Research progress of SiC composite microwave absorbing materials
-
摘要:
目的 吸波材料作为防雷达探测、电磁干扰和电磁污染的有效屏障得到了快速的发展。SiC是一种应用广泛的吸波材料,其具有一定的介电性能和出众的稳定性、耐腐蚀性,但也存在阻抗匹配不佳等缺点。构建SiC基复合吸波材料是提高其吸波性能的重要方法。本文综述了SiC的吸波性能和SiC基复合吸波材料的研究进展,并展望了SiC基复合吸波材料的发展方向。 方法 对SiC及其复合吸波材料的制备与性能进行归纳总结:(1)SiC的吸波性能和提高吸波性能的方法。SiC吸波材料主要依赖于介电损耗,内部缺陷、界面和表面、厚度和温度等因素会影响SiC的吸波性能。为克服SiC材料阻抗匹配不佳、损耗机制单一等不足,常用的方法有:掺杂改性和制备SiC复合材料。(2)SiC复合材料的制备策略:零维SiC纳米颗粒、一维SiC纳米线、三维结构SiC材料分别与导电材料、介电材料和磁性材料相复合,以提高SiC基材料的介电性能、丰富吸收机制、优化阻抗匹配,进而提高吸波性能。 结果 SiC的吸波性能主要来自于介电弛豫损耗,并受到内部缺陷、界面和表面、厚度和温度的影响:SiC内部缺陷作为极化中心引起极化弛豫,提高介电常数;SiC的比表面积增大,会增加偶极极化和界面极化,促进多次反射;吸收体厚度为1/4波长的奇数倍时会产生干涉而衰减电磁波;温度的升高会降低SiC电阻率,进而提高其对电磁波吸收率。为提高SiC的吸波性能,可采用掺杂改性和制备SiC复合材料的 方法 对SiC的掺杂改性可以调控载流子浓度、提高介电性能;SiC复合吸波材料可以调节电磁参数、优化阻抗匹配、丰富损耗机制,提高吸收强度。不同维度的SiC用于吸波材料的优势有:SiC纳米颗粒抗氧化性能更好,更耐高温,纳米颗粒有效改善了SiC的电磁特性且制备方法较为成熟;SiC纳米线具有一维结构,比表面积较大,易于形成三维导电网络,具有较高的介电性能;三维SiC材料可通过不同的实验方法制备,多孔网络结构对电磁波产生反射、散射、干涉作用引起衰减。按照损耗类型分类,SiC复合材料主要分为三类:SiC与导电材料复合、SiC与介电材料复合、SiC与磁性材料复合。①导电材料以碳材料为代表,具有导电性高、密度小、稳定性好、易于调控的优势。导电材料与SiC相复合,促进了异质界面的形成,引入了导电路径,可以丰富损耗机制,优化阻抗匹配。②介电材料包括各种陶瓷材料,大多具有较高的力学性能和耐腐蚀性能。介电材料与SiC相复合,可以调控材料的介电性能,进一步提高介电损耗,并有在高温下服役的潜力。③磁性材料包括金属微粉和金属氧化物等,通过涡流损耗和自然共振等方式进行磁损耗,有些磁性材料也同时具备介电损耗,具有很高的吸波特性。磁性材料与SiC相复合,可以丰富损耗机制,提高吸波性能。 结论 本文综述了SiC复合吸波材料的最新研究进展:介绍了SiC的结构、吸波机理和影响因素,并根据SiC材料维度和损耗机理对复合材料进行分类总结和分析。最后对SiC基复合吸波材料的发展前景进行了展望,这为SiC基复合吸波材料的研究提供参考。 Abstract: In order to prevent the increasingly serious electromagnetic interference problem, the research and development of microwave absorbing materials has attracted more and more attention. As a microwave absorbing material with excellent dielectric properties, SiC also has the advantages of excellent stability, high strength and corrosion resistance. But it also has the disadvantages of poor impedance matching and single microwave absorbing mechanism. Compounding SiC with other materials is an important means to further improve the microwave absorbing properties of SiC materials. The structure, microwave absorbing mechanism and influencing factors of SiC were briefly introduced in the paper. Then the microwave absorbing properties of SiC composites with different dimensions were summarized in detail, including SiC nanoparticles, SiC nanowires, three-dimensional SiC materials with different kinds of materials such as metallic materials, carbon materials, ceramic materials, and polymer materials. Compared with a single SiC material, the composite materials can improve their dielectric properties, enrich the absorption mechanism, optimize the impedance matching, and then improve the microwave absorption ability. Finally, the development direction of SiC based composite microwave absorbing materials was prospected.-
Key words:
- microwave absorbing /
- compound material /
- silicon carbide /
- nanoparticles /
- nanowires /
- aerogel
-
图 4 退火温度为1650℃ (a) 和1800℃ (b) 时,匹配厚度为2或1.5~4 mm的范围内,退火态硅硼碳氮(SiBCN)的吸波性能和反射系数(RC)[27];(c) 匹配厚度为3 mm的SiOC和n-SiC/SiOC的吸收系数[29]
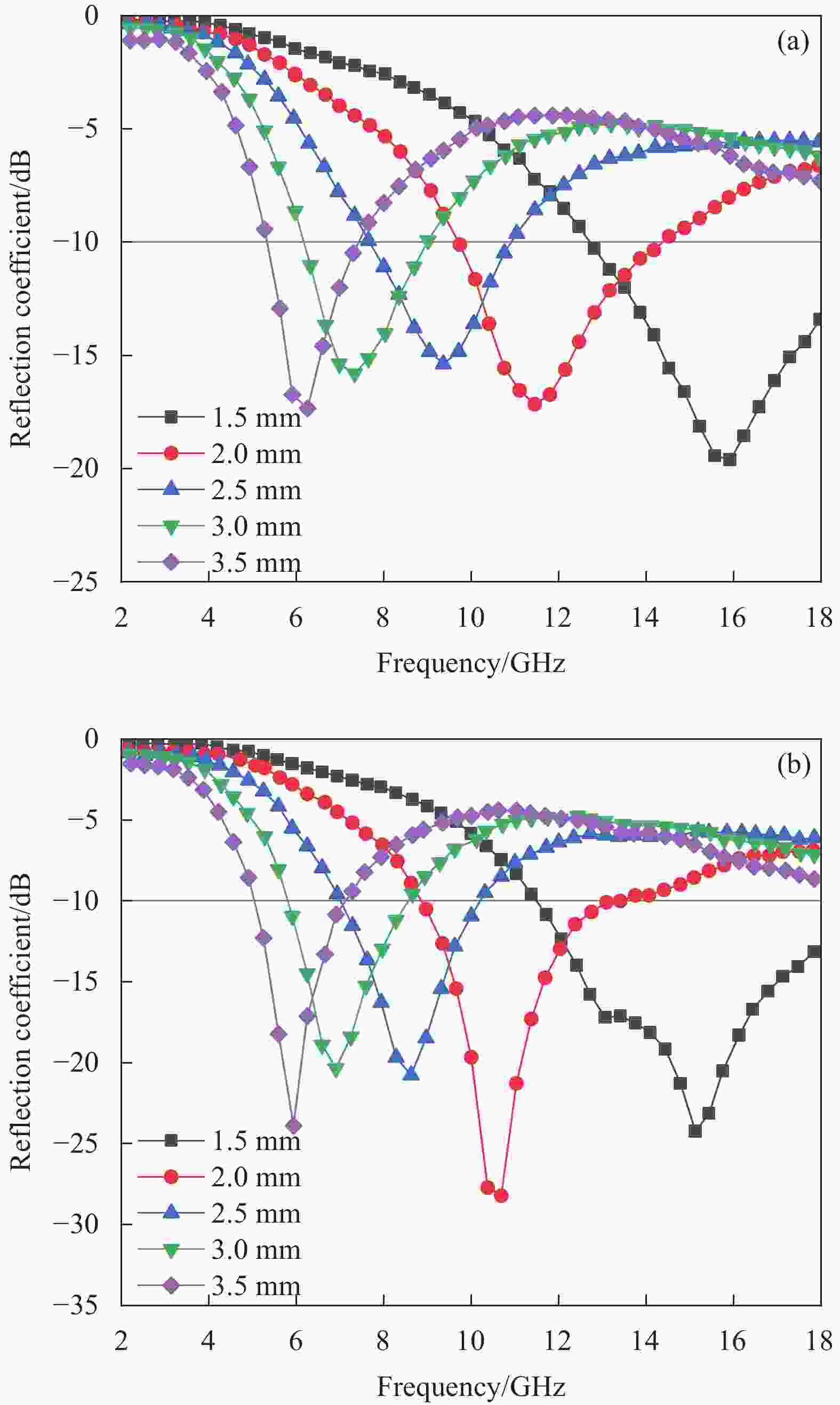
Figure 4. Reflection coefficient (RC) of the as-annealed siliconboron carbonitride (SiBCN) at 1650℃ (a) and 1800℃ (b) as a function of frequency at a matching thickness range of 2 or 1.5-4 mm[27]; (c) Absorption coefficients of SiOC and n-SiC/SiOC with a matching thickness of 3 mm[29]
图 7 SiC纳米线低放大TEM图像 (a)、高放大TEM图像( b);(c)为图(b)中划出区域的HRTEM图像;((d), (e)) 对应(c)中含缺陷1和无缺陷2区的FFT衍射图[37]; SiC 纳米线(NWs) (f) 和SiC@石墨烯 (g) 的SEM图像、SiC NWs (h) 和SiC@石墨烯 (i) 的TEM图像(插图为相应的HRTEM图像);(j) 不同厚度SiC@石墨烯的RL值[42]
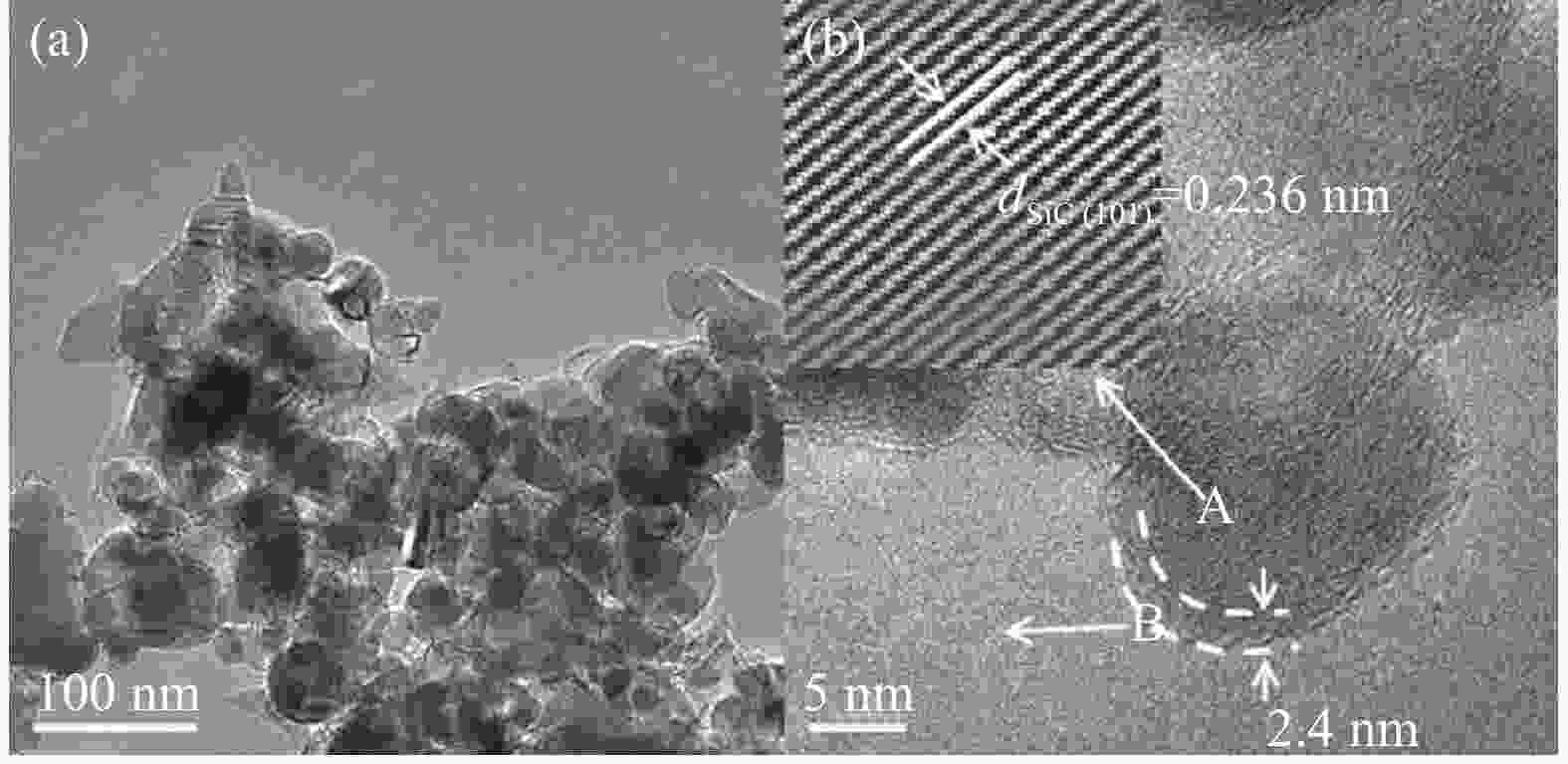
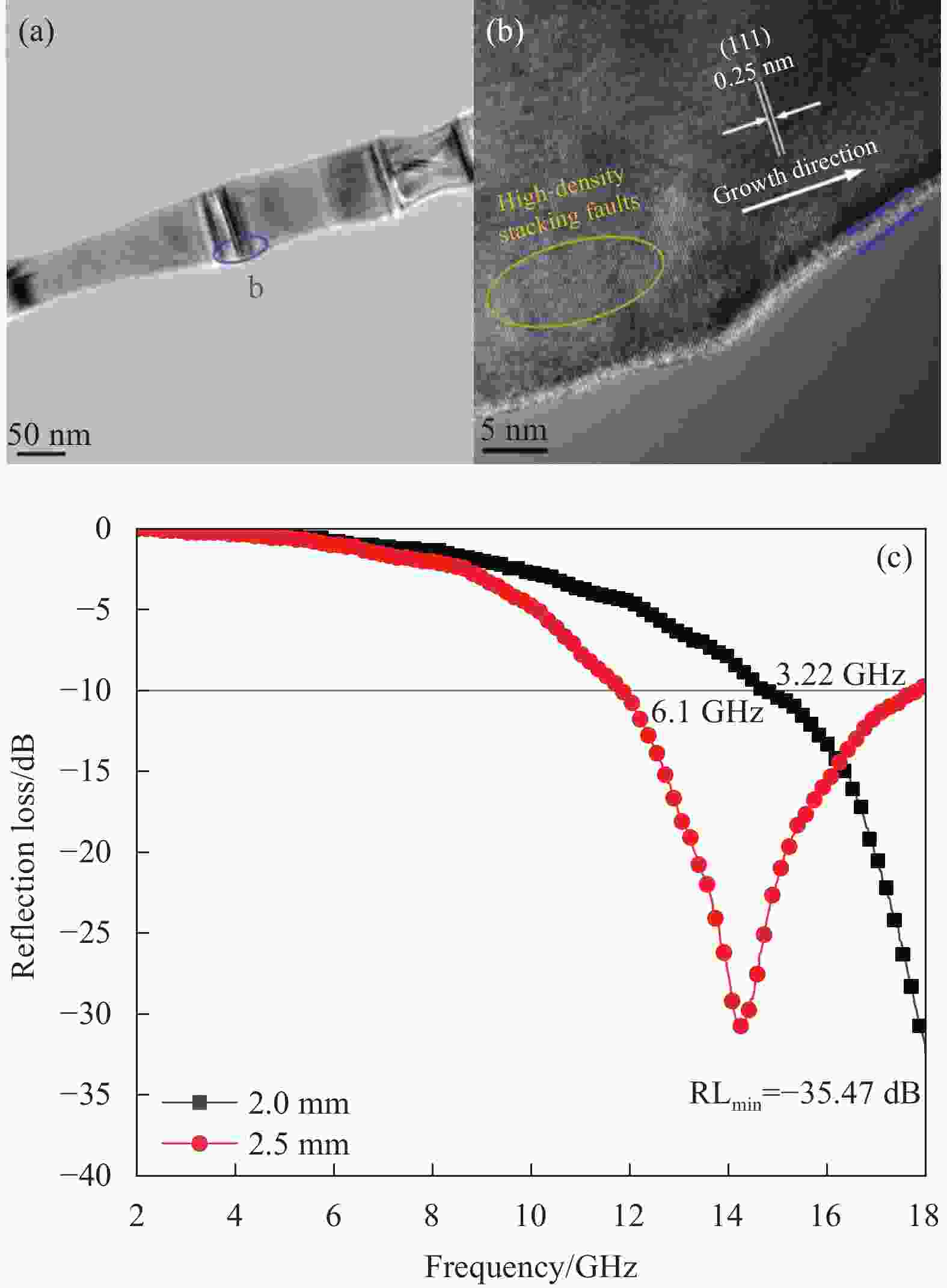
Figure 7. SiC nanowires low-magnified TEM image (a), high-magnified TEM image (b) showing high-density stacking faults and micro-twins within nanowires; (c) HRTEM image recorded from the white square area in Fig.(b); ((d), (e)) Corresponding the FFT diffraction patterns obtained from defect-containing (1) and defect-free (2) regions in (c), respectively[37]; SEM images of nanowires (NWs) (f) and SiC@graphene (g); TEM images of SiC NWs (h) and SiC@graphene (i) (insets are corresponding HRTEM images); (j) RL values of SiC@graphene with various thicknesses[42]
TB—Twin boundaries; SF—Stacking faults; VG—Vertically oriented graphene; NW—Nanowire
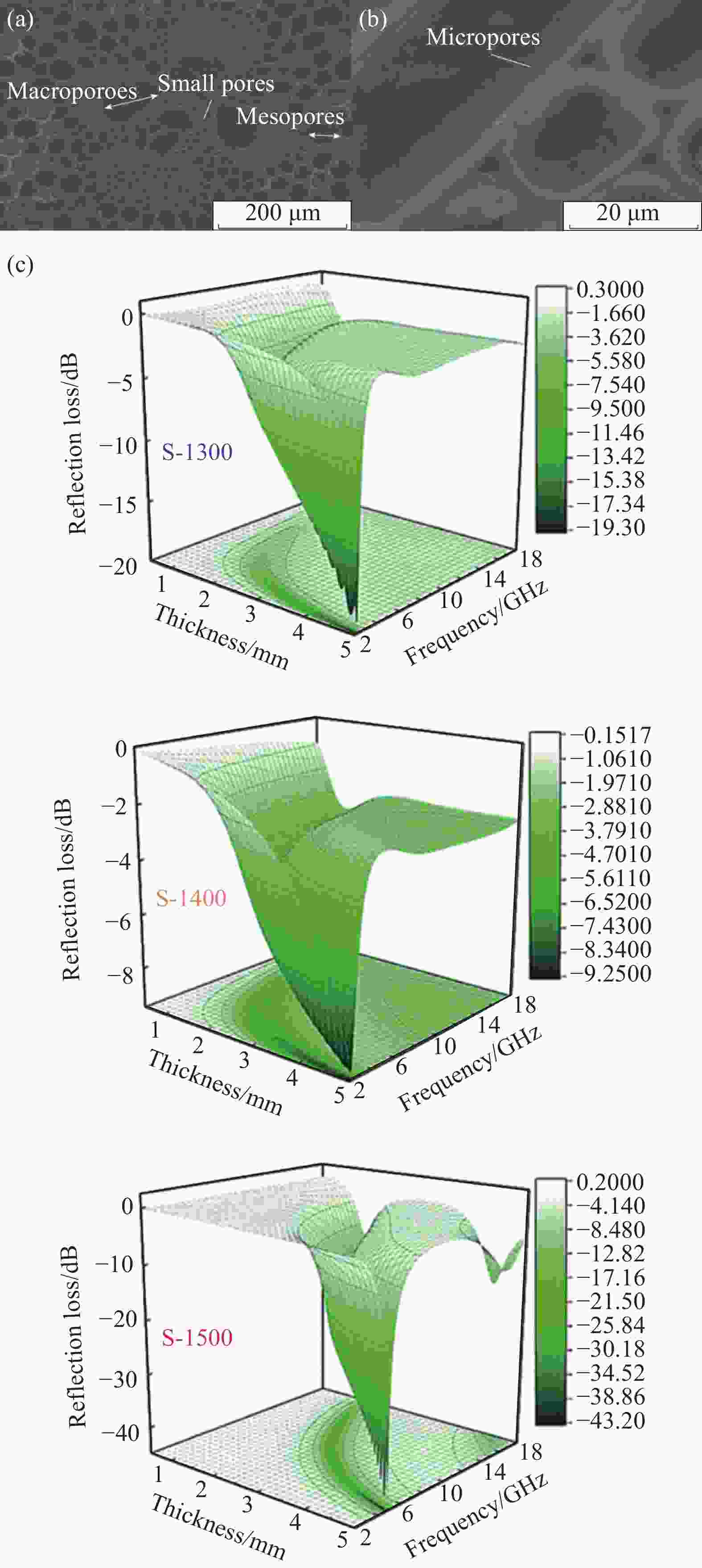
图 9 ((a), (b)) 包埋法制备的BC/SiC复合材料的SEM图像[54];(c) 经1300℃、1400℃、 1500℃热处理的3种样品(S-1300、S-1400、S-1500)的RL三维表征[55]
Figure 9. ((a), (b)) SEM images of BC/SiC composites by investing method; (c) Three-dimensional presentations of RL of 3 kinds of samples were heat treated at 1300℃, 1400℃ and 1500℃ (S-1300, S-1400, S-1500)[55]
-
[1] REPACHOLI M H. Low-level exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields: Health effects and research needs[J]. Bioelectromagnetics,1998,19(1):1-19. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-186X(1998)19:1<1::AID-BEM1>3.0.CO;2-5 [2] 张卫东, 冯小云, 孟秀兰. 国外隐身材料研究进展[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2000(3):1-4, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2000.03.001ZHANG Weidong, FENG Xiaoyun, MENG Xiulan. Status and development of foreign study on new stealthy materials[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2000(3):1-4, 10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2000.03.001 [3] BALAJI ANANTH P, ABHIRAM N, HARI KRISHNA K, et al. Synthesis of radar absorption material for stealth application[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2021,47:4872-4878. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.196 [4] GUAN H, LIU S, DUAN Y, et al. Investigation of the electromagnetic characteristics of cement based composites filled with EPS[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2007,29(1):49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2006.08.001 [5] LIU L, DUAN Y, MA L, et al. Microwave absorption properties of a wave-absorbing coating employing carbonyl-iron powder and carbon black[J]. Applied Surface Science,2010,257(3):842-846. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.07.078 [6] 王志江, 梁彩云. 堆垛层错对SiC纳米线吸波性能的影响机制[C]//中国国际复合材料科技大会. 杭州: 中国复合材料学会, 2017: 481-488.WANG Z J, LIANG C Y. Influence mechanism of stacking faults on microwave absorbing properties of SiC nanowires[C]//China International Congress on Compo-site Materials. Hangzhou: Chinese Society of Composite Materials, 2017: 481-488(in Chinese). [7] 米越姗, 陈旸, 郑占申. 氮改性多结构SiC吸波材料的研究[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2020, 56(9):24-30. doi: 10.16521/j.cnki.issn.1001-9642.2020.09.005MI Y S, CHEN Y, ZHENG Z S. Research on N-modified SiC absorbing materials with multiple structures[J]. China Ceramics,2020,56(9):24-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.16521/j.cnki.issn.1001-9642.2020.09.005 [8] LAN X, WANG Z. Efficient high-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption enabled by structuring binary porous SiC with multiple interfaces[J]. Carbon,2020,170:517-526. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.08.052 [9] STARKE U, BERNHARDT J, SCHARDT J, et al. SiC surface reconstruction: Relevancy of atomic structure for growth technology[J]. Surface Review and Letters,1999,6(6):1129-1141. doi: 10.1142/S0218625X99001256 [10] DONG H, FANG Z, YANG T, et al. Single crystalline 3 C-SiC whiskers used for electrochemical detection of nitrite under neutral condition[J]. Ionics,2016,22(8):1493-1500. doi: 10.1007/s11581-016-1666-5 [11] SHEN Z, CHEN J, LI B, et al. Recent progress in SiC nanowires as electromagnetic microwaves absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,815:152388. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152388 [12] LAN X, QIU Z, YAN B, et al. Growing dendritic SiC on 1D SiC nanowire: Enhancement of electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Physics and Che-mistry of Solids,2020,136:109124. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.109124 [13] KUANG J, JIANG P, LIU W, et al. Synergistic effect of Fe-doping and stacking faults on the dielectric permittivity and microwave absorption properties of SiC whiskers[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2015,106(21):212903. doi: 10.1063/1.4921627 [14] JIN Y, ZHANG B, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of skeleton pore size on the microstructure and electromagnetic absorbing property of the SiC nanowires/SiC composites[J]. Materials Letters,2021,295:129867. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129867 [15] CAI Z, SU L, WANG H, et al. Hydrophobic SiC@C nanowire foam with broad-band and mechanically controlled electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS Appllied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(7):8555-8562. [16] HOU Y, XIAO B, SUN Z, et al. High temperature anti-oxidative and tunable wave absorbing SiC/Fe3Si/CNTs compo-site ceramic derived from a novel polysilyacetylene[J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(13):16369-16379. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.165 [17] HAN T, LUO R, CUI G, et al. Effect of SiC nanowires on the high-temperature microwave absorption properties of SiCf/SiC composites[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2019,39(5):1743-1756. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.01.018 [18] ZHANG D D, ZHAO D L, ZHANG J M, et al. Microwave absorbing property and complex permittivity and permeability of graphene-CdS nanocomposite[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2014,589:378-383. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.195 [19] LU X, DONG C, GUO X, et al. Effect of B, Al, Ga doping on the electronic structure and optical property of 4 H-SiC system by the first principles calculation[J]. Modern Physics Letters B,2021,35(5):2150091. doi: 10.1142/S0217984921500913 [20] REN F, XUE J, LIU X, et al. In situ construction of CNWs/SiC-NWs hybrid network reinforced SiCN with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties in X band[J]. Carbon,2020,168:278-289. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.06.081 [21] ZHANG M, LI Z, WANG T, et al. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Fe3Si/SiC@SiO2 nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,362:619-627. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.039 [22] 梁飞. 碳化硅纳米颗粒的吸波性能研究[J]. 渭南师范学院学报, 2013, 28(9): 137-140.LIANG Fei. Research on absorbing EMW properties of SiC nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Weinan Normal University, 2013, 28(9): 137-140(in Chinese). [23] 陈兆晨, 冯振宇, 杨倩一, 等. 碳化硅颗粒填充的碳纳米管/环氧树脂复合材料的吸波性能[J]. 功能材料与器件学报, 2011, 17(3):258-261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4252.2011.03.005CHEN Zhaochen, FENG Zhenyu, YANG Qianyi, et al. Microwave absorbing properties of carbon nanotubes/epoxy resin composites with SiC particles[J]. Journal of Functional Materials and Devices,2011,17(3):258-261(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4252.2011.03.005 [24] 张磊, 赵东林, 沈曾民. 碳纳米管/纳米碳化硅复合材料的制备及其微波电磁特性[C]//2008全国功能材料科技与产业高层论坛论文集. 天津: 中国仪器仪表学会, 2008: 639-641.ZHANG L, ZHAO D L, SHEN Z M. Preparation and microwave electromagnetic properties of carbon nanotube/nano silicon carbide composites[C]//Proceedings of 2008 National High Level Forum on Functional Materials Technology and Industry. Tianjin: China Instrument and Control Society, 2008: 639-641(in Chinese). [25] 卓绝, 黄昊, 丁昂. 直流电弧法制备SiC@C核壳型纳米粒子及吸波性能研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2016, 39(6):78-82. doi: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20161014.003ZHUO J, HUANG H, DING A. Microwave absorbing properties of SiC@C core/shell nanoparticles prepared arc discharge method[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engi-neering,2016,39(6):78-82(in Chinese). doi: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20161014.003 [26] YUAN X, CHENG L, ZHANG L. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of SiC/SiO2 composites with ordered inter-filled structure[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2016,680:604-611. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.309 [27] YE F, ZHANG L, YIN X, et al. Dielectric and EMW absorbing properties of PDCs-SiBCN annealed at different temperatures[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2013,33(8):1469-1477. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.01.006 [28] ZHANG P P, WANG H S, LI L, et al. Preparation and properties of Si3N4-SiC radar wave-absorbing nanocomposites[J]. Key Engineering Materials,2016,697:462-466. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.697.462 [29] DUAN W, YIN X, YE F, et al. Synthesis and EMW absorbing properties of nano SiC modified PDC-SiOC[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2016,4(25):5962-5969. doi: 10.1039/C6TC01142J [30] 王玉江, 黄威, 黄玉炜, 等. SiC/Fe3O4/rGO复合材料的制备及吸波性能[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(10):1624-1629. doi: 10.11896/cldb.18060055WANG Y J, HUANG W, HUANG Y W, et al. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of SiC/Fe3O4/rGO composite materials[J]. Materials Reports,2019,33(10):1624-1629(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.18060055 [31] KUANG J, JIANG P, HOU X, et al. Dielectric permittivity and microwave absorption properties of SiC nanowires with different lengths[J]. Solid State Sciences,2019,91:73-76. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.03.015 [32] GUO C, CHENG L, YE F. Synthesis of multifunctional foam-like isotropic high volume fraction SiC nanowires preform via a simple method[J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(7):9569-9577. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.091 [33] LI B, MAO B, HUANG H, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of bamboo-like β-SiC nanowires[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology,2020,17(4):1869-1881. doi: 10.1111/ijac.13516 [34] LIANG C, QIN W, WANG Z. Cobalt doping-induced strong electromagnetic wave absorption in SiC nanowires[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,781:93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.047 [35] 李敏, 刘宏达, 乔宁, 等. SiCw-Co复合材料的制备及吸波性能的研究[J]. 中国陶瓷, 2020, 56(3):39-44.LI M, LIU H D, QIAO N, et al. Research on preparation and absorbing properties of SiCw-Co composite materials[J]. China Ceramics,2020,56(3):39-44(in Chinese). [36] KUANG J, HOU X, XIAO T, et al. Three-dimensional carbon nanotube/SiC nanowire composite network structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(5):6263-6267. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.12.107 [37] WU R, YANG Z, FU M, et al. In-situ growth of SiC nanowire arrays on carbon fibers and their microwave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2016,687:833-838. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.106 [38] QIAN J, DU B, CAI M, et al. Preparation of SiC nanowire/carbon fiber composites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,2021,23(10):5100434. [39] WANG P, CHENG L, ZHANG Y, et al. Electrospinning of graphite/SiC hybrid nanowires with tunable dielectric and microwave absorption characteristics[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,104:68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.10.012 [40] HAN M, YIN X, HOU Z, et al. Flexible and thermostable graphene/SiC nanowire foam composites with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. ACS Appllied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(13):11803-11810. [41] HAN M, YIN X, DUAN W, et al. Hierarchical graphene/SiC nanowire networks in polymer-derived ceramics with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing capability[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2016,36(11):2695-2703. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.04.003 [42] ZHAO D, YUAN X, LI B, et al. Silicon carbide nanowire covered by vertically oriented graphene for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Chemical Physics,2020,529:110574. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphys.2019.110574 [43] XIAO T, KUANG J, PU H, et al. Hollow SiC microtube with multiple attenuation mechanisms for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,862(1):158032. [44] YAN L, HONG C, SUN B, et al. In situ growth of core-sheath heterostructural SiC nanowire arrays on carbon fibers and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. ACS Appllied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(7):6320-6331. [45] 郑海康, 武志红, 张路平, 等. 念珠状碳化硅/二氧化硅纳米线的制备及电磁波吸收性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(1):8-14. doi: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20190211ZHENG H K, WU Z H, ZHANG L P, et al. Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of beaded silicon carbide/silica nanowires[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(1):8-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20190211 [46] DUAN W, YIN X, LI Q, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of SiC nanowires reinforced SiOC ceramic[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society,2014,34(2):257-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.08.029 [47] DONG Y, FAN X, WEI H, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of a novel SiC nanowires reinforced SiO2/3Al2O3·2SiO2 porous ceramic[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(14):22474-22481. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.006 [48] ZHONG B, SAI T, XIA L, et al. High-efficient production of SiC/SiO2 core-shell nanowires for effective microwave absorption[J]. Materials & Design,2017,121:185-193. [49] WANG P, CHENG L, ZHANG L. Lightweight, flexible SiCN ceramic nanowires applied as effective microwave absorbers in high frequency[J]. Chemical Engineering Jour-nal,2018,338:248-260. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.008 [50] DUAN W, YIN X, CAO F, et al. Absorption properties of twinned SiC nanowires reinforced Si3N4 composites fabricated by 3D-prining[J]. Materials Letters,2015,159:257-260. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2015.06.106 [51] ZHOU W, YIN R M, LONG L, et al. Enhanced high-tempera-ture dielectric properties and microwave absorption of SiC nanofibers modified Si3N4 ceramics within the gigahertz range[J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(11):12301-12307. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.017 [52] LI X, YIN X, XU H, et al. Ultralight MXene-coated, interconnected SiCnws three-dimensional lamellar foams for efficient microwave absorption in the X-band[J]. ACS Appllied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(40):34524-34533. [53] 朱新文, 江东亮, 谭寿洪. 碳化硅网眼多孔陶瓷的微波吸收特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002(6):1152-1156.ZHU X W, JIANG D L, TAN S H. Microwave absorption characteristics of silicon carbide mesh porous ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2002(6):1152-1156(in Chinese). [54] 武志红, 李妤婕, 张聪, 等. 竹炭/SiC复合材料结构及其吸波性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46(1):150-155.WU Z H, LI Y J, ZHANG C, et al. Structure and microwave absorption properties of bamboo charcoal/SiC compo-sites[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,46(1):150-155(in Chinese). [55] DONG S, HU P, ZHANG X, et al. Carbon foams modified with in-situ formation of Si3N4 and SiC for enhanced electromagnetic microwave absorption property and thermostability[J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(6):7141-7150. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.156 [56] HOU Z, XUE J, WEI H, et al. Tailorable microwave absorption properties of RGO/SiC/CNT nanocomposites with 3D hierarchical structure[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(11):18160-18167. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.137 [57] WANG Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG G, et al. Microwave absorbing properties of novel SiC/Cf composites containing SiC array modified coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2021,36(3):306-312. doi: 10.15541/jim20200364 [58] LAN X, HOU Y, DONG X, et al. All-ceramic SiC aerogel for wide temperature range electromagnetic wave attenuation[J]. ACS Appllied Materials & Interfaces,2022,14(13):15360-15369. [59] DAI D, LAN X, WU L, et al. Designed fabrication of lightweight SiC/Si3N4 aerogels for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and thermal insulation[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,901:163651. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163651 [60] LIU D, ZHOU Z, WANG Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of polymer-derived SiC ceramic aerogels toward excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2022,19:507-519. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.062 [61] WANG Z, ZHAO H, DAI D, et al. Ultralight, tunable monolithic SiC aerogel for electromagnetic absorption with broad absorption band[J]. Ceramics International,2022,48(18):26416-26424. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.332 [62] CAI Z, SU L, WANG H, et al. Alternating multilayered Si3N4/SiC aerogels for broadband and high-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption up to 1000°C[J]. ACS Appllied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(14):16704-16712. [63] SONG L, CHEN Y, GAO Q, et al. Low weight, low thermal conductivity, and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption of three-dimensional graphene/SiC-nanosheets aerogel[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2022,158:106980. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106980 [64] ZENG G, LI X, WEI Y, et al. Significantly toughened SiC foams with enhanced microwave absorption via in situ growth of Si3N4 nanowires[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,426:131745. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131745 [65] DAI D, LAN X, WANG Z. Hierarchical carbon fiber reinforced SiC/C aerogels with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2023,248:110376. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110376 -





 下载:
下载: