Fabrication and properties of coaxial electrospun PLA/PEG composite nanofibers for thermal regulation
-
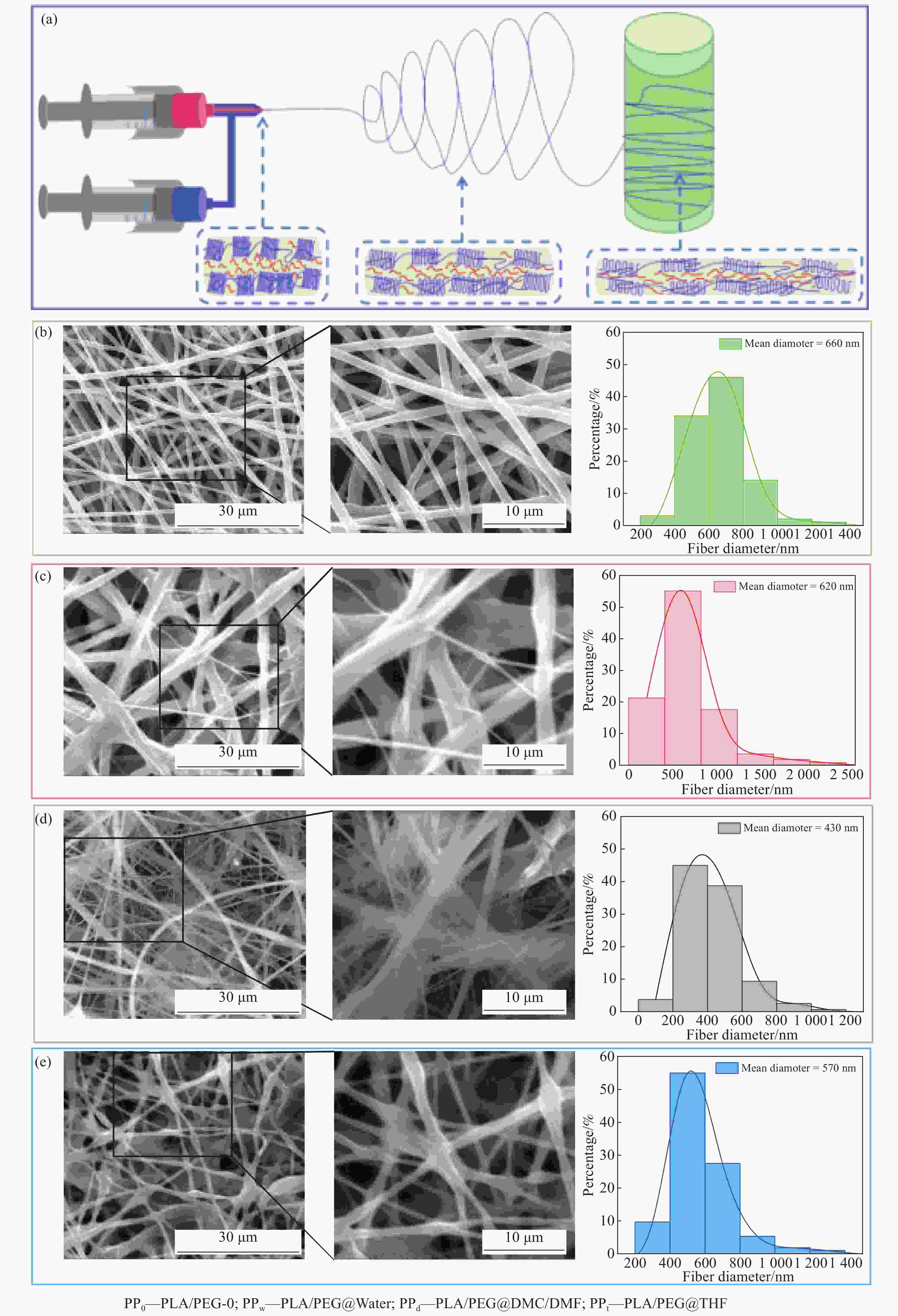
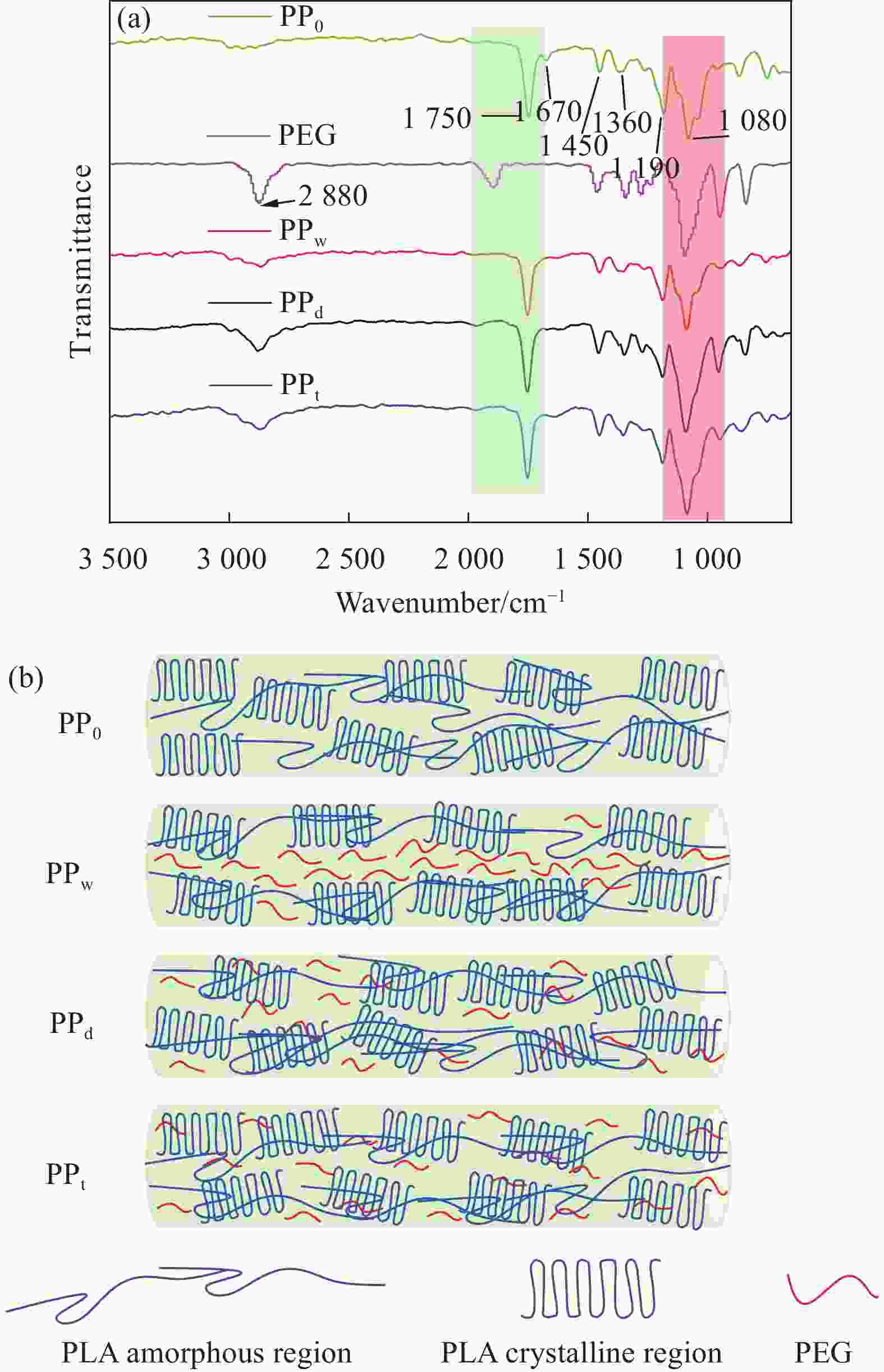
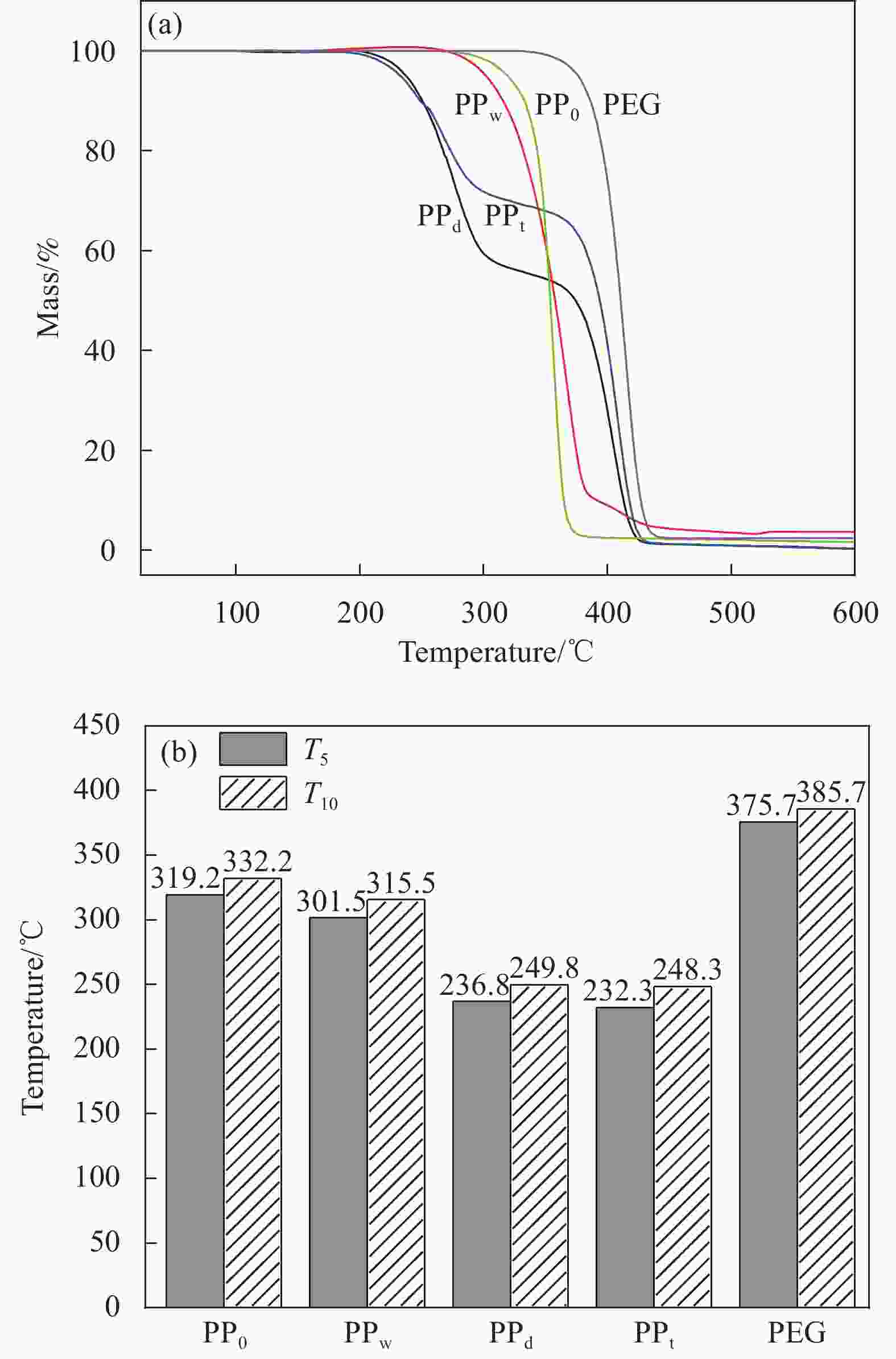
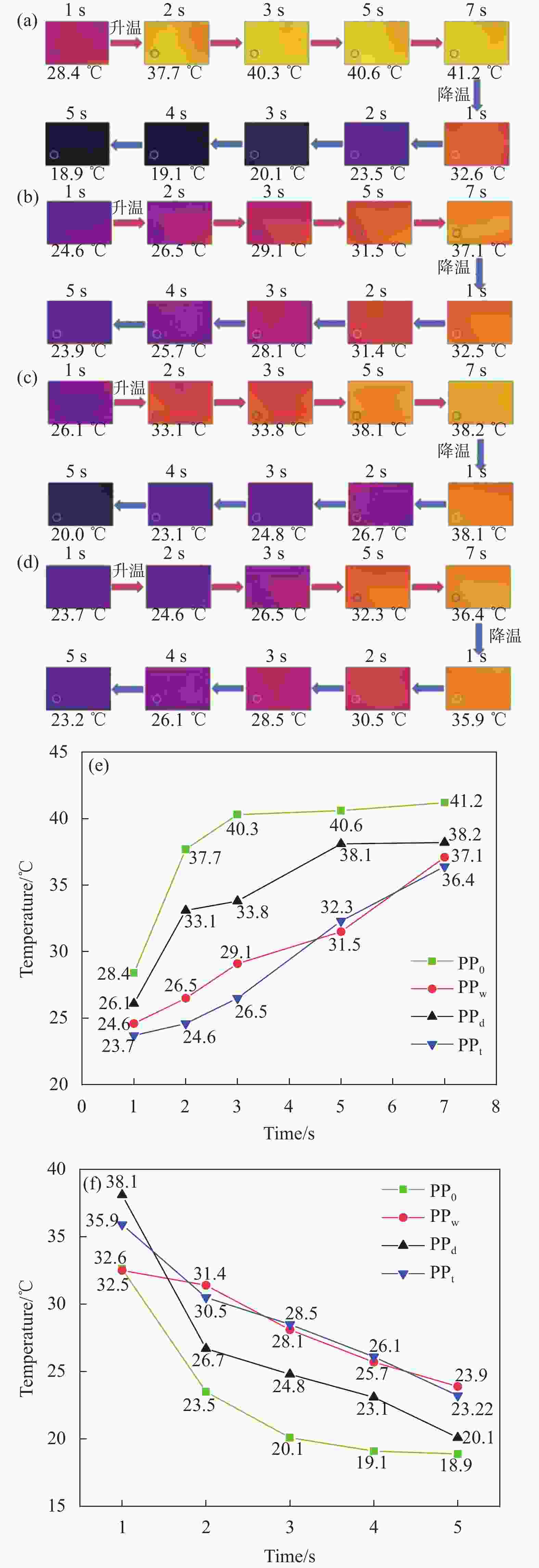
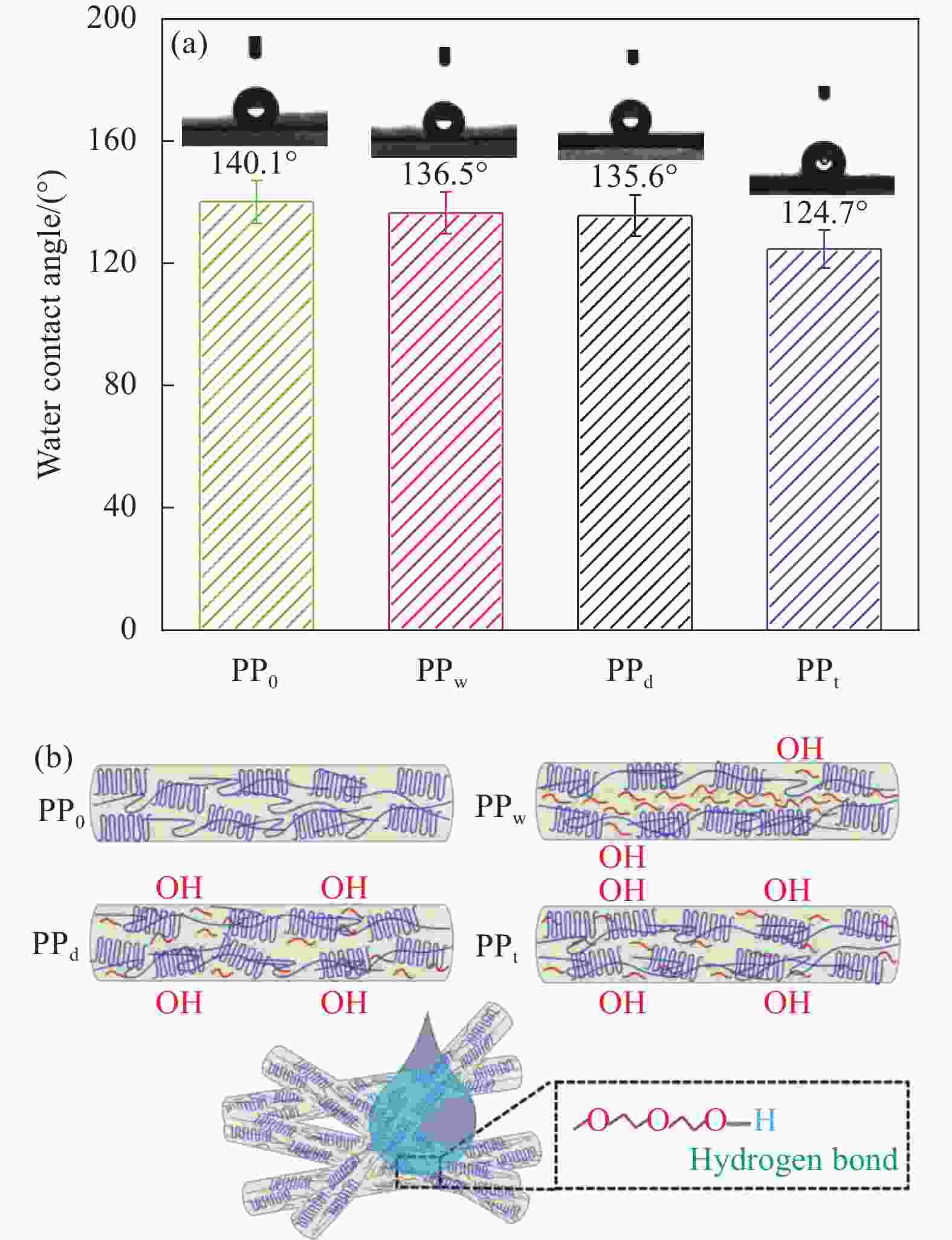
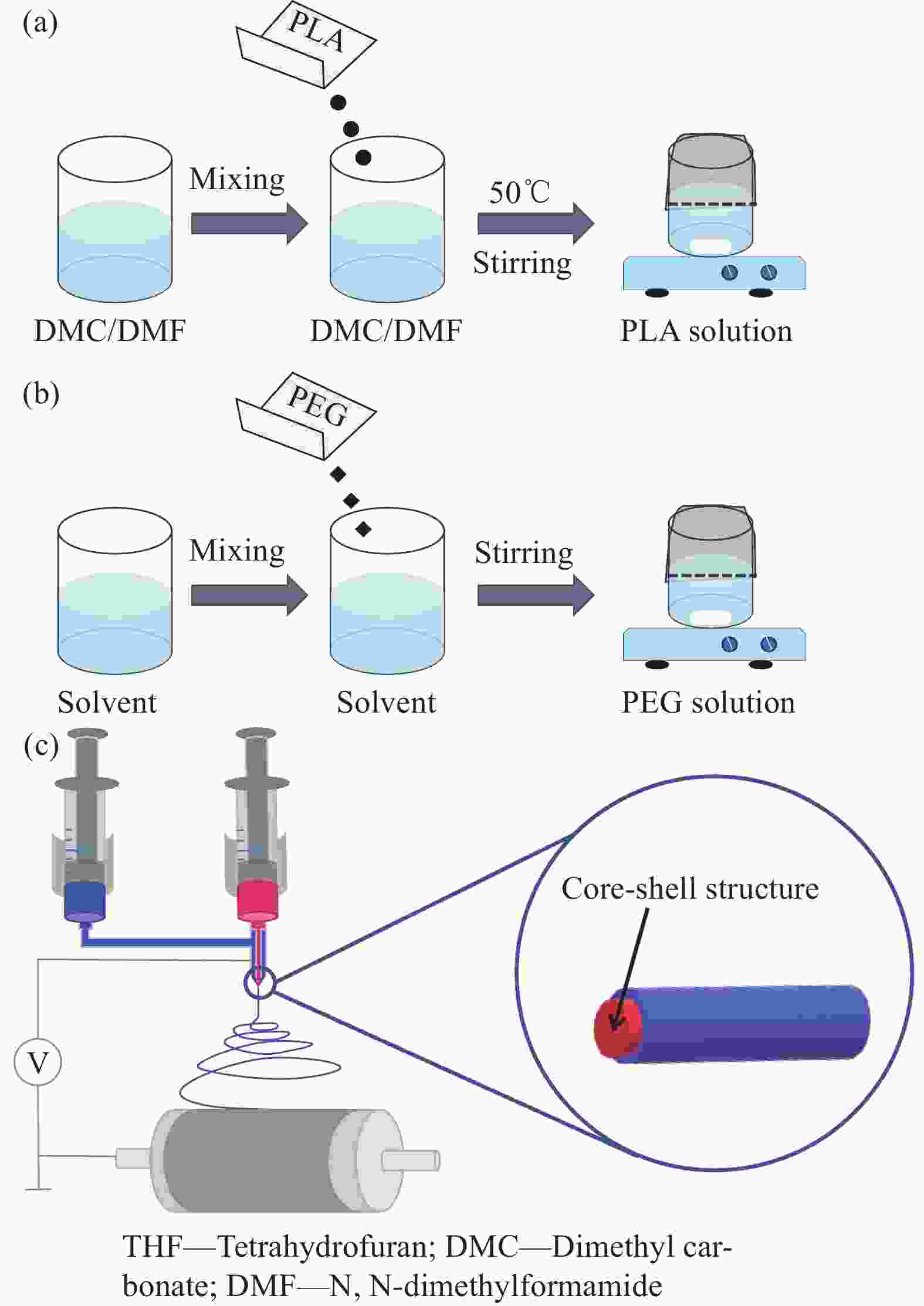
摘要: 为探讨纺丝溶剂对同轴电纺纳米纤维的影响,并制备热调控用纳米纤维,分别以聚乙二醇(PEG)和聚乳酸(PLA)溶液为内、外层纺丝液,利用同轴电纺制备了PLA/PEG复合纳米纤维(NfC-S)。通过调整内层纺丝溶剂制备了三种NfC-S,分别为以去离子水为内层溶剂的NfC-S(PPw)、以四氢呋喃(THF)为内层溶剂的NfC-S(PPt)和以碳酸二甲酯(DMC)/N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)为内层溶剂的NfC-S(PPd)。对NfC-S的形貌、化学结构、结晶性能、力学性能、热性能和亲水性进行了研究,并考察了NfC-S的热调控功能。结果显示:PPw获得两种尺度的纤维,平均直径相比PPd增加190 nm。PPw获得较大的弹性模量和断裂应力,断裂应力相比PPt增加0.54 MPa,而PPd和PPt获得较大的断裂应变。NfC-S具备归因于PEG的熔融吸热能力,其中PPt和PPw在升、降温过程中具有较大的温度滞后性,显示较强的热调控能力。NfC-S的疏水性相比纯PLA(PP0)较小,PPw的水接触角(136.5°)最接近PP0。总之,通过探讨内层纺丝溶剂对NfC-S性能的影响,开发了热调控用NfC-S,其中PPw的综合性能较优秀,为热调控用纳米纤维的可控制备提供参考。Abstract: To investigate the effect of spinning solvents on coaxial electrospun nanofibers and prepare thermal regulation nanofibers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA) solutions were used as inner and outer layer spinning solutions respectively, and PLA/PEG nanofibers (NfC-S) were prepared by coaxial electrospinning. Three types of NfC-S were prepared using deionized water, Tetrahydrofuran (THF), and Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) /N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as inner solvents, named PPw, PPt, and PPd, respectively. The morphology, chemical structure, crystalline properties, mechanical properties, thermal properties, and hydrophilicity of NfC-S were studied, and the thermal regulation function was further investigated. The results showed that PPw obtained fibers with two different scales, and the average diameter increased by 190 nm compared to PPd. PPw exhibited higher elastic modulus and breaking stress, while PPd and PPt showed higher breaking strain, with the breaking stress of PPw increasing by 0.54 MPa compared to PPt. NfC-S possessed the melting endothermic capacity attributed to PEG, with PPt and PPw exhibiting significant temperature hysteresis during heating and cooling processes, demonstrating excellent thermal regulation capability. The hydrophobicity of NfC-S was lower compared to pure PLA (PP0), with the water contact angle of PPw (136.5°) being closest to PP0. In conclusion, thermal regulation NfC-S was developed based on the research for inner layer solvent, with PPw showing superior comprehensive performance, providing a reference for the controllable preparation of thermal regulation nanofibers.
-
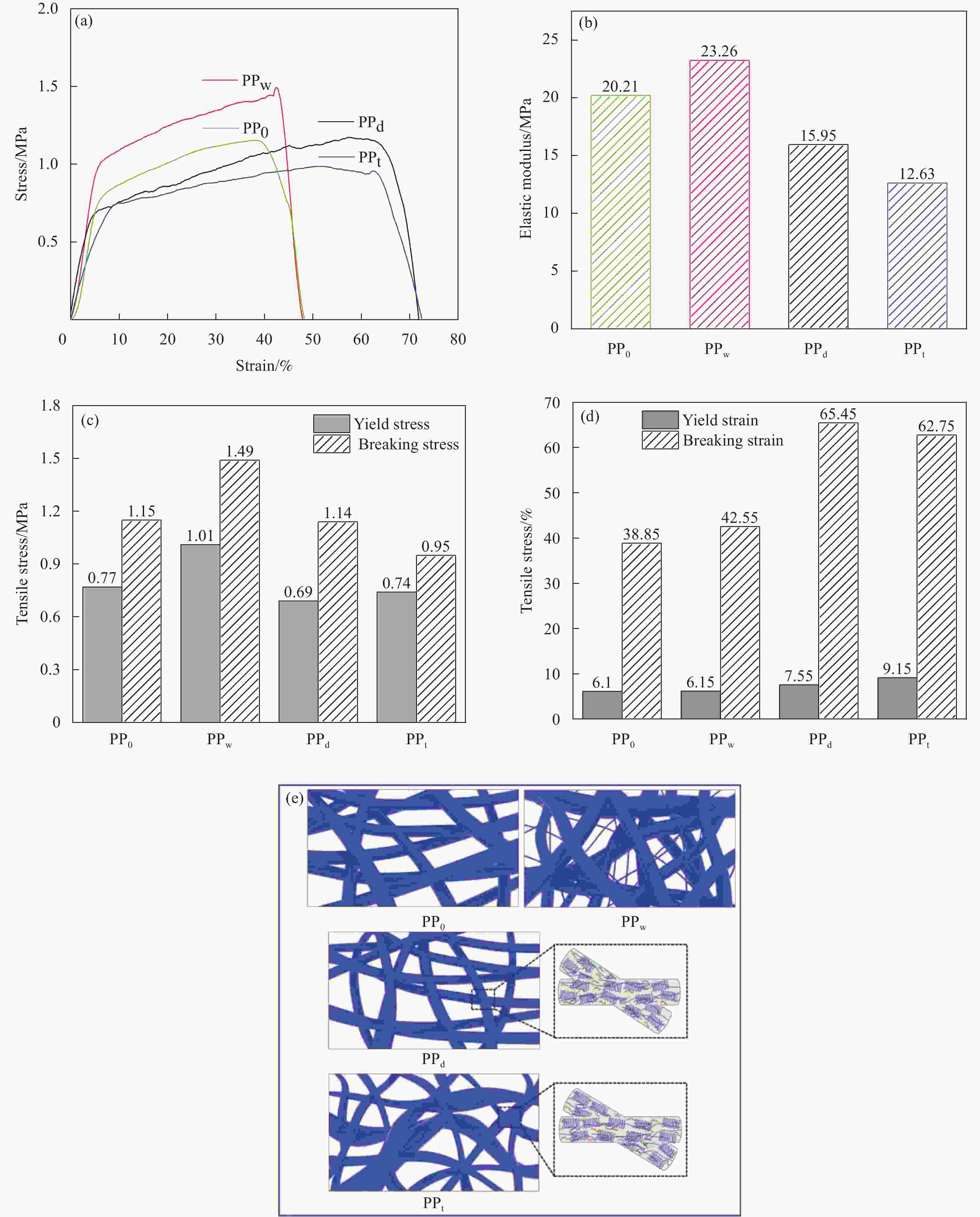
图 5 (a) NfC-S应力-应变曲线;(b) NfC-S弹性模量柱状;(c) NfC-S屈服应力和断裂应力统计柱状;(d) NfC-S屈服应变和断裂应变统计柱状;(e)各NfC-S的分子结构
Figure 5. (a) Stress-strain curve of NfC-S, (b) column chart of elastic modulus of NfC-S, (c) statistics of yield stress and breaking stress of NfC-S, (d) statistics of yield strain and breaking strain of NfC-S, (e) molecular structure of NfC-S
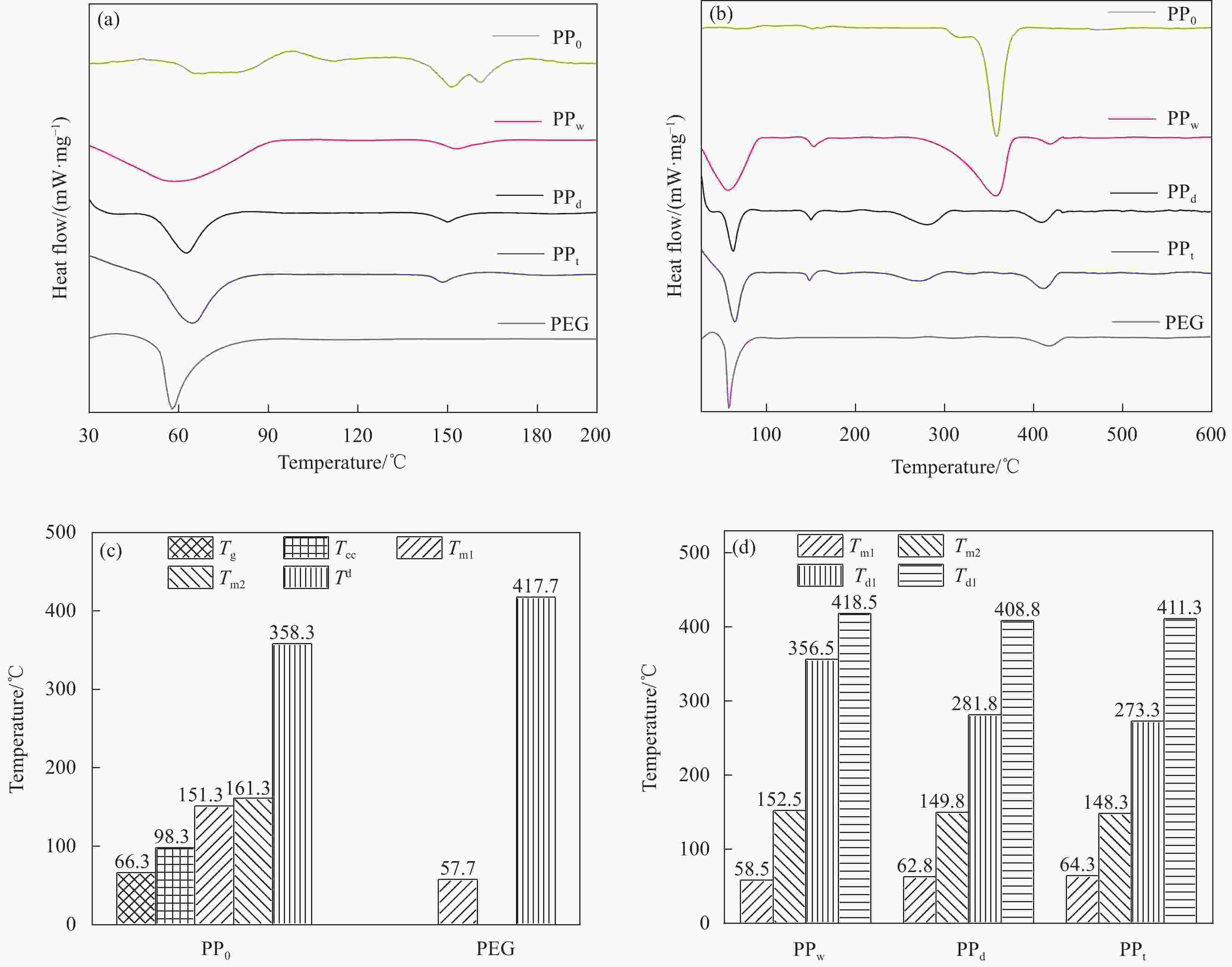
图 7 (a) NfC-S与PEG在30-200℃范围的DSC曲线;(b) NfC-S与PEG在30-600℃范围的DSC曲线;(c) PP0与PEG的Tg、Tcc、Tm和Td统计;(d) NfC-S的Tm1、Tm2、Td1和Td2统计
Figure 7. DSC curves of NfC-S and PEG in the temperature range of (a) 30-200℃ and (b) 30-600℃, (c) statistics of Tg, Tcc, Tm, and Td for PP0 and PEG, (d) statistics of Tm1, Tm2, Td1, and Td2 for NfC-S
-
[1] SIDDHARTH A N, PRAMOD B S. Thermal management of lithium-ion battery module using the phase change material[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2023, 237(23): 5767-5776. [2] ABDOLMALEKI L, SADRAMELI S, PIRVARAM A. Application of environmental friendly and eutectic phase change materials for the efficiency enhancement of household freezers[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 145: 233-241. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.035 [3] PENG Hao, GUO Wenhua, FENG Shiyu, et al. A novel thermoelectric energy harvester using gallium as phase change material for spacecraft power application[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 322: 119548. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119548 [4] MENG Duo, DANG Xin, WANG Anqi, et al. Optimization of double-layer shaped phase change wallboard in buildings in twotypical climate areas in China[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 61: 106698. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.106698 [5] G. D P, BALASUBRAMANIAN K. A Review on Polymeric-Based Phase Change Material for Thermo-Regulating Fabric Application[J]. Polymer Reviews, 2020, 60(3): 389-419. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2019.1677709 [6] TANATHEP L, DENIS F, MINH H H, et al. Insulated box and refrigerated equipment with PCM for food preservation: State of the art[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2022, 317: 110874. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2021.110874 [7] UR H R, FAWAD N, MUHAMMAD H A. An experimental case study of solar food dryer with thermal storage using phase change material[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2023, 51: 103611. doi: 10.1016/j.csite.2023.103611 [8] GUO Huixuan, LIANG Yuzhang, HUANG Yuhang, et al. Multiwavelength camouflage metamaterials with adjustable emissivity[J]. Optics express, 2023, 31(22): 36770-36780. doi: 10.1364/OE.497472 [9] XUE Qianqian, NIE Wen, GUO Lidian, et al. Determining the optimal airflow rate to minimize air pollution in tunnels[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 157: 115-130. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.10.039 [10] 杨效田, 沈梁玉, 王彩龙等. 石蜡对无机复合相变储热体系的改性研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(05): 2421-2429.YANG Xiaotian, SHEN Liangyu, WANG Cailong, et al. Study on paraffin modifying inorganic composite phase change heat storage system[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 157: 115-130(in Chinese). [11] CAO Qian, DING Hongyuan, XIE Jianghui, et al. Synthesis of highly thermal conductive carbon nanotubes on cellulose nanofiber film-loaded polyethylene glycol phase change material with flame retardancy by layered double hydroxide[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73(PA): 108717. [12] ALPER A A, GIZEM T. Synthesis and characterization of new organic phase change materials (PCMs): Diesters of suberic acid[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2021, 220: 110822. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110822 [13] 许俊, 曹楠普, 肖尧鑫等. 聚乙二醇生物相容性与结合水关系的单分子力谱研究[J]. 高分子学报, 2020, 51(7): 754-761. doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2019.19219XU Jun, CAO Nanpu, XIAO Yaoxin, et al. Revealing the relationship between the biocompatibility and the bound Water of Poly(ethylene glycol) by single-molecule force spectroscopy[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2020, 51(7): 754-761(in Chinese). doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2019.19219 [14] ANDREW K, ALEXANDRA N W, BHOJE E G, et al. Recent Progress in PEG-Based Composite Phase Change Materials[J]. Polymer Reviews, 2023, 63(4): 1078-1129. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2023.2220041 [15] HUANG Caoxing, ZHAO Xiaoxue, ZHENG Yayue, et al. Revealing the mechanism of surfactant-promoted enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute acid pretreated bamboo[J]. Bioresource technology, 2022, 360: 127524. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127524 [16] KENTO M, SEIICHI O, TAICHI I. Analysis of model drug permeation through highly crosslinked and biodegradable polyethylene glycol membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 645: 120218. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2021.120218 [17] DU Changhe, YU Tongtong, WU Zishuai, et al. Achieving macroscale superlubricity with ultra-short running-in period by using polyethylene glycol-tannic acid complex green lubricant[J]. Friction, 2023, 11(5): 748-762. doi: 10.1007/s40544-022-0660-3 [18] WANG XueTing, DENG Xudong, ZHANG TuoDi, et al. A Versatile Hydrophilic and Antifouling Coating Based on Dopamine Modified Four-Arm Polyethylene Glycol by One-Step Synthesis Method[J]. ACS macro letters, 2022, 11(6): 805-812. doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.2c00277 [19] MOHAMED I, TARO S, HIDENORI A, et al. Investigation of anti-PEG antibody response to PEG-containing cosmetic products in mice[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2023, 354: 260-267. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.012 [20] D K W, L M D. Characterization of a solid-supported aqueous biphasic system for the sorption of dyes from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2023, 1705: 464215. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464215 [21] SUN Q, ZHANG N, ZHANG H, et al. Functional phase change composites with highly efficient electrical to thermal energy conversion[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 145: 2629-2636. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.08.007 [22] PENG Luxi, QIU Jiajun, LIU Lidan, et al. Preparation of PEG/ZIF-8@HF drug delivery system for melanoma treatment via oral administration[J]. Drug delivery, 2022, 29(1): 1075-1085. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2058649 [23] YIN Guang-Zhong, YANG Xiao-Mei, MARTA A L, et al. Highly thermal conductive Boron Nitride/Polyrotaxane encapsulated PEG-based phase change materials[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2023, 199: 112431. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.112431 [24] QIU Lin, YAN Kening, FENG Yanhui, et al. Nano additives-enhanced PEG /AlN composites with high cycle stability to improve thermal and heat storage properties[J]. Energy, 2023, 278: 127794. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.127794 [25] BAI Shijie, ZHANG Kaixi, ZHANG Qun, et al. Intrinsic Flame Retardancy and Flexible Solid-Solid Phase Change Materials with Self-Healing and Recyclability[J]. ACS applied materials interfaces, 2023, 15(41): 48613-48622. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c09722 [26] JIN Weizhun, HUANG Qinghua, HUANG Haimeng, et al. The preparation of a suspension of microencapsulated phase change material (MPCM) and thermal conductivity enhanced by MXene for thermal energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73(PA): 108868. [27] 孙宗旭, 张焕芝, 荆锐等. 相变复合纳米纤维的研究与应用[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(7): 231-238.SUN Zongxu, ZHANG Huanzhi, JING Rui, et al. Research and application of phase change composite nanofibers[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(7): 231-238(in Chinese). [28] PATEL Dev, WEI Wanying, SINGH Harmann, et al. Efficient and Secure Encapsulation of a Natural Phase Change Material in Nanofibers Using Coaxial Electrospinning for Sustainable Thermal Energy Storage[J]. ACS sustainable chemistry engineering, 2023, 11(31): 11570-11579. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c02094 [29] ANDRES S, ELENA A, LAURA A, et al. Electrospun composite fibers containing organic phase change materials for thermo-regulation: Trends[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 187: 113648. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113648 [30] YU Chengbin, SONG Youngseok. Modified Supporting Materials to Fabricate Form Stable Phase Change Material with High Thermal Energy Storage[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(3): 1309. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031309 [31] 文美玲, 高翔, 刘阳等. 静电纺纳米纤维表面形貌的制备及其生物医学应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 42: 1-13.WEN Meiling, GAO Xiang, LIU Yang, et al. Preparation of surface morphology of electrospun nanofibers and their biomedical applications[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 42: 1-13(in Chinese). [32] ARCHANA S, OLEKSANDR N, ROMAIN B. Wet spinning of strong cellulosic fibres with incorporation of phase change material capsules stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2023, 312: 120734. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120734 [33] SONG Shaokun, AI Hong, LV Linda, et al. Novel smart coaxial electrospinning textiles for efficient thermal interface management and electromagnetic compatibility in electronics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 472: 144854. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.144854 [34] TANATCHPORN S, PITT S, KORAKOT S. Titanium (IV) oxide composite hollow nanofibres with silver oxide outgrowth by combined sol–gel and electrospinning techniques and their potential applications in energy and environment[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2023, 6(3): 115. doi: 10.1007/s42114-023-00690-9 [35] HOSSEIN B, MARYAM M, JUKKA S, et al. Form-stable phase change electrospun nanofibers mat with thermal regulation and biomedical multi-functionalities[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 68: 107660. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2023.107660 [36] WEI Jia, LONG Yan, WANG Binqi, et al. Structure and properties variations of regenerated cellulose fibers induced by metal ion impurity[J]. International journal of biological macromolecules, 2023, 255: 128124. [37] YIN JiaYi, CARLO B, ALESSANDRA L, et al. Piezoelectric field enhanced photocatalytic efficiency of PVDF/TiO2 core/shell nanofibrous membrane via coaxial electrospinning[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 110298. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110298 [38] 王曙东, 董青, 王可等. 还原氧化石墨烯增强聚乳酸纳米纤维膜的制备及其性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2021, 42(12): 28-33.WANG Shudong, DONG Qing, WANG Ke, et al. Preparation and properties of polylactic acid nanofibrous membrane reinforced by reduced graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2021, 42(12): 28-33(in Chinese). [39] 成锡婷, 辜鹏程, 胡辉等. 明胶@左旋聚乳酸核壳结构纳米纤维的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(11): 6374-6382.CHENG Xiting, GU Pengcheng, HU Hui1, et al. Preparation and properties of gelatin@poly(L-lactic acid) core-shell nanofibers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(11): 6374-6382(in Chinese). [40] 徐兆宝, 何翠, 赵瑾朝等. 同轴静电纺多级微纳米纤维膜的制备及其相变调温性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2022, 43(2): 69-73+80.XU Zhaobao, HE Cui, ZHAO Jinchao, et al. Preparation of coaxially electrospun multi-level fiber membrane and its phase change temperature-regulating performance[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2022, 43(2): 69-73+80(in Chinese). [41] WEN F, SHENG Y Z, WEN Y S, et al. Coaxial electrospun membranes with thermal energy storage and shape memory functions for simultaneous thermal/moisture management in personal cooling textiles[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2020, 145: 110245. -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 108
- HTML全文浏览量: 56
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: