Enhanced theory and finite element method for wrinkling analysis of composite sandwich structure
-
摘要: 复合材料软核夹芯结构承受面内载荷,面板可能出现褶皱。一旦面板出现褶皱,夹芯结构将失去承载能力。因此,需要发展准确的理论模型预测软核夹芯结构褶皱行为。夹芯结构褶皱是典型三维(3D)问题,鲜有高阶模型能准确预测此类问题。为此,提出考虑局部形变和三维效应的增强型高阶模型。基于此理论,推导了梁单元公式,并分析了不同边界条件复合材料夹芯结构的起皱行为。通过与准三维弹性解和三维有限元解对比,提出方法的准确性得到验证。为了提高夹芯结构抗起皱能力,尝试使用复合材料面板代替金属面板。数值分析结果表明,发展的增强型高阶模型可以准确分析复合材料夹芯结构褶皱行为,并且使用复合材料面板可有效提升夹芯结构抗起皱能力。Abstract: Panels wrinkling behaviors may occur when composite soft-core sandwich structures subjected to coplanar compression loads. Once the panels wrinkling appears, the sandwich structures will lose its load-bearing capacity. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an accurate model to predict the wrinkling behaviors of soft-core sandwich structures. Sandwich structure wrinkling is a typical three-dimensional (3D) problem, and few high-order models can accurately predict such issues. Therefore, this paper proposed an enhanced higher-order model including the local deformation and the 3D effects. Based on the proposed theory, the beam element formulation was derived, and the wrinkling behaviors of sandwich structures with different boundary conditions were analyzed. By comparing with the quasi-3D elasticity solution and the 3D finite element results, accuracy of the proposed method has been verified. In order to improve the capability of sandwich structures resisting the wrinkling deformation, this work attempted to use composite face sheets instead of metal panel in the sandwich structure. Numerical results show that the developed enhanced high-order model can accurately predict the wrinkling behaviors of the composite sandwich structures, and the use of composite panels can effectively resist the wrinkling behaviors of sandwich structures.
-
Key words:
- composite /
- sandwich structures /
- enhanced higher-order theory /
- wrinkling /
- beam element
-
表 1 3D有限元边界条件
Table 1. Boundary condition for 3D finite element
x=0 x=a y=0 y=1 U2=U3=UR3=0 U3=UR3=0 U2=0 U2=0 Notes: a—Length of the sandwich beam; U2, U3, UR3—Translational and rotational degrees of freedom in ABAQUS, respectively. 表 2 三层铝面板夹芯梁屈曲载荷
Table 2. Buckling load of three-layer sandwich beam with aluminum panels
tc/tf a/h 3D-FEM
(270000 elements)BE18
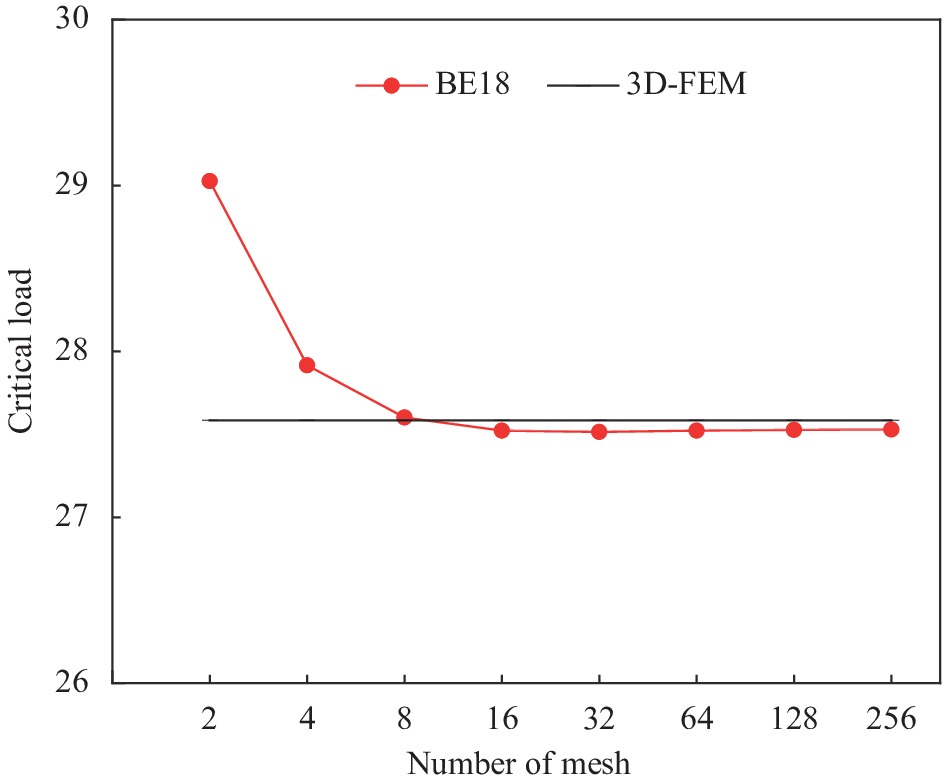
(64 elements)HYF11[20] HYF21[20] HOST[21] Allen[22] 5 2 6.6111 6.7131(1.54) 6.2220(5.89) 37.551(468.00) 37.238(463.26) 6.3544(3.88) 5 14.7065 14.838(0.89) 14.320(2.63) 159.0500(981.49) 159.3200(983.33) 14.385(2.19) 10 41.6580 41.8190(0.39) 41.0840(1.38) 329.6300(691.28) 321.2600(671.18) 41.1150(1.30) 25 2 1.5342 1.5600(1.68) 1.5299(0.28) 2.3207(51.26) 2.3112(50.64) 1.5923(3.79) 5 9.0749 9.1046(0.33) 9.0314(0.48) 13.1300(44.68) 13.1130(44.50) 9.0971(0.24) 10 31.6490 31.6550(0.02) 31.0960(1.75) 42.4330(34.07) 42.4360(34.08) 31.1590(1.55) 50 2 1.4432 1.4640(1.44) 1.4419(0.09) 1.8335(27.04) 1.8301(26.81) 1.5074(4.45) 5 8.5657 8.6504(0.99) 8.5553(0.12) 10.3110(20.38) 10.3010(20.26) 8.6191(0.62) 10 27.5850 27.5220(0.23) 26.7620 (2.98) 30.7460(11.46) 30.7690(11.54) 26.8490(2.67) Notes: tc/tf—Core and panel thickness ratio; a/h—Span thickness ratio of sandwich beam; BE18—Present model; HYF11—Quasi-3D model; HYF21 and HOST—Higher-order models; Allen represents the model proposed by Allen. 表 3 三层铝面板夹芯梁褶皱载荷
Table 3. Wrinkling loads of three-layer sandwich beam with aluminum panels
tc/tf a/h 3D-FEM
( 270000 elements)BE18
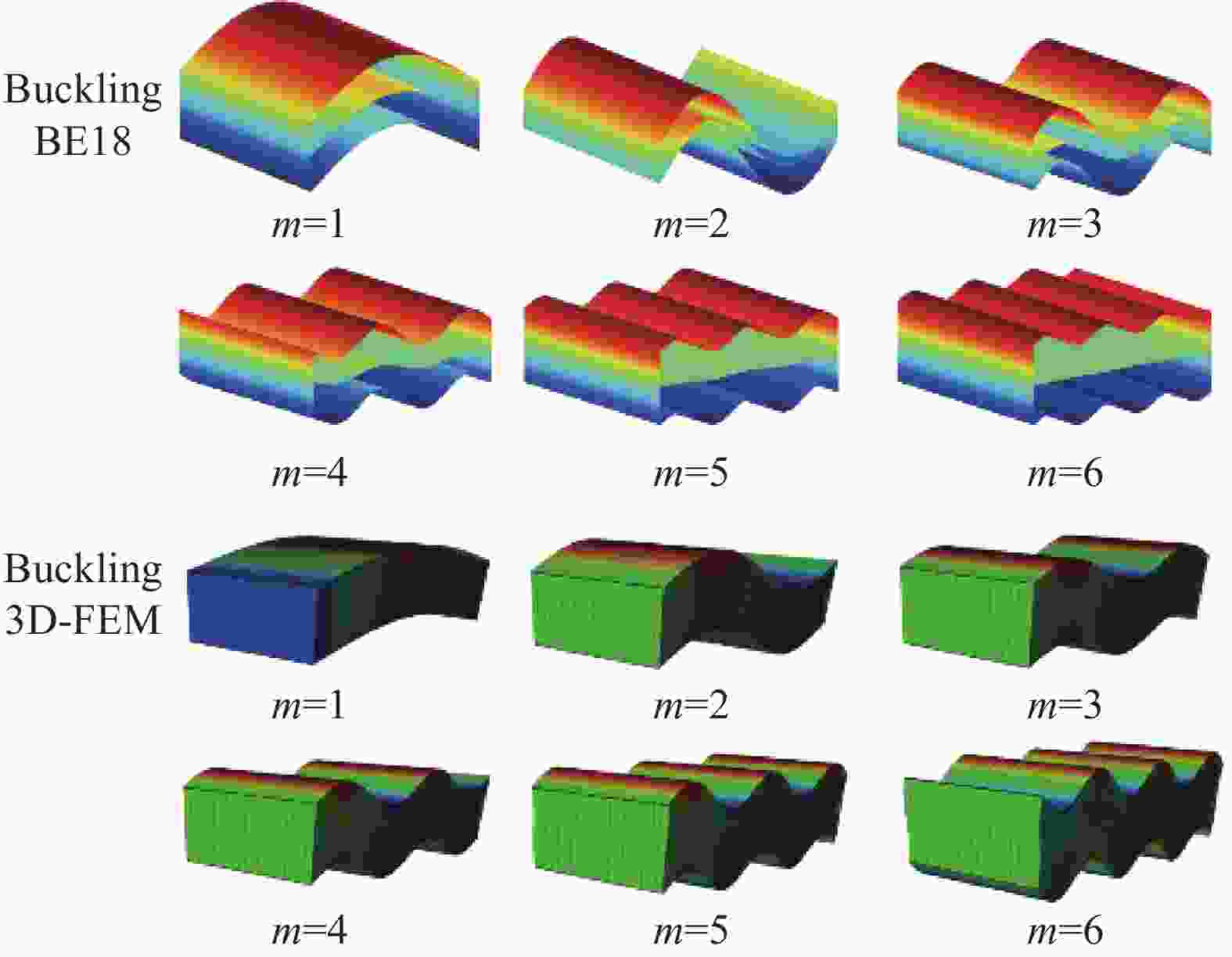
(480 elements)HYF11[20] HYF21[20] Allen[22] 50 2 0.7311 (5) 0.7632 (5) 0.7073 (6) 0.8074 1.3020 (9) 5 4.5097 (13) 4.7147 (14) 4.3583 (14) 5.0048 8.1376 (23) 10 18.0910 (27) 18.8830 (27) 17.4330 (28) 20.0190 – 100 2 0.2610 (9) 0.2845 (9) 0.2517 (9) 0.3121 0.6638(9) 5 1.6318 (22) 1.7768 (22) 1.5736 (23) 1.9480 4.1486 (22) 10 6.5273 (44) 7.1612 (43) 6.2921 (45) 7.7921 16.594 (45) Note: Numbers in brackets represent half-wave numbers. 表 4 三层复合材料夹芯梁屈曲载荷
Table 4. Buckling load of three-layer composite sandwich beam
tc/tf a/h 3D-FEM
(270000 elements)BE18
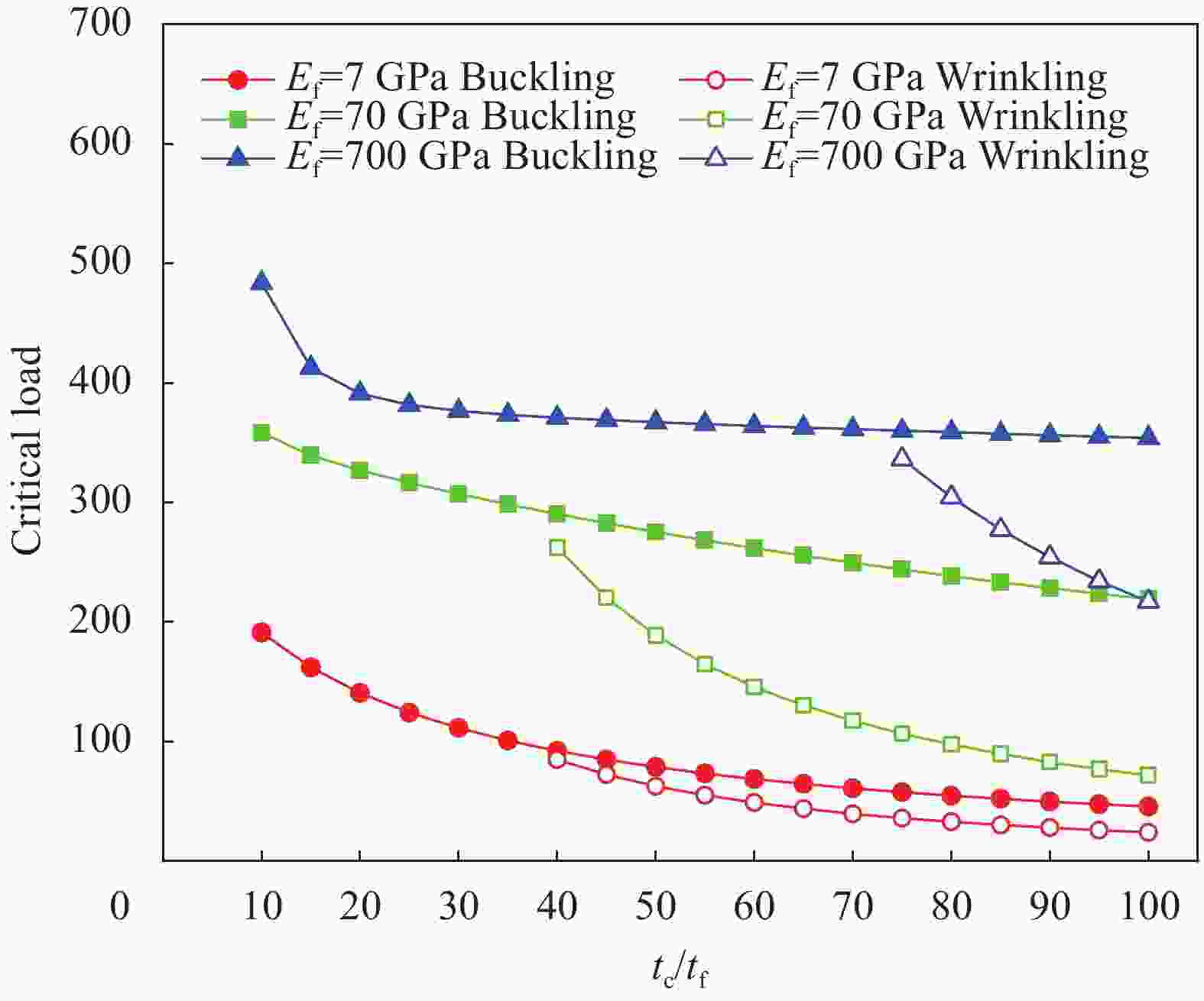
(240 elements)BHSDT[24] RHSDT[25] 25 2 11.301 11.457 14.951 15.525 5 64.288 64.441 85.873 89.282 10 239.100 239.200 313.650 325.220 50 2 10.016 10.135 13.442 12.360 5 61.853 61.978 80.805 73.963 10 222.560 222.510 280.980 259.830 Notes: BHSDT—Higher order model proposed by Babu et al[24]; RHSDT—Higher-order model proposed by Reddy[25]. 表 5 三层复合材料夹芯梁褶皱载荷
Table 5. Wrinkling load of three-layer composite sandwich beam
tc/tf a/h SS CC 3D-FEM
(270000 elements)BE18
(480 elements)3D-FEM
(270000 elements)BE18
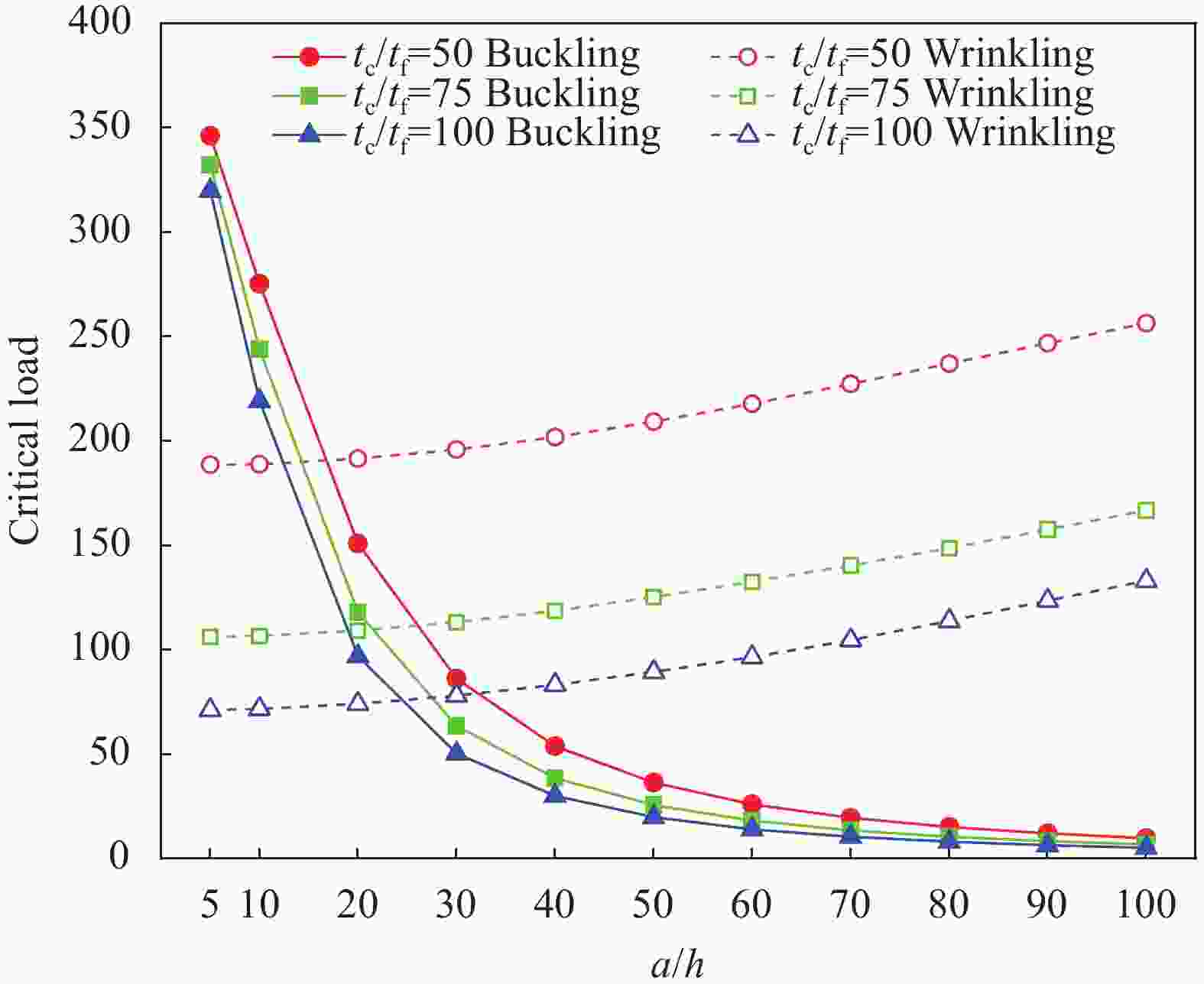
(480 elements)50 2 7.5768 (4) 8.0174 (4) 8.0246 (4) 8.5964 (4) 5 46.4130 (11) 49.2650 (11) 47.1010 (11) 50.0860 (11) 10 185.7200 (22) 197.4900 (22) 186.4300 (21) 198.3100 (21) 100 2 2.7004 (7) 2.8531 (7) 2.7806 (7) 2.9505 (7) 5 16.8350 (18) 17.8290 (18) 16.9290 (18) 17.9370 (18) 10 7.3330 (36) 1.7410 (36) 7.4410 (36) 1.8490 (36) Notes: SS—Simply supported boundary conditions; CC—Clamped supported boundary conditions; Numbers in brackets represent half-wave numbers. -
[1] 杜冰, 刘后常, 潘鑫, 等. 热塑性复合材料夹芯结构熔融连接研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3044-3058. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220228.001DU Bing, LIU Houchang, PAN Xin, et al. Progress in fusion bonding of thermoplastic composite sandwich structures[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3044-3058(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220228.001 [2] 熊健, 李志彬, 刘惠彬, 等. 航空航天轻质复合材料壳体结构研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6):1629-1650. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210107.002XIONG Jian, LI Zhibin, LIU Huibin, et al. Advances in aerospace lightweight composite shell structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(6):1629-1650(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210107.002 [3] JI W, WAAS A M. Global and local buckling of a sandwich beam[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2007,133(2):230-237. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2007)133:2(230) [4] VADAKKE V, CARLSSON L A. Experimental investigation of compression failure of sandwich specimens with face/core debond[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2004,35:583-590. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2003.10.004 [5] KHALILI S M R, KHEIRIKHAH M M, FARD K M. Buckling analysis of composite sandwich plates with flexible core using improved high-order theory[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures,2015,22(4):233-247. doi: 10.1080/15376494.2012.736051 [6] BENSON A S, MAYERS J. General instability and face wrinkling of sandwich plates-Unified theory and applications[J]. AIAA Journal, 1967, 5(4): 729-739. [7] HADI B K, MATTHEWS F L. Development of Benson-Mayers theory on the wrinkling of anisotropic sandwich panels[J]. Composite Structures,2000,49(4):425-434. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(00)00077-5 [8] DAFEDAR J B, DESAI Y M, MUFTI A A. Stability of sandwich plates by mixed, higher-order analytical formulation[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2003,40(17):4501-4517. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(03)00283-X [9] LOPATIN A V, MOROZOV E V. Symmetrical facing wrinkling of composite sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2008,10(6):475-497. [10] JI W, WAAS A M. Wrinkling and edge buckling in orthotro-pic sandwich beams[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2008,134(6):455-461. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2008)134:6(455) [11] HU H, BELOUETTAR S, POTIER-FERRY M, et al. A novel finite element for global and local buckling analysis of sandwich beams[J]. Composite Structures,2009,90(3):270-278. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.02.002 [12] YU K, HU H, TANG H, et al. A novel two-dimensional finite element to study the instability phenomena of sandwich plates[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2015,283:1117-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2014.08.006 [13] DOUVILLE M A, LE GROGNEC P. Exact analytical solutions for the local and global buckling of sandwich beam-columns under various loadings[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2013,50:2597-2609. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.04.013 [14] D'OTTAVIO M, POLIT O. Linearized global and local buckling analysis of sandwich struts with a refined quasi-3D model[J]. Acta Mechanica,2015,226(1):81-101. doi: 10.1007/s00707-014-1169-2 [15] D'OTTAVIO M, POLIT O, JI W, et al. Benchmark solutions and assessment of variable kinematics models for global and local buckling of sandwich struts[J]. Composite Structures,2016,156:125-134. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.01.019 [16] VESCOVINI R, D'OTTAVIO M, DOZIO L, et al. Buckling and wrinkling of anisotropic sandwich plates[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science,2018,130:136-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijengsci.2018.05.010 [17] HUANG Q, LIU Y, HU H, et al. A Fourier-related double scale analysis on the instability phenomena of sandwich plates[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,2017,318:270-295. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2017.01.021 [18] CHEN X, NIE G, WU Z. Global buckling and wrinkling of variable angle tow composite sandwich plates by a modified extended high-order sandwich plate theory[J]. Composite Structures,2022,292:115639. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115639 [19] 朱秀杰, 郑坚, 熊超, 等. 基于精确板理论的复合材料格栅/波纹夹芯结构屈曲特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):399-411. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210309.003ZHU Xiujie, ZHENG Jian, XIONG Chao, et al. Buckling characteristics of composite grid/corrugated sandwich structure based on refined plate theory[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):399-411(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210309.003 [20] DAFEDAR J B, DESAI Y M. Stability of composite and sandwich struts by mixed formulation[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2004,130(7):762-770. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:7(762) [21] KANT T, PATIL H S. Buckling loads of sandwich columns with a higher-order theory[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,1991,10(1):102-109. doi: 10.1177/073168449101000107 [22] ALLEN H G. Analysis and design of structural sandwich panels[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1969. [23] SZE K Y, CHEN R, CHEUNG Y K. Finite element model with continuous transverse shear stress for composite laminates in cylindrical bending[J]. Finite Elements in Analysis & Design,1998,31(2):153-164. [24] BABU R T, VERMA S, SINGH B N, et al. Dynamic analysis of flat and folded laminated composite plates under hygrothermal environment using a nonpolynomial shear deformation theory[J]. Composite Structures,2021,274:114327. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114327 [25] REDDY J N. A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1984,51(12):745-752. -





 下载:
下载: