Preparation and tribological properties of high density polyethylene based hydrogel composite coating
-
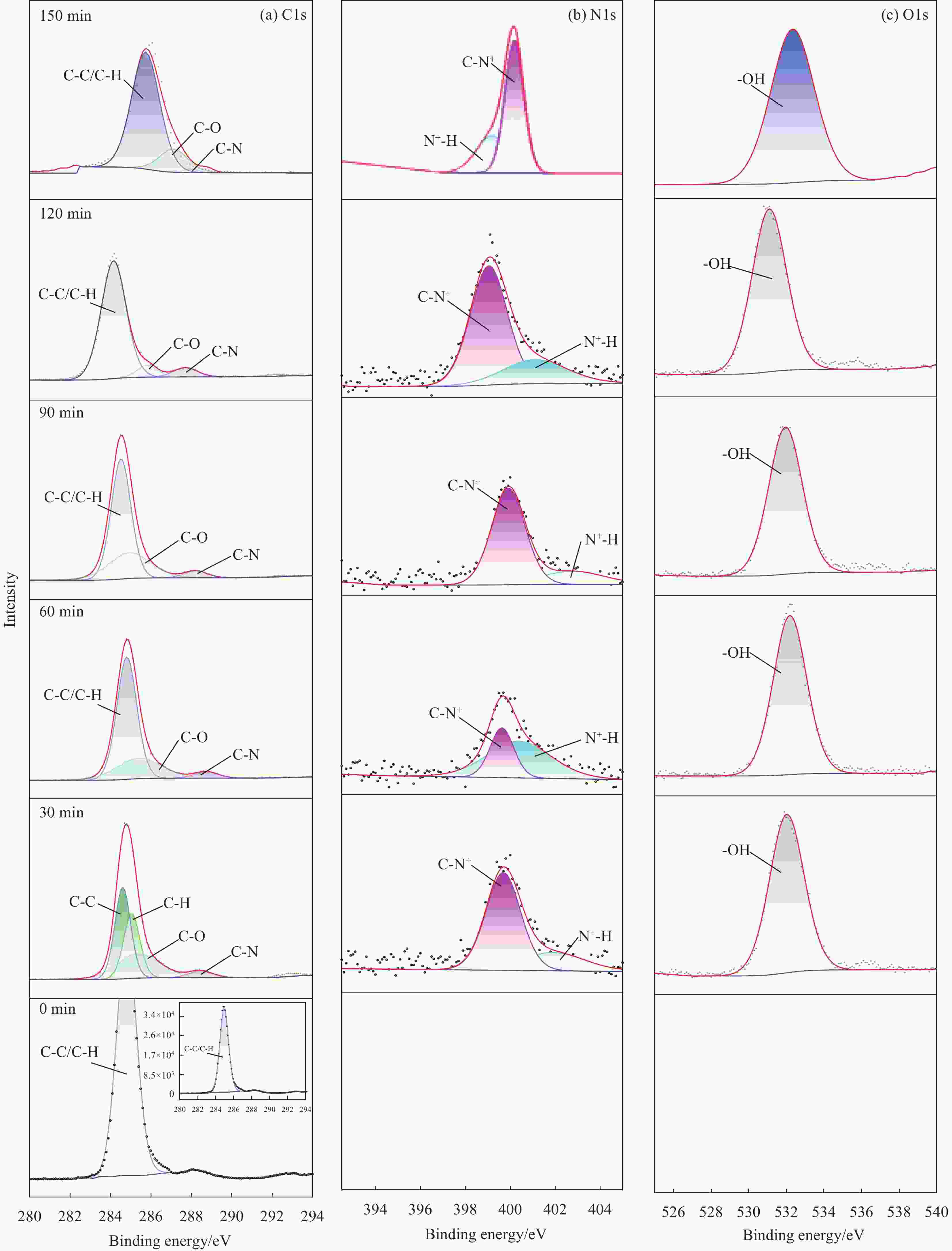
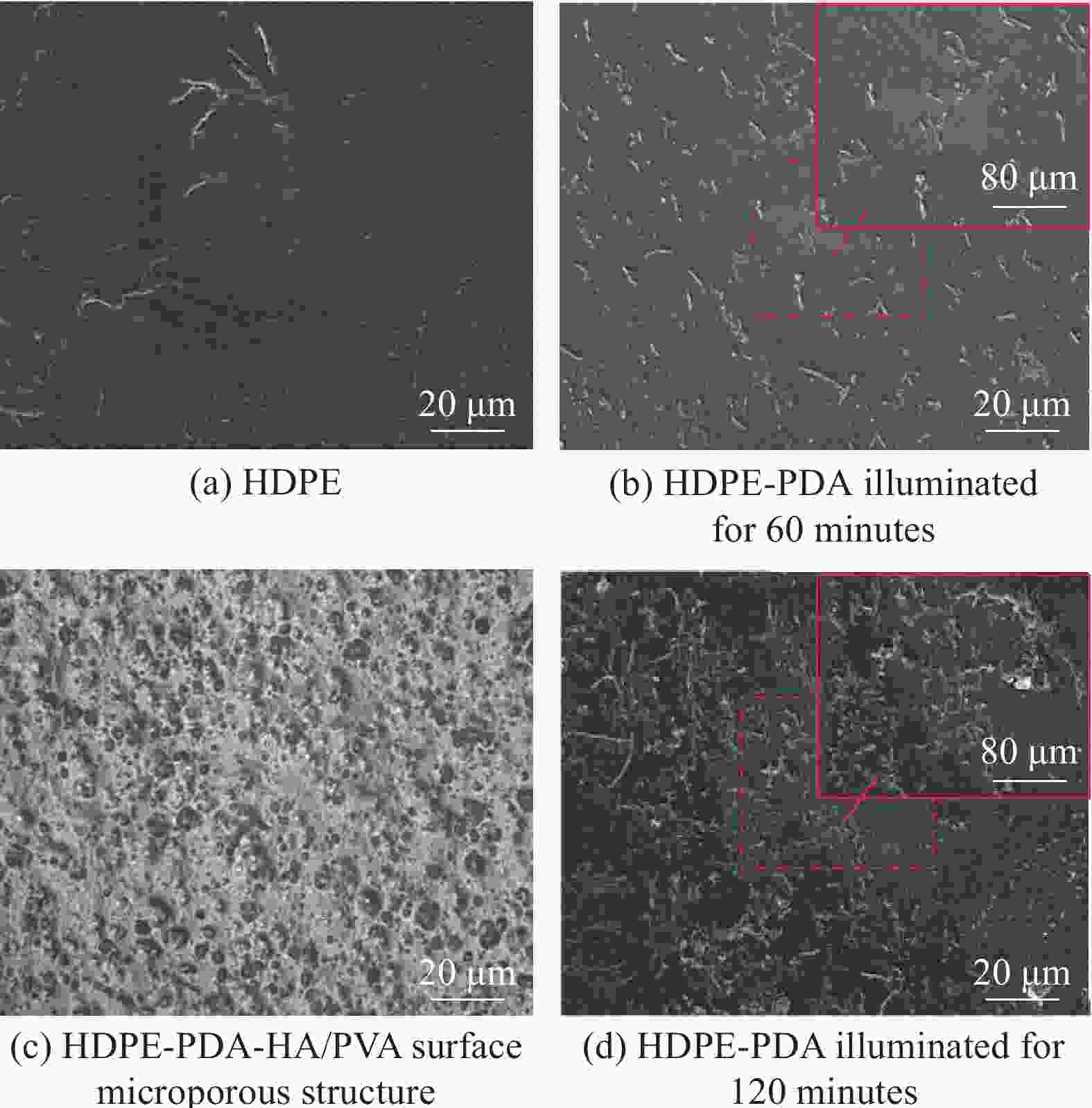
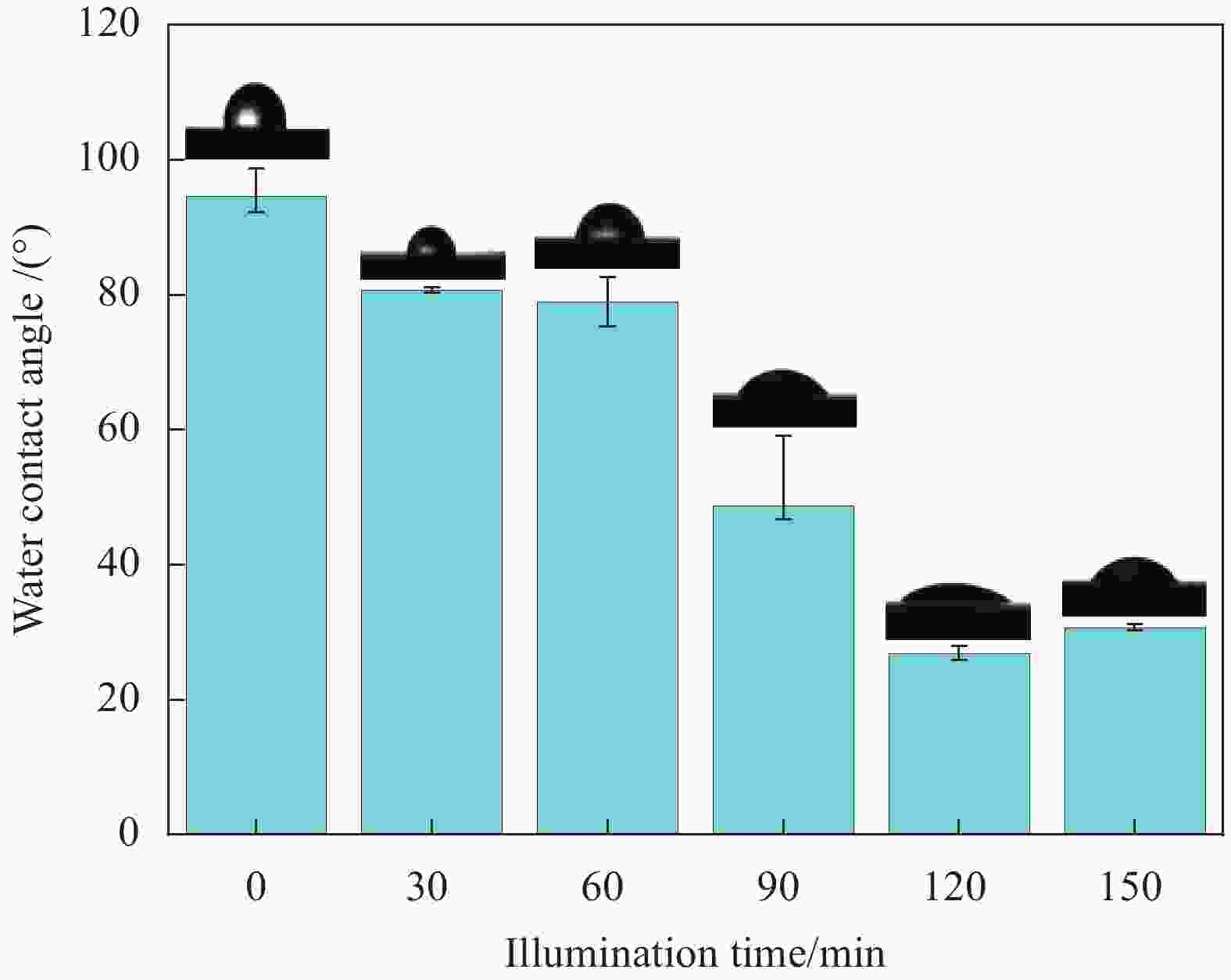
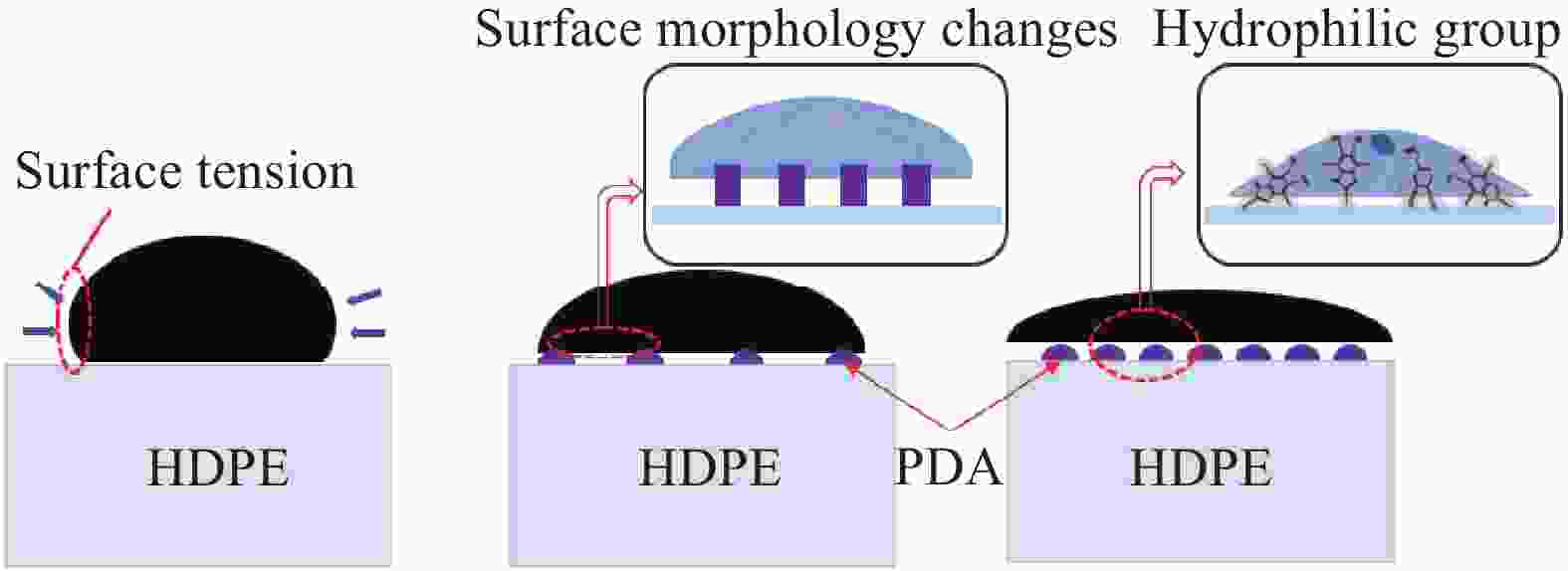
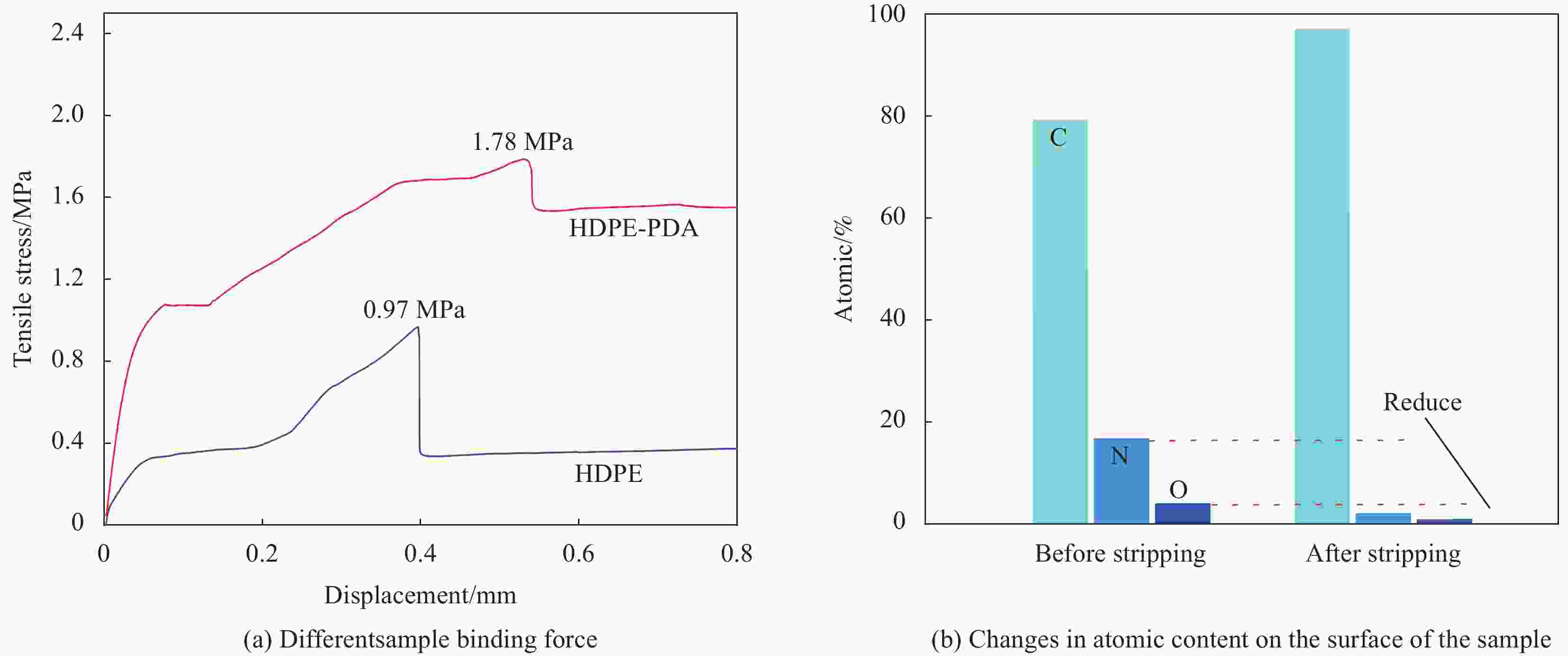
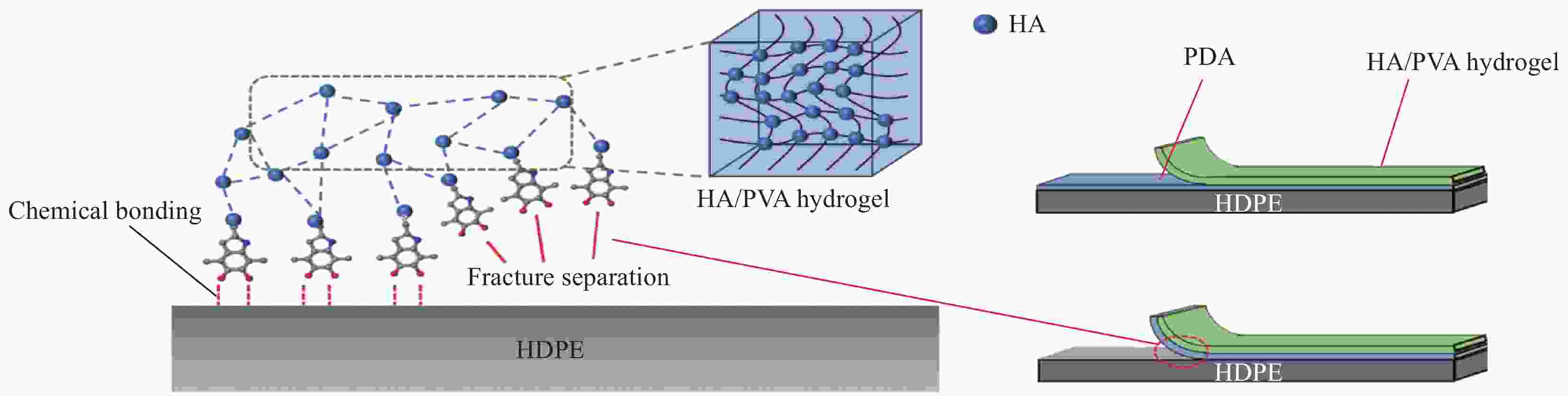
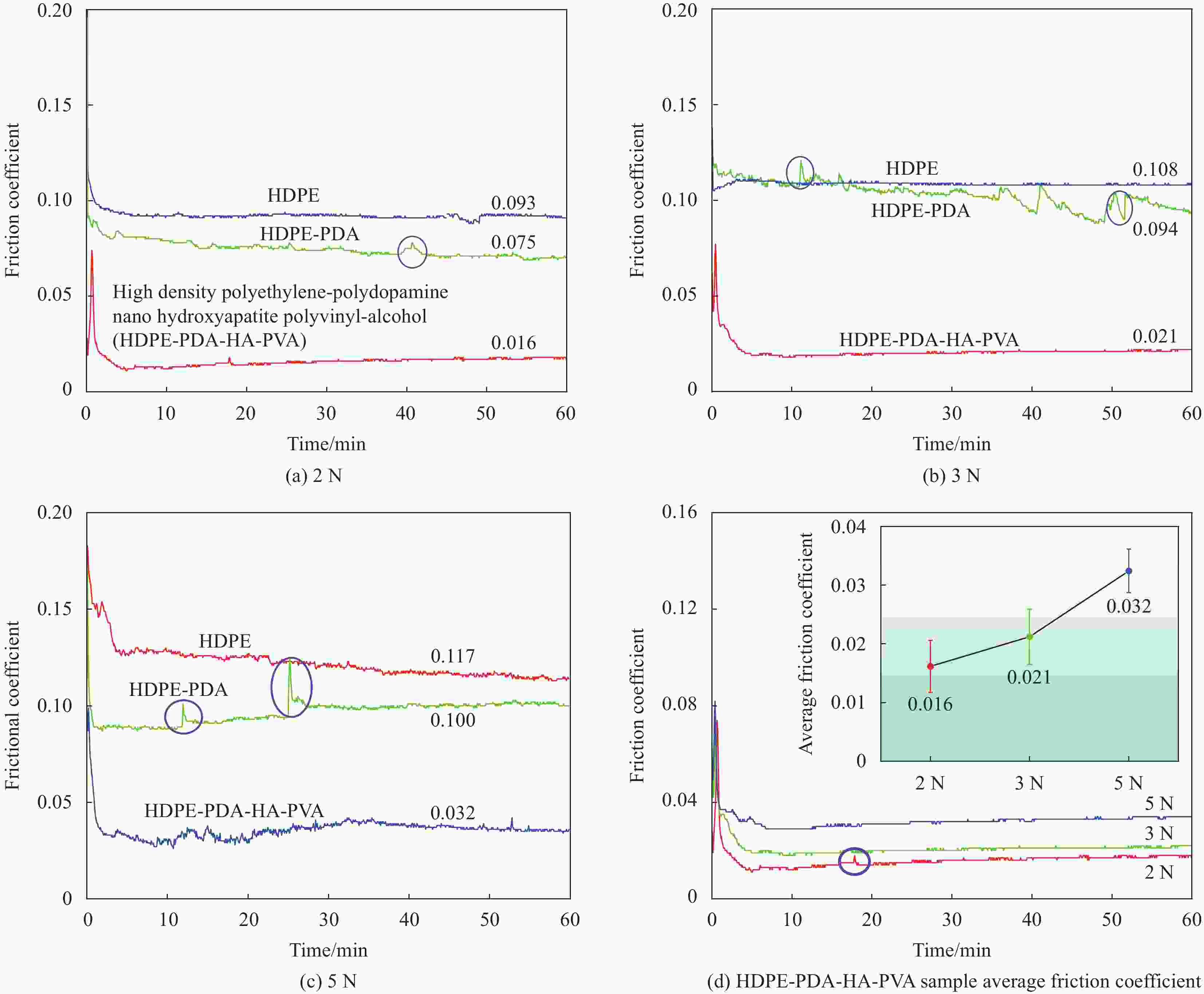
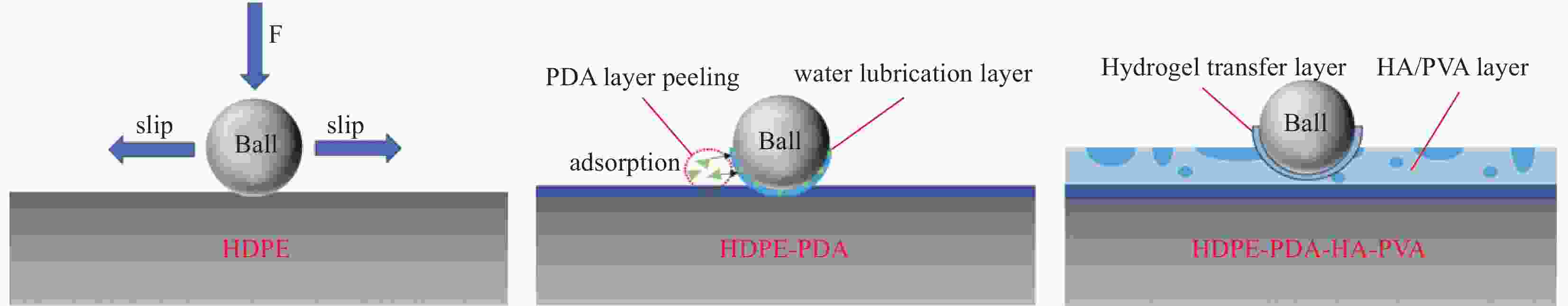
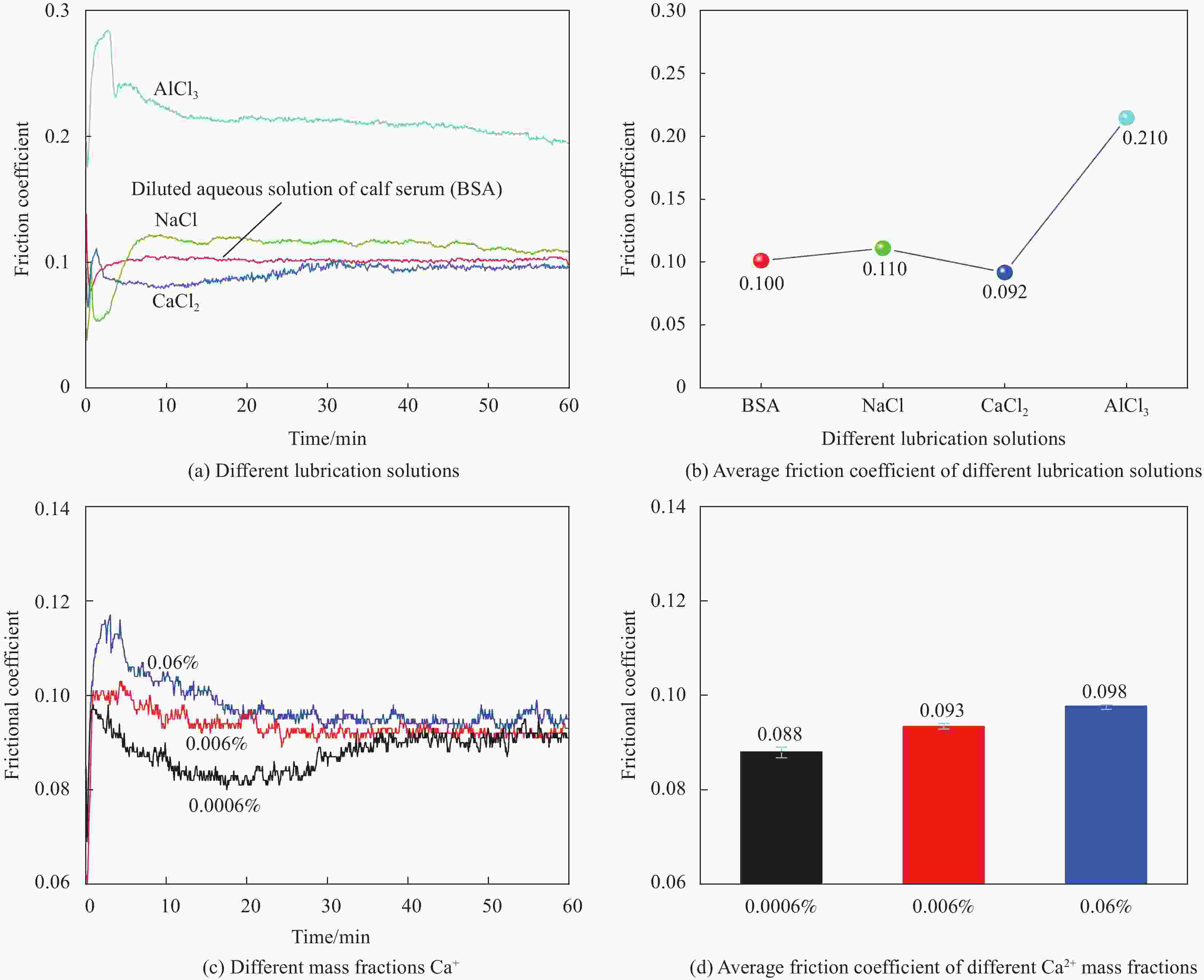
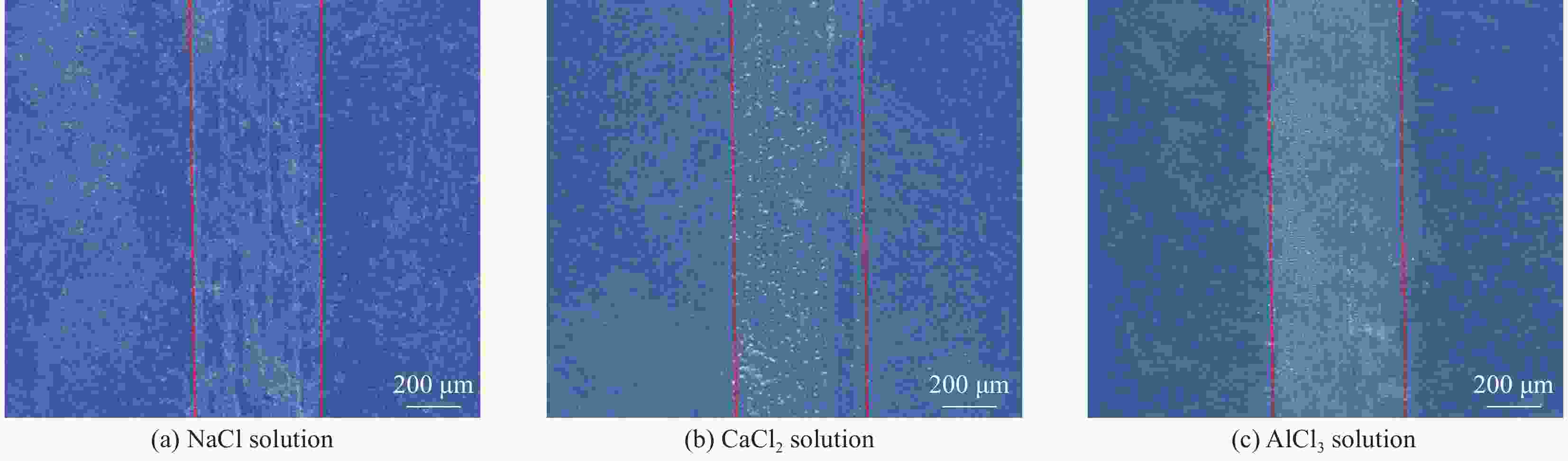
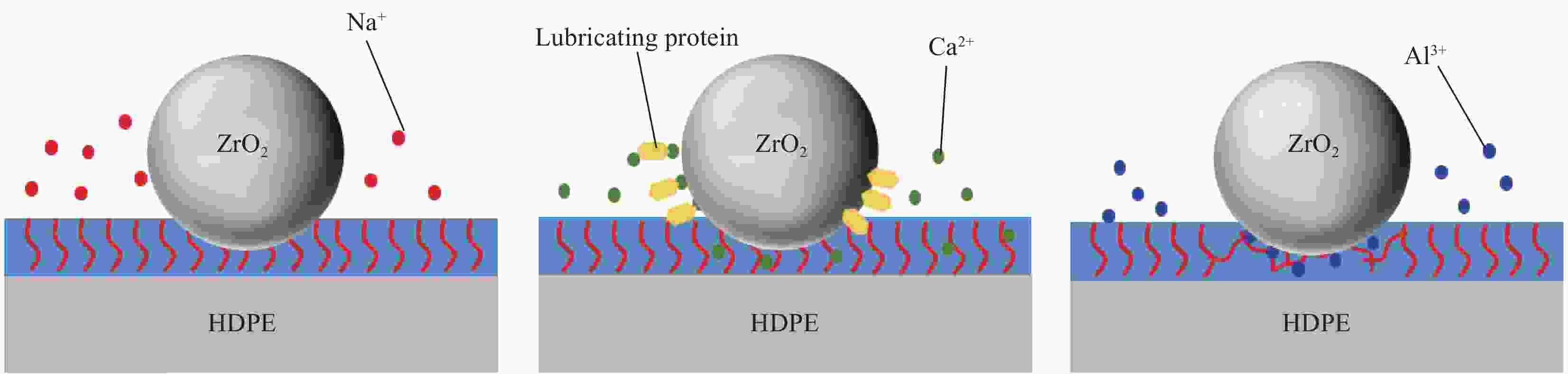
摘要: 受天然关节结构启发,在高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)表面构建水凝胶涂层,从而提升材料润湿性能及承载性能。然而水凝胶与HDPE基体结合性能差易脱落,因此采用紫外诱导多巴胺(DA)聚合形成聚多巴胺(PDA)接枝在HDPE上,得到高密度聚乙烯-多巴胺(HDPE-PDA)样品,随后在HDPE-PDA表面构建纳米羟基磷灰石-聚乙烯醇(HA-PVA)水凝胶涂层,得到高密度聚乙烯基-聚多巴胺-纳米羟基磷灰石-聚乙烯醇水凝胶复合涂层(HDPE-PDA-HA-PVA)样品。研究了样品的润湿性能、生物相容性、界面结合性能及摩擦学特性等。将HDPE-PDA-HA-PVA置于分别加入Na+、Ca2+、Al3+的小牛血清稀释润滑(BSA)溶液中,探究了金属离子对摩擦副的影响规律。综上发现 :HDPE-PDA的静态水接触角由未接枝前的94.57°降低至26.87°,抗菌性能提升98%,与水凝胶的结合力提升了84%。在摩擦学性能研究中发现,HDPE-PDA-HA-PVA在2 N载荷水润滑条件下的摩擦系数低至0.012,仅存在微量磨损。当载荷增大至5 N时,与HDPE相比平均摩擦系数和磨损量分别降低了73%和46%。在探究含金属离子的润滑溶液对摩擦学性能的影响中发现,在3 N载荷下,含Ca2+的润滑溶液表现出较好的润滑性能,这是由于Ca2+能增强材料对润滑蛋白的吸附,易形成润滑层,表现出比其他含金属离子的润滑溶液更好的润滑特性。Abstract: Inspired by the natural joint structure, a hydrogel coating is constructed on the surface of high density polyethylene (HDPE) to improve the wettability and bearing capacity of materials. However, the adhesion between hydrogel and HDPE matrix is poor and easy to fall off, so UV induced dopamine (DA) polymerization is used to form polydopamine (PDA) grafted onto HDPE to obtain High density polyethylene-dopamine(HDPE-PDA)sample, and then nano hydroxyapatite polyvinyl alcohol (HA-PVA) hydrogel coating is constructed on the surface of HDPE-PDA to obtain High density polyethylene polydopamine nano hydroxyapatite polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel composite coating(HDPE-PDA-HA-PVA)sample. Studied the wetting performance、biocompatibility、interface bonding performance and tribological characteristics of the sample. The effect of metal ions on friction pairs was investigated by placing HDPE-PDA-HA-PVA in a diluted lubrication (BSA) solution of calf serum containing Na+、Ca2+ and Al3+, respectively. To sum up: it is found that the static water contact angle of HDPE-PDA is reduced from 94.57° before grafting to 26.87°, the antibacterial performance is increased by 98%, and the adhesion with hydrogel is increased by 84%. In the study of tribological properties, it was found that the friction coefficient of HDPE PDA-HA-PVA under 2 N load water lubrication conditions was as low as 0.012, with only slight wear. When the load increased to 5 N, the average friction coefficient and wear amount decreased by 73% and 46% respectively compared to HDPE. In exploring the effect of lubrication solutions containing metal ions on tribological properties, it was found that under a 3N load, lubrication solutions containing Ca2+ exhibited better lubrication performance. This is because Ca2+ can enhance the material's adsorption of lubricating proteins, easily forming a lubrication layer, and exhibiting better lubrication characteristics than other lubrication solutions containing metal ions.
-
Key words:
- high density polyethylene /
- polydopamine /
- hydrogel /
- cartilaginous material /
- tribological properties
-
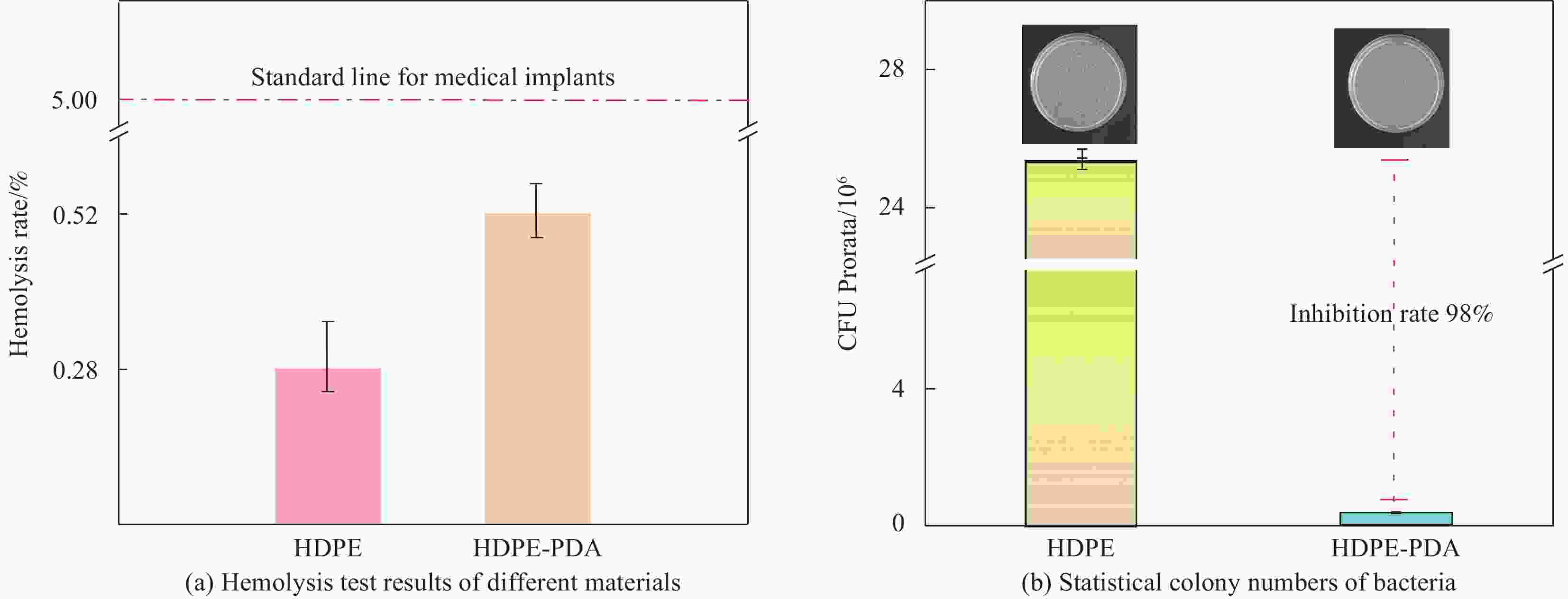
表 1 溶血吸光度测试结果
Table 1. Hemolytic absorbance test results
Group 1 2 3 4 $\overline X $ Negative control 0.0253 0.0249 0.0252 0.0254 0.0252 Positive control 0.6975 0.6949 0.7001 0.6981 0.6976 HDPE 0.0269 0.0269 0.0274 0.0271 0.0270 HDPE-PDA 0.0287 0.0288 0.0287 0.0286 0.0287 表 2 不同样品磨损量分析
Table 2. Analysis of wear amount of different products
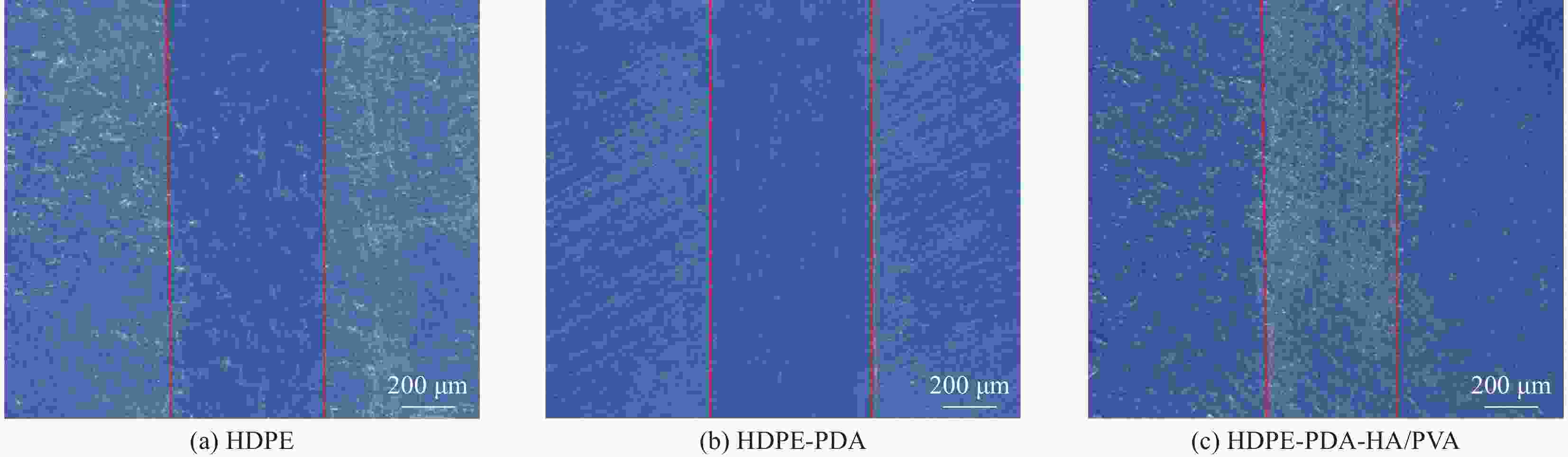
HDPE HDPE-PDA HDPE-PDA-HA/PVA Wear width/µm 582 546 432 Wear depth /µm 6.60 6.20 4.81 Wear value/10−6 mm3(N·m)−1 21.34 18.81 11.54 -
[1] ZHANG Hao, GUO Yuhai, TIAN Feng, et al. Discussion of orientation and performance of crosslinked ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene used for artificial joints[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2022, 14(25): 29230-29237. [2] 任姗姗, 陆海林, 董光能. 氧化石墨烯/聚乙二醇复合材料在人工关节材料上的润滑性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(11): 2598-2604REN Shanshan, LU Hailin, DONG Guangneng. Tribological properties of graphene oxide/polyethylene glycol composites applied on artificial joint[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(11): 2598-2604(in Chinese). [3] AMIR Elhadad A, ANA Alcudia, BELEN Begines, et al. A multidisciplinary perspective on the latest trends in artificial cartilage fabrication to mimic real tissue[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2022, 29: 101603. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101603 [4] LUO Chunhui, GUO Andi, LI Jing, et al. Janus hydrogel to mimic the structure and property of articular cartilage[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2022, 14(31): 35434-35433. [5] YU Shrike Zhang, ALI Khademhosseini. Advances in engineering hydrogels[J]. Science, 2017, 356: eeaf3627. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf3627 [6] 郭玺, 曹金珍, 王佳敏. 聚乙二醇改性相变微胶囊-木粉/高密度聚乙烯复合材料的制备与热性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(6): 1185-1190GUO Xi, CAO Jinzhen, WANG Jiamin. Preparation and thermal properties of WF/HDPE composites filled with microcapsules modified by polyethylene glycol[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(6): 1185-1190(in Chinese). [7] CAO Yi, XIONG Dangsheng, WANG Kun, et al. Semi-degradable porous poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel scaffold for cartilage repair: Evaluation of the initial and cell-cultured tribological properties[J]. Journal of the mechanical behavior of biomedical materials, 2017, 68: 163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.02.001 [8] ZHANG Xinyue, LOU Zichen, YANG Xuehui, et al. Fabrication and characterization of a multilayer hydrogel as a candidate for artificial cartilage[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2021, 3(10): 5039-5050. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.1c00807 [9] 刘雨晗, 刘德, 王意, 等. 多巴胺表面修饰在医疗领域的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2022, 51(11): 164-173LIU Yuhan, LIU De, WANG Yi, et al. Research progress of the surface modification by dopamine in medical field[J]. Surface Technology, 2022, 51(11): 164-173(in Chinese). [10] CHEN Qin, ZHANG Xinyue, LIU Siyu, et al. Cartilage-bone inspired the construction of soft-hard composite material with excellent interfacial binding performance and low friction for artificial joints[J]. Friction, 2022, 11: 1177-1193. [11] CHEN Kai, CHEN Guangyan, WEI Sheng, et al. Preparation and property of high strength and low friction PVA-HA/PAA composite hydrogel using annealing treatment[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C, 2018, 91: 579-588. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.05.080 [12] FANG Zhonghang, TU Qunzhang, SHEN Xinmin, et al. Biomimetic surface modification of UHMWPE fibers to enhance interfacial adhesion with rubber matrix via constructing polydopamine functionalization platform and then depositing zinc oxide nanoparticles[J]. Surfaces and interfaces, 2022, 29: 101728. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101728 [13] TAMARE Posati, CLAUDIA Ferroni, ANNALISA Aluigi, et al. Mild and effective polymerization of dopamine on keratin films for Innovative photoactivable and biocompatible coated materials[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2018, 303(8): 1700653. doi: 10.1002/mame.201700653 [14] FANG Hui, QI Xiaoyun, ZHOU Shicheng, et al. High-efficient vacuum ultraviolet-ozone assist-deposited polydopamine for poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-coated pure Zn toward biodegradable cardiovascular stent applications[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2022, 14(2): 3536-3550. [15] CAI Tun, ZHAN Shengpeng, YANG Tian, et al. Study on the tribological properties of UHMWPE modified by UV-induced grafting under seawater lubrication[J]. Tribology International, 2021, 168: 107419. [16] YANG Biao, DUAN Xiaobo, HUANG Jijun. Ultrathin, biomimetic, superhydrophilic layers of cross-linked poly(phosphobetaine) on polyethylene by photografting[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(3): 1120-1126. doi: 10.1021/la5031137 [17] YANG Lumin, ZHAO Xiaoduo, MA Zhengfeng, et al. An overview of functional biolubricants[J]. Friction, 2022, 11(1): 23-47. [18] 刘国强, 郭文清, 刘志鲁, 等. 聚合物仿生润滑剂研究进展[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2015, 35(1): 108-120LIU Guoqiang, GUO Wenqing, LIU Zhilu, et al. Research Progress on Polymer-based Biomimetic Lubricants[J]. Tribology, 2015, 35(1): 108-120(in Chinese). [19] KIRK J Samaroo, MINGCHEE Tan, DAVID Putnam, et al. Binding and lubrication of biomimetic boundary lubricants on articular cartilage[J]. Journal of orthopaedic research, 2017, 35(3): 548-557. doi: 10.1002/jor.23370 [20] 邓宇星, 刘思思, 刘金刚, 等. 接枝-游离态两性离子聚合物刷的制备及润滑特性研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2023, 43(7): 717-727DENG Yuxing, LIU Sisi, LIU Jingang, et al. Preparation and lubricating properties of grafted-free zwitterionic polymer brushes[J]. Tribology, 2023, 43(7): 717-727(in Chinese). [21] JELENA Zec, NATASA Tomic Z, MILORAD Zrilić, et al. Optimization of Al2O3 particle modification and UHMWPE fiber oxidation of EVA based hybrid composites: compatibility, morphological and mechanical properties[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2018, 153: 36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.07.031 [22] XIAN peng, CHEN Yingqi, GAO Shuai, et al. Polydopamine (PDA) mediated nanogranular-structured titanium dioxide (TiO2) coating on polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for oral and maxillofacial implants application[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2020, 401: 126282. [23] YUAN Junya, ZHANG Zhaozhu, YANG Mingming, et al. Surface modification of hybrid-fabric composites with amino silane and polydopamine for enhanced mechanical and tribological behaviors[J]. Tribology International, 2017, 107: 10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2016.11.013 [24] JIANG Jinhong, ZHU Liping, LI Xiaolin, et al. Surface modification of PE porous membranes based on the strong adhesion of polydopamine and covalent immobilization of heparin[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 364(1-2): 194-202. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2010.08.017 [25] ZHU Liping, JIANG Jinhong, ZHU Baoku, et al. Immobilization of bovine serum albumin onto porous polyethylene membranes using strongly attached polydopamine as a spacer[J]. Colloids & Surfaces B:Biointerfaces, 2011, 86(1): 111-118. [26] 刘宗光, 屈树新, 翁 杰. 聚多巴胺在生物材料表面改性中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2015, 27(2/3): 212-219LIU Zongguang, QU Shuxin, WENG Jie. Application of polydopamine in surface modification of biomaterials[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2015, 27(2/3): 212-219 (in Chinese). [27] 周 磊, 李 涛, 翁习生, 等. 超低磨损聚乙烯人工关节材料的生物相容性评价[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(4): 7ZHOU Lei, LI Tao, WENG Xisheng, Li Tao, Weng Xisheng, et al. Biocompatibility of the artificial joint material ultra-low-wear polyethylene[J]. Chinese Journal of Orthopedics, 2015, 23(4): 7(in Chinese). [28] RATAN Dey K, ALOK Ray R, SYNTHESIS, characterization, and blood compatibility of polyamidoamines copolymers[J]. Biomaterials, 2003, 24(18): 2985-2993. [29] 姜福贵, 伍俊峰, 杨 标, 等. 原发性关节感染与关节假体周围感染病原学[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2323, 33(24): 3762-3765JIANG Fugui, WU Junfeng YANG Biao, et al. Etiological characteristics of primary joint infection and periprosthetic joint infection[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2323, 33(24): 3762-3765(in Chinese). [30] WU Qing, RAZZAK Abdur, BAI Huanhuan, et al. Dopamine concentration-dependent surface modification for gaining carbon fiber composites with enhanced interfacial adhesion[J]. Composites Communications, 2022, 29: 101047. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2021.101047 [31] GREENE George W, THAPA Rajiv, HOLT Stephen A, et al. Structure and property changes in self-assembled lubricin layers induced by calcium ion interactions[J]. Langmuir the Acs Journal of Surfaces & Colloids, 2017, 33(10): 2559-2570. -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 31
- HTML全文浏览量: 17
- 被引次数: 0





 下载:
下载: