Preparation and antibacterial properties of ZnFe2O4@Ag nanocomposites
-
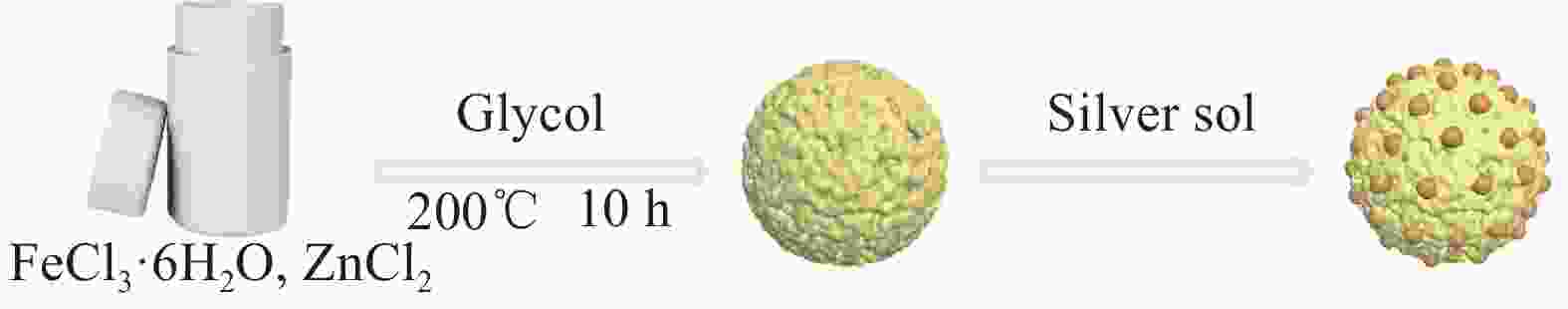
摘要: 由于传统抗生素和抗菌剂的过度使用,导致大量耐药菌滋生,对社会公共安全和人类健康产生严重威胁。因此,迫切需要开发新一代的抗菌材料来应对耐药菌危害。本研究以三氯化铁(FeCl3)、氯化锌(ZnCl2)和醋酸钠(NaOAc)为原料,采用“一锅法”合成磁性ZnFe2O4纳米微球,并把平均粒径尺寸为8.8 nm的银纳米颗粒(Ag NPs)吸附到ZnFe2O4表面,制备得到ZnFe2O4@Ag磁性纳米复合材料。该材料可有效防止Ag NPs的团聚,同时小粒径的纳米银可大幅度提升复合材料的抑菌活性,且Zn和Fe元素的引入可提升生物相容性。利用TEM、XPS、XRD、UV-Vis、FT-IR以及VSM等对复合材料进行系统表征。以革兰氏阴性菌大肠杆菌(E. coli)、革兰氏阳性金黄色葡萄球菌(S. aureus)为测试菌,研究复合材料的抑菌活性和抑菌机制。实验结果表明,ZnFe2O4@Ag在浓度为200 μg/mL时,60 min内对E. coli和S. aureus的抑菌活性可达到99.9%,抑菌机制显示,ZnFe2O4@Ag破坏细菌细胞壁与细胞膜,使得细菌内容物以及离子泄露,从而使细菌渗透压失衡,导致细菌死亡。同时该复合材料的生物相容性较Ag NPs也大幅度提升。
-
关键词:
- 纳米材料 /
- ZnFe2O4@Ag /
- 抑菌 /
- 抑菌机制 /
- 磁分离
Abstract: The overuse of traditional antibiotics and antimicrobial agents has led to the growth of a large number of drug-resistant bacteria, which represents a serious threat to public safety and human health. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop new-generation antimicrobial materials to cope with the hazards posed by drug-resistant bacteria. In this study, magnetic ZnFe2O4 nanorods were synthesised using ferric chloride (FeCl3), zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and sodium acetate (NaOAc) as raw materials. Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) with an average particle size of 8.8 nm were then adsorbed onto the surface of ZnFe2O4, resulting in the formation of ZnFe2O4@Ag magnetic nanocomposites.This material can effectively prevent the agglomeration of Ag NPs, while the small diameter of the nanoparticles significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the composite material, and the introduction of Zn and Fe elements can improve biocompatibility. The composite material was systematically characterized using TEM, XPS, XRD, UV-Vis, FT-IR, and VSM, among others. The antibacterial activity and mechanism of the composite material were studied against Gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) as test bacteria. Experimental results show that ZnFe2O4@Ag has an antibacterial activity of 99.9% against E. coli and S. aureus within 60 minutes at a concentration of 200 μg/mL. The mechanism of antibacterial action indicates that ZnFe2O4@Ag disrupts the bacterial cell walls and membranes, causing leakage of bacterial contents and ions, thereby leading to osmotic imbalance and resulting in bacterial death. At the same time, the biocompatibility of this composite material is significantly improved compared to Ag NPs alone.-
Key words:
- Nanomaterials /
- ZnFe2O4@Ag /
- Bacteriostasis /
- Inhibition mechanism /
- Magnetic separation
-
表 1 溶剂、Ag NPs、ZnFe2O4、ZnFe2O4@Ag对E. coli、S. aureus的抑菌圈尺寸
Table 1. Solvent, Ag NPs, ZnFe2O4, and ZnFe2O4@Ag on E. coli, S. aureus Circle of Inhibition Size
Bacterial Concentration/ (μg·mL-1) inhibition zones/cm(±0.05) H2O Ag ZnFe2O4 ZnFe2O4@Ag E. coli 50 0.6 0.65 0.6 0.8 100 0.6 0.75 0.6 1.0 200 0.6 1.0 0.6 1.4 400 0.6 1.3 0.6 1.7 S. aureus 50 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.7 100 0.6 0.7 0.6 1.0 200 0.6 0.9 0.6 1.2 400 0.6 1.1 0.6 1.5 -
[1] CAMELENA F, LIBERGE M, REZZOUG I, et al. In vitro activity of apramycin against 16S-RMTase-producing Gram-negative isolates[J]. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance, 2023, 33: 21-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2023.02.005 [2] BOZZI CN, LUCACCIONI L, PIETRELLA E, et al. Common morbidities and main intestinal microbial groups in very preterm neonates: a pilot study[J]. Antibiotics, 2022, 11(2): 237. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020237 [3] DO PC, ASSEFA YA, BATIKAWAI SM, et al. Strengthening antimicrobial resistance surveillance systems: a scoping review[J]. BMC Infectious Diseases, 2023, 23: 593. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08585-2 [4] 梅洁, 李彬欣, 朱仁广, 等. 纳米银的制备及抑菌性能研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2023, 35(4): 961-967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2023.04.032MEI J, LI B X, ZHU R G, et al. Preparation and antibacterial properties of nanosilver[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2023, 35(4): 961-967(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2023.04.032 [5] KAUSHAL A, KHURANA I, YADAV P, et al. Advances in therapeutic applications of silver nanoparticles[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 2023, 382: 110590. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110590 [6] 倪方方, 王博林, 宋腾蛟, 等. 纳米银颗粒的毒性效应及作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2016, 32(5): 593-598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.05.001NI F F, WANG B L, SONG T G, et al. Progress in the study of toxic effects and mechanism of action of silver nanoparticles[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Pharmacology, 2016, 32(5): 593-598(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.05.001 [7] XIE X, SUN T C, XUE J, et al. Ag nanoparticles cluster with Ph-triggered reassembly in targeting antimicrobial applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(17): 2000511. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000511 [8] FANG Q, XU K, ZHANG J, et al. Hybrid Polydopamine/Ag Shell-Encapsulated Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanosphere with High Antibacterial Activity[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(17): 3872. doi: 10.3390/ma13173872 [9] TIE JX, ZHANG M, SHEN CL, et al. Preparation of Ce/ferroferric oxide/food waste-derived biochar for aqueous Cr(VI) adsorption[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2023, 98(1): 168-178. doi: 10.1002/jctb.7232 [10] LIN, Y, ZHI, H, LIU, S, et al. Green synthesis, characterization and application on the proanthocyanidins-functionalized Fe3O4@Ag nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Papers, 2023, 77: 2115-2124. doi: 10.1007/s11696-022-02614-1 [11] Cui J, Wu D, Li Z, et al. Mesoporous Ag/ZnO hybrid cages derived from ZIF-8 for enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(11): 15759-15770. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.148 [12] Ma M, Zhao M, Ji R, et al. Adjusting the Dose of Ag-Ion Implantation on TiN-Ag-Modified SLA-Ti Creates Different Micronanostructures: Implications on Bacteriostasis, Biocompatibility, and Osteogenesis in Dental Implants[J]. ACS omega, 2023, 8(42): 39269-39278. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04769 [13] JI XH, HAN YY, WU YH, et al. Synthesis of nano-Fe3O4/ZnO composites with enhanced antibacterial properties and plant growth promotion via one-pot reaction[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30: 87016-87027. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-28534-5 [14] 郝慧敏, 王黎明, 沈勇, 等. 基于热沉淀法制备的空心结构ZnFe2O4吸波性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(10): 10150-10156. (in Chinese doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.10.022HAO H H, WANG L M, SHEN Y, et al. Study on the wave-absorbing properties of hollow-structured ZnFe2O4 prepared based on thermal precipitation[J]. Functional Materials, 2021, 52(10): 10150-10156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.10.022 [15] SHI J, ZHENG J, LIANG B, et al. Silver-decorated amino-modified Fe3O4@SiO2@mTiO2 core-shell nanocomposites with catalytic and antimicrobial bifunctional activity[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 668: 131402-131415. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.131402 [16] 史娟, 梁犇, 宋凤敏, 等. ZnFe2O4@PDA@Ag纳米复合材料的制备及其抑菌性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(12): 6774-6788.SHI J, LIANG B, SONG F M, et al. Preparation of ZnFe2O4@PDA@Ag nanocomposites and their bacteriostatic properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(12): 6774-6788(in Chinese). [17] 徐晓玲. 氧化锌抗菌及降解有机污染物活性研究[D]. 西南交通大学, 2012.XU X L. Study on the antibacterial and degradation activity of zinc oxide on organic pollutants [D]. Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012. (in Chinese) [18] PU J, ZHANG Z H, ZHANG H J, et al. Efficacy of Bactericides Against Potato Common Scab Caused by Streptomyces in Yunnan, China[J]. American Journal of Potato Research, 2022, 99: 326-335. doi: 10.1007/s12230-022-09883-2 [19] WU X W, ZHAO X L, WANG X, et al. Bioaccessibility of polypropylene microfiber-associated tetracycline and ciprofloxacin in simulated human gastrointestinal fluids[J]. Environment International, 2023, 179: 108193. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2023.108193 [20] OUDIH SB, TAHTAT D, KHODJA AN, et al. Chitosan nanoparticles with controlled size and zeta potential[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science, 2023, 63(3): 1011-1021. doi: 10.1002/pen.26261 [21] VAN AT, THEINER, S, BOLEA, FE. et al. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 2023, 52(3): 52. [22] TAO S, YANG T, YIN Y, Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote mitochondrial damage in high glucose- induced dysfunction and apoptosis of human dental pulp cells[J]. Journal of Dental Sciences, 2023, (19)1: 292-302. [23] 刘振兴. ZnFe2O4纳米光催化剂制备方法研究进展[J]. 化学工程师, 2023, 37(4): 62-66.LIU Z X. Progress in the preparation method of ZnFe2O4 nanophotocatalyst[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2023, 37(4): 62-66(in Chinese). [24] WANG L, SAGAGUCHI T, OKUHATA T, et al. Electron and phonon dynamics in hexagonal Pd nanosheets and Ag/Pd/Ag sandwich nanoplates[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(2): 1180-1188. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07082 [25] SUN SG, ZHANG XY, Wu YP, et al. Synthesis of ZnFe2O4@MnO2 multilevel nanosheets structure and its electrochemical properties as positive electrodes for asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Chemistry Select, 2019, 4(17): 5168-5177. [26] Mottley C, Connor H D, Mason R P. [17O] oxygen hyperfine structure for the hydroxyl and superoxide radical adducts of the spin traps DMPO, PBN and 4-POBN[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 1986, 141(2): 622-628. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(86)80218-2 [27] FANG Y, HONG C Q, CHEN F R, et al. Green synthesis of nano silver by tea extract with high antimicrobial activity[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2021, 132: 108808. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108808 [28] CHEN TW, RAJAJI U, Chen SM, et al. A novel nanocomposite with superior electrocatalytic activity: a magnetic property based ZnFe2O4 nanocubes embellished with reduced graphene oxide by facile ultrasonic approach[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2019, 57: 116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.05.007 [29] HOVHANNISYAN Z, TIMOTINA M, MANOYAN J, et al. Ribes nigrum L. Extract-Mediated Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Action Mechanisms of Silver Nanoparticles[J]. Antibiotics, 2022, 11(10): 1415. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101415 [30] MALGORZATA O R, WALDEMAR P, AGNIESZKAO S. Tetracyclines-an important therapeutic tool for dermatologists[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(12): 7246. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127246 [31] FRANCO D, CALABRESE G, CONOCI S, et al. Metal-Based Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Mechanisms and Biomedical Application[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(9): 1778. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091778 [32] WOOLSTON B M. , STEPHANOPOULOS G. Engineering E. coli to grow on methanol[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(10): 2070-2072. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.09.019 [33] XU X, LI Y L, WANG L X, et al. Triple-functional polyetheretherketone surface with enhanced bacteriostasis and anti-inflammatory and osseointegrative properties for implant application[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 212: 98-114. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.05.014 [34] ZHU B, LI Y, LIN Z, et al. Silver nanoparticles induce HePG-2 cells apoptosis through ROS-mediated signaling pathways[J]. Nanoscale research letters, 2016, 11: 1-8. doi: 10.1186/s11671-015-1209-4 [35] PARMAR S, KAUR H, SINGH J, et al. Recent Advances in Green Synthesis of Ag NPs for Extenuating Antimicrobial Resistance[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(7): 1115. doi: 10.3390/nano12071115 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 44
- HTML全文浏览量: 30
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载:








