Preparation and fretting tribological properties of carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone composite osteoinductive repair implants
-
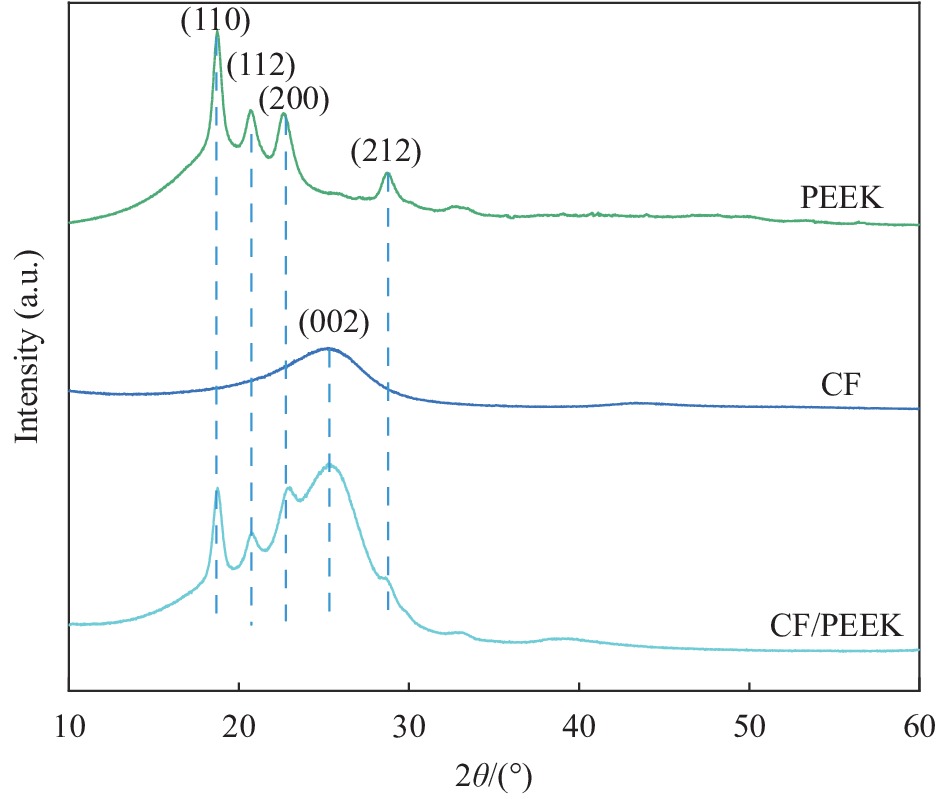
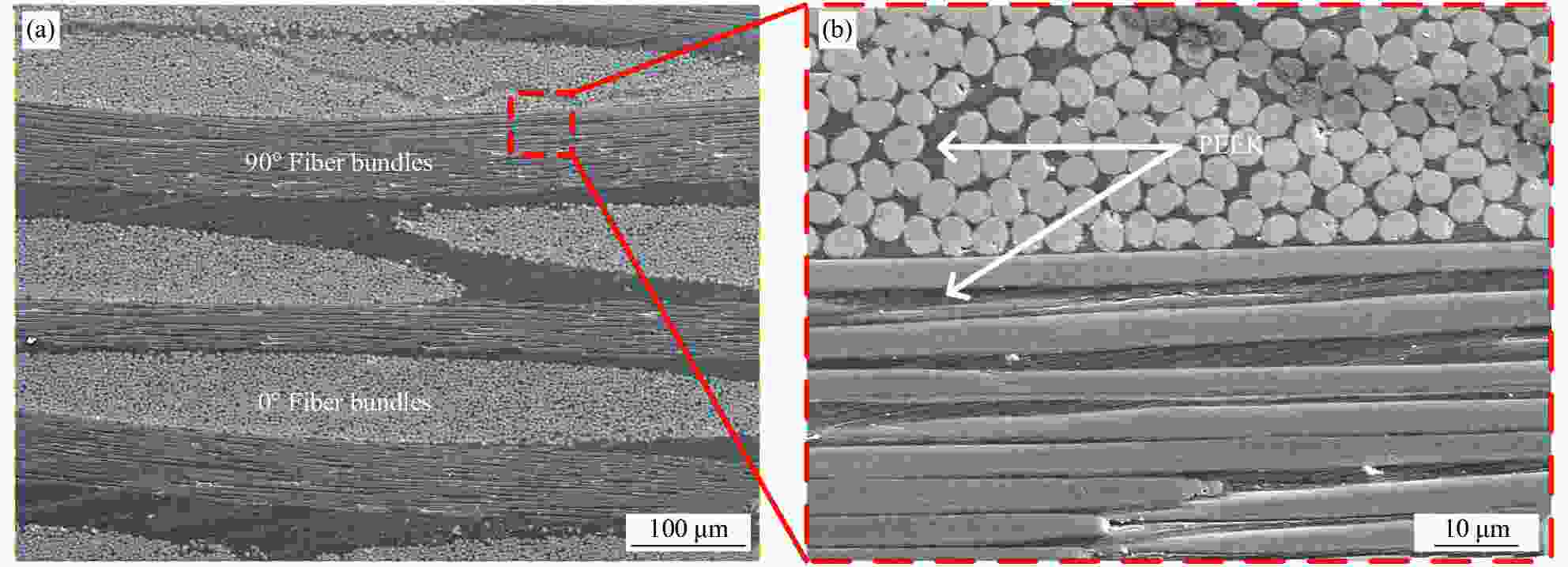
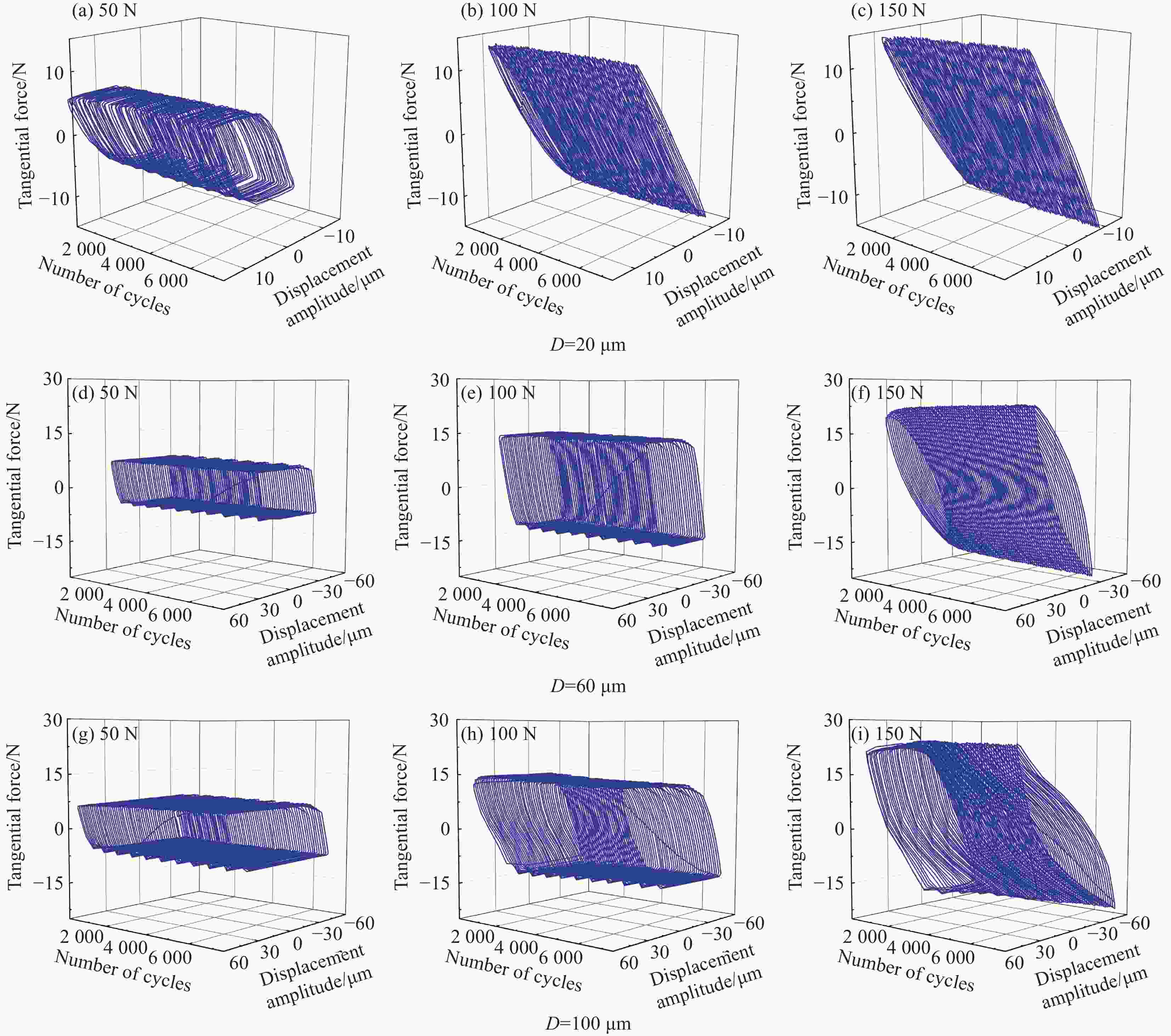
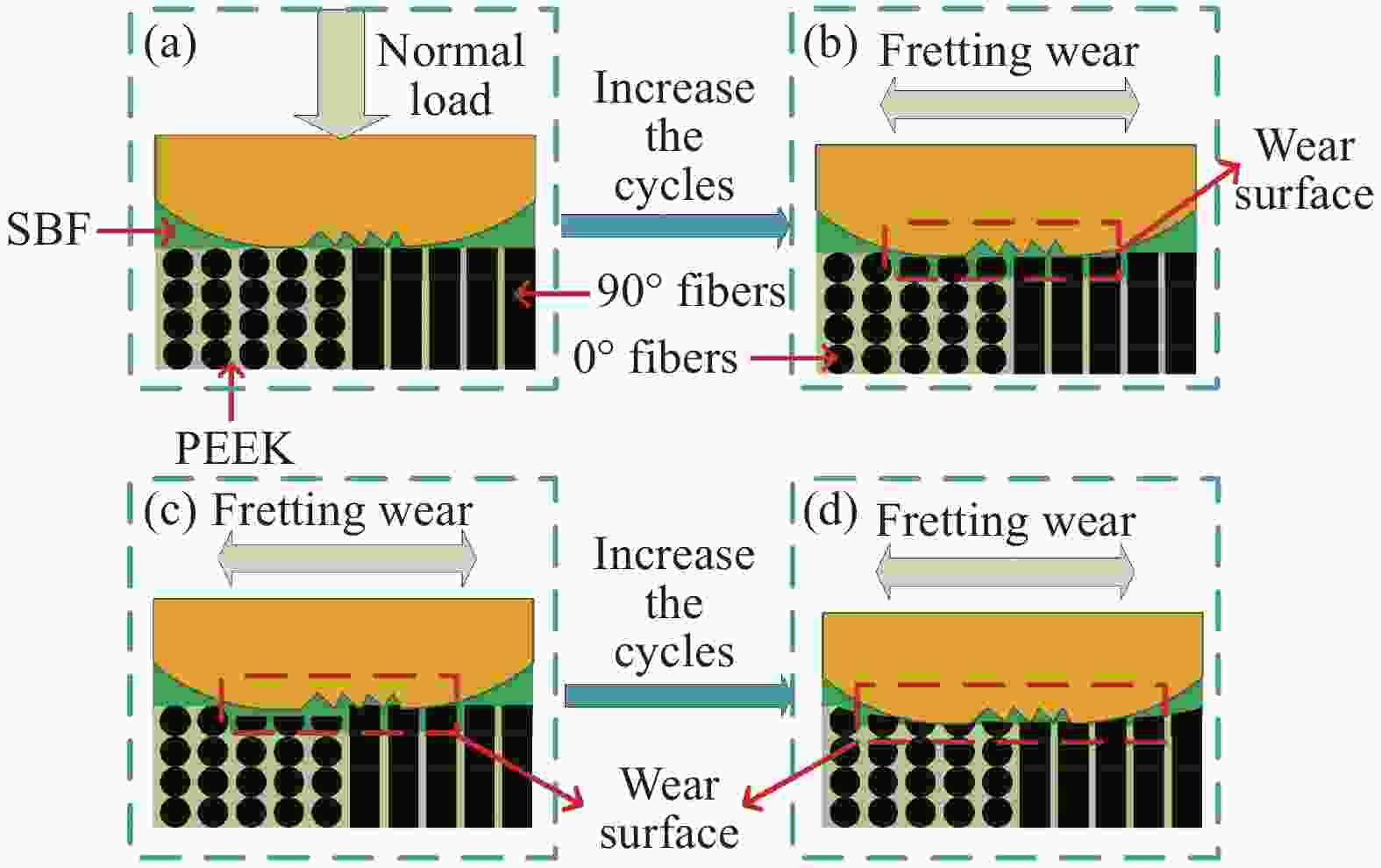
摘要: 引起植入体无菌松动的主要原因是植入体与骨组织之间的微动磨损。通过层叠法制备了碳纤维(CF)增强聚醚醚酮(PEEK)复合材料,在模拟体温37℃、模拟体液(SBF)润滑条件下,探究CF/PEEK复合材料的基本力学性能和截面微动摩擦学性能。通过改变法向载荷和位移幅值,建立了摩擦力(Ft)-位移幅值(D)曲线、微动运行工况图和摩擦系数曲线,通过三维白光干涉仪、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对CF/PEEK复合材料进行磨损机制探究。结果表明:随着法向载荷的减少和位移幅值的增加,微动由部分滑移区、混合区向滑移区转变。摩擦系数曲线整体较为平稳,摩擦系数随着法向载荷的增加而降低,随着位移幅值的增加而增加,磨损体积随着载荷和位移幅值的增加而增加。且CF/PEEK复合材料截面也有较好的微动性能,磨损机制主要为磨粒磨损和疲劳磨损。通过对复合材料截面摩擦学特性分析,为CF/PEEK复合材料替代金属植入体提供一定的理论基础。Abstract: The main reason for the aseptic loosening of the implant is the fretting wear between the implant and the bone tissue. A carbon fiber (CF) reinforced polyetheretherketone (PEEK) composite material was prepared by a layered method. Under simulated body temperature of 37℃ and simulated body fluid (SBF) lubrication conditions, the basic mechanical properties and the fretting tribological properties of the section of CF/PEEK composites were explored. By changing the normal load and displacement amplitude, the frictional force(Ft)-displacement (D) curve, the fretting operating condition diagram and the friction coefficient curve were established. And the wear mechanism of the CF/PEEK composite material was explored through a three-dimensional white light interferometer and a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that with the decrease of the normal load and the increase of the displacement amplitude, the fretting changes from partial slip regime and mixed regime to slip regime. The overall friction coefficient curve is relatively stable. The friction coefficient gradually decreases with the increase of normal load and increases with the rise of displacement amplitude. The wear volume increases with load and displacement amplitude increases. In addition, CF/PEEK composites have better fretting properties, and the main wear mechanisms are abrasive wear and fatigue wear. The analysis of the tribological characteristics of composite materials provides a specific theoretical basis for CF/PEEK composite materials to replace metal implants.
-
Key words:
- carbon fiber /
- thin films /
- composites /
- fretting wear /
- weaving /
- polyetheretherketone /
- implant
-
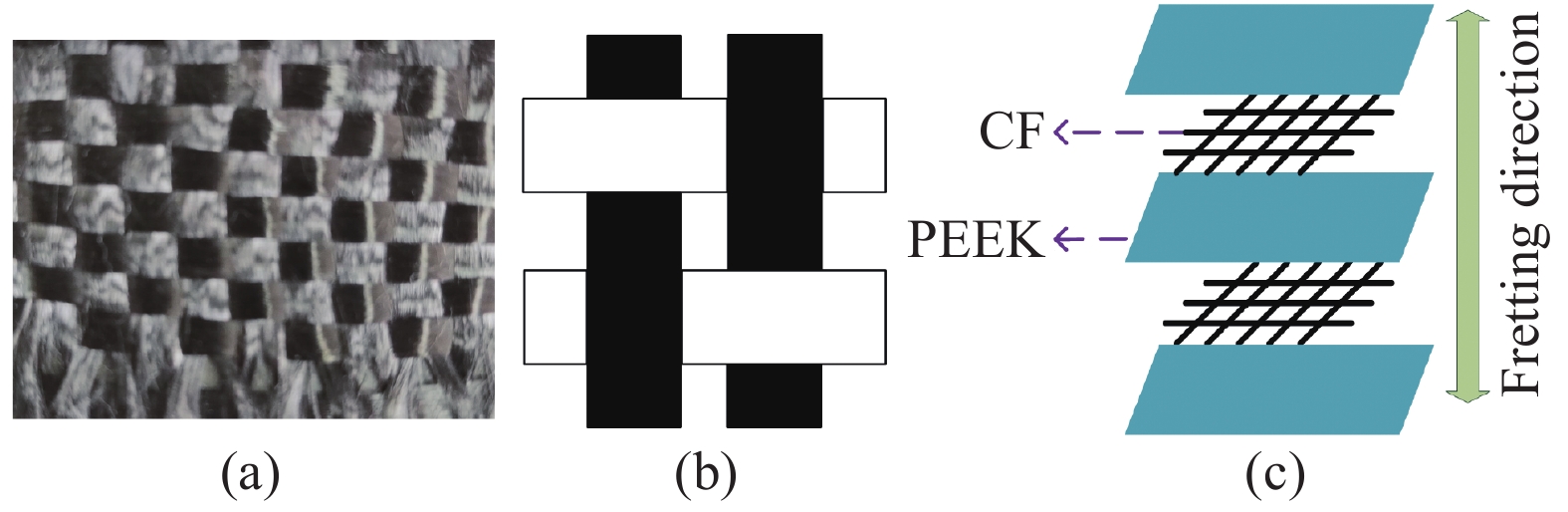
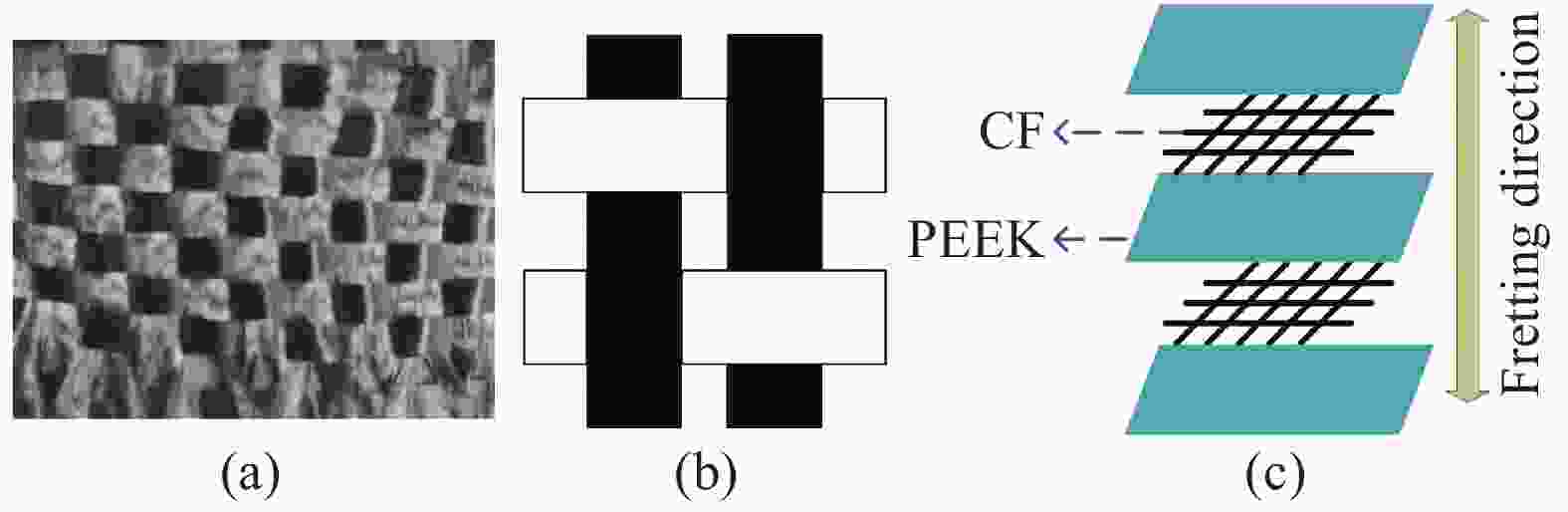
图 1 碳纤维取向为(0°/90°)的碳纤维增强聚醚醚酮(CF/PEEK)复合材料排布方法: (a)碳纤维织物;(b)编织原理图;(c)纤维层叠示意图
Figure 1. Arrangement method of carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone (CF/PEEK) composite material with carbon fiber orientation (0°/90°): (a) Carbon fiber woven fabric; (b) Weaving principle diagram; (c) Schematic diagram of fiber stacking
表 1 模拟体液溶液离子浓度
Table 1. Concentration of ions in the solution of simulated body fluid
mmol/L Formulation Na+ K+ Mg2+ Ca2+ Cl− HCO3− HPO42− SO42− SBF 142.0 5.0 1.5 2.5 103.0 10.0 1.0 0.5 Blood plasma 142.0 5.0 1.5 2.5 103.0 27.0 1.0 0.5 表 2 CF/PEEK复合材料微动磨损试验主要参数
Table 2. Experiment parameters of fretting wear of CF/PEEK composite
Experimental parameters CF/PEEK Tangential force/N 50, 100, 150 Displacement amplitude/μm 20, 60, 100 Frequency/Hz 2 表 3 CF/PEEK复合材料和Ti6Al4V材料的力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of CF/PEEK composite material and Ti6Al4V material
Sample Density /(g·cm−3) Hardness Tensile strength/MPa Bend strength/MPa CF/PEEK 1.56 120 HRR 880 670 Ti6Al4V 4.5 260 HV 895 993 -
[1] 武太勇, 付海军, 李健, 等. 血液源性原发脊柱肿瘤诊断及治疗的研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2021, 29(13):2350-2354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2021.13.034WU Taiyong, FU Haijun, LI Jian, et al. Research progress in diagnosis and treatment of hematogenous primary spinal tumors[J]. Modern Oncology,2021,29(13):2350-2354(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2021.13.034 [2] 姜屿. 微型钛板内固定与BOLD加压螺钉手术在足部骨折患者治疗中的应用分析[J]. 中外医学研究, 2020, 18(30):117-118.JIANG Yu. Analysis of the application of micro-titanium plate internal fixation and BOLD compression screw surgery in the treatment of patients with foot fractures[J]. Chinese and Foreign Medical Research,2020,18(30):117-118(in Chinese). [3] AKKAN C K, HAMMADEH E M, MAY A, et al. Surface topography and wetting modifications of PEEK for implant applications[J]. Lasers in Medical Science,2014,29(5):1633-1639. doi: 10.1007/s10103-014-1567-7 [4] MENG X C, ZHANG W, YUAN Z G, et al. A partial hemi-resurfacing preliminary study of a novel magnetic resonance imaging compatible polyetheretherketone mini-prosthesis for focal osteochondral defects[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation,2021,26:67-73. [5] ZHU J J, XIE F, DWYER-JOYCE R S. PEEK composites as self-lubricating bush materials for articulating revolute pin joints[J]. Polymers,2020,12(3):665. doi: 10.3390/polym12030665 [6] 孙会娟. 光诱导自引发接枝聚合PEEK植入体研究进展[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2021, 49(4):153-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2021.04.030SUN Huijuan. Progress in PEEK implants by photoinduced self-initiated graft polymerization[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2021,49(4):153-156(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2021.04.030 [7] 潘月秀, 解锡明, 吴宁, 等. 碳纤维束间的摩擦磨损特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8):1838-1846.PAN Yuexiu, XIE Ximing, WU Ning, et al. Frictional and worn behavior of inter-carbon fiber tows[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(8):1838-1846(in Chinese). [8] 武扬, 李英. 碳纤维加强型聚醚醚酮的制备探索[J]. 全科口腔医学电子杂志, 2016, 3(15):5-8.WU Yang, LI Ying. The compression molding of CF-PEEK composite material[J]. General Journal of Stomatology,2016,3(15):5-8(in Chinese). [9] 赵荻, 黄文旵. 骨修复用生物玻璃复合材料研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2008, 03(39):353-354,357.ZHAO Di, HUANG Wenhai. Advance in research on bioactive glass composites for bone repair[J]. Journal of Funcyional Materials,2008,03(39):353-354,357(in Chinese). [10] FLECK C, EIFLER D. Corrosion, fatigue and corrosion fatigue behaviour of metal implant materials, especially titanium alloys[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2010,32(6):929-935. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2009.09.009 [11] RONY L, LANCIGU R, HUBERT L. Intraosseous metal implants in orthopedics: A review[J]. Morphologie,2018,102(339):231-242. doi: 10.1016/j.morpho.2018.09.003 [12] JAUCH S Y, COLES L G, NG L V, et al. Low torque levels can initiate a removal of the passivation layer and cause fretting in modular hip stems[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics,2014,36(9):1140-1146. [13] 杨学萍. CCF/PEEK复合材料制备及应用研究进展[J]. 合成纤维, 2021, 50(5):41-51.YANG Xueping. Research progress in preparation and application of CCF/PEEK composites[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China,2021,50(5):41-51(in Chinese). [14] GODARA A, RAABE D, GREEN S. The influence of sterilization processes on the micromechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced PEEK composites for bone implant applications[J]. Acta Biomaterialia,2007,3(2):209-220. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2006.11.005 [15] 滕凌虹, 曹伟伟, 朱波, 等. 纤维增强热塑性树脂预浸料的制备工艺及研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2021, 49(2):42-53.TENG Linghong, CAO Weiwei, ZHU Bo, et al. Research progress in the preparation of fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin prepreg[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2021,49(2):42-53(in Chinese). [16] PAN G L, GUO Q, ZHANG W D, et al. Fretting wear behaviors of nanometer Al2O3 and SiO2 reinforced PEEK composites[J]. Wear,2009,266(11):1208-1215. [17] WANG Q F, WANG Y X, WANG H L, et al. Comparative study of the effects of nano-sized and micro-sized CF and PTFE on the thermal and tribological properties of PEEK composites[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2017,29:896-905. [18] SONG J, LIAO Z H, SHI H Y, et al. Fretting wear study of PEEK-based composites for bio-implant application[J]. Tribology Letters,2017,65(4):1-11. [19] CHEN B B, WANG J Z, YAN F Y. Comparative investigation on the tribological behaviors of CF/PEEK composites under sea water lubrication[J]. Tribology International,2019,52:170-177. [20] American Society of Testing Materials. Standard test methods for density and specific gravity (relative density) of plastics by displacement: ASTM D792[S]. Pennsylvania, American: American Society of Testing Materials International, 2013. [21] American Society of Testing Materials. Standard test method for rockwell hardness of plastics and electrical insulating materials: ASTM D785[S]. Pennsylvania, American: American Society of Testing Materials International, 2015. [22] American Society of Testing Materials. Standard test method for tensile properties of polymer matrix composite materials: ASTM D3039[S]. Pennsylvania, American: American Society of Testing Materials International, 2017. [23] American Society of Testing Materials. Standard test method for flexural properties of polymer matrix composite materials: ASTM D7264[S]. Pennsylvania, American: American Society of Testing Materials International, 2015. [24] XIAO T, WEN D S, WANG S R, et al. Investigation on fretting wear of Al-Li alloy[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2020, 72(7): 913-921. [25] 张鑫. 人工关节金属假体材料界面间的摩擦腐蚀行为[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.ZHANG Xin. Study on wear and corrosion behaviors of contact interface between metallic materials of artificial hip joint[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017 (in Chinese). [26] 耿浩. 人工髋关节材料界面间微动腐蚀行为研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2014.GENG Hao. Study on the fretting corrosion behaviors of contact interface between materials of artificial hip joint [D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2014 (in Chinese). [27] 高姗姗. 两种牙科合金的微动磨损机理研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2007.GAO Shanshan. Research on characteristics of fretting wear of two kinds of dental alloys[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2007 (in Chinese). [28] 王梦婕, 彭金方, 庄文华, 等. 碳纤维切向微动磨损特性研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2019, 39(03): 330-339.WANG Mengjie, PENG Jinfang, ZHUANG Wenhua, et al. Fretting wear damage characteristics of carbon fiber[J]. Tribology, 2019, 39(03): 330-339 (in Chinese). [29] ERINC M, SILLEKENS W H, MANNENS R G T M, et al. Applicability of existing magnesium alloys as biomedical implant materials[A]//The Materials Society Annual Meeting[C]. San Francisco, CA: Cambridge University Press, 2009: 209. [30] 周仲荣. 微动磨损[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 78-79; 47-49.ZHOU Zhongrong. Fretting wear[M]. Beijng: Science Press, 2002: 78-79; 47-49 (in Chinese). [31] SHERMA M, RAO M I, BIJWE J. Influence of fiber orientation on abrasive wear of unidirectionally reinforced carbon fiber–polyetherimide composites[J]. Tribology International, 2010, 43: 959-964. -





 下载:
下载: