Adsorption of Cd(II) in water by graphene oxide/calcium alginate hydrogel composite membrane
-
摘要: 将氧化石墨烯(GO)、致孔剂与海藻酸钠共混后与CaCl2交联制备的GO/海藻酸钙(CA)水凝胶复合膜作为含重金属废水的吸附材料。采用SEM和TEM表征了复合膜的表面形貌及透射性能,且分析了GO的加入对复合膜的力学性能、平均孔径、水通量及表面官能团的影响。为探究GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的吸附性能,考察了其吸附Cd(II)的影响因素:pH(6~7)值、初始离子浓度、接触时间、温度(三者均正相关)。用FTIR、XPS在吸附前后对复合膜进行了表征;引入了吸附动力学和等温线模型分析其吸附机制。探究结果表明GO的加入提高了复合膜的力学性能、平均孔径及水通量;吸附过程遵循Langmuir等温线,属于单层吸附,拟合得到的最大吸附量为173.61 mg/g;伪一级和伪二级吸附动力学分别在低浓度和高浓度时能较好地描述吸附过程的动力学行为;吸附机制主要为物理作用力吸附和离子交换。经过5个连续的吸附-解吸循环证明了GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的可重复利用性。Abstract: The crosslinked graphene oxide (GO)/calcium alginate (CA) hydrogel composite membranes, prepared by blending GO, porogenas as well as Na alginate hydrogel (SA), cross-linking with CaCl2, were used as adsorbent for wastewater containing heavy metal ions. SEM and TEM were used to characterize the composite membranes. The influences of GO on the mechanical properties, average pore diameter, water flux and surface functional groups of the composite membrane were analyzed. To explore the adsorption performance of GO/CA hydrogel composite membrane, the influencing factors of Cd(II) adsorption including pH (6-7), initial ion concentration, contact time and temperature (all positively correlated) were investigated. The composite membranes before and after adsorption of Cd(II) were characterized by FTIR and XPS; The adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherm model were introduced to analyze the adsorption mechanism. The results show that the introduction of GO improves the mechanical properties, average pore diameter and water flux of the composite membrane. The adsorption process follows the Langmuir isotherm, belonging to the monolayer adsorption. The maximum adsorption capacity is 173.61 mg/g. The pseudo-first and pseudo-second adsorption kinetics could describe the adsorption process at low and high concentration, respectively. The adsorption mechanism is mainly physical force adsorption and ion exchange. The recyclability of the GO/CA hydrogel composite membranes was demonstrated by five successive adsorption-desorption cycles.
-
Keywords:
- graphene oxide /
- hydrogel /
- composite membrane /
- adsorption /
- Cd(II)
-
重金属对水环境的污染是当今面临的最严重的一类环境污染,主要由采矿、冶金、电镀、石油化工和纺织业等行业的发展引起的[1-2]。与有机污染物不同,重金属污染具有不可降解性。未经处理的或未处理完全的含重金属废水排放到环境中,会通过生物累积危害到食物链的各环节,破坏生态平衡。Cd(II)是一种典型的毒性极大的重金属离子,美国环保署将其列为B1类致癌物,对人体的肾脏有极大的危害[3-4]。因此,工业废水中Cd(II)的去除是至关重要的。
去除水中Cd(II)常用方法有混凝-絮凝、微生物、膜分离、吸附等。其中吸附法因其效果好、成本低、工艺简单等优点成为最常用的方法[5-8]。海藻酸钠(SA)是一种天然多糖,可与CaCl2溶液交联形成一种吸附性能极好的水凝胶材料—海藻酸钙CaAlg(CA)。以CA为基材的小球在重金属的吸附方面效果显著[9]。氧化石墨烯(GO)是石墨多次化学氧化后得到的含有大量羟基和羧基的常见改性材料。它具有极高的比表面积和电负性,这些特性也使其成为一种理想的重金属离子吸附材料[10]。将SA、致孔剂和GO混合后再与CaCl2交联,GO的含氧基团也能参与到交联过程,从而使三者形成有机统一的多孔材料,而且各组分间的相互作用更强,这对其吸附性能和力学性能都有很大的提升。
在吸附过程,相对于球型吸附剂,膜上的吸附位点能够更准而快地捕捉重金属离子[11]。将GO与致孔剂共混在SA溶液中,与CaCl2交联制得的GO/CA水凝胶复合膜将会是一种优良的重金属离子吸附剂。由于SA良好的成膜性[12],此复合膜还可用作膜过滤技术。将其吸附性能与截留性能结合,从而可在实际水处理工程中达到更好的应用效果。目前还没有关于它对重金属离子吸附性能的相关公开报道。
本文将制备一种新型的GO/CA复合膜材料,用于探究其对Cd(II)的吸附性能和吸附机制。将吸附前后的GO/CA水凝胶复合膜进行表征;并探究常见的变量因素对其吸附容量的影响。还将引入吸附动力学、吸附等温线来分析其吸附机制。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
海藻酸纳(Sodium alginate,分析纯)、硝酸镉(Cd(NO3)2,分析纯)、HNO3(分析纯),购于国药化学试剂有限公司;天然鳞片石墨,购于南京先丰纳米有限公司;尿素(Urea)、CaCl2、KMnO4、NaNO3 H2O2,分析纯,均购于天津科密欧化学试剂有限公司;浓HCl、浓H2SO4,分析纯,均购于成都科隆化学品有限公司。
1.2 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的制备
将2.5 g SA和2.5 g尿素加入100 mL超声均匀的GO(制备参考文献[13])溶液(0.3 wt%),室温下用磁力搅拌器以400 r/min的速率搅拌36 h。搅拌均匀的铸膜液在室温下静置36 h以脱除气泡。将铸膜液倒在玻璃板上,用刮膜棒将其铺平后将玻璃板平行地放入2.5 wt%的CaCl2溶液中交联。膜从玻璃板脱落后取出玻璃板。复合膜在48 h后取出,以达到交联完全和尿素溶出的目的。将交联完全的膜用去离子水洗脱后即可置于1 wt%的CaCl2溶液中保存备用。为制备纯CA水凝胶膜,将2.5 g SA和2.5 g尿素加入100 mL去离子水中,其余步骤同上。
1.3 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的表征
用扫描电镜(SEM,JMS6510LV, Japan)和透射电镜(TEM, JEM-2100, Japan)来表征GO/CA水凝胶复合膜是否制备成功;将GO/CA水凝胶复合膜裁成10 cm×1 cm的样本条,用拉力测定仪(电子单纱强力仪,HD021NS,南通宏大实验仪器有限公司)进行力学性能测试,每个样品测10次,取平均值;用称重法计算GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的平均孔径:先将膜片浸没在去离子水中24 h,取出后用滤纸擦干表面水分。将此湿膜片称重,通过称重法[13]确定其孔隙率ε,再用Guernout-Elford-Ferry公式[13]计算平均孔径r;两种复合膜的水通量使用小型平板纳滤错流过滤系统在25℃、0.1 MPa的条件下进行测定。试验前,在0.15 MPa的压力下用去离子水预压,用通量计算公式[13]计算通量;GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的表面官能团用傅里叶衰减全反射红外光谱仪(FTIR-ATR, Thermoelectroncorp, iS50, 美国)测定。
1.4 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能测试
本文将探究溶液pH、Cd(II)初始离子浓度、接触时间、温度等因素对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响。溶液的pH用0.1 mol/L HNO3溶液调节。每组实验均将300 mL Cd(NO3)2溶液置于500 ml的烧杯中,然后加入复合膜片0.06 g,用保鲜膜封存静置。在固定时间,每次从同一位置的上层溶液用滴管吸取5 mL的样品,并测定其Cd(II)浓度。达到吸附平衡后,用镊子将膜片夹出。Cd(II)在膜上的吸附量按下式计算:
Vnt(i)=Vnt(i−1)−5 (1) Qnt=n∑i=1(Cnt(i−1)−Cnt(i))⋅Vnt(i−1)m (2) 式中:Qnt是在时间t的吸附容量(mg·g−1);Cnt是第i次采样时的Cd(II)浓度(mg·L−1);Vnt(i)是第i次取样时Cd(NO3)2溶液的体积(mL);m是用于吸附的GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的重量(g)。溶液中的Cd(II)浓度由电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-5000,聚光科技(杭州)股份有限公司)测定。
为探究pH的影响,将溶液pH分别调至3、4、5、6、7,在初始离子浓度为80 mg·L−1、温度为318 K的条件下进行吸附;为探究GO的影响,在pH=7、288 K、初始离子浓度50 mg·L−1的条件下,分别将0.06 g的CA膜和GO/CA水凝胶复合膜加入Cd(NO3)2溶液进行静态吸附实验;为探究初始离子浓度的影响,在pH=7、318 K的条件下,配制梯度浓度(10、40、80 mg·L−1)的溶液进行静态吸附实验;为探究温度和接触时间的影响,在初始离子浓度为50 mg·L−1、pH=7的条件下,设置三组温度(288 K、303 K、318 K)的静态吸附实验;为探究GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的再生性,在pH=7,初始浓度为80 mg·L−1的条件下进行5个吸附-解吸循环。选取0.4 mol/L HCl溶液作为洗脱剂,洗脱后用去离子水冲洗。置于CaCl2溶液中12 h恢复强度后,进入下一循环。
1.5 吸附机制
为探究吸附过程的动力学规律,引入伪一级、伪二级、Elovich动力学模型[1]和颗粒内扩散模型[2];引入Freundlich和Langmuir模型[2]对吸附过程进行拟合来探究Cd(II)在GO/CA水凝胶复合膜上的平衡吸附;由复合膜本身的性质及其对重金属离子的吸附特点可知,吸附过程存在离子交换。定量检测吸附平衡后的Cd(NO3)2溶液,确定溶液中Ca(II)的增加量,来判定Cd(II)与Ca(II)的离子交换在吸附中所占的比例。RL和N分别为单独定义的一个无量纲常数和Freundlich液相吸附等温指数。
1.6 吸附检测方法
用傅里叶红外衰减全反射红外光谱仪定性表征吸附Cd(II)前后的GO/CA水凝胶复合膜。对吸附Cd(II)前后的GO/CA水凝胶复合膜喷金处理后进行X射线能谱分析(XPS K-Alpha Thermo, AlKα)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的表面形貌、微观结构、渗透性能及力学性能
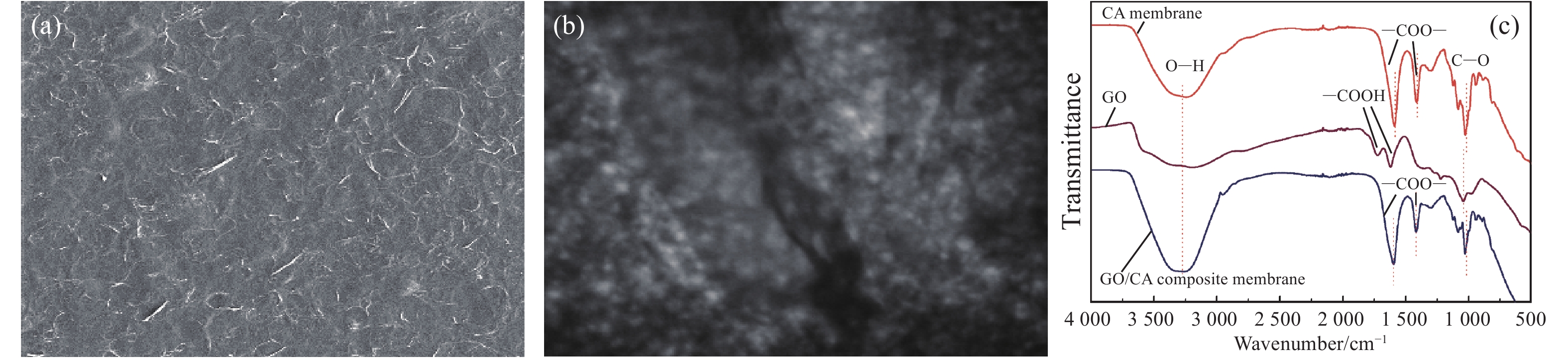
GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的表面形貌和微观结构如图1(a)和图1(b)所示。从图1(a)可以看出,GO/CA水凝胶复合膜表面平整,有烘干留下的褶皱。从图1(b)可以看出,在水凝胶均匀的网络骨架结构上有片层状的GO,两者均匀地结合,说明成功制备了GO/CA水凝胶复合膜。
纯CA膜和GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的红外光谱如图1(c)所示。可见,加入GO后,膜表面官能团的类型未发生变化。在3 300 cm−1附近的特征峰为—OH的伸缩振动峰,1 600和1 400 cm−1附近的特征峰为羧酸盐的反对称和对称伸缩峰,1 300 cm−1附近为C—H的伸缩振动峰,1 000 cm−1附近的峰为C—O的伸缩振动峰。而对于GO,羧基的特征峰位于1 723和1 618 cm−1。以上结果也说明了加入到铸膜液中的GO,参与了制膜过程的交联反应,从而使其由羧基状态转化成了羧酸盐状态。
表1是CA和GO/CA水凝复合膜的渗透性能。可以看出,加入GO后,膜的孔隙率和平均孔径都明显地增大。这是由于加入GO使水凝胶骨架之间有更大的支撑空间,进而膜的内部结构更加立体。内部孔隙率的增加也提升了膜的输水性能,从而使膜的水通量增大。
表 1 CA膜和GO/CA水凝复合膜的渗透性能Table 1. Permeability of CA membrane and GO/CA hydrogel composite membraneMembrane Mean pore size/nm Poriness/% Water flux/(L·m-2h-1) CA 10.6 86.5 14.7 GO/CA 12.6 90.1 18.1 CA膜和GO/CA水凝复合膜的力学性能如表2所示。可以看出GO的加入明显提升了其机械强度。这是由于GO加入后,三者相互交联,形成比CA膜更稳定的结构。
表 2 CA膜和GO/CA水凝复合膜的力学性能Table 2. Mechanical properties of the CA membrane and GO/CA hydrogel composite membraneMembrane Elongation at break/% Fracture energy/(kJ·m−2) Stress/MPa CA 95 34 914 GO/CA 143 65 1 725 2.2 GO对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响
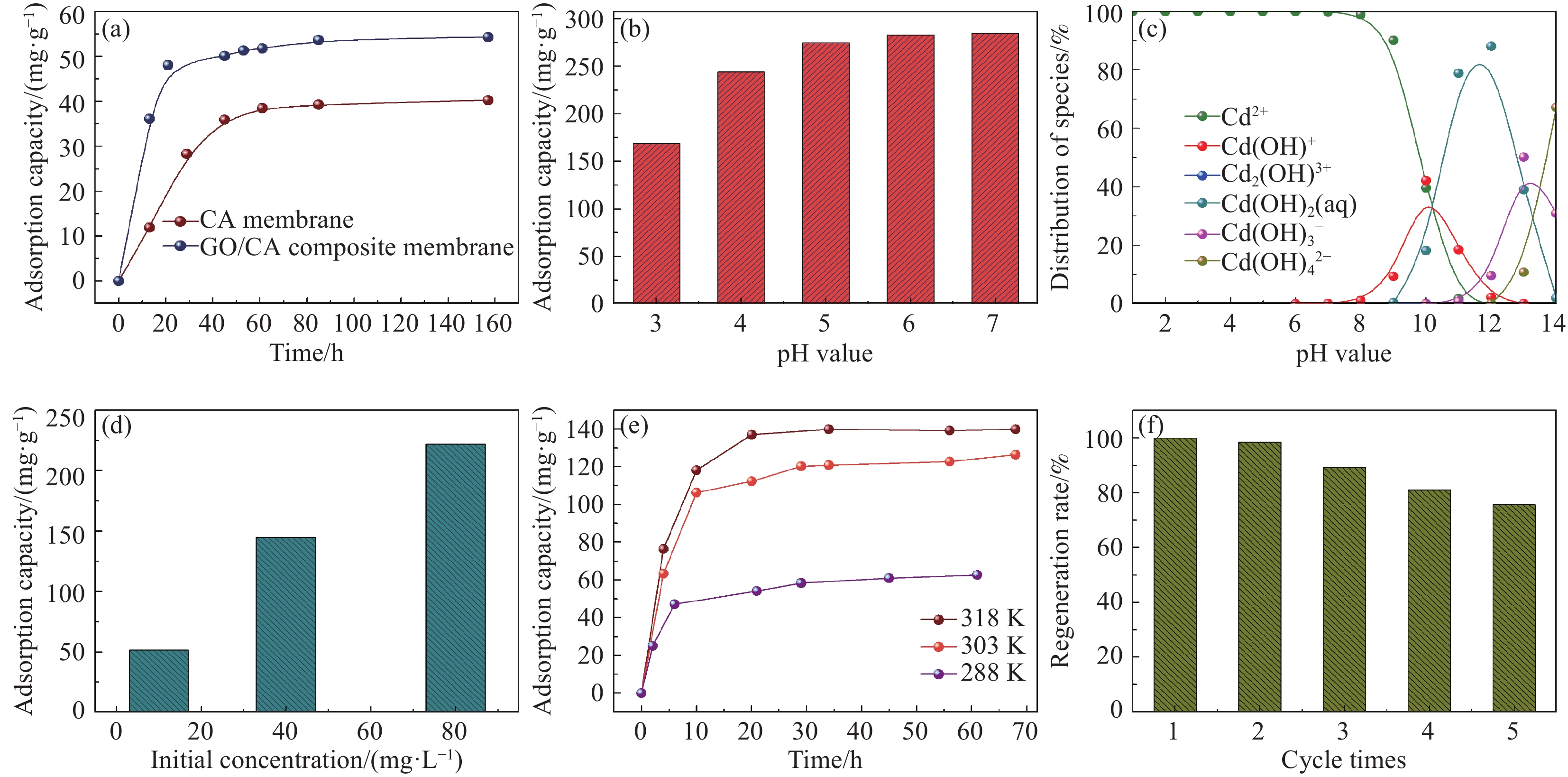
图2(a)是CA膜和GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的比较。可以看出,在添加GO后,膜的吸附性能明显提升。由于加入GO,膜表面有了更多的吸附位点(含氧基团),提高了膜的吸附能力。且加入GO会增大膜的孔隙率,为吸附提供更大的空间。
2.3 溶液初始pH值对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响
溶液初始pH值对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响如图2(b)所示。可以看出在低pH时,吸附效果较差。随pH升高,吸附容量逐渐增大,在pH为6~7时保持稳定。这是由于pH影响膜的表面电性。GO/CA水凝胶复合膜表面有大量羧基等含氧基团。在溶液中H+浓度较大时(pH<pKa (3.38~3.65)[14]),含氧基团被质子化,使膜表面带正电。这严重影响带正电的重金属离子与膜的静电吸引作用,阻碍了吸附反应。随着pH升高,膜表面质子化逐渐消失,负电性恢复,吸附容量也逐渐增加,在pH=6~7时达到稳定。从Cd(II)离子种类分布(图2(c))可看出,pH升到弱碱性时,Cd(II)的水解增强,形成氢氧化物甚至会出现沉淀,这会影响吸附反应的进行。因此pH=6~7是最适宜的条件。
2.4 Cd(II)始浓度对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响
图2(d)为Cd(II)初始浓度不同时GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的吸附量。可以看出吸附量与浓度成正相关。由于离子浓度较大,溶液对金属离子会产生更强的驱动力[15]。较大的离子浓度,还会使离子与GO/CA水凝胶复合膜之间有更大的碰撞几率和接触密度[16]。这些是吸附的有利因素,因此Cd(II)初始浓度与吸附量呈正相关。
2.5 温度和吸附时间对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响
图2(e)为不同温度下时间与吸附量的关系。可以看出,吸附量随时间先迅速增长后缓慢增长,最后趋于稳定。这是由于吸附初期离子浓度大且空余吸附位点多。随吸附位点逐渐被占据,吸附速度减缓,在20 h达到平衡。由此可认为吸附最佳时间为20 h。还可知,吸附量与温度正相关。但当温度上升到一定值后其影响变小,这是由于膜表面吸附位点数量固定,吸附位点达到饱和,吸附量就基本保持稳定,不会再随温度升高而增大。
2.6 解吸次数对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附性能的影响
如图2(f)所示,解吸次数对GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)有一定的影响,但在5次吸附-解吸循环后仍能保持70%的吸附量,说明复合膜具有可重复利用性。在经过吸附-解吸循环后,膜的吸附量下降的原因是:吸附过程中,不可逆吸附占据一定的比例,使这部分吸附位点难以循环利用;且解吸过程具有不完全性,这也使膜在再吸附过程失去一部分吸附能力,使吸附量下降。
2.7 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附动力学
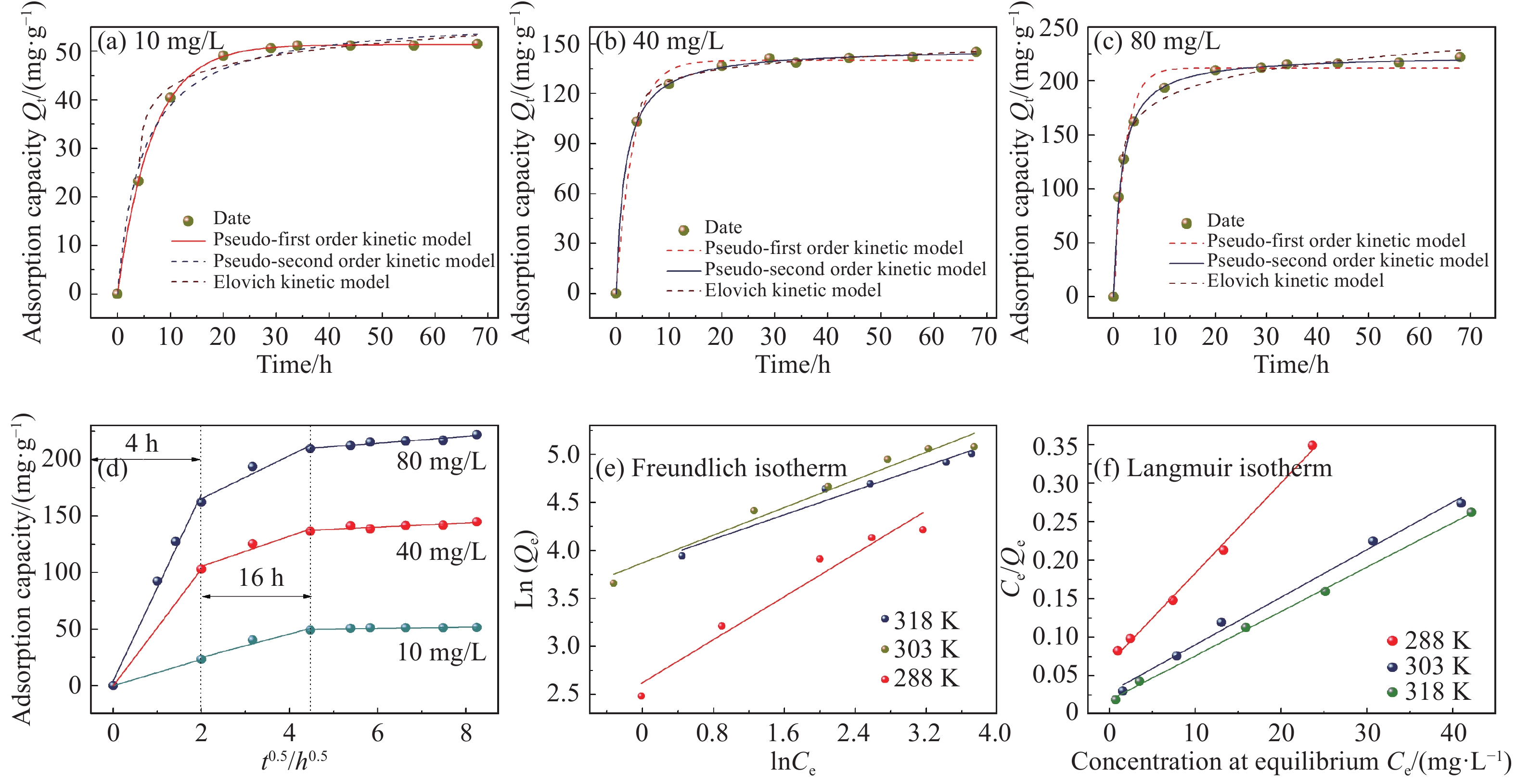
初始浓度C0不同时,GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)动力学拟合结果如图3(a)~3(d)和表3所示。在低浓度下,吸附过程与伪一级动力学模型更一致。拟合优度R2更接近于1,平衡吸附量Qe拟合值更接近于实验数据。而Cd(II)浓度增加到40 mg·L−1以上时,吸附过程则更符合伪二级吸附动力学模型。图3(d)是颗粒内扩散模型结果,可以看出复合膜吸附Cd(II)明显地分为了三个阶段:表面吸附阶段、颗粒内部扩散阶段和吸附平衡阶段。其中表面吸附阶段的反应时长为4 h,颗粒内扩散阶段的反应时长为16 h,因此第二阶段被认为是吸附过程的速率控制阶段,说明此吸附过程是颗粒内扩散为主的三阶段吸附[17]。
表 3 Cd(II)的初始浓度C0不同时GO/CA水凝复合膜吸附性能的动力学模型拟合参数Table 3. Kinetic model parameters of GO/CA hydrogel composite membrane adsorption at different initial concentration C0 of Cd(II)C0/(mg·L−1) Pseudo-first order kinetic model Pseudo-second order kinetic model Elovich model k1/min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) R2 A B R2 10 0.1530 51.37 0.9999 0.0826 57.28 0.9874 34.53 −4.497 0.964 1 40 0.3131 140.0 0.9919 0.0116 147.5 0.9993 113.7 −7.579 0.9785 80 0.4497 211.9 0.9804 0.0066 224.1 0.9993 135.3 −22.17 0.9714 Notes: C0—Initial concentration of Cd(II); R2—Goodness; Qe—Adsorption capacity at adsorption equilibrium; k1, k2 and A—Constant of kinetic models, respectively; B—Coefficient of elovich kinetic models. 2.8 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附等温线模型
图3(e)、3(f)和表4是不同温度下GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)等温线拟合结果。可以看出,此吸附过程更符合Langmuir模型,由于拟合优度R2更接近于1,说明吸附过程属于单层吸附[18]。计算得到在288、303和318 K时RL均在0~1范围内,说明GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)是有利吸附。Freundlich模型的R2都大于0.9,其参数有较大参考价值。通过拟合得到的N分别为1.79、2.77和3.15,可判断吸附过程属于物理吸附。
表 4 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)的吸附等温线模型参数Table 4. Isothermal adsorption model parameters of Cd(II) adsorbed by GO/CA hydrogel composite membraneTemper-
ature/KFreundlich isotherm Langmuir isotherm kf N R2 kl Qm/(mg·g−1) R2 288 13.81 1.787 0.9445 0.1766 85.40 0.9914 303 47.99 2.770 0.9618 0.2168 161.8 0.9952 318 47.67 3.147 0.9589 0.3146 173.6 0.9981 Notes: kf—Capacity factor of Freundlich; N—Liquid phase adsorption isotherm index of Freundlich; k1—Langmuir constant of affinity point; Qm—Adsorption capacity of single layer. 2.9 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜离子交换机制
在吸附达到平衡后,测定溶液中出现的Ca(II)的浓度为2.32 mg·L−1。由此可知离子交换作用在吸附过程占了较大的比重,经计算得到物理作用力吸附、离子交换作用及溶液中剩余的未被吸附的Cd(II)的比例分别是59.94%、32.33%、7.72%。
2.10 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜表面化学官能团
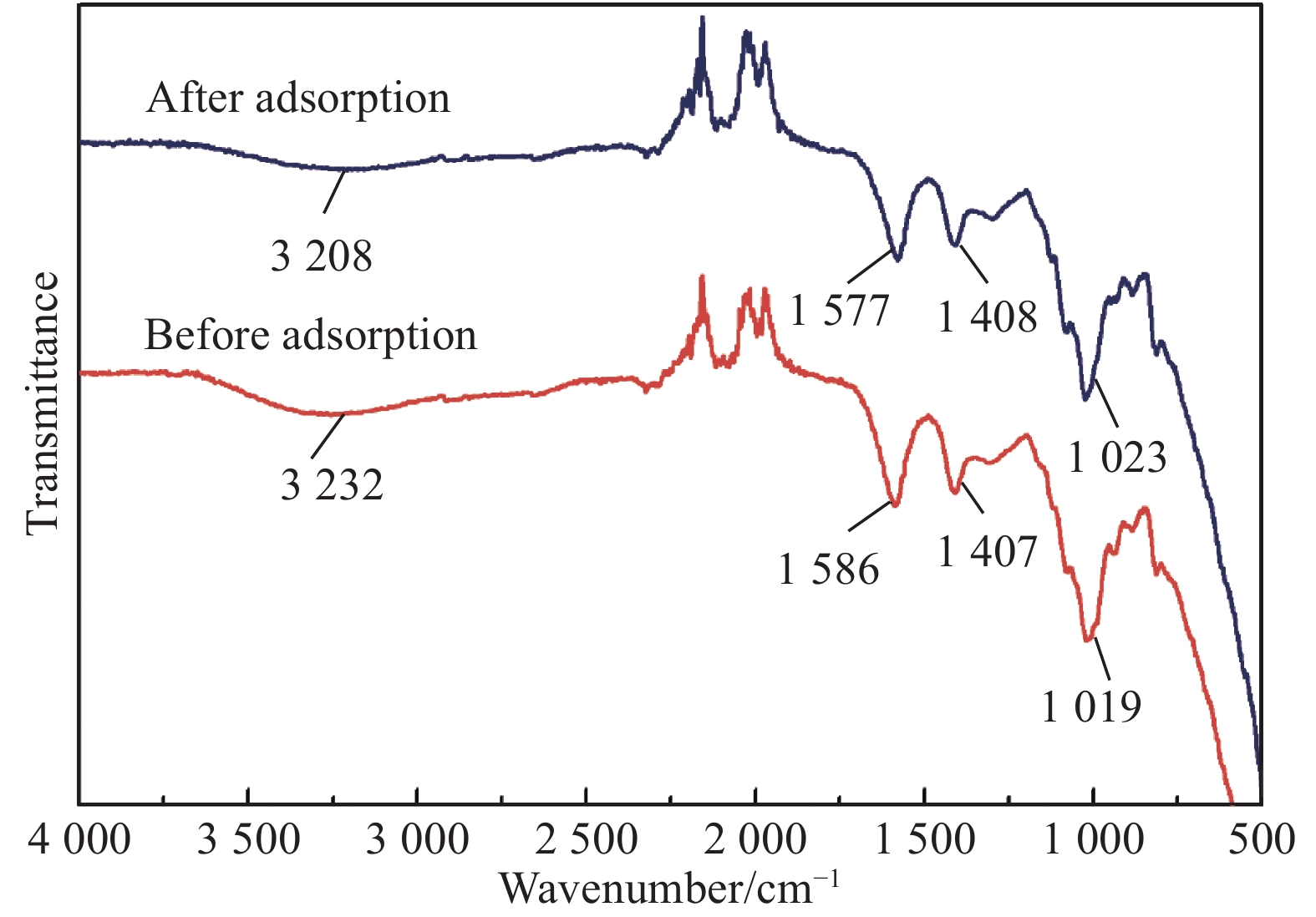
图4是吸附Cd(II)前后GO/CA水凝胶复合膜的FTIR图谱。在3 232、1 586、1 407和1 019 cm−1处的四个特征峰分别代表—OH、羧基上的—C=O和—C—OH及C—O的伸缩振动峰。证明膜表面有大量羟基和羧基等亲水基团。吸附后,四个特征峰的位置分别移动到3 208、1 577、1 408和1 023 cm−1,强度也轻微地降低。没有新的特征峰出现,说明吸附过程发生了配位反应或离子交换[19-20]。这表明化学吸附可能占有一定的比重,但Cd(II)在GO/CA水凝胶复合膜上的吸附仍然以物理吸附作用为主。
2.11 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜表面元素构成及化学态
图5是GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)前后的XPS能谱。图5(a)为吸附前后复合膜的XPS全谱。可以看出,吸附重金属离子后,Ca2+的吸收峰强度减弱,且在405 eV出现新的吸收峰,即Cd 3d的吸收峰图5(b)。证明吸附反应发生,也证明了Ca2+与Cd2+发生了离子交换作用。图5(c)为吸附前后膜的C元素的XPS拟合分峰结果。吸附后,羧基和羟基的强度减弱,峰位置也发生变化,说明复合膜中的羟基、羧基等基团参与了吸附过程,与金属离子形成了配合物。
3. 结 论
(1)成功制备了氧化石墨烯(GO)/海藻酸钙(CA)水凝胶复合膜。加入GO提高了GO/CA复合膜的力学性能、平均孔径、水通量及吸附性能。复合膜对Cd(II)的吸附性能良好,拟合得到的最大吸附量为173.61 mg·g−1,平衡时间为20 h。最适pH为6~7,吸附量与初始离子浓度、接触时间、温度都成正相关。
(2) GO/CA水凝胶复合膜对重金属离子Cd(II)的吸附过程符合Langmuir吸附等温线模型,属于单层有利的物理吸附。在低离子浓度,吸附过程遵循伪一级吸附动力学,在较高浓度遵循伪二级吸附动力学,是以颗粒内扩散为控速步骤的三阶段吸附。
(3)经过5个吸附-解吸循环,GO/CA水凝胶复合膜对Cd(II)的吸附量仍能保持原吸附量的70%,证明了其可重复利用性。
-
表 1 CA膜和GO/CA水凝复合膜的渗透性能
Table 1 Permeability of CA membrane and GO/CA hydrogel composite membrane
Membrane Mean pore size/nm Poriness/% Water flux/(L·m-2h-1) CA 10.6 86.5 14.7 GO/CA 12.6 90.1 18.1 表 2 CA膜和GO/CA水凝复合膜的力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of the CA membrane and GO/CA hydrogel composite membrane
Membrane Elongation at break/% Fracture energy/(kJ·m−2) Stress/MPa CA 95 34 914 GO/CA 143 65 1 725 表 3 Cd(II)的初始浓度C0不同时GO/CA水凝复合膜吸附性能的动力学模型拟合参数
Table 3 Kinetic model parameters of GO/CA hydrogel composite membrane adsorption at different initial concentration C0 of Cd(II)
C0/(mg·L−1) Pseudo-first order kinetic model Pseudo-second order kinetic model Elovich model k1/min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) R2 A B R2 10 0.1530 51.37 0.9999 0.0826 57.28 0.9874 34.53 −4.497 0.964 1 40 0.3131 140.0 0.9919 0.0116 147.5 0.9993 113.7 −7.579 0.9785 80 0.4497 211.9 0.9804 0.0066 224.1 0.9993 135.3 −22.17 0.9714 Notes: C0—Initial concentration of Cd(II); R2—Goodness; Qe—Adsorption capacity at adsorption equilibrium; k1, k2 and A—Constant of kinetic models, respectively; B—Coefficient of elovich kinetic models. 表 4 GO/CA水凝胶复合膜吸附Cd(II)的吸附等温线模型参数
Table 4 Isothermal adsorption model parameters of Cd(II) adsorbed by GO/CA hydrogel composite membrane
Temper-
ature/KFreundlich isotherm Langmuir isotherm kf N R2 kl Qm/(mg·g−1) R2 288 13.81 1.787 0.9445 0.1766 85.40 0.9914 303 47.99 2.770 0.9618 0.2168 161.8 0.9952 318 47.67 3.147 0.9589 0.3146 173.6 0.9981 Notes: kf—Capacity factor of Freundlich; N—Liquid phase adsorption isotherm index of Freundlich; k1—Langmuir constant of affinity point; Qm—Adsorption capacity of single layer. -
[1] SUN X F, HAO Y W, GAO Y Y, et al. Superadsor-bent hydrogel based on lignin and montmorillonite for Cu(II) ions removal from aqueous solution[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,127:511-519. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.058
[2] YU Z Z, DANG Q F, LIU C S, et al. Preparation and characterization of poly(maleic acid)-grafted cross-linked chitosan microspheres for Cd(II) adsorption[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,172:28-39. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.039
[3] PENG H B, GAO P, CHU G, et al. Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars[J]. Environmental Pollution,2017,229:846-853. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.004
[4] SHARMA A, LEE B K. Cd(II) removal and recovery enhancement by using acrylamide-titanium nanocomposite as an adsorbent[J]. Applied Surface Science,2014,313(15):624-632.
[5] CUI L, WANG Y G, GAO L, et al. EDTA functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for removal of Pb(II), Hg(II) and Cu(II) in water treatment: Adsorption mechanism and separation property[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,281:1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.043
[6] SASMAL D, KOLYA H, TRIPATHY T, et al. Amylopecting-poly(methylacrylate-co-sodium acrylate): An efficient Cd(II) binder[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,91:934-945. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.022
[7] AHMAD Z, GAO B, MOSA A, et al. Removal of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by biochars derived from potassium-rich biomass[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2017,180:437-449.
[8] SHAN Z B, ZAHNG L W, ZHAO X Y, et al. Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution by mercapto modified coal gangue[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2019,231:391-396.
[9] KARTHIK R, MEENAKSHI S. Removal of Cr(VI) ions by adsorption onto sodiumalginate-polyaniline nanofibers[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,72:711-717. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.09.023
[10] LIM J Y, MUBARAK N M, ABDULLAH E C, et al. Recent trends in the synthesis of graphene and graphene oxide based nanomaterials for removal of heavy metals: A review[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2018,66:29-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2018.05.028
[11] CHEN J H, LIU Q L, HU S R, et al. Adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by glutaraldehydecrosslinkedhumic acid-immobilized sodium alginate porous membrane adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2011,173:511-519. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.023
[12] ZHAO K Y, ZHANG X X, WEI J F, et al. Calcium alginate hydrogel filtration membrane with excellent anti-fouling property and controlled separation performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2015,492:536-546. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2015.05.075
[13] 朱振亚, 王磊, 姜家良, 等. 纳米SiO2-氧化石墨烯/聚偏氟乙烯杂化膜的制备及特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(4):785-792. ZHU Z Y, WANG L, JIANG J L, et al. Preparation and properties of nano SiO2-GO/polyvinylidene fluoride hybrid membrane[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2018,35(4):785-792(in Chinese).
[14] LODEIRO P, FUENTES A, HERRERO R, et al. CrIII binding by surface polymers in natural biomass: The role of carboxylic groups[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2008,5(5):355-365. DOI: 10.1071/EN08035
[15] CHEN J H, LI G P, LIU Q L, et al. Cr(III) ionic imprinted polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate (PVA/SA) porous composite membranes for selective adsorption of Cr(III) ions[J]. Chemical Engneering Journal,2010,165(2):465-473. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.09.034
[16] NAG S, MONDAL A, ROY D N, et al. Sustainable bioremediation of Cd(II) from aqueous solution using natural waste materials: Kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics, toxicity studies and GA-ANN hybrid modeling[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2018,11:83-104.
[17] 谢水波, 罗景阳, 刘清, 等. 羟乙基纤维素/海藻酸钠复合膜对六价铀的吸附性能及吸附机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(1):268-275. XIE S B, LUO J Y, LIU Q, et al. Adsorption characteristics and mechanism of hydroxyethyl cellulose/sodium alginate blend films for uranium(VI)[J]. Acta Materiae Compo-sitae Sinica,2015,32(1):268-275(in Chinese).
[18] DIVISEKARA T, NAVARATNE A N, ABEY-SEKARA A S K. Impact of a commercial glyphosate formulation on adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions on paddy soil[J]. Chemosphere,2018,198:334-341. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.155
[19] 于长江, 王苗, 董心雨, 等. 海藻酸钙@Fe3O4/生物碳磁性复合材料的制备及其对Co (II)的吸附性能和机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(6):1549-1557. YU C J, WANG M, DONG X Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of calcium alginate@Fe3O4/biochar magnetic microsphere and its adsorption characteristics and mechanism for Co (II)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(6):1549-1557(in Chinese).
[20] ALGOTHMI W M, BANDARU N M, YU Y, et al. Alginate–graphene oxide hybrid gel beads: An efficient copper adsorbent material[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2013,397:32-38. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.01.051
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张恒,张保平,肖煜坤,王尹. 氨基硫脲/季铵木质素对铂的吸附. 复合材料学报. 2022(10): 4674-4684 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 狄婧,刘海霞,姜永强,郭金鑫,赵国虎. 聚吡咯/壳聚糖复合膜的制备及其对Cu(Ⅱ)和Cr(Ⅵ)吸附机制. 复合材料学报. 2021(01): 221-231 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 苏凯,廖明旭,张胜利,贺玉龙. 蒙脱石-纤维素复合膜对Cd(Ⅱ)吸附性能研究. 矿物岩石. 2020(04): 1-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-





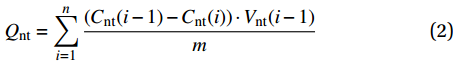
 下载:
下载: