Multi-scale prediction model of chloride diffusivity of fiber reinforced concrete
-
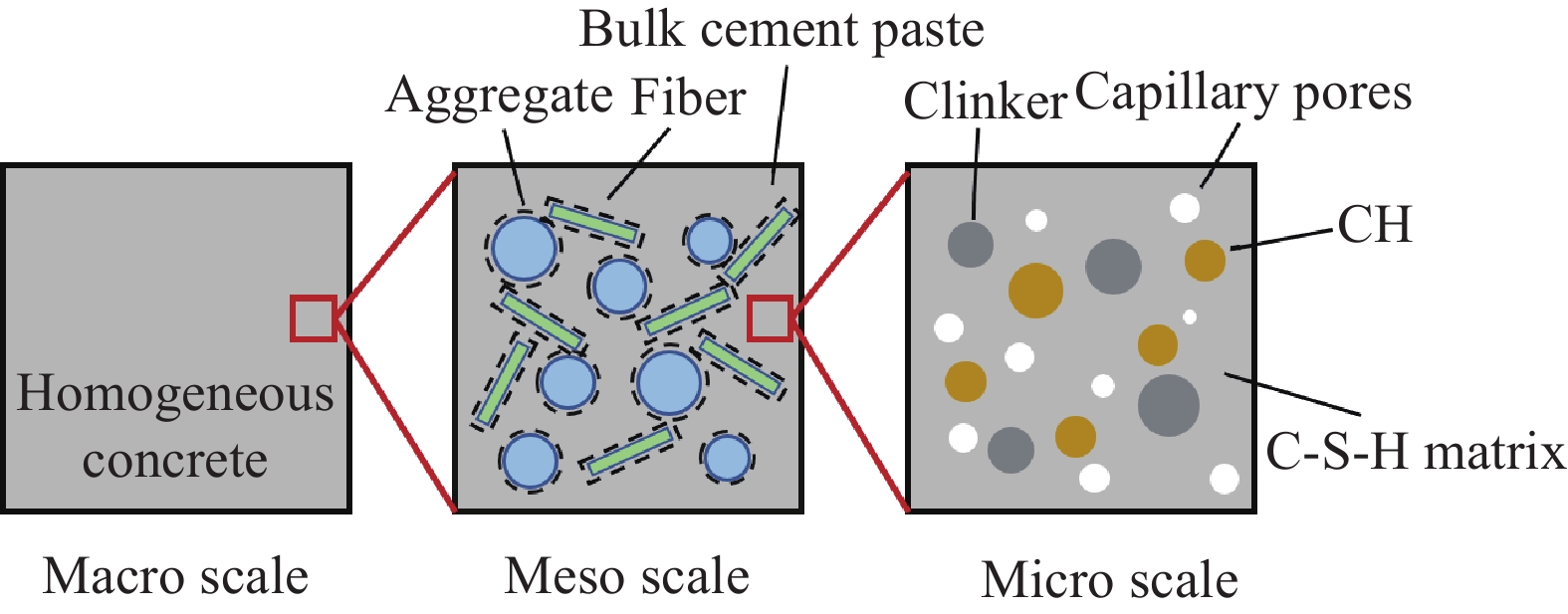
摘要: 纤维增强混凝土材料属于多相非均质复合材料,其宏观耐久性能由微观和细观的组分占比和夹杂关系共同决定。为考虑纤维增强混凝土材料不同尺度下的非均质性对整体氯离子扩散系数的影响,本文基于从微观到宏观的多尺度方法选取了不同层级代表单元,建立了纤维增强混凝土氯离子扩散系数多尺度预测模型。模型在充分考虑微观水泥水化过程和阈值效应的基础上,分析了细观尺度下纤维、骨料及其与水泥浆体的结合界面对混凝土宏观扩散性能的共同影响,并探究了纤维尺寸、纤维-浆体界面过渡区厚度等因素与扩散系数之间的影响关系,且通过第三方试验对模型的可靠性进行了验证。参数化分析的结果表明,当水灰比大于一定限值(约为0.45),水泥浆体的氯离子扩散系数与水灰比呈指数增长,而在细观层级上,纤维-浆体界面过渡区是影响混凝土整体扩散性能的主要因素:纤维掺量的增加和纤维直径的减小都会增大界面过渡区的体积,而较高的纤维过渡区体积占比和纤维界面扩散系数都会增大纤维增强混凝土的宏观氯离子扩散系数。结果还表明混凝土扩散系数与纤维掺量之间并无直接关系,而需要综合考虑纤维直径、界面过渡区厚度等各种因素的影响。本文所提模型能够有效预测纤维增强混凝土的扩散系数,进而更高效的评估纤维掺入对混凝土耐久性的影响,并基于预测结果为工程实践提供理论指导和技术参考。Abstract: Fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) is a complex heterogeneous composite material, and its macro durabi-lity will be determined by the microscopic and mesoscopic components. By electing representative elements, a multi-scale model was established in this study to predict the chloride diffusivity of FRC with the consideration of heterogeneous feathers from micro to macro scale. In the present model, the percolation effect and the interface transition zones (ITZs) between fiber, aggregate and cement paste were carefully considered. Taking basalt fiber concrete as an example, the model was verified by experimental data and the influential parameters were discussed in detail. The results show when the water to cement ratio (w/c) exceeds a certain limit (about 0.45), the chloride diffusivity of FRC increases exponentially with the w/c, and results also indicate that the chloride diffusivity of FRC is mainly affected by the ITZs between the fiber and the cement paste. Adding the fiber content or decreasing the diameter of fibers will all increase the volume fraction of ITZs and lead to a poor chloride resistance performance. However, it is interestingly to find that no fixed negative or positive relationship exist between chloride diffusivity of FRC and the fiber content. The proposed model can effectively predict the diffusivity of FRC and hope to provide guidance or reference for engineering practice.
-
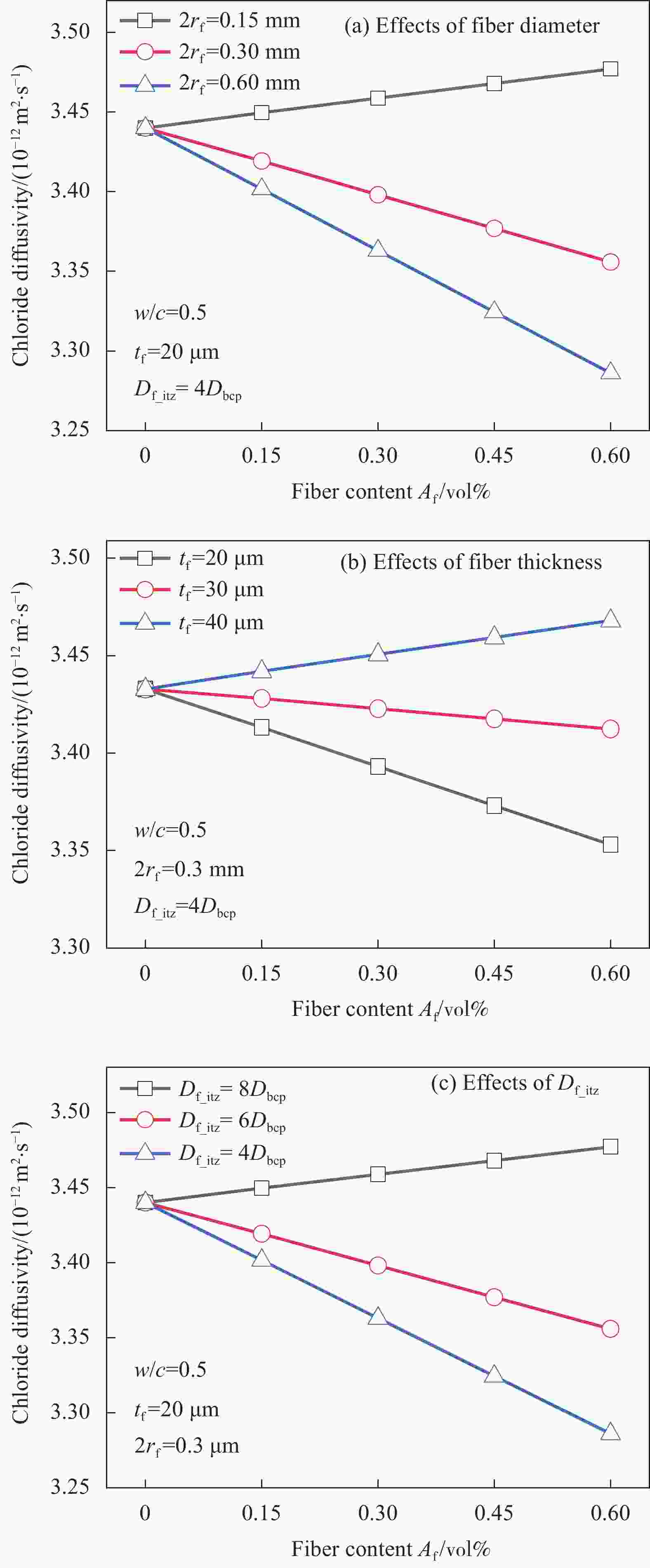
图 8 纤维直径 (a)、纤维界面厚度 (b)、纤维界面氯离子扩散系数 (c) 对纤维增强混凝土整体抗氯离子侵蚀能力的影响
Dbcp—Diffusivity of bulk cement paste; Df_itz—Diffusivity of interface transition zone of fiber
Figure 8. Effects of fiber diameter (a), fiber interface thickness (b) and fiber interface chloride diffusivity (c) on the overall chloride diffusivity of fiber reinforced concrete
表 1 试验获得的水泥基氯离子渗透扩散系数
Table 1. Experimental results of the chloride diffusivity in ordinary portland bulk cement paste
Reference Index w/c ${D}_{\mathrm{b}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{p} }^{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p} }$/(10−12 m2·s−1) Curing condition Ngala et al[46] N95 0.40 3.65 70 days in 0.035 mol NaOH solution 3.95 4.35 0.50 7.16 7.80 8.06 0.60 10.40 12.60 17.80 Ngala et al[47] N97 0.40 4.06 70 days in 0.035 mol NaOH solution 0.50 7.87 0.60 12.70 MacDonald et al[48] M95 0.40 2.56 56 days at 100% of relative humidity
No saturation before testing2.78 0.50 6.80 7.28 Princigallo[49] P12 0.30 1.38 420 days in 90% saturated NaCl solution 0.33 1.51 Notes: $ {D}_{\mathrm{b}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{p}}^{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}} $—Chloride diffusion coefficient of bulk cement paste tested by experiment; w/c—Water to cement ratio. 表 2 纤维增强混凝土试验参数与结果
Table 2. Experimental parameters and results of fiber reinforced concrete
Reference Fiber type w/c Fiber diameter/mm Fiber length/mm Aggregate volume
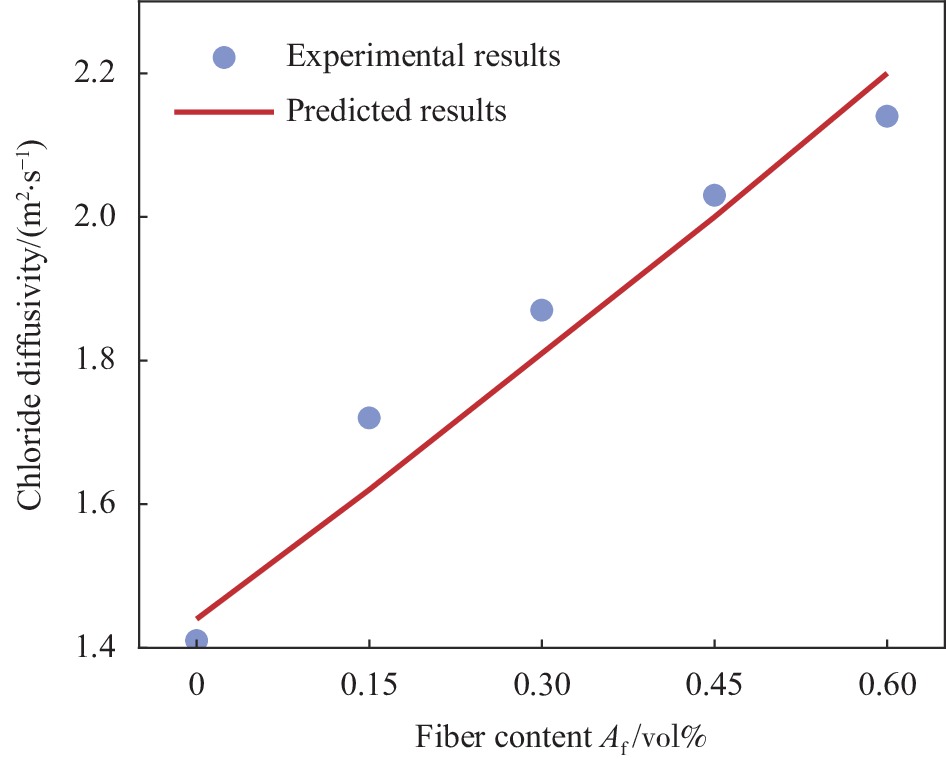
fraction/vol%Guo et al[13] BF 0.32 0.022 12 50 Experimental results Fiber volume fraction Af/vol% 0.00 0.15 0.30 0.45 0.60 Chloride diffusivity
${D}^{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p} }/({10}^{-12}\;{\mathrm{m} }^{2} \cdot{\mathrm{s} }^{-1})$1.41 1.72 1.87 2.03 2.14 Note: BF—Blast fiber. -
[1] LIU J, JIA Y, WANG J. Calculation of chloride ion diffusion in glass and polypropylene fiber-reinforced concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,215:875-885. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.246 [2] AFROUGHSABET V, BIOLZI L, MONTEIRO P J M. The effect of steel and polypropylene fibers on the chloride diffusivity and drying shrinkage of high-strength concrete[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,139:84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.11.047 [3] 段明翰, 覃源, 许增光, 等. 聚丙烯纤维对混凝土损伤渗透特性的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10):3474-3483.DUAN Minghan, QIN Yuan, XU Zengguang, et al. Effect of polypropylene fiber on the damage and permeability of concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(10):3474-3483(in Chinese). [4] WU C, LI V C. CFRP-ECC hybrid for strengthening of the concrete structures[J]. Composite Structures,2017,178:372-382. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.07.034 [5] 张成琳, 刘清风. 钢筋混凝土中氯盐和硫酸盐耦合侵蚀研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(1):69-77.ZHANG Chenglin, LIU Qingfeng. Coupling erosion of chlorides and sulfates in reinforced concrete: A review[J]. Materials Reports,2022,36(1):69-77(in Chinese). [6] 姜文镪, 刘清风. 冻融循环下混凝土中氯离子传输研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(2):258-272.JIANG Wenqiang, LIU Qingfeng. Chloride transport in concrete subjected to freeze-thaw cycles-A short review[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(2):258-272(in Chinese). [7] ASHRAF M, IQBAL M F, RAUF M, et al. Developing a sustainable concrete incorporating bentonite clay and silica fume: Mechanical and durability performance[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,337:130315. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130315 [8] MENG Z, LIU Q F, XIA J, et al. Mechanical-transport-chemical modeling of electrochemical repair methods for corrosion-induced cracking in marine concrete[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering,2022,37:1854-1874. doi: 10.1111/mice.12827 [9] PYO S, KOH T, TAFESSE M, et al. Chloride-induced corrosion of steel fiber near the surface of ultra-high performance concrete and its effect on flexural behavior with various thickness[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,224:206-213. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.063 [10] TONG L, ZHAO J, CHENG Z. Chloride ion binding effect and corrosion resistance of geopolymer materials prepared with seawater and coral sand[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,309:125126. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125126 [11] 陈伟康, 刘清风. 干湿交替下混凝土中水分和多离子耦合传输的数值研究[J]. 水利学报, 2021, 52(5):622-632.CHEN Weikang, LIU Qingfeng. Numerical study on coupled transport of moisture and multi ions in concrete under alternating dry and wet conditions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2021,52(5):622-632(in Chinese). [12] 苏丽, 牛荻涛, 黄大观, 等. 海洋环境中玄武岩/聚丙烯纤维增强混凝土氯离子扩散性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(131):44-53.SU Li, NIU Ditao, HUANG Daguan, et al. Chloride diffusion performance of basalt/polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete in marine environment[J]. Journal of Buliding Materials,2022,25(131):44-53(in Chinese). [13] GUO Y, HU X, LV J. Experimental study on the resistance of basalt fibre-reinforced concrete to chloride penetration[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,223:142-155. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.211 [14] CHEN W, ZHU H, HE Z, et al. Experimental investigation on chloride-ion penetration resistance of slag containing fiber-reinforced concrete under drying-wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,274:121829. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121829 [15] 张兰芳, 王道峰. 玄武岩纤维掺量对混凝土耐硫酸盐腐蚀性和抗渗性的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(6):1946-1950.ZHANG Lanfang, WANG Daofeng. Effect of basalt fiber content on sulfate resistance and impermeability of concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,37(6):1946-1950(in Chinese). [16] BEHFARNIA K, BEHRAVAN A. Application of high performance polypropylene fibers in concrete lining of water tunnels[J]. Materials & Design,2014,55:274-279. [17] FRAZÃO C, CAMÕES A, BARROS J, et al. Durability of steel fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2015,80:155-166. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.01.061 [18] ZHANG J, BIAN F, ZHANG Y, et al. Effect of pore structures on gas permeability and chloride diffusivity of concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,163:402-413. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.111 [19] BARY B, BÉJAOUI S. Assessment of diffusive and mechani-cal properties of hardened cement pastes using a multi-coated sphere assemblage model[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2006,36(2):245-258. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2005.07.007 [20] HONORIO T, BARY B, BENBOUDJEMA F. Multiscale estimation of ageing viscoelastic properties of cement-based materials: A combined analytical and numerical approach to estimate the behaviour at early age[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2016,85:137-155. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2016.03.010 [21] 刘清风. 基于多离子传输的混凝土细微观尺度多相数值模拟[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46(8):1074-1080.LIU Qingfeng. Multi-phase modelling of concrete at meso-micro scale based on multi-species transport[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,46(8):1074-1080(in Chinese). [22] FU Z, SU H, WEN Z. Multi-scale numerical analysis for linear elastic behavior of clay concrete[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2020,203:23-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2020.07.014 [23] 孙国文, 孙伟, 王彩辉. 现代混凝土传输行为与其微结构之间关系的研究方法及其进展[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(17):3010-3022. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.17.014SUN Guowen, SUN Wei, WANG Caihui. Relationship between the transport behavior of mordern concrete and its microstructures: Research methods and progress[J]. Materials Reports,2018,32(17):3010-3022(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.17.014 [24] MESHGIN P, XI Y. Multi-scale composite models for the effective thermal conductivity of PCM-concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2013,48:371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.06.068 [25] ACHOUR M, BIGNONNET F, BARTHÉLÉMY J F, et al. Multi-scale modeling of the chloride diffusivity and the elasticity of portland cement paste[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,234:117-124. [26] 王彩辉, 孙伟, 蒋金洋, 等. 水泥基复合材料在多尺度方面的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2011, 39(265):726-738.WANG Caihui, SUN Wei, JIANG Jinyang, et al. Development on cement-based composite materials in multi-scale[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2011,39(265):726-738(in Chinese). [27] 李林洁, 刘清风. 冻融循环下混凝土内部结冰及氯离子传输规律的数值研究[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50(8):2245-2256.LI Linjie, LIU Qingfeng. Freezing rate and chloride transport in concrete subjected to freeze-thaw cycles: A numerical study[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2022,50(8):2245-2256(in Chinese). [28] 陶毅, 张海镇, 史庆轩, 等. 内置FRP约束混凝土的方钢管混凝土轴压承载力[J]. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2017, 39(2):43-49.TAO Yi, ZHANG Haizhen, SHI Qingxuan, et al. Bearing capacity of steel tube-concrete-FRP-concrete composite columns[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University,2017,39(2):43-49(in Chinese). [29] LIU Q F, MENG Z, HOU D, et al. Numerical modelling on electrochemical deposition technique for healing alkali silica reaction induced damaged concrete[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2022, 276: 108765. [30] DUTRA V F P, MAGHOUS S, FILHO A C, et al. A micromechanical approach to elastic and viscoelastic properties of fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2010,40(3):460-472. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.10.018 [31] 邓方茜, 徐礼华, 池寅, 等. 基于均匀化理论的混杂纤维混凝土有效弹性模量计算[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2019, 47(2):161-170.DENG Fangqian, XU Lihua, CHI Yin, et al. Calculation of effective elastic modulus for hybrid fiber reinforced concrete based on homogenization theory[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2019,47(2):161-170(in Chinese). [32] 齐玉军, 冯鹏, 叶列平, 等. 大跨度纤维增强复合材料编织网结构建造成形模型试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2012, 33(8):117-126.QI Yujun, FENG Peng, YE Lieping, et al. Model test of construction and formation of large-span FRP woven web structures[J]. Journal of Building Structures,2012,33(8):117-126(in Chinese). [33] 唐巍, 张广泰, 董海蛟, 等. 纤维混凝土耐久性能研究综述[J]. 材料导报, 2014, 28(11):123-127.TANG Wei, ZHANG Guangtai, DONG Haijiao, et al. Review on durability of fiber concrete[J]. Materials Reports,2014,28(11):123-127(in Chinese). [34] 胡哲, 刘清风. 荷载作用下开裂混凝土中多离子传输的数值研究[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(9):1-15.HU Zhe, LIU Qingfeng. Numerical study of multi-species transport in cracked concrete under external load[J]. Materials Reports,2023,37(9):1-15(in Chinese). [35] 高云, 吴凯, 穆松. 基于孔隙结构预测水泥基体的氯离子扩散系数[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(4): 375-380.GAO Yun, WU Kai, MU Song. A pore structure based prediction of chloride diffusivity for cement paste[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2022, 25(4): 375-380(in Chinese). [36] DRIDI W. Analysis of effective diffusivity of cement based materials by multi-scale modelling[J]. Materials and Structures,2012,46(1-2):313-326. [37] LU P. Further studies on Mori-Tanaka models for thermal expansion coefficients of composites[J]. Polymer,2013,54(6):1691-1699. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.01.021 [38] VENKOVIC N, SORELLI L, SUDRET B, et al. Uncertainty propagation of a multiscale poromechanics-hydration model for poroelastic properties of cement paste at early-age[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics,2013,32:5-20. doi: 10.1016/j.probengmech.2012.12.003 [39] HU J, STROEVEN P. Depercolation threshold of porosity in model cement: Approach by morphological evolution during hydration[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2005,27(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2004.02.039 [40] MA H, HOU D, LU Y, et al. Two-scale modeling of the capillary network in hydrated cement paste[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2014,64:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.04.005 [41] BERNARD O, ULM F J, LEMARCHAND E. A multiscale micromechanics-hydration model for the early-age elastic properties of cement-based materials[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2003,33(9):1293-1309. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(03)00039-5 [42] TIAN Y, TIAN Z, JIN N, et al. A multiphase numerical simulation of chloride ions diffusion in concrete using electron microprobe analysis for characterizing properties of ITZ[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,178:432-444. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.047 [43] LIU Q F, HU Z, WANG X E, et al. Numerical study on cracking and its effect on chloride transport in concrete subjected to external load[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,325:126797. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126797 [44] XU L, DENG F, CHI Y. Nano-mechanical behavior of the interfacial transition zone between steel-polypropylene fiber and cement paste[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,145:619-638. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.035 [45] 彭立港, 赵羽习, 曾维来, 等. 再生骨料混凝土界面参数研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(7):737-743.PENG Ligang, ZHAO Yuxi, ZENG Weilai, et al. Interface parameter of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2022,25(7):737-743(in Chinese). [46] NGALA V T, PAGE C L, PARROTT L J, et al. Diffusion in cementitious materials: II, further investigations of chloride and oxygen diffusion in well-cured OPC and OPC/30%PFA pastes[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,1995,25(4):819-826. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(95)00072-K [47] NGALA V T, PAGE C L. Effects of carbonation on pore structure and diffusional properties of hydrated cement paste[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,1997,27(7):995-1007. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(97)00102-6 [48] MACDONALD K A, NORTHWOOD D O. Experimental measurements of chloride ion diffusion rates using a two-compartment diffusion cell: Effects of material and test variables[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,1995,25(7):1407-1416. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(95)00135-Y [49] PRINCIGALLO A. Cálculo del transporte de cloruros en la pasta de cemento[J]. Materiales de Construcción,2012,62(306):151-161. [50] 康亚明, 刘长武, 韩小刚, 等. 钢纤维几何尺寸对钢纤维混凝土损伤变形特性的影响[J]. 土木工程学报, 2010, 43(4):119-124.KANG Yaming, LIU Changwu, HAN Xiaogang, et al. A study of the damage and deformation characteristics of steel fiber reinforced concrete with different steel fiber sizes[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2010,43(4):119-124(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: