Research progress of PEO-based composite solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries
-
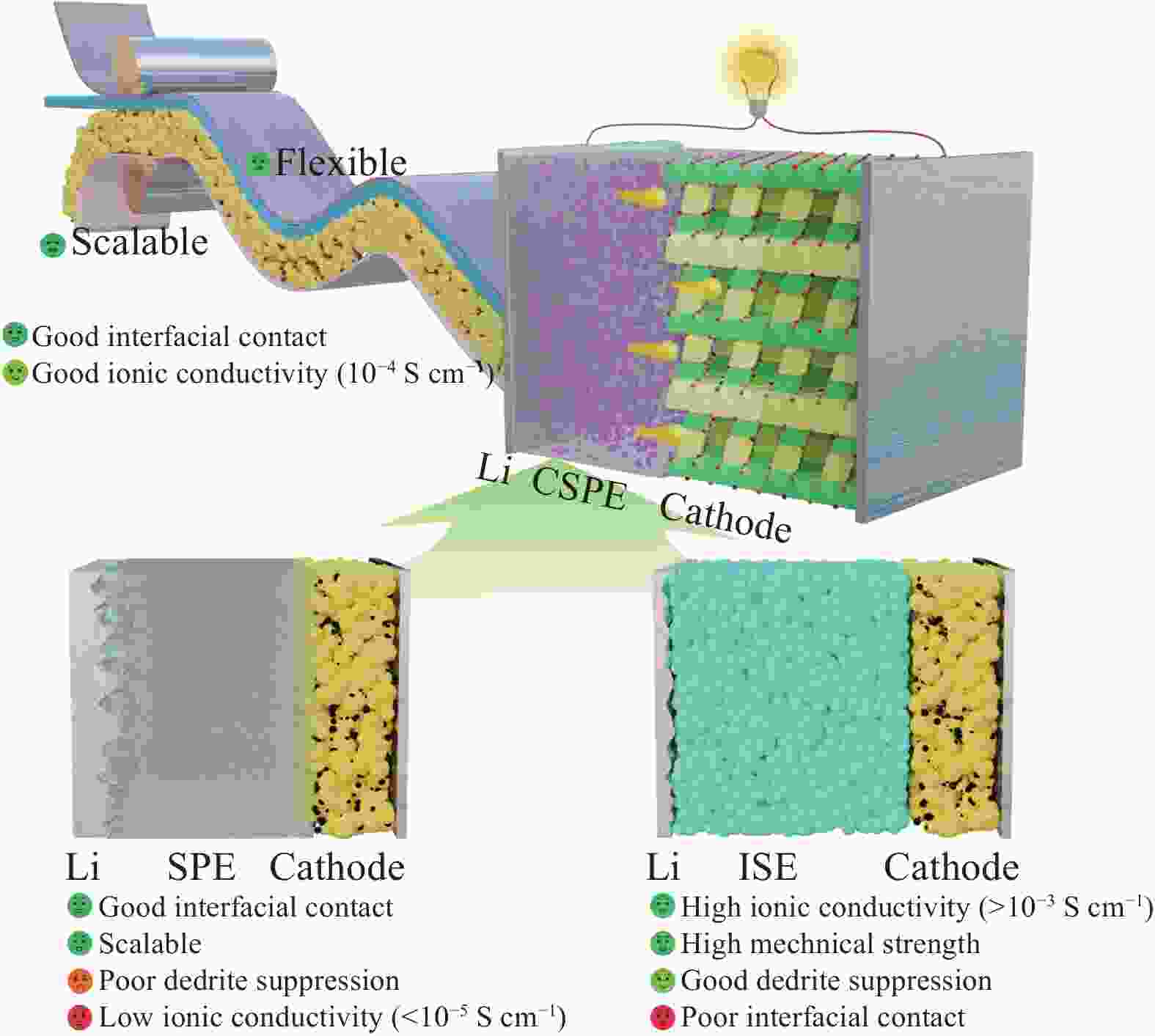
摘要: 固态锂离子电池能量密度高、安全性强,是突破电池技术瓶颈的关键,受到了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。固态电解质是固态电池的核心,其中聚氧化乙烯(PEO)基聚合物固态电解质在改善电极界面相容性方面具有优势,是最有潜力的电解质材料之一。本文系统阐述了PEO与无机填料间的协同作用,及其对复合固态电解质的离子传输性和界面相容性的影响机制。首先对PEO基复合固态电解质做出概述,并探讨离子传输相关机制,然后分别综述了PEO-惰性填料和PEO-活性填料复合固态电解质体系的设计、制备、性能及机制,最后,对复合固态聚合物电解质的未来发展和优化设计做出展望。
-
关键词:
- 固态锂电池 /
- 聚氧化乙烯 /
- 复合固态聚合物电解质 /
- 离子传输机制 /
- 无机填料
Abstract: Featured with high energy density and sound safety, solid-state lithium-ion battery is the key to breaking through the bottleneck shackling battery technology, gathering wide attention from academia and industry. Solid-state electrolytes are the core of solid-state batteries, among which polyethylene oxide (PEO) polymer solid-state electrolyte excels at improving electrode interface compatibility and is one of the most potential electrolyte materials. This paper systematically elucidated the synergistic effect of PEO with inorganic modified fillers and its influence on ion transport and interfacial compatibility of composite solid-state electrolytes. Following an overview of the PEO-based composite solid-state electrolyte, the mechanism of ion transport was discussed. Then, the design, preparation, performance, and mechanism of PEO-inert filler and PEO-active filler composite solid-state electrolyte systems were reviewed respectively. Finally, an outlook on the future development and optimization design of composite solid-state polymer electrolytes was presented. -
图 3 (a) Li+分别在PEO相中、PEO相和PEO/陶瓷界面处、PEO相和陶瓷相以及PEO/陶瓷界面处的传导途径示意图[45];(b) 锂离子在LLZO (5wt%) -PEO (LiTFSI)、LLZO (20wt%) -PEO (LiTFSI) 和LLZO (50wt%) -PEO (LiTFSI)复合电解质中的路径示意图[46];(c) NPs、无序NWs和排列NWs在复合聚合物电解质中的锂离子传导途径[48];(d) 填料、聚合物和锂盐之间的路易斯酸碱相互作用示意图[36]
Figure 3. (a) Schematic illustration of the Li+ conduction pathways in the PEO phase,PEO phase and PEO/ceramic interface,PEO phase and ceramic phase and PEO/ceramic interface, respectively[45]; (b) Schematic of Li-ion pathways within LLZO (5wt%)–PEO (LiTFSI), LLZO (20wt%)–PEO (LiTFSI) and LLZO (50wt%)–PEO (LiTFSI) composite electrolytes[46]; (c) Li-ion conduction pathways in composite polymer electrolytes with NPs,random NWs and aligned NWs[48]; (d) Illustration of Lewis acid-base interaction between fillers, polymer, and Li salt[36]
图 4 (a) 三种不同类型Al2O3与PEO的表面相互作用和Al2O3-PEO CSPEs的电导率图[56];(b) AAO -聚合物复合电解质制备工艺示意图[58];(c) 分别为AAO圆盘中单个纳米通道中聚合物电解质示意图、各组分的离子电导率、界面离子电导率以及AAO-聚合物复合电解质(APCE)界面层厚度[58];(d) 功能化Al2O3 (F- Al2O3)的合成及其制备杂化聚合物电解质(HPE)[59];分散在硅片上PEO薄膜中的颗粒的SEM图像: (e) Al2O3, ( f) F- Al2O3[59]
Figure 4. (a) Surface interactions between three diferent type Al2O3 and PEO and conductivity plots of Al2O3-PEO CSPEs[56]; (b) Schematics of fabrication procedures of AAO-polymer composite electrolyte[58]; (c) Schematics of polymer electrolyte in individual nanochannel of the AAO disc, the ionic conductivities of each component, the interface ion conductivities, and the thickness of interfacial layer of AAO-polymer composite electrolyte (APCE), respectively[58]; (d) Synthesis of functionalized Al2O3 (F-Al2O3) and preparation of hybrid polymer electrolyte (HPE) using F-Al2O3[59]; SEM images of the particles dispersed in PEO film on a Si wafer: (e) Al2O3, (f) F- Al2O3[59]
图 5 (a) PEO链与MUSiO2的原位水解过程及相互作用机制示意图[60];(b) SiO2-Li2SO4-PEO CSPEs的制备工艺示意图以及由Li2SO4衍生的SiO2纤维CSPE实现Li+快速传导的原理图[61];(c) 原位水解制备CSPEs的示意图[62];(d) 不同成分聚合物电解质的离子电导率[65];(e) PEO-LiTFSI电解质和PEO-LiTFSI -3 wt% TiO2@PDA复合电解质的DSC曲线[65];(f) CPEs中缺氧TiO2表面相互作用示意图[66];TiO2样品的XPS光谱(g)和Ti 2 p的高分辨率光谱(h)[67]
Figure 5. (a) Schematic figures showing the procedure of in situ hydrolysis and interaction mechanisms among PEO chains and MUSiO2[60]; (b) Schematic diagram of preparation process of SiO2/Li2SO4/PEO CSPEs and schematics of fast Li+ conduction enabled by the Li2SO4-derived SiO2 fibers CSPEs [61];(c) The schematic diagram of CPSEs prepared by in situ hydrolysis[62]; (d) The ionic conductivities of the polymer electrolytes with different compositions[65]; (e) DSC curves of the PEO–LiTFSI electrolyte and PEO–LiTFSI-3 wt% TiO2@PDA composite electrolyte[65]; (f) Schematic illustrations of surface interaction of oxygen-deficient TiO2 in CPEs[66]; XPS survey spectra of the TiO2 sample (g) and high-resolution spectra of the Ti 2 p (h)[67]
图 6 (a) 锂对称电池中多尺度排列的介孔石榴石Li6.4La3Zr2Al0.2O12 (LLZO)膜与聚合物电解质结合示意图[81];(b) 石榴石-木膜阻抗随温度升高而下降的Nyquist图,插图为测试单元的结构[81];(c) 石榴石木和PEO聚合物电解质在不同温度下的离子电导率对比示意图[81];(d) 以陶瓷石榴石纳米纤维为增强层,锂离子导电聚合物为基体的复合固态电解质示意图[83];(e) 纤维素衍生的CPE的制备工艺示意图[88];(f) 纤维素/陶瓷增强CPE中Li+导电机制示意图[88];(g) PEO|PEO−钙钛矿|PEO复合电解质的表面SEM图像、横截面SEM图像及横截面形貌详细视图[90]
Figure 6. (a) Schematic of multi-scale aligned mesoporous garnet Li6.4La3Zr2Al0.2O12 (LLZO) membrane incorporated with polymer electrolyte in a lithium symmetric cell[81]; (b) Nyquist plot showing the decrease in the impedance of the garnet-wood membrane with increasing temperature, the inset schematic shows the structure of the testing cell[81]; (c) Comparison of the ionic conductivity of the garnet-wood and PEO based polymer electrolyte at different temperatures[81]; (d) Schematic of the composite solid electrolyte, where ceramic garnet nanofibers function as the reinforcement and lithium-ion conducting polymer functions as the matrix[83]; (e) Schematic illustration of fabrication procedures for the cellulose derived CPE[88]; (f) Schematic of proposed Li+ conducting mechanism in the cellulose/ceramic reinforced CPE[88]; (g) SEM image of the surface, cross-sectional SEM image and detailed view of the cross-section morphology of the PEO|PEO−perovskite|PEO composite electrolyte[90]
表 1 PEO基复合固态电解质文献报道汇总
Table 1. Summary of literature reports on PEO-based composite solid electrolyte
Polymer matrix lithium salt Filler Ionic Conductivity/( S·cm−1) ESW/(V vs.Li/Li+) tLi+ Ref. PEO LiTFSI Al2O3 5.82 ×10−4 (RT) — — [58] PEO LiTFSI Al2O3 9.6 ×10–4 (25℃) 5 0.81 [97] PEO LiTFSI SiO2 1.8 ×10–4 (30℃) 5.3 0.42 [62] PEO LiClO4 SiO2 1.2 ×10–3 (60℃) >5.5 — [98] PEO LiClO4 SiO2 1.1 ×10–4 (30℃) >4.8 — [99] PEO LiClO4 TiO2 1 ×10–5 (30°C) 5 0.3 [100] PEO LiTFSI TiO2@PDA 4.36 ×10–4 (55°C) 5 0.19 [65] PEO LiTFSI Ti3+-TiO2 1 ×10–4 (30℃) 5.5 0.36 [67] PEO LiBF4 ZrO2 4.4 ×10–4 (80℃) — 0.68 [72] PEO LiCF3SO3 ZrO2 1.38 ×10–4 (RT) — — [74] PEO LiTFSI LLZTO 1.9 ×10–4 (40℃) 5.1 0.67 [101] PEO LiTFSI LLZTO 3.03×10–4 (55℃) 4.5 0.117 [102] PEO LiTFSI LLZTO 5.6×10–4 (60℃) 4.75 0.46 [103] PEO LiTFSI LLZO 5.5×10–4 (30℃) >5.7 0.21 [104] PEO LiTFSI LLZO 2.39 ×10–4 (25℃) >5.5 — [105] PEO LiTFSI LATP 4 ×10–4 (60℃) 4.7 — [106] PEO LiTFSI LATP 3.61×10–4 (60℃) 4.8 — [107] PEO LiTFSI LAGP 6.76×10–4 (60℃) 5.3 0.378 [108] PEO LiTFSI LAGP 1.6×10–5 (20℃) — — [109] PEO LiTFSI LLTO 2.04×10–4 (25℃) 4.7 — [110] PEO LiTFSI LLTO 2.3×10–4 (RT) 4.5 — [111] PEO LiTFSI LLTO 1.8×10–4 (RT) 4.5 0.33 [112] PEO LiTFSI LGPS 1.21×10–3 (80℃) 5.7 0.26 [95] PEG-PEO LiTFSI LGPS 9.83×10–4 (RT) — 0.68 [96] Notes: ESW is Electrochemical stability window; tLi+ is Lithium-ion transference number; RT is Room Temperature; PDA is polydopamine; LLZTO is Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12/Li6.75La3Zr1.75Ta0.25O12; LLZO is Li7La3Zr2O12; LATP is Li1.4Al0.4Ti1.6(PO4)3; LAGP is Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3; LLTO is Li0.33La0.557TiO3; LGPS is Li10GeP2S12; PEG is Polyethylene glycol. -
[1] JIN B. Research on performance evaluation of green supply chain of automobile enterprises under the background of carbon peak and carbon neutralization[J]. Energy Reports, 2021, 7: 594-604. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.10.002 [2] HU Y, XIE X, LI W, et al. Recent progress of polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(4): 1253-1277. [3] YANG X, LIU J, PEI N, et al. The critical role of fillers in composite polymer electrolytes for lithium battery[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 74. doi: 10.1007/s40820-023-01051-3 [4] CHEN X, LI X, LUO L, et al. Practical application of all-solid-state lithium batteries based on high-voltage cathodes: Challenges and progress[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(35): 2301230. doi: 10.1002/aenm.202301230 [5] XIAO Z, LONG T, SONG L, et al. Research progress of polymer-inorganic filler solid composite electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2021: 1-12. [6] CHEN S, DAI F, CAI M. Opportunities and challenges of high-energy lithium metal batteries for electric vehicle applications[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2020, 5(10): 3140-3151. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c01545 [7] XI G, XIAO M, WANG S, et al. Polymer-based solid electrolytes: Material selection, design, and application[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(9): 2007598. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202007598 [8] TANG S, GUO W, FU Y. Advances in composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries and beyond[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(2): 2000802. doi: 10.1002/aenm.202000802 [9] YANG Y, ZHOU H, XIE J, et al. Organic fast ion-conductor with ordered Li-ion conductive nano-pathways and high ionic conductivity for electrochemical energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 66: 647-656. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.09.011 [10] NGUYEN A G, PARK C J. Insights into tailoring composite solid polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 675: 121552. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2023.121552 [11] FAMPRIKIS T, CANEPA P, DAWSON J A, et al. Fundamentals of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for batteries[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(12): 1278-1291. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0431-3 [12] FAN P, LIU H, MAROSZ V, et al. High performance composite polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(23): 2101380. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202101380 [13] HOU W, OU Y, LIU K. Progress on high voltage PEO-based polymer solid electrolytes in lithium batteries[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 2022, 38(3): 735-743. doi: 10.1007/s40242-022-2065-2 [14] SUN J, LIU C, LIU H, et al. Advances in ordered architecture design of composite solid electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. The Chemical Record, 2023, 23(6): e202300044. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202300044 [15] MANTHIRAM A, YU X, WANG S. Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2(4): 1-16. [16] MEYER W H. Polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced materials, 1998, 10(6): 439-448. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199804)10:6<439::AID-ADMA439>3.0.CO;2-I [17] LIU X, BI Z, WAN Y, et al. Composition regulation of polyacrylonitrile-based polymer electrolytes enabling dual-interfacially stable solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 665: 582-591. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.03.166 [18] ZHANG W, KOVERGA V, LIU S, et al. Single-phase local-high-concentration solid polymer electrolytes for lithium-metal batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2024: 1-15. [19] WU Y, LI Y, WANG Y, et al. Advances and prospects of PVDF based polymer electrolytes[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 64: 62-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.04.007 [20] LI Z, ZHANG S, JIANG Z, et al. Deep eutectic solvent-immobilized PVDF-HFP eutectogel as solid electrolyte for safe lithium metal battery[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2021, 267: 124701. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124701 [21] SU X, XU X P, JI Z Q, et al. Polyethylene oxide-based composite solid electrolytes for lithium batteries: Current progress, low-temperature and high-voltage limitations, and prospects[J]. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2024, 7(1): 2. doi: 10.1007/s41918-023-00204-7 [22] ZHANG D, LI L, WU X, et al. Research progress and application of PEO-based solid state polymer composite electrolytes[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2021, 9: 726738. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2021.726738 [23] FENG J, WANG L, CHEN Y, et al. PEO based polymer-ceramic hybrid solid electrolytes: a review[J]. Nano Convergence, 2021, 8: 1-12. doi: 10.1186/s40580-020-00251-6 [24] 周伟东, 黄秋, 谢晓新, et al. 固态锂电池聚合物电解质研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(6): 1788-1805.ZHOU Weidong, HUANG Qiu, XIE Xiaoxin, et al. Research progress of polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(6): 1788-1805 (in Chinese). [25] SZCZĘSNA-CHRZAN A, MARCZEWSKI M, SYZDEK J, et al. Lithium polymer electrolytes for novel batteries application: The review perspective[J]. Applied Physics A, 2022, 129(1): 37. [26] WANG H, SHENG L, YASIN G, et al. Reviewing the current status and development of polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 33: 188-215. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.08.014 [27] DING Z, LI J, LI J, et al. Review-interfaces: Key issue to be solved for all solid-state lithium battery technologies[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(7): 070541. doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/ab7f84 [28] ZHENG Y, LI X, LI C Y. A novel de-coupling solid polymer electrolyte via semi-interpenetrating network for lithium metal battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 29: 42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.04.002 [29] LIU S, LIU W, BA D, et al. Filler-integrated composite polymer electrolyte for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 35(2): 2110423. [30] ROLLO-WALKER G, MALIC N, WANG X, et al. Development and progression of polymer electrolytes for batteries: Influence of structure and chemistry[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(23): 4127. doi: 10.3390/polym13234127 [31] YUE L, MA J, ZHANG J, et al. All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 5: 139-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2016.07.003 [32] KUNDU S, EIN-ELI Y. A review on design considerations in polymer and polymer composite solid-state electrolytes for solid Li batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 553: 232267. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.232267 [33] MARZANTOWICZ M, DYGAS J R, KROK F, et al. Influence of crystalline complexes on electrical properties of PEO: LiTFSI electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 53(4): 1518-1526. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2007.03.032 [34] MARZANTOWICZ M, DYGAS J R, KROK F, et al. Crystalline phases, morphology and conductivity of PEO: LiTFSI electrolytes in the eutectic region[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 159(1): 420-430. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.02.044 [35] GRUNDISH N S, GOODENOUGH J B, KHANI H. Designing composite polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2021, 30: 100828. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2021.100828 [36] ZHOU Q, MA J, DONG S, et al. Intermolecular chemistry in solid polymer electrolytes for high-energy-density lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(50): 1902029. doi: 10.1002/adma.201902029 [37] WU N, CHIEN P H, QIAN Y, et al. Enhanced surface interactions enable fast Li+ conduction in oxide/polymer composite electrolyte[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(10): 4131-4137. doi: 10.1002/anie.201914478 [38] ROJAEE R, CAVALLO S, MOGURAMPELLY S, et al. Highly-cyclable room-temperature phosphorene polymer electrolyte composites for Li metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(32): 1910749. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910749 [39] JEON Y M, KIM S, LEE M, et al. Polymer-clay nanocomposite solid-state electrolyte with selective cation transport boosting and retarded lithium dendrite formation[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(47): 2003114. doi: 10.1002/aenm.202003114 [40] XU S, SUN Z, SUN C, et al. Homogeneous and fast ion conduction of PEO-based solid-state electrolyte at low temperature[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(51): 2007172. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202007172 [41] LIU M, CHENG Z, GANAPATHY S, et al. Tandem interface and bulk Li-ion transport in a hybrid solid electrolyte with microsized active filler[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(9): 2336-2342. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b01371 [42] 宋鑫, 高志浩, 骆林, et al. 全固态锂电池有机-无机复合电解质研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4): 1857-1878.SONG Xin, GAO Zhihao, LUO Lin, et al. Research progress of organic-inorganic composite electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(4): 1857-1878(in Chinese). [43] YANG T, WANG C, ZHANG W, et al. A critical review on composite solid electrolytes for lithium batteries: Design strategies and interface engineering[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 84: 189-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2023.05.011 [44] CHEN H, ZHENG M, QIAN S, et al. Functional additives for solid polymer electrolytes in flexible and high-energy-density solid-state lithium-ion batteries[J]. Carbon Energy, 2021, 3(6): 929-956. doi: 10.1002/cey2.146 [45] SU Y, XU F, ZHANG X, et al. Rational design of high-performance PEO/ceramic composite solid electrolytes for lithium metal batteries[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 82. doi: 10.1007/s40820-023-01055-z [46] ZHENG J, HU Y-Y. New insights into the compositional dependence of Li-ion transport in polymer-ceramic composite electrolytes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(4): 4113-4120. [47] SHI C, SONG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Revealing the mechanisms of lithium-ion transport and conduction in composite solid polymer electrolytes[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2023, 4(3). [48] LIU W, LEE S W, LIN D, et al. Enhancing ionic conductivity in composite polymer electrolytes with well-aligned ceramic nanowires[J]. Nature Energy, 2017, 2(5): 1-7. [49] SHEN Z, CHENG Y, SUN S, et al. The critical role of inorganic nanofillers in solid polymer composite electrolyte for Li+ transportation[J]. Carbon Energy, 2021, 3(3): 482-508. doi: 10.1002/cey2.108 [50] SEN S, TREVISANELLO E, NIEMöLLER E, et al. The role of polymers in lithium solid-state batteries with inorganic solid electrolytes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(35): 18701-18732. doi: 10.1039/D1TA02796D [51] ZHENG Y, YAO Y, OU J, et al. A review of composite solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: Fundamentals, key materials and advanced structures[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(23): 8790-8839. doi: 10.1039/D0CS00305K [52] LI J, JING M-X, LI R, et al. Al2O3 fiber-reinforced polymer solid electrolyte films with excellent lithium-ion transport properties for high-voltage solid-state lithium batteries[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2022, 4(10): 7144-7151. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.2c01034 [53] WANG C, YANG T, ZHANG W, et al. Hydrogen bonding enhanced SiO2/PEO composite electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(7): 3400-3408. doi: 10.1039/D1TA10607D [54] HUA S, LI J L, JING M X, et al. Effects of surface lithiated TiO2 nanorods on room-temperature properties of polymer solid electrolytes[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(8): 6452-6462. doi: 10.1002/er.5379 [55] WIECZOREK W, SUCH K, WYCIŚLIK H, et al. Modifications of crystalline structure of PEO polymer electrolytes with ceramic additives[J]. Solid State Ionics, 1989, 36(3-4): 255-257. doi: 10.1016/0167-2738(89)90185-9 [56] CROCE F, PERSI L, SCROSATI B, et al. Role of the ceramic fillers in enhancing the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2001, 46(16): 2457-2461. doi: 10.1016/S0013-4686(01)00458-3 [57] PARK C H, KIM D W, PRAKASH J, et al. Electrochemical stability and conductivity enhancement of composite polymer electrolytes[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2003, 159(1-2): 111-119. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2738(03)00025-0 [58] ZHANG X, XIE J, SHI F, et al. Vertically aligned and continuous nanoscale ceramic-polymer interfaces in composite solid polymer electrolytes for enhanced ionic conductivity[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(6): 3829-3838. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01111 [59] BAE H W, SUK J, PARK H S, et al. Incorporating ethylene oxide functionalized inorganic particles to solid polymer electrolytes for enhanced mechanical stability and electrochemical performance[J]. Advanced Energy and Sustainability Research, 2023, 4(3): 2200125. doi: 10.1002/aesr.202200125 [60] LIN D, LIU W, LIU Y, et al. High ionic conductivity of composite solid polymer electrolyte via in situ synthesis of monodispersed SiO2 nanospheres in poly (ethylene oxide)[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(1): 459-465. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04117 [61] YU J, WANG C, LI S, et al. Li+-containing, continuous silica nanofibers for high Li+ conductivity in composite polymer electrolyte[J]. Small, 2019, 15(44): 1902729. doi: 10.1002/smll.201902729 [62] WANG C, YANG T, ZHANG W, et al. Hydrogen bonding enhanced SiO2/PEO composite electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(7): 3400-3408. doi: 10.1039/D1TA10607D [63] CHUNG S, WANG Y, PERSI L, et al. Enhancement of ion transport in polymer electrolytes by addition of nanoscale inorganic oxides[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 97: 644-648. [64] WIECZOREK W, FLORJANCZYK Z, STEVENS J. Composite polyether based solid electrolytes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1995, 40(13-14): 2251-2258. doi: 10.1016/0013-4686(95)00172-B [65] ZHAO E, GUO Y, ZHANG A, et al. Polydopamine coated TiO2 nanofiber fillers for polyethylene oxide hybrid electrolytes for efficient and durable all solid state lithium ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2022, 14(3): 890-897. doi: 10.1039/D1NR06636F [66] LUO B, WANG W, WANG Q, et al. Facilitating ionic conductivity and interfacial stability via oxygen vacancies-enriched TiO2 microrods for composite polymer electrolytes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 460: 141329. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.141329 [67] LI C, HUANG Y, CHEN C, et al. High-performance polymer electrolyte membrane modified with isocyanate-grafted Ti3+ doped TiO2 nanowires for lithium batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 563: 150248. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150248 [68] BAE J, LI Y, ZHANG J, et al. A 3D nanostructured hydrogel-framework-derived high-performance composite polymer lithium-ion electrolyte[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(8): 2096-2100. doi: 10.1002/anie.201710841 [69] BAE J, LI Y, ZHAO F, et al. Designing 3D nanostructured garnet frameworks for enhancing ionic conductivity and flexibility in composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 15: 46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2018.03.016 [70] CHEN W, XIONG X, ZENG R, et al. Enhancing the interfacial ionic transport via in situ 3D composite polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(7): 7200-7207. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.0c01269 [71] XU H-M, JING M-X, LI J, et al. Safety-enhanced flexible polypropylene oxide-ZrO2 composite solid electrolyte film with high room-temperature ionic conductivity[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(33): 11118-11126. [72] CROCE F, SETTIMI L, SCROSATI B. Superacid ZrO2-added, composite polymer electrolytes with improved transport properties[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2006, 8(2): 364-368. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2005.12.002 [73] DAM T, TRIPATHY S N, PALUCH M, et al. Investigations of relaxation dynamics and observation of nearly constant loss phenomena in PEO20-LiCF3SO3-ZrO2 based polymer nano-composite electrolyte[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 202: 147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.134 [74] MOHD YASIN S M, JOHAN M R. Thermal, structural and morphology studies of PEO-LiCF3SO3-DBP-ZrO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolytes[J]. Malaysian NANO-An International Journal, 2021, 1(1): 1-17. doi: 10.22452/mnij.vol1no1.1 [75] XU L, LI J, SHUAI H, et al. Recent advances of composite electrolytes for solid-state Li batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 67: 524-548. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.10.038 [76] LI J, ZHU K, YAO Z, et al. A promising composite solid electrolyte incorporating LLZO into PEO/PVDF matrix for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26: 1101-1108. doi: 10.1007/s11581-019-03320-x [77] LIU L, CHU L, JIANG B, et al. Li1.4Al0.4Ti1.6(PO4)3 nanoparticle-reinforced solid polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2019, 331: 89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2019.01.007 [78] DAEMS K, YADAV P, DERMENCI K B, et al. Advances in inorganic, polymer and composite electrolytes: Mechanisms of lithium-ion transport and pathways to enhanced performance[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2024, 191: 114136. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.114136 [79] 国洪瑶, 吴晓萌, 吴勇民, 等. 无机填料在复合固态电解质中的作用机制研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(S1): 9-16.GUO Hongyao, WU Xiaomeng, WU Yongmin, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of action of inorganic fillers in composite solid electrolytes[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(S1): 9-16(in Chinese). [80] LIU Y, XU B, ZHANG W, et al. Composition modulation and structure design of inorganic-in-polymer composite solid electrolytes for advanced lithium batteries[J]. Small, 2019, 16(15): 1902813. [81] DAI J, FU K, GONG Y, et al. Flexible solid-state electrolyte with aligned nanostructures derived from wood[J]. ACS Materials Letters, 2019, 1(3): 354-361. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.9b00189 [82] LIU M, GUAN X, LIU H, et al. Composite solid electrolytes containing single-ion lithium polymer grafted garnet for dendrite-free, long-life all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 445: 136436. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136436 [83] FU K, GONG Y, DAI J, et al. Flexible, solid-state, ion-conducting membrane with 3D garnet nanofiber networks for lithium batteries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(26): 7094-7099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600422113 [84] XIAO W, WANG J, FAN L, et al. Recent advances in Li1+xAlxTi2-x(PO4)3 solid-state electrolyte for safe lithium batteries[J]. Energy Storage Mater, 2019, 19: 379-400. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2018.10.012 [85] KOTOBUKI M, KOISHI M. Preparation of Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolyte via a sol-gel route using various Al sources[J]. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(4): 4645-4649. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.206 [86] ZHAO E, GUO Y, XIN Y, et al. Enhanced electrochemical properties and interfacial stability of poly(ethylene oxide) solid electrolyte incorporating nanostructured Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 fillers for all solid state lithium ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 45(5): 6876-6887. [87] WANG G, LIU H, LIANG Y, et al. Composite polymer electrolyte with three-dimensional ion transport channels constructed by NaCl template for solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 45: 1212-1219. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.11.021 [88] WANG C, HUANG D, LI S, et al. Three-dimensional-percolated ceramic nanoparticles along natural-cellulose-derived hierarchical networks for high Li+ conductivity and mechanical strength[J]. Nano Letters, 2020, 20(10): 7397-7404. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c02721 [89] 黄永浩, 朱霨亚, 廖友好, 等. 金属锂电池用复合固体电解质的研究进展[J]. 电池, 2023, 53(1): 93-97.HUANG Yonghao, ZHU Weiya, LIAO Youhao, et al. Research progress in composite solid electrolytes for metal lithium metal battery[J]. Batteries, 2023, 53(1): 93-97(in Chinese). [90] LIU K, ZHANG R, SUN J, et al. Polyoxyethylene (PEO)| PEO-perovskite| PEO composite electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(50): 46930-46937. [91] ZHU P, YAN C, DIRICAN M, et al. Li0.33La0.557TiO3 ceramic nanofiber-enhanced polyethylene oxide-based composite polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(10): 4279-4285. doi: 10.1039/C7TA10517G [92] TENG Y, GUO J, WANG Y, et al. 3D perovskite LLTO nanotubers networks for enhanced Li+ conductivity in composite solid electrolytes[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2022, 33(33): 25342-25354. doi: 10.1007/s10854-022-09240-3 [93] KAMAYA N, HOMMA K, YAMAKAWA Y, et al. A lithium superionic conductor[J]. Nature materials, 2011, 10(9): 682-686. doi: 10.1038/nmat3066 [94] LI M, KOLEK M, FRERICHS J E, et al. Investigation of polymer/ceramic composite solid electrolyte system: The case of PEO/LGPS composite electrolytes[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(34): 11314-11322. [95] ZHAO Y, WU C, PENG G, et al. A new solid polymer electrolyte incorporating Li10GeP2S12 into a polyethylene oxide matrix for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 301: 47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.09.111 [96] PAN K, ZHANG L, QIAN W, et al. A flexible ceramic/polymer hybrid solid electrolyte for solid-state lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(17): 2000399. doi: 10.1002/adma.202000399 [97] SHI Y, FAN Z, DING B, et al. Atomic-scale Al2O3 modified PEO-based composite polymer electrolyte for durable solid-state Li-S batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2021, 881: 114916. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114916 [98] LIN D, LIU W, LIU Y, et al. High ionic conductivity of composite solid polymer electrolyte via in situ synthesis of monodispersed SiO2 nanospheres in poly(ethylene oxide)[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 16(1): 459-465. [99] XU Z, YANG T, CHU X, et al. Strong lewis acid-base and weak hydrogen bond synergistically enhancing ionic conductivity of poly(ethylene oxide)@SiO2 electrolytes for a high rate capability Li-metal battery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(9): 10341-10349. [100] CROCE F, APPETECCHI G, PERSI L, et al. Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries[J]. Nature, 1998, 394(6692): 456-458. doi: 10.1038/28818 [101] KHAN K, HANIF M B, XIN H, et al. PEO-based solid composite polymer electrolyte for high capacity retention all-solid-state lithium metal battery[J]. Small, 2024, 20(4): 2305772. doi: 10.1002/smll.202305772 [102] ZHUANG H, MA W, XIE J, et al. Solvent-free synthesis of PEO/garnet composite electrolyte for high-safety all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 860: 157915. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157915 [103] ZHANG J, ZHAO N, ZHANG M, et al. Flexible and ion-conducting membrane electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Dispersion of garnet nanoparticles in insulating polyethylene oxide[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 28: 447-454. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.09.002 [104] CHEN F, YANG D, ZHA W, et al. Solid polymer electrolytes incorporating cubic Li7La3Zr2O12 for all-solid-state lithium rechargeable batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 258: 1106-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.164 [105] WAN Z, LEI D, YANG W, et al. Low resistance-integrated all-solid-state battery achieved by Li7La3Zr2O12 nanowire upgrading polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite electrolyte and PEO cathode binder[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(1): 1805301. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201805301 [106] MA F, LIU Y, DU X, et al. Hybrid solid electrolyte with the combination of LATP ceramic and PEO polymer by a solvent-free procedure[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2024, 405: 116450. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2023.116450 [107] LIU L, CHU L, JIANG B, et al. Li1.4Al0.4Ti1.6(PO4)3 nanoparticle-reinforced solid polymer electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2019, 331: 89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2019.01.007 [108] ZHAO Y, HUANG Z, CHEN S, et al. A promising PEO/LAGP hybrid electrolyte prepared by a simple method for all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2016, 295: 65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2016.07.013 [109] PIANA G, BELLA F, GEOBALDO F, et al. PEO/LAGP hybrid solid polymer electrolytes for ambient temperature lithium batteries by solvent-free, “one pot” preparation[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2019, 26: 100947. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2019.100947 [110] LIU C, WANG J, KOU W, et al. A flexible, ion-conducting solid electrolyte with vertically bicontinuous transfer channels toward high performance all-solid-state lithium batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: 126517. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126517 [111] ZHU P, YAN C, ZHU J, et al. Flexible electrolyte-cathode bilayer framework with stabilized interface for room-temperature all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 17: 220-225. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2018.11.009 [112] WANG X, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Lithium-salt-rich PEO/Li0.3La0.557TiO3 interpenetrating composite electrolyte with three-dimensional ceramic nano-backbone for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(29): 24791-24798. -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 563
- HTML全文浏览量: 152
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载:






