Effects of aging precipitation and microstructure evolution on mechanical properties of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites
-
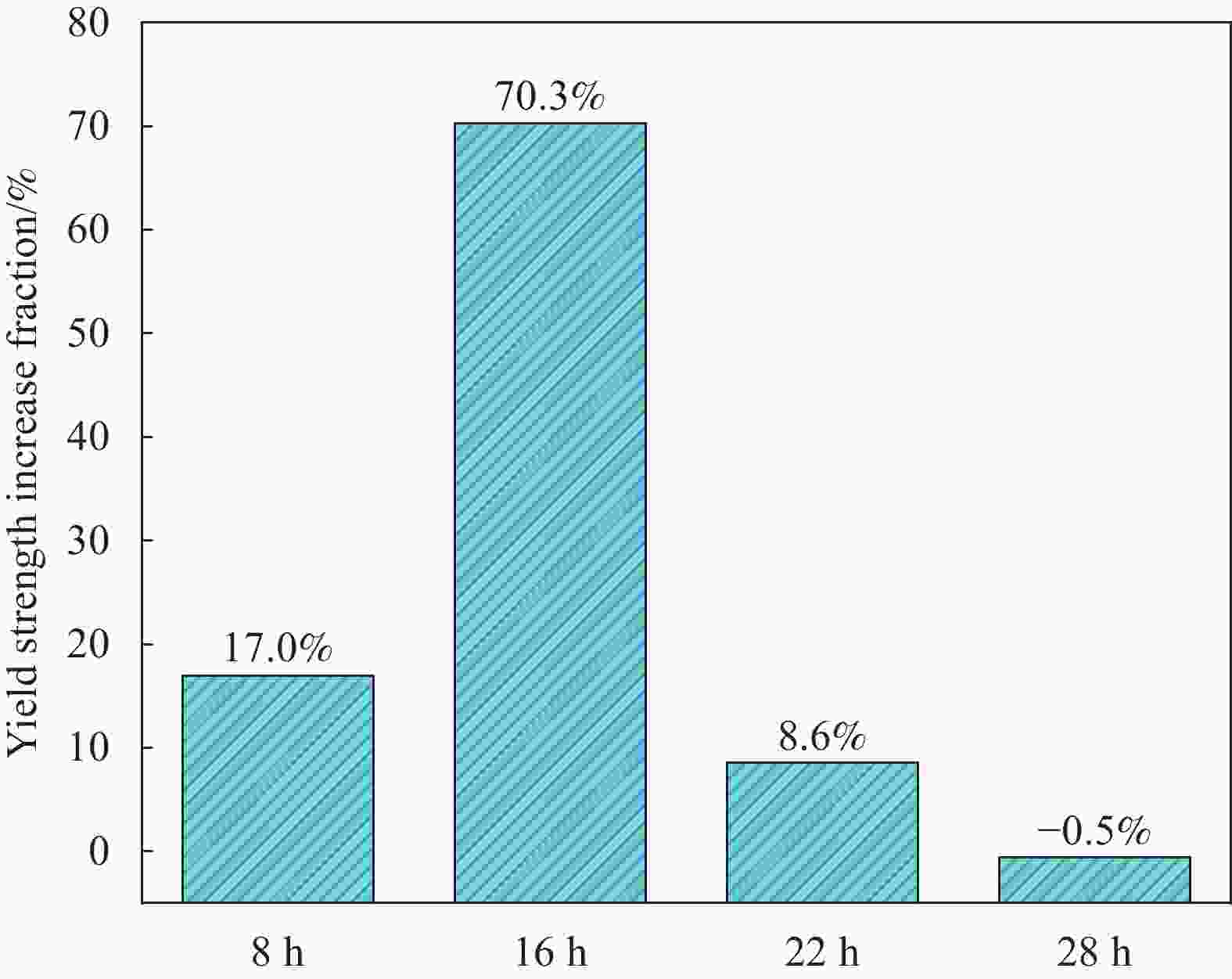
摘要: 研究了TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料T6工艺的微观组织演变和时效析出对力学性能的影响。通过气氛保护熔炼法制备了TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料。结果表明:在铸态合金的微观组织中,TiB2颗粒和共晶相主要分布在晶界周围。均匀化处理后,大部分共晶相回溶。轧制变形后,TiB2颗粒沿着轧制方向被拉长,产生了大量位错。固溶处理削弱了轧制产生的Brass织构和S织构,回溶了轧制产生的析出相。在175℃温度下进行时效,欠时效过程中,δ'(Al3Li)/β'(Al3Zr)为主要析出相。随着时效时间的增加,到22 h峰时效时,T1相为主要析出强化相。通过位错强化和析出强化的共同作用,随时效时间增加,屈服强度和抗拉强度先上升后下降,延伸率持续下降。复合材料峰时效的极限抗拉强度为562.7 MPa,屈服强度为475.9 MPa,延伸率为4.5%。
-
关键词:
- Al-Cu-Li合金 /
- TiB2 /
- 时效析出 /
- 轧制 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: The effects of microstructure evolution and aging precipitation during T6 process on the mechanical properties of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites were investigated. The TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites were prepared by protective atmosphere melting. The results show that within the microstructure of as-cast alloys, TiB2 particles and eutectic phases are mainly distributed around the grain boundaries. After homogenization treatment, the eutectic phase is mostly dissolved. After rolling deformation, TiB2 particles are elongated along the rolling direction and a large number of dislocations are generated. The solid solution treatment weakens the Brass texture and S texture generated by the rolling and the precipitated phases generated by the rolling are resolved. Aging is performed at 175℃, δ'(Al3Li)/β'(Al3Zr) is the main precipitated phase during under-aging. With the increase of aging time, the T1 phase is the main precipitation strengthening phase at 22 h peak aging. Through the combined effect of dislocation strengthening and precipitation strengthening, the yield strength and ultimate tensile strength increase and then decrease with increasing aging time, and the elongation continuously decreasing. The ultimate tensile strength, yield strength and elongation after peak aging reach 562.7 MPa, 475.9 MPa, and 4.5%, respectively.-
Key words:
- Al-Cu-Li alloy /
- TiB2 /
- aging precipitation /
- rolling /
- mechanical properties
-
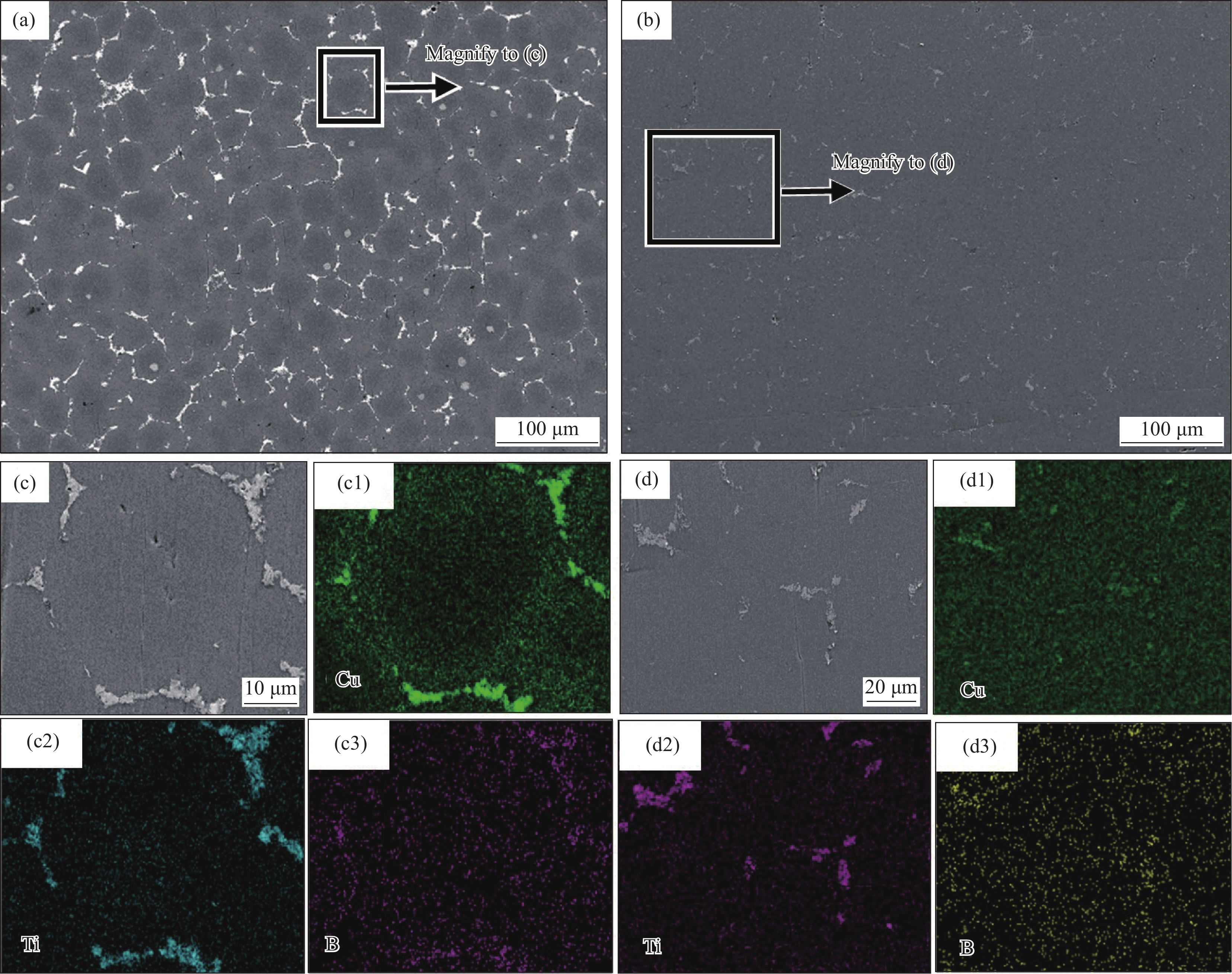
图 1 TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料微观组织及相分布:(a) 铸态组织背散射电子(BSE)图像;(b) 均匀态组织SEM图像;((c), (d)) 图1(a)和图1(b)中高倍BSE微观组织和相应的EDS元素分析
Figure 1. Microstructure and phase distribution of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites: (a) Backscattered electron (BSE) image of as-cast structure; (b) SEM image of homogeneous structure; ((c), (d)) High magnification BSE microstructure and corresponding EDS elements analysis in Fig.1(a) and Fig.1(b)
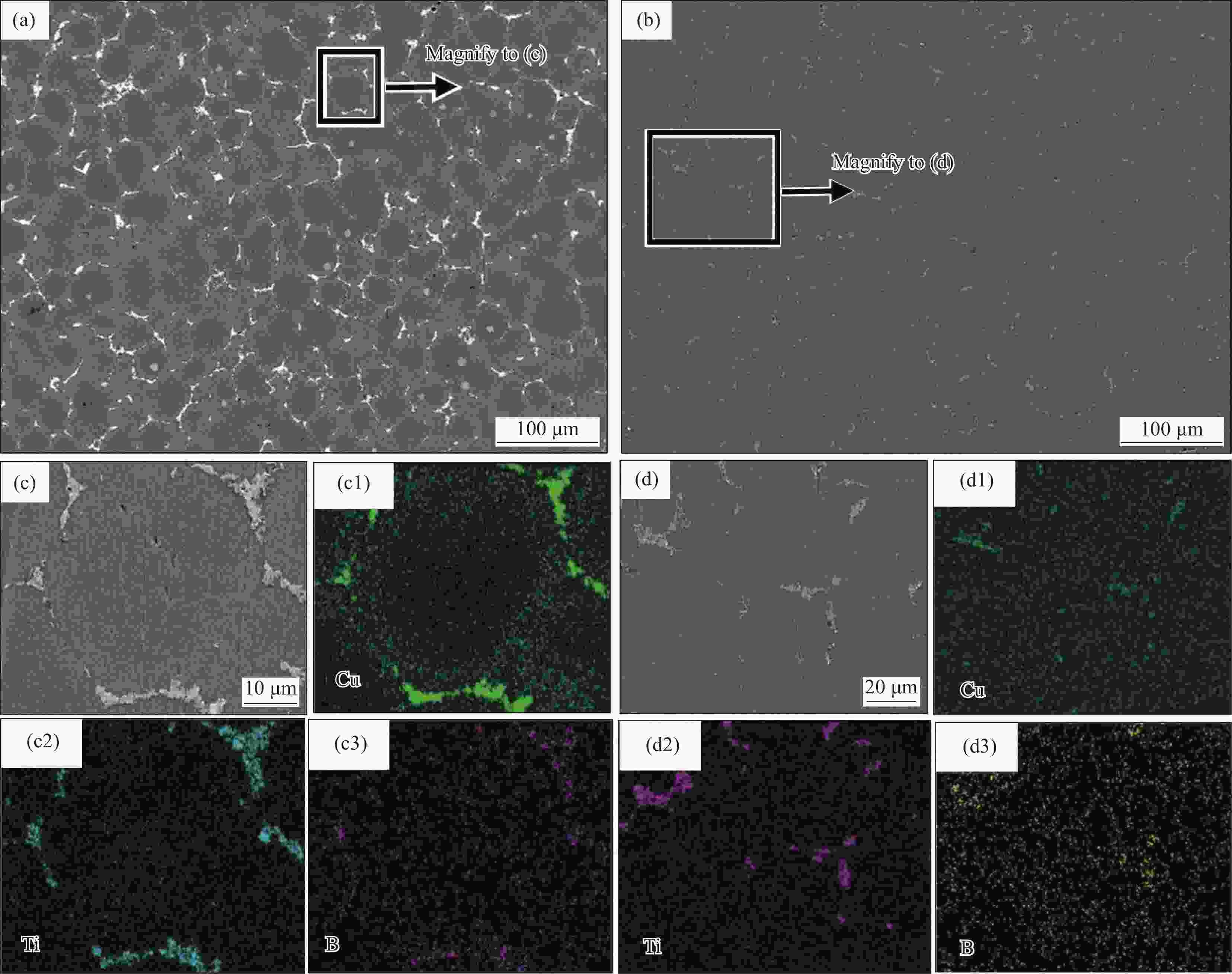
图 2 TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料微观组织及相分布:(a) 热轧态组织BSE图像;(b) 固溶态组织BSE图像;((c), (d)) 图2(a)和图2(b)中高倍BSE微观组织和EDS元素分析
Figure 2. Microstructure and phase distribution of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites: (a) BSE image of hot-rolled state; (b) BSE image of solid solution state; ((c), (d)) High magnification BSE microstructure and EDS elements analysis in Fig.2(a) and Fig.2(b)
ND—Normal direction; RD—Rolling direction
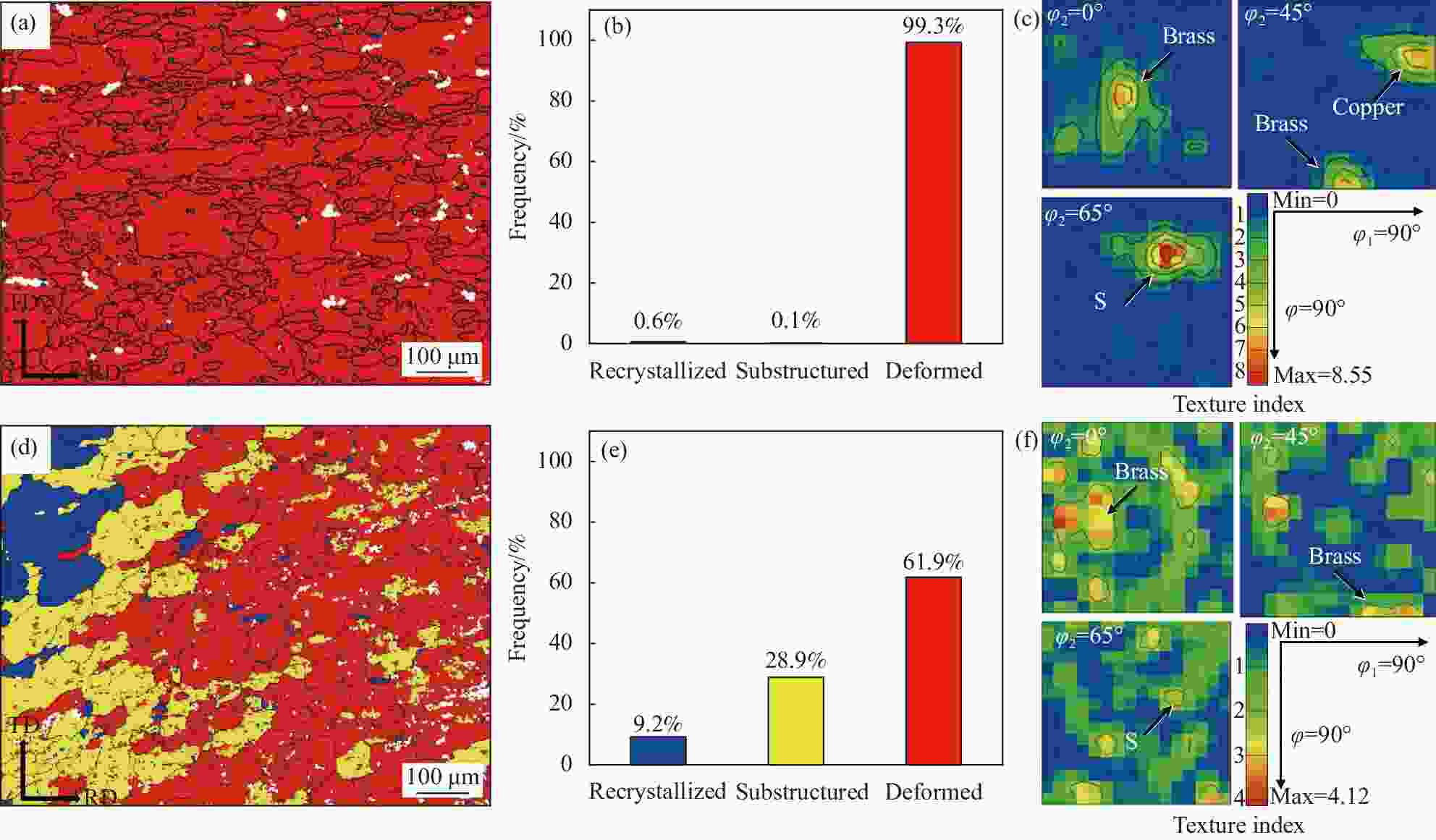
图 3 TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料电子背向散射衍射(EBSD)晶粒取向分布反极图(IPF)和晶粒尺寸统计:((a), (c)) 热轧态;((b), (d)) 固溶态
Figure 3. Electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) grain orientation distribution inverse pole figure (IPF) and grain size statistics of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites: ((a), (c)) Hot rolled state; ((b), (d)) Solid solution state
d—Diameter
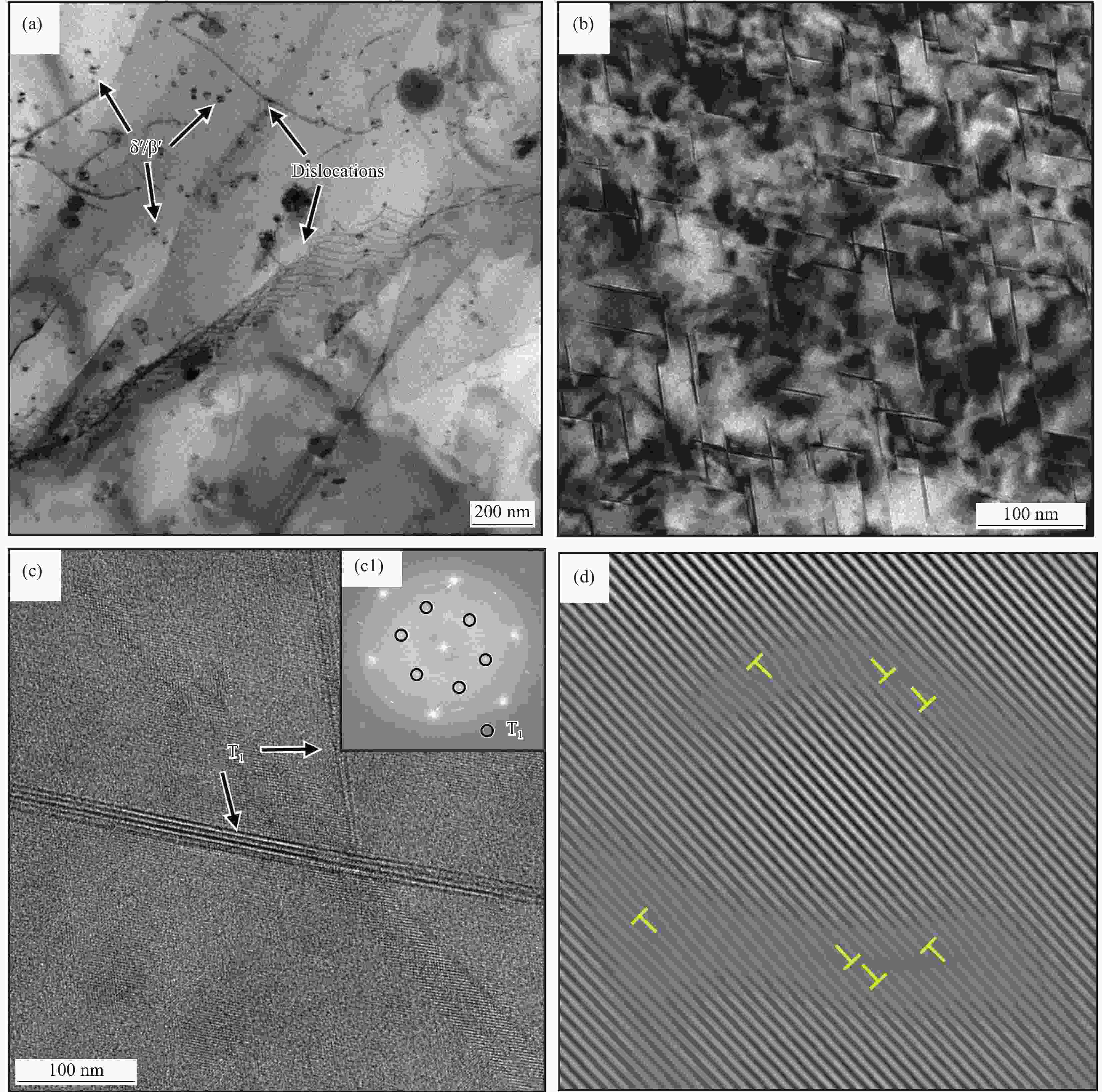
图 6 TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料TEM图像:(a) 8 h欠时效;(b) 22 h峰时效;(c) 峰时效T1相的HRTEM图像(图6(c1)为图6(c)的快速傅里叶变化(FFT)图像);(d) 图6(c)中T1相附近的位错的反傅里叶变化
Figure 6. TEM images of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites: (a) Under-ageing at 8 h; (b) Peak-ageing at 22 h; (c) HRTEM image of the peak-aged T1 phase (Fig.6(c1) is fast Fourier transform (FFT) image of Fig.6(c)); (d) Inverse Fourier filtered of the dislocations near the T1 phase in Fig.6(c)
表 1 TiB2/Al-Cu-Li复合材料的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composites
Element Content/wt% Li 1.32 Cu 4.43 Mg 0.39 Mn 0.23 Ag 0.39 Zn 0.27 Ti 1.35 B 0.57 Zr 0.02 Al Bal -
[1] ZHANG X S, CHEN Y J, HU J L. Recent advances in the development of aerospace materials[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,2018,97:22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2018.01.001 [2] 杨守杰, 陆政, 苏彬, 等. 铝锂合金研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2001, 29(5):44-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2001.05.012YANG Shoujie, LU Zheng, SU Bin, et al. Development of aluminum-lithium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Engi-neering,2001,29(5):44-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2001.05.012 [3] ABD EL-ATY A, XU Y, GUO X Z, et al. Strengthening mechanisms, deformation behavior, and anisotropic mechanical properties of Al-Li alloys: A review[J]. Journal of Advanced Research,2018,10:49-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2017.12.004 [4] NEIBECKER P, LEITNER M, KUSHAIM M, et al. L12 ordering and δ′ precipitation in Al-Cu-Li[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):3254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03203-z [5] ARAULLO-PETERS V, GAULT B, DE GEUSER F, et al. Microstructural evolution during ageing of Al-Cu-Li-x alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2014,66:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.12.001 [6] TSIVOULAS D, ROBSON J D. Heterogeneous Zr solute segregation and Al3Zr dispersoid distributions in Al-Cu-Li alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2015,93:73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.03.057 [7] DWYER C, WEYLAND M, CHANG L Y, et al. Combined electron beam imaging and ab initio modeling of T1 precipitates in Al-Li-Cu alloys[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2011,98(20):201909. doi: 10.1063/1.3590171 [8] HIROSAWA S, SATO T, KAMIO A. Effects of Mg addition on the kinetics of low-temperature precipitation in Al-Li-Cu-Ag-Zr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,1998,242(1):195-201. [9] CHEN X X, MA X W, XI H K, et al. Effects of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of extruded 2196 Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Materials & Design,2020,192:108746. [10] KIM N J, LEE E W. Effect of T1 precipitate on the anisotropy of Al-Li alloy 2090[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia,1993,41(3):941-948. doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(93)90028-Q [11] YE F, YU Y X, ZHANG B S, et al. Influence of pre-stretching at ambient and cryogenic temperatures on dislocation configuration, precipitation behaviour, and mechanical properties of 2195 Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2023,22:2983-2995. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.12.126 [12] APPS P J, BERTA M, PRANGNELL P B. The effect of dispersoids on the grain refinement mechanisms during deformation of aluminium alloys to ultra-high strains[J]. Acta Materialia,2005,53(2):499-511. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.09.042 [13] 马宗义, 毕敬, 吕毓雄, 等. SiCp/Al-Li复合材料的微观结构性能及断裂特征[J]. 复合材料学报, 1994, 11(1):43-47.MA Zongyi, BI Jing, LYU Yuxiong, et al. Microstructural properties and fracture characteristics of SiCp/Al-Li composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,1994,11(1):43-47(in Chinese). [14] LI J Y, LYU S L, WU S S, et al. Effects of nanoparticles on the solution treatment and mechanical properties of nano-SiCp/Al-Cu composites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2021,296:117195. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117195 [15] 赵敏, 姜龙涛, 武高辉. 挤压铸造TiB2P/Al复合材料室温力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(5):1-5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.05.001ZHAO Min, JIANG Longtao, WU Gaohui. Ambient mechanical properties of TiB2P/Al composites by squeeze casting[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(5):1-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.05.001 [16] SHEN Y W, LI X F, HONG T R, et al. Effects of TiB2 particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of an in-situ TiB2-Al-Cu-Li matrix composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2016,655:265-268. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.12.104 [17] WU L, ZHOU C, LI X F, et al. Effects of TiB2 particles on artificial aging response of high-Li-content TiB2/Al-Li-Cu composite[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,749:189-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.299 [18] WU L, LI X F, HAN G Y, et al. Precipitation behavior of the high-Li-content in-situ TiB2/Al-Li-Cu composite[J]. Materials Characterization,2017,132:215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.08.015 [19] ZHAO B W, YANG Q, WU L, et al. Effects of nanosized particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of an aged in-situ TiB2/Al-Cu-Li composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2019,742:573-583. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.032 [20] ZHAO K, LIU M M, KANG H J, et al. Formation mechanism of TiB2 nanoparticles and development of TiB2P/6201 nanocomposites as a neoteric conducting material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,916:165461. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165461 [21] DUAN S W, LIU Z L, GUO F Q, et al. Precipitates evolution during artificial aging and their influence on mechanical properties of a cast Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2023,22:2502-2517. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.12.123 [22] CHEN A T, PENG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of cast Al-3Li-1.5Cu-0.2Zr alloy during heat treatment[J]. Materials Characterization,2016,114:234-242. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2016.03.007 [23] DECREUS B, DESCHAMPS A, DE GEUSER F, et al. The influence of Cu/Li ratio on precipitation in Al-Cu-Li-x alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2013,61(6):2207-2218. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.12.041 [24] 马晓光, 李韶颖, 韩宝帅, 等. 时效前的预变形对喷射成形2195铝锂合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(1):15-26.MA Xiaoguang, LI Shaoying, HAN Baoshuai, et al. Effect of pre-stretch on microstructure and properties of 2195 Al-Li alloy prepared by spray forming[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2022,32(1):15-26(in Chinese). [25] LI L W, HAN Z H, GAO M Q, et al. Microstructures, mechanical properties, and aging behavior of hybrid-sized TiB2 particulate-reinforced 2219 aluminum matrix composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2022,829:142180. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.142180 [26] WU Y H, LIU B X, KANG H J, et al. Ultrasound-assisted dispersion of TiB2 nanoparticles in 7075 matrix hybrid composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2022,840:142958. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.142958 [27] CUI S, ZHANG C S, LIU M F, et al. Precipitation behavior of an Al-Cu-Li-X alloy and competing relationships among precipitates at different aging temperatures[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2021,814:141125. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141125 [28] ZHAO Y X, LI H, LIU Y, et al. The microstructures and mechanical properties of a highly alloyed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy: The role of Cu concentration[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2022,18:122-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.02.071 [29] LU B, LI Y, YU W, et al. Strength and ductility enhancement of twin-roll cast Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys with high solidification intervals through a synergistic segregation-controlling strategy[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2023,142:225-239. [30] DUMITRASCHKEWITZ P, TUNES M A, QUICK C R, et al. MEMS-based in situ electron-microscopy investigation of rapid solidification and heat treatment on eutectic Al-Cu[J]. Acta Materialia,2022,239:118225. [31] 林波, 王明辉, 张文馨, 等. 仿贝壳TiB2/Al-Cu层状复合材料的组织及其力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3554-3563.LIN Bo, WANG Minghui, ZHANG Wenxin, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of nacre-inspired TiB2/Al-Cu composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3554-3563(in Chinese). [32] GUO F, HUANG W J, YANG X S, et al. Variation of mechanical properties and microstructure of hot-rolled AA2099 Al-Li alloy induced by the precipitation during preheating process[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2022,110:198-209. [33] CHEN Z W, ZHAO K, FAN L. Combinative hardening effects of precipitation in a commercial aged Al-Cu-Li-X alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2013,588:59-64. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.09.016 [34] GILMORE D L, STARKE E A. Trace element effects on precipitation processes and mechanical properties in an Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,1997,28(7):1399-1415. doi: 10.1007/s11661-997-0203-6 [35] DAN C Y, CHEN Z, JI G, et al. Microstructure study of cold rolling nanosized in-situ TiB2 particle reinforced Al composites[J]. Materials & Design,2017,130:357-365. [36] YE F, MAO L, RONG J, et al. Influence of different rolling processes on microstructure and strength of the Al-Cu-Li alloy AA2195[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International,2022,32(1):87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2021.10.009 [37] TANG Y, XIAO D H, HUANG L P, et al. Dynamic microstructural evolution of Al-Cu-Li alloys during hot deformation[J]. Materials Characterization,2022,191:112135. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112135 [38] 马晓光, 杨玉艳, 罗锐, 等. 航空航天2050 Al-Cu-Li合金的热变形行为[J]. 航空材料学报, 2021, 41(5):44-50. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2021.000014MA Xiaoguang, YANG Yuyan, LUO Rui, et al. Investigation on hot deformation behavior of 2050 Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials,2021,41(5):44-50(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2021.000014 [39] DENG Y L, XU J J, CHEN J Q, et al. Effect of double-step homogenization treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Li-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2020,795:139975. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139975 [40] LIU Q B, FAN G L, TAN Z Q, et al. Precipitation of Al3Zr by two-step homogenization and its effect on the recrystallization and mechanical property in 2195 Al-Cu-Li alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2021,821:141637. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141637 [41] MAURICE C, DRIVER J H. Hot rolling textures of f.c.c. metals—Part I. Experimental results on Al single and polycrystals[J]. Acta Materialia,1997,45(11):4627-4638. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(97)00115-8 [42] ZHAO Q, LIU Z Y, ABDEL WAHAB M. Enhanced brass texture of hot-rolled Al-4Cu-1.6Mg alloy by 0.1% Zr addition[J]. Materials Characterization,2020,169:110643. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110643 [43] BOWEN A W. Texture development in high strength aluminium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology,1990,6(11):1058-1071. [44] CONTREPOIS Q, MAURICE C, DRIVER J H. Hot rolling textures of Al-Cu-Li and Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aeronautical alloys: Experiments and simulations to high strains[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2010,527(27):7305-7312. [45] JO H H, HIRANO K I. Precipitation processes in Al-Cu-Li alloy studied by DSC [J]. Materials Science Forum, 1987, 13-14: 377-382. [46] JIANG B, CAO F H, WANG H S, et al. Effect of aging time on the microstructure evolution and mechanical property in an Al-Cu-Li alloy sheet[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 740-741: 157-164. [47] DUAN S W, GUO F Q, WU D T, et al. Influences of pre-rolling deformation on aging precipitates and mechanical properties for a novel Al-Cu-Li alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2021,15:2379-2392. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.063 [48] WU H, WEN S P, HUANG H, et al. Effects of homogenization on precipitation of Al3(Er, Zr) particles and recrystallization behavior in a new type Al-Zn-Mg-Er-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2017,689:313-322. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.02.071 [49] GAO Z, CHEN J H, DUAN S Y, et al. Complex precipitation sequences of Al-Cu-Li-(Mg) alloys characterized in relation to thermal ageing processes[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters),2016,29(1):94-103. doi: 10.1007/s40195-016-0366-5 [50] MA J, LIU X C, YAN D S, et al. A novel GP-Li precursor and the correlated precipitation behaviors in Al-Cu-Li alloys with different Cu/Li ratio[J]. Acta Materialia,2023,243:118442. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2022.118442 [51] ZENG G J, LI H R, DENG S X, et al. Detailed investigation on microstructure and strengthening contribution of Al-xCu-1.3Li-X alloy sheets[J]. Materials Characterization,2023,205:113278. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2023.113278 [52] DONNADIEU P, SHAO Y, DE GEUSER F, et al. Atomic structure of T1 precipitates in Al-Li-Cu alloys revisited with HAADF-STEM imaging and small-angle X-ray scattering[J]. Acta Materialia,2011,59(2):462-472. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.09.044 [53] KUMAR K S, BROWN S A, PICKENS J R. Microstructural evolution during aging of an AlCuLiAgMgZr alloy[J]. Acta Materialia,1996,44(5):1899-1915. doi: 10.1016/1359-6454(95)00319-3 [54] GABLE B M, ZHU A W, CSONTOS A A, et al. The role of plastic deformation on the competitive microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of a novel Al-Li-Cu-X alloy[J]. Journal of Light Metals,2001,1(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/S1471-5317(00)00002-X [55] DUAN S Y, WU C L, GAO Z, et al. Interfacial structure evolution of the growing composite precipitates in Al-Cu-Li alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2017,129:352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.03.018 [56] LIN C, WU S S, LYU S L, et al. Effects of ultrasonic vibration and manganese on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with 2% Fe[J]. Intermetallics,2013,32:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2012.09.001 [57] DU R, GAO Q, WU S S, et al. Influence of TiB2 particles on aging behavior of in situ TiB2/Al-4.5Cu composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2018,721:244-250. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.02.099 -





 下载:
下载: