Effect of melt viscosity and impact energy of poly aryl ether ketone (PAEK) resins on the impact damage behavior of their composites
-
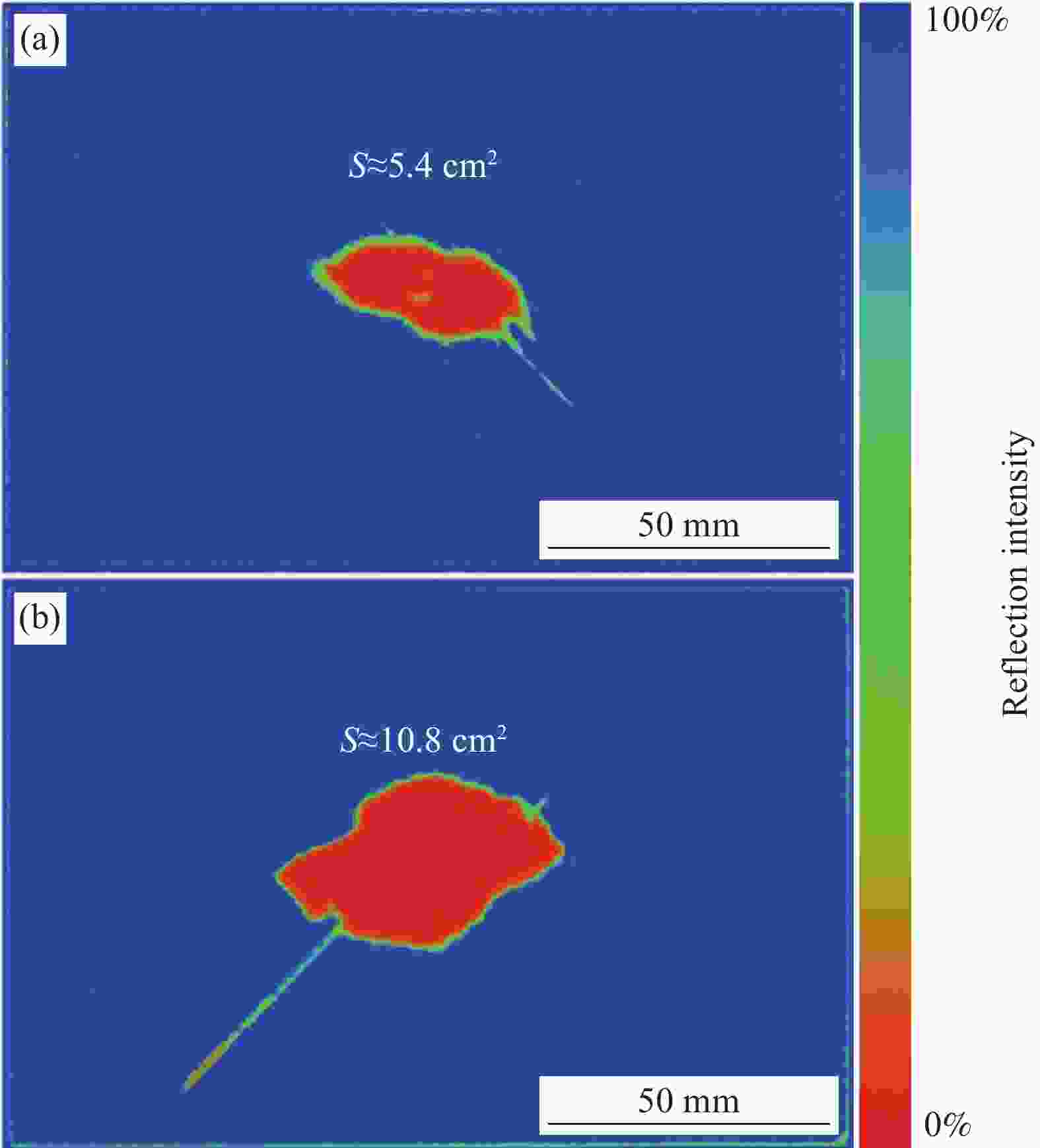
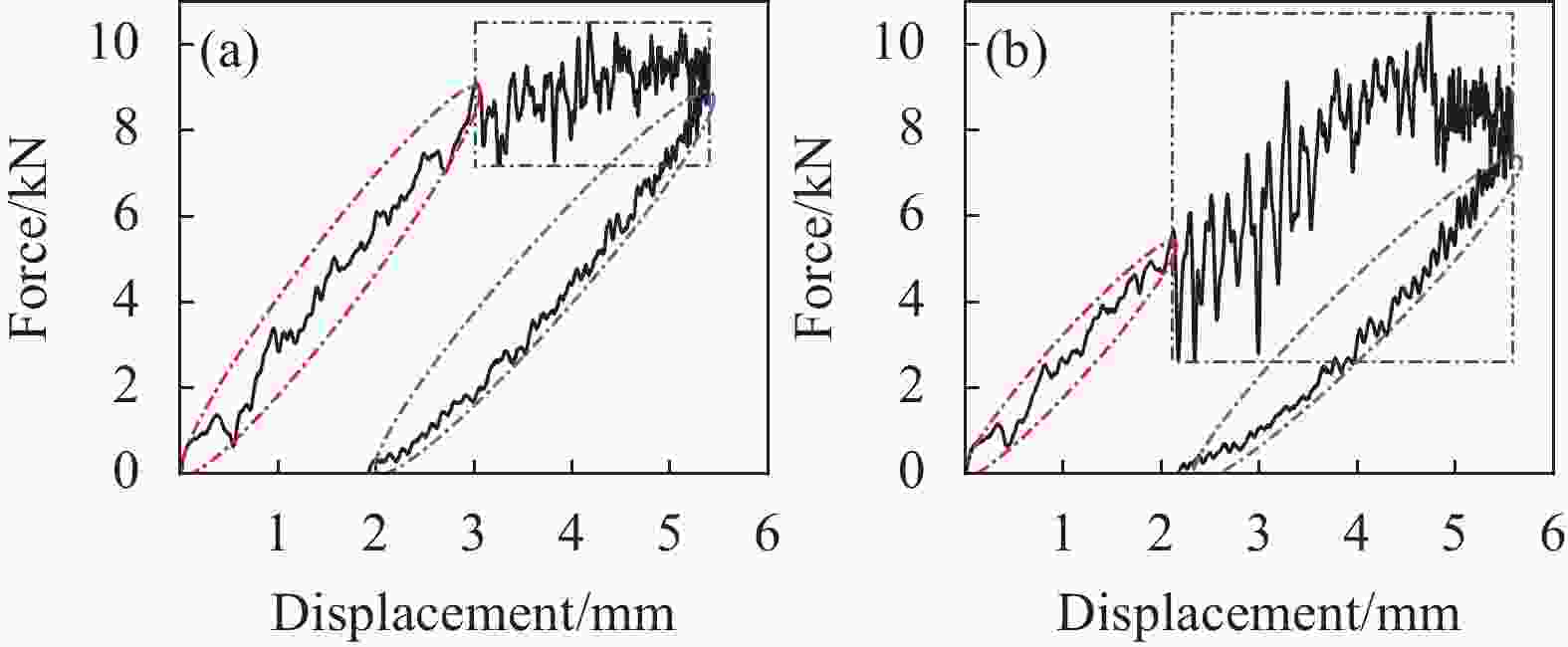
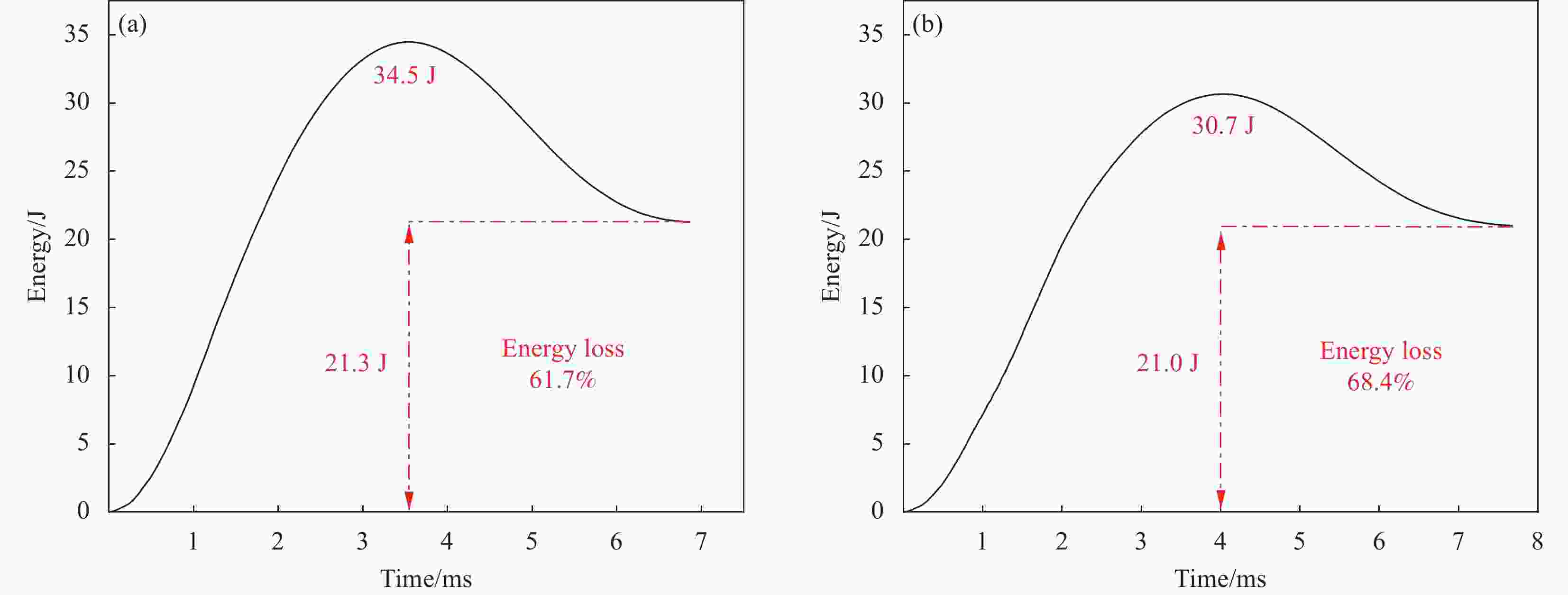
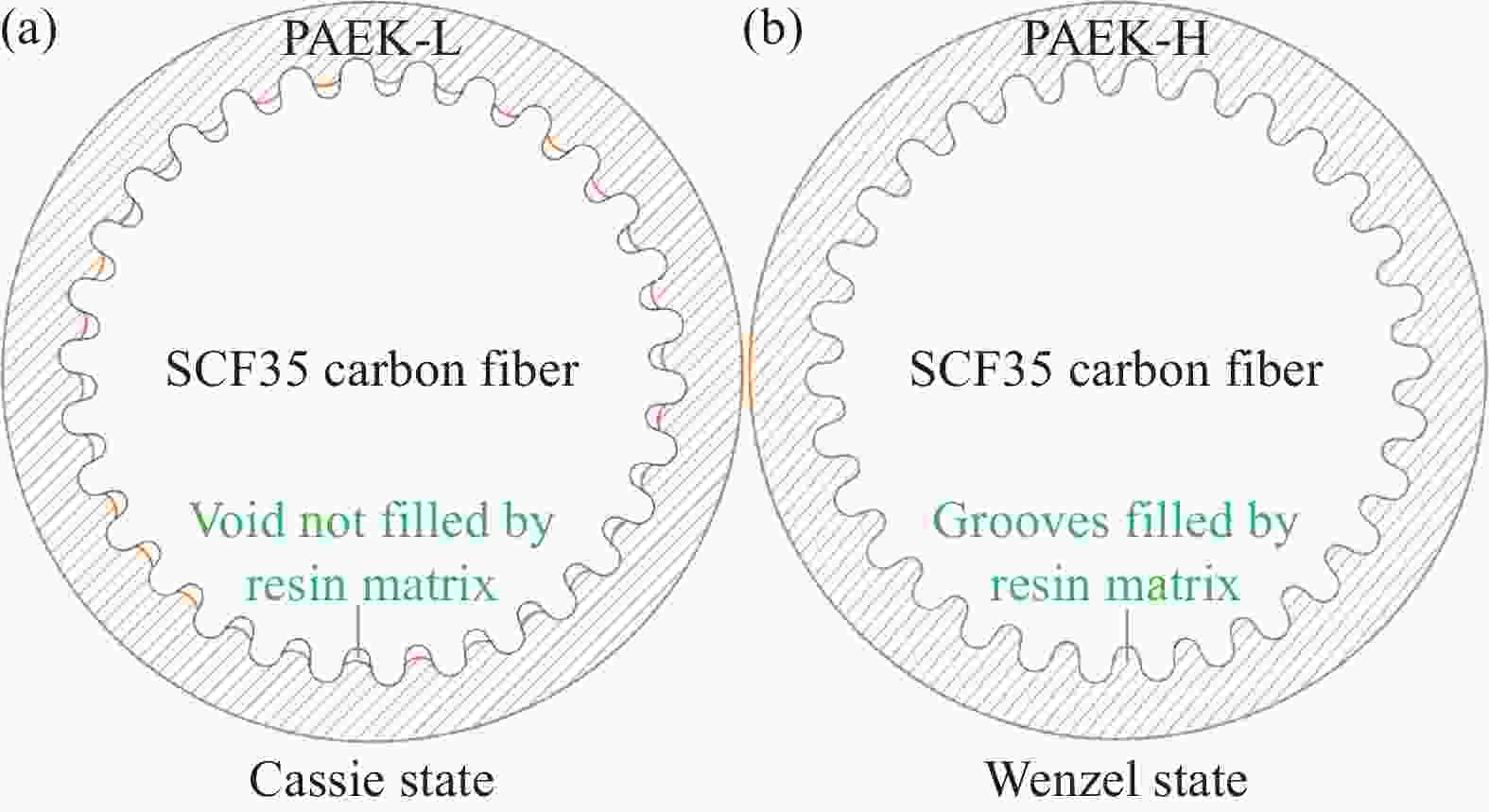
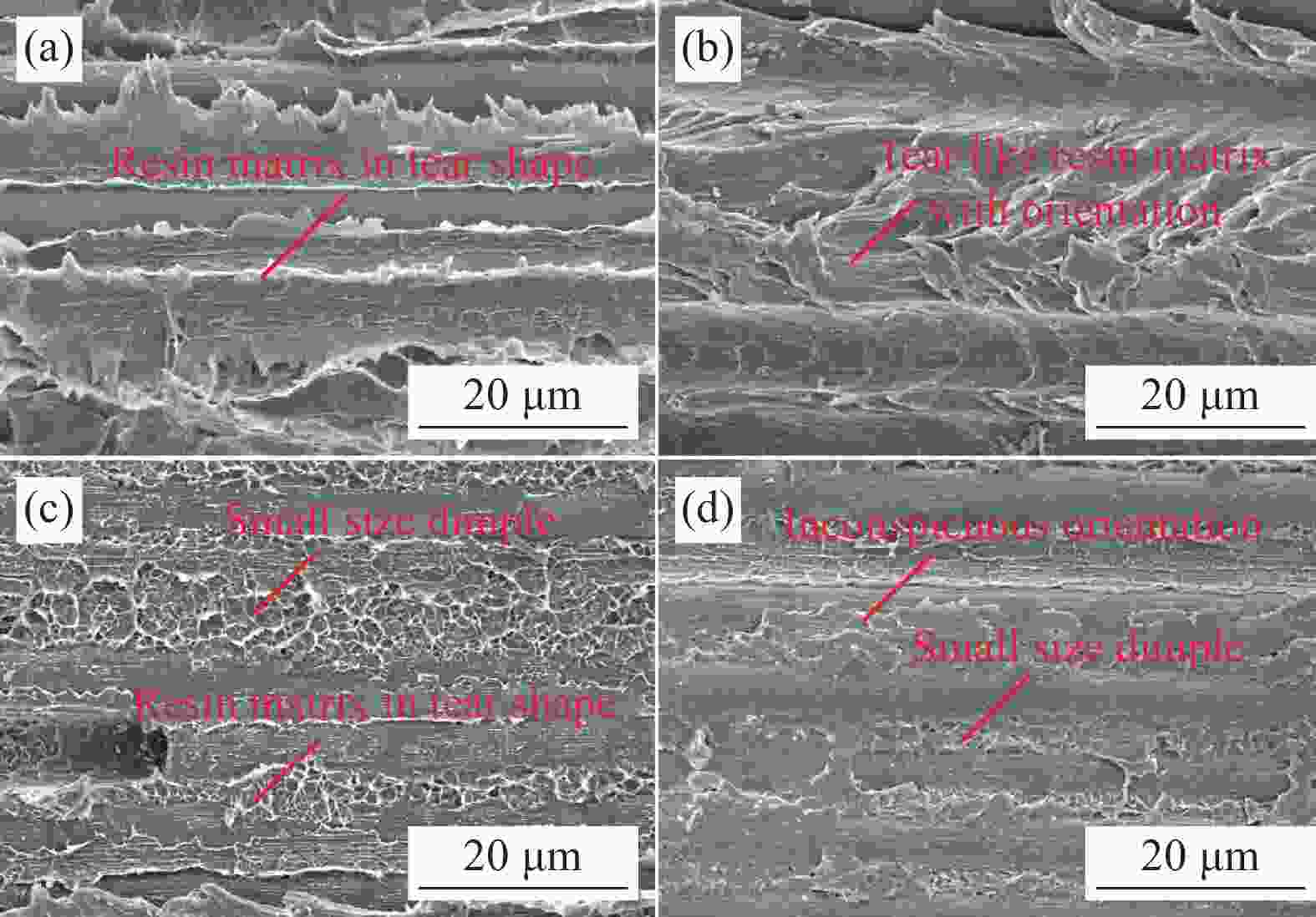
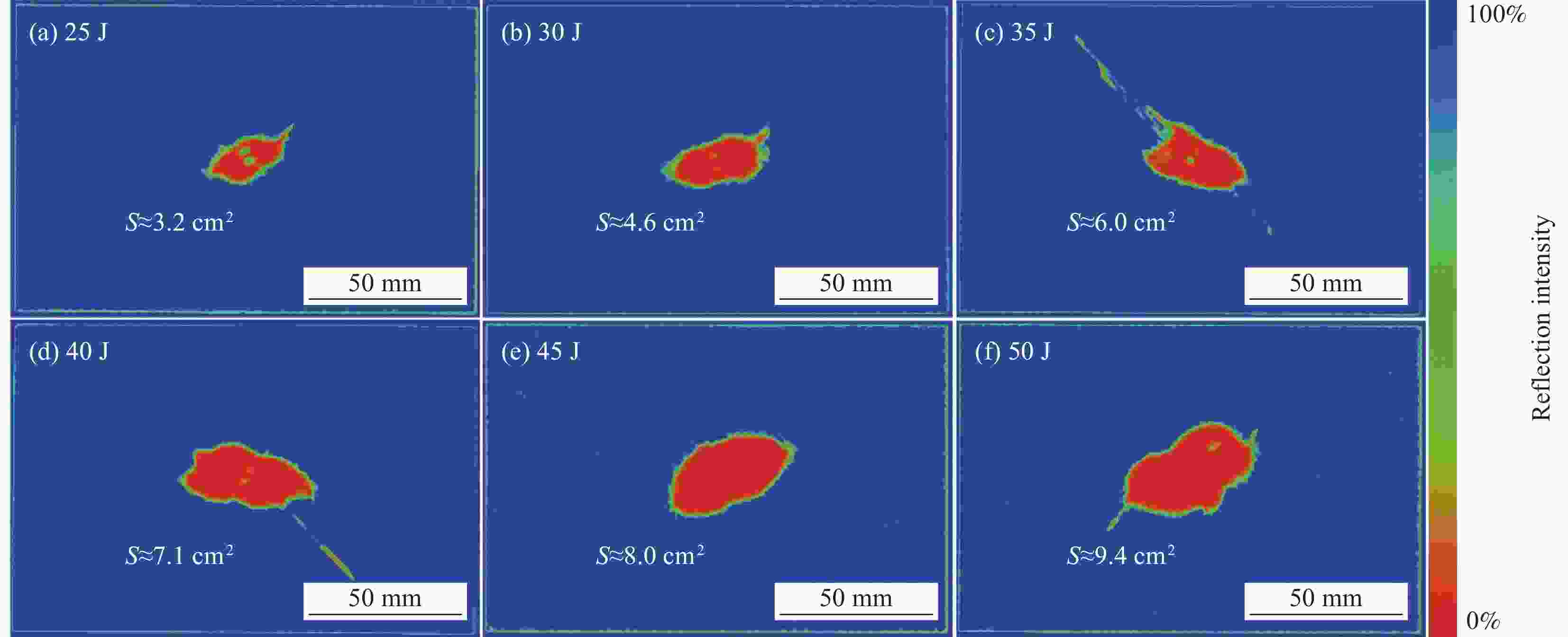
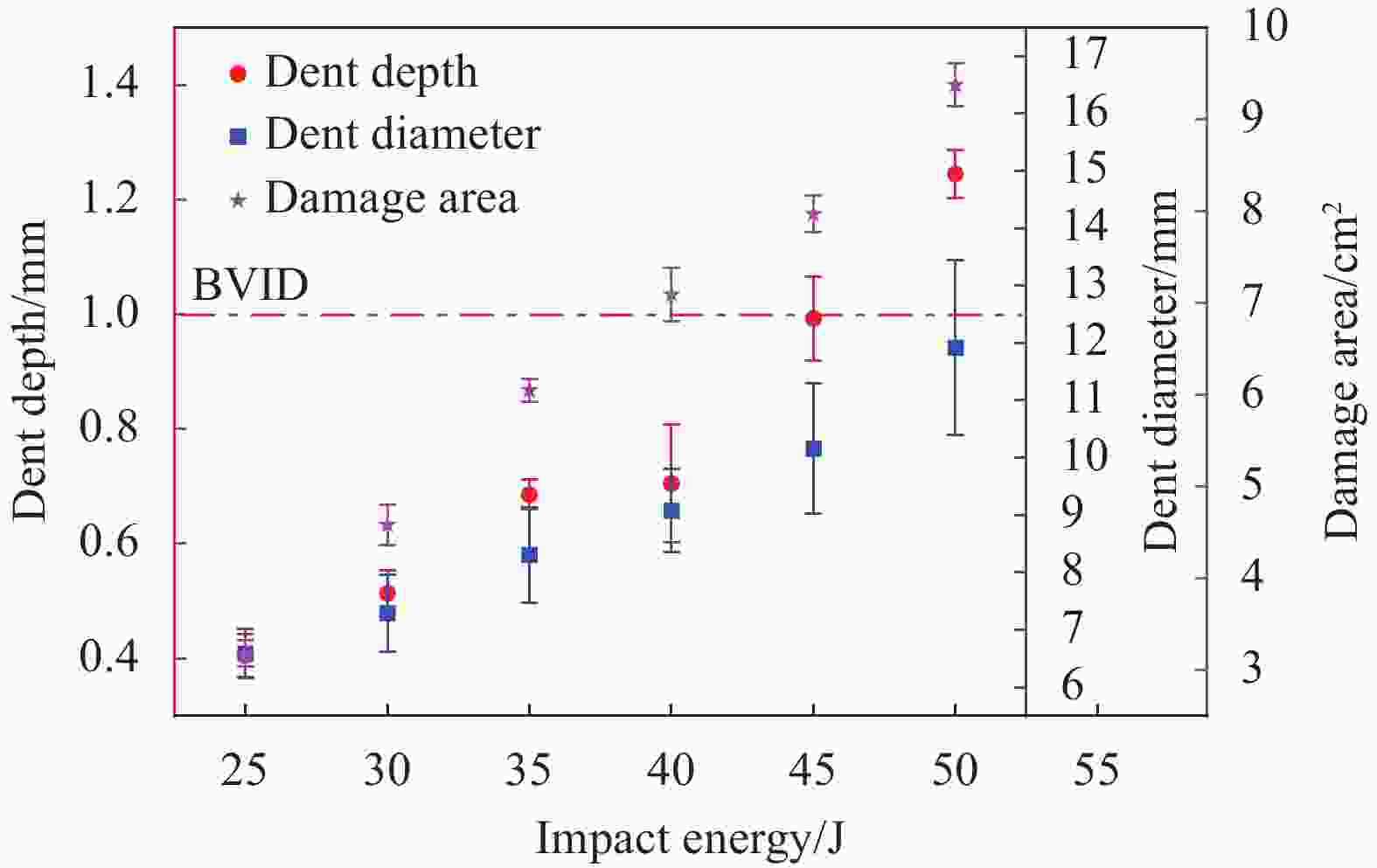
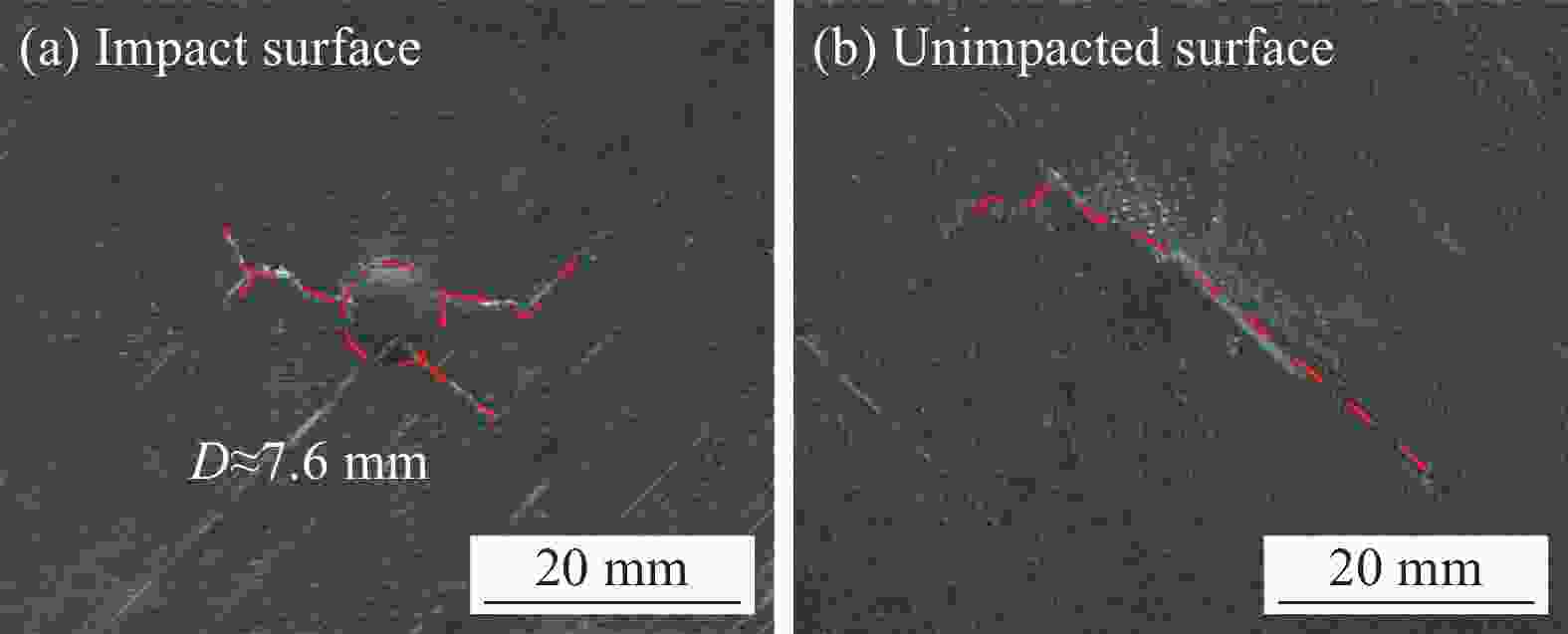
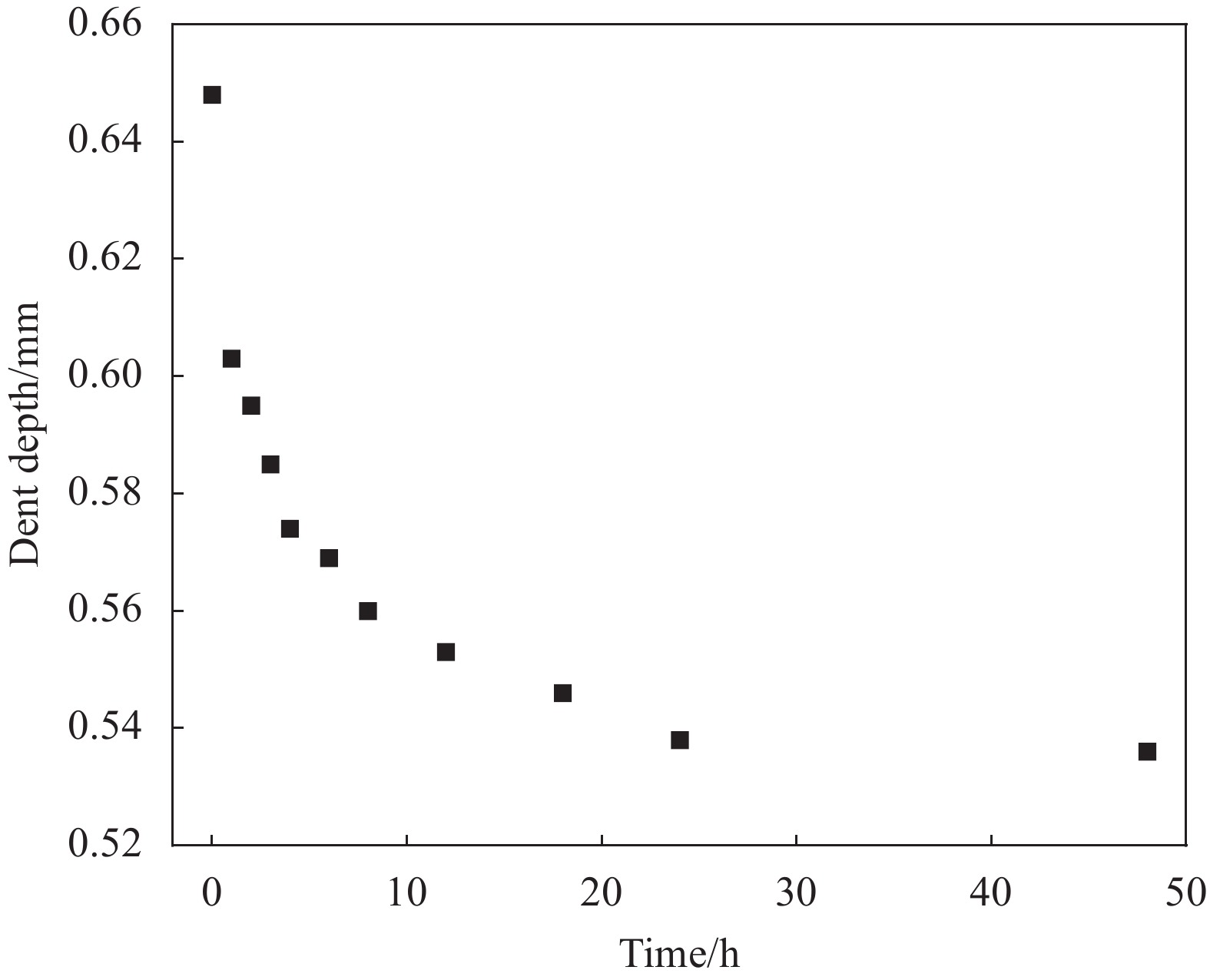
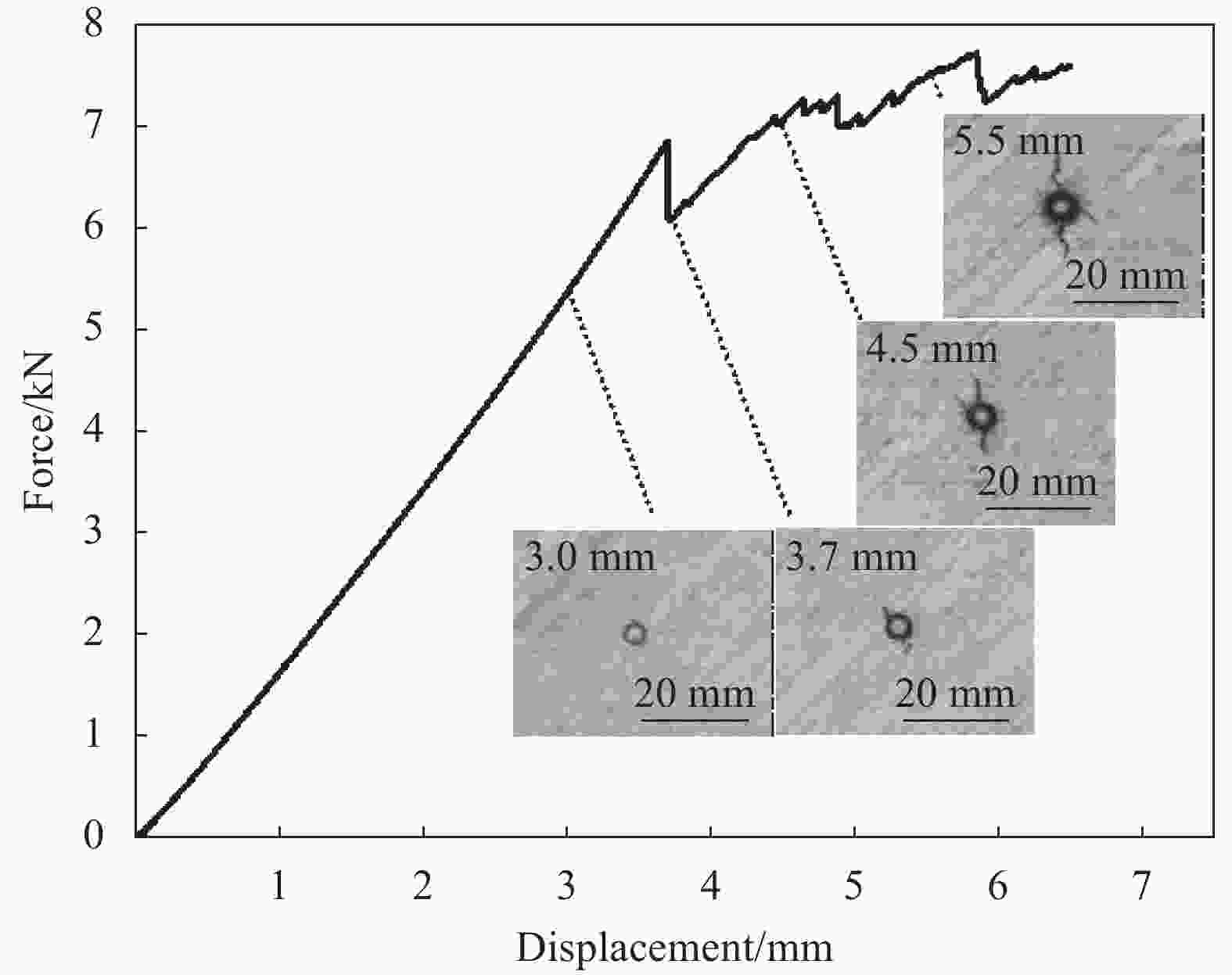
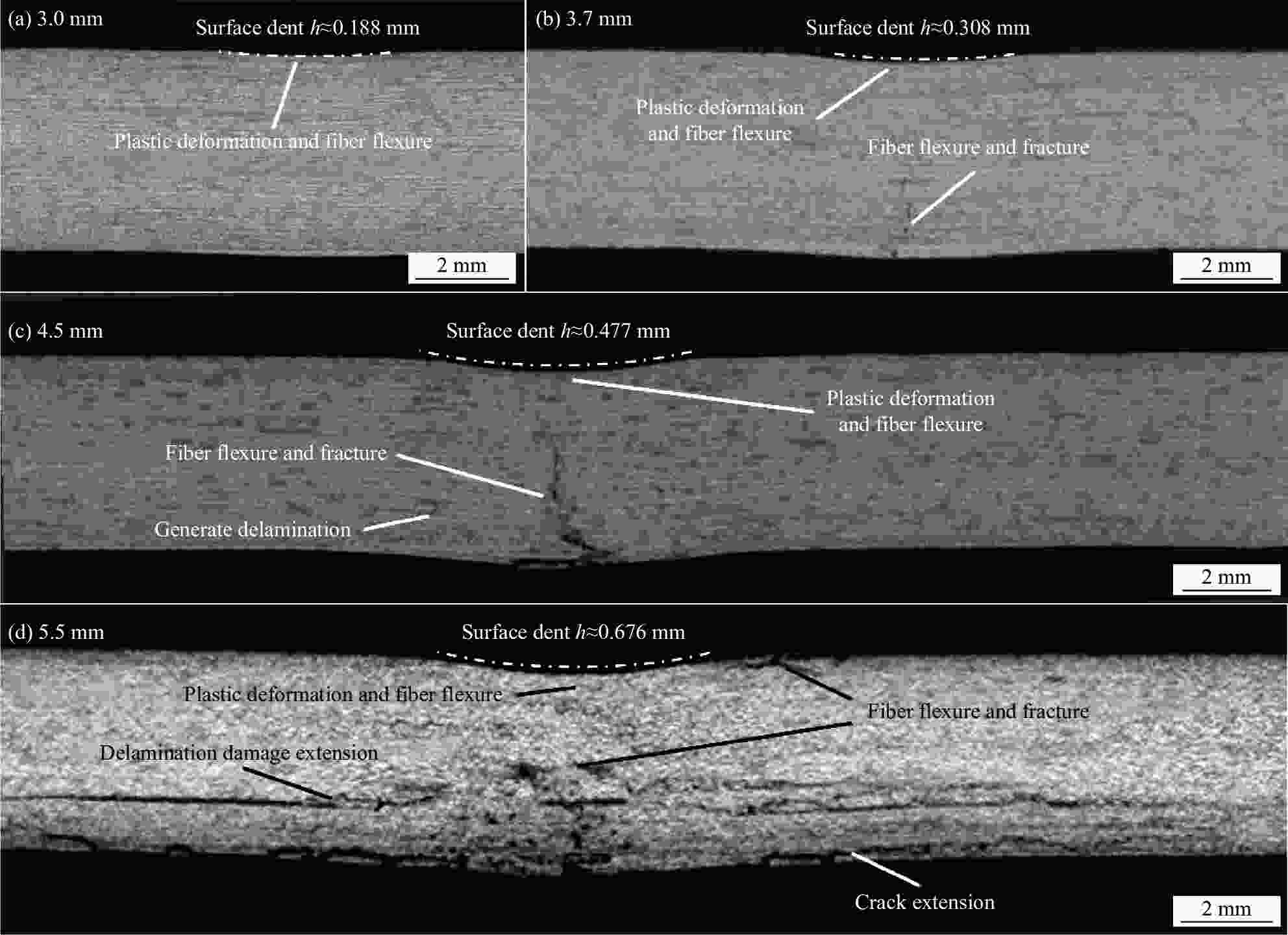
摘要: 采用两种不同熔体黏度的国产高性能聚芳醚酮树脂(PAEK-L、PAEK-H)及国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35),制备了碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(SCF35/PAEK)热塑性复合材料,研究了树脂基体黏度及冲击能量对复合材料冲击性能的影响,采用Micro-CT表征了准静态压入试样的内部形貌,研究了复合材料的冲击损伤机制。结果显示流动性较低的PAEK-L树脂基复合材料比流动性较高的PAEK-H树脂基复合材料具有更高的抗冲击性能,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料体系冲击能量的损耗比SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料体系低~7%,其损伤面积小~90%,在6.67 J/mm的冲击能量下,其冲击后压缩强度达到~307 MPa,比SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料体系冲击后压缩强度(205 MPa)高~50%;SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料中表面凹坑的深度随冲击能量的增加呈增加的趋势,冲击后压缩强度随冲击能量的增加呈降低的趋势,当复合材料的表面凹坑深度达到1.0 mm左右,即达到勉强目视可见冲击损伤(BVID)门槛值时,剩余压缩强度为~268 MPa。准静态压入实验结果显示,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料受到冲击后表面凹坑主要由树脂基体的塑性变形及纤维屈曲造成,表面凹坑周围的裂纹由压缩应力造成,冲击过程中试样背面的纤维在拉伸应力的作用下发生断裂,试样底层的纤维在剪切力的作用下萌生层间裂纹,随着试样挠曲变形程度的增加,纤维的断裂程度增加且层间裂纹逐渐扩展。
-
关键词:
- 聚芳醚酮(PAEK) /
- 热塑性复合材料 /
- 低速冲击 /
- 勉强目视可见冲击损伤(BVID) /
- 冲击后压缩
Abstract: Carbon fiber reinforced poly aryl ether ketone (SCF35/PAEK) thermoplastic composites were prepared using two different melt viscosities of domestic high performance poly aryl ether ketone resins (PAEK-L and PAEK-H) and domestic T300 grade carbon fibers (SCF35), and the effects of resin matrix viscosity and impact energy and impact energy on the impact properties of the composites were investigated. In addition, the internal morphology of quasi-static indentation specimens was characterized by Micro-CT to study the impact damage mechanism of the composites. The results show that PAEK-L resin matrix composite with lower fluidity has higher impact resistance than PAEK-H resin matrix composite with higher fluidity. The impact energy loss of the SCF35/PAEK-L composite system is ~7% lower than that of the SCF35/PAEK-H composite system, its damage area is ~90% smaller, and its compression strength after impact reaches ~307 MPa at an impact energy of 6.67 J/mm, which is ~50% higher than that of SCF35/PAEK-H composite system (205 MPa). The depth of surface dent in SCF35/PAEK-L composites tends to increase with the increase of impact energy, and the compression strength after impact tends to decrease with the increase of impact energy, and the compression strength after impact is ~268 MPa when the depth of surface dent of the composites reaches about 1.0 mm, i.e., when the threshold value of barely visible impact damage (BVID) is reached. In addition, the results of quasi-static indentation tests show that the surface dent of SCF35/PAEK-L composite after impact is mainly caused by plastic deformation of the resin matrix and fiber flexure, the cracks around the surface dent are caused by compressive stress, the fiber on the back side of the specimen is fractured under the action of tensile stress during the impact process, the fiber on the bottom layer of the specimen sprouts interlayer cracks under the action of shear force, with the increase of flexural deformation of the specimen, the degree of fiber fracture increases and the interlayer cracks gradually expand. -
表 1 国产 T300 级碳纤维(SCF35)/PAEK预浸带参数及其复合材料基本性能
Table 1. Parameters of domestic T300 grade carbon fiber (SCF35)/PAEK prepreg and its basic composite properties
Prepregs FAW/
(g∙m−2)FC/% RC/% Tensile properties (0°) Compression properties (0°) Flexural properties (0°) Strength/
MPaModulus/
GPaStrength/
MPaModulus/
GPaStrength/
MPaModulus/
GPaSCF35/PAEK-L 145±5 52±3 40±2 1730 119 1140 116 1400 117 SCF35/PAEK-H 1720 125 1200 118 1560 118 Notes: FAW—Fiber areal weight of SCF35/PAEK prepreg; FC—Fiber content by volume of SCF35/PAEK prepreg; RC—Resin content by weight of SCF35/PAEK prepreg; SCF35/PAEK-L—Composites of SCF35 carbon fiber reinforced low flowability poly aryl ether ketone; SCF35/PAEK-H—Composites of SCF35 carbon fiber reinforced high flowability poly aryl ether ketone. 表 2 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的抗冲击损伤性能
Table 2. Impact damage resistance of SCF35/PAEK composites
System Impact energy/(J·mm−1) Dent depth/mm Damage area/cm2 CAI/MPa SCF35/PAEK-L 6.67 0.6 ± 0.04 5.3 ± 0.3 307 ± 16 SCF35/PAEK-H 1.0 ± 0.09 10.0 ± 0.9 205 ± 11 Domestic T300/EP 0.3 ± 0.03 11.0 ± 1.34 197 ± 15 TC1225[23] 30.5 J — — 310 ± 11 Notes: CAI—Compression after impact strength of SCF35/PAEK composites; TC1225—Standard modulus carbon fiber reinforced PAEK prepreg manufactured by Toray Corporation of Japan; EP—Epoxy resin. -
[1] LIU H B, LIU J, DING Y Z, et al. The behaviour of thermoplastic and thermoset carbon fiber composites subjected to low-velocity and high-velocity impact[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2020,55(33):15741-15768. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-05133-0 [2] JOGUR G, NAWAZ KHAN A, DAS A, et al. Impact properties of thermoplastic composites[J]. Textile Progress,2018,50(3):109-183. doi: 10.1080/00405167.2018.1563369 [3] 谌广昌, 姚佳楠, 张金栋, 等. 高性能热塑性复合材料在直升机结构上的应用与展望[J]. 航空材料学报, 2019, 39(5):24-33. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2019.000035CHEN Guangchang, YAO Jia'nan, ZHANG Jindong, et al. Application and prospect of high performance thermoplastic composites in helicopter structure[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials,2019,39(5):24-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2019.000035 [4] 杨洋, 见雪珍, 袁协尧, 等. 先进热塑性复合材料在大型客机结构零件领域的应用及其制造技术[J]. 玻璃钢, 2017, 4(194):3-17.YANG Yang, JIAN Xuezhen, YUAN Xieyao, et al. Application and manufacturing technology of advanced thermoplastic composites in structural parts of large passenge aircraft[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics,2017,4(194):3-17(in Chinese). [5] 郭云竹. 热塑性复合材料研究及其在航空领域中的应用[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2016, 33(3):20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2016.03.005GUO Yunzhu. Research on thermoplastic composites and its application in the field of aviation[J]. Fiber Composites,2016,33(3):20-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2016.03.005 [6] 罗云烽, 姚佳楠. 高性能热塑性复合材料在民用航空领域中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2021, 64(16):93-102. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2021.16.093LUO Yunfeng, YAO Jia'nan. Applications of high performance thermoplastic composites in civil aviation[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2021,64(16):93-102(in Chinese). doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2021.16.093 [7] 王兴刚, 于洋, 李树茂, 等. 先进热塑性树脂基复合材料在航天航空上的应用[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2011, 28(2):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2011.02.011WANG Xinggang, YU Yang, LI Shumao, et al. The research on fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite[J]. Fiber Composites,2011,28(2):44-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2011.02.011 [8] 肇研, 刘寒松. 连续纤维增强高性能热塑性树脂基复合材料的制备与应用[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(8):49-61. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.000209ZHAO Yan, LIU Hansong. Preparation and application of continuous fiber reinforced high performance thermoplastic resin matrix composites[J]. Materials Engineering,2020,48(8):49-61(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.000209 [9] LAGACE P A, WILLIAMSON J E, WILSON TSANG P H, et al. A preliminary proposition for a test method to measure (impact) damage resistance[J]. Journal of reinforced Plastics and Composites,1993,12(5):584-601. doi: 10.1177/073168449301200508 [10] BYERS B A. Behavior of damaged graphite/epoxy laminates under compression loading[R]. Boeing Commercial Airplane Co. Seattle Wa, 1980. [11] 王俭, 沈真. 复合材料冲击损伤阻抗性能的试验研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2009(S1):161-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2009.z1.050WANG Jian, SHEN Zhen. Experimental study on impact damage resistance property of composites[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2009(S1):161-164(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2009.z1.050 [12] 沈真, 杨胜春, 陈普会. 复合材料层压板抗冲击行为及表征方法的实验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(5):125-133. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.05.021SHEN Zhen, YANG Shengchun, CHEN Puhui. Experimental study on the behavior and characterization methods of composite laminates to withstand impact[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2008,25(5):125-133(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.05.021 [13] Department of Defense. Composite materials handbook: MIL-H DBK-17F[S]. Virginia: US Department of Defense, 2002. [14] MORTEAU E, FUALDES C. Composites@airbus damage tolerance methodology[C]//Workshop for Composite Damage Tolerance and Maintenance. Chicago, IL: Federal Aeronautics Administration. 2006: 1. [15] LIU H, LIU J, DING Y, et al. Investigations on the impact behaviour of fibre-reinforced composites: Effect of impact energy and impactor shape[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity,2020,28:106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2020.10.014 [16] GE X, ZHANG P, ZHAO F, et al. Experimental and numerical investigations on the dynamic response of woven carbon fiber reinforced thick composite laminates under low-velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures,2022,279:114792. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114792 [17] BADER M G, BAILEY J E, BELL I. The effect of fibre-matrix interface strength on the impact and fracture properties of carbon-fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,1973,6(5):572-586. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/6/5/314 [18] BULL D J, SPEARING S M, SINCLAIR I. Investigation of the response to low velocity impact and quasi-static indentation loading of particle-toughened carbon-fibre composite materials[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,74:38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.03.016 [19] 顾洋洋, 姚佳楠, 王力风, 等. 聚芳醚酮树脂基体特性对复合材料界面性能和层间性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(8): 4486-4495.GU Yangyang, YAO Jia'nan, WANG Lifeng, et al. Influence of poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix properties on interfacial properties and interlayer properties of composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(8): 4486-4495(in Chinese). [20] ASTM. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/D7136 M-20[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2020. [21] ASTM. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer-matrix composite to a concentrated quasi-static indentation force: ASTM D6264/D6264 M-17[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2017. [22] ASTM. Standard test method for compressive residual strength properties of damaged polymer matrix composite laminates: ASTM D7137/D7137 M-17[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2017. [23] CLARKSON E. Medium toughness PAEK thermoplastics toray (Formerly TenCate) Cetex® TC1225 (LM PAEK) T700 GC 12 K T1 E unidirectional tape 145 gsm 34% RC material allowables statistical analysis report[D]. Wichita: Wichita State University, 2020. [24] LU T, CHEN X, WANG H, et al. Comparison of low-velocity impact damage in thermoplastic and thermoset composites by non-destructive three-dimensional X-ray microscope[J]. Polymer Testing,2020,91:106730. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106730 [25] YASAEE M, BOND I P, TRASK R S, et al. Damage control using discrete thermoplastic film inserts[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(6):978-989. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.01.011 [26] SHAH S Z H, KARUPPANAN S, MEGAT-YUSOFF P S M, et al. Impact resistance and damage tolerance of fiber reinforced composites: A review[J]. Composite Structures,2019,217:100-121. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.03.021 [27] ANDREW J J, SRINIVASAN S M, AROCKIARAJAN A, et al. Parameters influencing the impact response of fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite materials: A critical review[J]. Composite Structures,2019,224:111007. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111007 [28] TAN W, NAYA F, YANG L, et al. The role of interfacial properties on the intralaminar and interlaminar damage behaviour of unidirectional composite laminates: Experimental characterization and multiscale modelling[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,138:206-221. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.11.043 [29] LU C, WANG J, LU X, et al. Wettability and interfacial properties of carbon fiber and poly (ether ether ketone) fiber hybrid composite[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(34):31520-31531. [30] YAVAS D, ZHANG Z, LIU Q, et al. Interlaminar shear behavior of continuous and short carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites fabricated by additive manufacturing[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2021,204:108460. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108460 [31] XU W, DING J C. Correction of the large displacement effect on determination of mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of composite[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2020,238:107279. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107279 [32] WENZEL R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry,1936,28(8):988-994. [33] CASSIE A B D, BAXTER S. Wettability of porous surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1944,40:546-551. doi: 10.1039/tf9444000546 [34] DAVALLO M. Factors affecting fracture behaviour of composite materials[J]. International Journal of ChemTech Research,2010,2(4):2125-2130. [35] 李东明. 塑料冲击试验方法的评价[J]. 塑料, 1989, 18(4):46-50.LI Dongming. Evaluation of plastics impact test method[J]. Plastics,1989,18(4):46-50(in Chinese). [36] LOPRESTO V, CAPRINO G. Damage mechanisms and energy absorption in composite laminates under low velocity impact loads[M]//Dynamic Failure of Composite and Sandwich Structures. Dordrecht: Springer, 2013: 209-289. [37] RICHARDSON M O W, WISHEART M J. Review of low-velocity impact properties of composite materials[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,1996,27(12):1123-1131. doi: 10.1016/1359-835X(96)00074-7 [38] SUN X C, HALLETT S R. Failure mechanisms and damage evolution of laminated composites under compression after impact (CAI): Experimental and numerical study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,104:41-59. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.10.026 -






 下载:
下载: