Modeling active adjustment of negative Poisson's ratio mechanical metamaterials
-
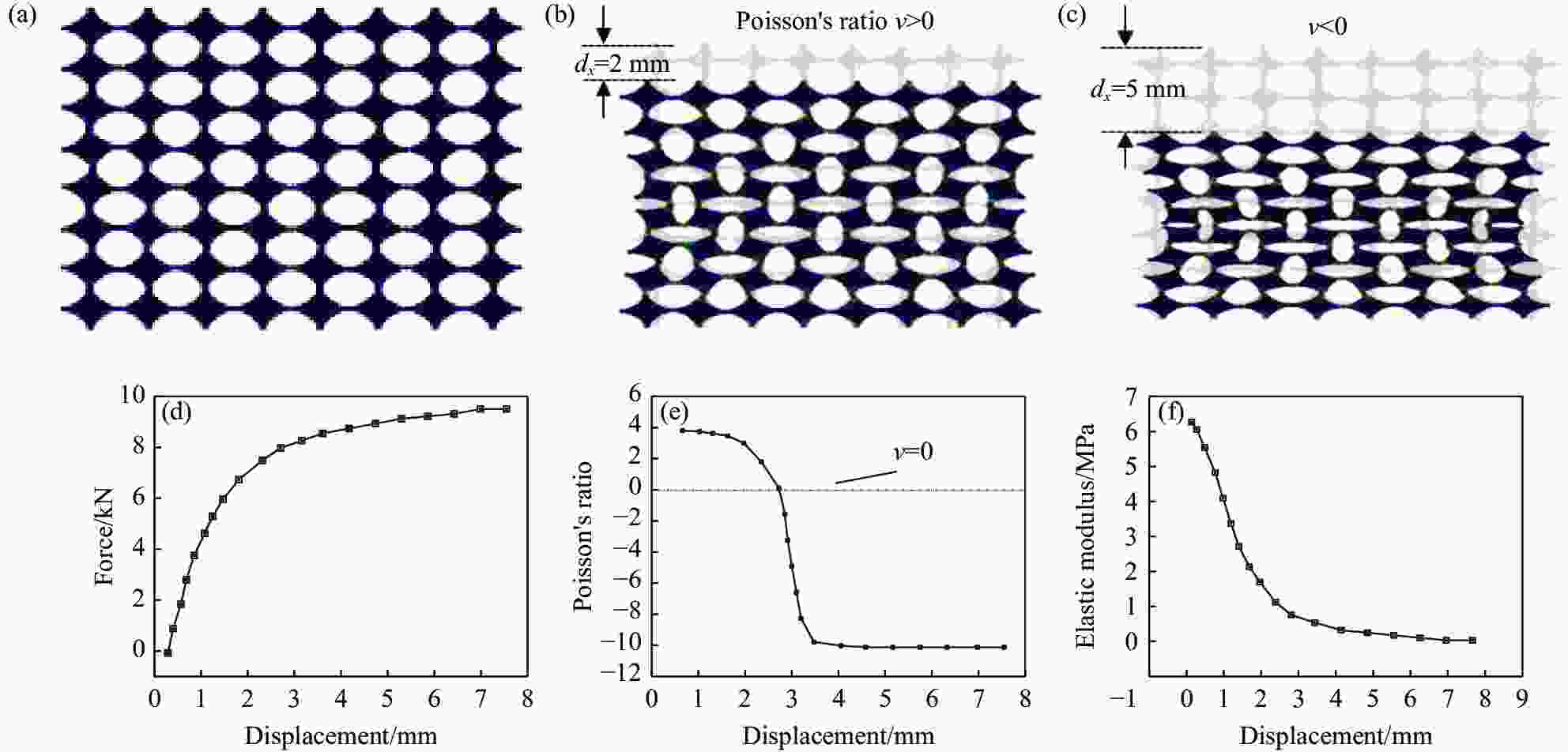
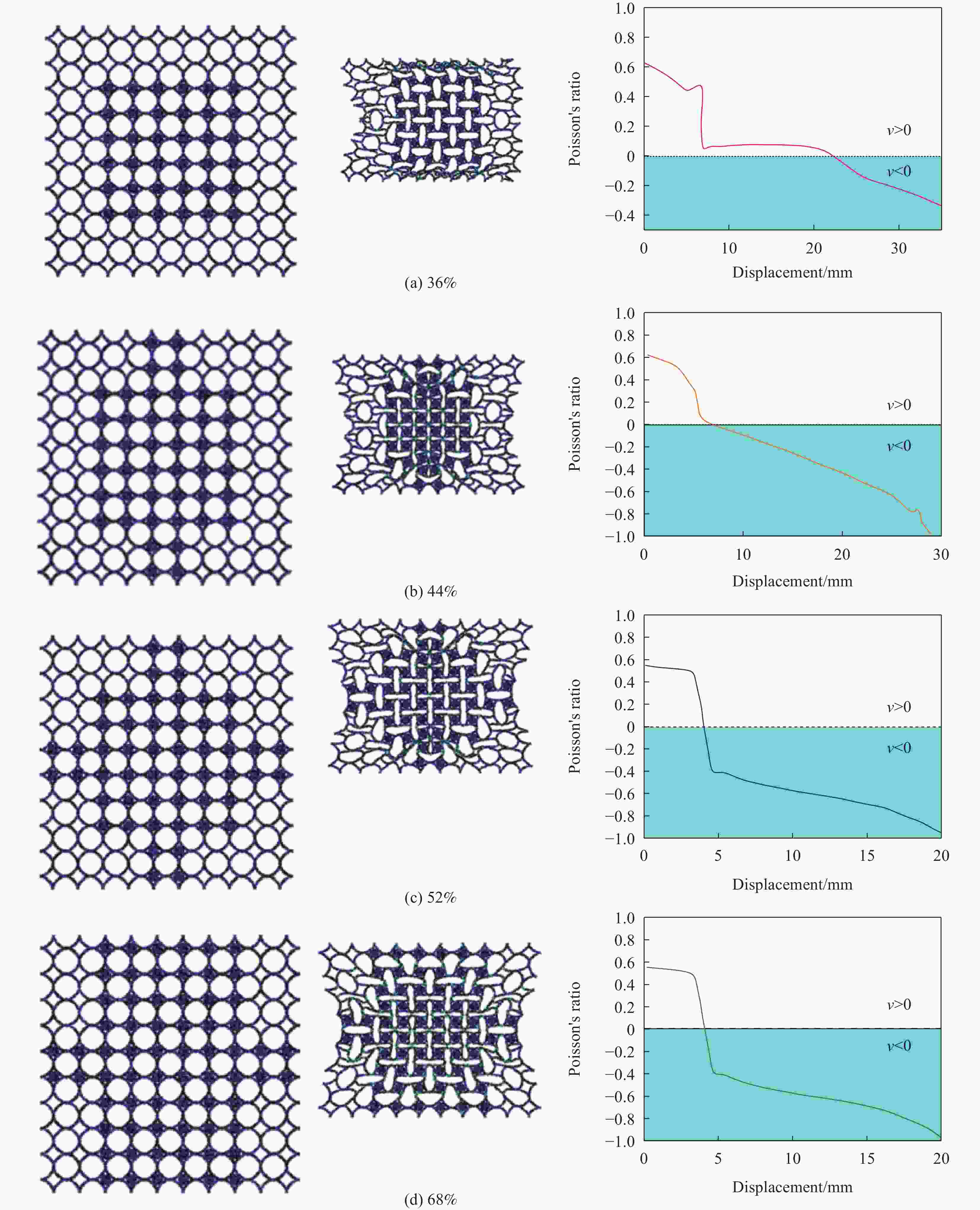
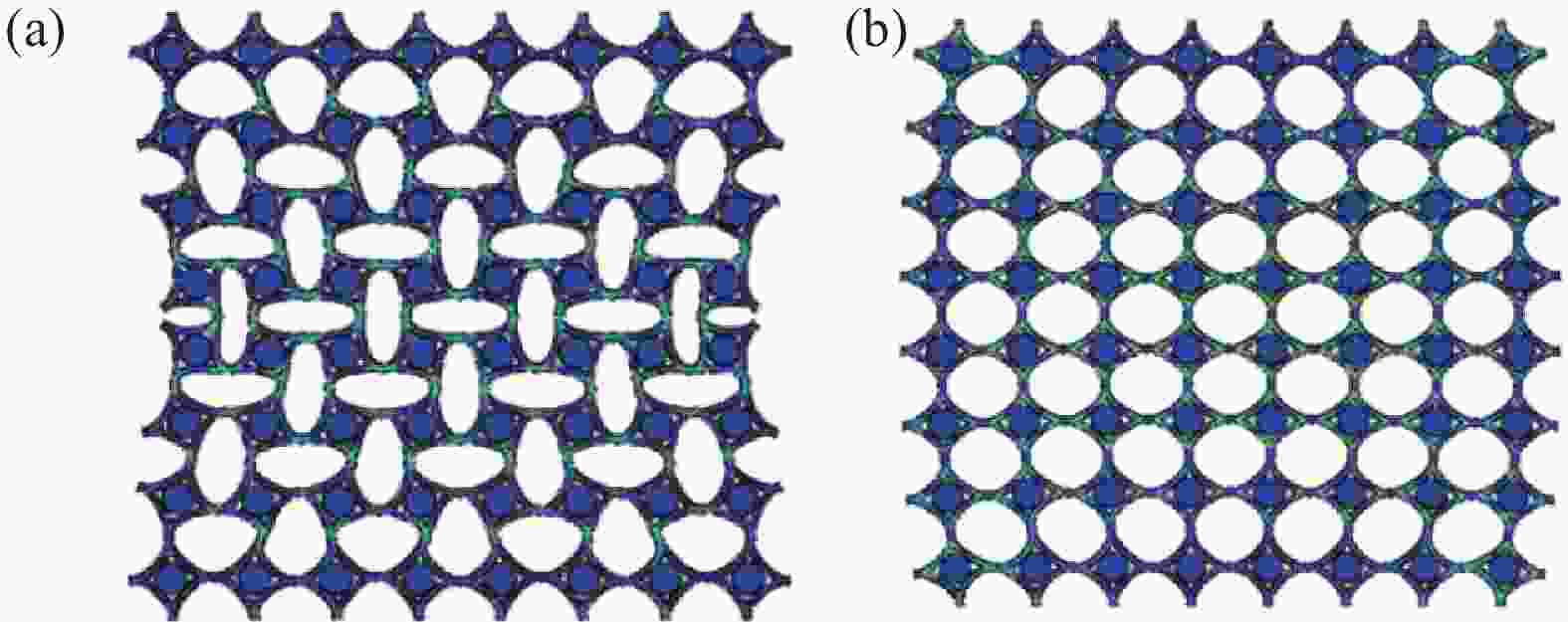
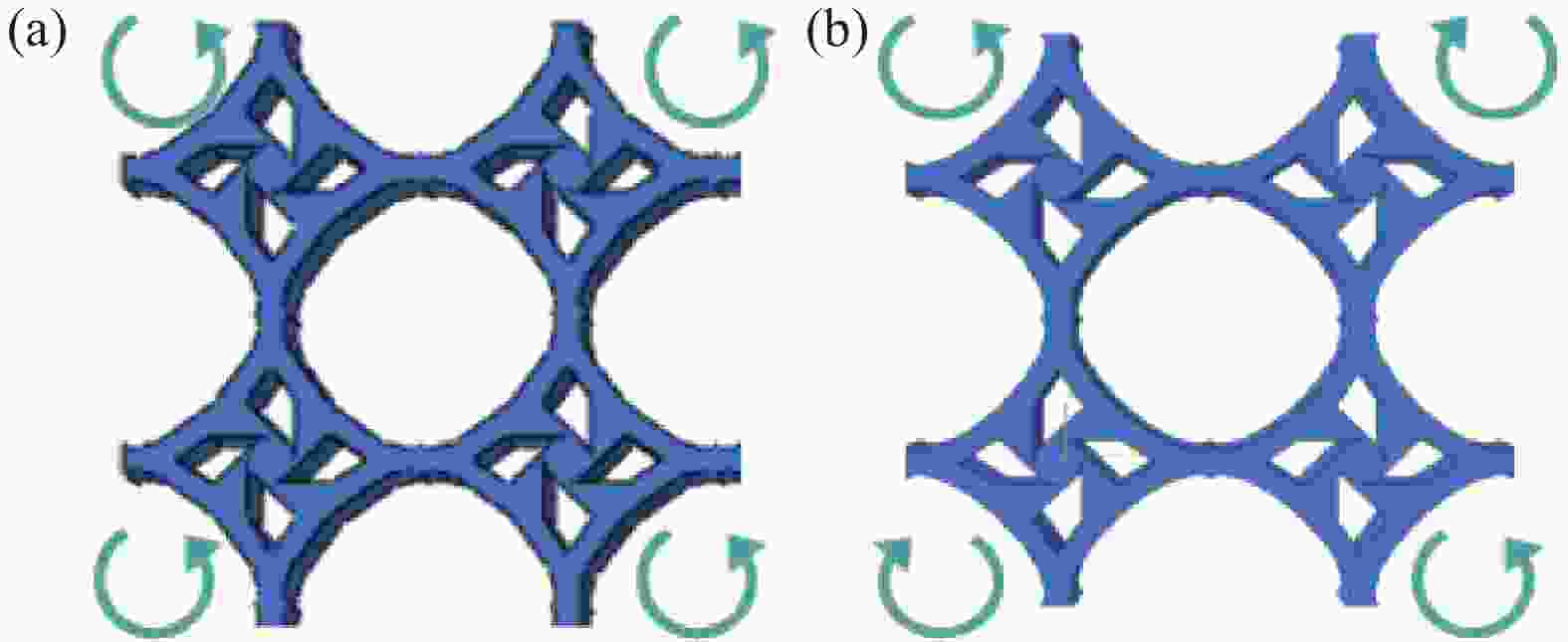
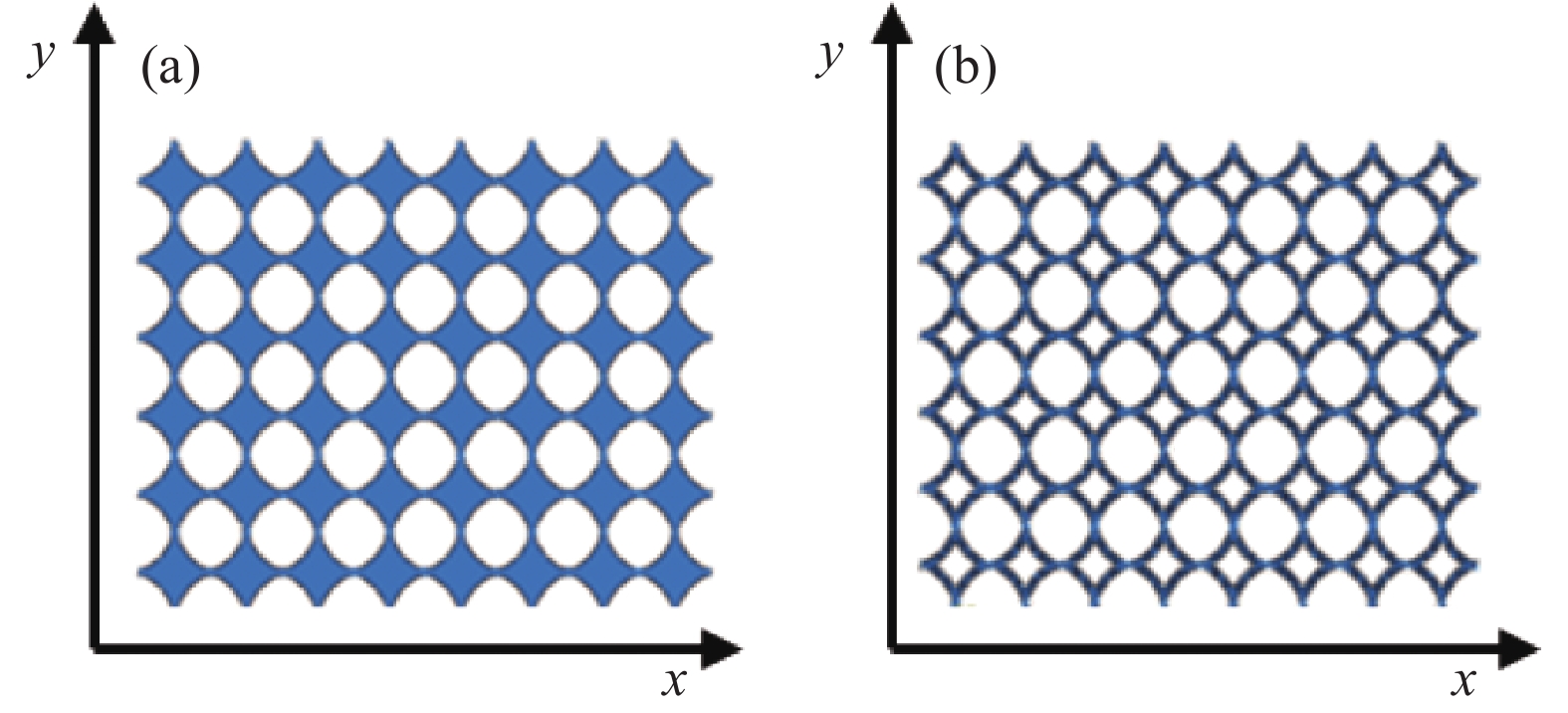
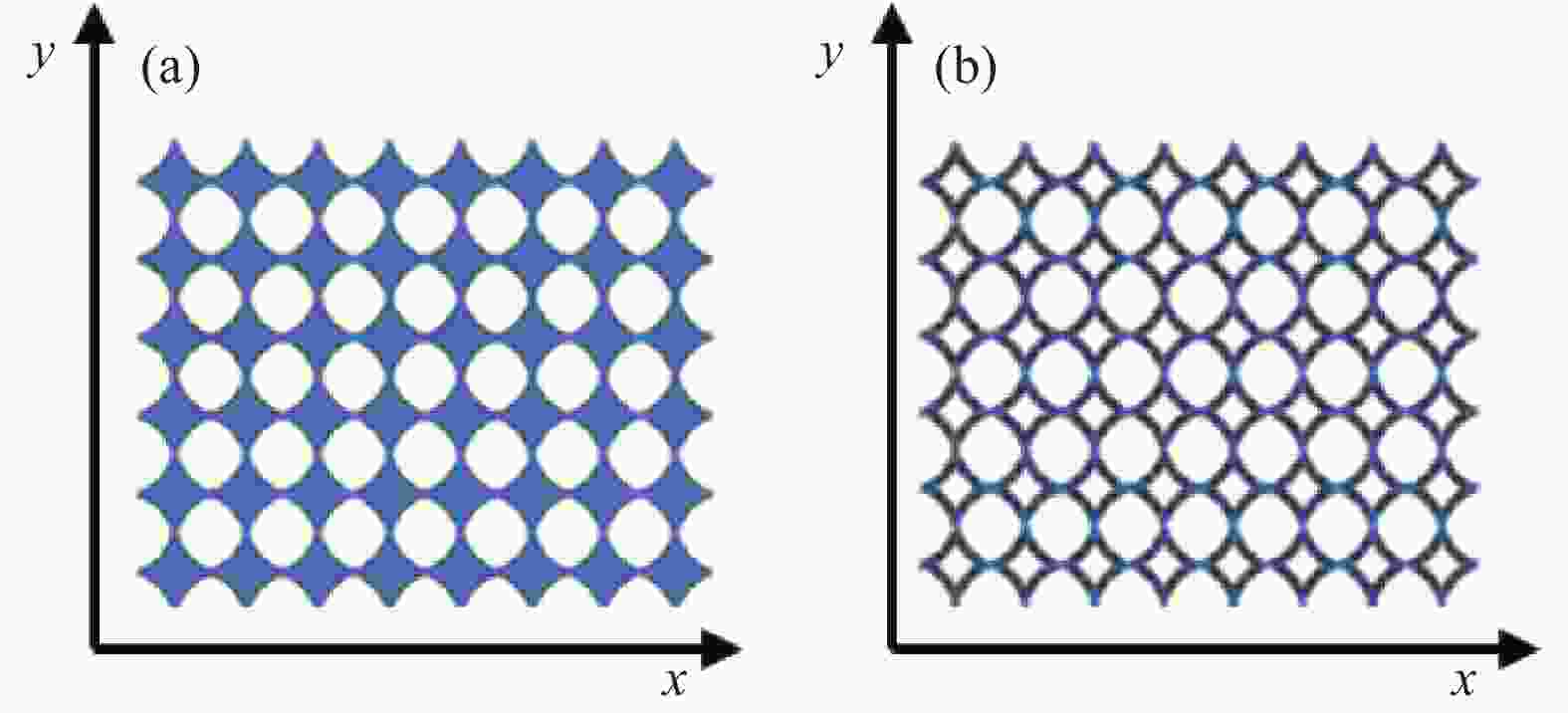
摘要: 负泊松比材料作为一种新型的超材料,鉴于其优异的力学性能,在航天、航空、工业、医药科学等领域具有广泛的应用前景。为得到性能、结构可主动调节的超材料,首先以负泊松比结构为基础,结合形状记忆智能材料,设计出性能可调控的超材料结构单元模型。然后通过基本梁理论计算,获得宏观结构泊松比正负转变与刚体结构之间的临界参数。其次,通过有限元仿真,确定材料泊松比正负调节与填充单元组合比例及排列方式之间的关系。最后对这种二维结构材料的振动特性和力学性能进行了详细的分析。结果表明:这种材料在调节结构力学性能和振动调控方面表现出优异的性能。调节内部单元的填充形式和排列方式,可以得到不同的力学性能和吸能效果;同时,通过引入形状记忆材料和微结构,使材料表现出优异的宏观结构和刚度智能调节性能。Abstract: As a new type of metamaterials, negative Poisson's ratio materials have great potential application prospects in aerospace, aviation, industry, medical science and other fields due to its excellent mechanical properties. In order to obtain metamaterials with actively adjustable performance and structure, a unit model of metamaterial structure was first designed based on the negative Poisson's ratio structure. Then, through the calculation of basic beam theory, the critical parameters between the positive and negative transition of the Poisson's ratio of the macrostructure and the rigid body structure were obtained. In addition, through finite element simulation, the relationship between positive and negative adjustment of Poisson's ratio of materials and the proportion and arrangement of filling elements was determined. Finally, the vibration characteristics and mechanical properties of this two-dimensional structural material were analyzed in detail. The results show that this material shows excellent performance in regulating the structure and reducing vibration. Adjusting the filling form and arrangement of the internal unit, we can obtain different mechanical properties and energy absorption effects. At the same time, by introducing shape memory materials and microstructures, the materials show excellent macrostructure and intelligent adjustment of stiffness.
-
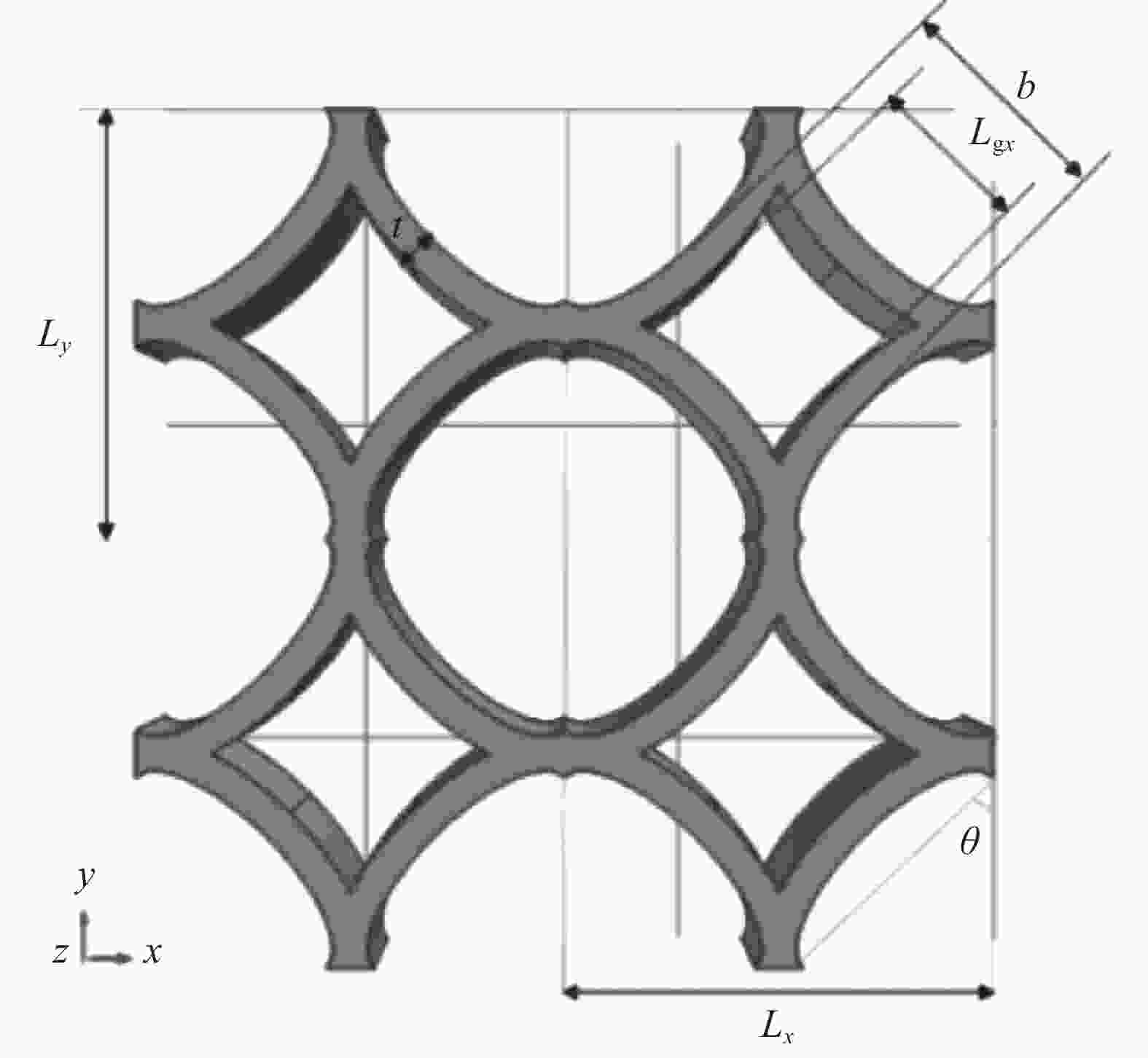
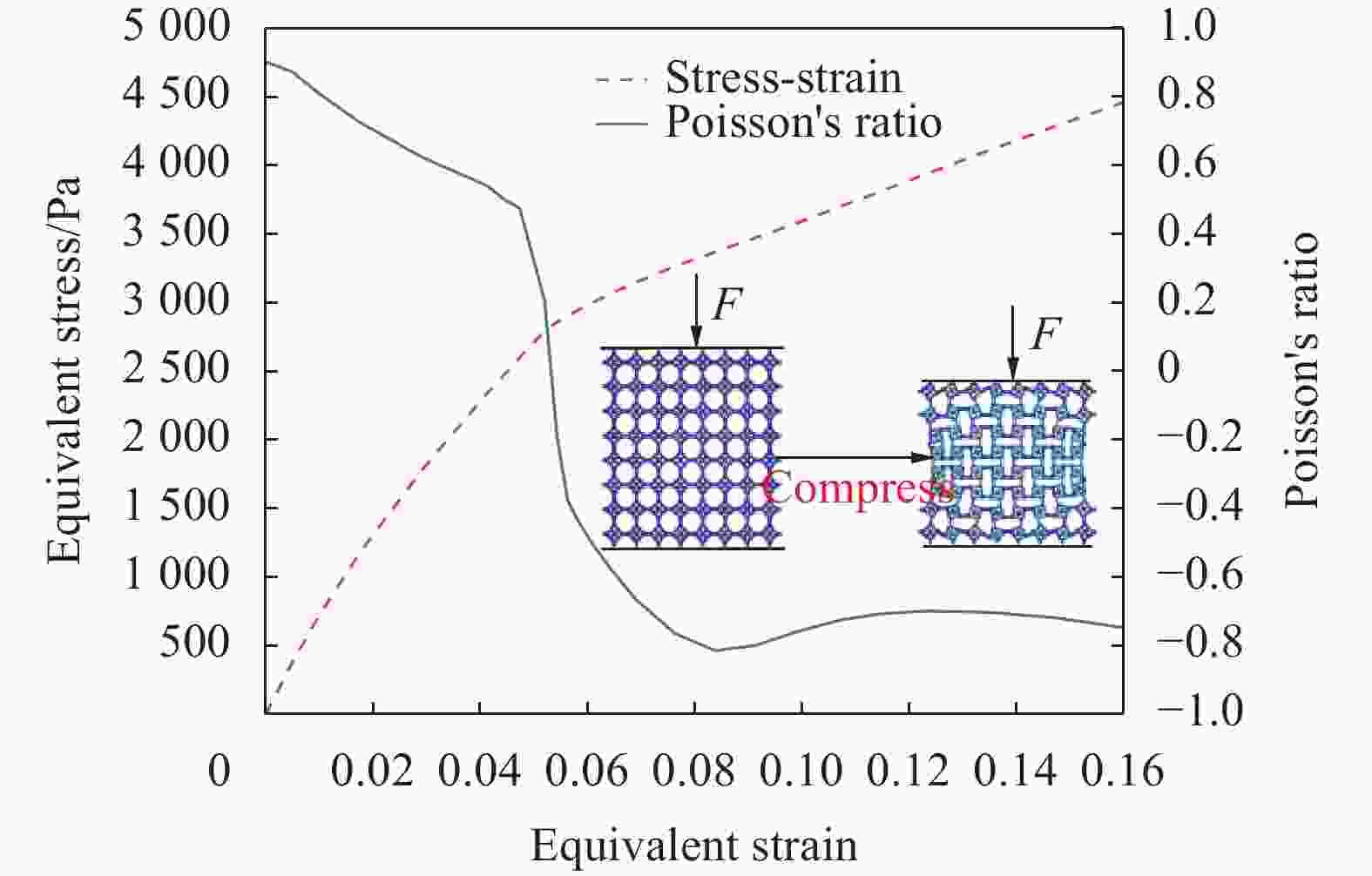
表 1 不同微结构泊松比拐点数值
Table 1. Poisson's ratio inflection point values of different microstructures
Type Poisson's ratio Equivalent strain Equivalent stress/Pa Cross bracing structure 0 0.053 2822 Co-directional
wheel shaft0 0.036 9616 Reverse wheel
shaft0 0.009 1992 -
[1] 程宗辉, 段本方, 陈云鹏, 等. 基于磁性衬底的宽频薄层超材料吸波体研究[J]. 磁性材料及器件, 2022, 53(4):41-47. doi: 10.19594/j.cnki.09.19701.2022.04.008CHENG Zonghui, DUAN Benfang, CHEN Yunpeng, et al. Study on broadband thin layer metamaterial absorber based on magnetic substrate[J]. Journal of Magnetic Materials and Devices,2022,53(4):41-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.19594/j.cnki.09.19701.2022.04.008 [2] 王凯, 周加喜, 蔡昌琦, 等. 低频弹性波超材料的若干进展[J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(10):2678-2694. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-108WANG Kai, ZHOU Jiaxi, CAI Changqi, et al. Some advances in low frequency elastic wave metamaterials[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2022,54(10):2678-2694(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-108 [3] 曹培政, 张宇, 刁顺, 等. 水下声学超材料研究[J]. 中国材料进展, 2021, 40(1):7-21. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.202007017CAO Peizheng, ZHANG Yu, DIAO Shun, et al. Research on underwater acoustic metamaterials[J]. Materials China,2021,40(1):7-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.202007017 [4] BOBA K, BIANCHI M, MCCOMBE G, et al. Blocked shape memory effect in negative Poisson's ratio polymer metamaterials[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(31):20319-20328. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b02809 [5] KOLKEN H M A, ZADPOOR A A. Auxetic mechanical metamaterials[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(9):5111-5129. doi: 10.1039/C6RA27333E [6] CHOI J B, LAKES R S. Nonlinear properties of metallic cellular materials with a negative Poisson's ratio[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1992,27(19):5375-5381. doi: 10.1007/BF02403846 [7] PRAWOTO Y. Seeing auxetic materials from the mechanics point of view: A structural review on the negative Poisson's ratio[J]. Computational Materials Science,2012,58:140-153. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.02.012 [8] LOVE A E. A treatise on the mathematical theory of elasticity[M]. New York: Dover Publications, 2013: 25-30. [9] 杨智春, 邓庆田. 负泊松比材料与结构的力学性能研究及应用[J]. 力学进展, 2011, 41(3):335-350. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-2011-3-lxjzJ2011-013YANG Zhichun, DENG Qingtian. Research and application of mechanical properties of materials and structures with negative Poisson's ratio[J]. Advances in Mechanics,2011,41(3):335-350(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-2011-3-lxjzJ2011-013 [10] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. The mechanics of two-dimensional cellular materials[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London,1982,382(1782):25-42. [11] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids: Structure and properties[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1988: 85-87. [12] LAKES R. Foam structures with a negative Poisson's ratio[J]. Science,1987,235(4792):1038-1040. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4792.1038 [13] LAKES R. Negative Poisson's ratio materials[J]. Science,1987,238(4826):551-556. doi: 10.1126/science.238.4826.551.a [14] MASTERS I G, EVANS K E. Models for the elastic deformation of honeycombs[J]. Composite Structures,1996,35(4):403-422. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(96)00054-2 [15] 孙龙, 任鑫, 张毅, 等. 一种刚度可调控的负泊松比管状结构[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(4):1813-1823. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210531.001SUN Long, REN Xin, ZHANG Yi, et al. An auxetic tubular structure with tuneable stiffness[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(4):1813-1823(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210531.001 [16] 邓二杰, 刘彦琦, 宋春芳. 负刚度蜂窝单胞结构制备及压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5):2161-2171. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210722.001DENG Erjie, LIU Yanqi, SONG Chunfang. Preparation and compression properties of negative stiffness honeycomb cell structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(5):2161-2171(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210722.001 [17] LIPTON J I, MACCURDY R, MANCHESTER Z, et al. Handedness in shearing auxetics creates rigid and compliant structures[J]. Science,2018,360(6389):632-635. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4586 [18] 于雅琳, 李健芳, 黄智彬, 等. 复合材料负泊松比格栅结构设计及力学性能评价[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4):1107-1114. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200623.002YU Yalin, LI Jianfang, HUANG Zhibin, et al. Structural design and mechanical characterization of an auxetic advanced grid structure composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(4):1107-1114(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200623.002 [19] OVERVELDE J T B, SHAN S, BERTOLDI K. Compaction through buckling in 2D periodic, soft and porous structures: Effect of pore shape[J]. Advanced Materials,2012,24(17):2337-2342. doi: 10.1002/adma.201104395 [20] HAN Y F, LU W F. Evolutionary design of nonuniform cellular structures with optimized Poisson's ratio distribution[J]. Materials & Design,2018,141:384-394. [21] RUBEN G, ROBERTO C, DAPHNE A, et al. On the properties of real finite sized planar and tubular stent-like auxetic structures[J]. Physica Status Solidi,2014,251(2):321-327. doi: 10.1002/pssb.201384257 [22] DONG W J, SUN Q. Airfoil design and numerical analysis for morphing wing structure[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2011,228-229:169-173. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.228-229.169 [23] LENG J S, LAN X, LIU Y J, et al. Shape-memory polymers and their composites: Stimulus methods and applications[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2011,56(7):1077-1135. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.03.001 [24] LIRA C, SCARPA F, TAI Y H, et al. Transverse shear modulus of silicomb cellular structures[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2011,71(9):1236-1241. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.04.008 [25] 杜善义, 张博明. 飞行器结构智能化研究及其发展趋势[J]. 宇航学报, 2007, 28(4):773-778. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2007.04.001DU Shanyi, ZHANG Boming. Research and development trend of aircraft structure intelligence[J]. Journal of Astronautics and Astronautics,2007,28(4):773-778(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2007.04.001 [26] 陈以金. 变体飞行器柔性蒙皮及支撑结构性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014.CHEN Yijin. Study on flexible skin and supporting substructure of morphing aircraft[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014(in Chinese). [27] LENG J S, DU S Y. Shape-memory polymers and multifunctional composites[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2010: 1-109. [28] LUO L, ZHANG F H, LENG J S. Multi-performance shape-memory epoxy resins and their composites with narrow transition temperature range[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2021,213(7):108899. [29] LI W B, LIU Y J, LENG J S. Programmable and shape-memorizing information carriers[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(51):44792-44798. -





 下载:
下载: