舜宇光学科技集团有限公司)、配有能谱仪(EDS)的扫描电子显微镜(SEM,MIRA3 LMH,TESCAN公司)和X射线衍射仪(XRD,SmartLsb SE,日本/RIGAKU CORPORATION)对不同工艺参数下的焊接接头微观组织和物相组成进行观察分析,探究焊接接头界面处的元素扩散机制及IMCs的形成机制。通过显微硬度仪(HV-1000,德卡精密量仪有限公司)和万能拉伸试验机(INSTRON5969,ITW集团英斯特朗公司)对焊接接头的力学性能进行测试分析,结合拉伸断口形貌对断裂机制进行分析。
表 3 EBW工艺参数Table 3. EBW process parametersElectron
beam
current/mASingle-side welding
(Type A)Double-side welding Type B Type C Ti side 60/70/80 50/60/65 70/75/80 Al side — 40/45 43/45 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 Ti/Al 层状复合板焊接接头微观组织分析
对Type A、Type B和Type C这3种焊接方式下得到的Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头的微观形貌进行金相组织分析。图2为Type A方式下得到的不同电子束流焊接接头微观组织形貌。从图2(a)和图2(b)中可以看出,当电子束流为60 mA和70 mA时,热输入能量足以熔透Ti层金属,熔化态Ti和Al发生了流动,由于TC4密度大于6061 Al,受重力因素的影响,Ti层金属向Al层流动,Al层金属向上翻涌,气体来不及溢出熔池,形成了冶金气孔。当电子束流为70 mA时,在Ti/Al界面处形成了较大的冶金气孔。
分析其原因是由于焊接热输入较大,熔池冷却速率较快,熔池中的气体不能及时逸出,冷却后形成了冶金气孔。另一方面原因是6061 Al的熔点为680℃左右,而TC4的熔点为1670℃,因此,在较大热输入的情况下,6061 Al中的Al、Mg等元素发生气化,也同样造成了气孔的形成。在图2(c)和图2(d)中均发现了岛状结构组织,这是由于Ti在Al中的溶解度较低所引起的[10]。
图3为Type B下得到的焊接接头微观组织形貌。其中,Ti层的电子束流为60 mA,Al层电子束流为45 mA。根据焊缝宏观形貌,Al层焊缝成形较差,沿焊缝方向出现贯穿裂纹。从图3(a)可以看出,电子束热输入能量不足以熔透Ti层,熔合区与热影响区界限分明,在熔合区有析出相产生,析出相为细小的片状枝晶α相。
由图3(c)可知,Al层熔合区出现明显裂纹,这是由于在焊接Ti层时,电子束对Al层造成了一定的热影响,产生温度梯度,导致其熔合区残余应力增大。当残余应力高于某一临界值时,引起熔池凝固过程中热裂纹的出现,在焊接Al层时,待液态Al冷却时,焊缝中的液态Al不足以填充由于冷却收缩造成的体积减小;另一方面,残余应力导致Al层抵抗高温蠕变开裂的能力降低,铝合金高温蠕变机制与晶界滑移和位错滑移有关,强化晶界和限制位错运动可以提高铝合金抗蠕变性能,而残余应力会加快位错运动的滑移。最终,导致Al层贯穿裂纹的出现[11]。其中,Al层热影响区形成了细长的柱状晶。
图4为Type C方式下得到的焊接接头微观组织形貌。可以看出,Ti/Al层状复合板界面处实现了良好的冶金结合,无较大的空洞缺陷。在Ti层电子束流为70 mA的条件下,Al层熔合区出现明显的熔化态的Ti合金,在Al层熔合区出现了图4(c)的结晶裂纹。这是由于Ti合金与Al合金的热膨胀系数差异较大,二者的收缩量不同,产生残余应力,最终形成结晶裂纹[12]。当Ti层电子束流为75 mA时,在Ti/Al界面处,形成了界面扩散层,呈锯齿状分布,并存在冶金裂纹。冶金裂纹的产生是由于在界面处IMCs相互生长阶段产生应力,导致在IMCs处产生裂纹[13],如图4(f)所示。当Ti层电子束流为80 mA时,热输入量足够熔透Al层,因此出现如图4(g)所示的Ti层熔合区贯穿Al层的现象,同时在Al层熔池中出现了棒状IMCs和岛状结构。
在不同的焊接方式下,Type C焊接方式下得到的焊接接头成形性能较好。主要是与焊接熔池内部的金属流动性能有关[9]。当电子束在Al层表面时,随着电子束流的增大,通过控制电子束流的大小,在Al层形成了独立的熔池,熔池底部会形成一个热量堆积区,当热量饱和时,Al层被瞬间熔透,熔池进入Ti层中,而Ti合金的熔点较高,因此,只会发生轻微熔化,并与熔化态的Al发生反应,生成IMCs,待Al层焊接完成后,对Ti层进行焊接,当焊接热输入较小时,如Ti层电子束流为70 mA和75 mA时,热输入不足以完全熔透Al层,Ti层的熔池将之前的Al层熔池熔化,在界面处形成了Ti-Al重熔熔池。当焊接热输入较大时,如Ti层电子束流为80 mA时,热输入足以熔透Al层,形成了Ti-Al的公共熔池和贯穿Al层的Ti熔池。
同时,由于Al合金的密度小于Ti合金,向熔池底部扩散的速率小于Ti合金,这也在一定程度上抑制了IMCs的生成。对于Type A和Type B两种焊接方式,由于焊接Ti层所需的热输入较大,而Al合金的熔点较低,当Ti层被熔透时,Al层也会被大面积熔化,在熔池流动的作用下,Ti和Al元素相互扩散,产生大量的IMCs且易产生缺陷,降低了接头的成形性能。
图5为3种焊接类型下焊接接头成形示意图。图5(a)为Type A焊接成形示意图。Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头成形过程分为3个阶段:(I) 熔化阶段:在热输入下,Ti层和Al层金属发生快速熔化,并且在电子束的驱动下,液态金属在熔池内部发生流动;(II) 扩散阶段:液态Ti在重力作用下向下进入Al层熔池中,而Al原子则由于其密度小和溶解度的差异向Ti层扩散;(III) 冷却阶段:电子束加热具有快速冷却的特点,熔池中的液态Al和Ti不足以发生完全反应,因此形成了如图所示的岛状组织。
图5(b)为Type B焊接方式下Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头成形示意图。焊接接头成形过程分为3个阶段:(I) Ti层焊接:由于Al合金的热膨胀系数远大于Ti合金,在焊接热输入的影响下,Al层合金的热膨胀系数较大,同时冷却时收缩量也较大,在此过程中,就在焊缝中心处形成了一定的残余应力,并且难以消除;(II) Al层焊接:Al层熔池形成过程中也会产生一定的残余应力,与Ti层产生的残余应力方向相反;(III) 在冷却阶段:由于两侧残余应力方向相反,产生拉应力,容易导致在Al层焊缝区域产生裂纹。
图5(c)为Type C方式下焊接接头成形示意图。在Al层焊接时,电子束热输入能量不足以熔透Al层,但由于热膨胀系数较大,在冷却过程中,焊接过程产生的残余应力难以消除;待板材冷却后,对Ti层焊接,电子束热输入较大,Al层在热传导的影响下发生熔化,Ti和Al原子在电子束流的推动下发生流动,并在界面处发生扩散,待焊件冷却时,Al层溶质原子向Ti层扩散,Ti层原子在Al中的溶解度较低。因此,在Al层中形成了岛状组织,在Ti/Al界面处形成了Ti-Al IMCs。
2.2 焊接接头组成成分及物相分析
对Type C方式下焊接接头熔合区界面处IMCs的组成进行EDS能谱分析,如图6所示。从图6(a)中可以看出,Ti/Al熔合区界面处存在明显的IMCs,且IMCs呈“锯齿状”分布。对IMCs进行EDS能谱分析。从图6(b)面扫描结果可以看出,熔合区界面处Ti、Al元素发生明显的扩散行为。图6(c)和图6(d)分别为图6(a)中Line 1和Line 2的线扫描结果。在Ti/Al界面处IMCs的厚度约为20 μm,从Ti层到Al层,Ti、Al元素开始时趋于稳定,当到达Ti/Al界面处时,Ti元素浓度发生急剧下降,Al元素浓度急剧上升,当二者浓度相同时相交,可以判断此位置产生的IMCs为TiAl相。随着Ti元素浓度进一步下降,Al元素溶度进一步上升,生成的IMCs依次为TiAl2、TiAl3,到达Al层时,几乎不存在Ti元素。通过Line 2的结果,熔化态Ti扩散到Al熔池中,扩散层厚度约为35 μm。对界面处进行点扫描分析,结果如图6(e)所示,Point 1处的Ti、Al原子比约为1∶1,为TiAl相,Point 2处的Ti、Al原子比约为1∶3,为TiAl3相。
为进一步分析Ti/Al熔合区界面处的物相组成,对不同工艺参数下的双面焊接接头进行XRD分析,结果如图7所示。可以看出,不同参数下得到的Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头熔合区的物相组成是相同的,为Ti、Al、TiAl、TiAl3相。其中,在电子束流为75 mA时得到的焊接接头存在TiAl2相,但焊接接头的强度较低。
由Ti-Al二元相图可知,Ti/Al之间还可以生成Ti3Al相,但并未在EDS及XRD图谱中发现,这可能是由于Ti原子不易向Al基体中发生扩散,宋玉强等[14]对Ti/Al扩散溶解机制进行研究,研究表明元素的扩散能力与元素的结合能和熔点有关,结合能与熔点越高,所需的扩散能越高,扩散越不容易发生。由于钛的高熔点和较大的元素结合能,在焊接过程中的相同温度下,铝原子向Ti层扩散比较容易,而钛原子向Al层几乎不扩散,这在一定程度上也抑制了Ti-Al IMCs的生成。
IMCs的形成实质上是焊接过程中钛、铝原子相互扩散的结果,与焊接过程中温度和钛、铝原子的扩散能力有关。IMCs的生长机制分为两个阶段:(1) 在Ti/Al界面处平行生长;(2) 沿厚度方向生长[15]。根据Ti-Al二元相图,Ti-Al体系中可能生成的IMCs有TiAl、TiAl2、Ti2Al5、TiAl3、Ti3Al等[16-17]。各IMCs反应生成式如下:
Ti+Al=TiAl1/4Ti+3/4Al=1/4TiAl33/4Ti+1/4Al=1/4Ti3Al (1) 由吉布斯自由能可知,吉布斯自由能越小,则该反应越容易进行,且化合物稳定性越好[18]。根据吉布斯自由能计算(表4[19])可知,相对于TiAl和Ti3Al,TiAl3是吉布斯自由能最低的IMCs,虽然TiAl2、Ti2Al5具有更低的吉布斯自由能,但其是TiAl作为中间物经过一系列反应的产物[20],因此,TiAl3是最先生成的化合物,这与EDS和XRD分析结果一致。
2.3 力学性能分析
对Type C方式下得到的双面焊接接头进行显微硬度测试,分别对焊接接头熔合区深度方向及垂直于焊缝方向进行测试,得到的显微硬度分布曲线如图8所示。从图8(a)中可以看出,自Al层向Ti层分析,Al层熔合区的显微硬度趋于稳定,平均硬度约为HV 76.5,相较于未焊接前的Ti/Al层状复合板母材,Al层的平均显微硬度提高了70%。在Al层处硬度发生突变,这是由于在焊接过程中,熔融态的Ti流入Al层熔池中,导致硬度突然升高。Ti/Al界面扩散层的平均硬度约为HV 281.7,相较于母材,平均硬度提高了1倍以上,这是由于在扩散层处生成脆而硬的TiAl、TiAl2、TiAl3等IMCs。Ti层平均显微硬度约为HV 548.5,相较于母材,显微硬度提高了55%。
从图8(b)中可以看出,Ti、Al垂直于焊缝方向的显微硬度分布均呈现“马鞍状”,即显微硬度在熔合区达到最大,向两侧分布逐渐降低。显微硬度分布区域分为母材区(Base metal,BM)、热影响区(Heat affected zone,HAZ)、熔合区(Fusion zone,FZ),显微硬度均是关于焊缝中心呈对称分布。对于Ti层焊接接头硬度分布,TC4的BM组织为α+β双相组织,HAZ组织以β相居多,FZ组织为硬度较高的α'相,β相的硬度要低于α'相,BM未发生相变。因此,Ti层的硬度分布是FZ>HAZ>BM。对于Al层焊接接头硬度分布,FZ硬度高是由于6061 Al的等轴晶粒细化和晶界强化的原因[21],HAZ的较低硬度是由于该区域发生的晶粒粗化造成的。
对Type C方式双面焊接接头进行拉伸性能测试,图9(a)为Ti/Al层状复合板双面焊接接头不同工艺参数下的应力-应变曲线。图9(b)为不同参数下复合板材焊接接头的力学性能,包括极限抗拉强度(Ultimate tensile strength,UTS)、屈服强度(Yield strength,YS)和延伸率(Elongation,EL)。可以看出,随着Ti层电子束流的增大,UTS与EL均呈现先增大后减小的趋势,YS缓慢提高。其中,在Ti层电子束流为75 mA时,焊接接头的抗拉强度和延伸率达到最大,分别为304.6 MPa和10.36%。相较于Ti/Al层状复合板母材,母材经拉伸测试,抗拉强度为537.8 MPa,焊接接头的抗拉强度达到了母材的57%。
抗拉强度先增大后减小的原因是当Ti层电子束流较小时,Ti/Al界面处容易形成空洞等缺陷,导致强度下降;当Ti层电子束流过大时,容易在焊接接头出现冶金裂纹等缺陷,导致强度降低。Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头强度与塑性低于母材是由于在焊接过程中形成了Ti-Al脆性相TiAl、TiAl2、TiAl3所致。
图10为Ti/Al层状复合板双面焊接接头的拉伸断口形貌。从图10(a)的断口宏观图可以看出,断口表面平齐,无剪切唇,典型的脆性断裂特征。从图10(b)的EDS图谱中可以看出,Al原子向Ti层有明显的扩散,表明有Ti-Al IMCs的形成。Ti/Al界面处分界轮廓明显,图10(d)中框线区域可观察到棒状IMCs,并且之间有空隙存在。这是由于熔化态金属在凝固过程中发生的收缩行为,铝合金与钛合金的热膨胀系数相差较大,同时Ti/Al界面处形成的棒状IMCs交互生长,化合物之间形成空隙,熔化态金属不能及时填充,最终导致缩孔的形成[7]。图10(f)为Ti层的断口形貌,其中Ti层存在大量的撕裂脊,断口形貌较光滑,图10(g)和图10(h)为Al层的断口形貌,Al层中可以发现一些光滑区域和尺寸较小的韧窝,表明Al层的断裂方式主要为脆性断裂,并伴有一部分韧性断裂[22]。总体而言,焊接接头的断裂机制主要为脆性断裂。
![]() 图 10 Type C焊接接头断口形貌:(a) 宏观图;(b) 断口EDS图谱;(c) Ti/Al界面处;(d) 图10(c)中(d)处的放大图;(e) 图10(c)EDS面扫图;(f) Ti层;((g), (h)) Al层Figure 10. Type C fracture profile of welded joint: (a) Macrograph; (b) Fracture EDS; (c) Ti/Al interface; (d) Put a large area of (d) in Fig.10(c); (e) EDS scanning map of Fig.10(c); (f) Ti layer; ((g), (h)) Al layer
图 10 Type C焊接接头断口形貌:(a) 宏观图;(b) 断口EDS图谱;(c) Ti/Al界面处;(d) 图10(c)中(d)处的放大图;(e) 图10(c)EDS面扫图;(f) Ti层;((g), (h)) Al层Figure 10. Type C fracture profile of welded joint: (a) Macrograph; (b) Fracture EDS; (c) Ti/Al interface; (d) Put a large area of (d) in Fig.10(c); (e) EDS scanning map of Fig.10(c); (f) Ti layer; ((g), (h)) Al layer3. 结 论
采用真空电子束焊对热压态Ti/Al层状复合板进行不同方式的焊接,对焊接接头的微观组织、界面行为及力学性能进行了分析,主要结论如下:
(1) Ti层在上单面焊接方式得到的焊接接头易在Ti/Al界面处形成空洞等缺陷;由于残余应力的影响,先Ti后Al双面焊接方式得到的焊接接头容易在Al层出现贯穿裂纹;先Al后Ti双面焊接方式得到的焊接接头表面成形性能良好,其中Ti层电子束流为75 mA,Al层电子束流为43 mA时,焊接接头成形性能较佳;
(2) Ti/Al焊接接头熔合区界面处形成了锯齿状的金属间化合物(IMCs)层,其中,包括TiAl、TiAl2和TiAl3相。显微硬度表明,焊接接头的显微硬度相较于母材有了明显提升,Ti层和Al层的显微硬度均呈现“马鞍状”分布;
(3)先Al后Ti双面焊接方式下,Ti/Al层状复合板焊接接头抗拉强度和延伸率呈现先升高后降低的趋势,当Ti层电子束流75 mA、Al层电子束流43 mA时,焊接接头的极限抗拉强度和延伸率分别为304.6 MPa和10.4%,焊接接头抗拉强度达到母材的57%。
-
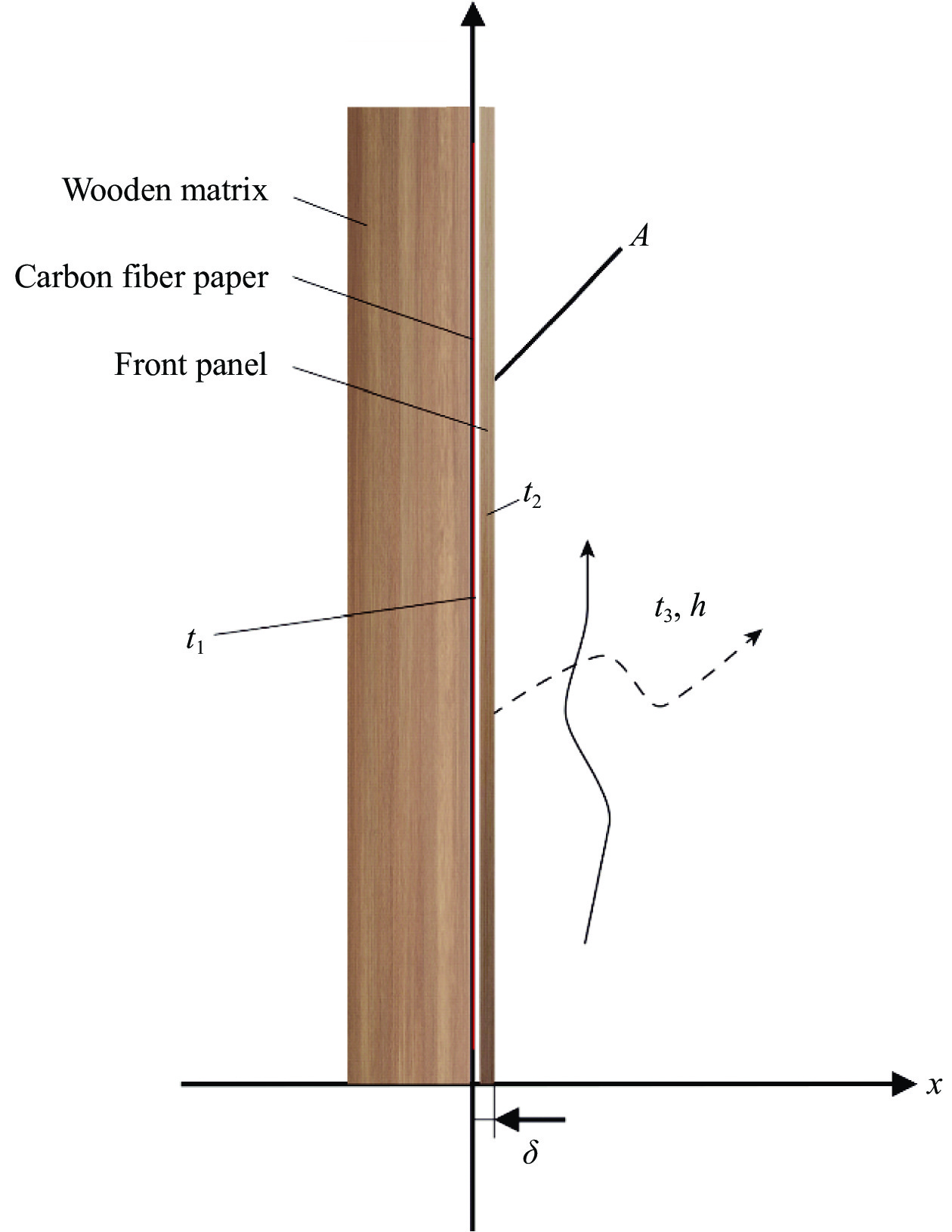
图 3 CFP木质电热复合材料传热过程示意图
Figure 3. Schematic representation of heat transfer of integrated wooden electric heating composites based on CFP
δ—Thickness of front panel; t1—Temperature of CFP; t2—Temperature of the front panel; t3 —Temperature of air; h—Surface coefficient of heat transfer; λ—Heat conductivity coefficient; A—Surface area of composite
表 1 CFP木质电热复合材料电气测试参数
Table 1 Electric parameters of integrated wooden electric heating composites based on CFP
Front panel thickness/mm Resistance/Ω Test voltage/V Actual power/kW 2 397 80 16.12 4 413 81.59 16.12 -
[1] EDIE D D. The effect of processing on the structure and properties of carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,1998,36(4):345-362. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6223(97)00185-1
[2] DALTON N, LYNCH R P, COLLINS M N, et al. Thermoelectric properties of electrospun carbon nanofibres derived from lignin[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:472-479. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.051
[3] 窦光宇. 初识碳纤维[J]. 科技潮, 1998(2):47. DOU Guangyu. Learning about carbon fiber[J]. Science and Gulture,1998(2):47(in Chinese).
[4] 王志平, 叶亮, 路鹏程. 基于介电性能研究碳纤维/环氧复合材料单向板电热作用机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(2):270-277. WANG Zhiping, YE Liang, LU Pengcheng. Electro-thermal influencing mechanism of carbon fiber/epoxy unidirectional laminated composites based on dielectric properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Siniea,2017,34(2):270-277(in Chinese).
[5] 王志平, 孙凌丰, 路鹏程, 等. 电热作用对碳纤维/树脂复合材料界面应力的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(6):1381-1388. WANG Zhiping, SUN Lingfeng, LU Pengcheng, et al. Influence of electro-thermal effect on interfacial stress of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Siniea,2019,36(6):1381-1388(in Chinese).
[6] 路鹏程, 毕亚芳, 王志平, 等. 电热作用对碳纤维树脂基复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(10):2223-2229. LU Pengcheng, BI Yafang, WANG Zhiping, et al. Effects of eletric thermal effect on mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Siniea,2016,33(10):2223-2229(in Chinese).
[7] 纪朝辉, 毕亚芳, 路鹏程, 等. 电热作用对碳纤维/环氧树脂基复合材料吸湿行为的影响[J]. 复合材料学报. 2017, 34(2): 308-313. JI Zhaohui, BI Yafang, LU Pengcheng, et al. Electric-thermal effects on moisture absorption behavior of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Siniea, 2017, 34(2): 308-313(in Chinese).
[8] 李果, 欧阳婷, 蒋朝, 等. 碳纤维/纳米石墨片网络体导热增强石蜡相变储能复合材料的制备及表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(5): 1130-1137. LI Guo, OUYANG Ting, JIANG Chao, et al. Preparation and characterization of carbon fiber-graphite nanoplatelets network renforced paraffin phase change composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Siniea, (in Chinese).
[9] DARZI Mohammad Ebrahimnejad, GOLESTANEH Seyyed Iman, KAMALI Marziyeh, et al. Thermal and electrical performance analysis of co-electrospun-electrosprayed PCM nanofiber composites in the presence of graphene and carbon fiber powder[J]. Renewable Energy,2019,135:719-728. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.028
[10] KONG Q Q, LIU Z, GAO J G, et al. Hierarchical graphene-carbon fiber composite paper as a flexible lateral heat spreader[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2014,24(27):4222-4228. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201304144
[11] REN J, LI L, CHEN C, et al. Twisting carbon nanotube fibers for both wire-shaped micro-supercapacitor and micro-battery[J]. Advanced Materials,2013,25(8):1155-1159, 1224. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201203445
[12] LE V T, KIM H, GHOSH A, et al. Coaxial fiber supercapacitor using all-carbon material electrodes[J]. ACS Nano,2013,7(7):5940-5947. DOI: 10.1021/nn4016345
[13] 施云舟, 王彪. 碳纤维导电纸的研究现状及其应用[J]. 化工新型材料, 2014, 42(4):192-197. SHI Yunzhou, WANG Biao. Research progress and application of carbon fiber reinforced conductive paper[J]. New Chemical Materials,2014,42(4):192-197(in Chinese).
[14] ZHANG Xuejun, SHEN Zengmin. Carbon fiber paper for fuel cell electrode[J]. Fuel,2002,81(17):2199-2201. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00166-7
[15] MA T Y, RAN J, DAI S, et al. Phosphorus-doped graphitic carbon nitrides grown in situ on carbon-fiber paper: Flexible and reversible oxygen electrodes[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International ed in English),2015,54(15):4646-4650. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201411125
[16] KONG D, WANG H, LU Z, et al. CoSe2 nanoparticles grown on carbon fiber paper: An efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2014,136(13):4897-4900. DOI: 10.1021/ja501497n
[17] SHI Y Z, WANG B. Mechanical properties of carbon fiber/cellulose composite papers modified by hot-melting fibers[J]. Progress in Natural Science-Materials International,2014,24(1):56-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2014.01.006
[18] KIM T J, CHUNG D D L. Carbon fiber mats as resistive heating elements[J]. Carbon,2003,41(12):2436-2440. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00288-4
[19] 汤龙其, 令旭霞, 王士华, 等. 聚吡咯/碳纤维纸电热复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6): 1426-1433. TANG Longqi, LING Xuxia, WANG Shihua, et al. Preparation and properties of polypyrrole/carbon fiber paper electricthermal composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Siniea, 2020, 37(6): 1426-1433 (in Chinese).
[20] 袁全平, 梁善庆, 傅峰. 碳纤维电热功能复合纤维板的制备工艺[J]. 木材工业, 2017, 31(4):14-18. YUAN Quanping, LIANG Shanqing, FU Feng. Electric heating composites made from carbon fiber paper and fiberboard[J]. China Wood Industry,2017,31(4):14-18(in Chinese).
[21] SONG Jianbin, YUAN Quanping, LIU Xueshen, et al. Combination of nitrogen plasma modification and waterborne polyurethane treatment of carbon fiber paper used for electric heating of wood floors[J]. Bioresources,2015,10(3):5820-5829.
[22] 肖瑞崇, 陈玉和, 包永洁, 等. 竹木电热复合材料的通电老化性能研究[J]. 木材工业, 2017, 31(4):19-23. XIAO Ruichong, CHEN Yuhe, BAO Yongjie, et al. Electrifying aging performance of bamboo-wood thermoelectric composites[J]. China Wood Industry,2017,31(4):19-23(in Chinese).
[23] 黄成建, 包永洁, 李能, 等. 不同胶黏剂竹木复合电热地板的基本特性[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2017, 34(2):369-373. DOI: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2017.02.023 HUANG Chengjian, BAO Yongjie, LI Neng, et al. Adhesives used to make bamboo/wood composite electro-thermal plywood[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University,2017,34(2):369-373(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11833/j.issn.2095-0756.2017.02.023
[24] 袁全平. 木质电热复合材料的电热响应机理及性能研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. YUAN Quanping. Performance and electric heating response mechanism of wooden electric heating composites[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2015(in Chinese).
[25] YUAN Quanping, FU Feng. Application of carbon fiber paper in integrated wooden electric heating composite[J]. Bioresources,2014,9(3):5662-5675.
[26] SONG J B, HU H B, ZHANG M X, et al. Thermal aging properties and electric heating behaviors of carbon fiber paper-based electric heating wood floors[J]. Bioresources,2017,12(4):9466-9475.
[27] 杨世铭, 陶文栓. 传热学[M]. 第四版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. YANG Shiming, TAO Wenshuan. Heat transfer[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006(in Chinese).
[28] 梁善庆, 李思程, 柴媛, 等. 内置电热层实木复合地板表面温度变化规律及模拟[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2018, 40(11):112-122. LIANG Shanqing, LI Sicheng, CHAI Yuan, et al. Change law and simulation of surface temperature for electric heating engineered wood flooring with built-in electrothermal layer[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2018,40(11):112-122(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李红斌,房桂干,邓拥军,施英乔,韩善明,焦健,盘爱享. 碳纤维纸张电热及温敏性效应研究. 材料科学与工艺. 2024(01): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 石姗姗,吕航宇,吕超雨,苏智博,孙直. 随机多孔碳纤维纸的非线性面外压缩本构模型. 工程力学. 2023(01): 249-256 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋耐超,王瑞琦,赵家豪,杜璇,王璐. 基于电缆局部碳纤维复合材料放电性能影响的试验分析. 粘接. 2023(01): 98-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘霄,于志明,张扬,郭晋,曾广琛. 半导体制热实木复合地板的传热性能评价. 北京林业大学学报. 2023(05): 155-162 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 梁善庆,陶鑫,李善明,姜鹏,张龙飞,傅峰. 碳系木质电热复合材料制备及耐老化研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2022(04): 1469-1485 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)
-




 下载:
下载: