Cattail-derived Fe/C composites for efficient microwave absorption
-
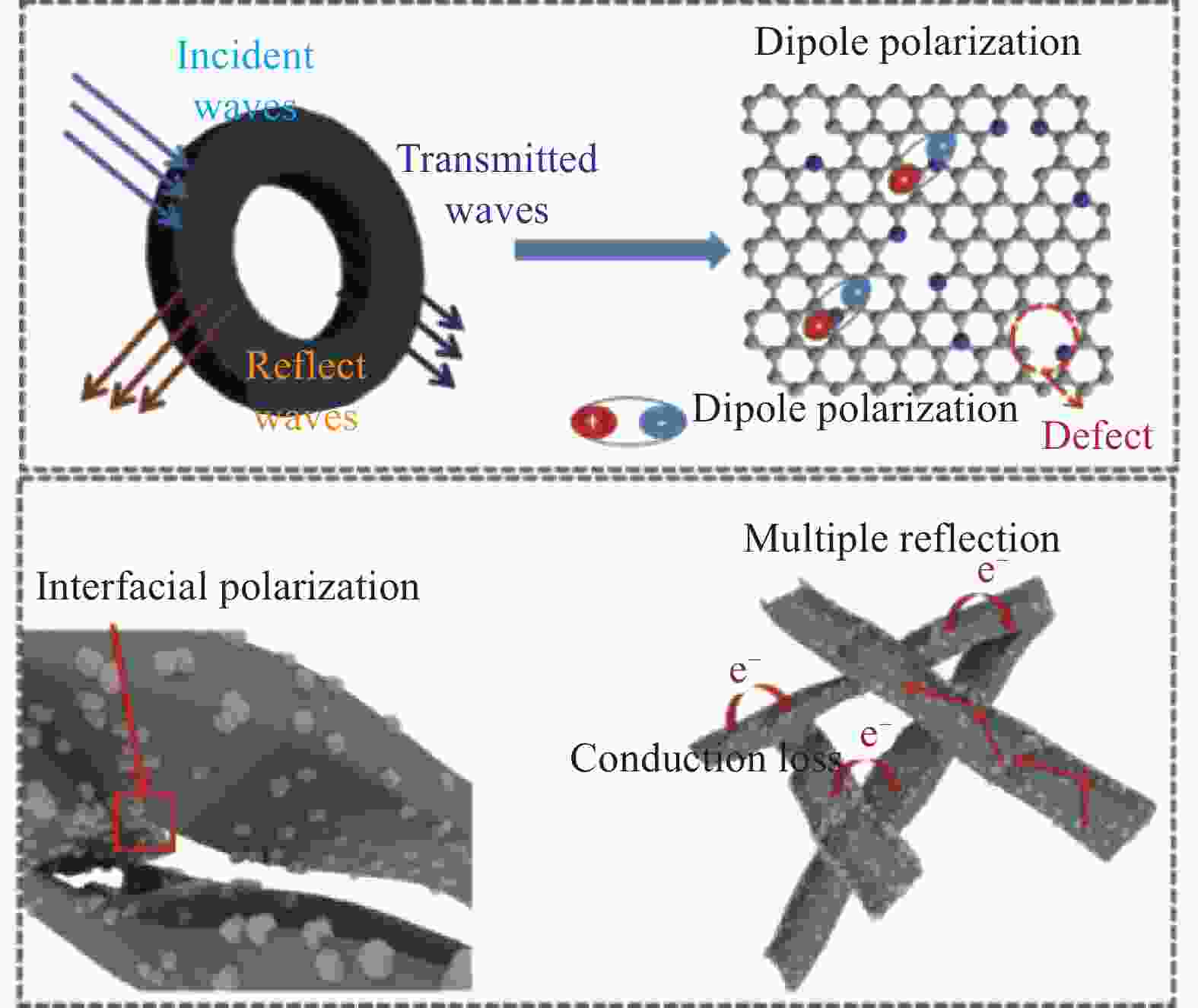
摘要: 生物质材料具有特异的微观形态和孔道结构,被认为是碳组分优良的形态遗传材料,且生物质材料来源广泛、价格低廉,亦符合国家可持续发展的战略需求。基于此,本文选取生物质香蒲为主要碳源,Fe3+为金属源,经原位吸附和碳热还原得到碳基底表面均匀负载的Fe纳米粒子(Fe/C复合材料),随着煅烧温度的升高,铁纳米粒子的结晶度增强;Fe/C-700复合材料在低频和高频具有多重共振行为,有助于介电损耗能力的提升;二维反射损耗结果显示,900℃的Fe/C复合材料的吸波性能最好,厚度为5 mm时,4.4 GHz处达到最大反射损耗−35 dB,复合材料优良的吸波性能取决于其较好的阻抗匹配特性和介电损耗与磁损耗的协同作用,本研究将为新型磁性碳基吸波材料的合成提供高效、便捷的合成策略。Abstract: Biomass materials have specific microscopic morphology and pore structure, which can be considered as excellent morphogenetic materials for carbon components. In addition, biomass materials are widely used, inexpensive and it is in line with the strategic needs of national sustainable development. In the research, we selects biomass cattail as the main carbon source and Fe3+ as the metal source. Fe/C composites can be obtained by in situ adsorption and carbon thermal reduction, where Fe nanoparticles are uniformly loaded on the surface of carbon substrate. Moreover, the crystallinity of Fe nanoparticles can be enhanced with the increase of calcination temperature. Fe/C-700 composites have multiple resonance behaviors at low and high frequencies, which contribute to the enhancement of dielectric loss capability. Two-dimensional reflection loss results show that Fe/C-900 composites exhibit the excellent microwave absorption performance, where the minimum reflection loss can reach −35 dB at 4.4 GHz with the thickness of 5 mm. The superior microwave absorption performance can be attributed to its better impedance matching characteristics and the synergistic effect of dielectric loss and magnetic loss, and the study will provide a new strategy for biomass-derived magnetic carbon-based microwave absorption composites.
-
Key words:
- Fe/C composites /
- biomass /
- microwave absorption /
- dielectric loss /
- magnetic loss
-
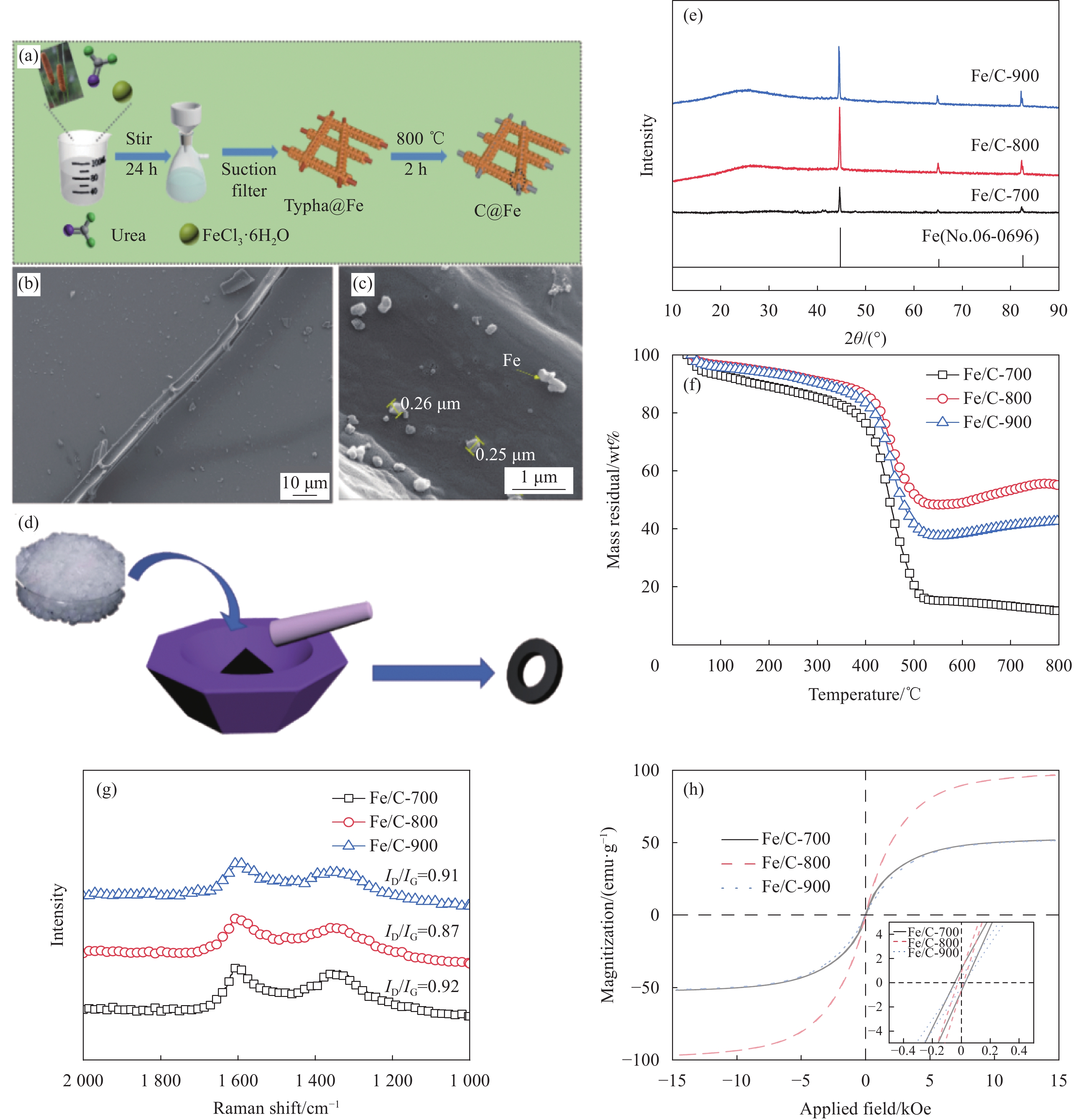
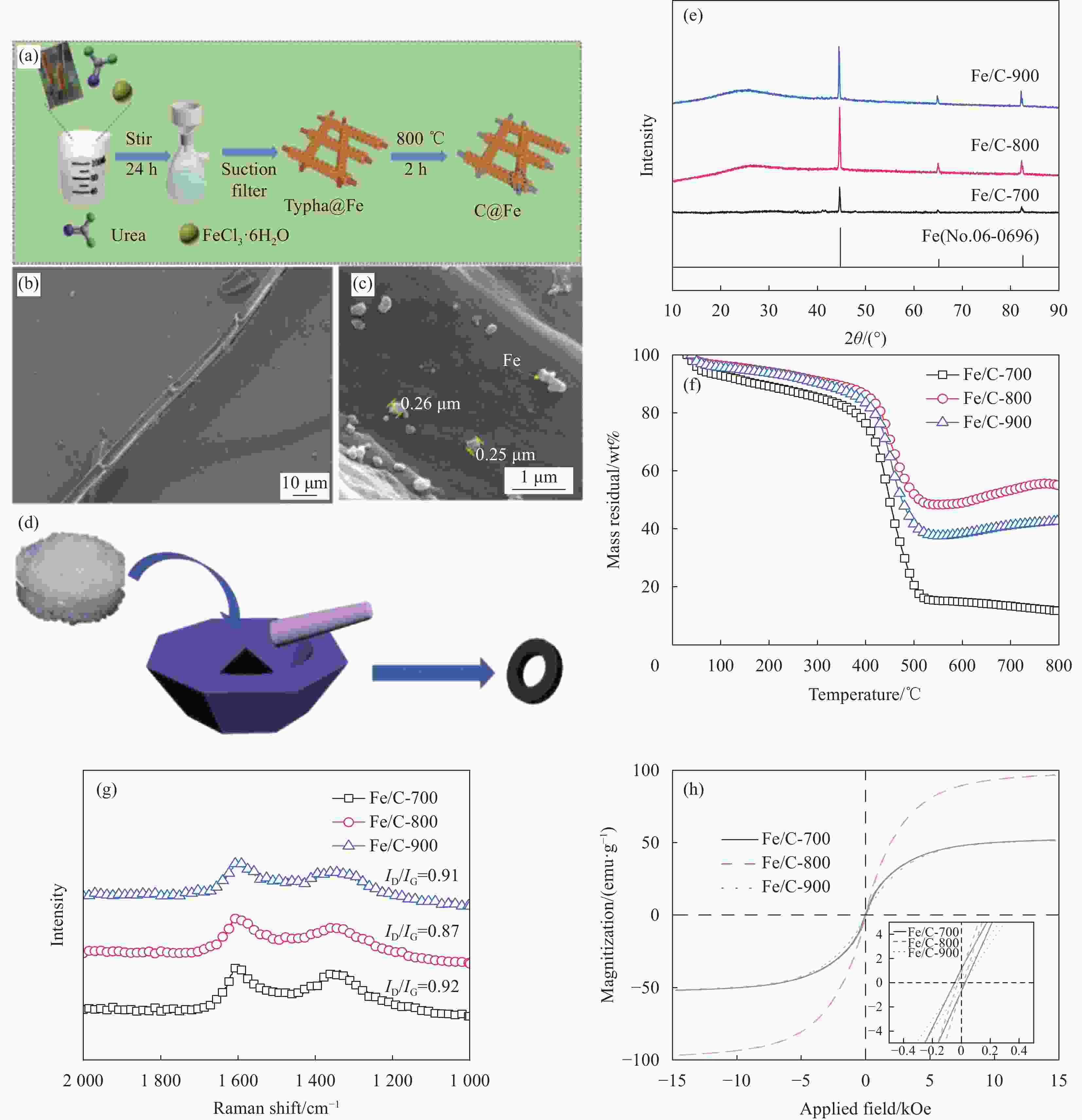
图 1 Fe/C复合材料的制备流程图 (a)、SEM图像 ((b)~(c))、吸波测试样品制备流程图 (d)、XRD图谱 (e)、热重图谱 (f)、拉曼图谱 (g)、 振动样品磁强计(VSM) (h)
Figure 1. Fe/C composite preparation flow chart (a), SEM images ((b)-(c)), flow chart for sample preparation for wave absorption testing (d), XRD (e), TG (f), Raman mapping (g), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) (h)
ID/IG—Intensity ratio of the D band and G band
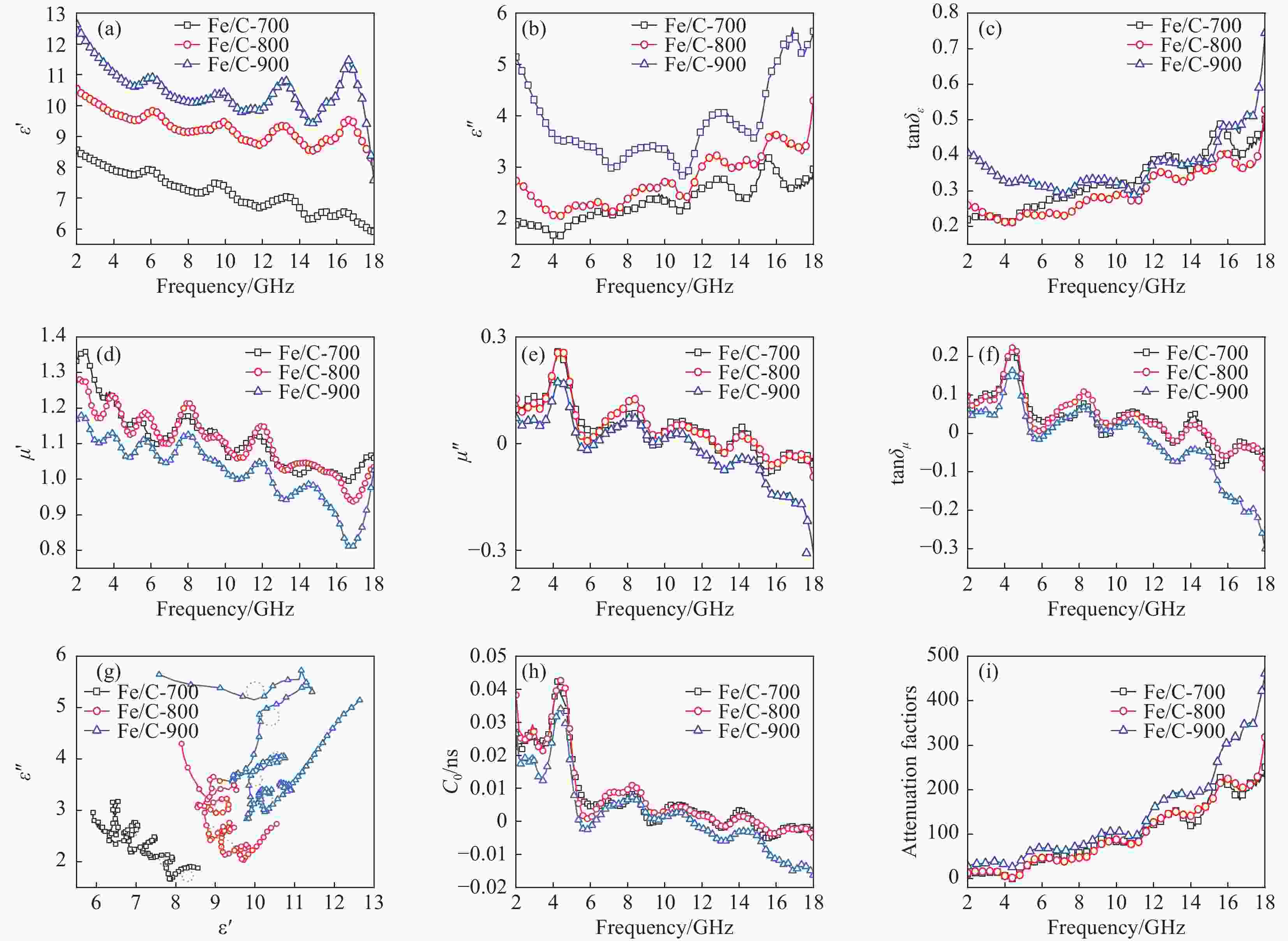
图 4 Fe/C复合材料的介电常数实部ε' (a)、介电常数虚部ε'' (b)、介电损耗正切值$ {\tan\delta }_{\epsilon } $(c)、复磁导率实部μ' (d)、复磁导率虚部μ'' (e)、复磁损耗正切值$ {\tan}{\delta }_{\mu } $(f)、Cole-Cole环 (g)、涡流损耗对磁损耗的贡献(C0) (h)、衰减因子谱 (i)
Figure 4. Fe/C composite real part of the dielectric constant ε' (a), Imaginary part of the dielectric constant ε'' (b), Dielectric loss tanδε (c), Complex magnetic permeability real part μ' (d), Complex magnetic permeability imaginary part μ'' (e), Complex magnetic loss tanδμ (f), Cole-Cole (g), Contribution of Eddy current loss to magnetic loss (C0) (h) and Attenuation factor mapping (i)
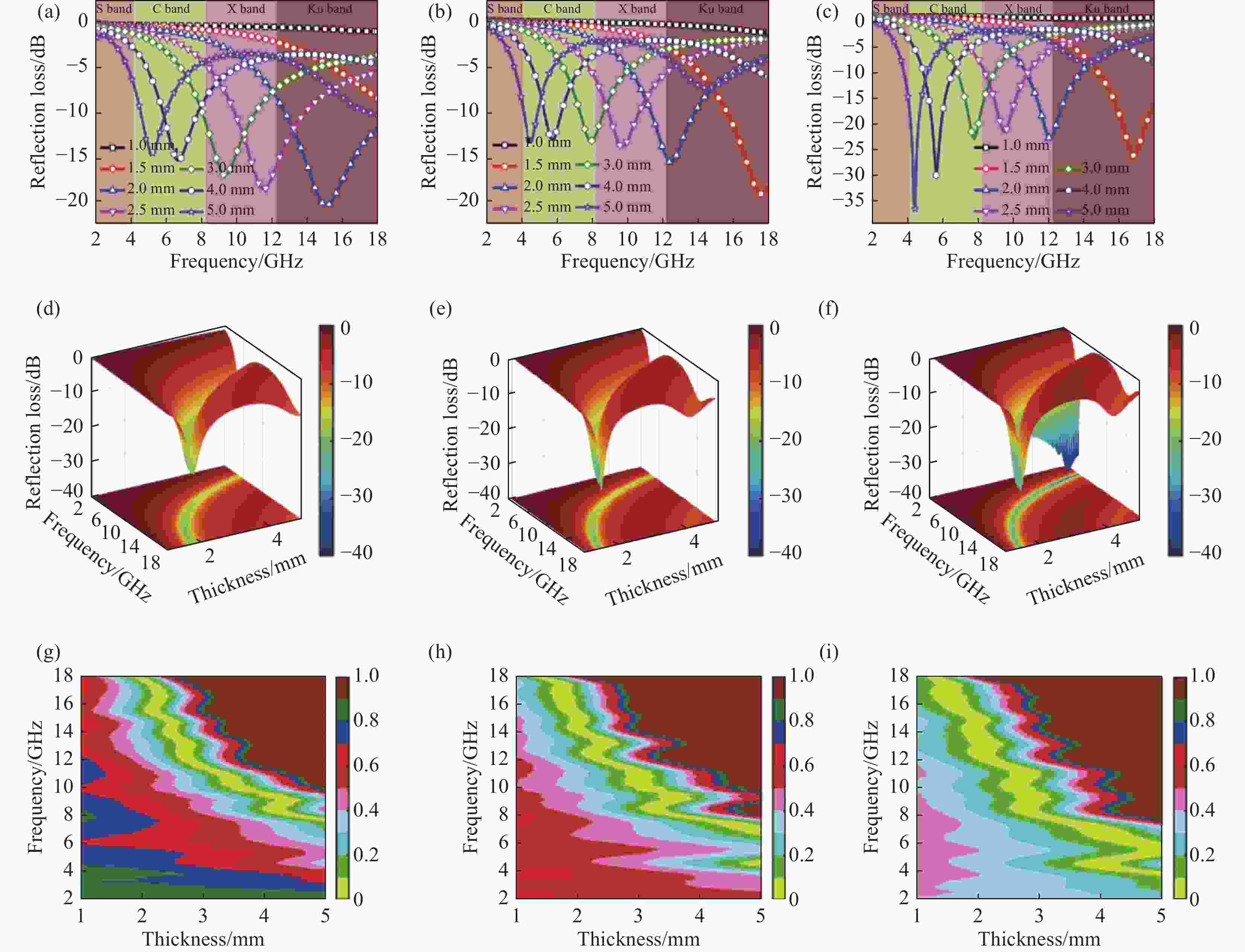
图 5 Fe/C-700 (a)、Fe/C-800 (b)、Fe/C-900 (c) 的二维反射损耗图;Fe/C-700 (d)、Fe/C-800 (e)、Fe/C-900 (f) 的三维反射损耗图;Fe/C-700 (g)、Fe/C-800 (h)、Fe/C-900 (i) 的阻抗匹配图
Figure 5. 2D reflection loss diagrams for Fe/C-700 (a), Fe/C-800 (b), Fe/C-900 (c); 3D reflection loss diagrams for Fe/C-700 (d), Fe/C-800 (e), Fe/C-900 (f); Impedance matching diagram for Fe/C-700 (g), Fe/C-800 (h), Fe/C-900 (i)
表 1 Fe/C复合材料的命名
Table 1. Naming of Fe/C composites
Sample Calcination temperature/℃ Fe/C-700 700 Fe/C-800 800 Fe/C-900 900 -
[1] WANG Y Q, WANG H G, YE J H,et al. Magnetic CoFe alloy@C nanocomposites derived from ZnCo-MOF for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 383: 123096. [2] LI Z J, LIN H, DING S Q, et al. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon[J]. Carbon,2020,167:148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.070 [3] MOU P P, ZHAO J C, WANG G Z, et al. BCN nanosheets derived from coconut shells with outstanding microwave absorption and thermal conductive properties[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,437(2):135285. [4] GAO T, ZHAO R Z, LI Y X, et al. Sub-nanometer Fe clusters confined in carbon nanocages for boosting dielectric polarization and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022,32(31):2204370. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202204370 [5] WANG C Y, MA Y Y, QIN Z H, et al. Synthesis of hollow spherical MoS2@Fe3O4-GNs ternary composites with enhanced microwave absorption performance[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,569:150812. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150812 [6] CUI C, GUO R H, REN E H, et al. MXene-based rGO/Nb2CTx/Fe3O4 composite for high absorption of electromagnetic wave[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,405:126626. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126626 [7] ZHOU X F, JIA Z R, FENG A L, et al. Synthesis of fish skin-derived 3D carbon foams with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Carbon,2019,152:827-836. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.06.080 [8] DONG S, TANG W K, HU P T, et al. Achieving excellent electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities by construction of MnO nanorods on porous carbon composites derived from natural wood via a simple route[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(13): 11795-11805. [9] XU Z J, HE M, ZHOU Y M, et al. Spider web-like carbonized bacterial cellulose/MoSe2 nanocomposite with enhanced microwave attenuation performance and tunable absorption bands[J]. Nano Research,2021,14(3):738-746. [10] ZHANG X, DONG Y Y, PAN F, et al. Electrostatic self-assembly construction of 2D MoS2 wrapped hollow Fe3O4 nanoflowers@1D carbon tube hybrids for self-cleaning high-performance microwave absorbers[J]. Carbon,2021,177:332-343. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.092 [11] 朱莉莉, 康帅, 胡祖明, 等. MXene及其复合吸波材料组成与结构的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(6):3167-3186. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20221014.002ZHU Lili, KANG Shuai, HU Zuming, et al. Research progress in composition and structure of MXene and its composite wave absorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2023,40(6):3167-3186(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20221014.002 [12] XIONG J, XIANG Z, DENG B W, et al. Engineering compositions and hierarchical yolk-shell structures of NiCo/GC/NPC nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,513:145778. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145778 [13] DONG Y Y, ZHU X J, PAN F, et al. Mace-like carbon fiber/ZnO nanorod composite derived from Typha orientalis for lightweight and high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials,2021,4(4):1002-1014. doi: 10.1007/s42114-021-00277-2 [14] YAN H, DONG Y Y, CAI L, et al. Construction of 1D biomass-derived tubular carbon fiber/Ni nanoparticles composite for broadband and lightweight microwave absorbers[J]. Carbon,2022,200:317-326. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.08.072 [15] DONG Y Y, ZHU X J, PAN F, et al. Fire-retardant and thermal insulating honeycomb-like NiS2/SnS2 nanosheets @ 3D porous carbon hybrids for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 426: 131272. [16] WANG L, HUANG M Q, QIAN X A, et al. Confined magnetic-dielectric balance boosted electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Small,2021,17(30):2100970. doi: 10.1002/smll.202100970 [17] SONG Z M, SUN X, LI Y, et al. Carbon fibers embedded with aligned magnetic particles for efficient electromagnetic energy absorption and conversion[J]. ACS Applied Materials& Interfaces,2021,13(4):5266-5274. [18] LIU Z K, CHEN J, QUE M D, et al. 2D Ti3C2T MXene/MOFs composites derived CoNi bimetallic nanoparticles for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,450(4):138442. [19] YAN X, HUANG X X, ZHONG B, et al. Balancing interface polarization strategy for enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption of carbon materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,391:123538. [20] YANG P G, HUANG Y X, LI R, et al. Optimization of Fe@Ag core-shell nanowires with improved impedance matching and microwave absorption properties[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,430:132878. [21] XUH L, YIN X W, ZHU M, et al. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(7):6332-6341. [22] XIANG J, LI J L, ZHANG X H, et al. Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(40):16905-16914. doi: 10.1039/C4TA03732D [23] QIANG R, DU Y C, ZHAO H T, et al. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(25):13426-13434. doi: 10.1039/C5TA01457C [24] QIAN X A, ZHANG Y H, WU Z C, et al. Multi-path electron transfer in 1D double-shelled Sn@Mo2C/C tubes with enhanced dielectric loss for boosting microwave absorption performance[J]. Small,2021,17(30):2100283. doi: 10.1002/smll.202100283 [25] LUO J L, HAO G Z, XIAO L, et al. Boosting electromagnetic wave absorption properties via the sulfidation strategy of Fe/Fe3C/N-doped carbon nanorods hybrids[J]. Ceramics International,2022,48(8):11346-11355. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.358 [26] LI C P, CHEN G B, JIANG W T, et al. High-performance electromagnetic wave absorption of FeNi/N, S-codoped carbon composites in 2-40 GHz[J]. Carbon,2021,174:201-213. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.12.033 [27] 叶信立, 张俊雄, 项俊锋, 等. 氧化热处理温度对多孔镍泡沫微观结构及吸波性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8):3794-3803. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211103.002YE Xinli, ZHANG Junxiong, XIANG Junfeng, et al. Effect of oxidation heat treatment temperature on microstructure and microwave absorption properties of porous nickel foam[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(8):3794-3803(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211103.002 [28] 曹敏, 邓雨, 希徐康, 等. 新型碳基磁性复合吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(12):3004-3016. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200825.002CAO Min, DENG Yu, XI Xukang, et al. Research progress of new carbon based magnetic composite electromagnetic waveabsorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(12):3004-3016(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200825.002 [29] TIAN H Y, QIAO J, YANG Y F, et al. ZIF-67-derived Co/C embedded boron carbonitride nanotubes for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,450(1):138011. [30] 杨亚楠, 夏龙, 张昕宇, 等. Fe3O4@锂铝硅微晶玻璃/还原氧化石墨烯复合材料的制备和吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36 (11): 2651-2664.YANG Yanan, XIA Long, ZHANG Xinyu, et al. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of Fe3O4@lithium aluminum silicateglass ceramic/reduced graphene oxide composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36 (11): 2651-2664(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: