Inner stress field in epoxy resin with moisture absorption
-
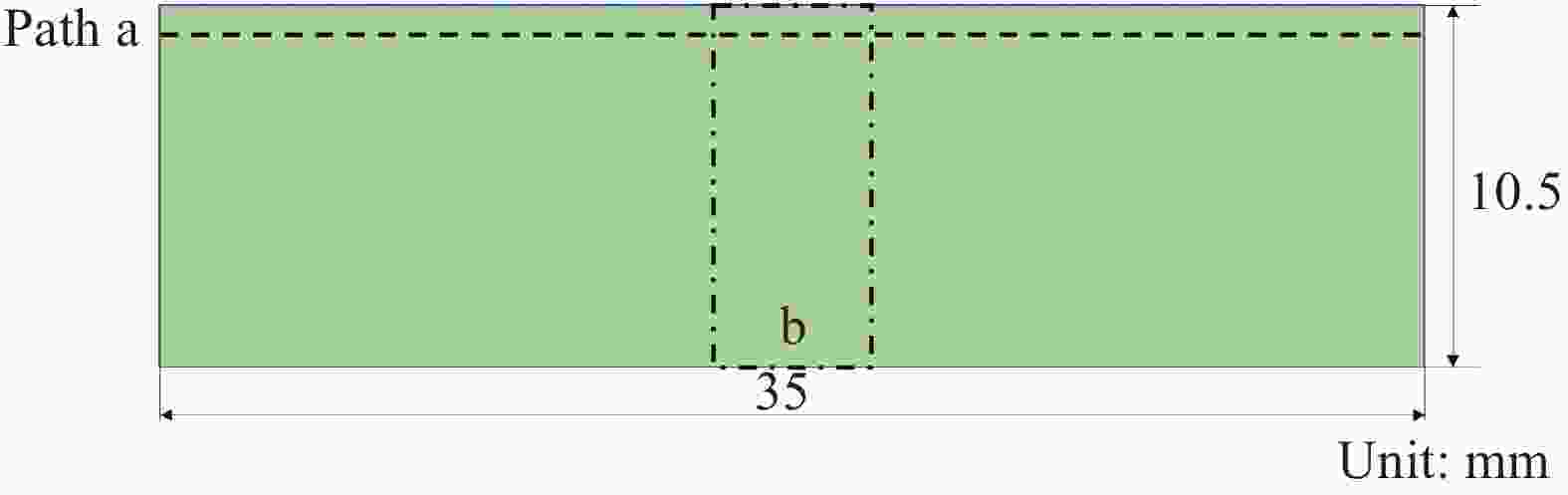
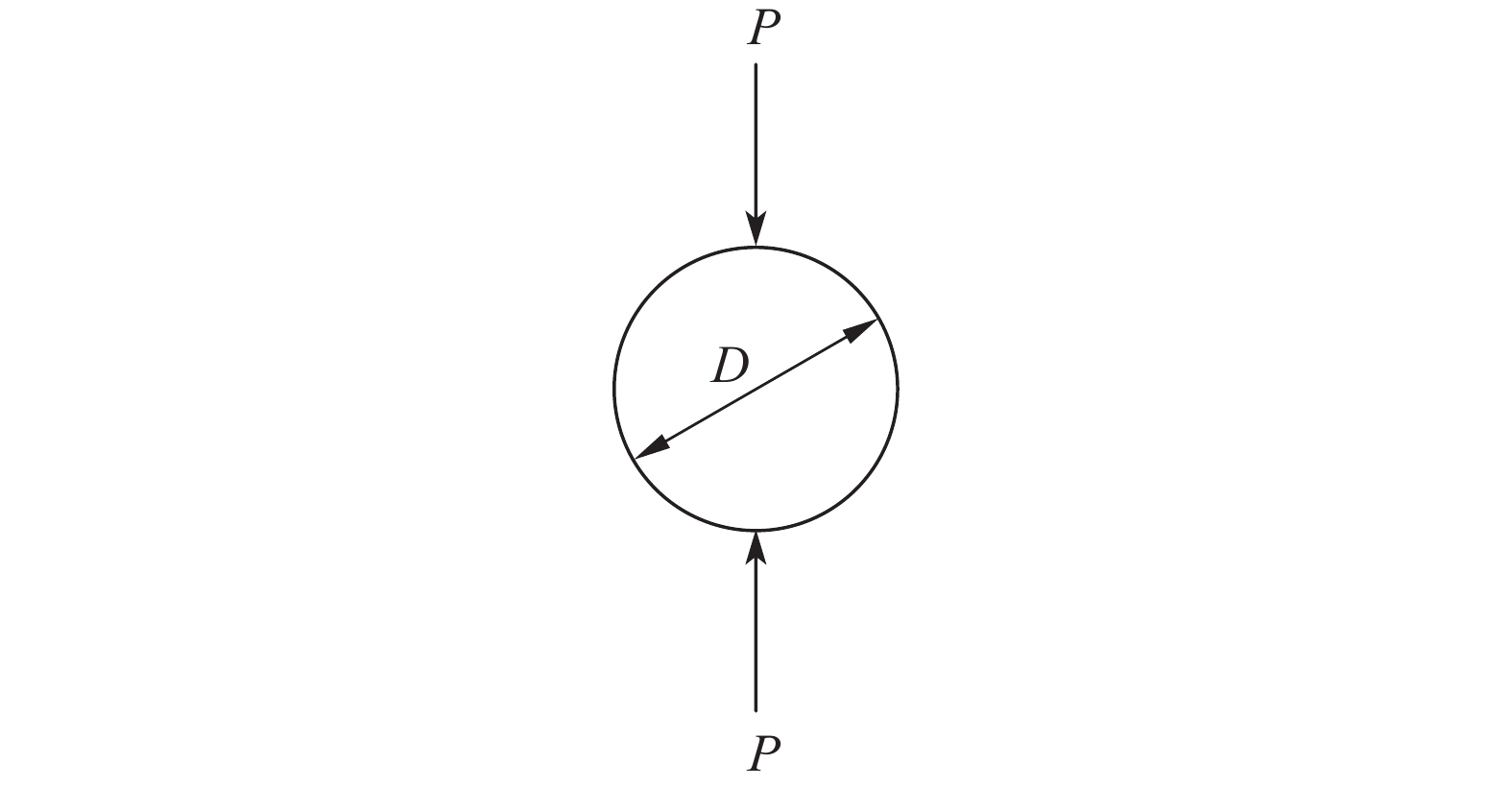
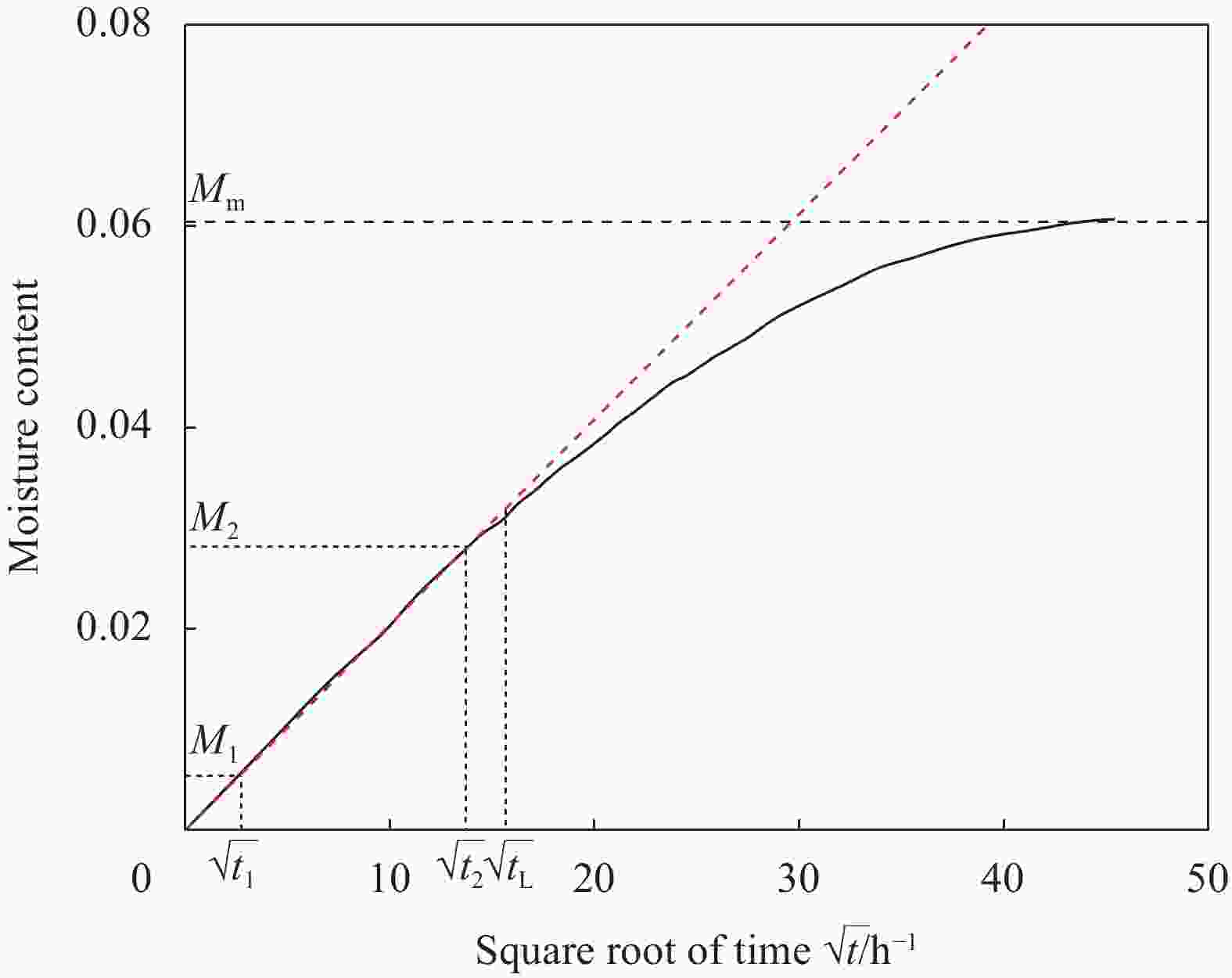
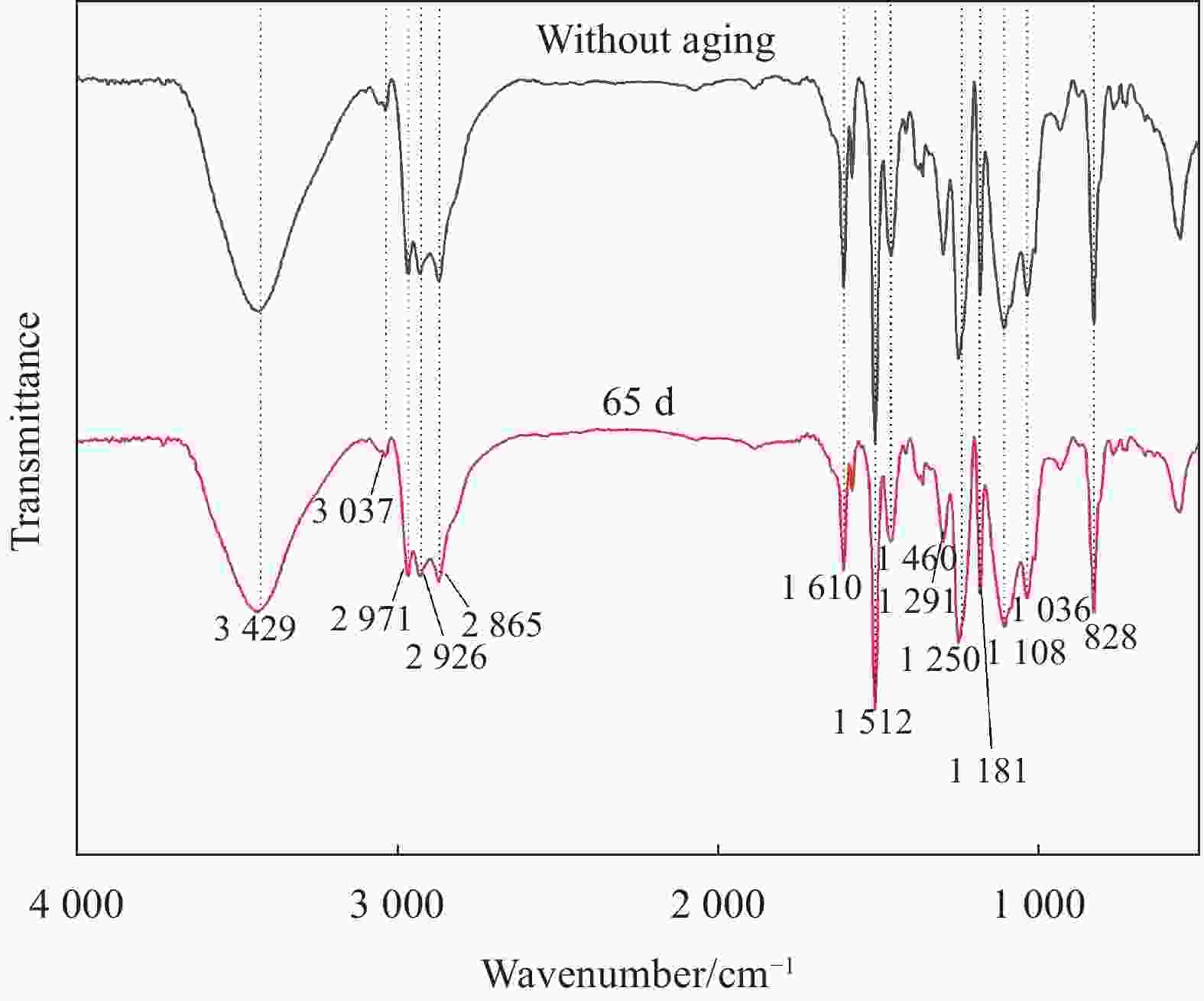
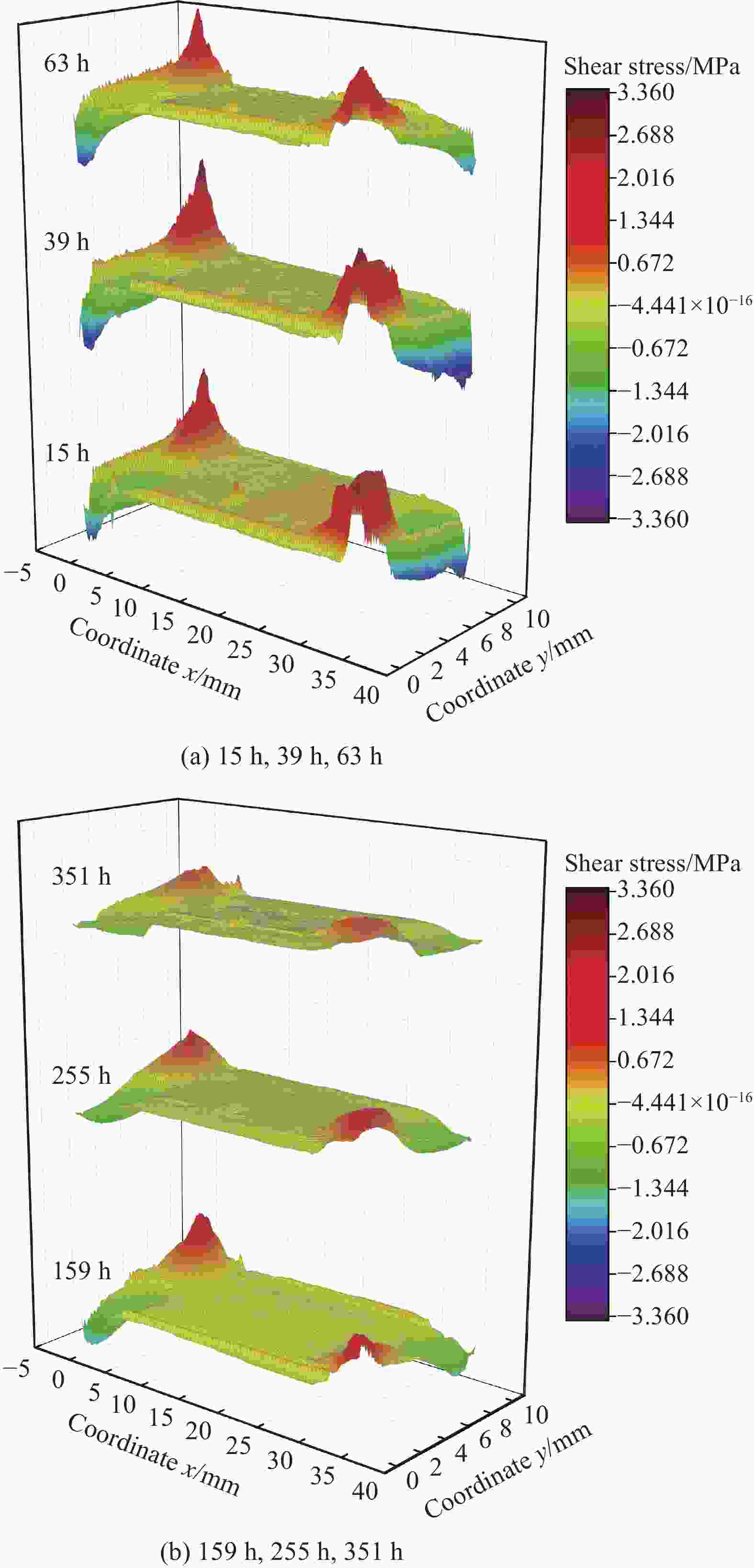
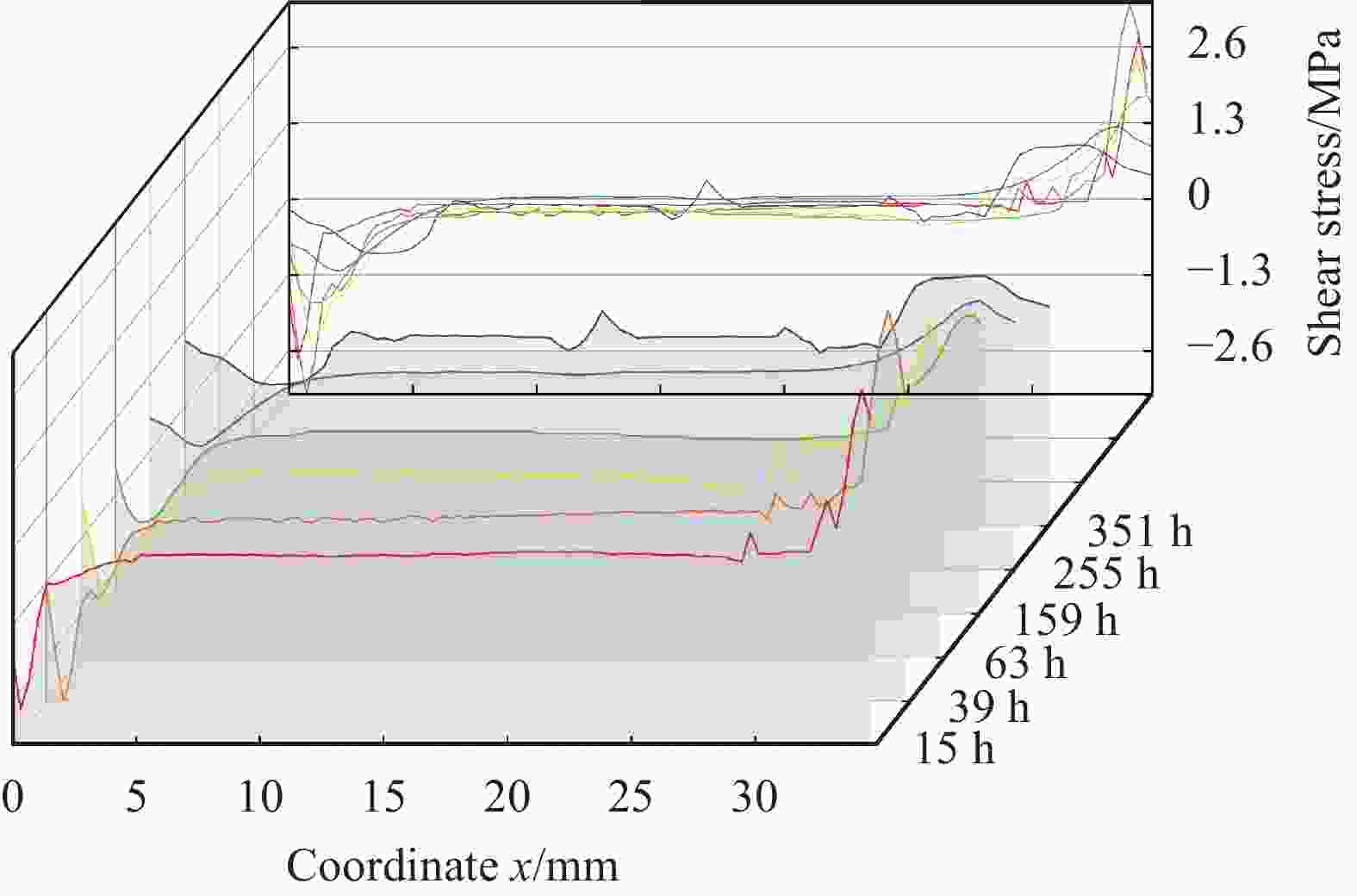
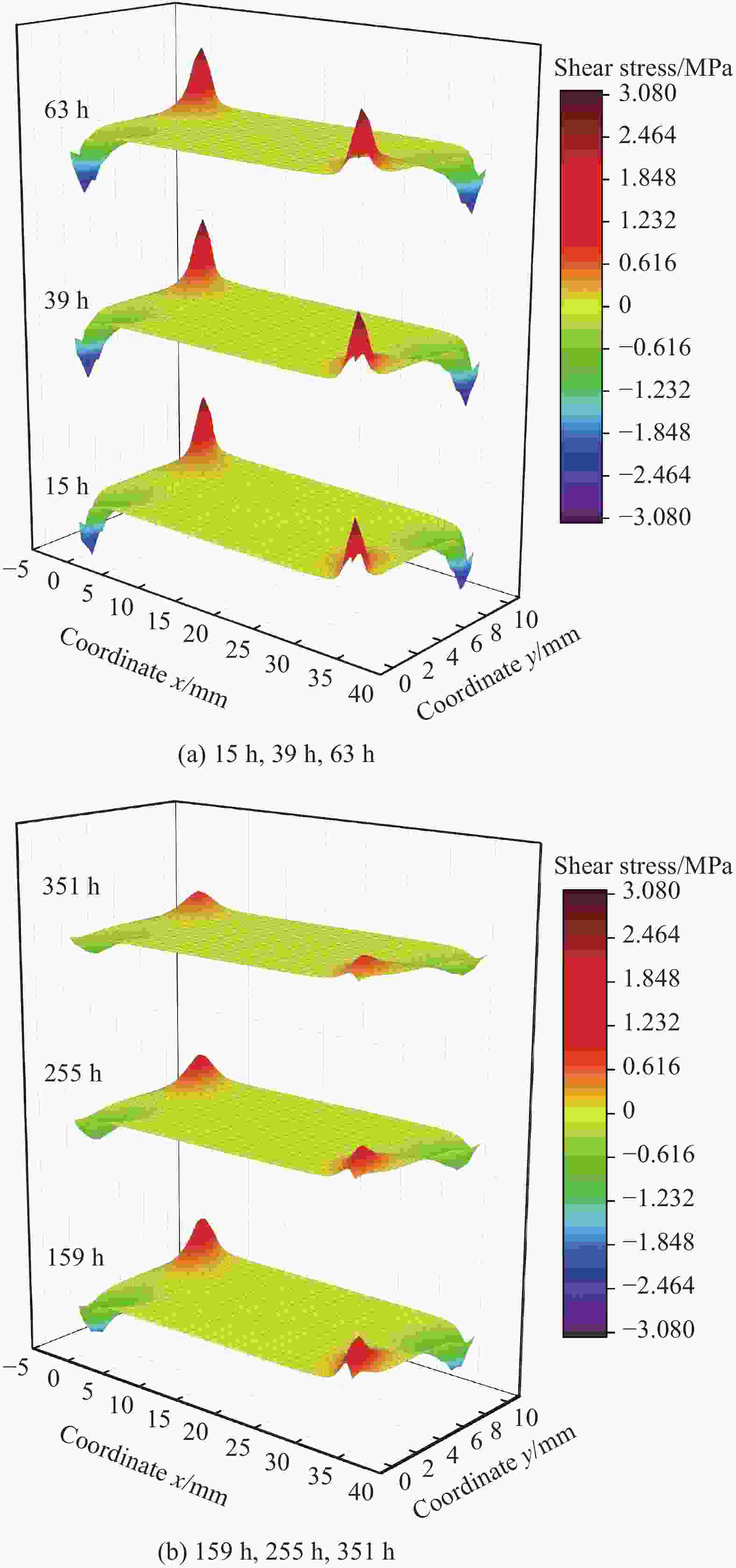
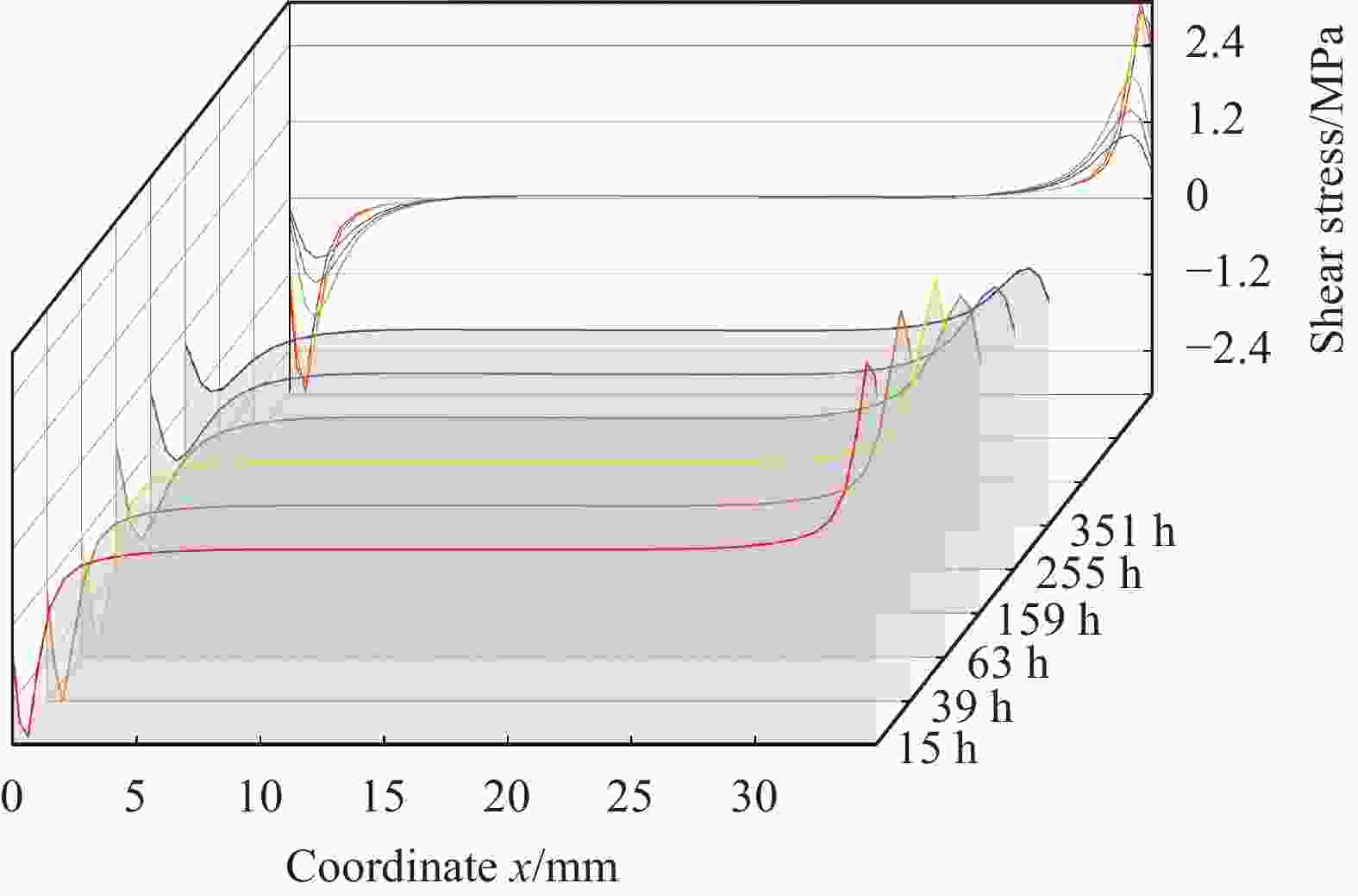
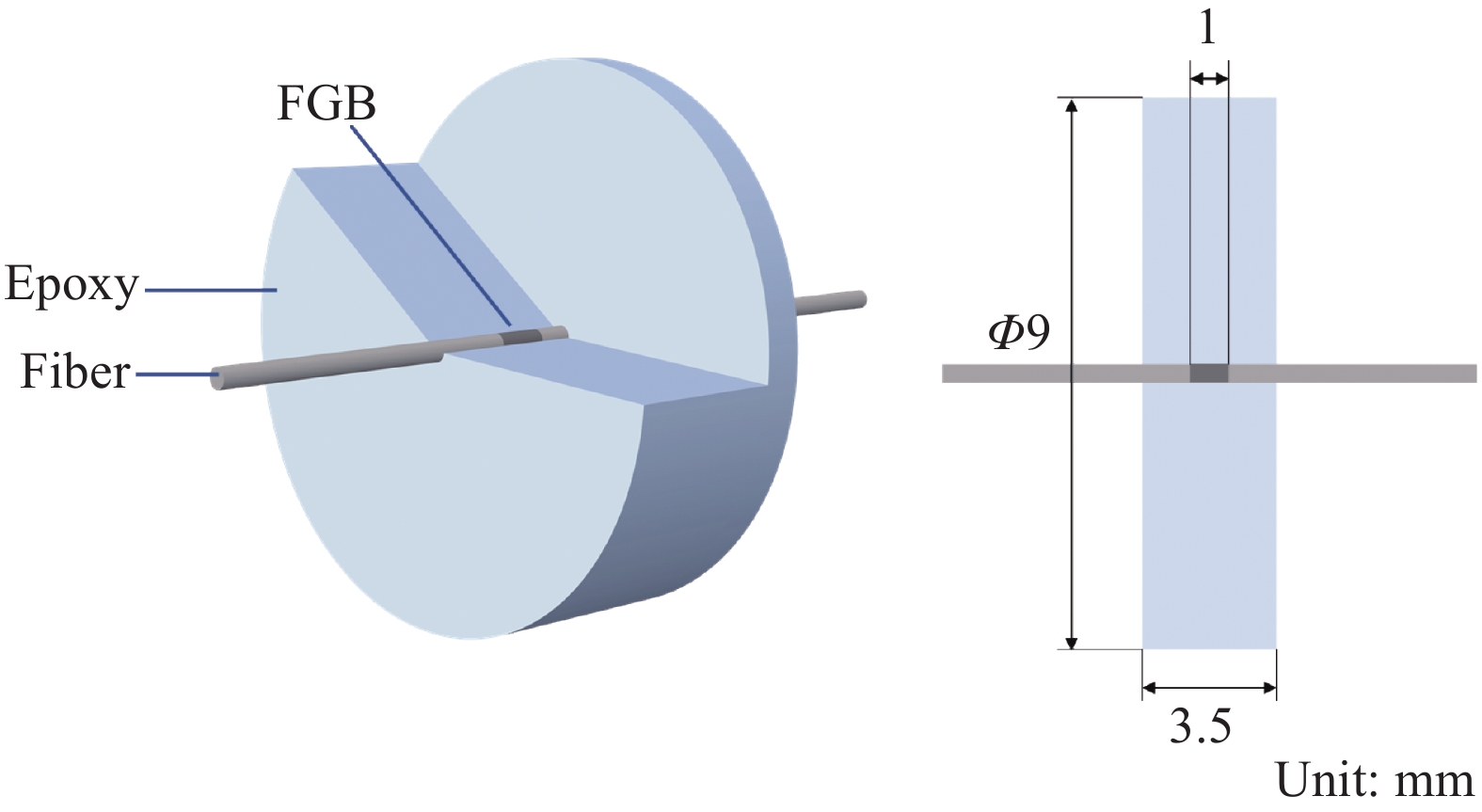
摘要: 环氧树脂及其制品因其优良性能广泛应用在船舶制造中,长期在潮湿环境中服役时,基体吸收水分易引起膨胀翘曲等变形,进而引发失效隐患。本文采用重量分析试验、光纤布拉格光栅(FBG)传感器应变监测技术,确定了环氧树脂中的饱和吸湿量、水分扩散系数和湿膨胀系数等吸湿系数,在此基础上构建了能够预测环氧树脂中随时间变化的水分扩散及应力场分布的湿-力模型,用有限元方法实现了对随吸湿时间变化的树脂中应力场的数值模拟。并结合相移数字光弹试验方法,将数值模拟结果与试验结果进行了比较,显示了良好的一致性,发现环氧树脂吸湿过程中切应力随时间呈现出先升后降的趋势。Abstract: Epoxy and epoxy-based components have been extensively used in marine industry due to their excellent performance. When exposed to moist environment, the matrix of such materials absorbs significant amount of water and damages are caused including warpage, expansion and other deformations. In this study, weight analysis experiment were carried out and fibre Bragg grating (FBG) sensors were used to monitor the effects of moisture absorption. The maximum water absorption, water diffusion coefficient, and coefficients of moisture expansion were determined thereafter. Numerical simulation was then built accordingly by finite element method to predict the evolution of moisture absorption and the stress field developed in the epoxy resin. Finally, the simulation results were compared with the experimental ones by phase-shift digital photoelastic method and good agreement is achieved. The shearing stresses in the resin show the trend of initial increase and later decline during the course of water absorption.
-
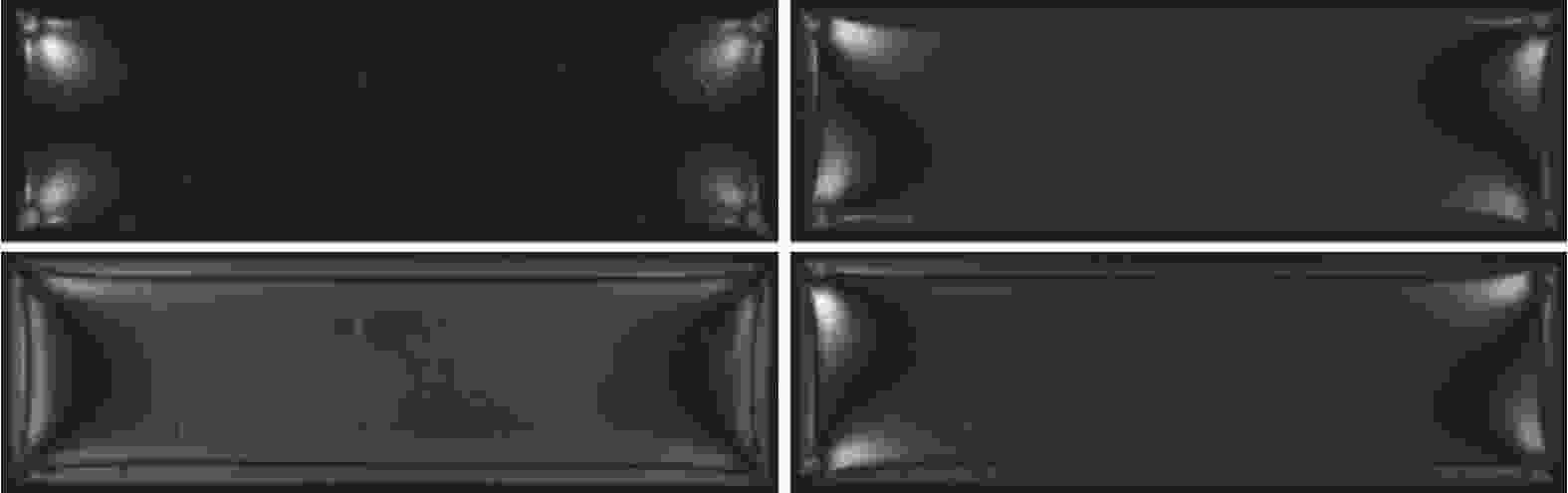
图 4 平面偏振光场元件及布置
Figure 4. Planar polarized light field set-up
$\alpha $—Angle between the transmission axis of the polarizer and the horizontal reference axis; $\beta $—Angle between the transmission axis of the analyser and the horizontal reference axis; P—Polarization direction of polarizer; A—Polarization direction of analyzer; ${\sigma _1}$,${\sigma _2}$—Principal stresses (${\sigma _1}$>${\sigma _2}$); CCD—Charge-coupled device; θ—Angle between the principal stress σ1 and the x axis direction
图 5 圆偏振光场元件及布置
Figure 5. Circularly polarized light field set-up
$\xi $—Angle between the horizontal reference axis and the fast axis of the input (P) quarterwave plate; $\eta $—Angle between the horizontal reference axis and the slow axis of the output (A) quarterwave plate; F—Fast axis of the output or the input quarter-wave plate; S—Slow axis of the output or the input quarter-wave plate
表 1 左右六步相移法的偏振光场设置与光强等式
Table 1. Polarized light field set-up and light intensities equations of six phase steps method
Α/(°) ξ/(°) η/(°) β/(°) Light intensities 90 135 45 90 I1 90 135 45 0 I2 90 135 0 0 I3 90 135 45 45 I4 90 45 0 0 I5 90 45 135 45 I6 表 2 四步相移法的偏振光场设置与光强等式
Table 2. Polarized light field set-up and light intensities equations of four phase steps method
α/(°) β/(°) Light intensities equation 90 0 I7 112.5 22.5 I8 135 45 I9 157.5 67.5 I10 -
[1] KARAD S K, JONES F R, ATTWOOD D. Moisture absorption by cyanate ester modified epoxy resin matrices. Part II. The reverse thermal effect[J]. Polymer,2002,43(21):5643-5649. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00484-6 [2] BAO L R, YEE A F. Moisture diffusion and hygrothermal aging in bismaleimide matrix carbon fiber composites: Part II - Woven and hybrid composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2002,62(16):2111-2119. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00162-8 [3] BAO L R, YEE A F. Effect of temperature on moisture absorption in a bismaleimide resin and its carbon fiber composites[J]. Polymer,2002,43(14):3987-3997. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00189-1 [4] PARK H, YANG S, HAN J, et al. Prediction of quasistatic constitutive equations of moisture-absorbed epoxy polymers using atomistic simulations[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2020, 41:100983. [5] JAIN D, MUKHERJEE A, KWATRA N. Effect of fibre topology on hygro-mechanical response of polymer matrix composites[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2015,86:787-795. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.03.054 [6] 李能. Non-Fickian溶剂扩散与凝胶溶胀变形的耦合行为研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2021.LI Neng. Non-Fickian solvent diffusion coupled with deformation of swelling gels[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [7] SHREEPANNAGA D, VIJAYA KINI M, PAI D. The ageing effect on static and dynamic mechanical properties of fibre reinforced polymer composites under marine environment-A review[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2022,52:689-696. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.10.084 [8] SUN T S, YU C G, YANG W C, et al. Experimental and numerical research on the nonlinear creep response of polymeric composites under humid environments[J]. Composite Structures,2020,251:112673. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112673 [9] GU J P, ZHAO S L, ZHANG X P, et al. A hygro-thermo-mechanical constitutive model for hygrothermally activated shape memory polymers under finite deformations[J]. Mechanics of Materials,2020,150:103594. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2020.103594 [10] KARALEKAS D, CUGNONI J, BOTSIS J. Monitoring of process induced strains in a single fibre composite using FBG sensor: A methodological study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2008,39(7):1118-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.04.010 [11] DAVIES P, RAJAPAKSE Y D. Durability of composites in a marine environment[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2014: 70-72. [12] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for water absorption of plastics[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials, 2008. [13] 孙亮亮. 碳纤维复合材料固化残余应力及变形研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.SUN Liangliang. Research on process-induced residual stress and deformation of CFRP[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [14] GENG X Y, JIANG M S, GAO L L, et al. Sensing characteristics of FBG sensor embedded in CFRP laminate[J]. Measurement,2017,98:199-204. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2016.12.003 [15] 孙亮亮. 复合材料基体裂纹预测分析与光纤光栅检测研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019.SUN Liangliang. Prediction and fiber bragg grating detection research on matrix cracks of composite materials[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [16] ANTONUCCI V, GIORDANO M, CUSANO A, et al. Real time monitoring of cure and gelification of a thermoset matrix[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2006,66(16):3273-3280. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.07.009 [17] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials, 2014. [18] HECKER F, MORCHE B. Computer-aided measurement of relative retardations in plane photoelasticity[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1986: 535-542. [19] 天津大学材料力学教研室光弹组. 光弹性原理及测试技术[M].北京: 科学出版社, 1980: 94.Photoelastic Group, Department of Material Mechanics, Tianjin University. Photoelastic principle and testing technology [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980: 94(in Chinese). [20] TOSCANO A, PITARRESI G, SCAFIDI M, et al. Water diffusion and swelling stresses in highly crosslinked epoxy matrices[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2016,133:255-263. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.09.004 [21] DUNDOVIĆ M, MARKOVIĆ K, FRANULOVIĆ M, et al. Digital light processing in photoelastic models production for material behavior modeling[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity,2021,31:111-115. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2021.03.018 [22] AJOVALASIT A, BARONE S, PETRUCCI G. A method for reducing the influence of quarter-wave plate errors in phase stepping photoelasticity[J]. The Journal of Strain Analysis for Engineering Design,1998,33(3):207-216. doi: 10.1243/0309324981512922 [23] 雷振坤. 结构分析数字光测力学 [M]. 大连: 大连理工大学出版社, 2012: 118-122.LEI Zhenkun. Digital photomechanics for structural analysis[M]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 2012: 118-122(in Chinese). [24] 黄兴, 冯捷敏, 吴凤琳, 等. 引入新型光弹性实验设备的实验教学实践与探索[J]. 中国现代教育装备, 2022(7):27-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1438.2022.7.zgxdjyzb202207010HUANG Xing, FENG Jiemin, WU Fenglin, et al. Experiment teaching practice and exploration with new photoelastic experimental equipment[J]. China Modern Education Equipment,2022(7):27-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1438.2022.7.zgxdjyzb202207010 [25] 戴福隆, 沈观林, 谢惠民. 实验力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2010: 312-315.DAI Fulong, SHEN Guanlin, XIE Huimin. Experimental mechanics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2010: 312-315(in Chinese). [26] VOLOSHIN A S, BURGER C P. Half-fringe photoelasticity: A new approach to whole-field stress analysis[J]. Experimental Mechanics,1983,23(3):304-313. doi: 10.1007/BF02319257 [27] SHEN C H, SPRINGER G S. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1976,10(1):2-20. doi: 10.1177/002199837601000101 [28] DANIEL I M, ISHAI O, DANIEL I M, et al. Engineering mechanics of composite materials[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 2006: 208-211. [29] PITARRESI G, SCAFIDI M, ALESSI S, et al. Absorption kinetics and swelling stresses in hydrothermally aged epoxies investigated by photoelastic image analysis[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2015,111:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.10.019 -






 下载:
下载: