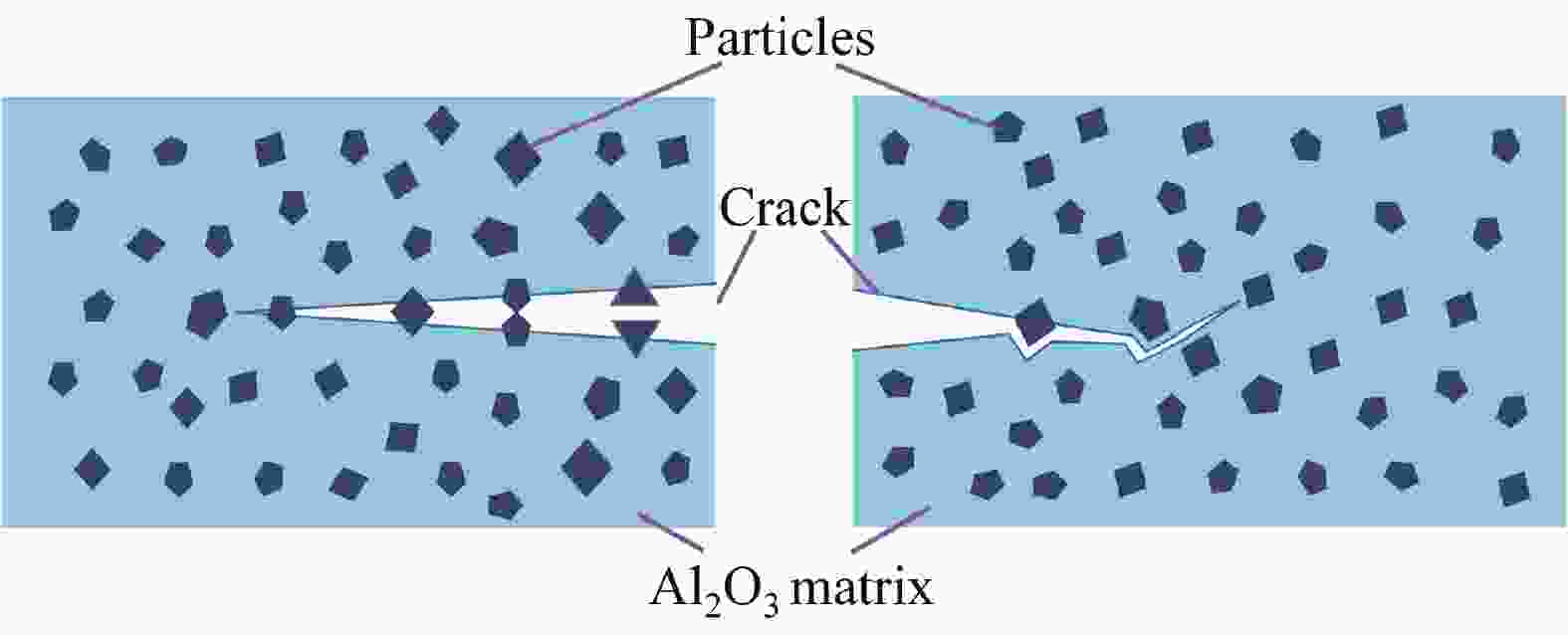
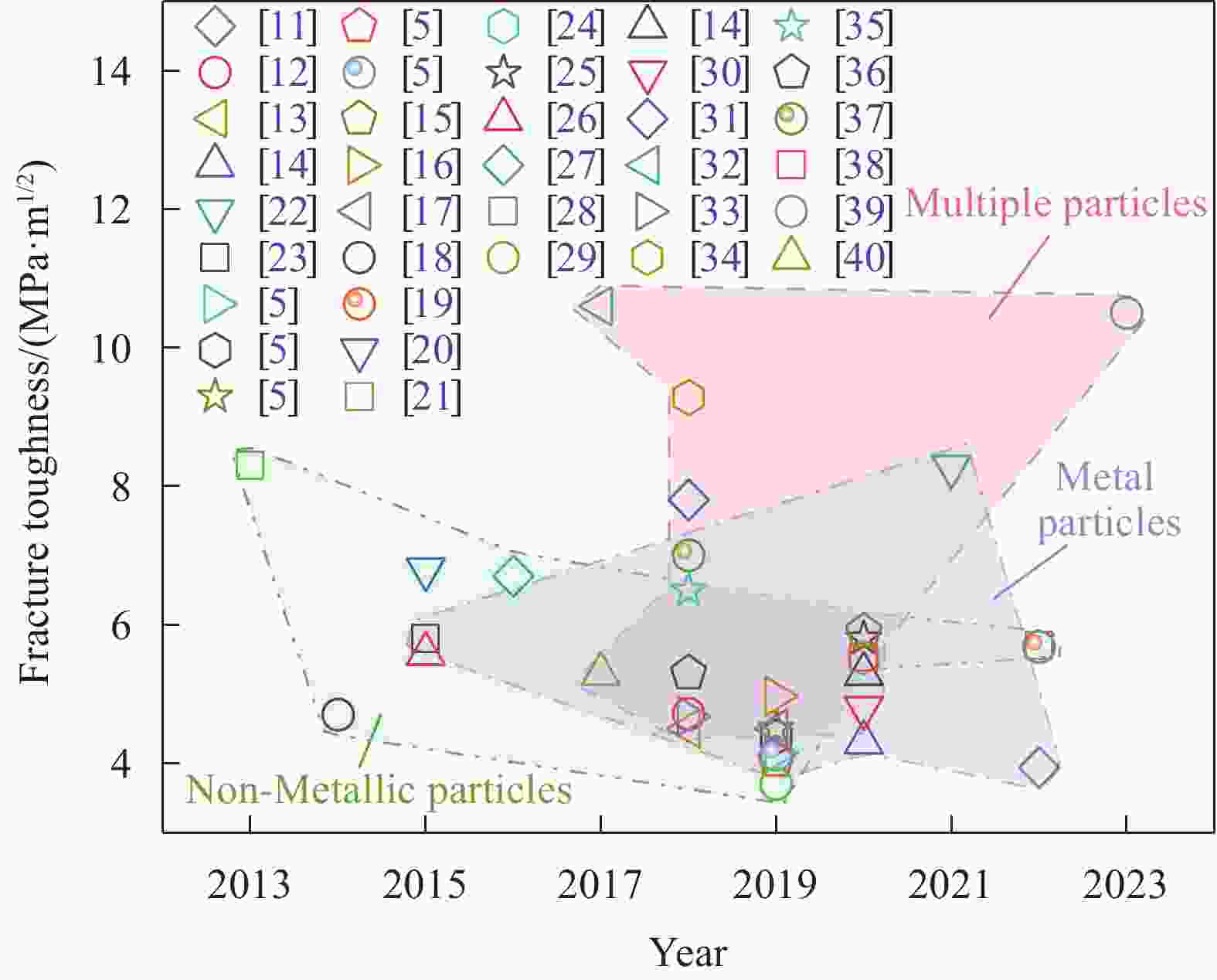
Research progress on toughening of alumina ceramic
-
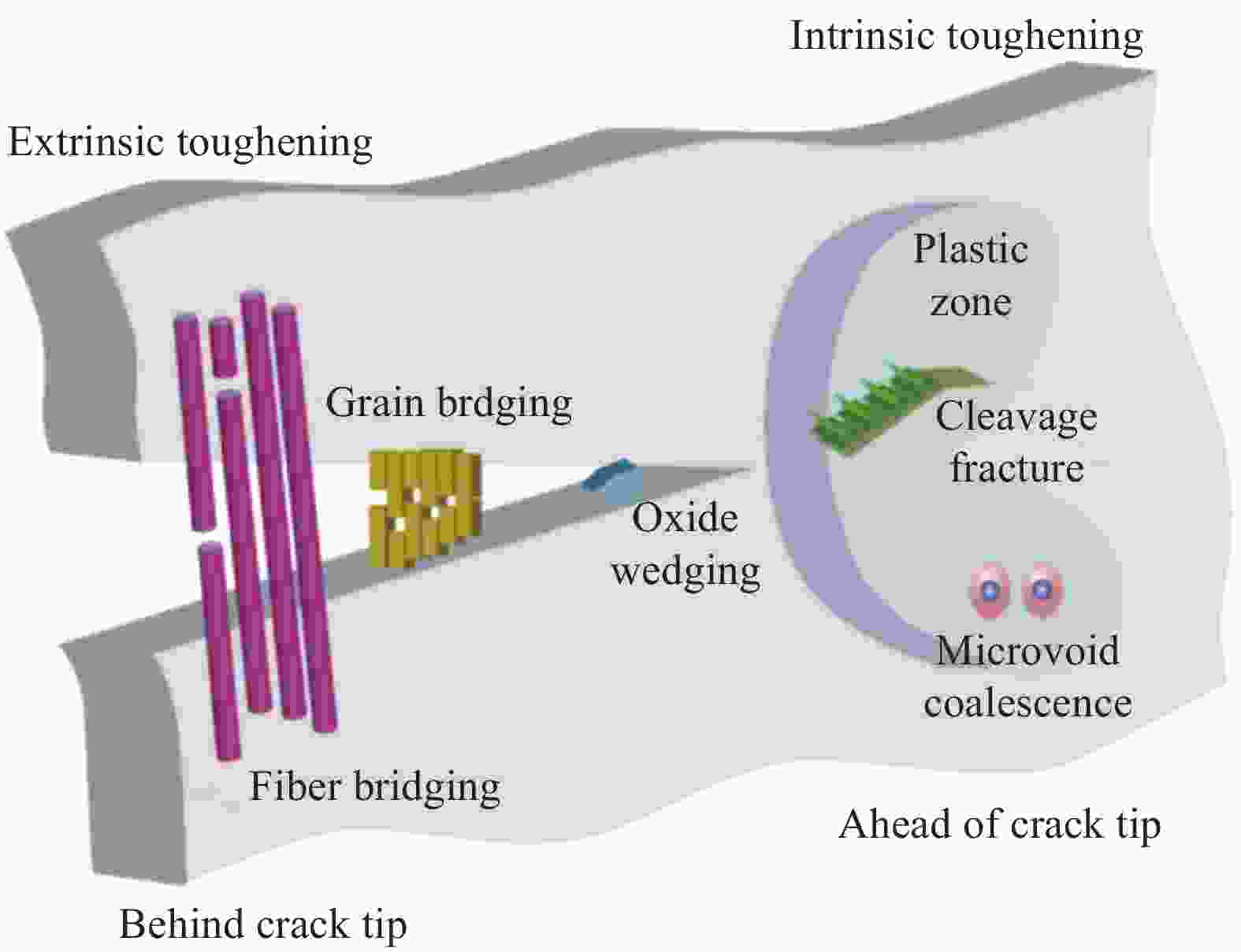
摘要: 作为研究最早和应用最广泛的陶瓷材料之一,氧化铝(Al2O3)陶瓷具有高强高硬、耐高温、耐磨损、耐腐蚀等许多优异特性,已在国防工业、航空航天以及生物医疗等领域得到了广泛应用。然而,固有的脆性极大地限制了Al2O3陶瓷在众多领域中的进一步应用。增韧始终是陶瓷材料研究中的一个核心研究课题,引入增韧相材料是提高陶瓷材料韧性的主要途径。本文首先简要概述了陶瓷材料的增韧机制,随即综述了Al2O3陶瓷增韧的最新研究现状,分析了增韧方法中存在的关键问题,展望了Al2O3陶瓷增韧的发展方向,以期为后续Al2O3陶瓷增韧的发展提供借鉴。Abstract: As one of the earliest researched and most widely used ceramics, alumina (Al2O3) have many excellent properties, such as high strength and hardness, high-temperature resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance, etc., and has been widely used in the fields of defense industry, aerospace and biomedicine. However, the inherent brittleness greatly limits the further application of Al2O3 ceramic in many fields. Toughening has always been a core research topic in the study of ceramic materials, and the introduction of toughened phase materials is the main way to improve the toughness of ceramic materials. In this paper, the toughening mechanism of ceramic materials is briefly summarized, and then the latest research status of Al2O3 ceramic toughening is reviewed, the key problems existing in the toughening method are analyzed, and the development direction of Al2O3 ceramic toughening is prospected, in order to provide reference for the subsequent development of Al2O3 ceramic toughening.
-
Key words:
- Al2O3 ceramic /
- toughness /
- toughening phase /
- toughening mechanism /
- review
-
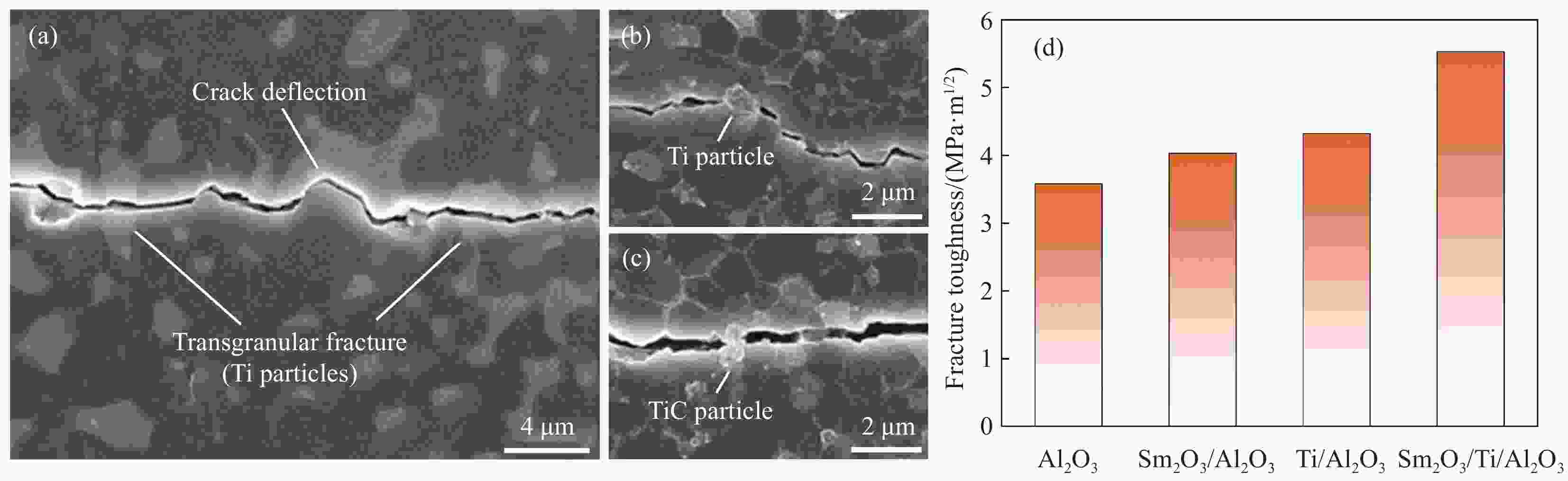
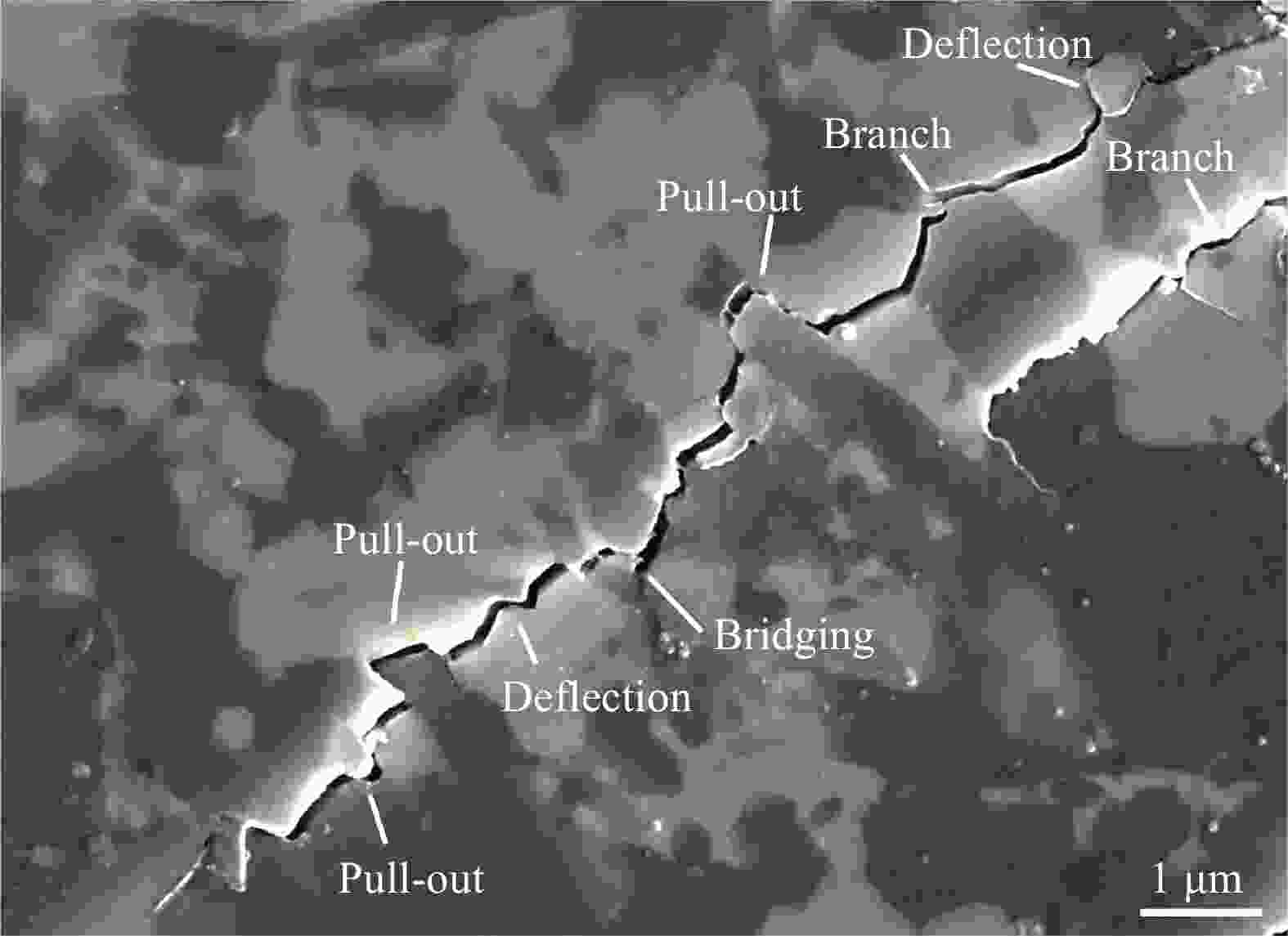
图 4 TiC/Ti/Al2O3复合材料表面裂纹的传播路径:(a)裂纹偏转和穿晶断裂,(b) Ti颗粒引起的裂纹桥联和(c) TiC颗粒引起的桥联[14];(d) Sm2O3/Ti/Al2O3复合材料的断裂韧性[38]
Figure 4. The propagation pathways of cracks introduced on the surface of TiC/Ti/Al2O3 composite: (a) Crack deflection and transgranular fracture, (b) Ti particle-induced crack bridging and (c) TiC particle-induced crack bridging[14]; (d) Fracture toughness of Sm2O3/Ti/Al2O3 composites[38]
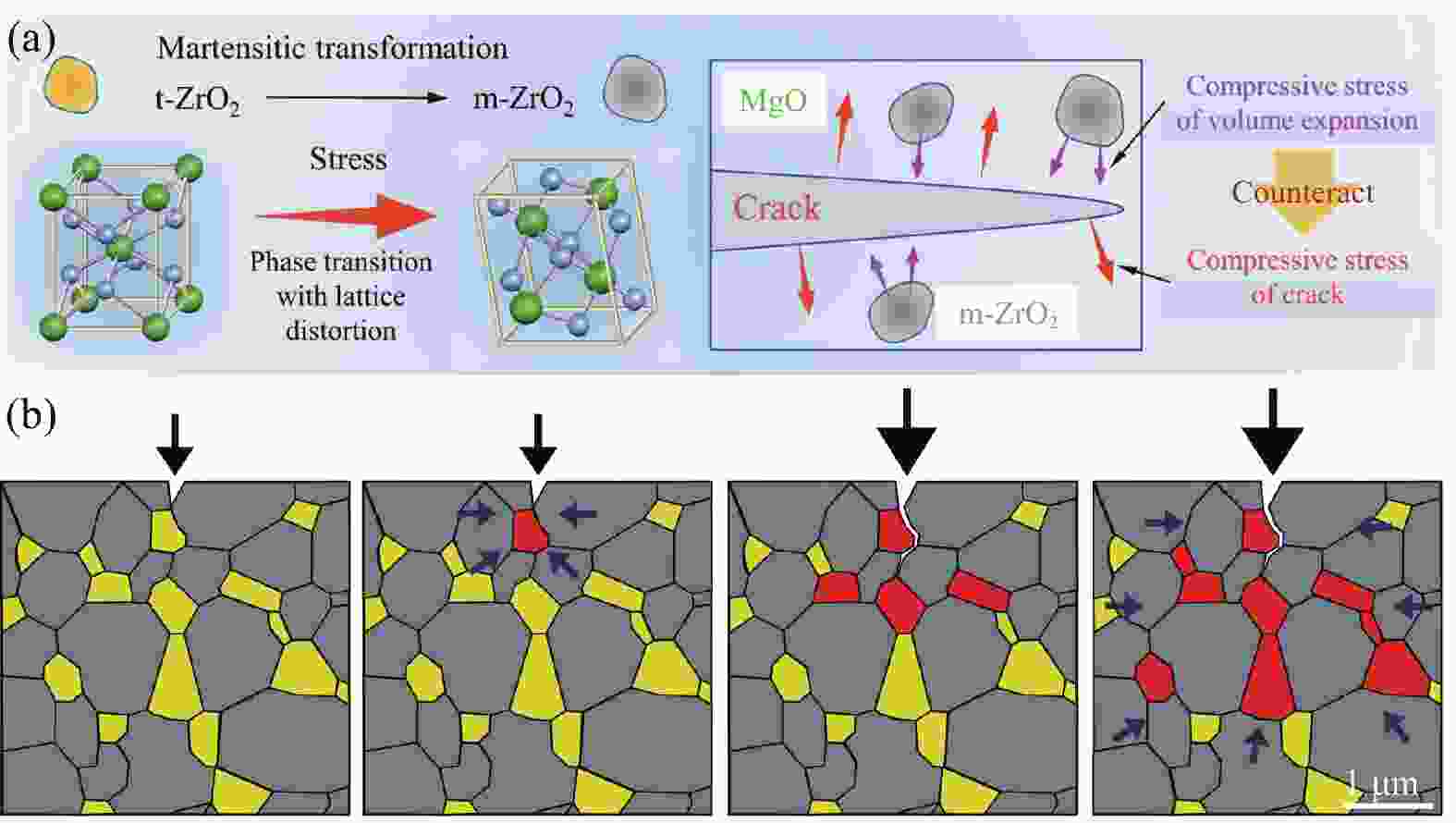
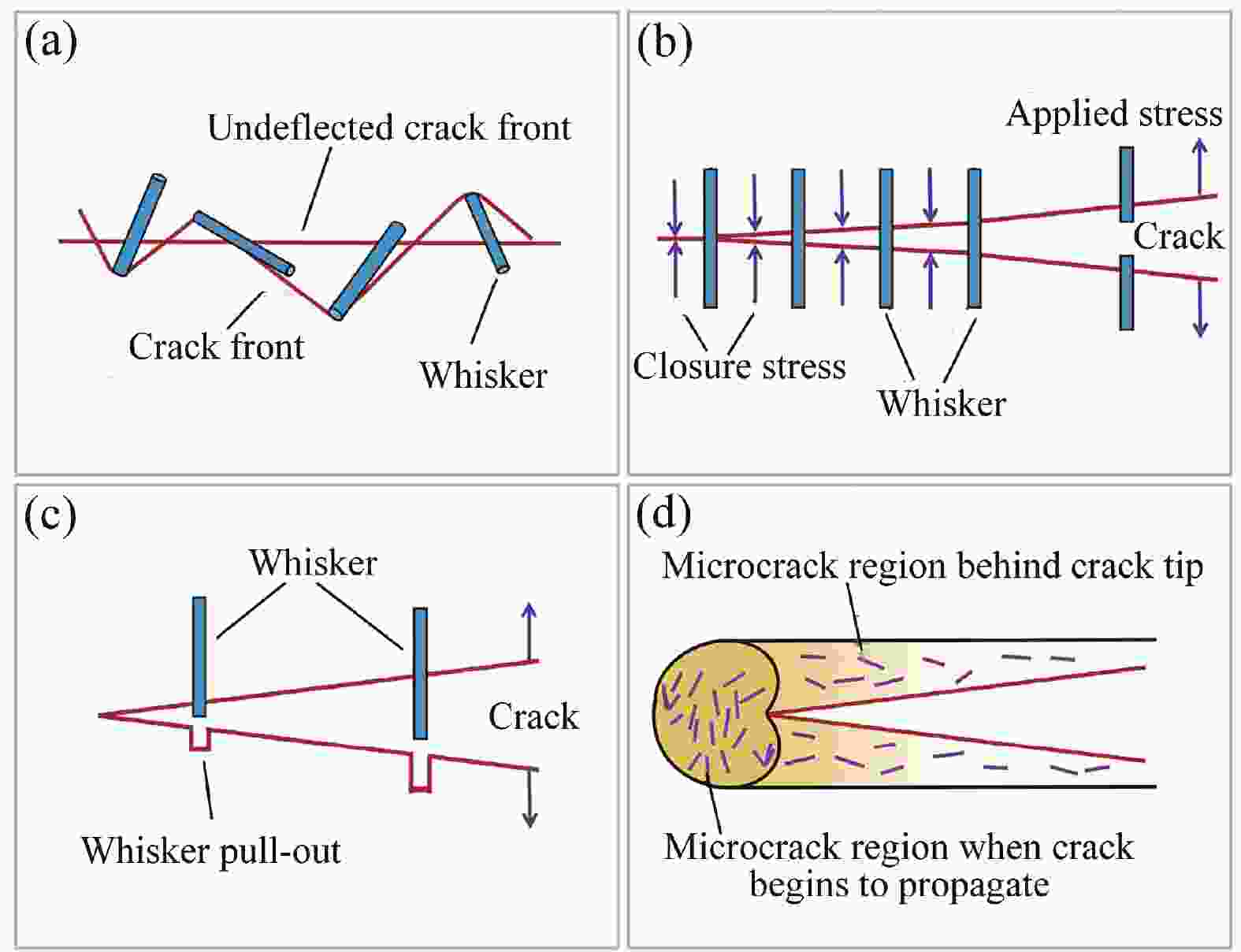
图 5 (a)塑性马氏体相变抑制裂纹传播示意图[42];(b) ZTA复合材料在裂纹萌发和扩展过程中的增韧机制(黄色颗粒表示四方相ZrO2,颜色变为红色表示向单斜相转化,箭头表示相变导致的压应力区域)[43]
Figure 5. (a) Schematic diagram of plastic martensite transformation Inhibiting the crack propagation[42]; (b) Toughening mechanism in ZTA composites at crack initiation and propagation (Yellow particles represent tetragonal zirconia, Color change to red indicates monoclinic phase transformation. Arrows show the region of compressive stresses due to phase transformation)[43]
t-ZrO2−Tetragonal zirconia; m-ZrO2−Monoclinic zirconia
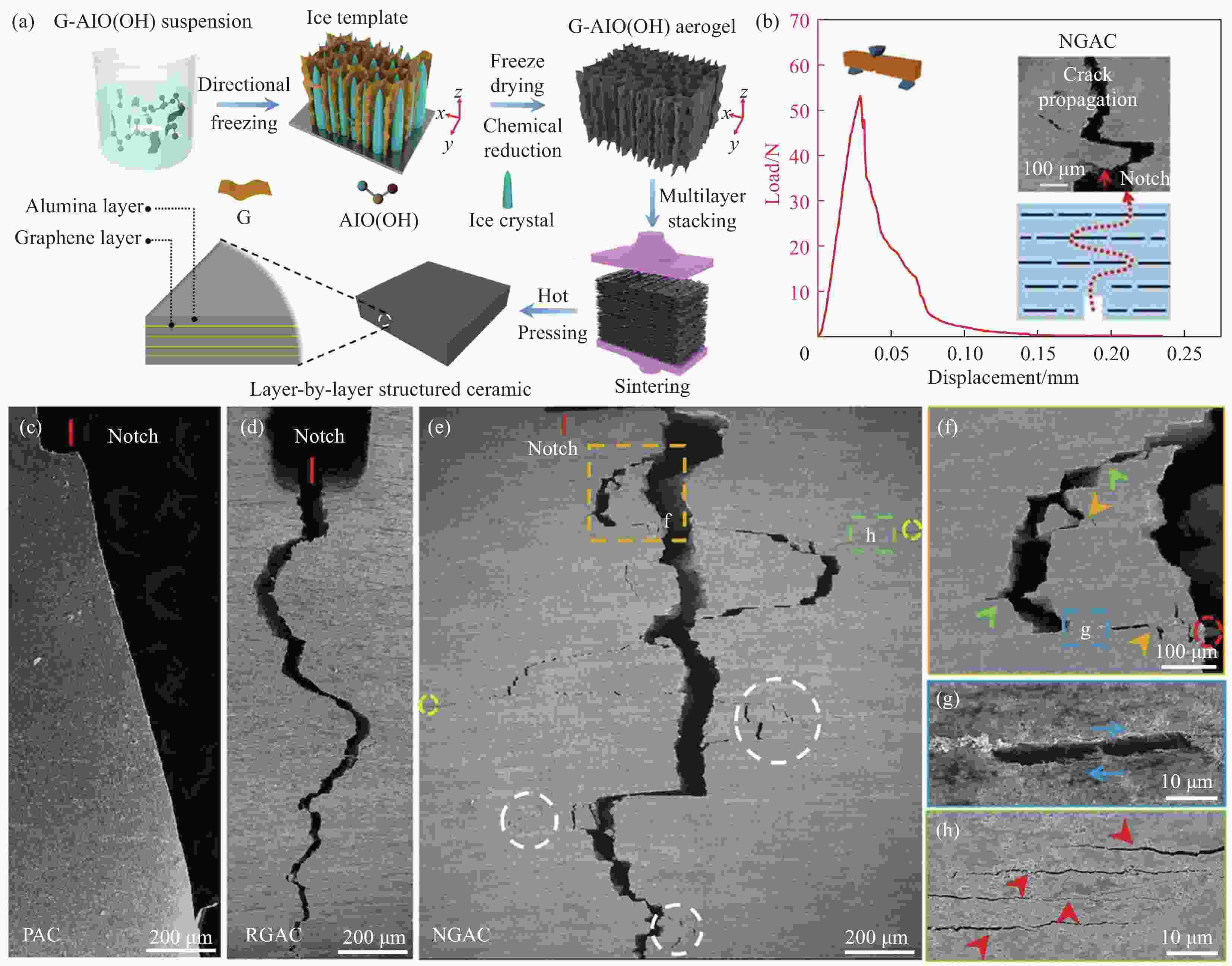
图 12 (a) NGAC的制备流程示意图;(b) NGAC的载荷-位移曲线;(c)PAC的裂纹传播路径;(d)RGAC的裂纹传播路径;(e)NGAC的裂纹传播路径(NGAC增韧机制:(f)裂纹偏转(绿色箭头),分支(黄色箭头),石墨烯拔出(红色圆圈),(g)界面摩擦(蓝色箭头)和(h)裂纹桥联(红色箭头))[82]
Figure 12. (a) Schematic diagram of preparation process for NGAC; (b) Load-displacement curve of NGAC; (c) Crack propagation path in PAC, (d) Crack propagation path in RGAC; (e) Crack propagation path in NGAC (Toughening mechanisms of NGAC including: (f) crack deflection (green arrow), bifurcation (yellow arrow) and pull-out of graphene (red cycle), (g) interfacial friction (blue arrow) and (h) crack bridging (red arrow))[82]
G−Graphene; PAC−Pure alumina ceramic; RGAC−Random distributed Graphene/alumina composites;NGAC−Nacre-like Graphene/alumina composites
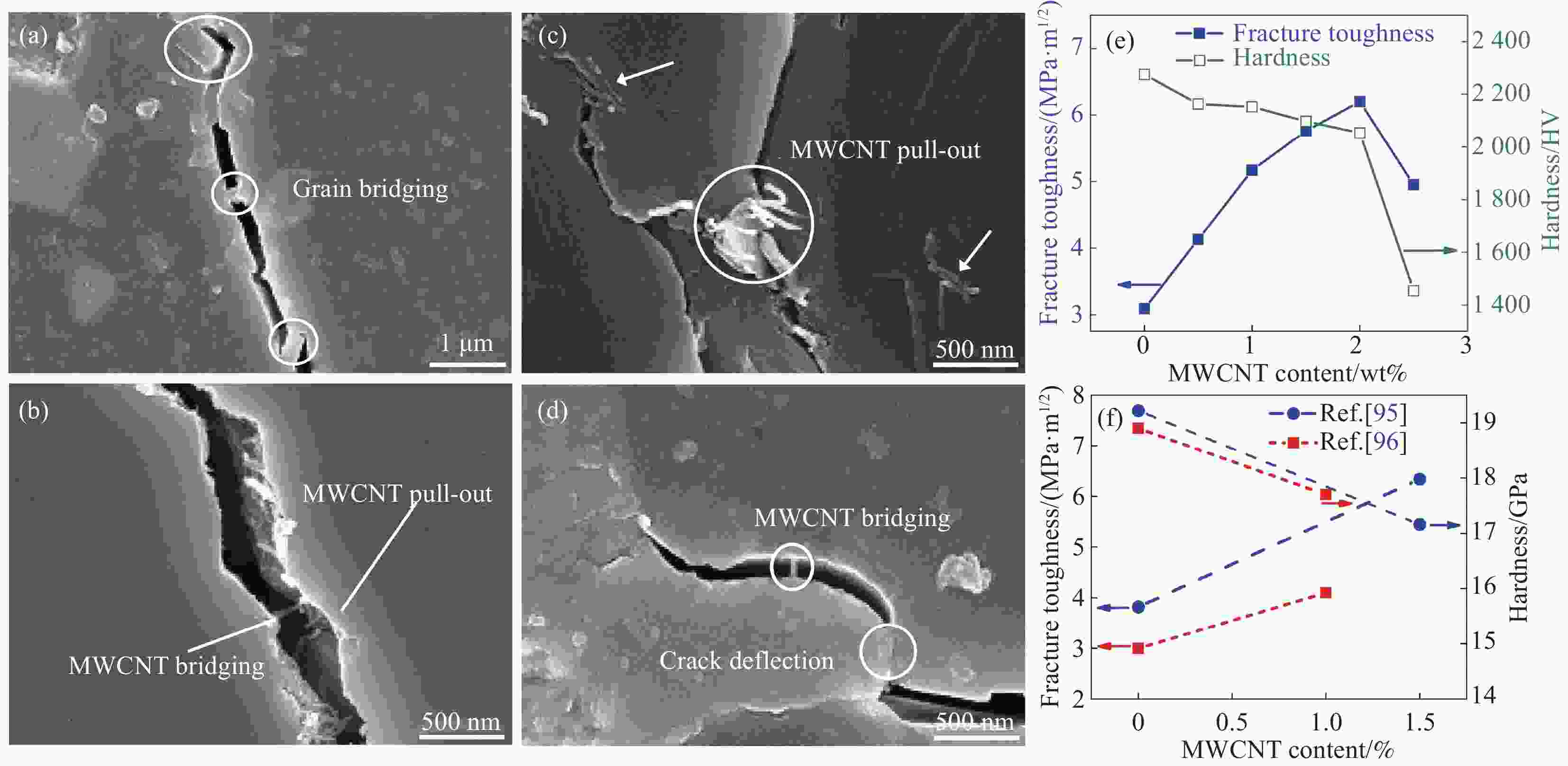
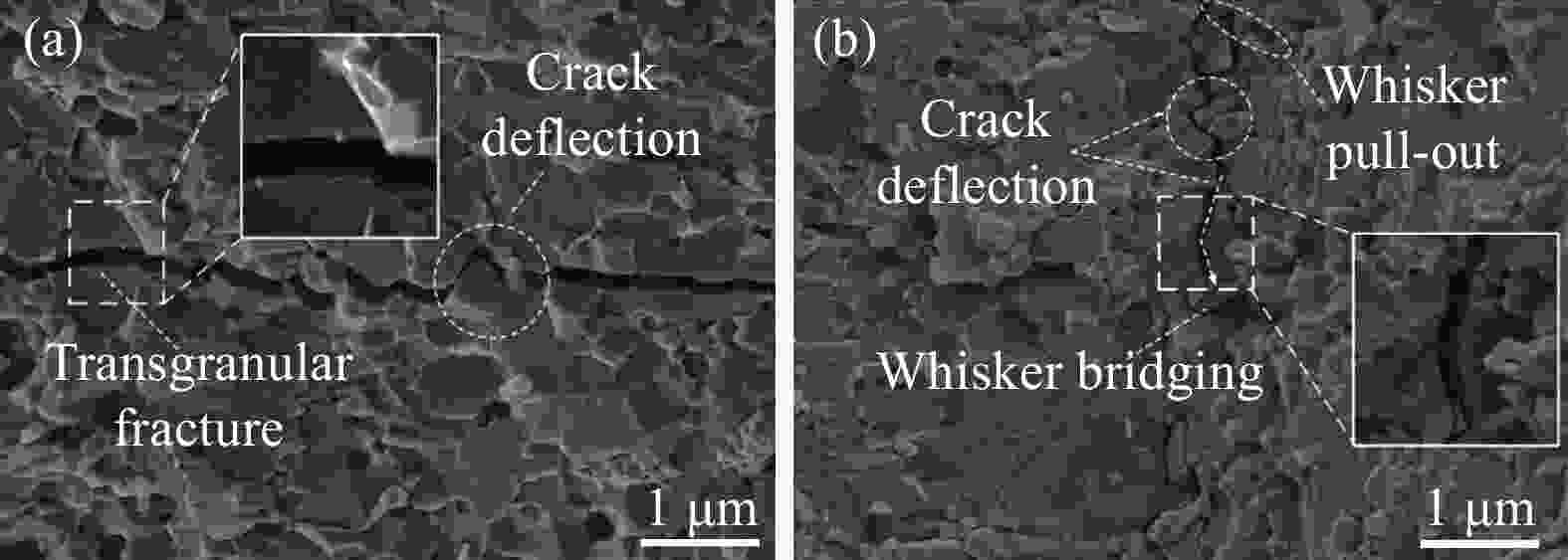
图 13 MWCNT/Al2O3复合材料的不同增韧机制:(a)晶粒桥联;(b) MWCNT拔出和桥联;(c) MWCNT拔出和(d)裂纹偏转和MWCNT桥联[94];((e),(f)) MWCNT/Al2O3复合材料的断裂韧性和硬度[95-97]
Figure 13. Different toughening mechanisms of MWCNT/Al2O3 composites: (a) grain bridging; (b) MWCNT pull-out and bridging; (c) MWCNT pull-out and (d) crack deflection and MWCNT bridging[94]; ((e),(f)) Fracture toughness and Hardness of the MWCNT/Al2O3 composites[95-97]
MWCNT−Multi-walled carbon nanotube
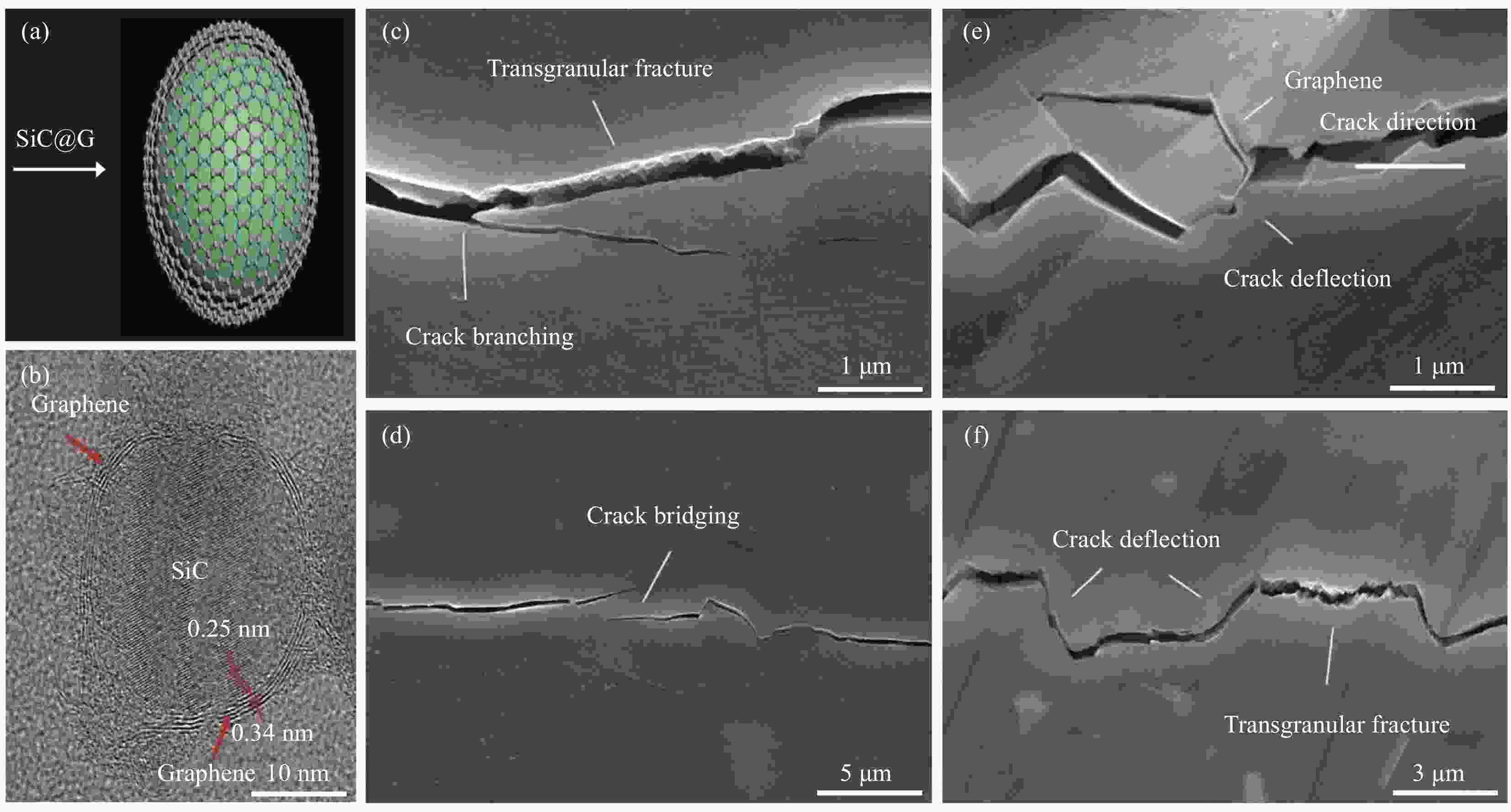
图 16 ((a),(b))SiC@石墨烯(SiC@G)的核壳结构;SiC@G/Al2O3复合材料的不同增韧机制:(c)裂纹分支,(d)裂纹桥联,(e)核壳结构导致的裂纹偏转和(f)裂纹偏转和穿晶断裂[114]
Figure 16. ((a),(b)) The core-shell structure of SiC@graphene(SiC@G); Different toughening mechanisms of SiC@G/Al2O3 composites: (c) crack branching, (d) crack bridging, (e) crack deflection caused by core-shell structure and (f) crack deflection and transgranular fracture[114]
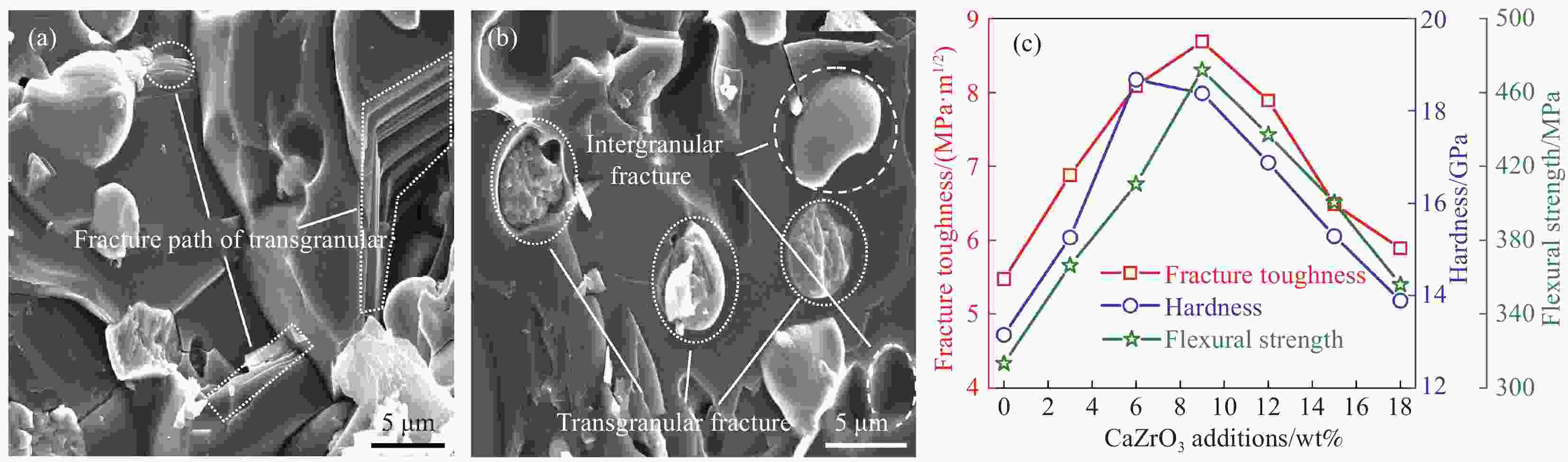
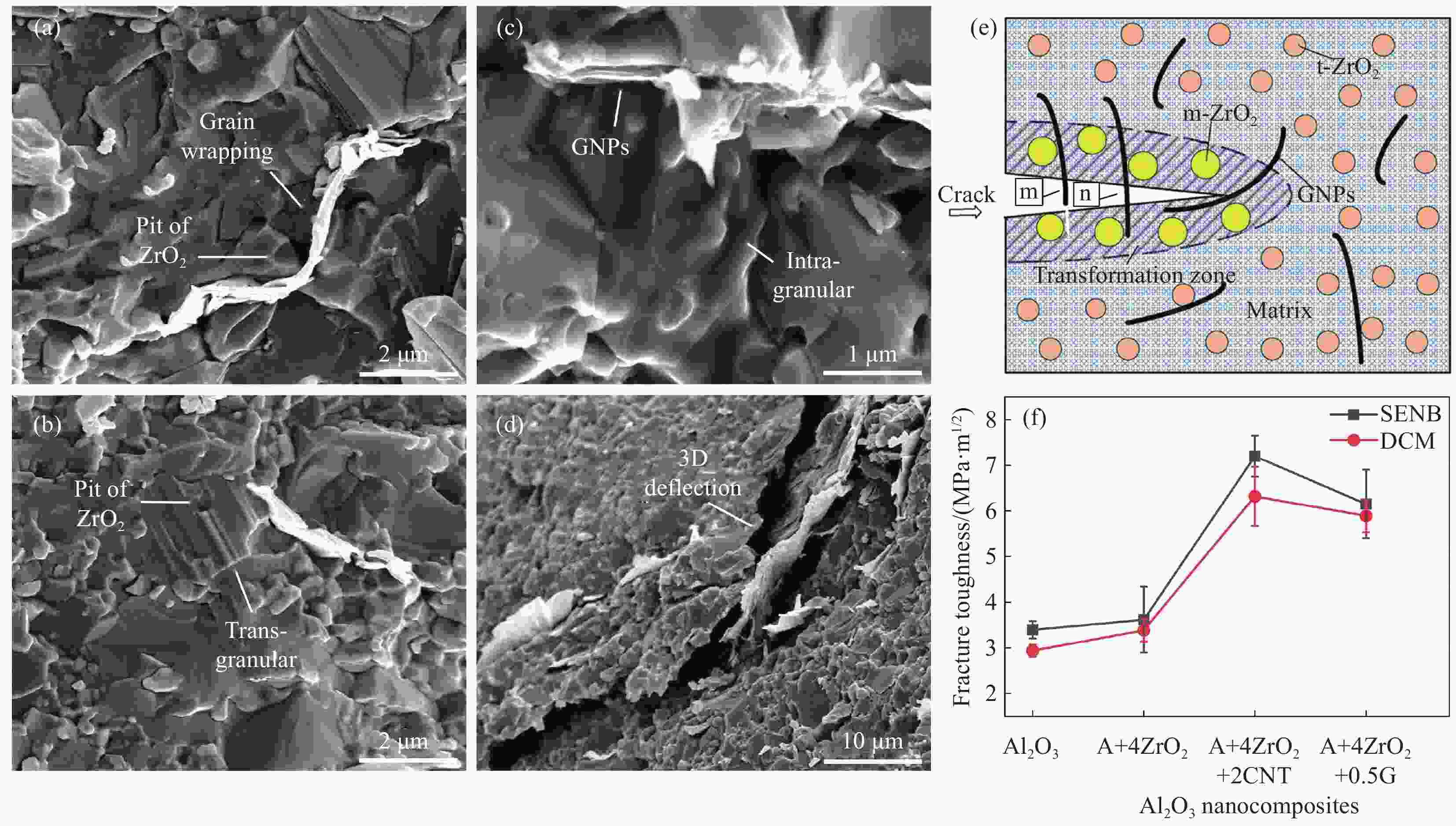
图 17 石墨烯纳米片(GNPs)和纳米ZrO2协同增韧Al2O3-Ti(C,N)复合材料不同的增韧机制:(a) GNPs拔出,(b)穿晶断裂,(c)沿晶断裂和(d) 3D裂纹偏转;(e) GNPs和纳米ZrO2的协同增韧机制示意图:(m)GNPs拔出和(n)裂纹桥联[117];(f) Al2O3纳米复合材料中的断裂韧性变化[118-119]
Figure 17. Different Toughening Mechanisms for Synergistic Toughening of Al2O3-Ti(C,N) Composites by Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNPs) and Nano-ZrO2: (a) pull-out of GNPs, (b) transgranular fracture, (c) intragranular fracture and (d) 3 D crack deflection; (e) Schematic diagram of the synergistic toughening mechanism of GNPs and nano-ZrO2: (m) pull-out of GNPs and (n) crack bridging[117]; (f) Fracture toughness variations in Al2O3 nanocomposites[118-119]
SENB−Single edge notched beam; DCM−Direct crack measurement
表 1 GO/GNPs增韧Al2O3复合材料的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of GO/GNPs toughened Al2O3 composites
-
[1] MUDRA E, HRUBOVCAKOVA M, SHEPA I, et al. Processing and characterization of fiber-reinforced and layered alumina-graphene composites[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(14): 4808-4817. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.03.039 [2] KRISHNAN S V, AMBALAM M M, VENKATESAN R, et al. Technical review: Improvement of mechanical properties and suitability towards armor applications-Alumina composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(17): 23693-23701. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.146 [3] XING H Y, ZOU B, WANG X F, et al. Fabrication and characterization of SiC whiskers toughened Al2O3 paste for stereolithography 3D printing applications[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828: 154347. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154347 [4] 穆柏春. 陶瓷材料的强韧化 [M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002: 33-40.MU B C. Toughening of Ceramic Materials [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002: 33-40(in Chinese). [5] ROCHA-RANGEL E, LÓPEZ-HERNÁNDEZ J, CALLES-ARRIAGA C A, et al. Effect of additions of metal submicron particles on properties of alumina matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2019, 34(17): 2983-2989. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2019.178 [6] 储爱民, 王志谦, 张德智, 等. Al2O3基陶瓷材料增韧的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(S1): 363-367,383.CHU A M, WANG Z Q, ZHANG D Z, et al. Review on toughening techniques for Alumina matrix ceramic material[J]. Materials Reports, 2017, 31(S1): 363-367,383(in Chinese). [7] 张长瑞, 郝元恺. 陶瓷基复合材料 [M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 2001: 54-96.ZHANG C R, HAO Y K. Ceramic Matrix Composites [M]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology Press, 2001: 54-96(in Chinese). [8] 李云凯, 周张健. 陶瓷及其复合材料 [M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2007: 4-39.LI Y K, ZHOU Z J. Ceramic and Composites of Ceramic Materials [M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2007: 4-39(in Chinese). [9] RITCHIE R O. The conflicts between strength and toughness[J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10: 817-822. doi: 10.1038/nmat3115 [10] IGHODARO O L, OKOLI O I. Fracture Toughness Enhancement for Alumina Systems: A Review[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2008, 5(3): 313-323. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7402.2008.02224.x [11] SHARMA N, KUMAR R, MITRA R, et al. Novel processing route for design and manufacturing of metal toughened nanoceramics: Al-Al2O3 nanocermets[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(17): 25168-25182. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.180 [12] IRSHAD H M, HAKEEM A S, AHMED B A, et al. Effect of Ni content and Al2O3 particle size on the thermal and mechanical properties of Al2O3/Ni composites prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2018, 76: 25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2018.05.010 [13] BOATEMAA L, VAN DER ZWAAG S, SLOOF W G. Self-healing of Al2O3 containing Ti microparticles[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(10): 11116-11126. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.119 [14] SHI S F, CHO S H, GOTO T, et al. CNT-induced TiC toughened Al2O3/Ti composites: Mechanical, electrical, and room-temperature crack-healing behaviors[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(8): 4573-4585. doi: 10.1111/jace.17152 [15] AKBARI E, KAKROUDI M G, SHAHEDIFAR V, et al. The influence of different SiC amounts on the microstructure, densification, and mechanical properties of hot-pressed Al2O3-SiC composites[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(2): 491-500. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13406 [16] HONG D B, YIN Z B, YAN S Y, et al. Fine grained Al2O3/SiC composite ceramic tool material prepared by two step microwave sintering[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(9): 11826-11832. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.061 [17] MORADKHANI A, BAHARVANDI H, NASERIFAR A. Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Grain Size and Mechanical Properties of Al2O3-SiC Nanocomposites[J]. Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society, 2019, 56(3): 256-268. doi: 10.4191/kcers.2019.56.3.01 [18] JOHNSON O T, ROKEBRAND P, SIGALAS I. Microstructure and Properties of Al2O3-SiC Nanomaterials[J]. Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, 2014, 2: 1317-1320. [19] CHAI J L, ZHU Y B, GAO X, et al. Effects of residual stress and intragranular particles on mechanical properties of hot-pressed Al2O3/SiC ceramic composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(16): 23258-23265. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.310 [20] BAI X L, HUANG C Z, WANG J, et al. Fabrication and characterization of Si3N4 reinforced Al2O3-based ceramic tool materials[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(10): 12798-12804. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.06.115 [21] YIN Z B, HUANG C Z, ZOU B, et al. Study of the mechanical properties, strengthening and toughening mechanisms of Al2O3/TiC micro-nano-composite ceramic tool material[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2013, 577: 9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.04.033 [22] LI Z Y, FU L P, GU H Z, et al. Fabrication of in-situ Ti(C, N) phase toughened Al2O3 based ceramics from natural bauxite[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(18): 25497-25504. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.05.273 [23] HUANG M Y, LI Z, WU J, et al. Multifunctional Alumina Composites with Toughening and Crack-Healing Features Via Incorporation of NiAl Particles[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(5): 1618-1625. doi: 10.1111/jace.13508 [24] NIE G L, LI Y H, SHENG P F, et al. Fabrication of Al2O3/AlN composite ceramics with enhanced performance via a heterogeneous precipitation coating process[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(13): 21156-21165. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.193 [25] KLIMCZYK P, WYZGA P, CYBORON J, et al. Phase stability and mechanical properties of Al2O3-cBN composites prepared via spark plasma sintering[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2020, 104: 107762. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107762 [26] CHEN W H, NAYAK P K, LIN H T, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of WC-reinforced Al2O3 ceramics via spark plasma sintering[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(1): 1317-1321. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.09.063 [27] WANG X M, LA P Q, WANG B J, et al. Toughening Effect of ZrB2 in Al2O3-ZrB2 Nanocomposite Ceramics[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(7): 1714-1718. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5372(16)30146-1 [28] WU J K, WANG H K, ZHANG Z C, et al. High-pressure synthesis of Al2O3-cBN composites: Effect of thermodynamic condition and cBN volume fraction on their microstructure and properties[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2022, 109: 105969. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2022.105969 [29] SARATH CHANDRA K, MONALISA M, CHOWDARY C V A, et al. Microstructure and mechanical behaviour of SrO doped Al2O3 ceramics[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2019, 739: 186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.038 [30] SHI S F, SEKINO T, CHO S H, et al. Ti and TiC co-toughened Al2O3 composites by in-situ synthesis from reaction of Ti and MWCNT[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2020, 777: 139066. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139066 [31] WANG D, XUE C, CAO Y, et al. Microstructure design and preparation of Al2O3/TiC/TiN micro-nanocomposite ceramic tool materials based on properties prediction with finite element method[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(5): 5093-5101. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.109 [32] NI X Y, ZHAO J, SUN J L, et al. Effects of metal binder on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al2O3-based micro-nanocomposite ceramic tool material[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2017, 24: 826-832. doi: 10.1007/s12613-017-1466-6 [33] SHI S F, CHO S H, GOTO T, et al. Combinative effects of Y2O3 and Ti on Al2O3 ceramics for optimizing mechanical and electrical properties[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(15): 18382-18388. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.054 [34] HENNICHE A, OUYANG J H, LIU Z G, et al. Effect of SiC addition on mechanical properties of hot-pressed Al2O3-GdAlO3 ceramics with eutectic composition[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(8): 9585-9592. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.182 [35] HE W, AI Y L, LIANG B L, et al. Effects of La2O3 and Nb2O5 dopants on the microstructural development and fracture toughness of Al2O3 ceramic[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 723: 134-140. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.057 [36] ZHANG M W, LI X D, ZHANG M, et al. Fabrication of a novel Al2O3-Ti(C0.7N0.3)-cBN composite with excellent performance in the turning of difficult-to-machine stellite alloys[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(11): 12815-12824. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.088 [37] FEI Y H, HUANG C Z, LIU H L, et al. The Influence of Ni Addition on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Al2O3-TiN-TiC Ceramic Materials[J]. Nanomanufacturing and Metrology, 2018, 1: 105-111. doi: 10.1007/s41871-018-0012-0 [38] SHI S F, CHO S H, GOTO T, et al. Ti and SmAlO3 co-affected Al2O3 ceramics: Microstructure, electrical and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 835: 155427. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155427 [39] WANG D, BAI Y F, QIU B, et al. Design of spark plasma sintering parameters and preparation of Al2O3/TiB2/TiC micro-nano composite ceramic tool material[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2023, 20(3): 1420-1431. doi: 10.1111/ijac.14284 [40] MORADKHANI A, BAHARVANDI H. Microstructural analysis of fracture surfaces and determination of mechanical properties of Al2O3-SiC-MgO nanocomposites[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2017, 67: 40-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.05.004 [41] SKTANI Z D I, ARAD L, MOHAMED J J, et al. Effects of additives additions and sintering techniques on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA): A review[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2022, 106: 105870. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2022.105870 [42] QIAN W F, ZHANG Z, WANG S, et al. Enhancing the toughness of nano-composite coating for light alloys by the plastic phase transformation of zirconia[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2023, 163: 103555. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2023.103555 [43] PICONI C, PORPORATI A A. Bioinert ceramics: zirconia and alumina [M] // ANTONIAC T V. Handbook of bioceramics and biocomposites. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 59-89. [44] LIU W, WU H D, XU Y R, et al. Cutting performance and wear mechanism of zirconia toughened alumina ceramic cutting tools formed by vat photopolymerization-based 3D printing[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(14): 23238-23247. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.04.153 [45] DU W Y, AI Y L, HE W, et al. Formation and control of “intragranular” ZrO2 strengthened and toughened Al2O3 ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(6): 8452-8461. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.080 [46] ZHU T B, XIE Z P, HAN Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZTA composites fabricated by oscillatory pressure sintering[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(1): 505-510. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.09.204 [47] RAO P K, JANA P, AHMAD M I, et al. Synthesis and characterization of zirconia toughened alumina ceramics prepared by co-precipitation method[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(13): 16054-16061. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.121 [48] SARKER S, MUMU H T, AL AMIN M, et al. Impacts of inclusion of additives on physical, microstructural, and mechanical properties of Alumina and Zirconia toughened alumina (ZTA) ceramic composite: A review[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2022, 62(6): 2892-2918. [49] AZHAR A Z A, LEE C C, MOHAMED H, et al. Effects of Cr2O3 addition on the mechanical properties, microstructure and wear performance of zirconia-toughened-alumina (ZTA) cutting inserts[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 513: 91-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.09.092 [50] MEENA K L, KARUNAKAR D B. Effect of ZrO2 and MgO added in alumina on the physical and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered nanocomposite[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2019, 81: 281-290. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.03.009 [51] MANSHOR H, ARIS S M, AZHAR A Z A, et al. Effects of TiO2 addition on the phase, mechanical properties, and microstructure of zirconia-toughened alumina ceramic composite[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(3): 3961-3967. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.11.080 [52] NAGA S M, HASSAN A M, AWAAD M. Physical and mechanical properties of Ta2O5 doped zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(5): 6248-6255. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.039 [53] HASSAN A M, NAGA S M, AWAAD M. Toughening and strengthening of Nb2O5 doped zirconia/alumina (ZTA) composites[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 48: 338-345. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.10.006 [54] REJAB N A, AZHAR A Z A, RATNAM M M, et al. The effects of CeO2 addition on the physical, microstructural and mechanical properties of yttria stabilized zirconia toughened alumina (ZTA)[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2013, 36: 162-166. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2012.08.010 [55] REJAB N A, LEE W K, SKTANI Z D I, et al. Hardness and toughness enhancement of CeO2 addition to ZTA ceramics through HIPping technique[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2017, 69: 60-65. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.08.002 [56] TAN P, YANG Y, SUI Y D, et al. Influence of CeO2 addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) composite prepared by spark plasma sintering[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(6): 7510-7516. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.249 [57] MAHMOOD A A, GAFUR M A, HOQUE M E. Effect of MgO on the physical, mechanical and microstructural properties of ZTA-TiO2 composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2017, 707(7): 118-124. [58] AZHAR A Z A, SITI H M S, MOHAMED H, et al. The effects of CeO2 addition on the physical and microstructural properties of ZTA-TiO2 ceramics composite[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 773: 27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.173 [59] SUI Y D, HAN L N, JIANG Y H, et al. Influence of Er2O3 content on microstructure and mechanical properties of ZTA-TiO2 composites[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2019, 37(3): 299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2018.06.003 [60] MANSHOR H, AZHAR A Z A, RASHID R A, et al. Effects of Cr2O3 addition on the phase, mechanical properties, and microstructure of zirconia-toughened alumina added with TiO2 (ZTA-TiO2) ceramic composite[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2016, 61: 40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2016.08.005 [61] SUI Y D, HAN L N, JIANG Y H. Effect of Ta2O5 addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TiO2-added yttria-stabilized zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14811-14816. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.112 [62] EGGIDI O, BEJUGAMA S, PANDEY A K. Effect of TiO2 addition on densification, microstructure, and mechanical properties of CSZTA[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 899: 163199. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163199 [63] ZHANG Y, SHU Y, LI W D, et al. Effect of MgO doping on properties of low zirconium content Ce-TZP/Al2O3 as a joint replacement material[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(2): 2807-2814. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.11.122 [64] BAKHTIERKHALZI M, ISLAM M W, SUZAUDDIN M, et al. Effect of TiO2 as sintering additive on microstructural, physical, and mechanical properties of CeO2 doped zirconia toughened alumina ceramic composite[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(4): 6666-6670. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.282 [65] SKTANI Z D I, REJAB N A, ROSLI A F Z, et al. Effects of La2O3 addition on microstructure development and physical properties of harder ZTA-CeO2 composites with sustainable high fracture toughness[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2021, 39(7): 844-849. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2020.06.005 [66] 郝元恺, 肖加余. 高性能复合材料学 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004: 51-55.HAO Y K, XIAO J Y. High Performance Composites [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004: 51-55(in Chinese). [67] CUI K K, ZHANG Y Y, FU T, et al. Toughening mechanism of mullite matrix composites: a review[J]. Coatings, 2020, 10: 672. doi: 10.3390/coatings10070672 [68] YANG S L, ZHU Y X, FAN L, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of SiCw-Al2O3-YAG ceramic composite by hot oscillatory pressing[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(15): 21231-21235. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.126 [69] ZHU T B, XIE Z P, HAN Y, et al. Improved mechanical properties of Al2O3-25 vol% SiCw composites prepared by oscillatory pressure sintering[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15437-15441. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.087 [70] TAMURA Y, MOSHTAGHIOUN B M, GOMEZ-CARZIA D, et al. Spark plasma sintering of fine-grained alumina ceramics reinforced with alumina whiskers[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(1): 658-663. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.210 [71] FANG Y H, CHEN N, DU G P, et al. Effect of Y2O3-stabilized ZrO2 whiskers on the microstructure, mechanical and wear resistance properties of Al2O3 based ceramic composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(13): 16504-16511. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.184 [72] JIA J G, LIU D Q, GAO C Q, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of short carbon fibers reinforced α-Al2O3-based composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(16): 19345-19351. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.07.163 [73] ZHAO X Q, YAN B J, LIU H C, et al. In situ synthesis of SiC nanofibers in Al2O3-based ceramics by using cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(11): 14098-14104. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.109 [74] WINKELBAUER J, PUCHAS G, SCHAFFÖNER S, et al. Short fiber-reinforced oxide fiber composites[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2022, 19(2): 1136-1147. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13931 [75] WINKELBAUER J, PUCHAS G, KRENKEL W, et al. Short fiber spraying process of all-oxide ceramic matrix composites: A parameter study[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2023, 20(2): 754-767. doi: 10.1111/ijac.14196 [76] WANG W Q, ZHANG L, DONG X J, et al. Additive manufacturing of fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites: Advances, challenges, and prospects[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(14): 19542-19556. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.146 [77] KRENKEL W, REICHERT F. Design Objectives and Design Philosophies, Interphases and Interfaces in Fiber-Reinforced CMCs [M] // Comprehensive composite materials Ⅱ. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018, 5: 1-18. [78] JIANG R, SUN X, LIU H T, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties improvement of the Nextel™ 610 fiber reinforced alumina composite[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(10): 5394-5399. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.04.031 [79] 刘海韬, 姜如, 孙逊, 等. 多孔Al2O3f/Al2O3复合材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(9): 22070158-10. doi: 10.11896/cldb.22070158LIU H T, JIANG R, SUN X, et al. Research Progress on the Porous Al2O3f/Al2O3 Composites[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(9): 22070158-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.22070158 [80] 刘海韬, 姜如, 孙逊, 等. 连续氧化铝纤维增韧陶瓷基复合材料 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 63-108.LIU H T, JIANG R, SUN X, et al. Continuous Alumina Fiber Reinforced Ceramic Matrix Composites [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022: 63-108(in Chinese). [81] DENG S K, BERRY V. Wrinkled, rippled and crumpled graphene: an overview of formation mechanism, electronic properties, and applications[J]. Materials Today, 2016, 19(4): 197-212. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.10.002 [82] LIANG L, HUANG C J, WANG C H, et al. Ultratough conductive graphene/alumina nanocomposites[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 156: 106871. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106871 [83] WANG X C, ZHAO J, CUI E Z, et al. Effects of sintering parameters on microstructure, graphene structure stability and mechanical properties of graphene reinforced Al2O3-based composite ceramic tool material[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(17): 23384-23392. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.040 [84] AKHIL RAJ V R, KOMALAKRUSHNA H, PREMANSHU J, et al. Improved Fracture Toughness and Crack Arrest Ability of Graphene-Alumina Nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2021, 30(2): 1234-1244. doi: 10.1007/s11665-020-05433-1 [85] AI Y L, LIU Y, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Microwave Sintering of Graphene-Nanoplatelet-Reinforced Al2O3-based Composites[J]. Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society, 2018, 55(6): 556-561. doi: 10.4191/kcers.2018.55.6.02 [86] LIU J, YANG Y, HASSSININ H, et al. Graphene-Alumina Nanocomposites with Improved Mechanical Properties for Biomedical Applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(4): 2607-2616. [87] CHEN Y F, BI J Q, YIN C D, et al. Microstructure and fracture toughness of graphene nanosheets/alumina composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(9): 13883-13889. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.05.107 [88] AHMAD I, SUBHANI T, WANG N N, et al. Thermophysical Properties of High-Frequency Induction Heat Sintered Graphene Nanoplatelets/Alumina Ceramic Functional Nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(6): 2949-2959. doi: 10.1007/s11665-018-3395-6 [89] WOZNIAK J, JASTRZEBSKA A, CYGAN T, et al. Surface modification of graphene oxide nanoplatelets and its influence on mechanical properties of alumina matrix composites[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(4): 1587-1592. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.11.010 [90] WANG L, BI J Q, WANG W L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of nacre-like alumina toughened by graphene oxide[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(7): 8081-8086. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.013 [91] WANG Q Z, RAMFÍREZ C, WATTS C S, et al. Fracture, fatigue, and sliding-wear behavior of nanocomposites of alumina and reduced graphene-oxide[J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 186: 29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.12.035 [92] VÍCTOR M F, ARTURO D R. Mechanical properties of ceramics reinforced with allotropic forms of carbon[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 128: 100966. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100966 [93] RUOFF R S, QIAN D, LIU W K. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes: theoretical predictions and experimental measurements[J]. Comptes rendus Physique, 2003, 4(9): 993-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.crhy.2003.08.001 [94] GUO C, LUO X, SHAH W A, et al. Mechanical and thermal properties of multiwalled carbon-nanotube-reinforced Al2O3 nanocomposites[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(11): 17449-17460. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.039 [95] TAN S L, ZHUANG Y Q, YI J H. Preparation and mechanic properties of multi-wall carbon nanotube reinforced alumina matrix composites by spray drying and hot-pressing sintering[J]. Materials Research Express, 2021, 8(6): 065005. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac0a01 [96] MUSTAFA T, HUANG J L, GAO J, et al. Nanoplates forced alignment of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in alumina composite with high strength and toughness[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(11): 5541-5547. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.05.004 [97] GHOBADI H, EBADZADEH T, SADEGHIAN Z, et al. Microwave-assisted sintering of Al2O3-MWCNT nanocomposites[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(8): 6105-6109. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.003 [98] IHSANULLAH I. MXenes (two-dimensional metal carbides) as emerging nanomaterials for water purification: Progress, challenges and prospects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124340. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124340 [99] 梁程, 程群峰. MXene纤维的制备、性能及应用研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(9): 4227-4243.LIANG C, CHENG Q F. Progress in preparation, properties and applications of MXene fiber[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(9): 4227-4243(in Chinese). [100] FEI M M, LIN R C, LU Y W, et al. MXene-reinforced alumina ceramic composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(18): 17206-17210. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.202 [101] LIANG L, SUN X X, NING Y H, et al. Mxene-toughened Al2O3 ceramic at high temperature[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 174: 107714. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2023.107714 [102] CYGAN T, WOZNIAK J, PETRUS M, et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Alumina Composites with Addition of Structurally Modified 2D Ti3C2 (MXene) Phase[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(4): 829. doi: 10.3390/ma14040829 [103] ZHAO B, LIU H L, HUANG C Z, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al2O3-SiCw-TiCnp ceramic tool material[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(13): 10224-10230. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.049 [104] LI Q, XIAO G C, CHEN Z Q, et al. Self-lubricating ceramic tool materials synergistically toughened by nano-coated particles and silicon carbide whiskers[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2021, 98: 105560. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105560 [105] ZHANG Z, LIU Y, LIU H L. Mechanical properties and microstructure of spark plasma sintered Al2O3-SiCw-Si3N4 composite ceramic tool materials[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(4): 5527-5534. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.097 [106] WANG Z, LIU Y, ZOU B, et al. Mechanical properties and microstructure of Al2O3-SiCw ceramic tool material toughened by Si3N4 particles[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(7): 8845-8852. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.12.129 [107] LI Y X, JING P P, GUO J, et al. Mechanical properties and wear behaviors of Cu-doped zirconia-toughened alumina ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(9): 14346-14354. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.01.023 [108] TAN P, WU P, GAO L, et al. Influence of Si3N4 content on the physical and mechanical properties of zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) ceramic composites[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6: 065205. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab0e54 [109] SEDLÁK R, IVOR M, KLIMCZYK P, et al. Micro/Nano Indentation Testing of Spark Plasma Sintered Al2O3+ZrO2+cBN Ceramics[J]. Ceramics, 2021, 4(1): 40-53. doi: 10.3390/ceramics4010004 [110] WANG Z Y, YI M D, ZHENG K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Al2O3-TiC-ZrO2 ceramics with intragranular nanostructure by spark plasma sintering[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2023, 20(4): 2281-2288. doi: 10.1111/ijac.14369 [111] ZHANG X, ZENG Y N, LIANG J S, et al. The microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni/Al2O3 composites by in-situ generated CaAl12O19 and ZrO2 via hot pressing sintering[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(9): 13144-13150. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.088 [112] LIU L Y, CHEN X Z, LI Q Y, et al. Preparation, mechanical properties, and toughening mechanisms of SiCw/SiCp-reinforced zirconia-toughened alumina ceramics[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2020, 17(5): 2083-2093. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13517 [113] NIU L J, LI S F, ZHU Y B, et al. Correlation between phase content and mechanical properties of SiCw-ZTA composites sintered by SPS[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(11): 15059-15066. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.063 [114] ZHANG X B, CHEN H, XIAO G C, et al. Alumina ceramic tool material with enhanced properties through the addition of bionic prepared nano SiC@graphene[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(12): 19753-19765. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.03.093 [115] AHMAD I, ISLAM M. Reinforcing ability and bonding characteristics of multiwall carbon nanotubes and silicon carbide nanoparticles in inductively sintered alumina ceramic hybrid nanocomposites[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2019, 81: 49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.02.010 [116] AHMAD I, PARVEZ S, SAEED K. Interfacial investigation, mechanical performance and thermal permanence of the inductively hot-pressed alumina ceramic hybrid nanocomposites reinforced by silicon carbide and multilayer graphene[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 788: 219-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.226 [117] CUI E Z, ZHAO J, WANG X C, Effects of nano-ZrO2 content on microstructure and mechanical properties of GNPs/nano-ZrO2 reinforced Al2O3/Ti(C, N) composite ceramics[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40: 1532-1538. [118] DUNTU S H, AGYAPONG J, AHMAD I, et al. Combined effect of low ZrO2 content and carbon nanostructures on mechanical and wear properties of hot-pressed Al2O3/ZrO2 hybrid nanocomposites[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(23): 34803-34816. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.08.069 [119] DUNTU S H, HUKPATI K, AHMAD I, et al. Deformation and fracture behaviour of alumina-zirconia multi-material nanocomposites reinforced with graphene and carbon nanotubes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2022, 835: 142655. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.142655 [120] SUN X N, WANG W L, SUN G X, et al. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of nacre-like alumina ceramic by the synergism of graphene oxide and Si3N4 whisker[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(1): 941-946. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.09.178 [121] GRIGORIEV S, PERETYAGIN P, SMIRNOV A, et al. Effect of graphene addition on the mechanical and electrical properties of Al2O3-SiCw ceramics[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(6): 2473-2479. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.01.027 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 219
- HTML全文浏览量: 149
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: