Tensile mechanical behavior of a new high-temperature resin, polyethersulfone ketones with diazanone structure
-
摘要:
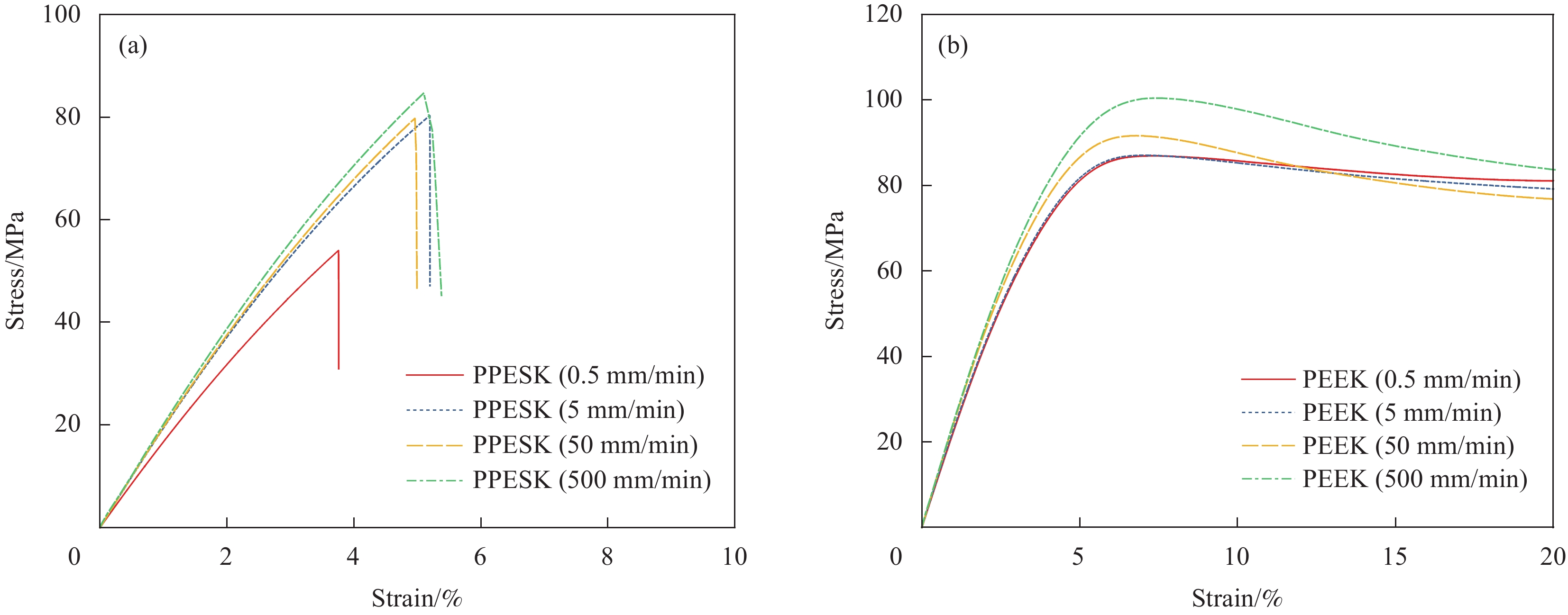
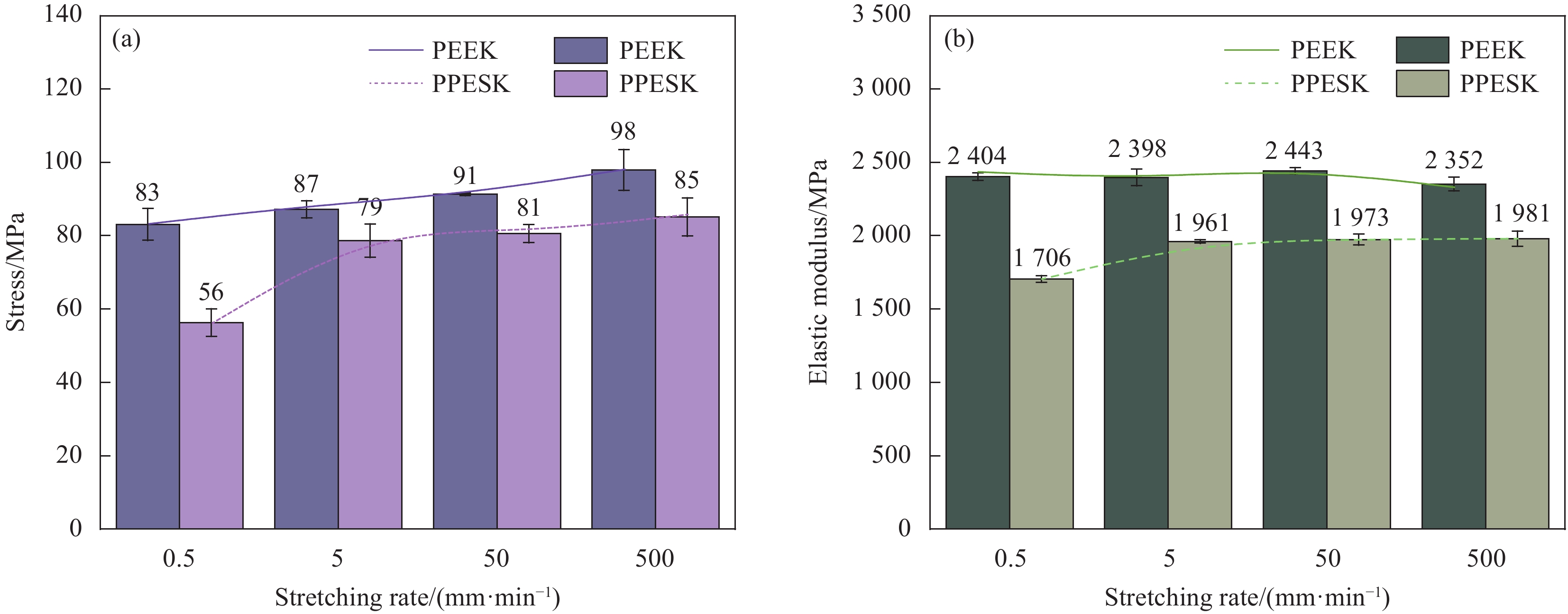
为探索新型耐高温树脂−含二氮杂萘酮结构的聚醚砜酮(PPESK)的拉伸力学行为,本文采用对比实验的方式,以典型商用树脂聚醚醚酮(PEEK)为参照,从耐热性、拉伸性能对拉伸速率变化的敏感性、拉伸变形-断裂行为3个层面详细分析了PPESK力学行为的特殊之处。研究表明:PPESK的耐热性远优于PEEK,且强度和模量对拉伸速率变化更敏感。在室温至250℃时,形变量在6%以内,发生脆性断裂;仅当温度达260℃及以上时,PPESK才出现较大变形,发生韧性断裂,这与各种条件下均产生大变形且韧性断裂的PEEK截然不同。上述特殊力学行为的产生,与PPESK结构中扭曲、非共平面的杂萘环以及强极性的砜基、羰基有关。这些基团使PPESK为无定形形态,且分子链刚性增大、分子间作用力增强,进而引起玻璃化转变温度升高、分子运动能力下降,导致PPESK更耐热、拉伸性能对拉伸速率变化更敏感,断裂形式以伴随主链断裂的脆性断裂为主。
-
关键词:
- 含二氮杂萘酮结构的聚醚砜酮 /
- 聚醚醚酮 /
- 拉伸力学行为 /
- 耐热性 /
- 断裂形式
Abstract:In order to explore the tensile mechanical behavior of a new high temperature resistant resin, polyethersulfone ketones with diazanone structure (PPESK), a comparative experiment was conducted in this paper, and a typical commercial resin, polyetheretherketone (PEEK), was used as a reference. The special mechanical behavior of PPESK was analyzed in detail from three aspects: Heat resistance, sensitivity of tensile property to the change of tensile rate, and tensile deformation to fracture behavior. It is shown that the heat resistance of PPESK is much better than that of PEEK, and the strength and modulus are more sensitive to tensile rate changes. At room temperature up to 250℃, the deformation is within 6%, and brittle fracture occurs; Only when the temperature reaches 260℃ and above, PPESK shows large deformation and toughness fracture occurs, which is very different from PEEK, which produces large deformation and toughness fracture under various conditions. The generation of the above special mechanical behavior is related to the twisted, non-coplanar heteronaphthalene ring in the structure of PPESK, as well as the strongly polar sulfone group and carbonyl group. These groups make PPESK amorphous form, and the molecular chain rigidity increases, the intermolecular forces increase, which in turn causes the glass transition temperature increases, the molecular movement ability decreases, resulting in more heat-resistant PPESK, tensile properties of more sensitive to changes in tensile rate, the form of fracture to the brittle fracture accompanied by the breakage of the main chain is dominant.
-
体外预应力技术是一种适用于中小跨径桥梁和建筑结构的有效加固/增强技术,该技术将预应力筋在结构体外进行张拉,利用预应力筋的回缩对结构产生预加力以抵消外荷载引起的内力,实现限制结构裂缝和变形、提高承载力的目的。体外预应力技术避免了体内预应力的孔道布置、灌浆等工序,且方便维护管理人员对预应力筋进行质量检查,一旦发现问题(如预应力筋受到腐蚀、火灾等外部因素的影响)可及时采取措施[1]。除锚固端外,体外预应力筋仅在转向块处与结构体接触,可减少孔道摩擦造成的预应力损失。预应力筋是预应力结构中的关键部件,在海洋等严酷环境下,布置在结构体外的预应力钢筋、钢绞线容易遭受外界腐蚀环境的影响,一旦高应力状态的预应力筋在腐蚀介质作用下发生锈蚀,将严重威胁结构安全性。
耐腐蚀的纤维增强树脂基复合材料(FRP)是工程界公认的严酷环境下替代传统钢筋,提升结构耐久性的理想材料,美国ACI 440.4R规范[2]建议碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(CFRP)筋和芳纶纤维增强树脂基复合材料(AFRP)筋作为预应力材料使用,从二十世纪八十年代起,CFRP筋和AFRP筋体外预应力技术(图1)开始在美日欧等发达国家得到大量应用[3-5],实现了结构承载力、刚度、抗裂性等综合性能提升。预应力玄武岩纤维增强树脂基复合材料(BFRP)筋的研发较晚,目前尚未在体外预应力实际工程中得到应用,但其优越的力学性能和高性价比在预应力工程中将具有显著优势[6,7]。由于FRP筋的材料性能与传统预应力钢筋、钢绞线区别较大,FRP筋体外预应力技术的应用需解决以下关键问题:①FRP筋长期力学性能(蠕变、松弛和疲劳)不明确;②FRP筋的横向强度远低于纵向强度,锚固工艺复杂;③转向区FRP筋弯折导致其力学性能降低明显;④需建立有效的设计计算方法。
针对上述瓶颈,各国学者开展了大量理论与试验研究,并取得了相关成果。本文从预应力FRP筋力学性能、体外预应力FRP筋应用关键技术(包括锚固和转向)和体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件三方面,归纳总结了国内外体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构的研究成果,并通过既有文献中42根体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁的试验结果,对国内外规范中设计方法的精度进行验证。
1. 预应力FRP筋力学性能
1.1 拉伸性能
FRP筋在大部分预应力工程中主要承受顺纤维方向的拉应力,因此拉伸性能是预应力FRP筋的最重要、最基本的性能,FRP筋、高强钢筋和钢绞线力学性能的拉伸性能如表1。从表中可以看出,CFRP筋的拉伸强度和弹性模量最高,但材料延伸率低,且热膨胀系数几乎为零,在温度作用下不能与混凝土结构同步变形,容易产生温度应力,AFRP筋的“热缩冷胀”特性也存在类似问题。虽然BFRP筋的强度和弹性模量不及CFRP筋,但BFRP延伸率较高,且热膨胀系数与混凝土接近,不易产生较大的温度应力。另一方面,BFRP筋的弹性模量较低,仅为CFRP的1/3左右,由混凝土收缩徐变产生的BFRP筋预应力损失将明显小于CFRP筋的相应值。
表 1 FRP筋、高强钢筋、钢绞线拉伸性能[8]Table 1. Tensile properties of FRP tendons, high-strength steel bar and steel strandType of
tendonDensity/
(g/cm3)Tensile
strength/MPaElastic
modulus/GPaElongation/
%Longitudinal thermal
expansivity/(10−6/℃)CFRP tendon 1.5 1500~2500 120~160 0.5~1.7 −2~0 BFRP tendon 2.0 800~1800 50~60 1.6~3.0 6~8 AFRP tendon 1.4 1000~2 000 40~120 1.9~4.4 −6~−2 High-strength steel bar 7.85 490~700 200 >10 11.7 Steel strand 7.85 1400~1 860 180~200 >4 11.7 相比于短期力学性能,FRP筋长期力学性能才是体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构服役性能的关键控制因素。例如,蠕变断裂性能是决定预应力FRP筋的设计应力取值的关键因素,FRP筋松弛是预应力损失的重要组成部分,疲劳性能限制了FRP筋使用期间的最大疲劳应力和应力幅。下文将介绍FRP筋蠕变、松弛和疲劳性能方面的既有研究结果,并给出面向设计的FRP筋蠕变断裂应力建议值、松弛率以及最大疲劳应力和应力幅限值。
1.2 蠕变和松弛性能
蠕变和松弛两种现象的本质相同,均由树脂的黏弹性变形引起。蠕变是材料在恒定应力下应变随时间的推移而增加的现象,反之,松弛是材料在恒定应变下应力随时间的推移而减少的现象。预应力FRP筋的蠕变和松弛会对结构长期性能造成不利影响,在过大的长期应力下,FRP筋在服役期间会发生断裂,该现象被称为蠕变断裂,保证FRP筋在一定时间(一般取50年、100年,或取50万小时、100万小时)不发生蠕变断裂的最大应力被称为蠕变断裂应力。关于蠕变断裂性能,国内外很多学者经过蠕变断裂试验研究,提出了CFRP筋、AFRP筋和BFRP筋的蠕变断裂应力(表2),其中,fu是FRP筋的抗拉强度。值得注意的是,虽然玻璃纤维增强树脂基复合材料(GFRP)筋也是土木工程中常用的FRP筋,但由于其蠕变断裂应力低(不超过0.3fu),因此各国规范中不建议GFRP筋作为预应力材料使用。
表 2 FRP筋的蠕变断裂应力Table 2. Values of creep rupture stress of FRP tendons从表2中可以看出,不同国家对FRP蠕变断裂应力的评价相差较大,这主要由各国学者采用的FRP材料生产工艺的差异引起。需要说明的是,文献[13]中的数据是碱溶液环境下的BFRP筋蠕变断裂应力。考虑到表2中美国ACI规范的权威性,且ACI 440.4R规范[2]是专门针对预应力FRP筋编制的规范,因此CFRP筋和AFRP筋的蠕变断裂应力建议值根据ACI 440.4R规范[2]取值。BFRP筋的蠕变断裂应力建议值根据Shi等[12]的研究取值(考虑95%可靠度),如表3。
表 3 FRP筋蠕变断裂应力建议值Table 3. Recommended values of the creep rupture stress of FRP tendonsType of tendon CFRP AFRP BFRP Creep rupture stress 0.70fu 0.55fu 0.54fu fu is the tensile strength of FRP tendon. 除了蠕变断裂应力外,松弛率也是预应力工程中关注的重要指标。然而,松弛试验的操作难度远大于蠕变试验,大部分松弛试验无法解决锚固端滑移导致的应力变化对松弛试验测量结果造成的影响。例如,对于BFRP松弛率的研究发现,在0.5fu的应力下50年的松弛率预测值为11%,这一过大的松弛率是由试验中的锚固问题以及采用了强度较低的BFRP筋导致[15]。而在预应力BFRP筋增强混凝土梁试验中,由于混凝土的徐变收缩效应的影响,所测得的BFRP筋松弛率高达20%[16],远高于BFRP筋实际的松弛率。为此,Shi等[17]和Zou[18]分别提出了能够有效排除锚固端滑移对FRP筋长期应力影响的松弛试验装置,对试验中由荷载传感器直接测得的荷载进行修正。采用修正方法得到CFRP筋和AFRP筋在0.5fu初始应力下1000小时松弛率分别为1%和8%。BFRP筋在0.4fu、0.5fu和0.6fu初始应力下1000 h松弛率分别为4.2%、5.3%和6.4%,高于预应力钢绞线在0.7fu初始应力下1000小时松弛率(2.5%)。
CFRP筋的低松弛率对预应力损失的控制十分有利,而AFRP筋的高松弛率由芳纶纤维本身的黏弹性变形造成,属于无法避免的材料特殊性能;BFRP筋的松弛率对于预应力工程的应用偏大,这种较大的长期变形主要是由原本弯曲的纤维在持荷初期阶段随着树脂黏弹性变形被拉直造成的[19],在该阶段之后,由于纤维被拉直,材料长期变形趋于稳定。因此,若能控制FRP在持荷初期由于弯曲纤维拉直造成的较大黏弹性变形,就能很大程度地抑制FRP的长期变形。基于上述机制分析,Wang等[20]提出了预张拉控制FRP筋松弛率的方法,在预张拉力的作用下,FRP中的树脂会发生黏弹性变形,伴随着树脂的变形,先天弯曲的纤维被调直,从而实现纤维的共同受力,控制FRP的黏弹性变形,如图2所示。图3的SEM图片进一步从微观角度展现了纤维束在预张拉前后的变化。试验表明,预张拉处理后的BFRP筋在0.5fu初始应力下1000小时松弛率仅为2.6%,比未进行预张拉处理的BFRP筋相应值降低50%,接近预应力钢绞线在0.7fu初始应力下1 000 h松弛率(2.5%)。
![]() 图 2 FRP筋蠕变松弛性能提升机制示意图[20]Figure 2. Schematic diagram for the improvement mechanism of creep and relaxation behaviors of FRP tendons
图 2 FRP筋蠕变松弛性能提升机制示意图[20]Figure 2. Schematic diagram for the improvement mechanism of creep and relaxation behaviors of FRP tendonsFRP筋的松弛率rr可以用对数曲线进行拟合,即rr=a1+a2lgt (其中t是时间),对于不同种类的FRP筋,a1和a2的值可通过试验获得,利用该公式可计算FRP筋百万小时松弛率预测值,如表4。
![]() 图 3 FRP筋内部初始弯曲纤维与预张拉后的拉直纤维[17]Figure 3. Initial uneven fibers and straightened fibers after pretensioned in a FRP tendon表 4 0.5fu初始应力下FRP筋百万小时松弛率预测值Table 4. Predictive values of the one-million-hour relaxation rates of FRP tendons at a 0.5fu initial level
图 3 FRP筋内部初始弯曲纤维与预张拉后的拉直纤维[17]Figure 3. Initial uneven fibers and straightened fibers after pretensioned in a FRP tendon表 4 0.5fu初始应力下FRP筋百万小时松弛率预测值Table 4. Predictive values of the one-million-hour relaxation rates of FRP tendons at a 0.5fu initial levelType of tendon CFRP AFRP BFRP Relaxation rate 3.0% 10~13% 6.7% 1.3 疲劳性能
疲劳是材料在交变荷载作用下产生局部不可恢复的损伤,进而扩展为宏观裂纹并进一步导致材料破断的现象。材料在远低于其极限荷载水平的交变荷载作用下,随着内部的初始缺陷或损伤的扩展所发生的破坏称为疲劳破坏。根据纤维弹性模量不同,FRP筋疲劳破坏机制有所区别,碳纤维弹性模量较高,纤维承担的疲劳应力较大,因此疲劳损伤主要由纤维控制;玄武岩纤维和芳纶纤维弹性模量较低,树脂承担的应力较大,疲劳损伤由树脂微裂纹扩展到纤维-树脂界面,并最终造成纤维断裂[21] (图4)。需要说明的是,虽然裂纹随循环次数扩展,在宏观疲劳破坏发生前,FRP筋的弹性模量不随疲劳荷载循环次数的增加而发生变化[22]。
![]() 图 4 图4 玄武岩纤维增强树脂基复合材料(BFRP)筋疲劳破坏机制[22]Figure 4. Mechanism of the fatigue failure of basalt fiber reinforced polymer (BFRP) tendon
图 4 图4 玄武岩纤维增强树脂基复合材料(BFRP)筋疲劳破坏机制[22]Figure 4. Mechanism of the fatigue failure of basalt fiber reinforced polymer (BFRP) tendon各国学者对FRP筋的疲劳性能进行了系统研究,并确定最大疲劳应力和应力幅为控制疲劳寿命的关键因素。例如,CFRP筋在0.9fu的最大疲劳应力(即疲劳强度)以及0.05fu的应力幅下能够保持200万次疲劳循环后不发生破坏,而AFRP筋的相应限值则较低,分别为0.5fu和0.025fu[23-24]。El Refai等[25]对BFRP筋的疲劳性能进行了研究,得出了0.04fu这一疲劳应力幅限值,并且当应力幅大于0.08fu时,BFRP筋均发生锚固区的疲劳破坏,而非筋材本身破坏,其结果不能反映材料真实的疲劳性能。因此,可靠的锚固方式是FRP筋疲劳试验结果有效性的重要保证。对于弹性模量较大的CFRP筋,可采用一般拉伸试验中的黏结型锚具,因为在疲劳荷载作用下CFRP筋试件变形很小,端部树脂剪切变形不足以引起树脂发热软化[26];反之,对于弹性模量较小的FRP筋(如BFRP筋),端部树脂剪切变形会引起树脂发热软化,锚固区的提前破坏使得FRP筋真实的疲劳性能无法通过试验直接获得。为此Wang等[22]提出了一种通过在FRP筋锚固区缠绕双向纤维布(200 g/m2)的锚固方法,避免了锚固区张拉端的应力集中,能够更加准确地测量FRP筋疲劳性能。CFRP筋、AFRP筋和BFRP筋的疲劳强度见表5。
表 5 FRP筋疲劳强度(括号中为对应的应力幅)Table 5. Values of the fatigue strength of FRP tendons (with the corresponding stress range in the brackets)References CFRP AFRP BFRP Saadatmanesh[23-24] 0.9fu (0.05fu) 0.5fu (0.025fu) / Adimi et al.[27] 0.35fu (0.21fu) / / El Refai[25,28] 0.5fu (0.1fu) / 0.39fu (0.04fu) Song et al.[29] 0.64fu (0.09fu)
0.53fu (0.19fu)
0.37fu (0.28fu)
/ / Xie et al.[30] 0.5fu (0.09fu) / / Zhuge et al.[31] 0.42fu (0.04fu) / / Zhang and Ou[32] 0.5fu (0.25fu) / / Odagiri et al.[33] / 0.54fu (0.05 fu) / Wang et al.[22] / / 0.6fu (0.05fu) Atutis et al.[34] / / 0.65fu (0.07fu) fu is the tensile strength of FRP tendon. 2. 体外预应力FRP筋应用关键技术
体外预应力FRP筋与混凝土之间没有黏结作用,FRP筋中的预应力完全依靠锚具和转向块传递给混凝土结构,因此锚固和转向是体外预应力的关键技术。与各向同性的钢材不同,FRP材料的横向强度远低于纵向强度,该特性导致体外预应力FRP筋的锚固和转向无法完全沿用传统预应力钢筋、钢绞线的工艺。首先,在锚固区的复杂受力情况下,切口效应将导致FRP筋在达到极限拉伸强度之前就发生锚固区破坏;其次,为了减小体外预应力结构二次效应而设置的转向块会造成FRP筋的弯折,从而导致FRP筋产生应力集中。本节将主要介绍预应力FRP筋的主要锚固形式,同时,基于转向块-FRP筋体系的力学性能研究,提出体外预应力FRP筋转向半径和转向角度限值。
2.1 预应力FRP筋锚具
目前的预应力FRP筋锚具主要分为黏结型锚具、摩擦型锚具和夹片式锚具(图5),其中黏结型锚具是利用锚固端黏结材料(树脂、水泥等)与FRP筋之间产生的化学黏结力进行锚固的方法。摩擦型锚固通过膨胀水泥等材料固化后的体积膨胀产生正压力,从而在套管和FRP筋之间形成摩擦力来实现锚固。夹片式锚具中的夹片数量一般有2、3、4三种,夹片材料可采用金属或超高强混凝土,为减小金属夹片对FRP筋的直接作用,可在FRP筋外套软质金属套筒,夹片通过软质金属套筒间接作用在FRP筋上,夹片和FRP筋组装后在锚杯的楔形作用力下实现挤压锚固。三类锚固工艺的优缺点如表6。
表 6 FRP筋主要锚具形式的优缺点Table 6. Advantages and deficiencies of the main types of anchor for FRP tendonsType of anchor Advantages Deficiencies Bond type No radial stress, hence inducing no decrease in strength of tendon Inconvenient grouting; prestress loss due to long-term creep deformation of the bonding material in anchor Friction type Radial stress is beneficial for the long-term
behavior of anchorInconvenient grouting Wedge type Convenient assembly Notch effect on FRP tendon 从表6可以看出,黏结型和摩擦型锚具难以提供预应力FRP筋长期服役过程中的有效锚固力,且现场灌浆不利于施工便利性。钢夹片锚具组装方便,但FRP筋的切口效应明显。为此,研究人员提出了一系列措施减小夹片式锚具的切口效应,除了在FRP筋表面套一根软金属薄管以分散径向应力外[35],还可采用整体式钢夹片保证夹片的同步跟进,实现均匀的应力分布[36]。另一种减小径向应力的方法是改变夹片的材料,例如采用聚苯硫醚(PPS)材料作为夹片[37],或采用分段式复合材料夹片(图6)[38],均能够更有效地减缓应力集中。分段式复合材料夹片采用模压工艺生产,原材料包括短切纤维、树脂、石英砂等,通过不同材料的组合实现变刚度,从而降低FRP筋的应力集中。相关试验结果表明,分段复合材料夹片锚具的锚固效率达到90%,且BFRP筋复合材料夹片锚具体系的疲劳应力幅限值、蠕变率等参数与BFRP筋本身的试验结果一致。
![]() 图 6 分段式复合材料夹片[38]Figure 6. Segmented composite wedge
图 6 分段式复合材料夹片[38]Figure 6. Segmented composite wedge2.2 FRP筋转向半径及角度的合理优化
目前,预应力FRP筋在转向处力学性能的研究较少。Zhu等[39]开展了转向块处FRP筋静力性能试验(图7),研究表明,由于弯折对筋材造成一定程度的附加应力,转向区外侧是FRP筋中应力最大的部分,FRP筋发生破坏时,弯折段外侧最大应变与FRP筋极限拉应变基本一致。由于弯折作用,FRP筋极限荷载相比于单向拉伸试验中FRP筋的极限荷载有不同程度的降低,下降率与转向半径和转向角度有关。
![]() 图 7 图7 FRP筋转向区试验装置[39]Figure 7. Test setup for FRP tendons at a deviator
图 7 图7 FRP筋转向区试验装置[39]Figure 7. Test setup for FRP tendons at a deviator1)转向半径的优化
图8(a)是不同转向半径下的FRP筋承载力保留率,通过对比可以发现,转向半径对FRP筋承载力保留率的影响显著。不同直径FRP筋的力学性能对弯折的敏感度不同,对于直径8mm的BFRP筋,当转向半径R与FRP筋半径r比值(R/r)从400变为200时,BFRP筋的承载力仅有5~8%的降低,当R/r从200变为100时,BFRP筋的承载力大幅下降;对于直径16 mm的BFRP筋,当R/r从200变为100时,承载力降低不到5%,当R/r从100变为50时,承载力大幅下降。此外,对于弹性模量较高的CFRP筋,R/r对转向处强度的影响更大,尤其是当R/r从200变为100时,承载力仅约为初始值的一半。
![]() 图 8 图8转向角度和转向半径对弯折FRP筋承载力保留率的影响[39]Figure 8. Effects of deviation radius and angle on the loading capacity of FRP tendon at deviator
图 8 图8转向角度和转向半径对弯折FRP筋承载力保留率的影响[39]Figure 8. Effects of deviation radius and angle on the loading capacity of FRP tendon at deviator2)转向角度的优化
图8(b)对比了不同转向角度下的FRP筋承载力保留率,可以看出,当FRP筋转角从0°变为14°时,承载力下降率超过10%,其中直径为8 mm的BFRP筋和CFRP筋的下降率分别为11%和13%。但当转向角度从14°变化到27°时,FRP筋的承载力下降率不超过5%。因此,为了严格限制FRP筋承载力降低,转向角度不得超过15°。对于弹性模量更大的FRP筋,转向角度限制更加严格,例如Santoh等[40]通过试验探讨了CFRP筋的拉伸强度和转向角度的关系,当转向角度从5°变化到25°时,拉伸强度的降低比较明显;转向角度大于25°时,强度降低趋势明显减缓,建议FRP筋的转向角度不超过5°。另一方面,转向角度越大,摩擦造成的FRP筋预应力损失也越大,因此FRP筋转向角度不宜过大。
综上,根据优化试验的结果,建议工程设计中转向半径和FRP筋半径的比值R/r不宜小于200。为了转向角度限值规定的一致性,建议FRP筋的转向角度不宜超过5°,但可根据FRP筋的种类适当放宽该限值。
3. 体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件研究
既有研究中,体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件大多以梁为主要研究对象,本节将主要介绍体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁力学性能相关研究成果。
3.1 静力性能研究
国际上关于体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁的研究大多采用CFRP和AFRP筋。Lou等[41]的数值分析表明,体外预应力CFRP筋混凝土梁的静力性能与预应力钢筋混凝土梁类似。在一定范围内适当提高体外预应力筋的配筋率,有助于显著提高结构的开裂荷载和屈服荷载,但会逐渐降低结构延性。另外,虽然体外预应力能显著提高混凝土梁的开裂荷载和屈服荷载,但在梁体内无任何配筋的情况下,结构的曲率分布会变得极其不规则,从而导致破坏时局部裂缝过大;反之,配置一定量的体内钢筋,可以使结构的曲率分布和开裂模式得到明显的改善。极限状态下的体外预应力FRP筋应力(以下简称“极限应力”)是决定构件承载力的重要参数[42],为此,Ghallab and Beeby[43]以极限应力的几个影响因素为变量,对16根梁进行了试验研究,结果表明,当体外预应力FRP筋的有效高度大于截面高度时,有效高度将对其极限应力产生显著影响。另外,预应力水平、混凝土强度、转向块数量和转向块间距等对FRP筋的极限应力影响较大。
Wang等[44]和史健喆等[45]对体外预应力BFRP筋混凝土梁的静力性能进行了试验研究,结果表明,体外预应力BFRP筋可以显著提高结构的开裂荷载、屈服荷载和极限荷载,并可以保证一定的结构延性,体外预应力BFRP筋梁的力学性能与体外预应力钢绞线梁各类力学性能类似,且由于FRP是线弹性材料,前者卸载后的残余变形明显小于后者。复合材料夹片锚具在体外预应力梁的加载过程中能够有效地对BFRP筋施加锚固力,夹片与筋之间不发生任何滑移,在梁体发生破坏时,锚固端未发生任何形式的损伤,从而证明了复合材料锚具在构件极限状态下的有效性。
3.2 长期持荷性能研究
既有文献中体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁的长期性能试验研究很少。史健喆[6]通过杠杆配重法开展了为期150天的体外预应力BFRP筋混凝土梁长期荷载试验,试件为全预应力混凝土梁。从图9可以看出,预应力越大,长期反拱值增量也越大;在初始预应力水平相同的情况下,由于钢绞线弹性模量较高,普通松弛钢绞线在结构中的长期预应力损失率比体外预应力BFRP筋高15%。混凝土强度等级为C60的梁长期反拱增长率比混凝土强度等级为C40的梁相应值低33%,这是因为高强混凝土的长期徐变比普通混凝土小。
曹国辉和方志[46]开展了长达1001天的体外预应力CFRP筋混凝土箱梁长期力学性能试验,试验结束时长期跨中挠度为初始挠度的2.3~2.4倍,且挠度经过前3个月的较快发展后逐渐趋于稳定。长期荷载作用下,顶板混凝土和受压钢筋的应变变化较大,而受拉钢筋应变变化较小。
3.3 疲劳性能研究
在实际工程中,大多数结构并非一直承受恒定荷载的作用,尤其是桥梁等直接承受风荷载、车辆荷载的结构。大量的疲劳试验已经表明,体外预应力CFRP筋混凝土梁和体外预应力AFRP筋混凝土梁具有优良的疲劳性能,在特定的疲劳荷载循环次数下(一般为200万次)未发生破坏[47-49]。体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构中,应力幅最大且最容易发生破坏的是混凝土内的非预应力钢筋[50]。因此,对于体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构,其结构疲劳破坏一般由非预应力钢筋应力集中导致的钢筋疲劳断裂控制,这一结论对于体外预应力FRP筋简支梁和连续梁同样适用。基于这一机制,研究人员提出了一系列基于钢筋疲劳断裂的体外预应力FRP筋加固结构疲劳寿命预测模型[47,50,51]。
除了体外预应力FRP筋简支梁外,少数学者还针对连续梁进行了疲劳研究。Grace等[49,52]开展了两跨连续梁试验,两跨循环荷载上限分别为极限承载力的13%和27%,前者挠度受疲劳荷载的影响不大,后者的挠度随着荷载循环次数的增加而增大,但未研究疲劳荷载作用下体外预应力FRP筋混凝土连续梁的内力重分布等塑性性能。程君[53]的试验研究表明,与简支梁类似,连续梁的疲劳破坏均始于疲劳加载跨控制截面附近主裂缝处的体内普通受拉钢筋疲劳断裂,试验梁疲劳加载跨跨内控制截面的抗弯刚度呈“快速减小-缓慢减小-迅速减小”的三阶段退化规律;与简支梁不同的是,疲劳荷载下连续梁纵向各截面刚度的不均匀退化会造成截面间相对刚度的变化,从而引起构件的疲劳内力重分布,随着疲劳次数增加,中支座截面弯矩迅速增加,在实际工程中应着重防止该处的疲劳破坏。
4. FRP筋体外预应力混凝土结构设计方法
由于体外预应力筋不能和混凝土结构协同变形,因此设计方法与体内有黏结混凝土结构存在明显区别。我国《纤维增强复合材料工程应用技术标准》GB 50608—2020[54]中对预应力FRP筋混凝土结构设计作了详细规定,并专门针对体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构提出了FRP筋应力增量、抗弯承载力等关键性能参数的计算方法。本节主要介绍GB 50608—2020[54]中涉及体外预应力FRP筋结构的设计方法以及国外规范中的相关规定,同时介绍了基于按龄期调整有效模量法(AEMM)[55]的结构时随变形和预应力损失预测。并利用既有文献中42根梁的试验数据和计算方法得到的理论值进行对比,验证了设计计算方法的准确性。
4.1 预应力FRP筋张拉控制应力
根据1.2节的介绍,张拉控制应力限值应适当低于蠕变断裂应力。但过低的张拉控制应力会造成FRP筋的强度无法充分发挥。GB 50608—2020[54]中给出的FRP筋张拉控制应力σcon上下限值如表7。
表 7 FRP筋张拉控制应力σconTable 7. Tension control stress σcon of FRP tendonsType of FRP CFRP AFRP BFRP Upper limit 0.65 fu 0.55 fu 0.50 fu Lower limit 0.50 fu 0.35 fu 0.35 fu fu is the tensile strength of FRP tendon. 4.2 预应力损失
1)张拉过程中的预应力损失
张拉过程中的预应力损失包括锚具变形和预应力筋内缩值a引起的预应力损失值σl1和预应力筋与转向块摩擦引起的预应力损失值σl2,各国规范针对该指标的计算方法基本一致,以GB 50608—2020[54]为例,σl1按下式计算:
σl1=alEp (1) 式中,
l−张拉端至锚固端之间的距离(mm);
Ep−FRP筋弹性模量。
对于黏结型锚具和夹片式锚具,a分别取1~2mm和8mm。
σl2按下式计算:
σl2=σcon(1−e−μθ) (2) 式中,
σcon−预应力FRP筋张拉控制应力值;
μ−预应力FRP筋与转向块的摩擦系数;
θ−预应力FRP筋转向角度。
当μ θ不大于0.2时,σl2可按σl2=μ θσcon计算,对于CFRP筋、AFRP筋和BFRP筋,μ分别取0.30、0.25和0.30。
2)结构服役期间的预应力损失
结构服役期间的预应力损失,可按σl4+σl5粗略估算。如需进行较为精确的预测,可参照4.6节中的方法进行计算。
(1)预应力FRP筋的松弛损失σl4按下式计算:
σl4=rrσcon (3) 式中,
rr−松弛损失率,根据1.2节的内容,可用对数曲线拟合松弛率,即rr=a1+a2logT,当无实测数据确定系数a1和a2时,对于设计基准期为100年的预应力FRP筋受弯构件,rr也可近似按表4的数值取用;
其余符号意义同前。
(2)预应力作用下混凝土收缩和徐变引起的预应力损失σl5按下式计算:
σl5=35+280σpc/fcu′(1+15ρe)⋅EpEs (4) 式中,
σpc−预应力FRP筋合力点处的混凝土法向压应力;
ρe−预应力FRP筋和非预应力钢筋的等效配筋率;
fcu′−施加预应力时的混凝土立方体抗压强度;
Es−普通钢筋弹性模量;
其余符号意义同前。
如需针对特定服役龄期进行较为精确的预测,σl5可按4.6节的方法计算。
4.3 极限状态下体外预应力FRP筋应力增量
极限状态下体外预应力FRP筋应力增量(Δσpu)是计算体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁极限荷载的重要参数,国外大部分混凝土设计规范在计算该应力增量时,均采用对体内无黏结预应力筋应力增量进行修正的方法,因此存在一定的局限性。例如,美国ACI 440.4R[2]规定极限荷载下的FRP筋应力增量按下式计算:
Δσpu=ΩuEpεcu(Rddpx0−1) (5) 式中,
Ωu−应变折减系数;
εcu−混凝土极限压应变;
Rd−折减系数;
dp−体外预应力FRP筋初始有效高度;
x0−极限状态下的中和轴高度。
欧洲fib规范[56]虽未给出具体计算公式,但建议极限极限荷载下的FRP筋应力增量以正常使用极限状态的应变为基准,按承载能力极限状态下的FRP筋的应变增量进行推算。
英国BS 8110规范[57]采用下式计算极限荷载下的FRP筋应力增量:
Δσpu=7000(1−1.7fuApfcbdp)Ldp (6) 式中,
fu−FRP筋抗拉强度;
Ap−FRP筋截面积;
fc−混凝土极限抗压强度;
b−构件截面宽度;
L−构件跨度;
其余符号意义同前。
我国GB 50608—2020[54]中基于Peng等[58]的计算理论,针对体外预应力FRP筋给出了极限状态下应力增量计算方法,具体如下:
Δσpu=EpLfp(X1+Y1εcux0)εcux0 (7) 式中,
X1、Y1−常数,按规范计算;
Lfp−锚固端之间的体外预应力FRP筋总长度;
其余符号意义同前。
4.4 转向区FRP筋应力
第2节中提到,体外预应力FRP筋在转向区容易产生应力集中,因此需限制转向区FRP筋的应力以保证该区域FRP筋的安全性。转向区FRP筋应力σdev可采用Dolan公式[59]计算,表达式如下:
σdev=P/Ap+Epr/R (8) 式中,
P−直线段FRP筋轴力;
r−预应力FRP筋半径;
R−转向半径;
其余符号意义同前。
基于Dolan公式,分别对CFRP筋、AFRP筋和BFRP筋提出不同转向半径下的强度折减系数(弯折后的断裂应力与初始强度的比值),如表8,CFRP筋、AFRP筋和BFRP筋的力学性能参照GB 50608—2020[54]规范取初始强度分别为1 800 MPa、1 300 MPa和1 300 MPa,弹性模量分别为140 GPa、65 GPa和55 GPa。需要说明的是,随着初始强度的提高和弹性模量的增加,折减系数将分别增大和减小,设计人员应根据实际的FRP筋力学性能适当选取折减系数。
表 8 不同R/r下的弯折FRP筋强度折减系数Table 8. Strength reduction coefficients of deviated FRP tendon at different values of R/rR/r CFRP tendon AFRP tendon BFRP tendon 200 0.61 0.75 0.79 300 0.74 0.83 0.86 400 0.81 0.88 0.89 4.5 正常使用极限状态计算
1)裂缝宽度
在荷载标准组合或准永久组合下,对于要求不出现裂缝的预应力FRP筋混凝土受弯构件(非预应力筋采用普通钢筋时),抗裂验算可按现行国家标准《混凝土结构设计规范》GB 50010—2010[60]方法进行;允许出现裂缝的预应力FRP筋混凝土受弯构件,根据GB 50608—2020[54]规范,最大裂缝宽度可按下式计算:
wmax (9) 式中,
ψ−裂缝间纵向受拉钢筋应变不均匀系数;
σsk−按荷载标准组合计算的受弯构件纵向受拉钢筋等效拉应力;
cs−最外层纵向受拉钢筋外边缘至受拉区底边的距离;
deq−受拉区纵向钢筋等效直径;
ρte−按有效受拉混凝土截面面积计算的纵向受拉钢筋的等效配筋率;
其余符号意义同前。
美国ACI 440.4R规范[2]建议采用Gergely-Lutz公式计算裂缝宽度w:
w = 0.076\beta \left( {{E_{\rm{s}}}{\varepsilon _{\rm{s}}}} \right)\sqrt[3]{{{d_{\rm{c}}}A}} (10) 式中,
β−中性轴到混凝土受拉边缘的距离与中性轴到受拉钢筋合力点距离之比;
εs−钢筋应变;
dc−混凝土保护层厚度;
A−混凝土有效受拉区面积。
欧洲fib规范[56]采用下式计算构件裂缝宽度wd:
{w_{\rm{d}}} = 2{l_{{\rm{s,}}\max }}\left( {{\varepsilon _{{\rm{sm}}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\rm{cm}}}} - {\varepsilon _{{\rm{cs}}}}} \right) (11) 式中,
ls,max−钢筋与混凝土发生相对滑移的长度;
εsm−ls,max范围内钢筋的平均应变;
εcm−ls,max范围内混凝土的平均应变;
εcs−混凝土收缩应变。
英国BS 8110规范[57]中的裂缝宽度为混凝土受拉区表面裂缝宽度,与其他规范不同,故在此不作介绍。
2)刚度
预应力FRP筋混凝土受弯构件的挠度可按现行国家标准《混凝土结构设计规范》GB 50010—2010[60]的有关规定计算。对于矩形、T形、倒T形和I形截面预应力FRP筋混凝土受弯构件,按荷载标准组合并考虑长期作用影响的截面抗弯刚度B可按下列公式计算:
B = \frac{{{M_k}}}{{{M_{\rm{q}}}(\theta - 1) + {M_k}}}{B_{\rm{s}}} (12) 式中,
Mk−按荷载标准组合计算的弯矩值;
Mq−按荷载准永久组合计算的弯矩值;
θ−虑荷载长期作用对挠度增大的影响系数,可取2;对于翼缘位于受拉区的倒T形截面,应增加20%。当有可靠工程经验或测试数据时,可按实际情况取值;
Bs−荷载标准组合计算的受弯构件的短期抗弯刚度;
其余符号意义同前。
Bs按下列规定计算:
不出现裂缝的受弯构件,
{B_{\rm{s}}} = 0.85{E_{\rm{c}}}{I_0} (13) 式中,
Ec−混凝土弹性模量;
I0−换算截面惯性矩;
其余符号意义同前。
允许出现裂缝的受弯构件,
{B_{\rm{s}}} = \frac{{0.85{E_{\rm{c}}}{I_0}}}{{{k_{{\rm{cr}}}} + (1 - {k_{{\rm{cr}}}})\omega }} (14) 式中,
kcr−预应力混凝土受弯构件正截面的开裂弯矩Mcr与弯矩Mk的比值,当kcr大于1.0时,取1.0;
ω−系数;
其余符号意义同前。
美国ACI 440.4R规范[2]采用下式中的修正有效惯性矩Ie计算结构刚度:
{I_{\rm{e}}} = {\left( {\frac{{{M_{{\rm{cr}}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{a}}}}}} \right)^3}{\beta _{\rm{d}}}{I_{\rm{g}}}{\rm{ + }}\left[ {1 - {{\left( {\frac{{{M_{{\rm{cr}}}}}}{{{M_{\rm{a}}}}}} \right)}^3}} \right]{I_{{\rm{cr}}}} \leqslant {I_{\rm{g}}} (15) 式中,
Ma−用于挠度验算的弯矩值;
βd−有效惯性矩折减系数;
Ig−全截面惯性矩;
Icr−开裂截面惯性矩;
其余符号意义同前。
欧洲fib规范[56]考虑钢筋的受拉刚化(Tension stiffening),采用下式计算构件有效刚度Beff:
{B_{{\rm{eff}}}} = \frac{{{B_{\rm{I}}} \cdot {B_{{\rm{II}}}}}}{{\zeta {B_{\rm{I}}} + \left( {1 - \zeta } \right){B_{{\rm{II}}}}}} (16) 式中,
BI−全截面刚度;
BII−未考虑受拉刚化的开裂后刚度;
ζ−受拉刚化系数。
英国BS 8110规范[57]仅通过跨高比限值来控制结构变形,未提出刚度计算公式。
4.6 梁体变形及预应力值的时随变化
Youakim and Karbhari[55]基于按龄期调整有效模量法,提出了预应力FRP筋混凝土结构长期性能参数计算方法。该方法大致分为四个步骤,首先计算恒定荷载施加时产生的瞬时应变与曲率;第二步,计算混凝土本身的自由蠕变应变εcr、收缩应变εsh以及蠕变产生的曲率变化Δφfree;第三步,对混凝土施加虚拟约束,使得第二步的应变和曲率变化完全恢复,计算相应的约束力ΔN和约束力矩ΔM;第四步,将ΔN和ΔM反向作用于考虑钢筋后的换算截面,求解换算截面的应变和曲率。根据该模型,考虑体外预应力FRP筋与构件变形的不一致性,截面曲率变化Δφ的计算方法分别如式下:
\Delta \varphi = {k_{\rm{I}}}\Delta {\varphi _{{\rm{free}}}} + \frac{{{k_{{\rm{cc}}}}}}{h}{(\Delta {\varepsilon _{{\rm{cc}}}})_{{\rm{free}}}} - \frac{{{A_{\rm{p}}}{y_{\rm{p}}}}}{{\overline I }}\frac{{\Delta {\sigma _{\rm{p}}}}}{{{{\overline E }_{\rm{c}}}}} (17) 式中,
kI、kcc−系数;
Δφfree−混凝土自由曲率变化值;
(Δεcc)free−混凝土因徐变产生的自由轴向变形;
h−截面高度;
yp−预应力筋截面形心到全截面中性轴的垂直距离;
Δσp−预应力FRP筋应力变化量;
\overline I −全截面惯性矩;{\overline E _{\rm{c}}} −按龄期调整的混凝土有效模量;体外预应力FRP筋应力变化Δσp按下式计算:
\Delta {\sigma _{\rm{p}}} = {E_{\rm{p}}}\frac{{\Delta {L_{\rm{p}}}}}{{{L_{{\rm{p0}}}}}} + \Delta {\sigma _{{\rm{pr}}}} (18) 式中,
ΔLp−梁体变形造成的体外预应力FRP筋的长度变化,该值与梁体本身的弯曲变形和体外预应力FRP筋的线形有关;
Lp0−体外预应力FRP筋初始长度;
Δσpr−松弛引起的应力下降,取值见1.2节;
其余符号意义同前。
4.7 梁构件力学性能理论值与试验值对比
为了验证规范中设计计算方法的合理性,从国内外收集了42根体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁的试验数据,对比试验值和计算方法得到的理论值,表9和表10列出了数据库的相关信息。除GB 50608—2020[54]的计算方法之外,还对比了美国规范ACI 440.4R-04[2]、欧洲混凝土规范fib[56]和英国规范BS8110[57]计算方法的精度,计算过程中的材料力学性能取实测值。
表 9 体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁抗弯性能研究数据库Table 9. Database of the studies on the flexural behaviors of concrete beams prestressed with external FRP tendons1)张拉过程中转向块摩擦导致的预应力损失
试验中,张拉完毕后张拉端和锚固端的FRP筋轴力差值反映了转向块摩擦造成的预应力损失σl2。各国规范计算σl2的方法相同,试验值与理论值比值的平均值为1.01,方差为0.05。因此,规范中计算公式具有足够的精确度,可直接用于摩擦损失计算。
2)极限状态下体外预应力FRP筋应力增量
表11列出了体外预应力FRP筋极限状态应力增量的理论值精度,其中GB 50608—2020[54]规范专门针对体外预应力FRP筋提出了应力增量计算方法,因此采用GB 50608—2020[54]计算的理论值最准确,但计算步骤较复杂。ACI 440.4R方法步骤简单,但精度不高。
表 11 体外预应力FRP筋极限状态应力增量Δσpu的试验值与理论值之比Table 11. Ratios of experimental value to theoretical value of the stress increment Δσpu of external prestressing FRP tendons at ultimate stateCodes ACI 440.4R BS 8110 fib GB 50608 Average value 1.39 2.14 1.58 1.01 Variance 0.58 0.89 0.45 0.20 3)极限抗弯承载力
表12中的数据表明,对于体外预应力FRP筋结构的极限抗弯承载力,GB 50608—2020[54]规范公式的计算精度最高。为了计算简便而选择ACI 440.4R时,计算精度可以接受。
表 12 体外预应力FRP筋混凝土梁抗弯承载力的试验值与理论值之比Table 12. Ratios of experimental value to theoretical value of the flexural capacity of concrete beams prestressed with external FRP tendonsCodes ACI 440.4R BS 8110 fib GB 50608 Average value 1.09 1.47 1.10 1.05 Variance 0.15 0.22 0.13 0.07 4)转向区FRP筋应力
用数据库中试验梁极限承载力下FRP筋应力的试验数据和Dolan公式计算得到的理论数据进行对比,得到试验值与理论值比值的平均值为1.02,方差为0.04。结果表明,Dolan公式对转向区FRP筋应力的预测结果与试验值的误差在3%以内,因此Dolan公式可以准确预测转向区FRP筋应力,设计时可直接采用。
5)正常使用荷载下的裂缝宽度
表13是不同规范中裂缝宽度计算方法精度对比,需要注意的是,规范中给出的裂缝计算公式考虑了长期混凝土收缩徐变作用的增大效应,而试验数据为短期裂缝宽度实测值,因此在计算过程中需将规范公式计算的理论值进行一定处理后,再和试验值对比。可以看出,我国规范计算的裂缝宽度计算精确度与美国和欧洲规范接近,实际设计时可直接采用GB 50608—2020[54]。
表 13 预应力FRP筋混凝土梁裂缝宽度的试验值与理论值之比Table 13. Ratios of experimental value to theoretical value of the crack width of concrete beams prestressed with external FRP tendonsCodes ACI 440.4R fib GB 50608 Average value 0.94 1.03 0.92 Variance 0.53 0.59 0.65 6)正常使用荷载下的短期挠度
将ACI 440.4R、fib和GB 50608—2020[54]规范计算的0.7倍极限荷载下的挠度理论值和试验值对比(表14)可知,与裂缝宽度计算类似,GB 50608—2020[54]规范计算正常使用极限状态短期挠度的精度与ACI 440.4R和fib接近,设计时可采用GB 50608—2020[54]规范。
表 14 预应力FRP筋混凝土梁挠度的试验值与理论值之比Table 14. Ratios of experimental value to theoretical value of the deflection of concrete beams prestressed with external FRP tendonsCodes ACI 440.4R fib GB 50608 Average value 0.94 0.95 0.92 Variance 0.34 0.38 0.25 7)长期挠度(反拱)及预应力损失预测
表15和表16是基于AEMM的结构长期挠度(反拱)及预应力损失的理论值精度。文献[46]中未测量预应力损失,且仅包含一个试件,因此文献[46]的长期挠度结果中无方差数据。对比结果表明,基于AEMM的长期性能预测方法考虑了混凝土徐变和FRP筋预应力损失之间的相互影响,计算结果准确。
表 15 预应力FRP筋混凝土梁长期挠度(反拱)试验结果与AEMM计算的理论值之比Table 15. Ratios of experimental value to theoretical value calculated using AEMM of the long-term deflection (camber) of concrete beams prestressed with external FRP tendons5. 结论与展望
围绕体外预应力纤维增强树脂基复合材料(FRP)筋混凝土结构,文章从预应力FRP筋、关键技术和构件三个层次展开介绍。在预应力FRP筋层次,重点阐述了FRP筋的长期性能(蠕变、松弛和疲劳),提出了面向设计的FRP筋应力限值和松弛率;在关键技术层次,综述了FRP筋主要锚具形式,并结合试验结果分析了转向区FRP筋性能的影响因素,优化了FRP筋转向参数。在构件层次,总结了体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件的试验研究结果,系统介绍了体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构的设计方法,并通过既有文献中42根FRP筋体外预应力梁的试验结果对计算方法的精度进行了验证。主要结论如下:
(1)在土木工程常用的几种预应力FRP筋中,碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(CFRP)筋的力学性能最好,玄武岩纤维增强树脂基复合材料(BFRP)筋和芳纶纤维增强树脂基复合材料(AFRP)筋次之。BFRP的弹性模量较低,由混凝土收缩徐变产生的预应力损失值明显小于CFRP筋的相应值。BFRP筋蠕变断裂应力为0.54fu (fu是FRP筋的抗拉强度),1000小时松弛率仅为2.6%,疲劳应力幅和最大应力限值分别为0.04fu和0.53fu,可以满足预应力材料对应力水平和松弛率的要求。AFRP筋的松弛率大,会导致服役期间较大的预应力损失。
(2) FRP筋锚固和转向是体外预应力FRP筋应用关键技术。预应力FRP筋锚具主要分为黏结型锚具、摩擦型锚具和夹片式锚具。黏结型锚具不会对筋材造成挤压,但长期力学性能不足;摩擦型锚具长期受力性能较好,但不利于施工便利性;夹片式锚具组装方便,但对FRP筋的切口效应明显。复合材料夹片锚具能够显著降低FRP筋端部应力集中,有效提供锚固力,锚固效率系数高于90%。
(3)转向造成的FRP筋的强度下降率随转向角度的增加而增大,随转向半径的增加而减小。相比于转向角度,转向半径对弯折FRP筋的影响更加显著,建议转向半径和FRP筋半径的比值(R/r)不宜小于200,转向角度不宜大于5°,但可根据FRP筋的种类适当放宽该限值。
(4)体外预应力FRP筋可显著提高钢筋混凝土结构的开裂荷载、屈服荷载和极限荷载,并可以保证一定的结构延性。在长期荷载下,体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构的变形和预应力损失呈现先快速增长后趋于稳定的规律,由于BFRP筋弹性模量较低,其预应力损失低于普通钢绞线。体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构疲劳破坏一般由内部的非预应力钢筋在裂缝处的疲劳断裂控制,可基于这一机制建立寿命预测模型。
(5)我国《纤维增强复合材料工程应用技术标准》GB 50608—2020中体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构设计计算方法的准确性得到42根FRP筋体外预应力梁的试验结果的验证;对于正常使用荷载下的长期变形和预应力损失预测,当精度要求较高时,建议采用按龄期调整有效模量法(AEMM)。
结合既有的国内外研究成果,未来尚需对体外预应力FRP筋混凝土结构开展的工作有以下几个方面:
(1)在FRP筋性能方面,还需全面研究FRP筋在多因素耦合作用下的耐久性,且尚需对弯折FRP筋的疲劳性能进行系统研究。
(2)在FRP筋锚固性能方面,应进一步提升锚固效率,开发适用于多根FRP筋的锚具,且尚需开展黏结型锚具、摩擦型锚具和夹片式锚具在不同应力水平下的疲劳性能研究。
(3)在体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件静力性能方面,应进一步开展构件抗弯承载力极限状态可靠度分析,同时进行构件受剪性能及其设计计算方法研究。
(4)在体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件疲劳性能方面,尚需考虑实际工程中的荷载情况,进行随机疲劳荷载下的构件性能研究,并建立相应的疲劳寿命预测方法。
(5)尚需开展体外预应力FRP筋混凝土构件的现场暴露试验,验证体外预应力FRP筋对严酷环境下结构力学性能和耐久性的提升效果。
-
表 1 拉伸性能测试条件
Table 1 Tensile properties test conditions
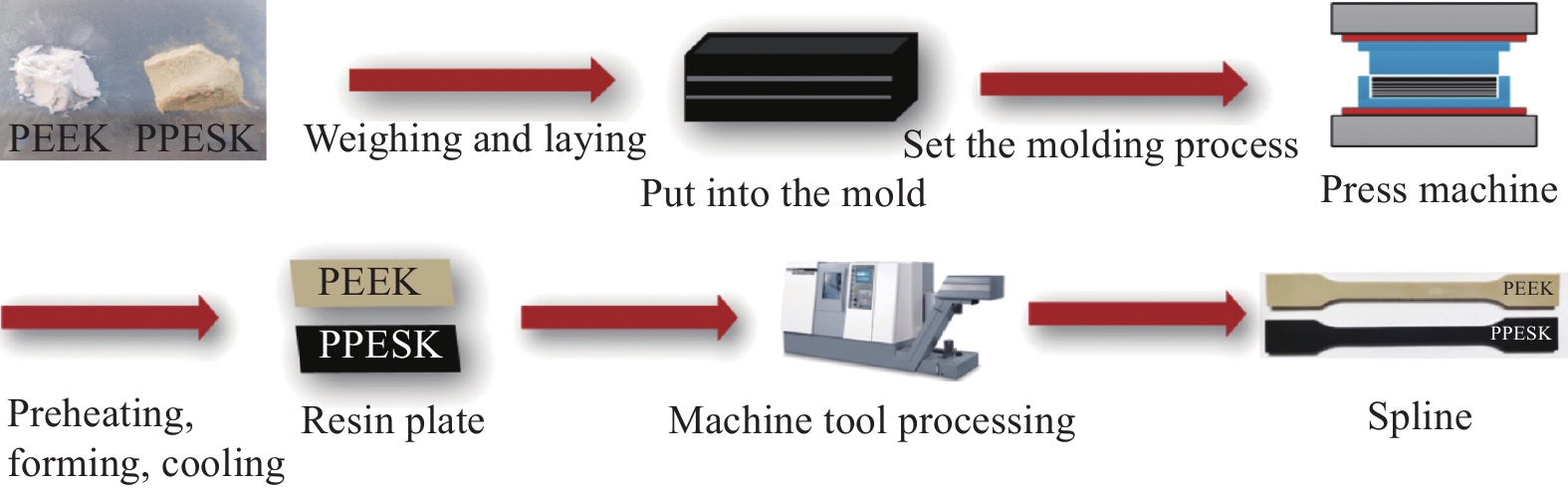
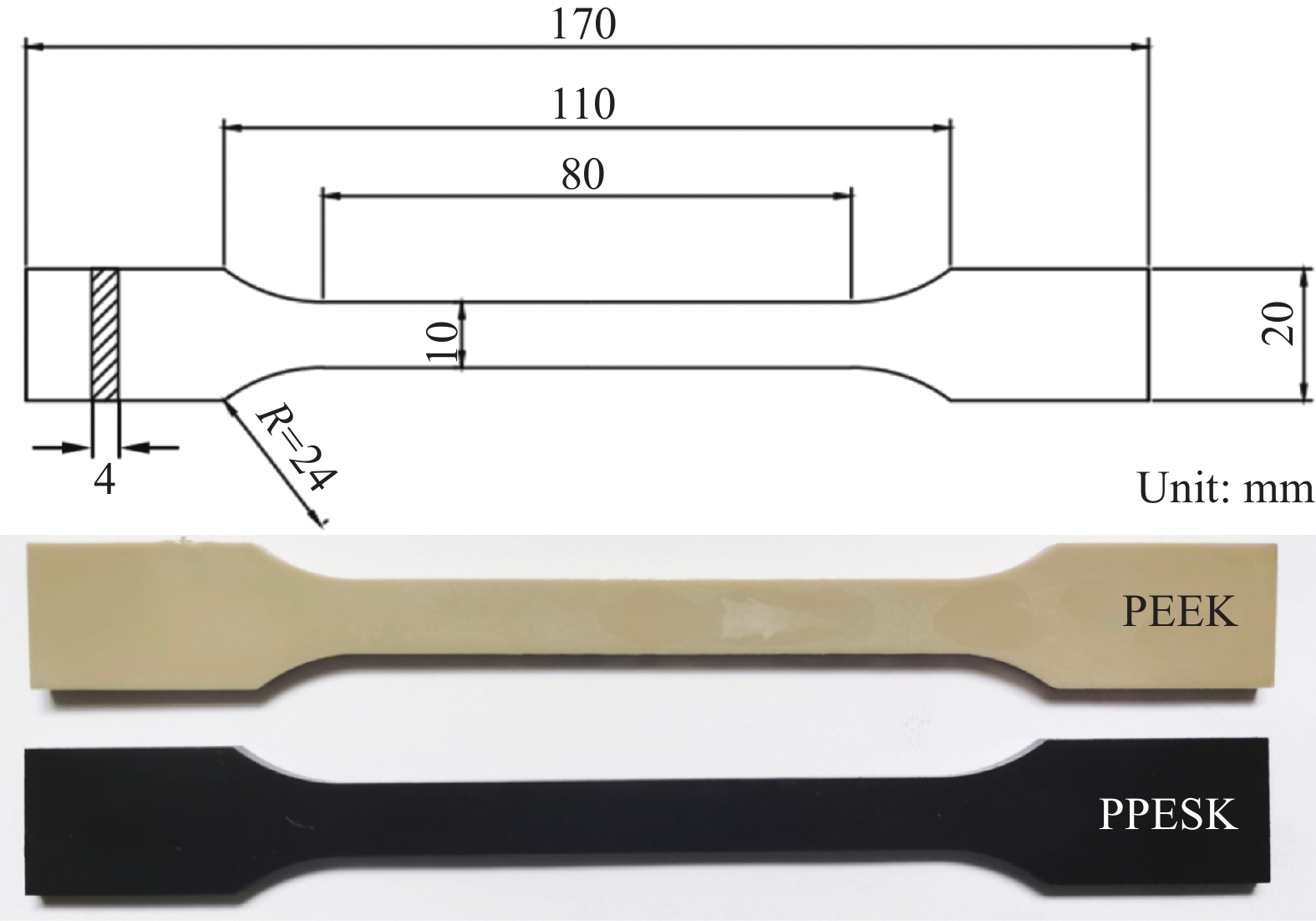
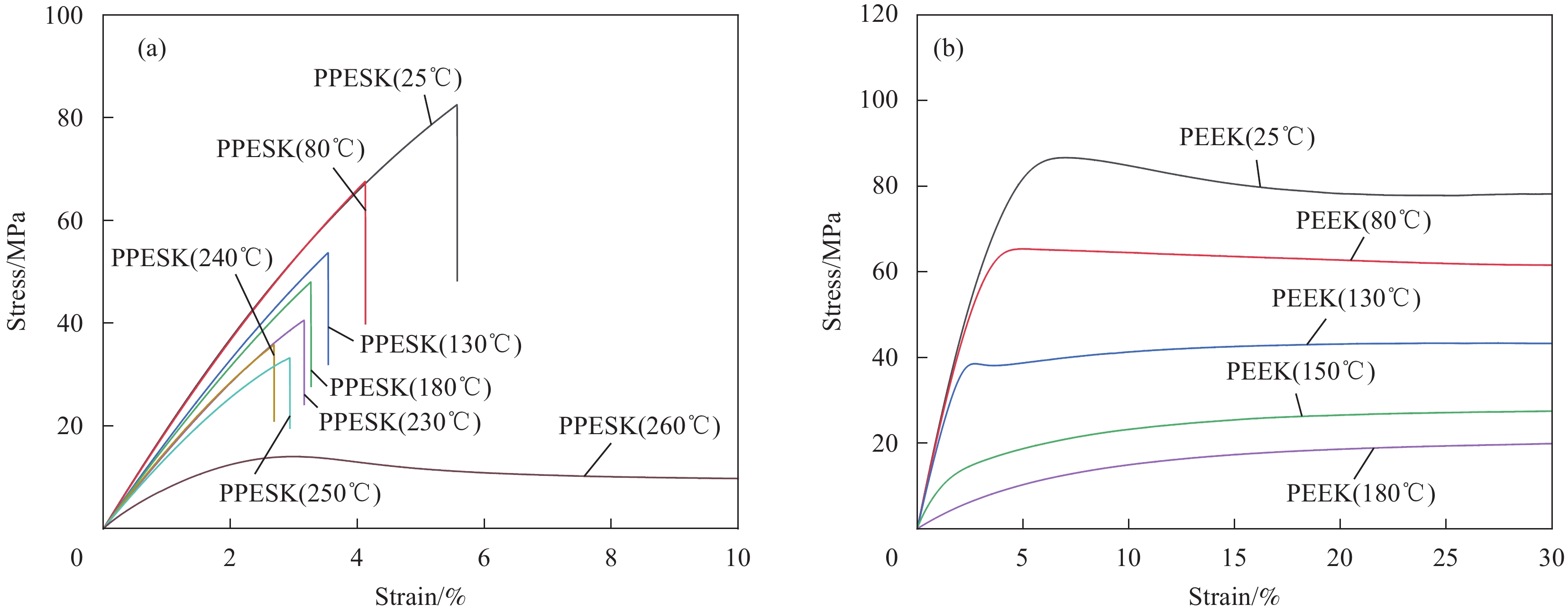
Tensile temperature/℃ Tensile speed 0.5 mm/min 5 mm/min 50 mm/min 500 mm/min 25 PPESK/PEEK PPESK/PEEK PPESK/PEEK PPESK/PEEK 80 — PPESK/PEEK — — 130 — PPESK/PEEK — — 150 — PEEK — — 180 — PPESK/PEEK — — 230 — PPESK — — 240 — PPESK — — 250 — PPESK — — 260 — PPESK — — -
[1] YANG G, PARK M, PARK S J. Recent progresses of fabrication and characterization of fibers-reinforced composites: A review[J]. Composites Communications, 2019, 14: 34-42. DOI: 10.1016/j.coco.2019.05.004
[2] 熊健, 李志彬, 刘惠彬, 等. 航空航天轻质复合材料壳体结构研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6): 1629-1650. XIONG Jian, LI Zhibin, LIU Huibin, et al. Research progress on aerospace lightweight composite shell structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(6): 1629-1650(in Chinese).
[3] 李雪芹, 陈科, 刘刚. 基于ANSYS的复合材料螺旋桨叶片有限元建模与分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(4): 591-598. LI Xueqin, CHEN Ke, LIU Gang. Finite element modeling and analysis of composite propeller blade based on ANSYS[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(4): 591-598(in Chinese).
[4] 谭伟, 那景新, 任俊铭, 等. 高温环境下碳纤维增强树脂复合材料的层间力学性能老化行为与失效预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(4): 859-868. TAN Wei, NA Jingxin, REN Junming, et al. Aging behavior and failure prediction of interlaminar mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced resin composites under high temperature environment[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(4): 859-868(in Chinese).
[5] 蹇锡高, 王锦艳. 含二氮杂萘酮联苯结构高性能工程塑料研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2012, 31(2): 16-23. DOI: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2012.02.03 JIAN Xigao, WANG Jinyan. Progress of high-performance engineering plastics containing diazanaphthone biphenyl structure[J]. Materials China, 2012, 31(2): 16-23(in Chinese). DOI: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2012.02.03
[6] 何伟, 廖功雄, 刘程, 等. PPESK/PTFE共混物的热性能和动态机械性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2005(5): 464-470. HE Wei, LIAO Gongxiong, LIU Cheng, et al. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of PPESK/PTFE blends[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2005(5): 464-470(in Chinese).
[7] ZHU T Q, REN Z Y, XU J, et al. Damage evolution model and failure mechanism of continuous carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin matrix composite materials[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2023, 244: 110300.
[8] 王子健, 周晓东. 连续纤维增强热塑性复合材料成型工艺研究进展[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2021(10): 120-128. WANG Zijian, ZHOU Xiaodong. Research progress of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites[J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2021(10): 120-128 (in Chinese).
[9] 王孟, 刘程, 张玉, 等. 成型温度对CF/PPEK复合材料的缺陷和力学性能影响[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2024(3): 5-12. WANG Meng, LIU Cheng, ZHANG Yu, et al. Effect of molding temperature on defects and mechanical properties of CF/PPEK composites[J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2024(3): 5-12(in Chinese).
[10] 顾轶卓, 张佐光, 李敏, 等. 复合材料变厚层板热压成型缺陷类型与成因实验研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008(2): 41-46. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.008 GU Yizhuo, ZHANG Zuoguang, LI Min, et al. Experimental study on the types and causes of defects in hot compression molding of composite variable-thickness laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2008(2): 41-46(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.008
[11] 龚颖, 张佐光, 顾轶卓, 等. 热压工艺参数对单向复合材料层板密实状态的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2006(1): 12-16. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.01.002 GONG Ying, ZHANG Zuoguang, GU Yizhuo, et al. Influence of hot pressing process parameters on the compact state of unidirectional composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2006(1): 12-16(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.01.002
[12] DAI G, ZHAN L, GUAN C, et al. Optimization of molding process parameters for CF/PEEK composites based on Taguchi method[J]. Composites and Advanced Materials, 2021, 30(14):713-715.
[13] FUJIHARA K, HUANG Z M, RAMAKRISHNA S, et al. Influence of processing conditions on bending property of continuous carbon fiber reinforced PEEK composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2004, 64(16): 2525-2534. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2004.05.014
[14] XU Z, ZHANG M, GAO S, et al. Study on mechanical properties of unidirectional continuous carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK composites fabricated by the wrapped yarn method[J]. Polymer Composites, 2019, 40(1): 56-69. DOI: 10.1002/pc.24600
[15] SALEK M H. Effect of processing parameters on the mechanical properties of carbon/PEKK thermoplastic composite materials[D]. Montreal: Concordia University, 2005.
[16] 赵亮, 肖纳敏. 先进树脂基复合材料成型工艺仿真软件研发综述[J]. 软件导刊, 2021, 20(10): 1-6. DOI: 10.11907/rjdk.212032 ZHAO Liang, XIAO Namin. Overview of the research and development of simulation software for advanced resin matrix composites molding process[J]. Software Guide, 2021, 20(10): 1-6(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11907/rjdk.212032
[17] TRENDE A, ASTROM B T. Heat transfer in compression molding of thermoplastic composite laminates and sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 2002, 15(1): 43-63.
[18] LI X, HAN X, DUAN S, et al. A two-stage genetic algorithm for molding parameters optimization for minimized residual stresses in composite laminates during curing[J]. Applied Composite Materials, 2021, 28(4): 1315-1334. DOI: 10.1007/s10443-021-09912-z
[19] TAO Q, PINTER G, ANTRETTER T, et al. Model free kinetics coupled with finite element method for curing simulation of thermosetting epoxy resins[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(27): 46408. DOI: 10.1002/app.46408
[20] LI H Z, XIAO X Z, LIAO W H, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study regarding the cross-sectional morphology of PEEK monofilament deposition during FDM-based 3D printing[J]. Langmuir, 2023, 39(37): 13287-13295.
[21] QIN X D, WU X Z, LI H, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of orthogonal cutting of carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone (CF/PEEK)[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 119(1-2): 1003-1017.
[22] ZHU L, ZHANG H, GUO J, et al. Axial compression experiments and finite element analysis of basalt fiber/epoxy resin three-dimensional tubular woven composites[J]. Materials, 2020, 13(11): 2584. DOI: 10.3390/ma13112584
[23] ZAL V, NAEINI H M, SINKE J, et al. A new procedure for finite element simulation of forming process of non-homogeneous composite laminates and FMLs[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 163: 444-453.
[24] LIANG Q Q, WU X Q. Research status of carbon fibre-reinforced PEEK composites[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 834: 225-228.
[25] 常保宁. 碳纤维增强高性能热塑性复合材料本构模型与增材制造工艺研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2022. CHANG Baoning. Research on the intrinsic model and additive manufacturing process of carbon fiber reinforced high performance thermoplastic composites[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2022(in Chinese).
[26] El-QOUBAA Z, OTHMAN R. Strain rate sensitivity of polyetheretherketone's compressive yield stress at low and high temperatures[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2016, 95: 15-27.
[27] 庄靖东. 聚醚醚酮板材热成型性能研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2017. ZHUANG Jingdong. Research on thermoforming properties of polyetheretherketone sheet[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[28] 蹇锡高, 陈平, 廖功雄, 等. 含二氮杂荼酮结构新型聚芳醚系列高性能聚合物的合成与性能[J]. 高分子学报, 2003(4): 469-475. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3304.2003.04.002 JIAN Xigao, CHEN Ping, LIAO Gongxiong, et al. Synthesis and properties of novel polyarylether series high-performance polymers containing diazepinone structure[J]. Acta Macropolymers, 2003(4): 469-475(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3304.2003.04.002
[29] 蹇锡高, 朱秀玲, 陈连周. 二甲基取代杂环联苯聚芳醚的合成与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2001(11): 1932-1935. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0251-0790.2001.11.028 JIAN Xigao, ZHU Xiuling, CHEN Lianzhou. Synthesis and properties of dimethyl-substituted heterocyclic biphenyl polyarylether[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2001(11): 1932-1935(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0251-0790.2001.11.028
[30] 欧洲标准协会. 塑料制品 拉伸性能的测定 第2部分: 模塑和挤塑制品的试验条件: ISO 527-2[S]. 布鲁塞尔: 欧洲标准协会, 2012. European Standards Institute. Plastic products—Determination of tensile properties—Part 2: Test conditions for molded and extruded products: ISO 527-2[S]. Brussels: European Standards Institute, 2012(in Chinese).
[31] 何曼君, 张红东, 陈维孝, 等. 高分子物理 [M]. 3版. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2019: 210. HE Manjun, ZHANG Hongdong, CHEN Weixiao, et al. Polymer physics[M]. 3rd edition. Shanghai: Fudan University Press, 2019: 210(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 颜秀花,房娟,唐兰勤. 磁性纳米ZnFe_2O_4/Ag_3PO_4复合材料的合成及光催化降解性能. 环境科学学报. 2025(01): 135-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蒋莉萍,张雪乔,钟晓娟,魏于凡,肖利,郭旭晶,羊依金. 钒渣酸浸提铁工艺优化及复合光催化剂的制备. 化工进展. 2025(01): 538-548 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-
目的
随着科技水平的不断发展,装备使役性能要求日益提升,对复合材料构件高温下的力学性能也提出了更高要求。含二氮杂萘酮结构的聚醚砜酮(简称“PPESK”)不仅耐温性能出色,且力学性能优异,其复合材料在新一代装备中拥有广阔的应用前景。而鉴于此类耐高温树脂的分子结构特殊,其力学行为势必不同于传统树脂。本文聚焦拉伸工况,针对PPESK特殊的拉伸力学行为展开探索性研究,旨在为后续全面掌握PPESK的力学行为,进而发展与之相匹配的先进制造工艺提供数据基础。
方法研究工作采用对比实验的方式开展,对照组选用典型商用树脂——聚醚醚酮(简称“PEEK”)。首先,以拉伸强度和模量保持率为指标,对比了PPESK与PEEK在25~180℃下的耐热性,并通过开展动态热机械分析测试(DMA),分析了耐热性差异的内在原因;在此基础上,采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM),测量了断裂时的变形量,观察了断口形貌,据此对比了PPESK与PEEK的拉伸变形-断裂行为,并通过多功能X射线衍射测试(XRD)分析了行为差异的本质因素;最后,在0.5~500 mm/min拉伸速率范围内开展了多组实验,根据强度与模量的变化趋势,对比了PPESK与PEEK的拉伸性能对拉伸速率变化的敏感性,并基于高分子物理相关理论分析了敏感性存在差异的主要原因。
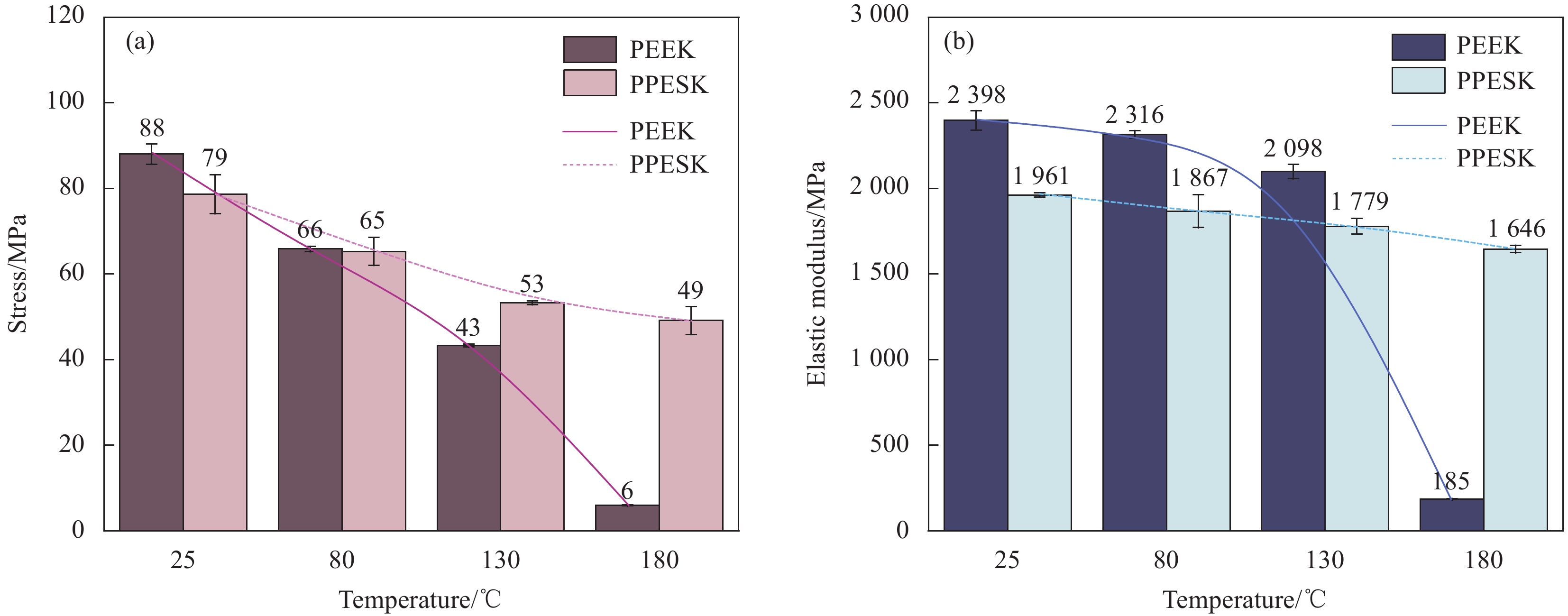
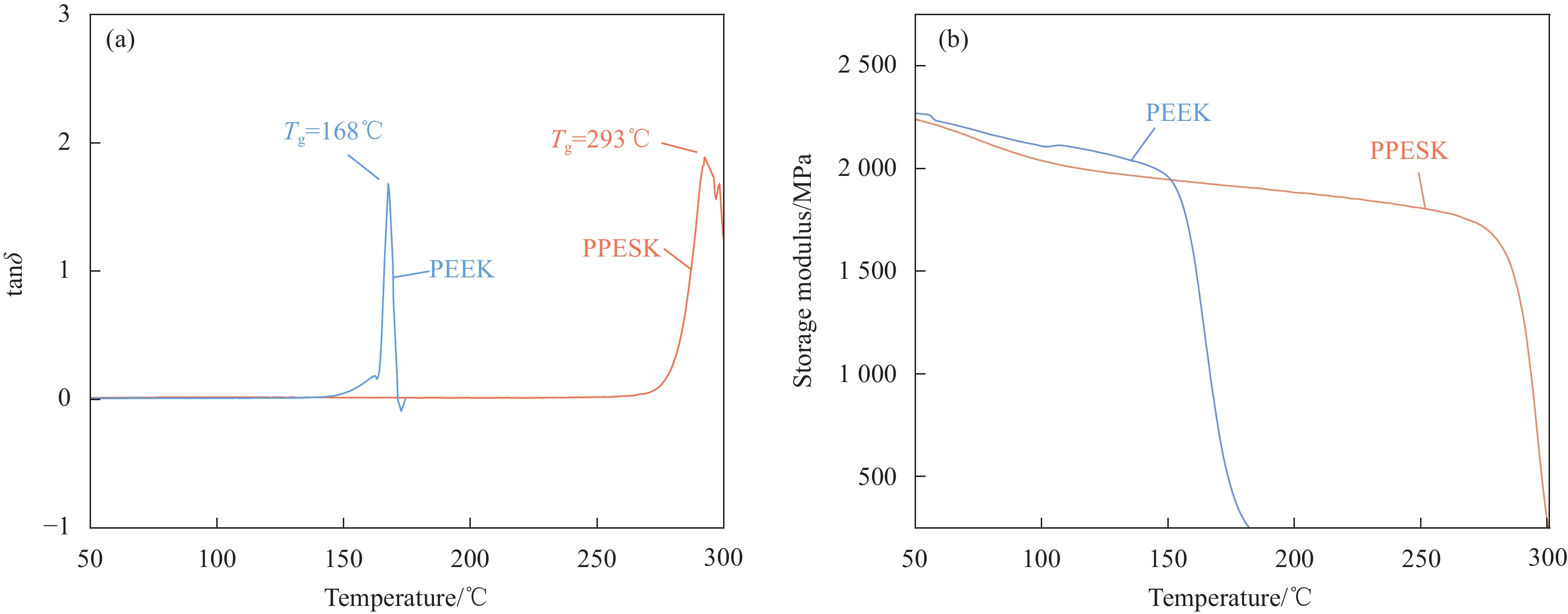
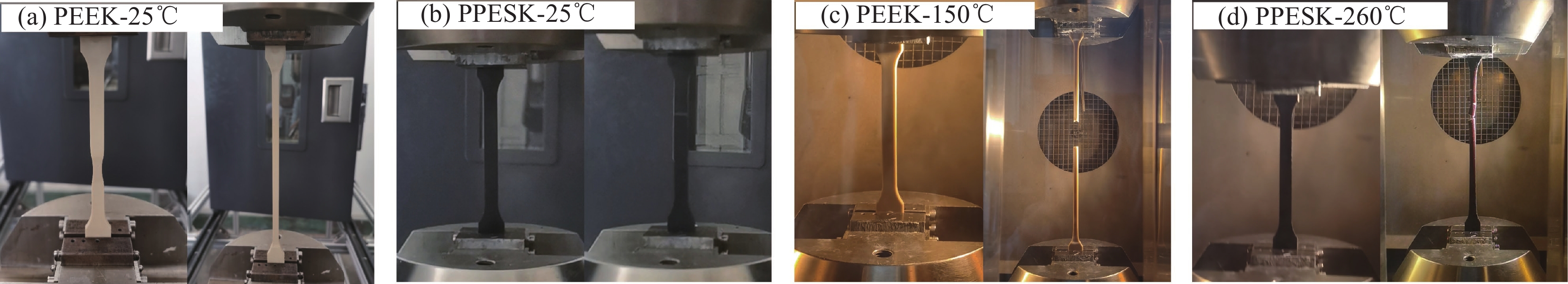
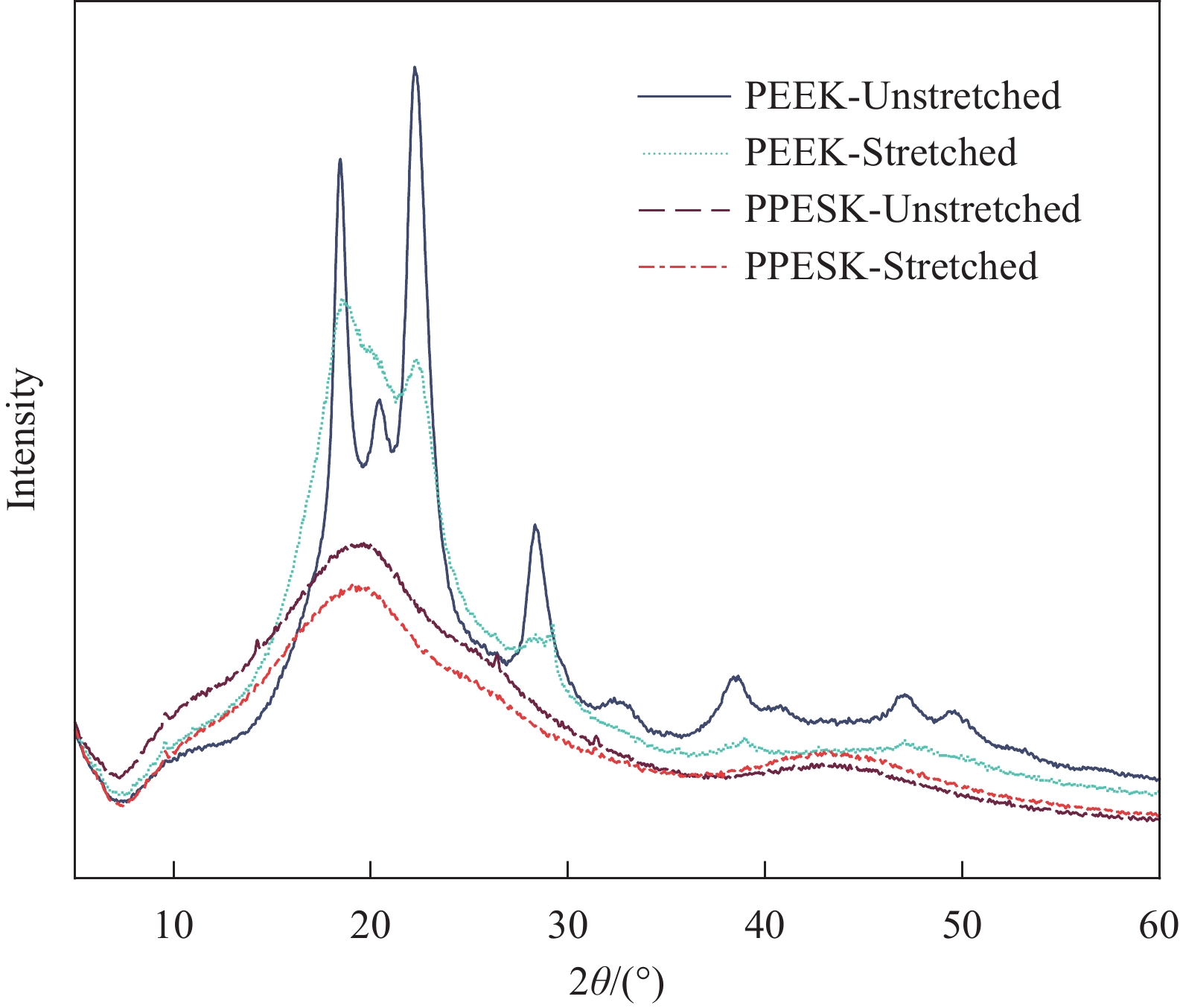
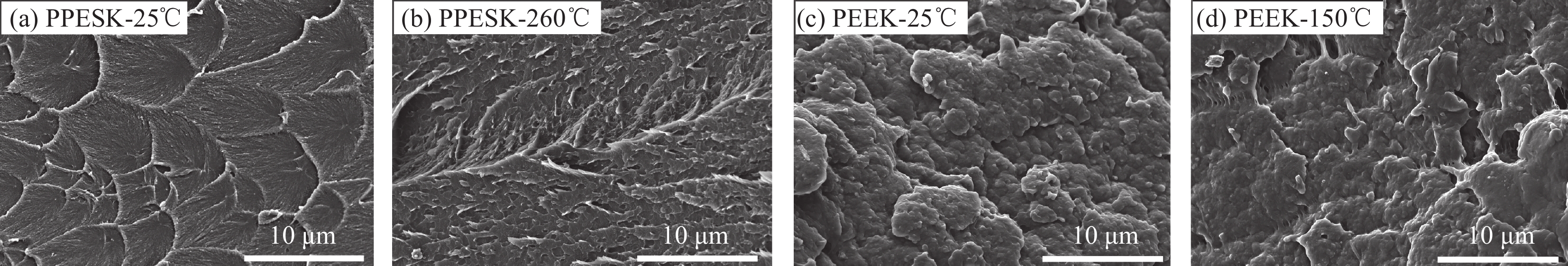
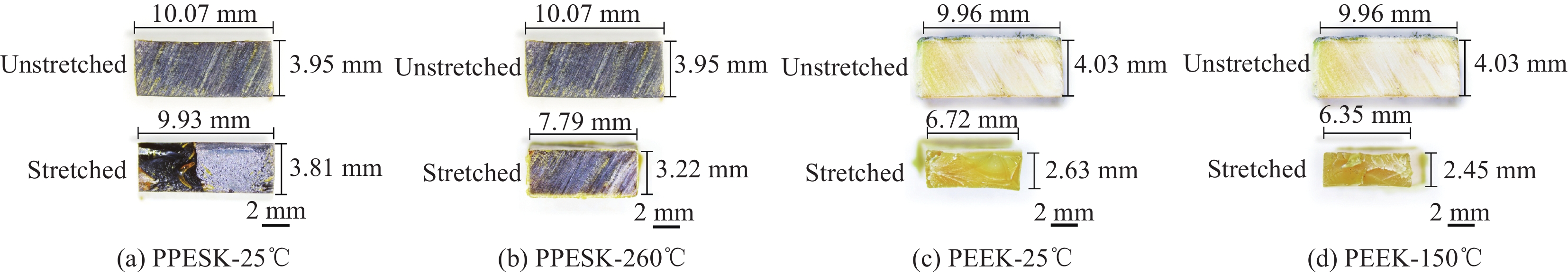
结果研究发现,PPESK与PEEK的拉伸力学行为差异主要包括以下三个方面:①耐热性不同,PPESK的耐热性远优于PEEK。当温度升高到180℃左右时,PPESK拉伸强度保持率为62.03%,模量保持率高达83.94%;而PEEK的拉伸强度保持率低至6.82%,模量保持率仅有7.72%。这是由于PPESK的玻璃化转变温度远高于PEEK,所以耐热性明显更优。②拉伸变形-断裂行为不同。PPESK在温度不超过250℃的情况下只发生小变形,最终脆性断裂;仅当温度超过260℃时,PPESK才产生大变形,最终韧性断裂。而PEEK在各种工况下拉伸均会产生大变形,并发生韧性断裂。PPESK特有的小变形-脆性断裂行为,是由其无定形的结构和高刚性的分子链引起的。其中,无定形结构使其形变时分子链仅发生取向不发生相变,因而形变量小;分子链的高刚性导致其运动能力差,使横截面上的法向正应力优先达到拉伸强度,引发脆性断裂。③拉伸性能对拉伸速率敏感性不同,PPESK的强度和模量对拉伸速率的变化更加敏感。这是由于,PPESK的分子链刚性更强,运动能力更差,所以当拉伸速率增加时,需更大的外力来促使链段发生运动以产生相应的形变。这在宏观上表现为强度和模量的增幅更大。
结论以上研究结果表明,PPESK与以PEEK为典型代表的商用树脂在拉伸力学行为方面存在着显著差异。这就意味着,经典的本构模型、失效准则等理论无法适用于PPESK,使得以PPESK为基体的复合材料的力学行为无法被准确描述,直接阻碍了此类复合材料先进制造工艺的发展。因此,未来需在本文研究结果的基础上,针对PPESK及其复合材料研发专用的本构模型、失效准则,进而为早日提出其复合材料构件的先进制造工艺提供必要条件。





 下载:
下载: