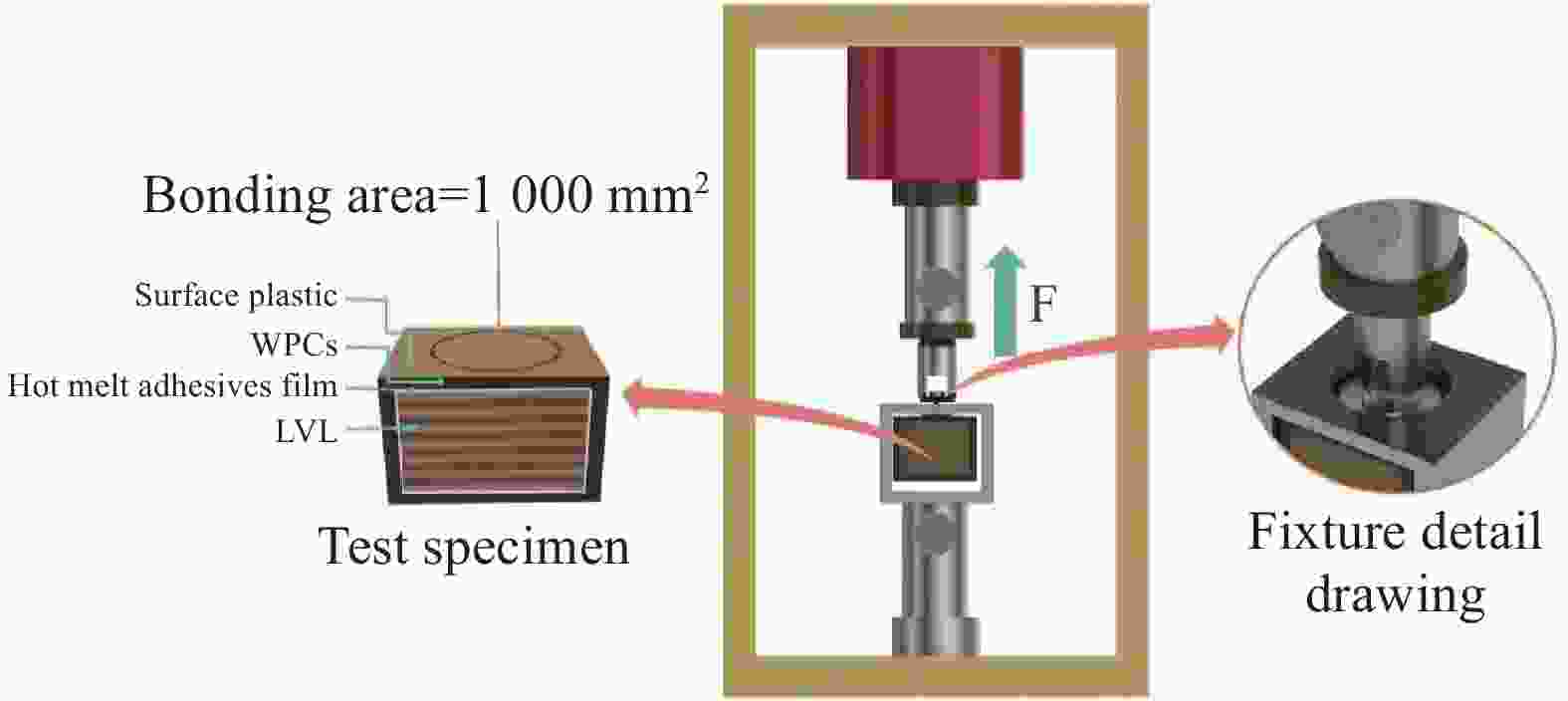
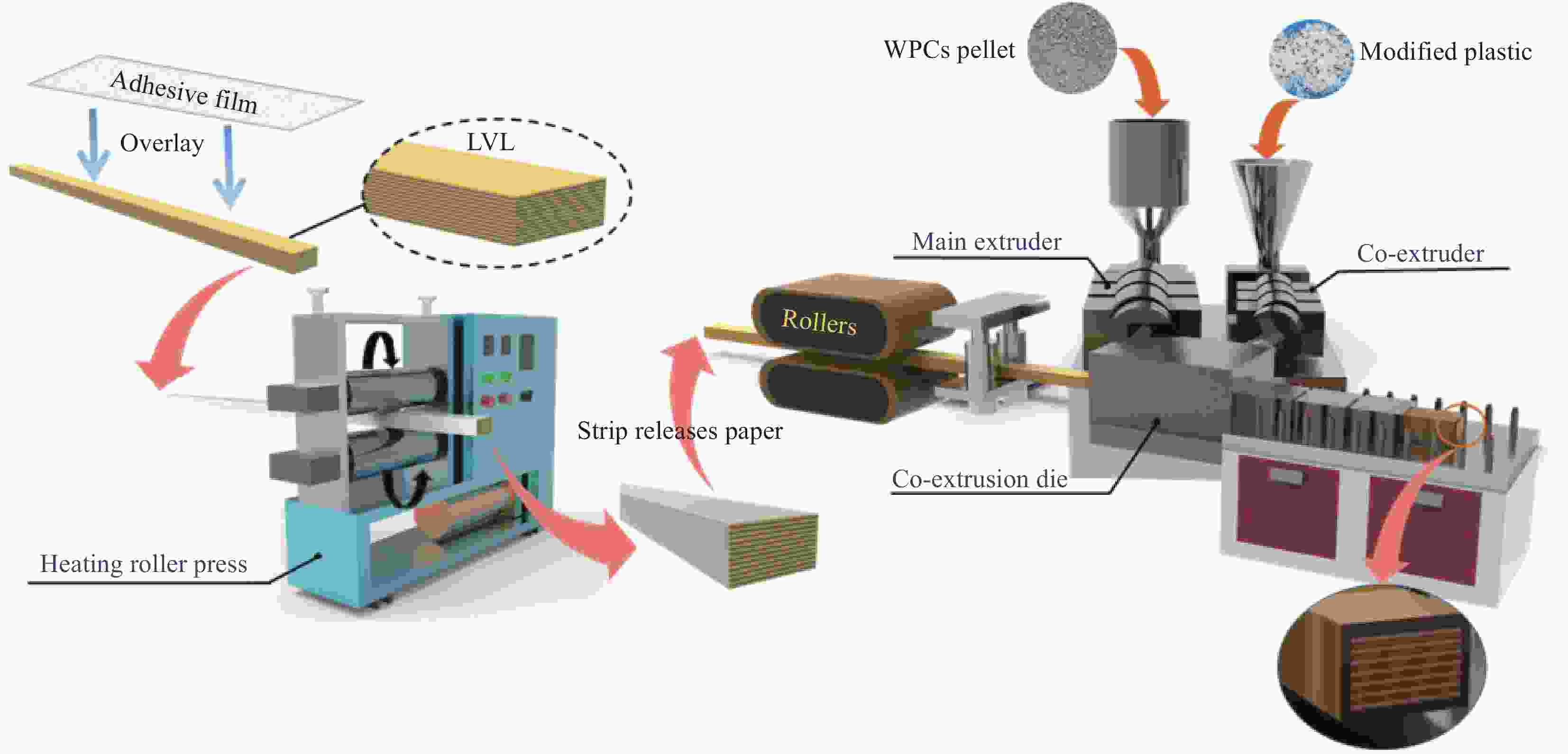
Interfacial bonding properties of multi-phase co-extruded wood-plastic composites
-
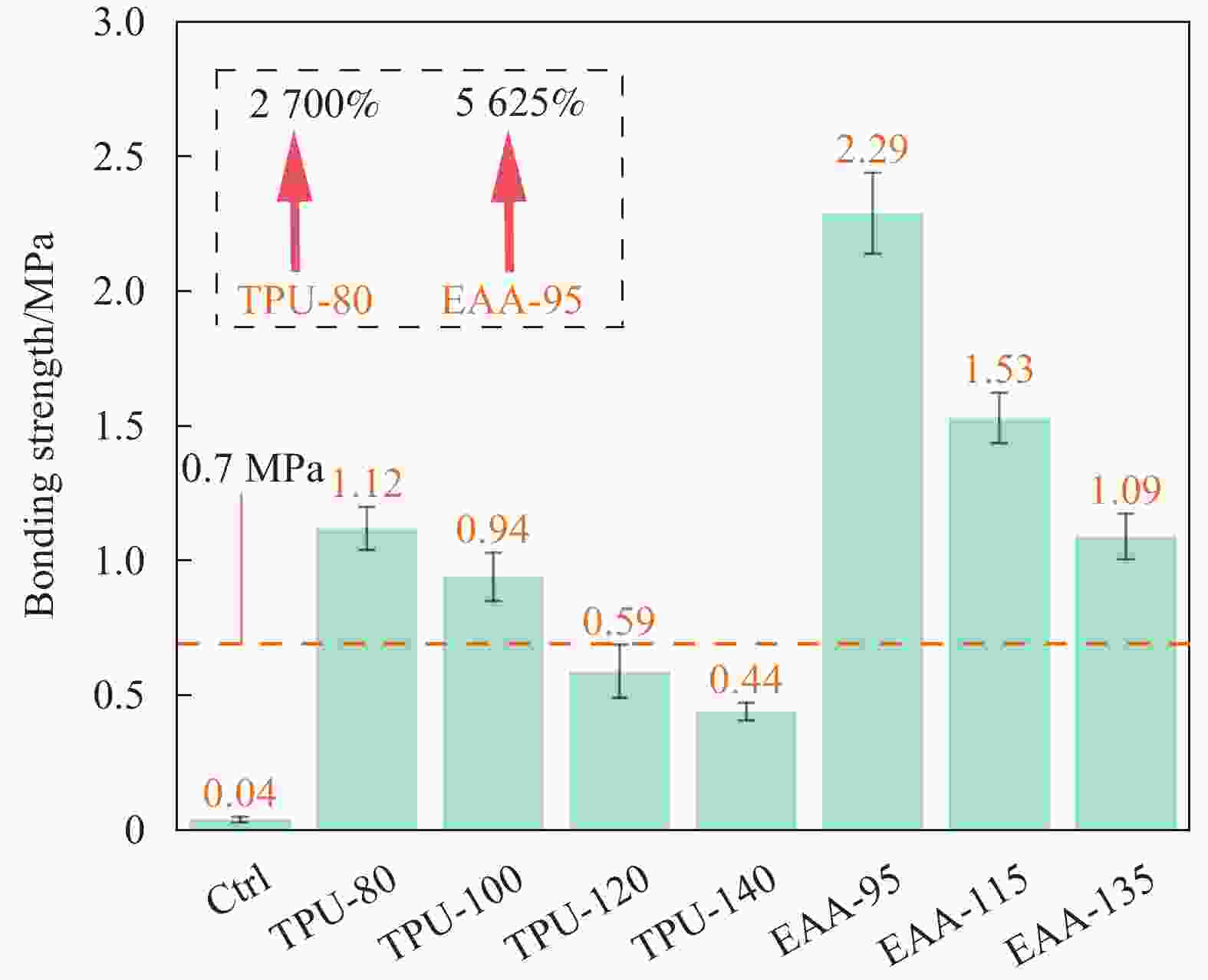
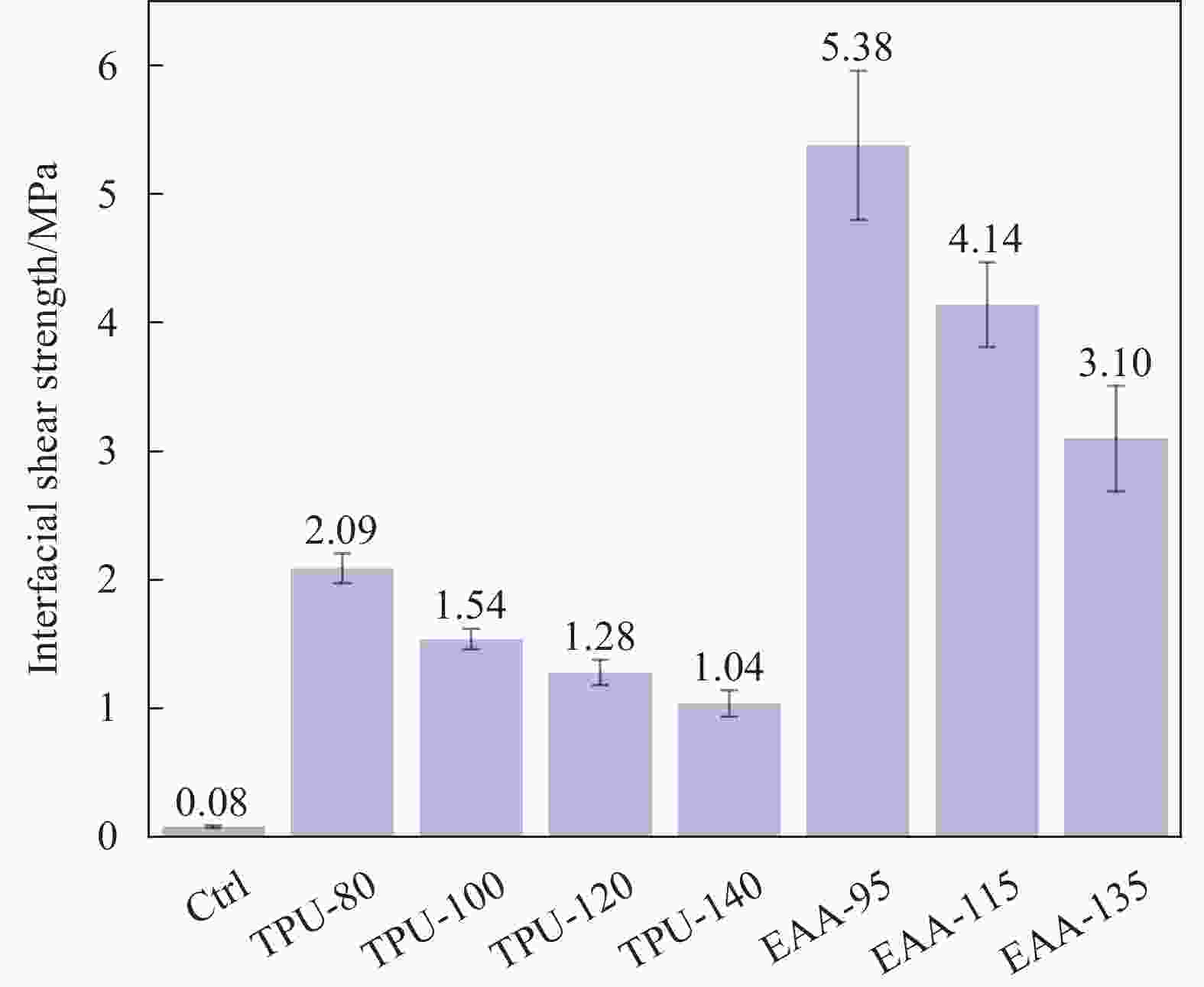
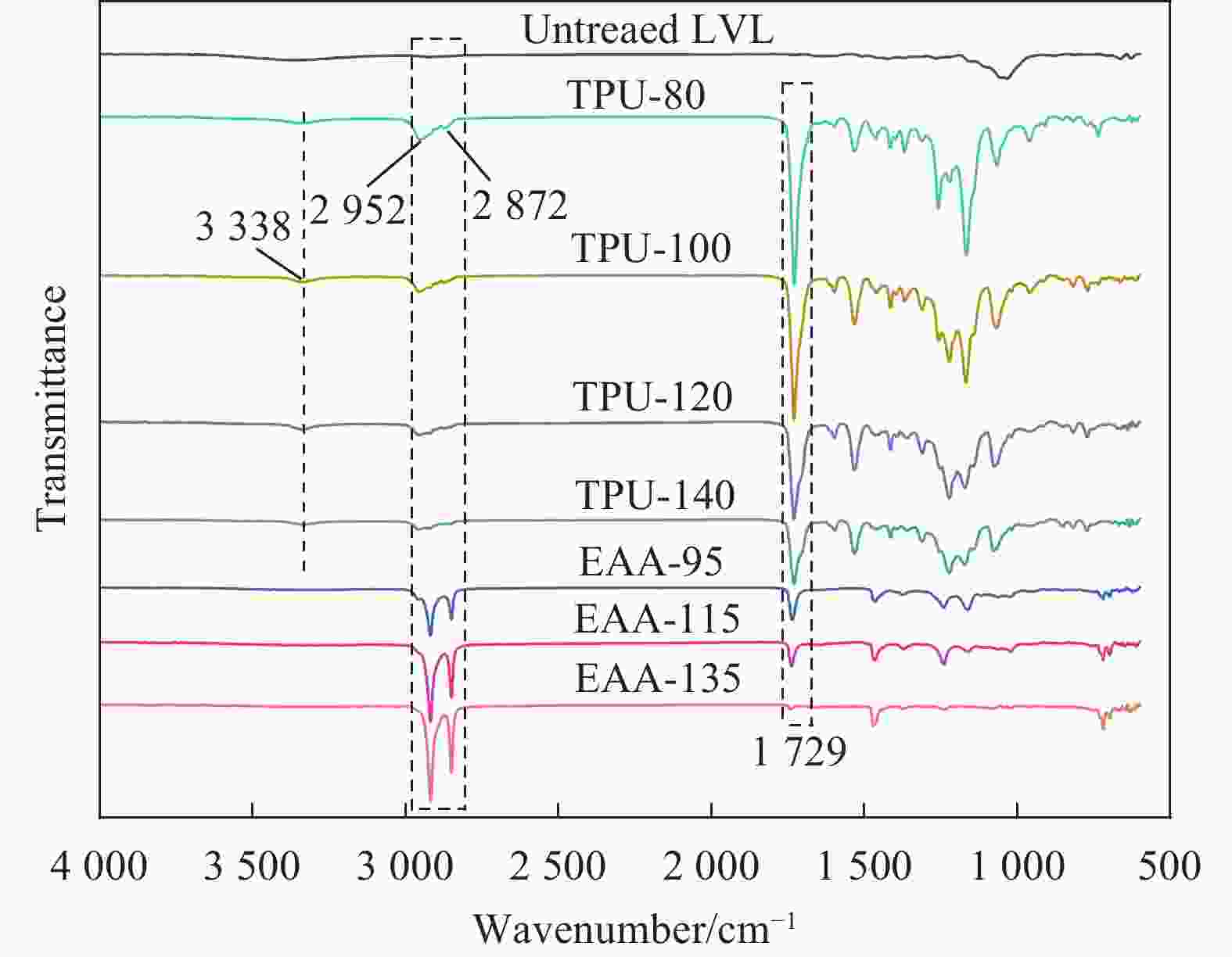
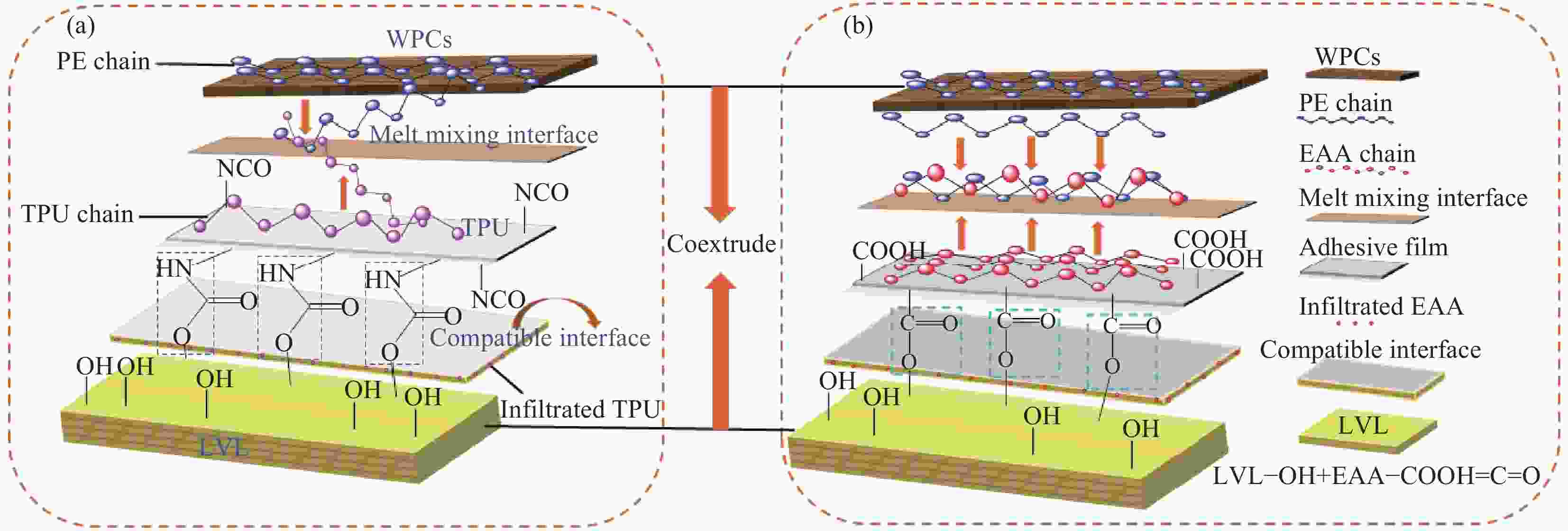
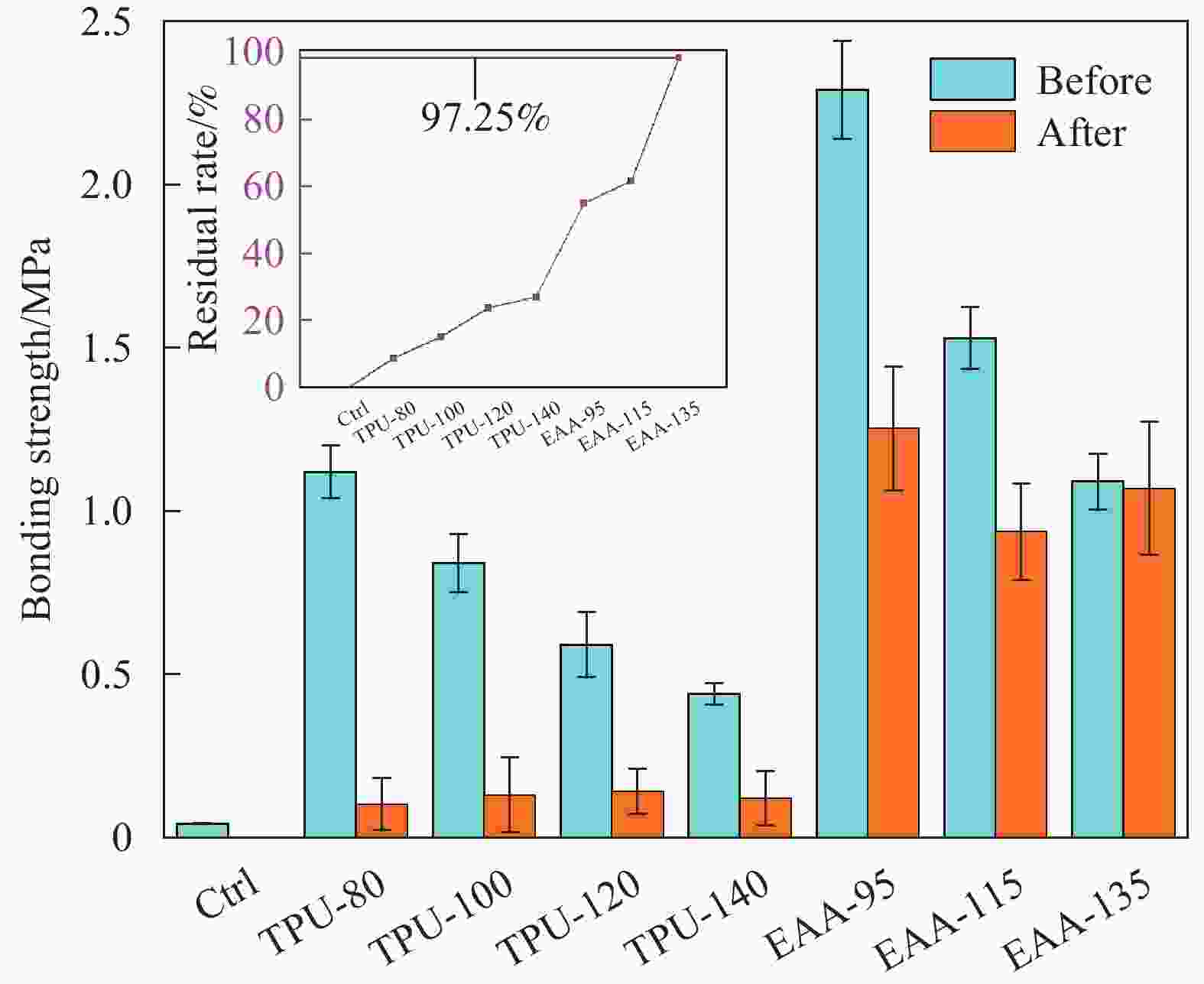
摘要: 针对新型多元共挤出复合材料存在的次表层木塑复合材料(WPCs)与核层实木界面结合强度低,使用过程中易发生界面剥离导致复合材料力学性能和使用寿命降低的问题,本文采用聚氨酯热熔胶胶膜(TPU)和乙烯-丙烯酸共聚物胶膜(EAA)包覆单板层积材(LVL)与塑料/木塑制备了高界面结合强度的多元共挤出复合材料(Co-WPCs-LVL)。研究结果表明:TPU和EAA均能有效提高WPCs层与核层LVL的界面结合强度,界面结合强度随着胶膜熔点的增加而逐渐降低,其中引入TPU (熔点80℃)和EAA (熔点95℃)的WPCs与LVL界面结合强度相对于未处理组分别提高了27倍、56倍。EAA可以显著提升WPCs与LVL的界面耐水性能,Ⅱ类浸渍实验后界面未发生剥离。证明胶膜在高温的挤出作用下能够渗入LVL表面与羟基(—OH)发生反应,同时能与聚乙烯分子链混合扩散形成牢固的界面结合。经过人工加速老化后,胶膜处理组的WPCs与LVL仍具有较高的界面结合强度,界面结合强度剩余率随着熔点的增大而增大,其中EAA(熔点135℃)实验组表现出最好的界面耐久性,界面结合强度剩余率达到97.25%。Abstract: To address the problems of low interfacial bonding strength between sub-surface wood-plastic composites (WPCs) and solid wood in the core layer of new multi-phase co-extruded composites and easy interfacial peeling in the process of use leading to the reduction of the mechanical properties and service life of the composites, this paper adopts a polyurethane hot-melt adhesive film (TPU) and an ethylene acrylic acid copolymer adhesive film (EAA) to wrap veneer laminated lumber (LVL) with plastic/wood-plastic. Multi-co-extruded composites (Co-WPCs-LVL) with high interfacial bond strength were prepared. The results showed that both TPU and EAA could effectively improve the interfacial bonding strength between WPCs layer and core layer LVL, and the interfacial bonding strength decreased gradually with the increase of the melting point of the adhesive film, among which, the interfacial bonding strength between WPCs and LVL introduced with TPU (melting point of 80℃) and EAA (melting point of 95℃) was increased by 27 and 56 times, respectively, relative to that of the untreated group. The EAA could significantly increase the interfacial bonding strength of the water resistance of the interface between WPCs and LVL, and the interface did not peel off after the Type II impregnation experiment. It proves that the adhesive film can penetrate into the surface of LVL and react with hydroxyl group (-OH) under the extrusion at high temperature, and at the same time, it can mix and diffuse with the molecular chain of polyethylene to form a strong interfacial bond. After artificially accelerated aging, the WPCs and LVL in the adhesive film treatment group still had high interfacial bonding strength, and the residual rate of interfacial bonding strength increased with the increase of melting point, among which the experimental group of EAA (melting point of 135℃) showed the best interfacial durability, and the residual rate of interfacial bonding strength reached 97.25%.
-
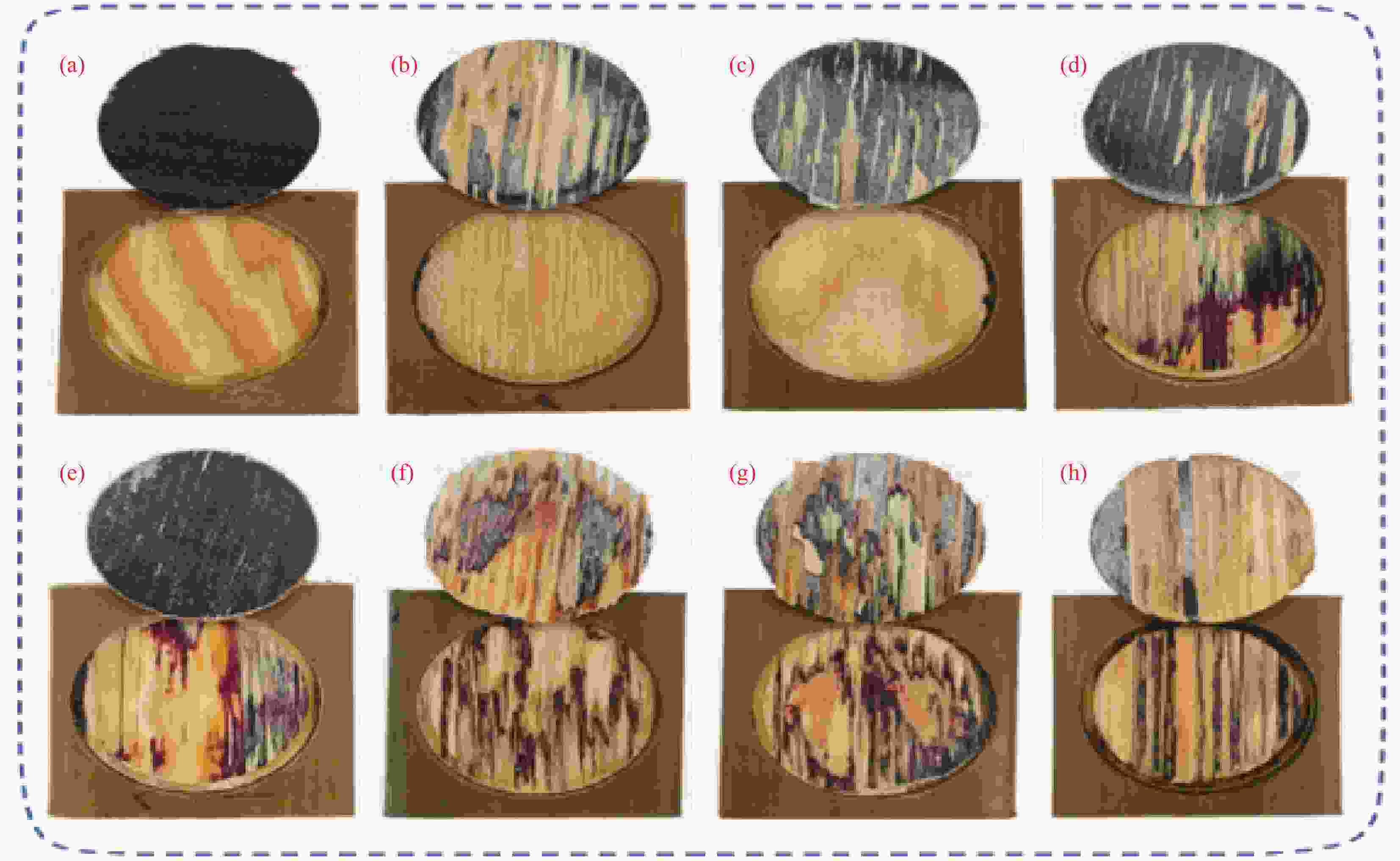
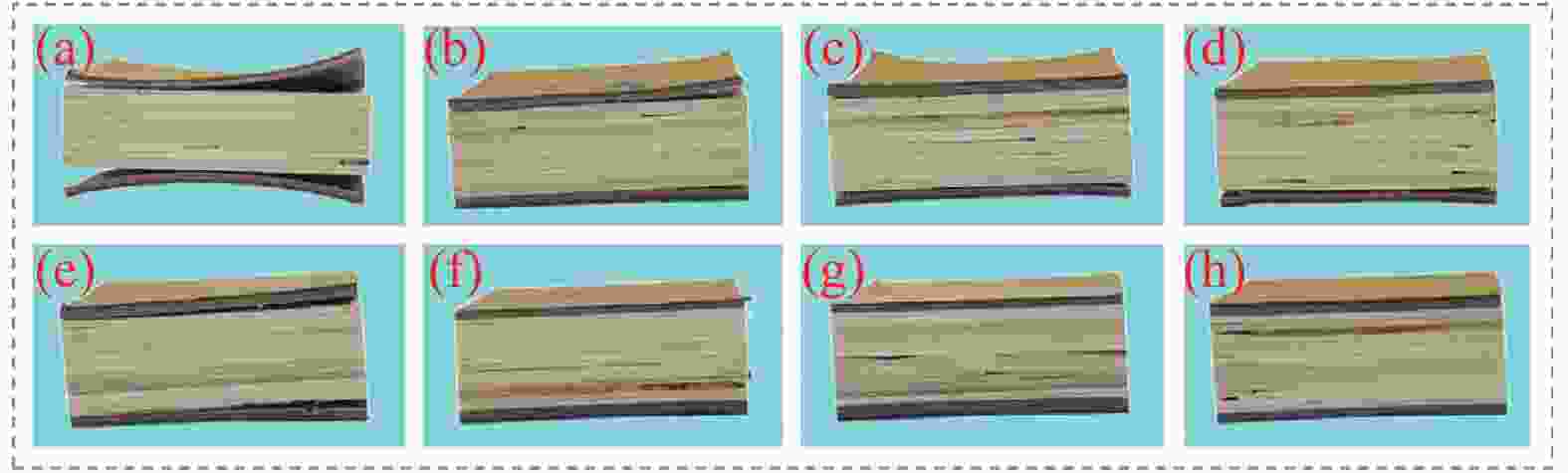
图 4 不同试件WPCs与LVL界面结合强度测试后木破率(a) Control;(b) TPU-80;(c) TPU-100;(d) TPU-120;(e) TPU-140;(f)EAA-95;(g) EAA-115;(h) EAA-135
Figure 4. Wood failure ratio of different specimens after WPCs and LVL interfacial bond strength test (a) Control; (b) TPU-80; (c) TPU-100; (d) TPU-140; (e) TPU-140; (f) EAA-95; (g) EAA-115; (h) EAA-13
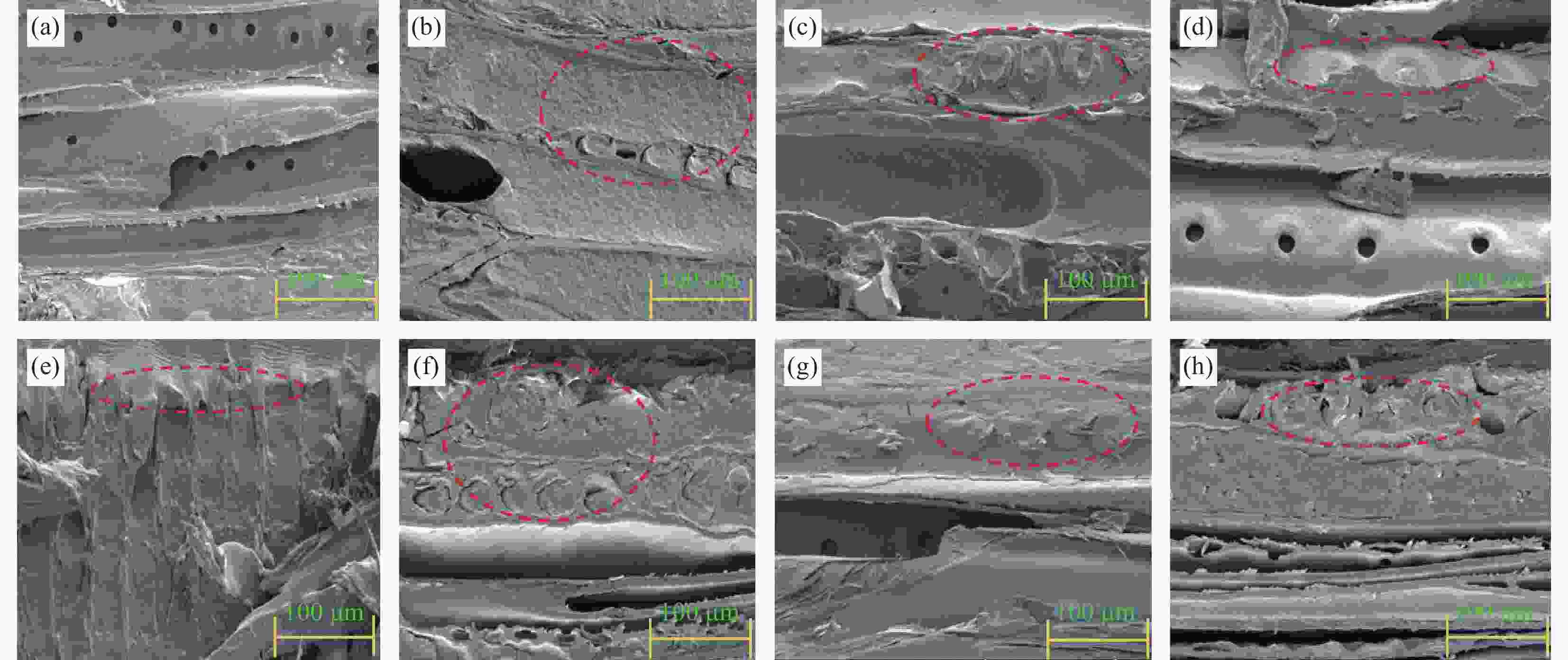
图 8 不同试件的胶膜渗入LVL的截面图像(a) Control;(b) TPU-80;(c) TPU-100;(d) TPU-120;(e) TPU-140;(f) EAA-95;(g) EAA-115;(h) EAA-135
Figure 8. Cross-sectional images of adhesive film infiltrated into LVL for different specimens (a) Control; (b) TPU-80; (c) TPU-100; (d) TPU-120; (e) TPU-140; (f) EAA-95; (g) EAA-115; (h) EAA-135
图 10 不同Co-WPCs-LVL试件Ⅱ类浸渍剥离强度测试表面形貌(a) Control;(b) TPU-80;(c) TPU-100;(d) TPU-120;(e) TPU-140;(f) EAA-95;(g) EAA-115;(h) EAA-135
Figure 10. Surface morphology of different Co-WPCs-LVL specimens tested for peel strength by Type II impregnation (a) Control; (b) TPU-80; (c) TPU-100; (d) TPU-120; (e) TPU-140; (f) EAA-95; (g) EAA-115; (h) EAA-135
表 1 不同Co-WPCs-LVL试件的组成
Table 1. Composition of different Co-WPCs-LVL specimens
Sample Surface layer WPCs layer Adhesive film layer Core layer PE-RT/
wt%SEBS/
wt%Additive/
wt%HDPE/
wt%LDPE/
wt%BF/
wt%Additive/
wt%Type Thickness/mm Melting
Point/℃Solid
WoodCtrl 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 - - - LVL TPU-80 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 TPU 0.08 80 LVL TPU-100 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 TPU 0.08 100 LVL TPU-120 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 TPU 0.08 120 LVL TPU-140 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 TPU 0.08 140 LVL EAA-95 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 EAA 0.08 95 LVL EAA-115 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 EAA 0.08 115 LVL EAA-135 80 10 10 20 5 65 10 EAA 0.08 135 LVL Notes: In the Sample column of the table, WPCs means wood-plastic composites, LVL means laminated veneer lumber, TPU means polyurethane hot melt adhesive film, EAA means ethylene acrylic acid copolymer adhesive film, and the number connected to the back represents the melting point of the adhesive film. For example: TPU-80 means that the LVL surface of Co-WPCs-LVL specimen is covered with polyurethane hot melt adhesive film with a melting point of 80℃. 表 2 不同Co-WPCs-LVL 试样的Ⅱ类浸渍剥离长度
Table 2. Type Ⅱ impregnation peeling length of different Co-WPCs-LVL samples
Sample Ctrl TPU-80 TPU-100 TPU-120 TPU-140 EAA-95 EAA-115 EAA-135 Length of impregnation
and peeling/mm300 256 235 242 238 0 0 0 表 3 不同Co-WPCs-LVL试样的Ⅰ浸渍剥离长度
Table 3. Type Ⅰ impregnation peeling length of different Co-WPCs-LVL samples
Sample EAA-95 EAA-115 EAA-135 Length of impregnation
and peeling/mm300 276 0 -
[1] 王清文, 王伟宏. 木塑复合材料与制品[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 1-4.WANG Qingwen, WANG Weihong. Wood-plastic com-posites and products [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007: 1-4(in Chinese). [2] PICKERING K L, ARUAN EFENDY M G, LE T M. A review of recent developments in natural fibre coposites and their mechanical performance[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 83: 98-112. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.08.038 [3] OMAR Faruk, ANDRZER K , BLEDZKI, HANS-PETER Fink, MOHINI Sain. Biocomposites reinforced with natural fibers: 2000–2010[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2012 37 (11): 1552-1596. [4] HORTAR J, SIMOES F, MATEUS A. Study of wood-plastic composites with reused high density polyethylene and wood swdust[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2017, 12: 1552-1596. [5] PAUL Wambua, JAN Ivens, IGNASS Verpoest. Natural fibres: can they replace glass in fibre reinforced plastics[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2003, 63(9): 1259-1264. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00096-4 [6] 杨兆哲. 麦秸粉/热塑性塑料复合材料的制备及性能研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2014.YANG Zhaozhe. Research of preparation and properties of composites of wheat straw and properties of composites of wheat straw and thermoplastics [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2014 (in Chinese). [7] ROWELL M R. Challenges in biomass-thermoplastic composites[J]. Journal of polymers and the environment, 2007, 15(4): 229-235. doi: 10.1007/s10924-007-0069-0 [8] TURKU I, KARKI T. Research progress Thermoplastic composite materials, in wood-plastic nanocomposites: a review[J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 2014, 27(2): 180-204. [9] 郝笑龙. 基于壳层增强聚乙烯基共挤出木塑性能研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2018.HAO Xiaolong. Study of coextruded wood/HDPE composites with a reinforced shell layer [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2018(in Chinese). [10] TANG W, XU J J, F Q, et al. Rheological behavior and mechanical properties of ultra-high-filled wood fiber/polypropylene composites using waste wood sawdust and recycled polypropylene as raw materials[J]. Constructiona and Building Materials, 2022, 351: 128977. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128977 [11] 郏文博. 意杨LVL正交肋梁箱型楼盖的蠕变性能试验研究 [D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2022.JIA Wenbo. Experimental study on creep behavior of poplar LVL [D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2022(in Chinese). [12] CITRA Yanto Ciki Purba; GUILLAUME Pot; JOFFREY Viguier; JULIEN Ruelle; LOUIS Denaud. The influence of veneer thickness and knot proportion on the mechanical propertie of laminated veneer lumber (LVL) made from secondary quality hardwood[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2019, 77: 393-404. doi: 10.1007/s00107-019-01400-3 [13] SöZEN E, KAYAHAN K, BARDAK T, BARDAK S. The effects of the moisture content of laminated veneer lumber on bending strength and deformation determination via two-dimensional digital image correlation[J]. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci, 2021, 235(21): 5603-5615. doi: 10.1177/0954406220986181 [14] 王清文, 王小玉, 黄浪等. 一种木塑包覆实木复合材料及其制备方法[P], 中国专利, ZL 2014104682601, 2014-12-24.WANG Qingwen, WANG Xiaoyu, HUANG Lang, et al. A wood plastic covered solid wood composite material and its preparation method[P], Chinese patent, ZL 2014104682601, 2014-12-24(in Chinese). [15] 王清文, 朱巍, 王海刚, 等. 木塑实木复合门窗及其制作方法[P], 中国专利, ZL 201310494898, 2013-10-21(in Chinese).WANG Qingwen, ZHU Wei, WANG Haigang, et al. Wood-plastic solid wood composite doors and windows and its production method[P], Chinese patent, ZL 201310494898, 2013- 10-21(in Chinese). [16] BEKIR Cihad Bal. Some physical and mechanical propertiesof reinforced laminated veneer lumber[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 68(IS): 120-126. [17] ZONG G, GONG J, SHI Z, HAO J, YANG X, WANG F. Effect of coupling treatment on interfacial bonding properties of wood veneer/wood flour–polyvinyl chloride composites with sandwich structure. [J] Forests , 2023, 14(11), : 2147. [18] SUN Y, GUO L, LIU Y, et al. Glue wood veneer to wood-fiber-high-density-polyethylene composite[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2019, 351: 128977 [19] NEčASOVÁ B, LIšKA P, KELAR J, ŠLANHOF J. Comparison of adhesive properties of polyurethane adhesive system and wood-plastic composites with different polymers after mechanical, chemical and physical surface treatment[J]. Polymers, 2019, 11: 397. doi: 10.3390/polym11030397 [20] ZONG G, ZHOU J, ZHANG M, MA Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Effect of mortise and tenon structure on the properties of wood flour polyvinyl-laminated veneer lumber co-extruded composites[J]. Polymers 2023, 15(9): 2151. [21] 宗广功. 杨木LVL-PVC木塑核-壳共挤复合材料制备与性能研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019.ZONG Guanggong. Preparation and properties of co-extruded lumber-wood flour polyvinyl chloride composites with core-shell structure [D]. Harbin: Forestry University, 2019(in Chinese). [22] LIU Y , LI X, WANG W, et al. Decorated wood fiber/high density polyethylene composites with thermoplastic film as adhesives[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2019, 95: 102391. [23] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法: GB/T 17657-2013[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Test methods of evaluating the properties of woodbased panels and surface decorated wood-based panels: GB/T 17657-2013 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2013(in Chinese). [24] 刘一楠. 单板贴面木塑板材制备技术及粘合机制研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022.LIU Yinan. Preparation technology and mechanism of laminating wood veneer with wood plastic composites [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2022(in Chinese). [25] KHAN F, AHMED W, NAJMI A. Understanding consumers’ behavior intentions towards dealing with the plastic waste: perspective of a devel-oping country[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2019, 142: 49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.11.020 [26] ZHOU X, SHEN T, SUN Y, et al. Improve the bonding between wood veneer and wood fiber/high-density polyethylene composite board for decoration[J]. Polymer Composites, 2022, 43(4): 2163-2174. doi: 10.1002/pc.26529 [27] 孙亚楠. 薄木饰面WF/HDPE复合材料制备技术与胶合机制研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2022.SUN Yanan. Study on the preparation and adhesion mechanism of wood veneer decorated WF/HDPE composites [D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2022(in Chinese). [28] 周雪莲, 郝硕, 单伟东等. 织物装饰木塑板的制备工艺及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41: 1-11.ZHOU Xuelian, HAO Shuo, SHAN Weidong, et al. Preparation and performance of fabric decorative wood plastic composites. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica. 2024, 41: 1-11(in Chinese). [29] 唐伟. 轻质高强耐候木塑木材多元复合材料共挤成型与性能研究 [D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2023.TANG Wei. Preparation and properties study of light- high-strength and weather-resistant WPC/wood multiple co-extruded composite [D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University 2023 (in Chinese). -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 121
- HTML全文浏览量: 70
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: