Research Progress of Magnetic Silicate Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants
-
摘要: 光催化是去除水中难降解有机污染物的有效措施,因其高效的矿化能力而显示出巨大的潜力。然而,大多数光催化剂的实际应用受到其粉末形态的制约,使大规模应用成为一个难题。近年来,磁性硅酸盐复合材料在材料科学中因为其稳定和可回收的特性获得了越来越多的关注。本综述回顾了磁性硅酸盐复合材料作为光催化剂的研究现状,探讨了合成、修饰及其降解机制方面的最新进展。最后,对磁性硅酸盐复合材料的研究结果和未来的挑战进行了展望。Abstract: Photocatalysis is an effective method for removing recalcitrant organic pollutants from water, demonstrating significant potential due to its high mineralization efficiency. However, the practical application of most photocatalysts is hindered by their powder form, posing challenges for large-scale use. Recently, magnetic silicate composite materials have garnered increasing attention in the field of materials science due to their stability and recyclability. In this review, we examine the current state of research on magnetic silicate composite materials as photocatalysts, exploring the latest advancements in synthesis, modification, and degradation mechanisms. Finally, we provide an outlook on the research findings and future challenges associated with magnetic silicate composite materials.
-
Key words:
- Photocatalysis /
- Magnetic Materials /
- Organic Pollutants /
- Silicates /
- Degradation /
- Wastewater
-
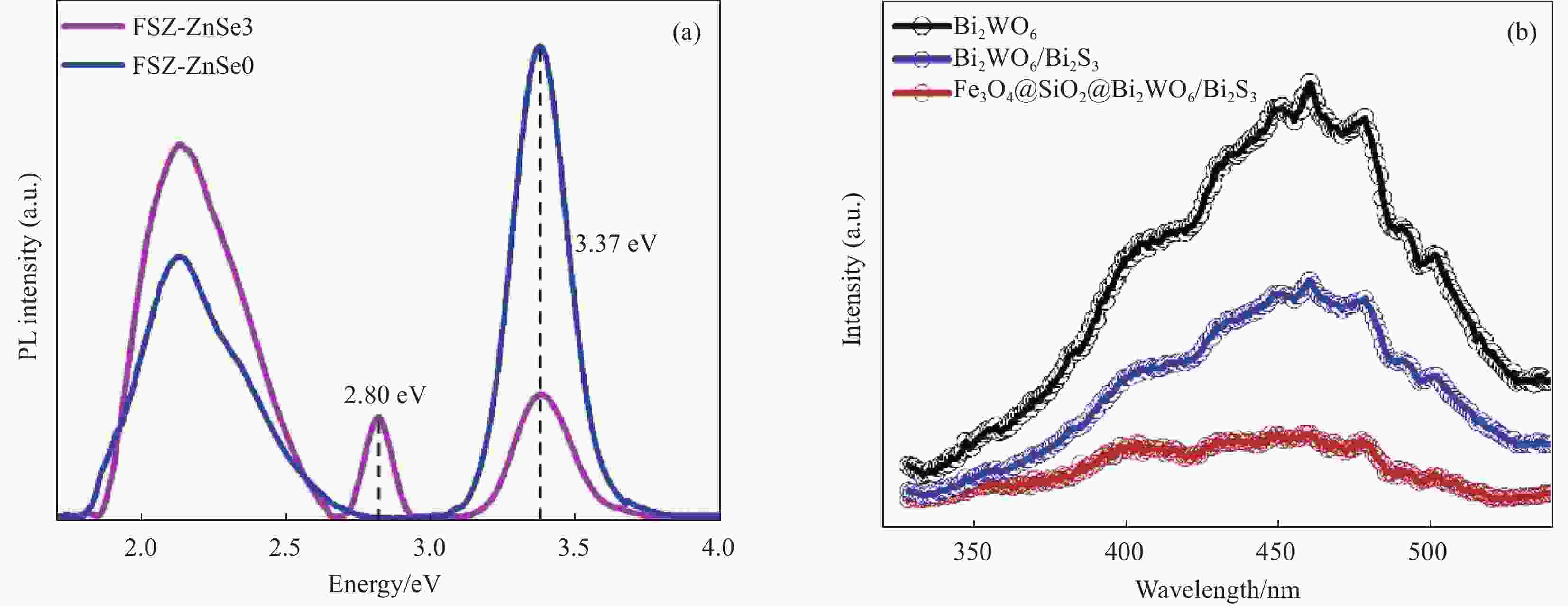
图 3 (a) 室温下的FSZ-ZnSe0 and FSZ-ZnSe3光致发光(PL)光谱[39];(b) 室温下的Bi2WO6, Fe3O4@SiO2@/Bi2WO6 and Fe3O4@SiO2@/Bi2WO6/Bi2S3光致发光(PL)光谱[40]
Figure 3. (a) Room-temperature PL spectra of FSZ-ZnSe0 and FSZ-ZnSe3 samples[39]; (b) PL spectrum of Bi2WO6, Fe3O4@SiO2@/Bi2WO6 and Fe3O4@SiO2@/Bi2WO6/Bi2S3 nanoarchitecture[40]
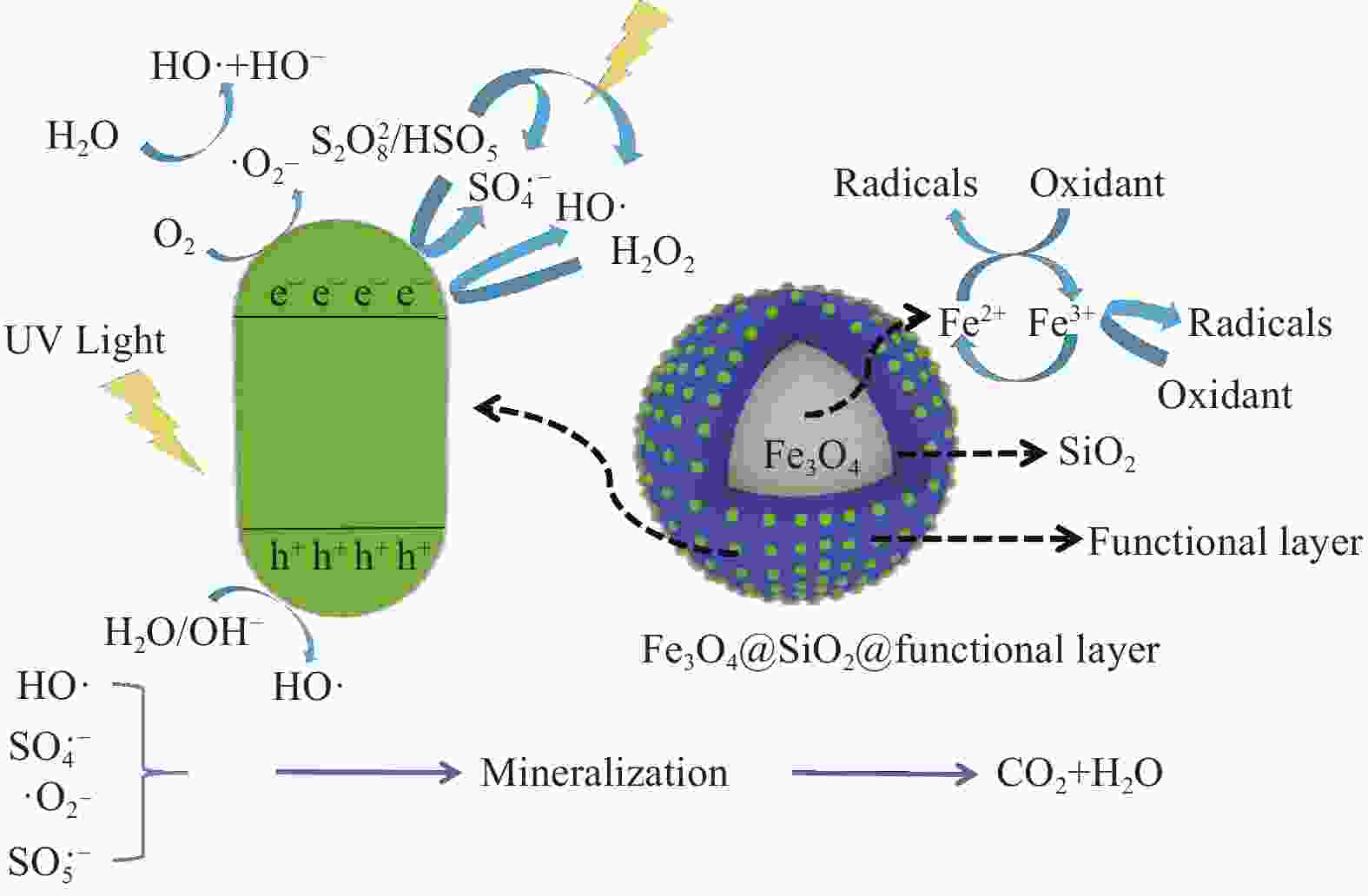
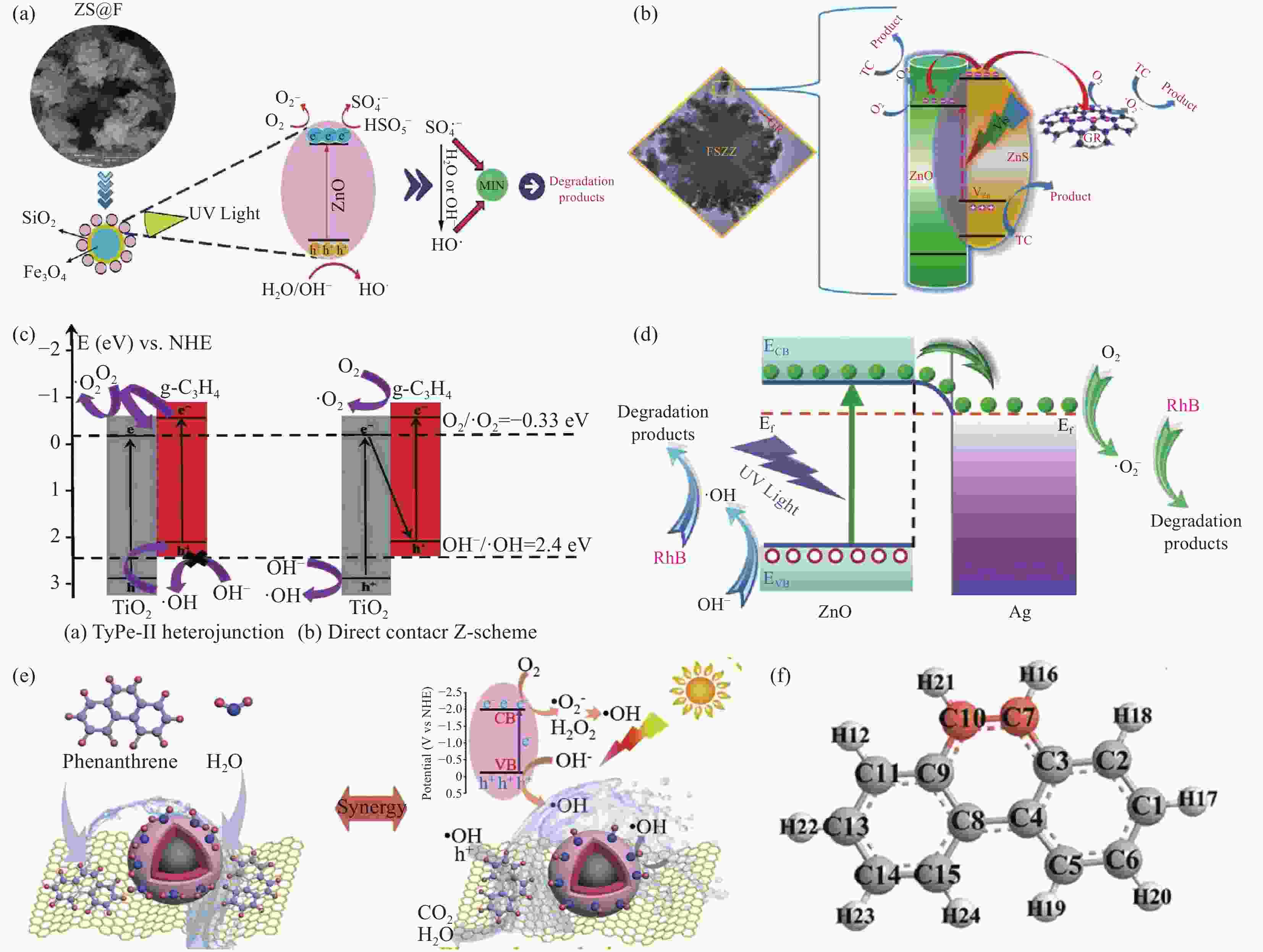
图 5 (a) 磁性硅酸盐材料光-芬顿反应中自由基形成机制[42];(b) Ⅱ型异质结构改性磁性硅酸盐光催化机制图[53];(c) Z型异质结改性磁性硅酸盐构光-芬顿机制图[47];(d) 金属掺杂改性磁性硅酸盐光催化机制图[19];(e) 非金属掺杂改性磁性硅酸盐结构光催化机制图 (f) 菲的化学结构[51]
Figure 5. (a) Free Radical Formation Mechanism in Photocatalytic Fenton Reaction of Magnetic Silicate Materials[42]; (b) Photocatalysis mechanism of type II heterojunction modified magnetic silicate [53]; (c) Photocatalysis mechanism of Z-type heterojunction modified magnetic silicate[47]; (d) Photocatalysis mechanism of metal-doped modified magnetic silicate[19]; (e) Photocatalysis mechanism of non-metal-doped modified magnetic silicate structure (f) Chemical structure of phenanthrene[51]
表 1 磁性硅酸盐复合物的制备方法
Table 1. Synthesis methods for magnetic silicate composite
Composite Synthesis technique Magnetism/
(emu·g−1)Average Size/
nmRef Core Shell Functional shell Fe3O4@SiO2 @TiO2 Solvothermal method Stöber method Solvothermal method 44 230 [18] Fe3O4@SiO2 @TiO2–Ag Carbon reduction Modifed stöber
MethodMulti- method 37 375 [19] Fe/Si/Zn–Pr6O11 Co-precipitation method Stöber method Co-precipitation method 13.6 65 [11] Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO/ZnS Solvothermal method Stöber method Multi- method 14 700 [17] Fe3O4@SiO2-MnO2 Solvothermal method Sodium silicate water glass Co-precipitation method - 100 [20] GO-Fe3O4@SiO2@N-TiO2 Solvothermal method Modified stöber method Crosslinking method 46.2 ~350 [21] Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2/rGO Co-precipitation method Stöber method Self-assembly 14.82 500 [22] Notes: GO—graphene oxide; rGO—reduced graphene oxide 表 2 Fe3O4/SiO2的主要制备工艺比较
Table 2. Comparison of Main Preparation Processes for Fe3O4/SiO2
Magnetic silicate preparation Method Source Reaction condition solvent Advantages Ref Fe3O4 preparation Co-precipitation
methodFeCl3·6 H2O
FeCl2∙4 H2OStir 1-5 h
(alkaline
environment)DI Easy to operate, with relatively mild reaction conditions [11, 22, 27, 28] solvothermal
methodFeCl3·6 H2O 200°C
12-16 hEG high quality under long duration,
high temperature, and pressure.[17, 18, 21] SiO2 wrapping Sol-gel TEOS Stir
30 min-10 hEthanol/DI Mild conditions, controllable
components, high purity[11, 17, 18, 21-23, 27, 28] water glass Na2SiO3 Stir 3 h(pH=6) DI controllable process,
Low cost[20] Notes:DI−Deionized water; EG−Ethylene glycol 表 3 原始光催化剂复合磁性硅酸盐前后的带隙能值对比
Table 3. Comparison of band gap energy values before and after composite magnetic silicates
表 4 未改性磁性硅酸盐复合材料降解有机污染物的应用
Table 4. Application of pristine magnetic silicate composite materials in the degradation of organic pollutants
Composite Target
pollutantReaction condition (light source; Pollutant
concentration Photocatalyst dosage; pH)Degrading
efficiency/%Reuse
Efficiency%Ref Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 GMC 150 W UV lamp;
20 ppm, 195 mg/L; 6.963 min, 94.7 67 / 5 [32] Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 ketamine 1.5 kW xenon arc lamp;
0.3 μM; 0.1 g/L; 720 min, 100 91 / 6 [34] Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 MO UV irradiation (15 W, λ = 365 nm); 10 mg/L;0.25 g/L; - 1.5 h, 93.5 89.3 / 5 [41] ZnO@SiO2@Fe3O4/PMS DZ 8 W UV-C lamp; 20 mg/L; 0.3 g/L; 9.0 ± 0.2; 2 mM PMS 1 h, 95 39.3 / 5 [42] ZnO@SiO2@Fe3O4/PMS MTN 8 W UV-C lamp; 20 mg/L; 0.3 g/L; 5.5 ± 0.5; 2 mM PMS 1 h, 79.3 63.3 / 5 [43] BiOBr/ Fe3O4@SiO2 IBU 8 W Philips (E14) lamp 2 mg/L; 1 g/L; 7 1 h, 100 80 / 5 [35] Notes: GMC−Gentamicin; MO−Methyl orange; DZ− diazinon; MTN− malathion; IBU− Ibuprofen 表 5 改性磁性硅酸盐复合材料降解有机污染物的应用
Table 5. Application of modified magnetic silicate composite materials in the degradation of organic pollutant
Modification method Composite Targetpollutant Reaction condition(light source;Pollutant concentration Photocatalyst dosage;pH) Degrading efficiency/% Reuseefficiency/% andcycle times Ref Forming heterojunctions Fe3O4@SiO2@ Ag2WO4@Ag2S MB LED lamps +Xenon lamp;30 ppm;1 g/L; 7 2.5 h, 99.9 76 / 5 [46] Fe3O4@SiO2/
Bi2WO6/Bi2S3RhB 500 W Xe-arc lamp;20 mg/L; 1 g/L; - 2.5 h, 100 ~100 / 5 [40] g-C3N4/TiO2/
Fe3O4@SiO2IBU Eight lamps (8 W, Philips);2 mg L−1; 1 g/L; - 1 h, 98 87 / 3 [47] Fe3O4@SiO2@
ZnO/ZnSeRhB 250 W mercury lamp;7 mg/L; 0.3 g/L; - 1 h, 97 90 / 4 [39] Metal doping Fe3O4@SiO2@
ZnO-Agphenol 25 W lamp50 mg/L; 0.2 g/L; pH=3 2.5 h, 98.1 90.1 / 4 [19] Fe3O4@SiO2/
TiO2-mRhB 250 W mercury lamp;7 mg/L; 1 g/L; - 2 h, 98.1 96.65 / 5 [45] Fe3O4@SiO2@
Sn-TiO2phenol 300 W xenon lamp;20 mg/L; 1 g/L; - 1.5 h, 95 ~95 / 3 [48] Fe3O4@SiO2@
Pt/mTiO2-xTC 300 W Hg lamp (365 nm);10 mg/L; 4 g/L; - 40 min, 98.2 85.1 / 5 [49] Fe3O4@SiO2@
N-TiO2RhB 500 W xenon lamp;10 mg/L; 3.3 g/L; - 50 min, 98 ~98 / 5 [50] Non-metal doping Fe3O4@SiO2@
N-TiO2IBU 9 W CFLs;2 mg/L; 1 g/L; 2 5 h, 94 - [27] Fe3O4@SiO2@
N-TiO2PQ LEDs;10 mg/L; 0.4 g/L; 6 3 h, 98.7 86.32 / 8 [28] GO-FSNT Phenanthrene 300 W Xe lamp;1 mg/L; 0.1 g/L; - 4 h, 94.9 65.7 / 5 [51] Notes: MB−Methylene Blue; RhB−Rhodamine b; IBU− Ibuprofen; TC−Tetracycline; PQ−Paraquat -
[1] YANG L, DU C, TAN S, et al. Improved photocatalytic properties of Fe(III) ion doped Bi2MoO6 for the oxidation of organic pollutants[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(4): 5786-5794. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.10.165 [2] DU C, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Fe-based metal organic frameworks (Fe-MOFs) for organic pollutants removal via photo-Fenton: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133932. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133932 [3] NISTICò R, CELI L R, BIANCO PREVOT A, et al. Sustainable magnet-responsive nanomaterials for the removal of arsenic from contaminated water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 260-269. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.08.034 [4] WANG C, CAI M, LIU Y, et al. Facile construction of novel organic–inorganic tetra (4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin/Bi2MoO6 heterojunction for tetracycline degradation: Performance, degradation pathways, intermediate toxicity analysis and mechanism insight[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 605: 727-740. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.137 [5] WU N, WYART Y, LIU Y, et al. An overview of solid/liquid separation methods and size fractionation techniques for engineered nanomaterials in aquatic environment[J]. Environmental Technology Reviews, 2013, 2(1): 55-70. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2013.788073 [6] WANG D, HAN D, YANG J, et al. Controlled preparation of superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO-Au core-shell photocatalyst with superior activity: RhB degradation and working mechanism[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 327: 489-499. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.12.088 [7] RASHEED T Magnetic nanomaterials: Greener and sustainable alternatives for the adsorption of hazardous environmental contaminants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 362: 132338. [8] ZHANG Z, NIU Y, CHEN H, et al. Feasible One-Pot Sequential Synthesis of Aminopyridine Functionalized Magnetic Fe3O4 Hybrids for Robust Capture of Aqueous Hg(II) and Ag(I)[J]. Acs Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(7): 7324-7337. [9] PANG S C, KHO S Y, CHIN S F Fabrication of Magnetite/Silica/Titania Core-Shell Nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2012, 2012: 427310. [10] 牛乙涛, 包国庆, 吴纯鑫, 等 功能化纳米复合材料Fe3O4@SiO2-3-氨丙基三甲氧基硅烷的制备及其对Pb(II)的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(6): 3350-3365.NIU Yitao, BAO Guoqing, WU Chunxin, et al. Preparation of functionalized nanocomposites Fe3O4@SiO2-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane and its adsorption to Pb(Ⅱ)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(6): 3350-3365. [11] CHANHOM P, CHAROENLAP N, MANIPUNTEE C, et al. Metalloporphyrins-sensitized titania-silica-iron oxide nanocomposites with high photocatalytic and bactericidal activities under visible light irradiation[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2019, 475: 602-610. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.11.090 [12] NARZARY S, ALAMELU K, RAJA V, et al. Visible light active, magnetically retrievable Fe3O4@SiO2@g-C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite as efficient photocatalyst for removal of dye pollutants[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104373. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104373 [13] MAO K, ZHU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Effective loading of well-doped ZnO/Ag3PO4 nanohybrids on magnetic core via one step for promoting its photocatalytic antibacterial activity[J]. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 603: 125187. [14] LIU S, YU B, WANG S, et al. Preparation, surface functionalization and application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2020, 281: 102165. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2020.102165 [15] EBRAHIMZADEH M A, MORTAZAVI-DERAZKOLA S, ZAZOULI M A Eco-friendly green synthesis of novel magnetic Fe3O4/SiO2/ZnO-Pr6O11 nanocomposites for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2020, 38(1): 13-20. [16] TIAN Y, YU B, LI X, et al. Facile solvothermal synthesis of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocrystals with precise size control of one nanometre as potential MRI contrast agents[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(8): 2476-2481. doi: 10.1039/c0jm02913k [17] XU T, WANG P, WANG D, et al. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of hyper-dispersed type-II tubular Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO/ZnS core/shell heterostructure for improved visible-light photocatalysis[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 838: 155689. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155689 [18] KIZILTAS H, TEKIN T, TEKIN D Preparation and characterization of recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 composite photocatalyst, and investigation of the photocatalytic activity[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 2021, 208(7): 1041-1053. [19] GHASEMY-PIRANLOO F, DADASHIAN S, BAVARSIHA F Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2-Ag cubes with core/shell/shell nano-structure: synthesis, characterization and efficient photo-catalytic for phenol degradation[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(13): 12757-12768. [20] ZHANG H, CHEN S, SHAN Y, et al. Highly Effective Lead Ion Adsorption by Manganese-Dioxide-Supported Core-Shell Structured Magnetite[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 925205. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.925205 [21] LI T, WANG M, HOU Q, et al. Visible-light-enhanced-hydrophilicity promoted adsorption-photodegradation of phenanthrene with core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2@N-TiO2 loaded on graphene oxide[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 605: 154672. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154672 [22] MIRZAHEDAYAT B, NOORISEPEHR M, DEHGHANIFARD E, et al. Evaluation of photocatalytic degradation of 2, 4-Dinitrophenol from synthetic wastewater using Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2/rGO magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 264: 571-578. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.102 [23] MA M, YANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of MB dye by the magnetically separable 3D flower-like Fe3O4/SiO2/MnO2/BiOBr-Bi photocatalyst[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 861: 158256. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158256 [24] CARDONA F A, URQUIZA E S, PRESA P D L, et al. Enhanced magnetic properties and MRI performance of bi-magnetic core–shell nanoparticles[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6: 77558-77568. doi: 10.1039/C6RA14265F [25] GIRGIS E, WAHSH M M S, OTHMAN A G M, et al. Synthesis, magnetic and optical properties of core/shell Co1-xZnxFe2O4/SiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2011, 6: 1-8. [26] LIU C, JIANG X, WANG X, et al. Magnetic polyphenol nanocomposite of Fe3O4/SiO2/PP for Cd(II) adsorption from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Technology, 2022, 43(6): 935-948. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1811394 [27] KUMAR A, KHAN M, FANG L, et al. Visible-light-driven N-TiO2@SiO2@Fe3O4 magnetic nanophotocatalysts: Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic degradation of PPCPs[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 370: 108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.048 [28] POURZAD A, SOBHI H R, BEHBAHANI M, et al. Efficient visible light-induced photocatalytic removal of paraquat using N-doped TiO2@SiO2@Fe3O4 nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 299: 112167. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112167 [29] YE L, LI J, LI X, et al. Recyclable Flower-like Fe3O4@ SiO2@ NiO Nanoparticles for Rhodamine B Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 6(23): 21695-21706. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c03871 [30] XU J, WANG W, SHANG M, et al. Efficient visible light induced degradation of organic contaminants by Bi2WO6 film on SiO2 modified reticular substrate[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 93(3): 227-232. [31] REZAI P, BANIYAGHOOB S, SADR M H Fe3O4@SiO2@AgO Nanocomposite: Synthesis, Characterization, and Investigation of its Photocatalytic Application[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2019, 48(5): 3285-3296. [32] SHIRAZINEJAD A, JORFI S, TABATABAIE T, et al. Survey on removing gentamicin antibiotic from aqueous media by recyclable magnetic titania photocatalyst[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 103(18): 6260-6276. [33] KIZILTAS H, TEKIN T, TEKIN D Synthesis, characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO composite with a core-shell structure and evaluation of its photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104160. [34] CHEN Z-Y, LAI W W-P, LIN H H-H, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of ketamine using a reusable TiO2/SiO2@Fe3O4 magnetic photocatalyst under simulated solar light[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(6): 108637. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.108637 [35] KHAN M, FUNG C S L, KUMAR A, et al. Magnetically separable BiOBr/Fe3O4@SiO2 for visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen: Mechanistic investigation and prototype development[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 365: 733-743. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.053 [36] AZMOON P, FARHADIAN M, PENDASHTEH A, et al. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of oilfield produced water by visible-light driven superhydrophobic composite of MIL-101(Cr)/Fe3O4-SiO2: Synthesis, characterization and optimization[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 613: 155972. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155972 [37] LI T, WANG M, HAO Y Highly efficient photodegradation of magnetic GO-Fe3O4@SiO2@CdS for phenanthrene and pyrene: Mechanism insight and application assessment[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023, 857: 159254. [38] KAKAVANDI B, DEHGHANIFARD E, GHOLAMI P, et al. Photocatalytic activation of peroxydisulfate by magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2/rGO core–shell towards degradation and mineralization of metronidazole[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 570: 151145. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151145 [39] WANG D, HAN D, SHI Z, et al. Optimized design of three-dimensional multi-shell Fe3O4/SiO2/ZnO/ZnSe microspheres with type II heterostructure for photocatalytic applications[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2018, 227: 61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.01.002 [40] GUO L, ZHAO Q, WANG C, et al. Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2/Bi2WO6/Bi2S3 with visible-light driven photocatalytic oxidative desulfurization[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2019, 118: 110520. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110520 [41] LI Q-Y, SUN H, SUN S, et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic performance of a novel hollow network Fe3O4/SiO2/meso-TiO2 (FSmT) composite microspheres[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2019, 90(2): 339-347. doi: 10.1007/s10971-019-04942-3 [42] REZAEI S S, DEHGHANIFARD E, NOORISEPEHR M, et al. Efficient clean-up of waters contaminated with diazinon pesticide using photo-decomposition of peroxymonosulfate by ZnO decorated on a magnetic core/shell structure[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 250: 109472. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109472 [43] ISARI A A, MORADI S, REZAEI S S, et al. Peroxymonosulfate catalyzed by core/shell magnetic ZnO photocatalyst towards malathion degradation: Enhancing synergy, catalytic performance and mechanism[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 275: 119163. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119163 [44] ARUMUGAM M, KOUTAVARAPU R, SERALATHAN K-K, et al. Noble metals (Pd, Ag, Pt, and Au) doped bismuth oxybromide photocatalysts for improved visible light-driven catalytic activity for the degradation of phenol[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 324: 138368. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138368 [45] WANG J, ZHONG J, YANG J, et al. The influence of ZnO loading amount on the photocatalytic performance of Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO-Ag composites toward the degradation of organic pollutants and hydrogen evolution[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(41): 19283-19293. doi: 10.1039/D1NJ03195C [46] JABBAR Z H, EBRAHIM S E Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic degradation activity of core/shell magnetic nanocomposites (Fe3O4@SiO2@Ag2WO4@Ag2S) under visible light irradiation[J]. Optical Materials, 2021, 122: 111818. [47] KUMAR A, KHAN M, ZENG X, et al. Development of g-C3N4/TiO2/Fe3O4@SiO2 heterojunction via sol-gel route: A magnetically recyclable direct contact Z-scheme nanophotocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic removal of ibuprofen from real sewage effluent under visible light[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 353: 645-656. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.153 [48] BIELAN Z, KOWALSKA E, DUDZIAK S, et al. Mono- and bimetallic (Pt/Cu) titanium(IV) oxide photocatalysts. Physicochemical and photocatalytic data of magnetic nanocomposites' shell[J]. Data in Brief, 2020, 31: 105814. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.105814 [49] LU F, CHEN K, FENG Q, et al. Insight into the enhanced magnetic separation and photocatalytic activity of Sn-doped TiO2 core-shell photocatalyst[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(5): 105840. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105840 [50] LI Z, WANG Y, ELZATAHRY A A, et al. Stepwise construction of Pt decorated oxygen-deficient mesoporous titania microspheres with core-shell structure and magnetic separability for efficient visible-light photocatalysis[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2020, 31(6): 1598-1602. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.10.016 [51] GUO L, ZHANG K L, SHEN H, et al. Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2/Bi2WO6-xF2x photocatalyst with well-designed core-shell nanostructure for the reduction of Cr(VI)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 370: 1522-1533. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.037 [52] 孙玉伟, 陈畴, 祁昕, 等 Ag3PO4/MIL-125(Ti) Z型异质结的构建及其光催化还原Cr(Ⅵ) 的性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2023, 37(11): 871-880.SUN Yuwei, CHEN Chou, QI Xin, et al. Synthesis of Z-scheme Ag3PO4/MIL-125(Ti) Heterojunction and lts Performance in PhotocatalyticReduction of Cr(VI)[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2023, 37(11): 871-880. [53] LIU X, XU T, WANG P, et al. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activities of 3D Fe3O4@SiO2@ZnO/ZnS nanocomposites by assembling 2D graphene sheets[J]. Physica E-Low-Dimensional Systems & Nanostructures, 2021, 134: 114926. [54] LI J, ZHANG M, LI X, et al. Effect of the calcination temperature on the visible light photocatalytic activity of direct contact Z-scheme g-C3N4-TiO2 heterojunction[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 212: 106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.061 [55] HAMED N, AHMAD M, HAIROM N, et al. Dependence of photocatalysis on electron trapping in Ag-doped flowerlike rutile-phase TiO2 film by facile hydrothermal method[J]. 2020, 534: 147571. [56] OYEKUNLE D T, GENDY E A, IFTHIKAR J, et al. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate by metal and non-metal catalyst for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 437: 135277. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135277 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 151
- HTML全文浏览量: 109
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: