Biosynthesis and properties of AgNPs/chitosan composite antibacterial agent
-
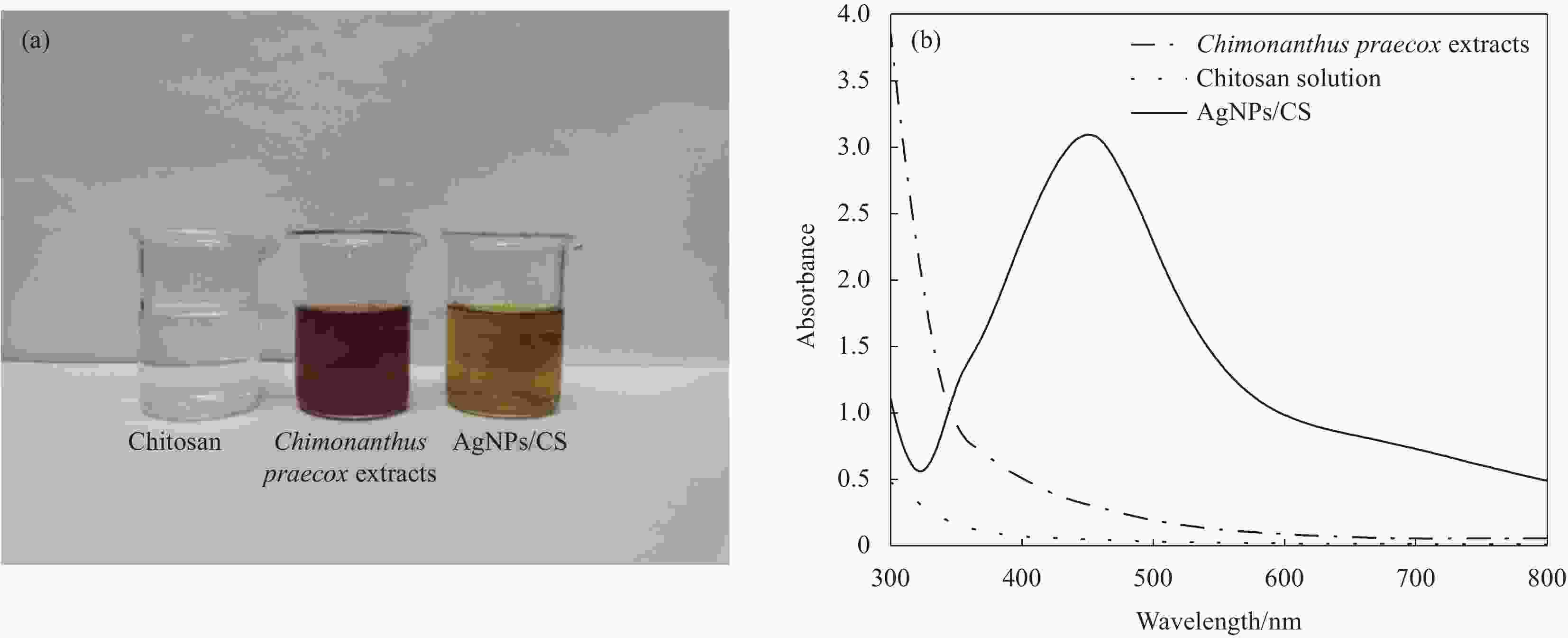
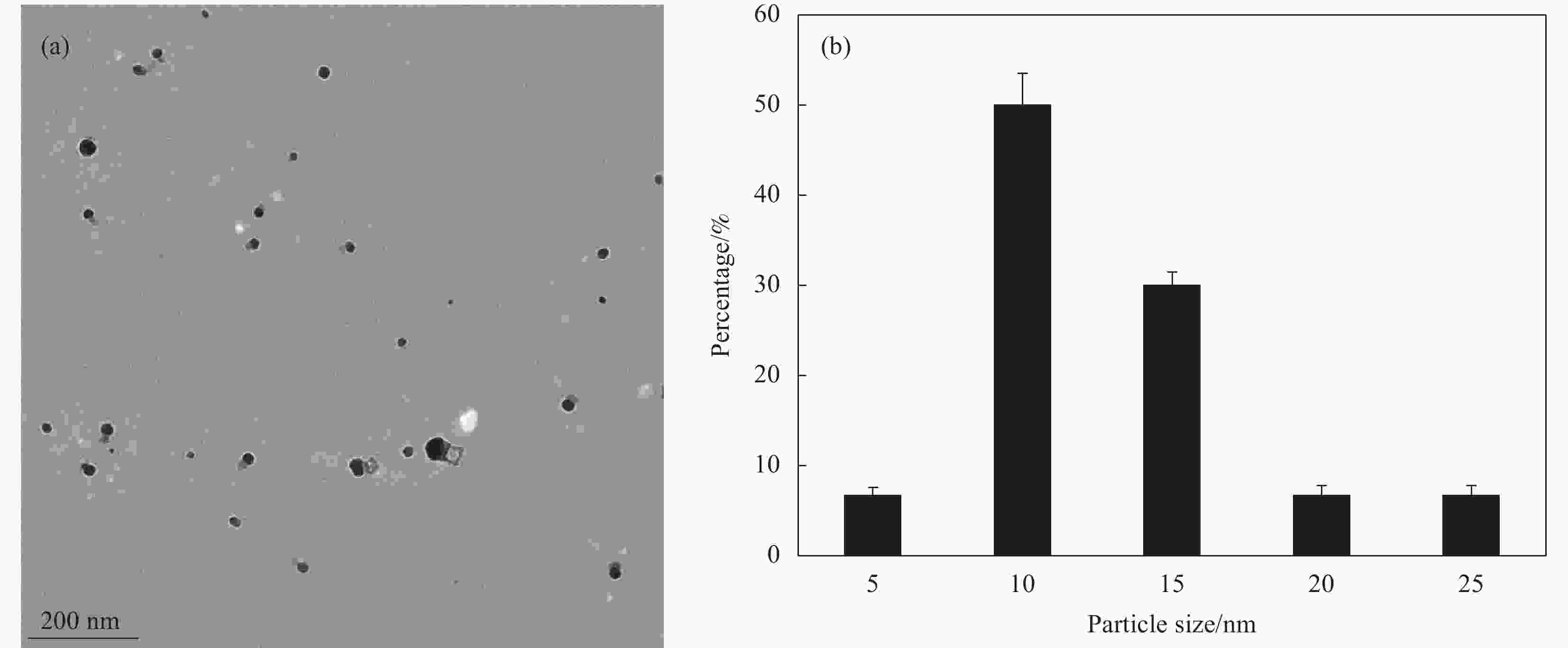
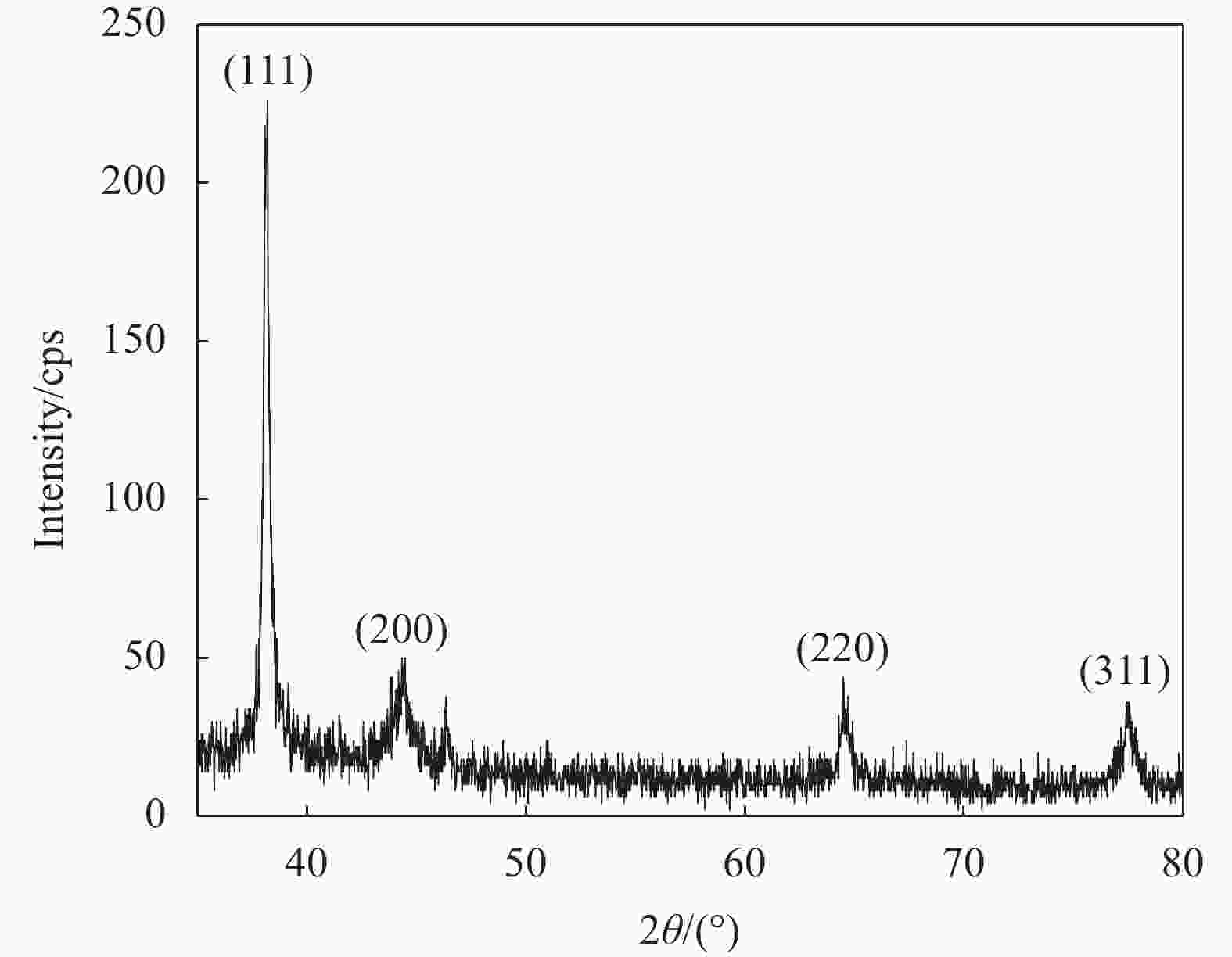
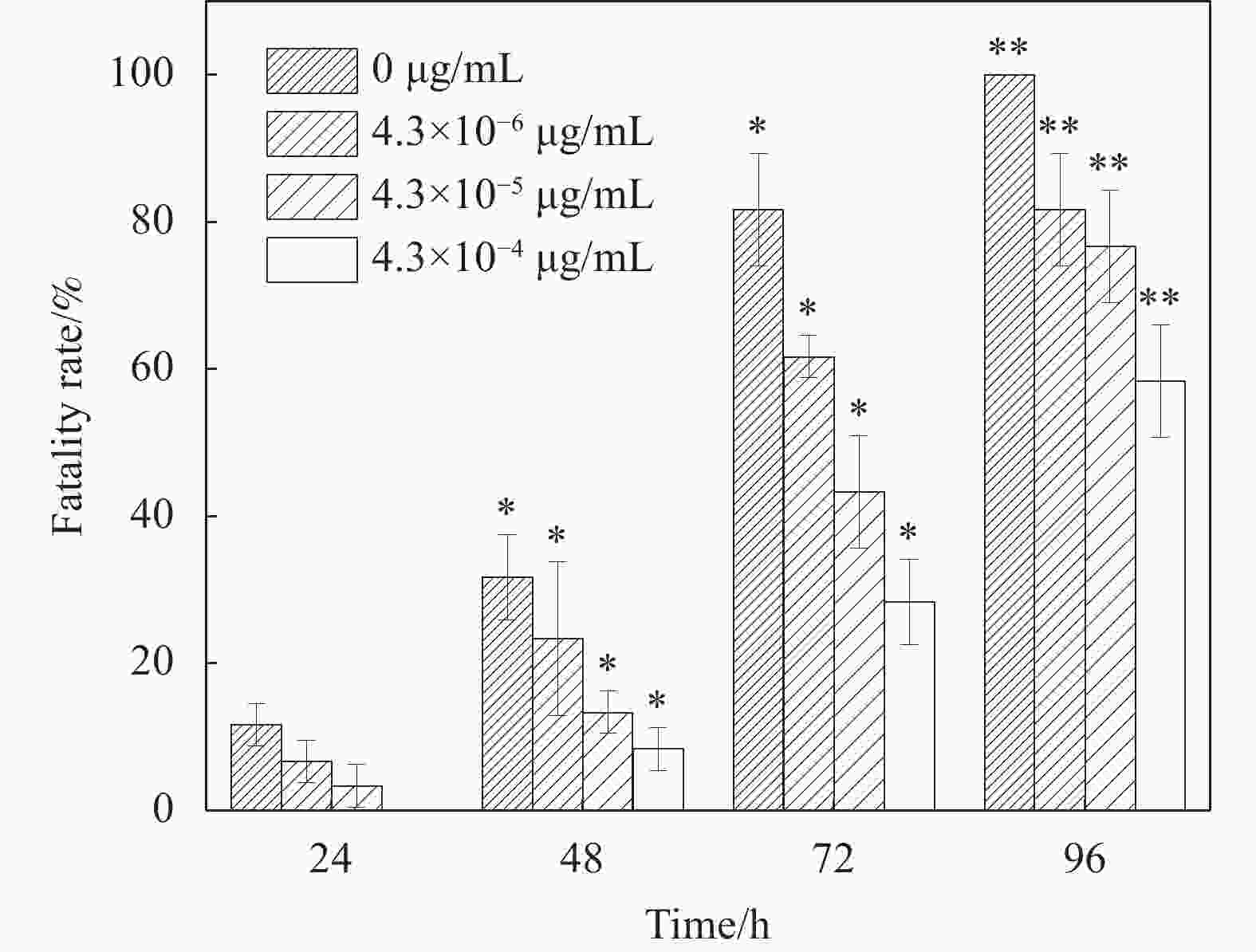
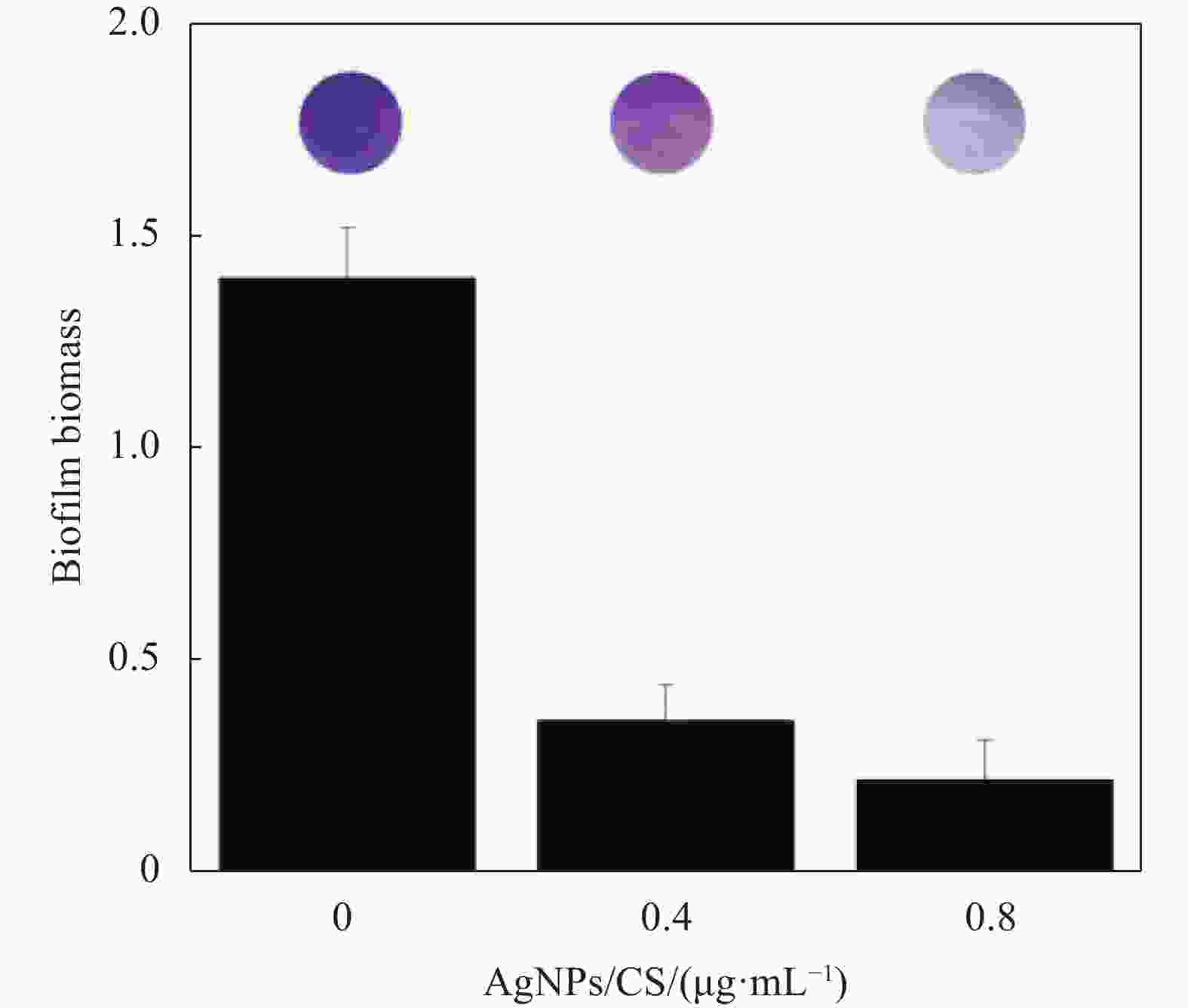
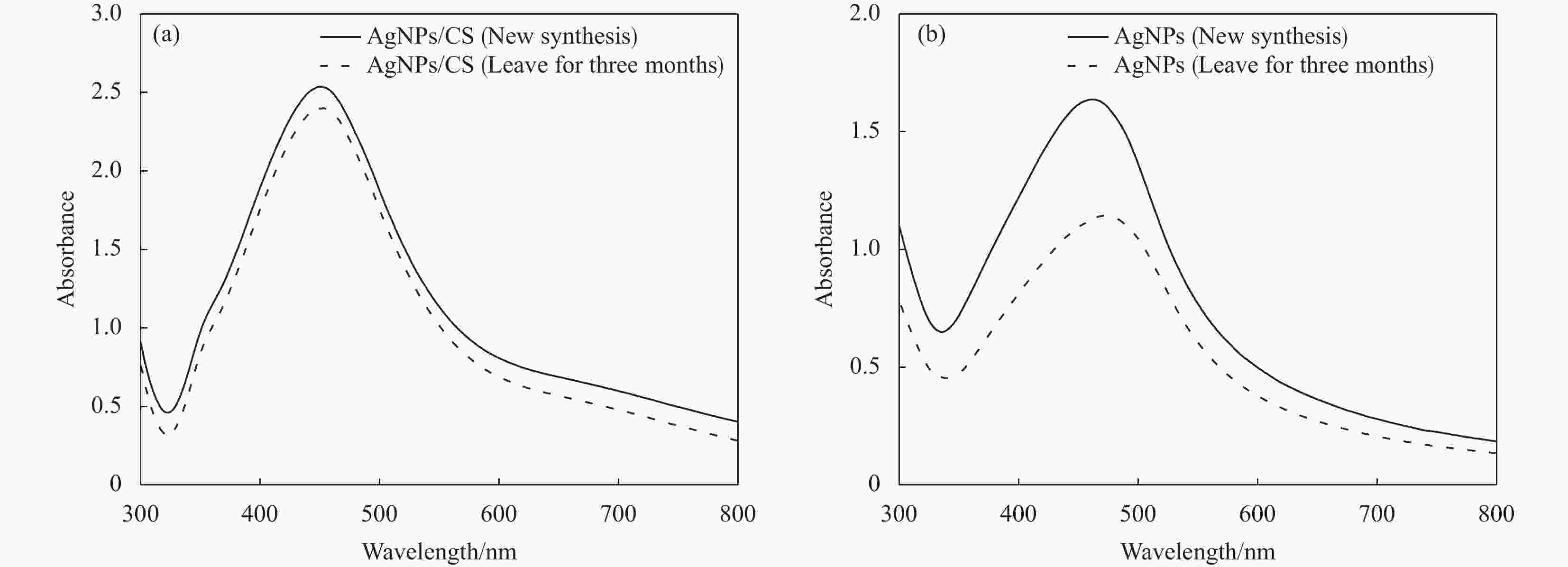
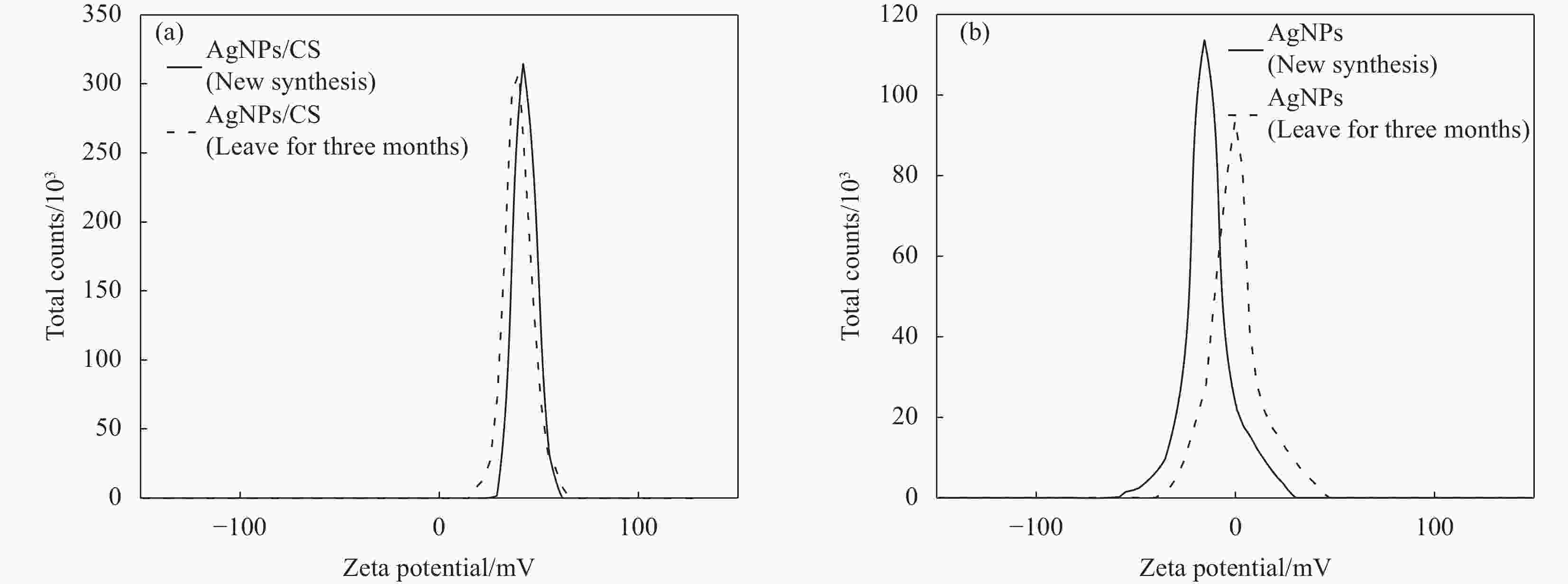
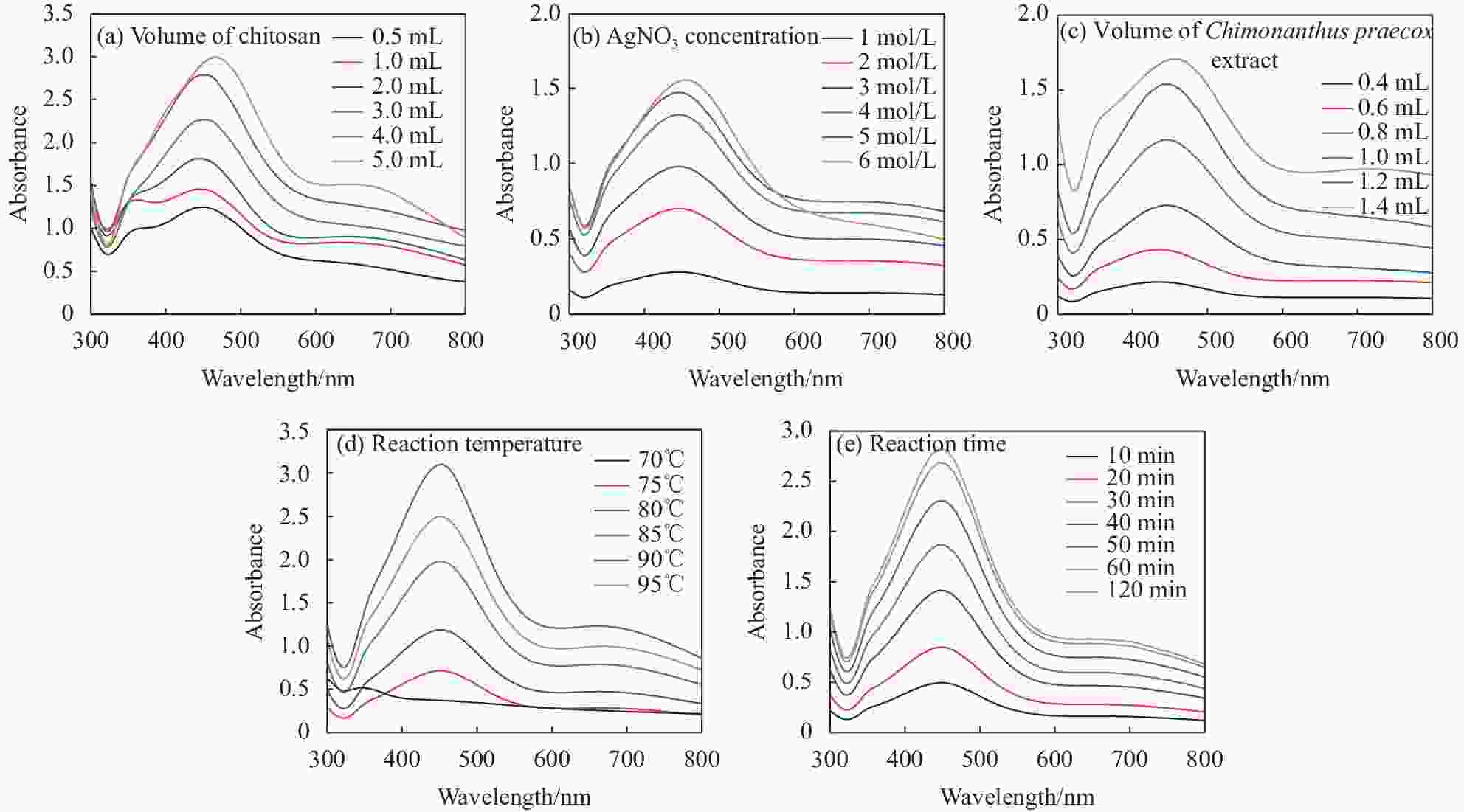
摘要: 为制备安全、稳定、高效的新型纳米银抑菌剂,本文分别以腊梅花瓣提取液和壳聚糖作为还原剂和稳定剂采用一步法生物合成纳米银/壳聚糖(AgNPs/CS)复合抑菌剂。通过单因素实验确定了最佳制备工艺,制备的产品利用紫外-可见吸收光谱、TEM、X 射线衍射等技术进行表征,并对其抑菌活性、抗耐药性、稳定性及生物安全性进行全面的评价。实验结果表明:AgNPs/CS在451 nm处有AgNPs的特征吸收峰,AgNPs呈球形,均匀分散,平均粒径为12.83 nm,为面心立方结构晶体。AgNPs/CS在离体和活体抑菌实验中对水产病原菌均表现出显著的抑菌活性,并表现出优良的抗耐药性、生物安全性和稳定性。因此,AgNPs/CS是一种理想的复合抑菌剂,在水产养殖领域中具有广阔的应用前景。Abstract: In order to prepare a new type of safe, stable and efficient nano silver composite antibacterial agent, silver nanoparticles/chitosan (AgNPs/CS) was biosynthesized by one-step method using Chimonanthus praeco petal extract and chitosan as reducing agent and stabilizing agent, respectively. The optimal preparation procedure was determined by single factor experiment. The products were characterized by UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, TEM and X-ray diffraction, and their antibacterial activity, anti-drug resistance, stability as well as biological safety were comprehensively evaluated. The experimental results show that the AgNPs/CS has the characteristic absorption peak of AgNPs at 451 nm, and the evenly dispersed AgNPs are spherical with average diameter of 12.83 nm, and the crystals have a face-centered cubic structure. The AgNPs/CS show antibacterial activity against aquatic pathogens both in vitro and in vivo, and has excellent anti-drug resistance, biosafety and stability. Therefore, AgNPs/CS is an ideal composite antibacterial agent, which has a prospective application in aquaculture field.
-
Key words:
- silver nanoparticles /
- chitosan /
- biosynthesis /
- antibacterial activity /
- drug resistance /
- stability
1) 吴承宗和魏亚楠为共同第一作者,对本文具有同等贡献 -
表 1 AgNPs/CS浓度对体外细胞相对增值率和细胞毒性评级的影响
Concentration(μg/mL) OD value RGR(%) cytotoxicity 0 0.896±0.126 100.00 0 0.25 0.847±0.085 94.534 1 0.5 0.832±0.073 92.818 1 1.0 0.768±0.094 85.707 1 5.0 0.639±0.082 71.317 2 10.0 0.568±0.065 63.393 2 20.0 0.492±0.071 54.911 2 40.0 0.061±0.041 6.885 4 80.0 0.046±0.023 5.154 4 表 1 对6种病原菌的抑菌圈直径(n=3)
Table 1. Diameter of inhibition zone against 6 pathogens (n=3)
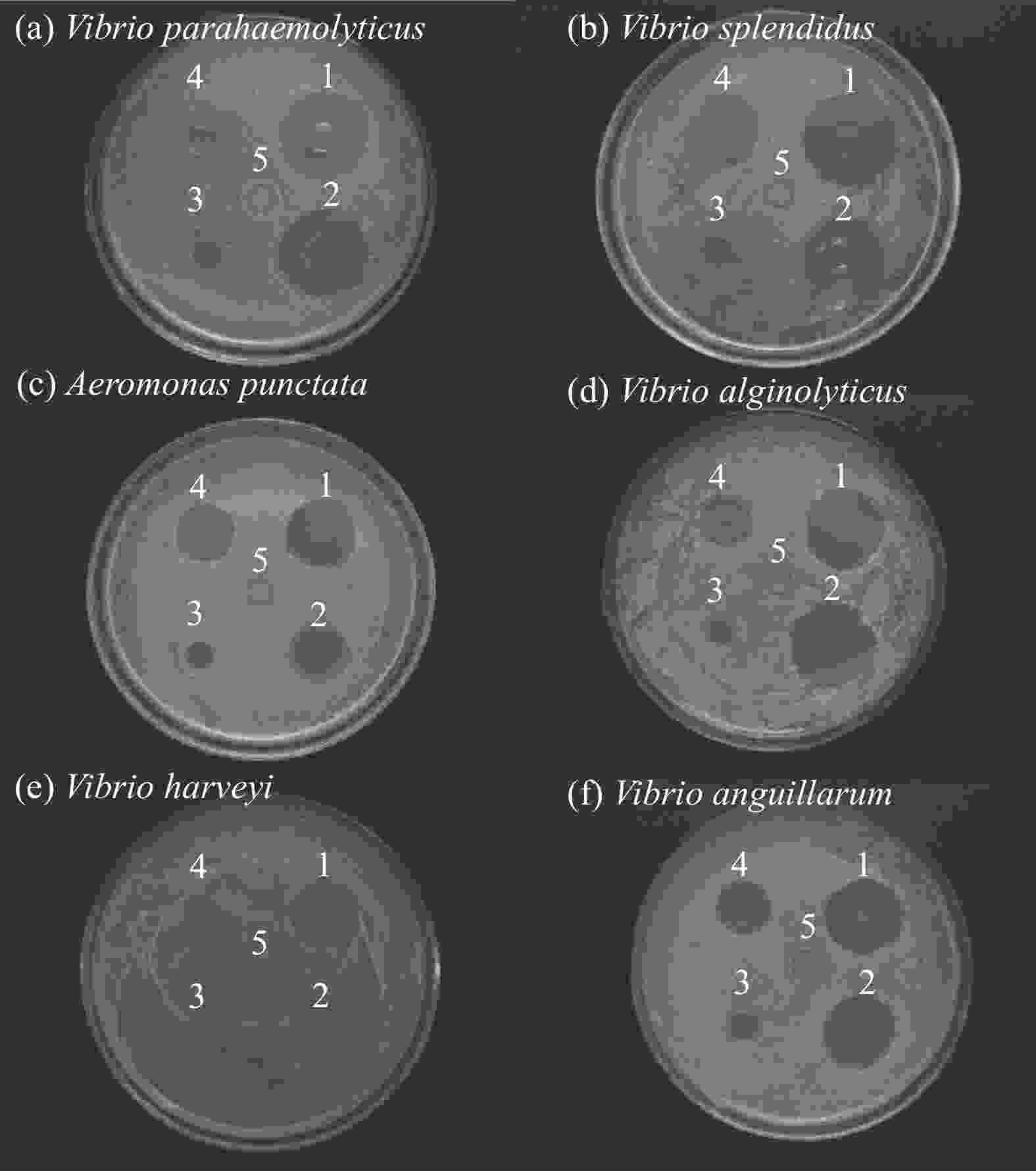
Strain Inhibition zone diameter/mm AgNPs/CS AgNPs Ampicillin (Amp) Aeromonas punctata 19.24±0.47 16.73±0.53 16.25±0.86 Vibrio alginolyticus 23.39±1.03 21.07±0.19 15.72±0.28 Vibrio parahaemolyticus 24.52±0.76 23.35±1.08 23.17±0.10 Vibrio anguillarum 22.01±0.37 19.93±0.11 15.35±0.28 Vibrio harveyi 18.11±0.25 17.98±0.66 9.03±0.34 Vibrio splendidus 26.59±0.65 22.93±2.26 21.20±1.47 表 2 AgNPs对灿烂弧菌的最小抑菌浓度(MIC)和最小杀菌浓度(MBC) (n=3)
Table 2. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) tests of AgNPs against Vibrio splendidus (n=3)
Number Concentration/(μg·mL−1) AgNPs/CS Concentration/(μg·mL−1) AgNPs 24 h 48 h 24 h 48 h 1 112.50 − − 33.33 − − 2 56.30 − − 16.67 − − 3 28.10 − − 8.33 − − 4 14.10 − − 4.17 − − 5 7.03 − − 2.08 − − 6 3.51 − − 1.04 − − 7 1.75 − − 0.52 − + 8 0.87 − − 0.26 + + 9 0.43 − + 0.13 + + 10 0.21 + + 0.07 + + 表 3 AgNPs/CS对多次传代灿烂弧菌MIC的测试(n=3)
Table 3. MIC tests of AgNPs/CS against multigenerational Vibrio splendidus (n=3)
Passage number MIC/(μg·mL−1) AgNPs/CS Amp 1 0.43 9.76 2 0.43 19.53 3 0.43 19.53 4 0.43 39.06 5 0.43 78.13 6 0.87 78.13 7 0.87 312.5 8 0.87 312.5 9 0.87 312.5 10 0.87 625 11 0.87 625 12 0.87 625 13 0.87 625 14 0.87 1250 15 0.87 1250 16 0.87 1250 17 0.87 1250 18 0.87 1250 19 0.87 1250 20 0.87 1250 表 4 AgNPs/CS浓度对体外细胞相对增值率(RGR)和细胞毒性评级的影响
Table 4. Effect of AgNPs/CS concentration on relative growth rate (RGR) and cytotoxicity rating of cells in vitro
Concentration/(μg·mL−1) Absorption value RGR/% Cytotoxicity 0 0.896±0.126 100.00 0 0.25 0.847±0.085 94.534 1 0.5 0.832±0.073 92.818 1 1.0 0.768±0.094 85.707 1 5.0 0.639±0.082 71.317 2 10.0 0.568±0.065 63.393 2 20.0 0.492±0.071 54.911 2 40.0 0.061±0.041 6.885 4 80.0 0.046±0.023 5.154 4 -
[1] 王秋水, 刘悦, 邓婕, 等. 动物性水产品及其养殖环境中抗生素抗性基因的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2022, 13(5):1453-1461. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.5.spaqzljcjs202205013WANG Qiushui, LIU Yue, DENG Jie, et al. Research progress of antibiotic resistance genes in animal aquatic products and aquaculture environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(5):1453-1461(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.5.spaqzljcjs202205013 [2] 孙宇洁, 孟令轩, 朱琳, 等. 水产养殖尾水中抗生素抗性基因的去除及磺胺类耐药细菌研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(5):286-295.SUN Yujie, MENG Lingxuan, ZHU Lin, et al. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes and sulfonamides resistant bacteria in aquaculture tail water[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2022,42(5):286-295(in Chinese). [3] SCHAR D, ZHAO C, WANG Y, et al. Twenty-year trends in antimicrobial resistance from aquaculture and fisheries in Asia[J]. Nature Communications,2021,12:5384. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25655-8 [4] 樊晨, 倪琦, 朱婷, 等. 纳米银抗菌材料的研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2022, 50(9): 229-234, 241.FAN Chen, NI Qi, ZHU Ting, et al. Recent progress on antibacterial material of Ag nanoparticle[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2022, 50(9): 229-234, 241(in Chinese). [5] DUTTA T, GHOSH N N, DAS M, et al. Green synthesis of antibacterial and antifungal silver nanoparticles using Citrus limetta peel extract: Experimental and theoretical studies[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2020,8(4):104019. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104019 [6] NOURI A, TAVAKKOLI YARAKI M, LAJEVARDI A, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Mentha aquatica leaf extract for enhanced antibacterial properties and catalytic activity[J]. Colloid and Interface Science Communications,2020,35:100252. doi: 10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100252 [7] KUBAVAT K, TRIVEDI P, ANSARI H, et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using dietary antioxidant rutin and its biological contour[J]. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences,2022,11(1):1-14. doi: 10.1186/s43088-022-00297-x [8] 姚圣楠, 徐冉, 王安琪, 等. 树莓果渣多酚纳米银的制备、表征及抗菌活性研究[J]. 食品科技, 2022, 47(6): 290-297.YAO Shengnan, XU Ran, WANG Anqi, et al. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activity of raspberry pomace polyphenols silver nanoparticle[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(6): 290-297(in Chinese). [9] GUL A R, SHAHEEN F, RAFIQUE R, et al. Grass-mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their drug delivery evaluation: A biocompatible anti-cancer therapy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,407:127202. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127202 [10] 包善思, 姚瑶, 孙博瑞, 等. 腊梅花抗氧化活性物质微波辅助提取的响应面优化研究[J]. 食品科技, 2019, 44(10):229-234.BAO Shansi, YAO Yao, SUN Borui, et al. Optimization for microwave-assisted extraction of antioxidant active substances in plum blossoms by response surfaces[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(10):229-234(in Chinese). [11] CU T S, CAO V D, NGUYEN C K, et al. Preparation of silver core-chitosan shell nanoparticles using catechol-functionalized chitosan and antibacterial studies[J]. Macromolecular Research,2014,22(4):418-423. doi: 10.1007/s13233-014-2054-5 [12] SHARIFI-RAD M, POHL P. Synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgCl-NPs) using a Pulicaria vulgaris gaertn. aerial part extract and their application as antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant agents[J]. Nanomaterials,2020,10(4):638. doi: 10.3390/nano10040638 [13] SULIMAN Y A O, ALI D, ALARIFI S, et al. Evaluation of cytotoxic, oxidative stress, proinflammatory and genotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells[J]. Environmental Toxicology,2015,30(2):149-160. doi: 10.1002/tox.21880 [14] 郝和平. 医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2000.HAO Heping. Implementation guide of biological evaluation standards for medical devices[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2000(in Chinese). [15] 刘冲冲, 王磊, 徐慧, 等. 姜提取物生物合成纳米银抑菌活性的研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2017, 36(6):590-597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2017.06.005LIU Chongchong, WANG Lei, XU Hui, et al. Antibacterial study of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized with ginger extract[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2017,36(6):590-597(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2017.06.005 [16] 薛海燕, 张颖, 张宝艳, 等. 安石榴苷还原壳聚糖/纳米银溶胶制备表征及其抑菌性能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(4):306-314.XUE Haiyan, ZHANG Ying, ZHANG Baoyan, et al. Preparation characterization and bacteriostatic properties of punicalagin reducing chitosan/nano silver sol[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2018,34(4):306-314(in Chinese). [17] 邢亚阁, 廖兴梅, 李文秀, 等. 不同制备条件对纳米银绿色合成的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(7):231-237.XING Yage, LIAO Xingmei, LI Wenxiu, et al. Effect of different preparation conditions on the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(7):231-237(in Chinese). [18] MUNIR T, MAHMOOD A, SHAFIQ F, et al. Experimental and theoretical analyses of nano-silver for antibacterial activity based on differential crystal growth temperatures[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences,2021,28(12):7561-7566. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.058 [19] 李晖, 廖跃华, 徐晓慧, 等. 纳米材料修饰电化学生物传感器在食品检测中的应用[J]. 分析科学学报, 2020, 36(6):900-905.LI Hui, LIAO Yuehua, XU Xiaohui, et al. Application of biosensor with nanomaterial modified electrod in food detection[J]. Journal of Analytical Science,2020,36(6):900-905(in Chinese). [20] SADEGHI B, GHOLAMHOSEINPOOR F. A study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2015,134:310-315. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.046 [21] SAHARIAH P, MÁSSON M. Antimicrobial chitosan and chitosan derivatives: A review of the structure-activity relationship[J]. Biomacromolecules,2017,18(11):3846-3868. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b01058 [22] JUNLABHUT P, BOONRUANG S, MEKPRASART W, et al. Ag nanoparticle-doped SiO2/TiO2 hybrid optical sensitive thin film for optical element applications[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2016,306:262-266. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.06.033 [23] MIRI A, SARANI M, BAZAZ M R, et al. Plant-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Prosopis farcta extract and its antibacterial properties[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2015,141:287-291. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2015.01.024 [24] MOSTAFA M, RAMADAN H E, EL-AMIR M A. Sorption and desorption studies of radioiodine onto silver chloride via batch equilibration with its aqueous media[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity,2015,150:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.07.022 [25] 崔升, 袁美玉, 付俊杰, 等. 抗菌用壳聚糖及其金属粒子复合材料研究进展[J]. 精细化工, 2021, 38(9):1757-1764, 1778.CUI Sheng, YUAN Meiyu, FU Junjie, et al. Research progress of chitosan and its metal particle composite materials for antibacterial application[J]. Fine Chemicals,2021,38(9):1757-1764, 1778(in Chinese). [26] ZHANG T, PAN J F, HUNT D E, et al. Organic matter modifies biochemical but not most behavioral responses of the clam Ruditapes philippinarum to nanosilver exposure[J]. Marine Environmental Research,2018,133:105-113. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2017.10.016 [27] 郭峻宁, 邓雪婷, 高蓉蓉, 等. 细菌生物膜在农田土壤污染修复中的应用研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2022(9):3919-3932.GUO Junning, DENG Xueting, GAO Rongrong, et al. Application of bacterial biofilm in remediation of polluted farmland soil: A review[J]. Microbiology China,2022(9):3919-3932(in Chinese). [28] OTARI S V, PATIL R M, GHOSH S J, et al. Intracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticle by actinobacteria and its antimicrobial activity[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2015,136:1175-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.10.003 [29] XU L, WANG Y Y, HUANG J, et al. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety[J]. Theranostics,2020,10(20):8996-9031. doi: 10.7150/thno.45413 [30] 熊玲, 蒋学华, 陈亮, 等. 不同粒径银粒子的体外细胞毒性比较[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2007, 26(4):600-604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2007.04.023XIONG Ling, JIANG Xuehua, CHEN Liang, et al. Comparison of cytotoxicity of silver particles with different particle sizes in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering,2007,26(4):600-604(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2007.04.023 [31] 张富强, 佘文珺, 傅远飞. 六种纳米载银无机抗菌剂的体外细胞毒性比较[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2005, 40(6):504-507.ZHANG Fuqiang, SHE Wenjun, FU Yuanfei. Comparison of the cytotoxicity in vitro among six types of nano-silver base inorganic antibacterial agents[J]. Chinese Journal of Stomatology,2005,40(6):504-507(in Chinese). [32] 马守栋, 李明春, 叶勇, 等. 纳米银的制备与表征[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2011, 46(13):1007-1010.MA Shoudong, LI Mingchun, YE Yong, et al. Study on preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticle colloid solution[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2011,46(13):1007-1010(in Chinese). [33] 蔡运成. 银纳米复合物的制备与性能研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017.CAI Yuncheng. Preparation and properties of silver nanocomplexes[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [34] 秦社宣, 童细焱, 孙林煌, 等. 新型纳米银体外广谱抗菌作用及机制[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2018, 30(9):1024-1028.QIN Shexuan, TONG Xiyan, SUN Linhuang, et al. The broad-spectrum antibacteria effects and mechanism of new-type silver nanoparticles in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology,2018,30(9):1024-1028(in Chinese). [35] VALLAPA N, WIARACHAI O, THONGCHUL N, et al. Enhancing antibacterial activity of chitosan surface by heterogeneous quaternization[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,83(2):868-875. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.075 [36] AZIZ N, FARAZ M, PANDEY R, et al. Facile algae-derived route to biogenic silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial, and photocatalytic properties[J]. Langmuir,2015,31(42):11605-11612. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b03081 -





 下载:
下载: