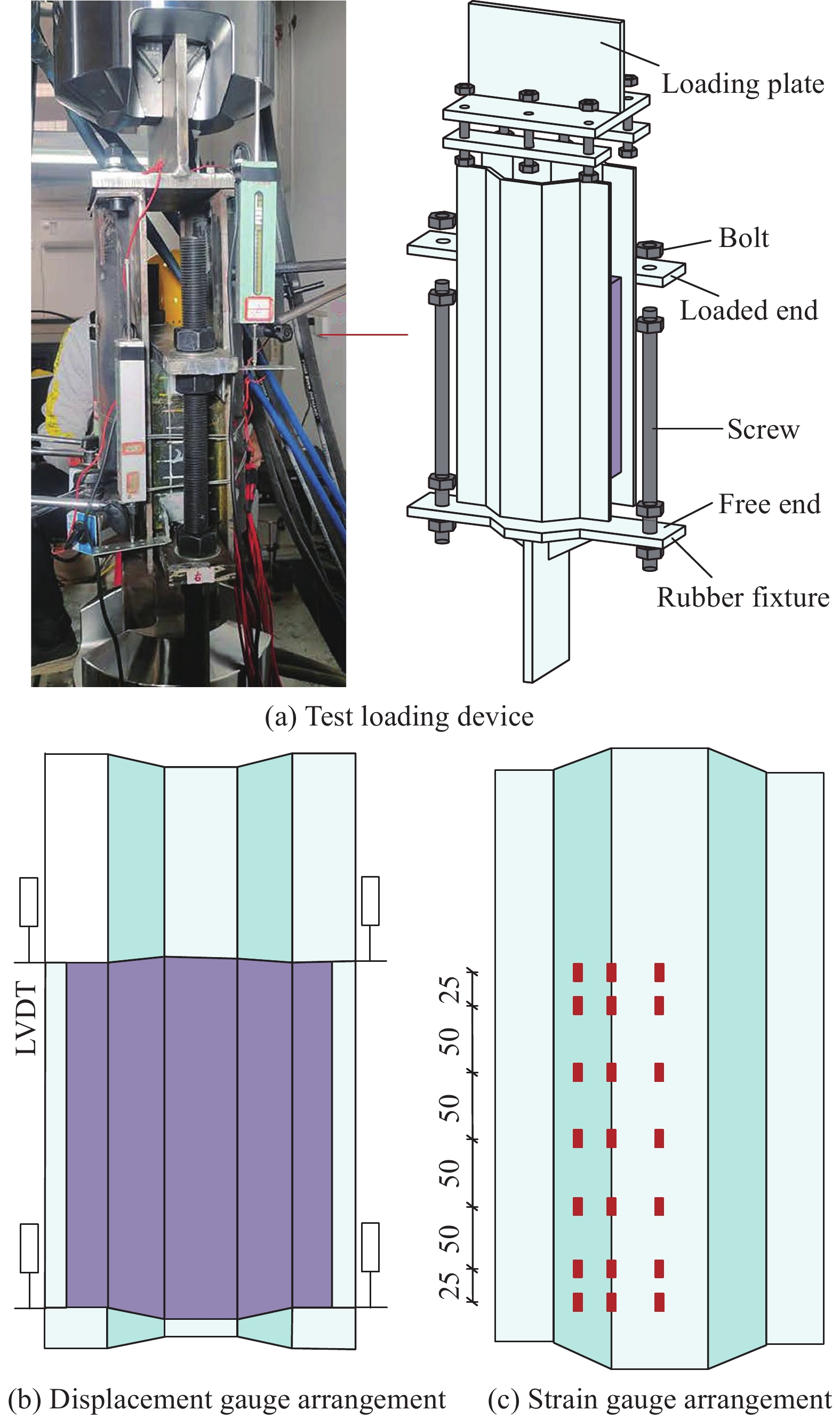
Bond-slip properties of corrugated steel plate-rubber interface
-
摘要:
波形钢板-橡胶构件因波形钢板的几何形状优势,表现出良好的抗震性能,对其界面黏结滑移性能有待研究。考虑波形钢板与橡胶界面的黏结长度、粗糙度和试件的加载方式对两者界面性能的影响,设计了6个波形钢板-橡胶试件进行往复加载试验,根据黏结破坏过程、界面耗能、应变分布和影响因素分析试件的黏结性能。结果表明:波形钢板-橡胶界面受往复荷载作用时,黏结破坏依次经历微滑移、滑移、破坏、曲线下降和残余阶段;从能量角度分析发现:黏结长度的长短显著影响界面耗能;合理控制粗糙度,可改善试件界面耗能,提高界面黏结性能;波形钢板-橡胶构件在荷载较大时,应变发生突变且波脊处影响最大;与单调加载相比,往复加载下试件的残余黏结滑移降低29%;波形钢板-橡胶试件的极限特征黏结强度随黏结长度和粗糙度的增大呈现出先增加后逐步减弱;最后确定了波形钢板与橡胶构件的特征黏结强度计算公式,并进行了计算值与试验值的比较,其吻合度较好。
-
关键词:
- 波形钢板-橡胶 /
- 往复加载试验 /
- 黏结滑移性能 /
- 应变分布分析 /
- 特征黏结强度计算公式
Abstract:Due to the geometric advantages of corrugated steel plates, corrugated steel plates-rubber members exhibit good seismic performance. The bond-slip property of their interface requires investigation. To study the interface properties of corrugated steel plate and rubber, 6 specimens were designed for reciprocal loading tests, considering bonding length, roughness, and loading mode effects. Analysis of the specimens' bonding properties involve examining bonding failure processes, interfacial energy dissipation, strain distribution and influencing factors. Results indicate that under reciprocal loads, bonding failure progresses through microslip, slip, failure, curve decline and residual stages. Energy analysis reveals that the bond length's magnitude significantly affects the interfacial energy dissipation. Reasonable control of roughness can improve the specimen interfacial energy dissipation and improve the interfacial bonding performance. High loads on corrugated steel plates and rubber members cause abrupt strain changes, with the wave ridge experiencing the most significant impact. Residual bond slip under reciprocal loading is 29% lower than under monotone loading. The ultimate characteristic bond strength of the corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens shows an increase and then a gradual decrease with the increase of bond length and roughness; Formulas for calculating characteristic bond strength for these members are established, with calculated values compared to experimental results showing a good coincidence.
-
碳量子点(CDs)是小于10 nm的准球形碳纳米颗粒[1]。CDs具有与半导体量子点相当的光致发光性能,而CDs在低毒、环境友好、低成本、合成路线选择广泛和易于表面功能化等方面优于其他量子点[2-4]。各种基于CDs的纳米复合材料,包括碳纳米点、碳量子点、石墨烯量子点和其他元素掺杂的CDs,已经被开发出来并广泛应用于生物传感、光催化、治疗诊断和生物医学应用[5-8]。
CDs的合成方法包括自上而下和自下而上两种[9]。自上而下的方法是指石墨[10-11]、碳纳米管[1, 12]、碳烟[13]和活性炭[14]等块状碳材料通过电弧放电、激光灼蚀、化学氧化和电化学氧化等方式进行断裂。自下而上的方法是通过水热、微波和焙烧等方法,从柠檬酸盐[15]、碳水化合物[16]和不同的生物质(豆奶、草等)[17]等分子前体中产生CDs。由于原料和加工方法的不同,CDs由非晶态到纳米晶核和各种表面官能团组成[18]。CDs的制备一般涉及氧化,因此引入了大量的含氧基团,如羧基、羰基和羟基[18]。含氧官能团主要存在于CDs的表面上,从而导致其水溶性[19]。CDs上的官能团也会导致溶解性,在水或极性有机溶剂中形成稳定的胶体,这比在普通溶剂中溶解度低的石墨烯量子点(GQD)更有优势[20]。表面基团也会赋予CDs的荧光特性[21]。
CDs的主要组成元素为C、H、O。此外,在CDs中掺杂金属或杂原子,如Fe[22]、N[23]和S[24],已成为改善CDs性能的有效方法,尤其是N掺杂CDs (N-CDs)受到了广泛的关注。金属或杂原子的掺杂可以通过稳定CDs中的电子排布,有效地去除活化表面活性位点,提高荧光性能和量子产率,改进表面缺陷[25]。表面缺陷可以消除或抑制原来的零能级的状态并促进辐射复合[26]。自2012年首次报道N掺杂量子点以来,越来越多的金属或杂原子被用来调节碳量子点的性质,通过调整其组成和结构,或者诱导多环芳烃结构形成新的表面态来增强荧光[27-29]。在以往报道的基于金属或杂原子掺杂碳量子点,一般分为3种:(1)无金属掺杂的碳点;(2)金属元素掺杂的碳点;(3)金属和非金属共掺杂的碳点。本文对以上3个方面的制备方法和相应的应用进行了研究与总结。
1. 杂原子掺杂的碳点
1.1 N掺杂的碳点
N是CDs掺杂中最常用的元素之一。N可以有效地改变CDs的发光性质,增强光致发光量子产率(PLQYs)[30],因其大小与C相似,N也有5个价电子,可以与C原子形成共价键[31]。此外,N较高的电子亲和力和电负性也能增强CDs的化学反应性。掺杂N的来源十分广泛天然生物质(草、果皮、花粉等)和小分子(氨基酸、乙二胺等)都可以作为制备碳点的原材料[32]。
Wang等[33]开发了一种无金属掺杂的人工纳米酶,是由氮掺杂碳纳米点(N-CNDs),通过茶多酚的抑菌能力和光触发氧化酶催化活性,协同有效地抑制细菌存活(图1)。N-CNDs 的制备过程:以乙二胺为氮源,茶多酚为碳源,采用水热法一步法合成N-CNDs。首先将0.10 g茶多酚和100 μL乙二胺溶解在10 mL超纯水中,并将混合物超声处理10 min。然后将获得的溶液转移到反压釜中,并在200℃下加热10 h。再自然冷却至室温后,获得深红色悬浮液(粗产物)。将粗产物以
8000 r/min离心10 min,然后在透析袋(100~500 Da)中透析12 h。除去溶剂,在真空冷冻干燥机中进一步冷冻干燥后,将纯化的N-CNDs分散在超纯水中供进一步使用。N-CNDs 在光下表现出优异的氧化酶模拟活性,这是由超氧自由基(•O−2)介导的,具有较高的最大反应速度Vmax (1.59 μmol/s)和较低的米氏常数Km (0.421 mmol/L)。此外,所构建的基于N-CNDs的纳米酶被证明可以作为复杂的生物材料平台,通过光驱动的氧分子产生•O−2来实现高效灭菌。值得注意的是,N-CDs 固有的抗菌能力可以有效抑制革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌,特别是对革兰氏阳性金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制浓度(MIC90)为375 μg/mL。N-CNDs单独对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的灭活率分别为59.72%和37.15%。然而,N-CDs在光作用下对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的灭活率分别高达97.91%和80.02%。Li等[34]通过热解含有葡萄糖的ZIF-8前驱体(G@ZIF-8),成功获得了氮掺杂碳(CDs@NC)中的碳点(图2)。CDs@NC的制备过程:(1) ZIF-8的制备:在含有2-甲基咪唑(2-MeIM)的甲醇(MeOH)溶液中加入ZnNO3·6H2O,将其搅拌,之后在室温静置并离心分离。最后在60℃下隔夜真空干燥,得到了ZIF-8粉末;(2) G@ZIF-8的合成:将ZIF-8粉末溶解在葡萄糖溶液中,搅拌并离心,最后在60℃下真空干燥;(3) CDs@ZIF-8的合成:G@ZIF-8粉末放入管式炉中,加热到200℃,维持3 h,冷却到室温后,得到了CDs@ZIF-8;(4) CDs@NC的合成:将CDs@ZIF-8粉末转移到管式炉中,从室温加热到900℃,保温3 h,冷却至室温后,得到了CDs@NC。通过X射线光电子能谱(XPS)分析可知,CDs@NC的元素组成是C、N和O。对于Zn,文章中仅限于ZIF-8的制备中有提到。CDs@NC 可以很容易地充当类过氧化物酶的纳米酶,用比色检测与早期胃癌相关的D-氨基酸。有趣的是,CDs@NC 的类过氧化物酶活性可以通过调整葡萄糖前体的含量来轻松调节。通过对催化机制的进一步研究,超氧自由基(•O−2)可能是参与过氧化物酶类催化反应的关键活性氧(ROS)。唾液测试的结果表明,比色法可用于快速区分早期胃癌患者与健康人群。
Liu等[35]通过在没有任何溶剂的情况下直接加热葡萄糖和双氰胺(DCDA)的混合物,可以轻松合成氮掺杂的CDs (N-CDs) (图3)。N-CDs的制备过程:N-CDs通过吹糖方法制备。将1.0 g葡萄糖和0.75 g DCDA加入到烧杯中,之后转移到烘箱中并在180℃下加热20 min。自然冷却至室温后,将固体产物加入500 mL水中,然后超声处理10 min。然后,借助35 µm的微孔滤膜,通过真空过滤去除大粒径碳材料,得到N-CDs分散体。通过旋转蒸发除去N-CDs分散体中的水,然后冷冻干燥处理,获得N-CDs固体样品。N-CDs的形成归因于糖和发泡剂在加热下发生独特的化学反应,其中糖聚合成小颗粒的纳米粒子,而氮原子来自于原位掺杂到碳基质中的发泡剂的分解。作为引发糖发泡过程的典型发泡剂,DCDA也可作为N-CDs的理想氮掺杂剂。引入Hg2+后,观察到N-CDs分散体在441 nm处出现显着的荧光猝灭。因此,合成的N-CDs 可作为检测Hg2+的高灵敏度荧光探针,具有50 nmol/L的低检出限和良好的选择性。
Madrid等[36]利用液体前驱体激光热解的精确控制来获得未掺杂和N掺杂的CDs (图4)。N-CDs的合成:通过甲苯和吡啶的激光热解合成了N-CDs。甲苯或吡啶从装有调节启闭阀的密封容器进入反应室。用30 cm3/min的六氟化硫(SF6)敏化红外激光,用130 cm3/min的Ar作为载气穿过有机前驱体储集层。放置一台二氧化碳激光器(λ=10.6 µm),以90°配置与反应物流相互作用。制备的纳米颗粒被直接收集在含有三乙甘醇(TREG)的液体捕捉器中。激光实验时间为6 h。将含有碳点的悬浮液离心并用乙醇洗涤以去除多余的TREG (15℃,
15000 r/min,30 min)。这种合成策略能够用轻元素(即 N、S、F)对生成的碳纳米结构进行受控掺杂,以调整其光致发光(PL)特性。并将这些CDs组装到 P25纳米颗粒上,并测试它们对葡萄糖的光催化转化、羟基自由基的产生,以及使用近红外 (NIR)光远程刺激治疗胶质母细胞瘤细胞 (U251-MG)的细胞内光催化测试。CDs具有成本低、导电性高、易改性、合成简单、电子转移快、比表面积大等优点,是电催化剂材料的潜在候选者[37]。需要注意的是,掺杂在CDs上的杂原子可以通过引入理想的活性位点来进一步增强光催化性能[38]。最近,许多课题组讨论使用CDs进行光催化和电催化。Wu等[39]制备了Cu-N掺杂CDs (Cu, N-CDs),并研究了掺杂促进的电子转移和光氧化反应中的CDs性能。Li等[40]提出了碱辅助电化学法制备水溶性CDs的方法,制备的CDs具有明显的上转换光致发光。Wu等[41]制备了限制在碳点(Zn, Cu-CDs)中的不饱和Zn和Cu掺杂剂的协同作用,以在掺杂的CDs中产生增强的电子转移和光氧化过程,Zn/Cu主要通过Cu-O(N)-Zn-O(N)-Cu配合物与碳基体进行螯合。Alhashimi等[42]使用牛奶作为前体,通过一锅溶剂热合成法制备氮掺杂碳点(N-CDs),并将其直接用作内滤效应(IFE)中的荧光团(图5)。N-CDs的合成过程:将1.0 mL牛奶与10.0 mL超纯水混合并搅拌10 min,然后放置于25.0 mL反应釜中。然后将混合物在180℃下加热4 h。冷却至室温后,将所得溶液用0.22 μm滤膜过滤以除去大颗粒,然后以
12000 r/min离心15 min。最后,以三氯甲烷为有机溶剂,采用溶剂萃取法进行进一步纯化。将含有绿色碳点的上层分离,用透析膜(1000 MWCO)进一步纯化并在室温下储存。通过常见的光谱和显微技术对制备的N-CDs进行了表征。N-CDs表现出与激发波长相关联的发射,荧光量子产率为10%。 N-CDs的荧光随着吸收剂(四环素)的添加而降低,这是由于荧光团(N-CDs)的激发光谱与吸收剂的吸收光谱相匹配。目前基于IFE的传感平台在2.0 mmol/L至200.0 mmol/L范围内表现出良好的线性关系(R2 =0.9960 ),并且其检测限为0.6 mmol/L。Wu等[43] 以1, 5-二氨基萘和DL-天冬氨酸为氮源,N-乙酰基-L-半胱氨酸为硫源,采用一步水热法直接合成N,S共掺杂的CDs(N, S-CDs) (图6)。与仅掺杂N元素的CDs相比,S的引入有效地改善了CDs的结构和荧光性能,光致发光光谱也发生较大的红移,从原来的蓝光发射到黄光发射,发射峰从430 nm红移到545 nm。N-CDs和N, S-CDs的合成:将1 mmol 1, 5-二氨基萘、1 mmol 天冬氨酸和1 mmol N-乙酰基-L-半胱氨酸溶解在10 mL去离子水中。然后将混合溶液超声处理10 min,使其完全溶解,然后将混合物转移到25 mL 反应釜的中。180℃下加热5 h。冷却至室温。对于N-CDs的合成,除了不添加S源之外,实验条件与N, S-CDs的合成过程完全相同。随后,首先使用孔径为0.22 μm的聚碳酸酯膜过滤器过滤纯化N, S-CDs,以去除杂质。最后,使用分子量为500 Da的透析管再次透析溶液24 h。其他科研团队也开发了这种有颜色的荧光碳量子点,例如,Wang等[44]以1, 1'-联萘-2, 2'-二胺(BNDM)和柠檬酸为碳源,通过一锅溶剂水热法制备了一种红色发光碳点(BNCDs);Dai等[45]基于包裹有分子印迹层的蓝色发射碳点(B-CDs@MIPs),提供响应信号,而红色发射碳点(R-CDs)作为内部参考,传感器的荧光信号比随着噻虫嗪(TMX)浓度的增加而增加,导致荧光颜色从红色到蓝色发生明显的变化;Zhong等[46]设计了发红光的碳点作为荧光探针,基于内滤效应(IFE)测定人血清中米托蒽醌(MITX)抗癌药物,该方法已成功应用于人血清样品中MITX的测定,显示出操作性好、成本低、准确度高等优点。
1.2 P掺杂的碳点
相较于N原子,P具有更大的原子半径,形成的C—P键长(0.177 nm)也明显比C—N键长(0.141 nm)更长,P原子的掺入会给碳材料结构带来更大的结构形变。就电负性而言,N(3.04)的电负性比C(2.55)大,而P(2.19)的电负性又比C小,因此C—P键的极性与C—N键的极性相反,这意味着磷掺杂碳点(P-CDs)可以产生更多的缺陷位以及不同于氮掺杂的新的活性位点[47]。
按照磷源引入的方式,可以将磷掺杂碳材料的合成方法分为原位合成法以及后处理合成法两大类。原位合成磷掺杂碳材料一般将磷源和前驱体碳源直接混合和均匀分散,在合适条件下进行高温处理使前驱体在碳化过程中同时实现磷元素的掺入[48]。从材料制备来看,无论是后处理还是原位处理,磷源一般有三苯基磷、磷酸、磷酸二氢钠、植酸以及含磷的离子液体等。碳源的选择则多种多样,除了含碳的化合物以外,生物质、活性炭、碳纳米管以及氧化石墨烯等多孔的碳材料均可以作为碳源。这些碳源和磷源通常都需要在合适的气氛下进行高温处理以获得磷掺杂碳材料[48]。
Jiang等[49]采用一锅法水热合成了具有良好光响应性的间氨基苯酚基磷酸掺杂碳点(P-CDs),并将其用于高效抑菌(图7)。P-CDs表现出光响应氧化酶样活性,这可能归因于P掺杂赋予了其更高的结晶度。有趣的是,这些P-CDs在光催化下产生的超氧自由基(•O−2)表现出优异的抗菌效果,最大反应速率为33.3×108 mol/s。结果表明,在1 W白色LED照射下,P-CDs对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌均有较好的抑制作用,对革兰氏阳性金黄色葡萄球菌具有良好的抗菌活性。平板计数实验结果表明,75 μg/mL P-CDs在光照60 min时对大肠杆菌的杀灭率为98%,而50 μg/mL P-CDs在相同光照时间下对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制率高达100%。针对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌活性,Tang等[50]开发了一种纳米试剂,是由荧光硅纳米颗粒(SiNPs)与葡萄糖聚合物并负载氯e6 (Ce6),通过一种依赖于三磷酸腺苷结合盒(ABC)转运蛋白途径的机制迅速内化到革兰氏阴性和革兰氏阳性细菌中。在660 nm照射下,纳米制剂对金黄色葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌的体内光动力抗菌效率分别为98%和96%。
Kalaiyarasan等[51]利用柠檬酸三钠(TSC)和磷酸通过水热法合成的磷掺杂碳量子点(P-CDs)的合成(图8)。P-CDs的形成过程:磷原子通过脱水反应与TSC分子的碳和氧原子共价结合,并在水热处理的碳化过程之前形成聚合物样结构,在完成碳化/芳构化之后,形成P-CDs。故Na不存在于CDs中。之后通过控制前驱体的浓度、反应时间和温度,探究了磷掺杂对光学特性和P-CDs形成的影响。在310/440 nm的激发/发射波长下P-CDs的荧光量子产率为16.1%。此外,P-CDs的光学和结构特性是通过各种光谱和显微技术来确定的。由于荧光非活性复合物(P-CDs-Fe3+)的形成,在P-CDs中添加Fe3+后,荧光发生静态猝灭。因此,这种化学反应导致了一种用于检测Fe3+的新荧光测定法的开发。检测Fe3+的检出限为9.5 nmol/L,线性拟合范围为20 μmol/L至3.0 μmol/L (R2=0.99)。
Momer等[52]采用一锅低温溶剂水热法,以乳糖和磷酸为原料,制备了尺寸约为3 nm 的高度钝化的P-CDs (图9)。P-CDs的制备过程:将3.0 g乳糖溶解在15 mL H3PO4中,然后将溶液在水浴中加热20~30 min,直到颜色从无色变为浅黄色、深黄色然后深棕色。将黑色溶液用1.0 mol/L 的NaOH稀释,并将pH调节至3~4,将溶液放置24 h。将溶液以
14000 r/min离心20 min以除去较大颗粒。水溶液中的P-CDs用氯仿提取和纯化(第一步纯化)。然后缓慢加热溶液以蒸发氯仿,留下P-CDS,随后将其溶解在水中,然后使用1000 MWCO透析膜,透析24 h (第二步纯化)。得到了透明的淡黄色P-CDs溶液。蓝移的程度和荧光增强的强度取决于金属离子和实际pH值。例如,P-CDs与Al3+的配合物的荧光会转移到较短的波长,并且荧光量子产率在490 nm处从 12%提高到近62%。Zn2+和Cd2+离子也会增强和移动荧光。P-CDs的荧光可被Fe2+、Fe3+、Hg2+、Cu2+ 和 Sn2+等离子猝灭。这种荧光猝灭归因于金属离子与P-CDs的钝化表面官能团(主要是磷的官能团)的螯合。无磷掺杂的CDs和低钝化P-CDs没有发生荧光猝灭。金属离子可增强了荧光猝灭的发生,可利用荧光强度来检测这些离子。Al3+的检测限为4 μmol/L,Zn2+的检测限为100 μmol/L。对加标药物制剂中的这两种离子进行了定量。回收率通常为102%。1.3 B、S掺杂的碳点
在众多掺杂剂中,B被有效掺杂的原因如下:第一,B在元素周期表中与C相邻,原子半径与碳相似;因此,在结构和理化性质上具有相似性,因此掺杂硼可以改善CDs的缺陷,改善光学性能[53]。其次,与N和S等掺杂元素不同,B的电负性低于碳,将硼原子掺杂到CDs中会导致碳原子周围呈正电荷分布[54]。
元素S作为CDs的常用掺杂元素之一。元素S和C的电负性相似,因此也能有效地与碳原子形成共价键[31]。S能够在CDs 表面增加更多缺陷,从而进一步提升碳点的发光效率[32]。
Ozkasapoglu等[53]以苯基硼酸(PBA)和谷氨酰胺(GLU)分别作为硼源和碳源,通过水热法制备了具有高荧光产率的硼掺杂碳纳米点(B-CDs)(图10)。B-CDs的合成过程:将0.25 g的PBA和GLU加入到反应釜中,并加入25.0 mL 1.0 mol/L的H2SO4。然后,将反应釜转移到烘箱中,在3种不同的温度(190、230和270℃)下加热2 h。冷却至室温后,用0.22 μm滤纸过滤B-CDs溶液。用Na2CO3将pH值调节为7.0~7.2。将B-CDs溶液在
14000 r/min的条件下离心30 min,以沉淀大颗粒。最后,用透析管(MWCO 2000)纯化溶液6 h,每2 h换水一次。将纯化后的溶液一部分保存在4℃下,另一部分使用冷冻干燥机制成粉末进行表征。通过FTIR光谱可知,硼原子与谷氨酰胺中的—NH共价结合,形成B-NH。首先,研究了温度对其荧光产率和B-CDs结构特征的影响。其次,检查了细胞毒性以及细胞死亡和增殖。通过MTT测定评估细胞毒性。间接免疫过氧化物酶技术后,通过caspase 3、Ki67、核纤层蛋白B1、P16和细胞色素C的分布来评估细胞特性。MTT测定后,采用1∶1稀释法,反应24 h。经过免疫组织化学分析,在230℃下合成的B-CDs并没有改变对照细胞的增殖,也没有触发细胞凋亡。Colo 320 CD133+和CD133−细胞诱导的细胞凋亡和细胞衰老是与合成温度有关。此外,Colo 320 CD133−细胞受B-CDs的影响较大。B-CDs控制或消除肿瘤组织中的肿瘤干细胞。Jia等[55]以苯基硼酸(PBA)为原料,采用一步水热法合成了硼掺杂碳量子点(B-CDs) (图11)。B-CDs的制备过程:将0.2 g PBA溶于20 mL的超纯水中,并在45℃下水浴搅拌。然后将溶液转移到50 mL反应釜中,加热到200℃,10 h,然后冷却到室温,溶液为淡黄色。溶液在
7060 g下离心15 min。上清液用0.22 μm的聚丙烯滤膜过滤除去大颗粒,然后用孔径为100 Da的透析管在超纯水中纯化48 h,除去未反应的反应物。最后,将含有B-CDs的溶液在真空干燥炉中干燥72 h,并将固体储存起来供进一步使用。利用B-CDs测定PS/VB12,并详细研究了B-CDs与PS/VB12的猝灭机制,对B-CDs的合成条件进行了优化。B-CDs的平均尺寸约为3.3 nm,激发/发射波长为247/323 nm,量子产率为12%。实验结果表明,B-CDs是山梨酸酯(PS)和维生素B12 (VB12)的可行荧光探针。B-CDs的荧光(FL)在PS或VB12存在下被猝灭,主要的原因是内滤效应(IFE),但不能排除B-CDs(作为供体)向PS/VB12(作为受体)的荧光共振能量转移(FRET)。该探针可以通过荧光法检测PS,在0.20~24 μmol/L浓度范围内具有线性响应,检测限为6.1 μmol/L。对于VB12,检出限为0.20~30 μmol/L和8.0 μmol/L。Othman等[56]以3-噻吩基硼酸作为原料,采用一步水热法合成了硼酸功能化的硫掺杂碳纳米点(B, S-CDs) (图12)。选择3-噻吩基硼酸作为前驱体,是由于它与π-电子云层富碳点核的配位能力很强。B, S-CDs的制备过程:将1.6.0 g 3-硫代二苯基硼酸溶解在20.0 mL去离子水中,然后搅拌30 min。将制备的溶液转移至反应釜中,加热至(180±3)℃持续6 h,然后冷却至室温。将含有B, S-CDs的溶液以
10000 r/min离心20 min,然后通过0.22 µm滤膜过滤。将所得上清液在透析袋中透析24 h。将纯化的B, S-CDs储存在4℃下以供进一步使用。由于硼酸和葡萄糖的顺式二醇基团之间的相互作用,S掺杂CDs用硼酸官能化后产生了更多具有较强选择性的葡萄糖传感发射点。B, S-CDs非常灵敏,可以将葡萄糖与其类似物以及其他潜在的唾液干扰物完全区分开来。2. 金属掺杂的碳点
2.1 Fe掺杂的碳点
Pan等[57]设计了一种新颖的壳聚糖(Chitosan,CS)接枝铁掺杂碳点(CS@Fe/CDs) (图13),通过选择性激活芬顿反应触发的过氧化物酶样催化活性来对抗刚性细菌生物膜以及壳聚糖的协同抗菌活性。CS@Fe/CDs的制备过程:将0.05 g CS、0.05 g柠檬酸、0.13 g FeSO4·7H2O和100 μL乙二胺加入含1%体积比(v/v) HAc的5 mL去离子水中。超声30 min后,迅速转移到反应釜中,在180℃下加热6 h。之后,将反应物自然冷却至室温,并以
12000 r/min离心10 min。取出上清液并通过0.22 µm滤膜以去除杂质。然后将所得产物在透析袋中透析24 h,每6 h换一次水。将纯化的CS@Fe/CDs在冷冻真空干燥器中冻干,并在4℃冰箱中避光储存。一方面,CS@Fe/CDs具有类过氧化物酶活性,可以催化H2O2产生羟基自由基(•OH),从而有效切割细胞外DNA(eDNA)。另一方面,CS能够通过静电相互作用与带负电的细胞膜结合,改变细胞膜的通透性并导致细菌生物膜内的细胞死亡。![]() 图 13 壳聚糖(CS)@Fe/CDs 纳米酶的合成:(a) CS@Fe/CDs纳米酶的一锅水热法合成示意图;(b) CS@Fe/CDs纳米酶对细菌的类过氧化物酶催化活性示意图;(c)基于CS@Fe/CDs的纳米酶消除细菌生物膜的示意图[57]Figure 13. Synthesis of chitosan (CS)@Fe/CDs nanozyme: (a) Schematic diagram of one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of CS@Fe/CDs nanozyme; (b) Schematic diagram of peroxide-like catalytic activity of CS@Fe/CDs nanozyme against bacteria; (c) Schematic diagram of bacterial biofilm elimination by nanozyme based on CS@Fe/CDs[57]eDNA—Extracellular DNA; hv—Lighting condition
图 13 壳聚糖(CS)@Fe/CDs 纳米酶的合成:(a) CS@Fe/CDs纳米酶的一锅水热法合成示意图;(b) CS@Fe/CDs纳米酶对细菌的类过氧化物酶催化活性示意图;(c)基于CS@Fe/CDs的纳米酶消除细菌生物膜的示意图[57]Figure 13. Synthesis of chitosan (CS)@Fe/CDs nanozyme: (a) Schematic diagram of one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of CS@Fe/CDs nanozyme; (b) Schematic diagram of peroxide-like catalytic activity of CS@Fe/CDs nanozyme against bacteria; (c) Schematic diagram of bacterial biofilm elimination by nanozyme based on CS@Fe/CDs[57]eDNA—Extracellular DNA; hv—Lighting conditionMa等[58]开发了由铁掺杂碳点(Fe-CDs)和金属有机骨架(Metal organic framework-808,MOF-808)组成的纳米反应器(图14),用于选择性降解以及对氧磷和对硫磷的灵敏检测。由于其优异的有机磷水解酶活性,选择MOF-808作为宿主并用于快速降解对氧磷。 Fe-CDs作为客体分子被切断,不仅可以用于光催化降解对硫磷,还可以用于传感检测有机磷农药(OPs)。通过主客体相互作用,合成了Fe-CDs/MOF-808和 Fe-CDs@MOF-808,分别用于级联降解和对氧磷和对硫磷的检测。对氧磷和对硫磷分别通过Fe-CDs/MOF-808和Fe-CDs@MOF-808的催化水解和光催化降解进行解毒。同时,纳米复合材料的荧光通过OPs降解产物4-硝基苯酚的内部过滤效应而被猝灭。Fe-CDs/MOF-808具有较宽的线性范围,可检测对氧磷(0.001~360 μmol/L),检出限(LOD)低至 0.3 μmol/L。Fe-CDs@MOF-808 对硫磷的线性范围为0.01~100 μmol/L,LOD 约为3.3 μmol/L。
Liu等[59]通过简单的一锅热解法开发了具有优异光热转换和光增强酶样特性的铁掺杂碳点纳米酶(Fe-CDs),用于抗菌治疗和伤口愈合(图15)。Fe-CDs的制备:将2 g乙二胺四乙酸铁钠(NaFeEDTA)放到管式炉中,350℃下以5℃/min的加热速率热解2 h。热解后,加入150 mL超纯水溶解产物。将悬浮液用超声处理15 min。之后,高速搅拌(
11000 r/min) 20 min以除去不溶的铁盐和钠盐之后,可以获得澄清的棕色溶液。此后,使用0.22 μm膜滤器过滤上层棕色溶液以除去碳碎片。之后,将所得溶液用超纯水透析2 d以除去小碎片和残留盐。最后,通过冷冻干燥获得纯棕色Fe-CDs粉末,并储存备用。特别是,Fe的掺杂使CDs具有光增强的过氧化物酶(POD)样活性,从而产生热量和活性氧(ROS)来杀死革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌。本文表明,Fe-CDs 通过预防感染、促进成纤维细胞增殖、血管生成和胶原蛋白沉积,具有显着的伤口愈合效率。Shen等[60]设计了一种一体化葡萄糖响应性光热纳米酶GOX/MPDA/Fe-CDs (图16),由葡萄糖氧化酶(GOX)、Fe掺杂碳点(Fe-CDs)和介孔聚多巴胺(MPDA)组成,以有效地治疗慢性糖尿病伤口细菌感染并消除生物膜,而不影响周围的正常组织。GOX/MPDA/Fe@CDs的制备:首先将100.0 μL1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳酰二亚胺(EDC) (0.1 mol/L)和100.0 μL N-羟基丁二酰亚胺(NHS) (0.1 mol/L)与0.2 mg/mL GOX在37℃下振荡(180 r/min),保温1 h。然后,将混合物与2 mg/mL MPDA/Fe@CDs在37℃连续摇动(180 r/min),保温12 h。所得溶液在
12000 r/min,离心3 min,沉淀用PBS缓冲液洗涤两次,得到最终的GOX/MPDA/Fe@CDs,分散在PBS缓冲液中供进一步使用。具体而言,GOX/MPDA/Fe-CDs 产生局部温度,以增强病原菌及其生物膜在近红外(NIR)808 nm 激光照射下的渗透性,从而引发内源性高血葡萄糖激活GOX在GOX/MPDA/Fe@CDs表面上的催化活性,实现H2O2和H+的同时自供给,通过随后的过氧化物酶模拟活性诱导的芬顿/类芬顿反应级联催化•OH的产生。![]() 图 16 葡萄糖氧化酶(GOX)/介孔聚多巴胺(MPDA)/Fe@CDs用于协同化学动力学-光热对抗感染[60]Figure 16. Glucose oxidase (GOX)/mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA)/Fe@CDs for collaborative chemical kinetics-photothermal fight against infection[60]MRSA—Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus; CDT—Chemodynamic therapy; PTT—Photothermal therapy
图 16 葡萄糖氧化酶(GOX)/介孔聚多巴胺(MPDA)/Fe@CDs用于协同化学动力学-光热对抗感染[60]Figure 16. Glucose oxidase (GOX)/mesoporous polydopamine (MPDA)/Fe@CDs for collaborative chemical kinetics-photothermal fight against infection[60]MRSA—Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus; CDT—Chemodynamic therapy; PTT—Photothermal therapyLi等[61]设计并通过简单的原位热解法合成了单原子铁掺杂碳量子点(SA Fe-CDs) (图17)。SA Fe-CDs的制备:将2 g NaFeEDTA粉末放入管式炉内,然后将样品在300℃、升温速率为5℃·min−1,热解2 h。热解后,将收集的黑色产物转移至10 mL 0.5 mol/L H2SO4溶液中并在60℃下搅拌8 h以除去Fe颗粒。样品用水中和至中性后,以60℃干燥并收集。然后,将产物分散在80 mL无水甲醇中。为了除去不溶性铁和钠盐,将深色悬浮液搅拌15 min,并以高速(
10000 r/min)离心两次,持续20 min。之后,使用0.22 μm膜过滤液体以除去碳碎片。最后将滤液在60℃下干燥得到SA Fe-CDs粉末。单原子Fe为SA Fe-CDs提供了氧化酶模拟活性,以快速响应(Vmax=10.4 nmol/s)和强亲和力(Km=168 µmol/L)催化3,3′,5,5′-四甲基联苯胺(TMB)氧化。同时,由于内过滤效应,其光致发光被TMB的氧化产物猝灭。磷酸根离子(Pi)通过与Fe活性中心的相互作用,可以抑制SA Fe-CDs的模拟氧化酶活性,并恢复其光致发光。基于这一原理,建立了一种灵敏度高、选择性好、响应快的比色-荧光双模式测定磷酸盐的方法。Song等[62]设计了一个比色-荧光双信号的传感器,通过单原子铁纳米酶(SA Fe-N-C纳米酶)和碳量子点(CDs)的合成,用于肉类新鲜度检测(图18)。SA Fe-N-C纳米酶的合成:将1.190 g Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和141 mg乙酰丙酮铁溶解在20 mL甲醇中并超声处理以制备溶液A。将1.314 g 2-甲基咪唑溶于15 mL甲醇中,得到溶液B。将溶液B与溶液A混合并搅拌10 min。此外,将混合溶液转移到50 mL 反应釜中,并放入到烘箱中120℃下加热4 h。用离心法收集橙色沉淀物,用N, N-二甲基甲酰胺洗涤6次,用甲醇洗涤2次,直至上清液无色透明,然后在80℃下干燥。将上述橙色沉淀物在950℃的管式炉煅烧3 h,升温速率为5℃/min,可得到SA Fe-N-C纳米酶。SA Fe-N-C纳米酶具有高过氧化物酶样(POD样)活性(40.22 U/mg),通过促进无色还原态TMB转化为其氧化产物(oxTMB)而充当催化剂。随后,由于oxTMB和CDs之间的内滤效应(IFE),CDs的荧光信号被猝灭。在食品腐败期间,挥发性胺的产生导致oxTMB的减少,其随后恢复CDs的荧光。因此,在0.5~50.0 mg/L的线性范围内,氨检测的检测限(LOD)为
0.9840 mg/L和0.0838 mg/L。2.2 其他金属掺杂的碳点
Lu等[63]设计并采用一步水热法合成了一种钼掺杂碳量子点(Mo-CDs)纳米酶(图19)。由于选择了合适的前体,碳点上掺杂了变价的钼,从而获得了优异的类过氧化氢催化活性,使得H2O2催化为1O2。单磷酸腺苷(AMP)与催化体系产生的1O2具有良好的反应活性,于是构建了一种检测AMP的比色传感器,其线性范围为
0.0500 ~100 μg/mL,检出限为12 ng/mL。在此基础上,建立了与智能手机相结合的比色试纸视觉传感平台,成功实现了水样中AMP的快速、便携、灵敏的视觉监测。基于纳米酶的比色检测,Fan等[64]建立了一种用于检测黄曲霉毒素B1的比色传感器,即具有类过氧化物酶活性的适配体修饰的花状L-半胱氨酸功能化的FeNiNPs(L-Cys-FeNiNPs);Zhang等[65]基于Pd@CeO2/N-PC-rGO的OXD和POD模拟机制,利用协同催化和级联催化放大策略,设计了一种还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)传感比色平台;Zhu等[66]基于独特的水解特性,提出了一种用于检测丁硫克百威的纳米酶比色传感器;Liu等[67]提出了一种利用铜纳米粒子(Cu NPs)作为活性中心、氮化碳作为骨架、三唑基团作为辅助因子的类漆酶纳米酶的新策略,Cu-g-C3N5纳米复合材料成功应用于聚碳酸酯微塑料释放的双酚A (BPA)的比色检测;Gao等[68]制备了一种新型的具有高过氧化物酶活性的双金属碳点(Fe, Cu-CDs)纳米酶,以此设计了一种便携式水凝胶试剂盒,用于现场可视化过氧化氢自供酶级联催化比色和光热信号协同放大双模态监测大气环境中的CH3SH。Lu等[69]以维生素B12 (VB12)和柠檬酸为前体,设计了一种新型的钴掺杂碳量子点(Co-CDs)纳米酶(图20)。Co-CDs的制备:首先将0.1 g VB12和1.0 g 柠檬酸(CA)完全溶解在20 mL超纯水中,然后将溶液转移到三颈圆底烧瓶中,在180℃,300 r/min下反应。当溶液为凝胶状时,缓慢连续加入超纯水保持凝胶3 h,即可得到红色凝胶产品。冷却后,将产品溶解在20 mL的超纯水中,以
8000 r/min的速度离心10 min,以去除任何沉淀物。最后,用0.22 μm的滤膜过滤,冷冻干燥后得到Co-CDs。钴均匀的掺杂在碳载体上,使得Co-CDs显示出类过氧化物酶样活性。基于Co-CDs对H2O2的高亲和力(Km=0.0598 mmol/L),将Co-CDs与葡萄糖氧化酶结合,构建了一种用于葡萄糖检测的比色传感器。纳米酶具有高催化活性和级联策略,在0.500~200 μmol/L范围内表现出良好的线性关系,检测限为0.145 μmol/L。该传感器实现了对人血清样品中葡萄糖的准确检测。此外,Co-CDs还能特异性地催化H2O2在癌细胞内产生多种活性氧,导致癌细胞死亡,在肿瘤催化治疗中具有潜在的应用价值。Zhang等[70]基于农用杀菌剂甲基硫菌灵(Thiophanate-methyl,TM)对纳米酶活性的独特抑制作用,提出了一种用于特异性检测的比色传感平台(图21)。Cu-CDs的制备:将鸟氨酸(5 g)和CuCl (50.0 mg)加入到去离子水中,室温搅拌12 h。然后将沉淀离心并干燥,得到给予白色粉末作为前体。以3℃/min的升温速率,在900℃下高温热解2 h,得到了Cu-CDs。由于TM含有对称的乙二胺和类二硫脲基团,对金属中心表现出很强的亲和力,导致催化活性的丧失。因此,设计了一种具有类过氧化酶活性的铜掺杂碳纳米酶(Cu-CDs),通过Cu2+诱导产生的活性氧促进底物由无色变为蓝色的氧化过程。纳米酶的活性受到TM地抑制,而其他农药无法抑制纳米酶的活性。因此,该分析方法对TM具有特异性响应,线性范围为0.2~15 μg/mL,最低检出限为0.04 μg/mL (信噪比(S/N)=3)。此外,通过识别显色系统的光学三原色亮度(RGB)值,实现了智能手机辅助的快速检测。针对智能设备的辅助检测,Jiao等[71]将红外热像技术与核酸适体检测技术相结合,提出了一种选择性、灵敏度高的检测水中卡那霉素的新方法,为了制造便携式传感装置,将该设备与智能手机集成在一起。
Li等[72]以去甲肾上腺素基碳点(Noradrenaline-based carbon dots,NA-CDs)为还原剂制备NA-CDs/AuNPs (图22)。纳米酶和 MeHg+之间金汞齐化 (Au@HgNPs) 的形成可以同时加速从Au和Hg到NA-CDs的电子转移以及自由基(即•OH、•O−2和•CH3)的产生。即使在不同汞存在的情况下,NA-CDs/AuNPs仍具有突出的抗干扰性能。进一步通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算表明,Au@HgNPs通过MeHg+形成的活化能显著降低,从而导致类过氧化物酶活性的产生和加速。这可以实现 MeHg+ 的快速(10 min)特异性比色检测,检出限为0.06 μg/L。针对金掺杂碳纳米酶,Chen等[73]通过超分子组装辅助热解策略制造了一种混合纳米酶-金纳米颗粒/氮掺杂多孔碳(AuNP/NPC),并被设计为过氧化物酶模拟物;Yu等[74]成功制备了易于回收的聚多巴胺(PDA)负载的金基纳米酶(PDA@AuNPs),并且可以催化多种单糖,包括葡萄糖、木糖、甘露糖和蔗糖。
![]() 图 22 (a)去甲肾上腺素基碳点(NA-CDs)/AuNPs的合成示意图;(b)通过增加Au@HgNPs汞合金的 POD活性对MeHg+进行比色测定;(c) NA-CDs/AuNPs对MeHg+的选择性及其机制[72]Figure 22. (a) Schematic synthesis of noradrenaline-based carbon dots (NA-CDs)/AuNPs; (b) Colorimetric determination of MeHg+ by increasing POD activity of Au@HgNPs amalgam; (c) Selectivity of NA-CDs/AuNPs to MeHg+ and its mechanism[72]EDA—Ethylenediamine; CA—Citric acid
图 22 (a)去甲肾上腺素基碳点(NA-CDs)/AuNPs的合成示意图;(b)通过增加Au@HgNPs汞合金的 POD活性对MeHg+进行比色测定;(c) NA-CDs/AuNPs对MeHg+的选择性及其机制[72]Figure 22. (a) Schematic synthesis of noradrenaline-based carbon dots (NA-CDs)/AuNPs; (b) Colorimetric determination of MeHg+ by increasing POD activity of Au@HgNPs amalgam; (c) Selectivity of NA-CDs/AuNPs to MeHg+ and its mechanism[72]EDA—Ethylenediamine; CA—Citric acidHe等[75]以邻苯二酚接枝碳量子点(DA-CQD@Pd)模板上原位合成Pd单原子,制备了酚类单原子纳米酶(SAN) (图23)。然后,通过SAN催化自由基聚合反应,制备了DA-CQD@Pd SAN和免疫佐剂CpGODN组成的生物黏附注射水凝胶。SAN表现出过氧化物酶样活性,可产生ROS并通过催化治疗杀死肿瘤细胞。该水凝胶持续性局部释放CpGODN,这限制了全身暴露的风险,降低了CpGODN毒性的影响,并保护CpGODN免于降解。针对水凝胶与纳米酶的结合,Li等[76]成功构建了一种基于 FeMo2Ox(OH)y 矿物(FM)水凝胶的新型三通道比色传感器阵列,用于监测自来水中的芳香胺(AA),该传感器阵列能够有效识别和区分AA污染物及其混合物,并在实际样品测试中表现良好。
![]() 图 23 DA-CQD@Pd@CpGODN水凝胶介导的原发性治疗肿瘤和远处未治疗肿瘤的催化免疫治疗示意图[75]Figure 23. DA-CQD@Pd@CpGODN schematic illustration of hydrogel-mediated catalytic immunotherapy of primary treated tumor and distant untreated tumor[75]PEGDA—Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate; APS—Ammonium persulfate; SAN—Single atom nanozyme; NK—Natural killer; pDC—Plasmacytoid dendritic cells; cDC—Classical dendritic cells; M1—Classical activated macrophages; M2—Alternatively activated macrophages; Anti-PD-L1—Anti programmed cell death ligand 1; MHC—Major histocompatibility complex; PD-L1—Programmed cell death ligand 1; TCR—T-cell receptor; PD1—Programmed death-1
图 23 DA-CQD@Pd@CpGODN水凝胶介导的原发性治疗肿瘤和远处未治疗肿瘤的催化免疫治疗示意图[75]Figure 23. DA-CQD@Pd@CpGODN schematic illustration of hydrogel-mediated catalytic immunotherapy of primary treated tumor and distant untreated tumor[75]PEGDA—Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate; APS—Ammonium persulfate; SAN—Single atom nanozyme; NK—Natural killer; pDC—Plasmacytoid dendritic cells; cDC—Classical dendritic cells; M1—Classical activated macrophages; M2—Alternatively activated macrophages; Anti-PD-L1—Anti programmed cell death ligand 1; MHC—Major histocompatibility complex; PD-L1—Programmed cell death ligand 1; TCR—T-cell receptor; PD1—Programmed death-1Zhang等[77]通过将碳纳米点(CDs)与铂纳米颗粒(PtNPs)整合,新型Pt-CDs纳米复合物被设计为高效的纳米酶(图24),其超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性分别为
12605 U/mg和3172 U/mg。通过原位化学分解Pt4+,将Pt NPs沉积在CDs表面,得到Pt-CDs,CDs模拟SOD,Pt NPs模拟CAT,形成级联抗氧化纳米酶体系。值得注意的是,Pt-CDs也可以显著抑制羟基自由基。CDs的羰基和羟基可以与Pt NPs结合,促进Pt NPs与CDs 之间的电子转移,使Pt-CDs具有优异的催化性能。此外,Pt-CDs可以进入活细胞并靶向线粒体,从而降低上调的活性氧(ROS)水平。体内实验结果表明,Pt-CDs能有效减轻ROS诱导的小鼠炎症反应。3. 金属和非金属共掺杂的碳点
金属和非金属共掺杂是通过将CDs掺杂Zn、Fe、Co、Ni、Cr等金属以及N、B和P等非金属来制备的,从而开发出具有增强光致发光的新型材料[78]。N、P、B等非金属的掺杂可以提高CDs的光学特性,而金属元素Fe、Zn等的掺杂不仅可以提高CDs的光学特性,还可以为CDs带来新颖、独特的功能[79]。混合掺杂CDs与金属或者非金属掺杂CDs相比具有响应时间快、pH相容性、优异的检测限、高灵敏度和选择性等特性[80]。金属和非金属共掺杂在碳点是以化学键的形式存在。
Zhao等[81]设计了一种N-CDs/UiO-66纳米复合材料,是由氮掺杂碳纳米酶(N-CDs)负载到金属有机框架(MOF,UiO-66)中形成的(图25)。UiO-66的高比表面积和孔隙率是支持多功能 N-CDs的理想载体。N-CDs/UiO-66纳米复合材料清除或产生活性氧 (ROS) 和自由基的能力得到了全面研究。实验结果表明,N-CDs/UiO-66可以清除内在自由基(•OH、•O−2和ABTS•+),表现出超氧化物歧化酶样活性和抗氧化能力。此外,N-CDs/UiO-66 在照射下可以有效产生 ROS (•OH、•O−2和1O2),表现出光诱导氧化酶样活性和促氧化能力。这表明 N-CDs/UiO-66 的抗氧化和促氧化活性可以通过光照射轻松调节。利用N-CDs/UiO-66的荧光特性和光激活氧化酶样活性,设计出了一种检测Fe3+和谷胱甘肽(GSH)的方法。
Xia等[82]构建了一种高分散、高纯度的α-Co/氮掺杂的碳纳米纤维纳米酶 (α-Co@NCNF),该纳米酶具有葡萄糖氧化酶 (GOD) 和过氧化物酶 (POD) 活性,可用于多种生物分子的比色测定(图26)。本研究利用原位静电纺丝Co-MOF到聚丙烯腈纳米纤维(PAN)中,然后通过热解过程合成α-Co@NCNF纳米酶。再利用原位静电纺丝策略,将α-Co纳米颗粒限制在连续多孔的NCNF中,以限制其生长并防止热解过程中的聚集和氧化。由此产生的特殊结构大大提高了类酶的活性。一系列实验证明,α-Co@NCNF纳米酶的类酶活性优于Co@CoO@NCNF和天然酶。此外,开发了基于α-Co@NCNF纳米酶的比色生物传感用于监测葡萄糖、H2O2和谷胱甘肽(GSH),相应的线性范围为0.1~50和50~900 μmol/L以及5~55和0.1~20 μmol/L,相应的低检测值0.03、1.66和0.03 μmol/L。
Lyu等[83]基于氮掺杂碳量子点(N-CDs)和具有过氧化物酶活性的磁性铁纳米粒子(Fe nanozymes,Fe NZs) (图27),建立了一种荧光和比色双模式传感平台,并将其应用于检测α-葡萄糖苷酶(α-glu)及其抑制剂。Fe NZs催化H2O2生成的•OH可氧化无色的2, 2′-连氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵(ABTS)生成绿色的oxABTS,并在417 nm处有明显的吸收峰。同时,oxABTS可以通过荧光共振能量转移(FRET)在402 nm处淬灭NCDs的荧光。2-O-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基-L-抗坏血酸(AAG)可被α-葡萄糖分解为葡萄糖和抗坏血酸(AA),AA可阻止ABTS的氧化,导致417 nm处的吸收降低。此外,oxABTS对NCDs的猝灭作用减弱,402 nm处的荧光恢复。因此,基于417 nm处吸收和402 nm处荧光的变化,荧光-比色双模式传感法可用于α-glu抑制剂阿卡波糖和伏格列波糖的测定。
![]() 图 27 基于具有过氧化物酶活性的磁性铁纳米粒子(Fe NZs)纳米酶检测α-glu活性及其抑制剂的原理图[83]Figure 27. Schematic diagram of α-glu activity and its inhibitors based on Fe nanozymes (Fe NZs) nanoenzyme[83]AA—Ascorbic acid; AAG—2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid; ABTS—2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate); oxABTS—ABTS oxidation product; NCDs—Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots
图 27 基于具有过氧化物酶活性的磁性铁纳米粒子(Fe NZs)纳米酶检测α-glu活性及其抑制剂的原理图[83]Figure 27. Schematic diagram of α-glu activity and its inhibitors based on Fe nanozymes (Fe NZs) nanoenzyme[83]AA—Ascorbic acid; AAG—2-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid; ABTS—2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate); oxABTS—ABTS oxidation product; NCDs—Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dotsZhao等[84]以柠檬酸为碳源,金属低共熔溶剂(MDES)为绿色溶剂和钝化剂,采用水热法合成了Cu, Cl共掺杂的CDs(Cu, Cl-CDs) (图28)。Cu, Cl-CDs的制备:将2.48 g乙二醇、1.70 g CuCl2·2H2O和1.40 g氯化胆碱在50℃下连续搅拌30 min,直至出现澄清透明的溶液。然后,将1 g柠檬酸和10 mL水加入到MDES溶液中。在相同的温度下,混合溶液充分搅拌,直到其均匀透明。然后,将溶液转移到50 mL反应釜中,并在180℃下加热6 h。冷却至室温后,以
10000 r/min离心10 min收集所得溶液,并用0.22 µm滤膜过滤。为了除去其他杂质,通过透析膜(500 Da)纯化Cu, Cl-CDs溶液12 h。最后,将Cu,Cl-CDs粉末冷冻干燥后,4℃保存备用。结果表明,所制备的Cu, Cl-CDs具有类氧化酶(OD-like)和类过氧化物酶(POD-like)催化活性。系统地研究了Cu, Cl-CDs的催化性能、反应机制和稳态动力学。基于Cu, Cl-CDs的类OD和类POD活性,以TMB为底物,建立了测定对苯二酚(HQ)和过氧化氢(H2O2)的双功能比色平台。线性范围为0.1~120 μmol/L,检出限(LOD)为0.08 μmol/L。H2O2在1~600 μmol/L范围内,褪色程度与H2O2呈线性关系,检出限为0.35 μmol/L。Su等[85]开发了钴和氮掺杂的碳点纳米酶(Co, N-CDs),具体表现出对邻苯二胺在非酸性环境中的过氧化物酶样活性(图29)。基于Co, N-CDs在中性环境中的过氧化物酶样活性和荧光特性,建立了一种比色-荧光双模式的传感平台(比色法和比率荧光成像),用于检测溶液和人血清样品中的胆固醇和黄嘌呤。该平台操作简单,与大多数报道的纳米酶相比,Co, N-CDs表现出检测时间缩短和的分析性能改善的特性。此外,过氧化物酶活性在中性pH值,Co, N-CDs具有良好的生物相容性和光稳定性,这有助于在体内监测内源性H2O2。
Cui等[86]开发了一种新型的碳点纳米酶Fe/N-CDs (图30),其具有良好的成膜能力、过氧化物酶活性和生物相容性。Fe/N-CDs的制备:Fe/N-CDs是通过FeSO4·7H2O和L-His的水热碳化制备的。将 1 g FeSO4·7H2O 和 0.2 g His 添加到 20 mL 去离子水中,并转移到 50 mL 反应釜中,在 180℃ 下保持 8 h。通过滤膜除去大部分不溶性杂质。然后,用透析膜(500 Da)纯化溶液约5 h。冷冻干燥后得到所需的粉末。Fe/N-CDs纳米酶催化H2O2分解为•OH的类过氧化物酶反应(Vmax/Km=1.07×10−6/s)是过氧化物酶(Vmax/Km=0.20×10−6/s)的5.35倍,表现出良好的广谱抗菌活性(甚至对多重耐药菌)。催化后抗菌活性提高了500倍以上。Fe/N-CDs纳米酶对Hafinia alvei生物膜的抑制率为80.2%,对胞外聚合物、总蛋白、AKP酶和ATP酶的抑制率均为80.2%。值得注意的是,在与Fe/N-CDs纳米酶共培养后没有观察到明显的细胞毒性和细菌抗性的发展。新鲜试验结果表明,Fe/N-CDs纳米酶能有效延长鲑鱼的货架期3~6 d。这些结果表明,纳米酶可以用于延长食品的保质期。
4. 挑战与展望
本篇综述了基于金属或杂原子掺杂碳量子点(CDs)的最新进展及其制备方法、催化特性和相应的应用。碳量子点具有成本低、稳定性好、产量高以及部分有可调节的类酶活性等优势,使其成为具有广泛应用前景的工具。虽然金属或杂原子掺杂碳量子点取得了巨大进展,但仍然存在一些挑战,必须进一步考虑和详细研究。
(1)金属或杂原子掺杂碳量子点绿色合成方法的报道很少。大多数方法依赖于高温处理,在制备过程中产生一定的风险。开发一个简单而强大的流程至关重要。此外,掺杂水平仍需进一步提高才能获得更好的纳米催化剂;
(2)要实现对合成的精确控制,制备出大小、成分和表面均一的CDs仍然是一个挑战,这依赖于对合成化学、生长机制和原位表征的深刻理解;
(3)在生物应用方面,CDs由于其低毒性和良好的生物相容性而具有巨大的潜力;
(4)在器件应用方面,CDs独特的核心/表面基团结构、多功能的光学性质和电子给予/接受能力为各种器件提供了新的机遇,但仍然存在巨大的挑战;
(5)在催化应用方面,CDs通过提供更强的光吸收、电荷转移、导电性和共催化中心,在光催化剂和电催化剂中显示出更广泛的用途。
总而言之,金属或杂原子掺杂的碳量子点表现出许多的优越性能仍然是不可替代的,这极大地促进了CDs在纳米技术领域的发展,使其在生物传感、光催化、治疗诊断、生物医学和催化治疗方面具有广阔的前景。
-
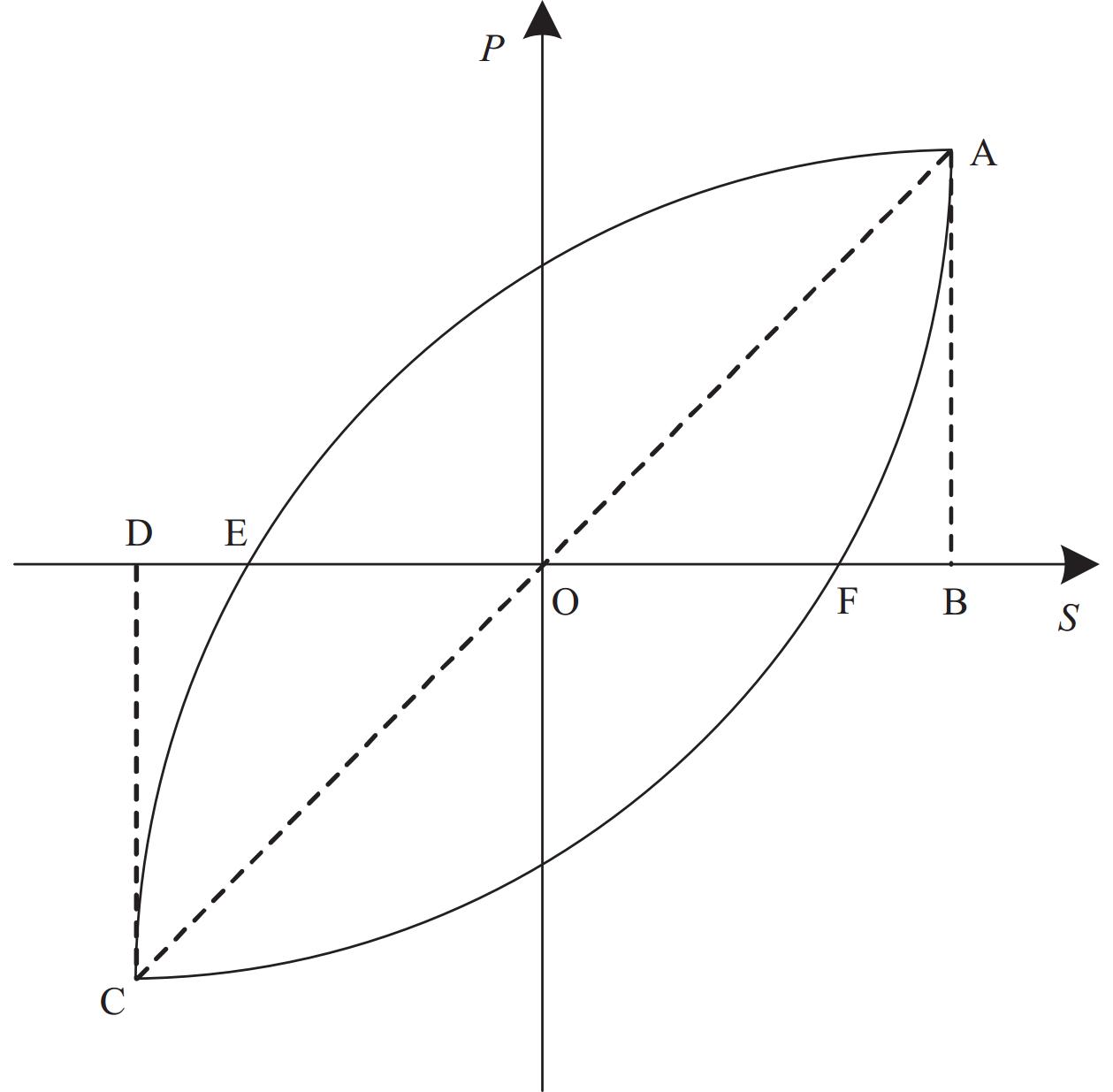
图 7 波形钢板-橡胶试件的特征荷载-滑移曲线
Figure 7. Characteristic load-slip curve of corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens
Ps−, Ps+—Microslip load; Ss−, Ss+—Displacement corresponding to microslip load; Pu−, Pu+—Peak load; Su−, Su+—Displacement corresponding to peak load; PD−, PD+—Destructive load; SD−, SD+—Displacement corresponding to destructive load; Pr−, Pr+—Residual load; Sr−, Sr+—Displacement corresponding to residual load
表 1 波形钢板-橡胶试件的基本参数
Table 1 Parameters of corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens
Specimen Bonding
length/mmRoughness/
mmLoading mode S-1 300 0.7 Push-out S-2 200 0.7 Cycle S-3 250 0.7 Cycle S-4 300 0.7 Cycle S-5 250 1.18 Cycle S-6 250 0.416 Cycle 表 2 钢板力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of steel plate
Plate Thickness/mm Yield strength/MPa Peak strength/MPa Q235 8 304 446 表 3 橡胶力学性能
Table 3 Mechanical properties of rubber
Shore A hardness/degree σa/(kN·m−1) E/MPa δ/% 70 19 2.68 330 Notes: σa—Tear strength; E—Modulus of elasticity; δ—Elongation at break. 表 4 波形钢板-橡胶试件的各特征荷载值
Table 4 Each characteristic load of corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens
Specimen Ps−/kN Ps+/kN Pu−/kN Pu+/kN PD−/kN PD+/kN Pr−/kN Pr+/kN S-1 — 2.27 — 33.20 — 26.68 — 2.38 S-2 −1.72 1.35 −13.71 12.94 −3.79 7.35 −1.36 1.82 S-3 −2.92 2.79 −26.14 29.83 −17.53 26.43 −1.45 1.75 S-4 −1.70 2.21 −25.71 30.46 −9.43 24.93 −1.21 1.45 S-5 −2.48 3.28 −23.30 27.00 −15.20 26.89 −1.91 1.94 S-6 −3.38 3.12 −25.80 28.36 −12.70 22.34 −2.23 1.93 表 5 波形钢板-橡胶试件的平均黏结应力
Table 5 Average bond stress of corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens
Specimen τs−/kPa τs+/kPa τu−/kPa τu+/kPa τD−/kPa τD+/kPa τr−/kPa τr+/kPa S-1 — 15.76 — 230.56 — 185.28 — 16.53 S-2 −17.92 14.06 −142.81 134.79 −39.48 76.56 −14.17 18.96 S-3 −24.33 23.25 −217.83 248.58 −146.08 220.25 −12.08 14.58 S-4 −11.81 15.35 −178.54 211.53 −65.49 173.13 −8.40 10.07 S-5 −20.67 27.33 −194.17 225.00 −126.67 224.08 −15.92 16.17 S-6 −28.17 26.00 −215.00 236.33 −105.83 186.17 −18.58 16.08 Notes: τs−, τs+—Microslip stress; τu−, τu+—Peak stress; τD−, τD+—Destructive stress; τr−, τr+—Residual stress. 表 6 波形钢板-橡胶试件的各特征黏结强度计算结果
Table 6 Calculation results of each characteristic bond strength of corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens
Specimen (τs−)′/kPa (τs+)′/kPa (τu−)′/kPa (τu+)′/kPa (τD−)′/kPa (τD+)′/kPa (τr−)′/kPa (τr+)′/kPa S-2 −19.26 13.61 −136.43 140.34 −42.74 82.23 −14.50 20.12 S-3 −26.76 24.36 −194.43 244.34 −131.24 218.73 −11.36 15.24 S-4 −10.26 13.61 −157.43 223.34 −72.74 185.23 −8.80 11.26 S-5 −22.15 25.53 −187.64 241.30 −141.66 237.70 −15.91 17.18 S-6 −29.48 23.66 −205.85 249.43 −120.85 199.82 −18.59 17.08 Notes: (τs−)′、(τs+)′—Calculated value of microslip strength; (τu−)′、(τu+)′—Calculated value of peak strength; (τD−)′、(τD+)′—Calculated value of destructive strength; (τr−)′、(τr+)′—Calculated value of residual strength. 表 7 波形钢板-橡胶试件的各特征黏结强度计算结果与试验结果对比
Table 7 Comparison of calculated and test results of each characteristic bond strength of corrugated steel plate-rubber specimens
Specimen (τs−)′/τs− (τs+)′/τs+ (τu−)′/τu− (τu+)′/τu+ (τD−)′/τD− (τD+)′/τD+ (τr−)′/τr− (τr+)′/τr+ S-2 1.07 0.97 0.96 1.04 1.08 1.07 1.02 1.06 S-3 1.10 1.05 0.89 0.98 0.90 0.99 0.94 1.05 S-4 0.87 0.89 0.88 1.06 1.11 1.07 1.05 1.12 S-5 1.07 0.93 0.97 1.07 1.12 1.06 1.00 1.06 S-6 1.05 0.91 0.96 1.06 1.14 1.07 1.00 1.06 Average value 1.032 0.950 0.932 1.042 1.070 1.052 1.002 1.070 -
[1] LEWANDOWSKI R, SLOWIK M, PRZYCHODZKI M. Parameters identification of fractional models of viscoelastic dampers and fluids[J]. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2017, 63(2): 181-193.
[2] AL-ANANY Y M, MOUSTAFA M A, TAIT M J. Modeling and evaluation of a seismically isolated bridge using unbonded fiber-reinforced elastomeric isolators[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2018, 34(1): 145-168. DOI: 10.1193/072416EQS118M
[3] SIERRA I E M, LOSANNO D, STRANO S, et al. Development and experimental behavior of HDR seismic isolators for low-rise residential buildings[J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 183: 894-906. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.01.037
[4] 王威, 李元刚, 苏三庆, 等. 波形钢板混凝土黏结滑移性能试验研究与数值模拟分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2019, 52(11): 13-24, 44. WANG Wei, LI Yuangang, SU Sanqing, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation on bond-slip behavior between corrugated steel plate and concrete[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2019, 52(11): 13-24, 44(in Chinese).
[5] 王威, 李鹏洛, 林忠良, 等. 波纹钢板-混凝土界面能耗及其本构关系[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(3): 1588-1600. WANG Wei, LI Pengluo, LIN Zhongliang, et al. Energy consumption and constitutive relationship of interface between corrugated steel plate and concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(3): 1588-1600(in Chinese).
[6] LI Y, WANG W, SU S, et al. Seismic performance assessment of eccentrically braced steel frame using demountable-metallic-corrugated-shear-panel dampers[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2023, 207: 107972. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2023.107972
[7] KUTENEVA S V, GLADKOVSKY S V, VICHUZHANIN D I, et al. Microstructure and properties of layered metal/rubber composites subjected to cyclic and impact loading[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 285: 115078. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.115078
[8] 邓雪松, 李家乐, 周云, 等. 双曲型钢管叠层黏弹性阻尼器性能分析研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(S2): 129-136. DENG Xuesong, LI Jiale, ZHOU Yun, et al. Performance analysis of laminated viscoelastic body filed hyperbolic type steel tube damper[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(S2): 129-136(in Chinese).
[9] ZHOU Y, LI J, SHI F, et al. Theoretical, experimental and numerical studies on a novel laminated viscoelastomer-filled steel tube damper[J]. Structures, 2022, 45: 1434-1451.
[10] 周云, 吴胜, 李家乐. 钢管叠层黏弹性阻尼器设计方法[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2023, 44(3): 79-86. ZHOU Yun, WU Sheng, LI Jiale. Design method of laminated viscoelastic body filled steel tube damper[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2023, 44(3): 79-86(in Chinese).
[11] 周云, 李家乐, 钟根全, 等. 钢管叠层黏弹性阻尼器性能研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2023, 56(10): 1-10. ZHOU Yun, LI Jiale, ZHONG Genquan, et al. Research on properties of laminated viscoelastic body filled steel tube damper[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2023, 56(10): 1-10(in Chinese).
[12] HE Z, SHI F, LIN Z, et al. Experimental characterization on cyclic stability behavior of a high-damping viscoelastic damper[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 371: 130749. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130749
[13] ZHOU Y, LI D, SHI F, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of the hybrid lead viscoelastic damper[J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 246: 113073. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.113073
[14] ZHOU Y, SHI F, OZBULUT O E, et al. Experimental characterization and analytical modeling of a large capacity high-damping rubber damper[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2018, 25(6): e2183. DOI: 10.1002/stc.2183
[15] 陈鹏, 周颖, 刘璐, 等. 橡胶隔震支座抗拉装置受力性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2017, 38(7): 113-119. CHEN Peng, ZHOU Ying, LIU Lu, et al. Experimental research on mechanical performance of tension-resistant device for rubber bearings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2017, 38(7): 113-119(in Chinese).
[16] WANG S, YUAN Y, TAN P, et al. Experimental study and numerical model of a new passive adaptive isolation bearing[J]. Engineering Structures, 2024, 308: 118044. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.118044
[17] 张增德, 周颖. 叠层厚橡胶支座竖向压缩与拉伸力学性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2024, 41(12): 167-175. ZHANG Zengde, ZHOU Ying. Study on compressive and tensile behaviors of thick rubber bearings[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2024, 41(12): 167-175(in Chinese).
[18] 张增德, 温玉君, 周颖, 等. 叠层厚橡胶支座力学性能及其震振双控性能分析[J]. 结构工程师, 2024, 40(1): 81-88. ZHANG Zengde, WEN Yujun, ZHOU Ying, et al. Mechanical properties of thick rubber bearing and its earthquake and subway-induced vibration control analysis[J]. Structural Engineers, 2024, 40(1): 81-88(in Chinese).
[19] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 钢及钢产品 力学性能试验取样位置及试样制备: GB/T 2975—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Steel and steel products—Location and preparation of samples and test pieces for mechanical testing: GB/T 2975—2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018(in Chinese).
[20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料 拉伸试验: 第1部分: 室温试验方法: GB/T 228.1—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Metallic materials—Tensile testing—Part 1: Method of test at room temperature: GB/T 228.1—2021[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021(in Chinese).
[21] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶拉伸应力应变性能的测定: GB/T 528—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic—Determination of tensile stress-strain properties: GB/T 528—2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009(in Chinese).
[22] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑抗震试验规程: JGJ/T 101—2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Specification for seismic test of buildings: JGJ/T 101—2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015(in Chinese).
[23] 国家技术监督局. 胶黏剂 主要破坏类型的表示法: GB/T 16997—1997[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1997. The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Adhesives—Designation of main failture patterns: GB/T 16997—1997[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1997(in Chinese).
[24] 方庆红, 宋博, 高雨, 等. 纳米石墨/天然橡胶复合材料的应力软化与动态性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(6): 1446-1451. FANG Qinghong, SONG Bo, GAO Yu, et al. Stress softening and dynamic properties of nano-graphite/natural rubber composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2014, 31(6): 1446-1451(in Chinese).
[25] 伍凯, 陈峰, 徐方媛, 等. 型钢与钢纤维混凝土界面黏结性能及损伤耗能试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2019, 52(3): 1-11, 19. WU Kai, CHEN Feng, XU Fangyuan, et al. Experimental study on interfacial bonding property and energy dissipation capacity between shape steel and steel fiber reinforced conerete[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2019, 52(3): 1-11, 19(in Chinese).
[26] 王威, 续鉴, 李昱, 等. 带栓钉波形腹板PEC柱界面黏结滑移性能与抗剪承载力试验研究[J/OL]. 工程力学, 1-13[2025-03-21]. WANG Wei, XU Jian, LI Yu. Experimental study on interface bond-slip properties and shear bearing capacity of corrugated webs PEC columns with stud[J/OL]. Engineering Mechanics, 2024, 1-13[2025-03-21](in Chinese).
[27] SHARMA S K, ALI M S M, GOLDAR D, et al. Plate-concrete interfacial bond strength of FRP and metallic plated concrete specimens[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2006, 37(1): 54-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2005.05.011
-
其他相关附件
-
目的
钢-橡胶构件是将钢与橡胶通过胶粘剂有效粘结而形成的组合构件。由于橡胶的高弹性、可压缩性、高阻尼等特性,钢-橡胶构件在小变形下就能发挥耗能作用,具有优异的抗震和减振性能。近年来,波形钢板凭借其独特的几何特性,被广泛应用于土木工程领域。由于波形钢板面外刚度大,将其应用在剪力墙结构中,不仅可提高构件的承载力,还可节省钢材用钢量;将其应用在阻尼器结构中,极大改善了阻尼器的延性和耗能能力。波形钢板因其独特的截面形状与橡胶结合,形成波形钢板-橡胶构件,有效增加了黏结面积和橡胶填充量,波形钢板对称布置使得界面处应力分布更加均匀,形成更好的组合机制,将极大增强建筑结构的抗震性能。目前针对钢-橡胶构件的研究大多集中在力学性能的研究,而波形钢板-橡胶构件间的黏结滑移性能是确保两种材料发挥各自优势的基础和关键,当前对波形钢板-橡胶界面间的黏结滑移性能研究尚未开展,这使得对其受力机制进行探讨具有一定必要性。
方法考虑界面粘结长度、波形钢板表面粗糙度和加载方式三个影响因素、设计了6个波形钢板-橡胶试件进行往复加载试验,根据黏结破坏过程、界面耗能、应变分布和影响因素等分析试件的黏结性能。最后建立了波形钢板-橡胶构件的计算特征黏结强度公式,并验证其准确性。
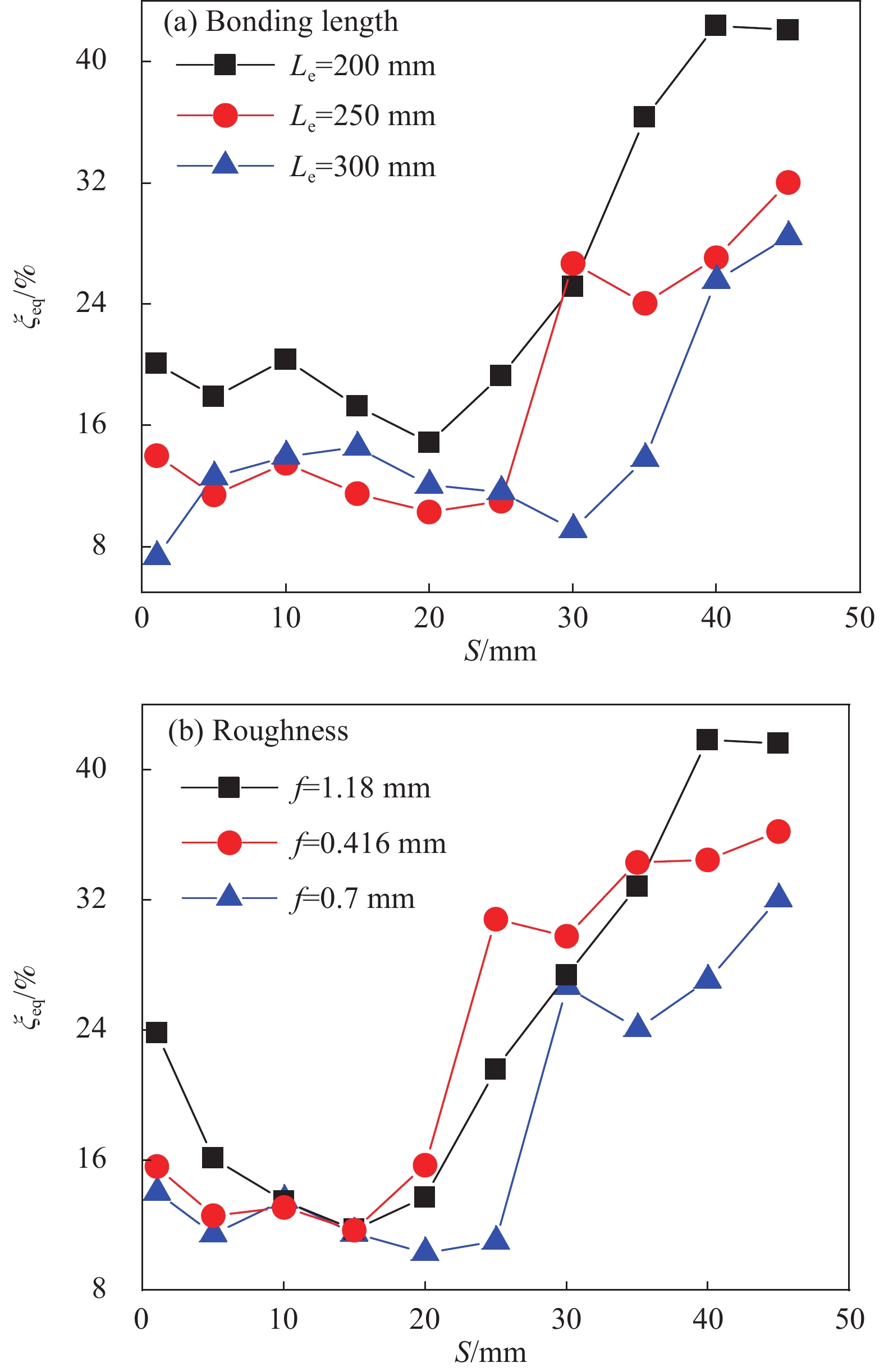
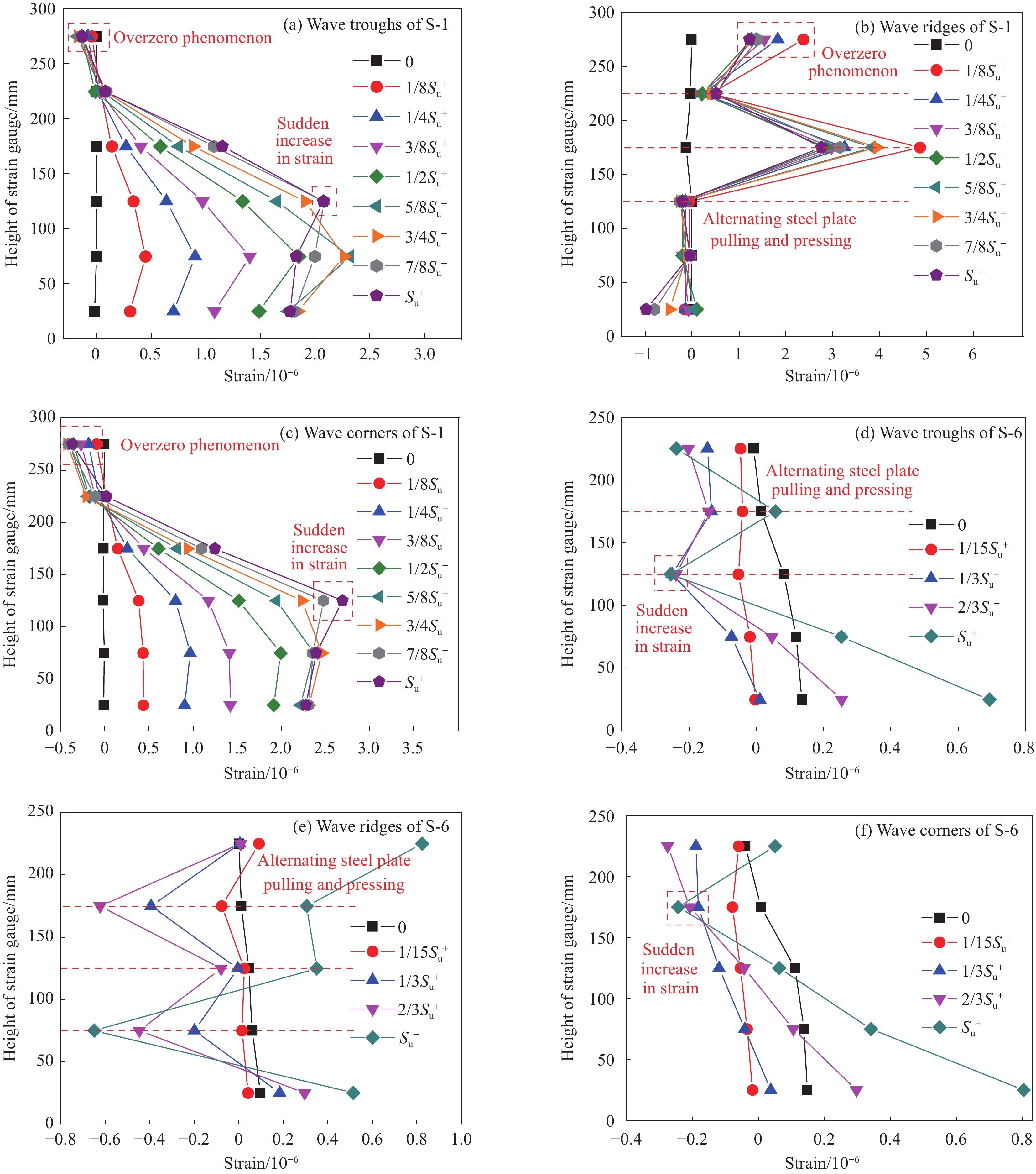
结果(1)波形钢板与橡胶界面在剪切力和挤压力作用下沿粘结长度方向大约45°出现斜向应力,剪切应力的增大使得橡胶向外膨胀变形。因橡胶具有迟滞效应和Mullins效应,这使得橡胶在卸载后仍继续挤压胶粘剂,橡胶与波形钢板间摩阻力增大,为破坏后胶粘剂发生内聚破坏提供一定条件。(2)根据黏结破坏过程,建立了试件的特征荷载-滑移曲线,定义了8个特征点和5个破坏阶段,8个特征点分别为:微滑移点A、A′;极限荷载点B、B′;破坏荷载点C、C′;残余荷载点D、D′;5个破坏阶段分别为:微滑移阶段(OA段、OA′段)、滑移阶段(AB段、A′B′段)、破坏阶段(BC段、B′C′段)、曲线下降阶段(CD段、C′D′段)、残余阶段(DE段、D′E′段)。(3)粘结长度的长短显著影响试件的等效阻尼比;合理控制粗糙度,可改善试件界面耗能,提高界面黏结性能。(4)因优先受力端部在荷载作用下内力传递最为强烈,使得试件的优先受力端部存在应变突变现象;由于波形钢板波脊处靠近变形区,在距加载端不同位置处均产生应变,但拉压变形程度不一致,使得钢板拉压交替呈波浪形;由于加载端存在滑移区,自由端处橡胶在受到橡胶夹具提供的向上的反力和胶粘剂对钢板施加向上的阻力,使得自由端钢板局部产生受拉区,单推试件S-1出现了应变过零现象。(5)相比于单调加载,往复加载下试件的残余黏结滑移降低了约29%,对界面的黏结性能产生更不利影响;波形钢板-橡胶试件的极限特征黏结强度随粘结长度和粗糙度的增大呈现出先增加后逐步减弱。(6)综合考虑试验结果和影响因素分析后,提出了针对波形钢板-橡胶的特征黏结强度计算式,并将其与试验结果进行了对比,其吻合度较好。
结论波形钢板-橡胶试件进入破坏阶段后胶粘剂加速断裂直至界面贯通,往复加载试件在进入破坏阶段后荷载下降速度加快,加卸载和循环圈数将进一步加大界面损伤,对影响因素分析表明波形钢板-橡胶试件的极限特征黏结强度随粘结长度和粗糙度的增大呈现出呈现出先增加后逐步减弱;结合影响因素和试验结果建立特征黏结强度公式,为相关构件研究提供一定参考。
-
波形钢板-橡胶构件因波形钢板的几何形状优势,表现出良好的抗震性能,波形钢板-橡胶构件间的黏结滑移性能是确保两种材料发挥各自优势的基础和关键,但目前对波形钢板-橡胶界面间的黏结滑移性能研究尚未开展,对其受力机制进行探讨具有一定必要性。
本文以界面粘结长度、波形钢板表面粗糙度和加载方式为设计参数设计了6个波形钢板-橡胶试件进行往复加载试验,界面在剪切力和挤压力共同作用下沿粘结长度方向大约45°出现斜向应力,剪切应力στ的增大使得橡胶向外膨胀变形;因迟滞效应和Mullins效应使得橡胶在卸载后仍继续挤压胶粘剂,挤压应力σr的存在为破坏后胶粘剂发生内聚破坏(CF)提供一定条件。根据界面黏结破坏过程,建立特征荷载-滑移曲线,定义了8个特征点和5个破坏阶段,确定波形钢板-橡胶试件的黏结破坏依次经历微滑移、滑移、破坏、曲线下降和残余阶段;从界面耗能角度分析了粘结长度和粗糙度对界面黏结性能的影响;对应变突变现象、波形钢板拉压交替现象、应变过零现象进行归纳分析,确定了在荷载较大时,应变发生突变且波脊处影响最大;通过对波形钢板-橡胶试件影响因素分析,往复加载相比于单调加载对界面的黏结性能产生更不利影响,波形钢板-橡胶试件的极限特征黏结强度随粘结长度和粗糙度的增大呈现出先增加后逐步减弱。进而确定了波形钢板与橡胶构件的特征黏结强度计算公式,并进行了计算值与试验值的比较,其吻合度较好。
试件界面破坏及应力状态

波形钢板-橡胶试件特征荷载-滑移曲线






 下载:
下载: