Preparation of polyvinyl chloride lithium ion sieve membrane and its lithium adsorption properties in brine
-
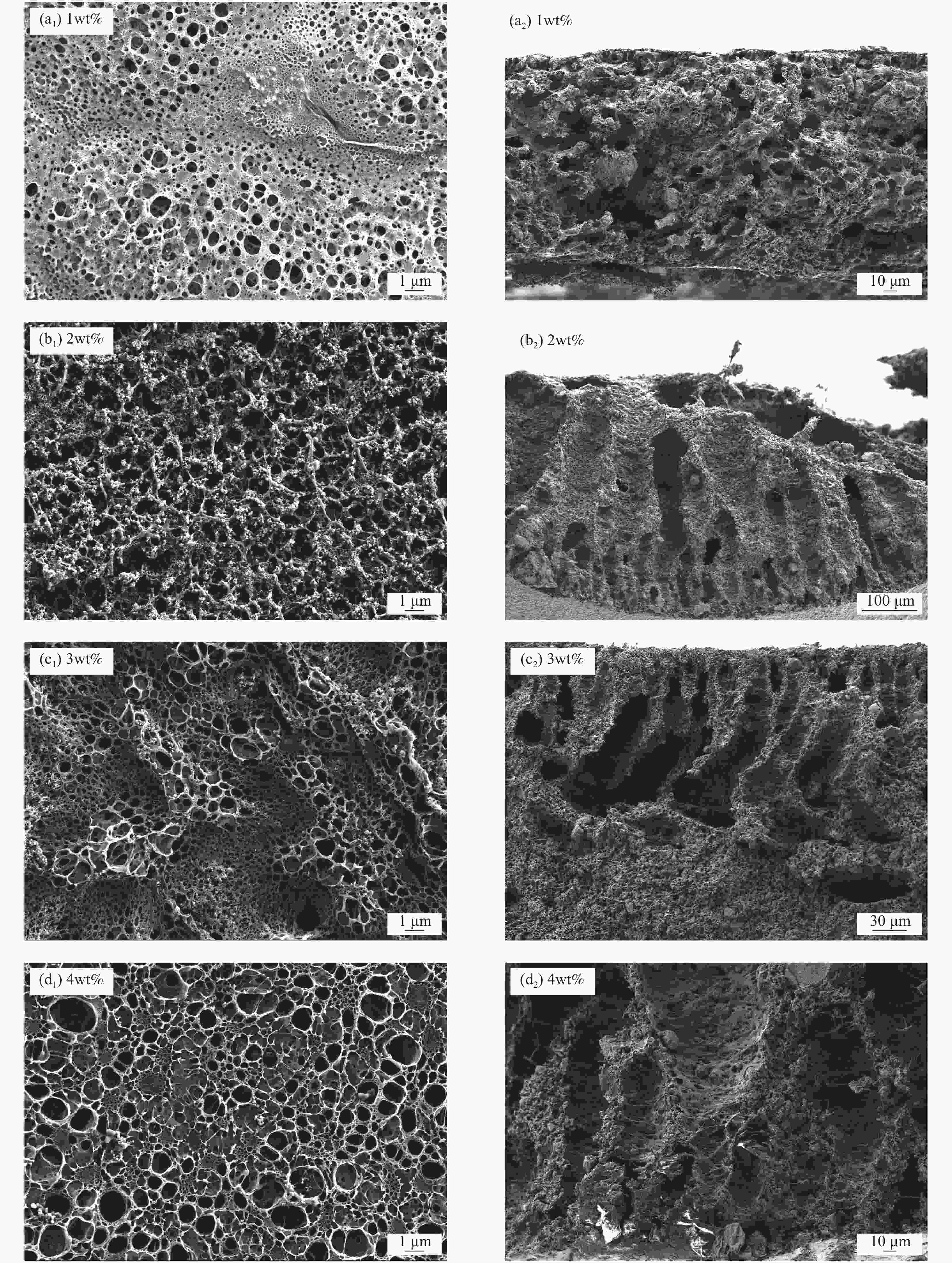
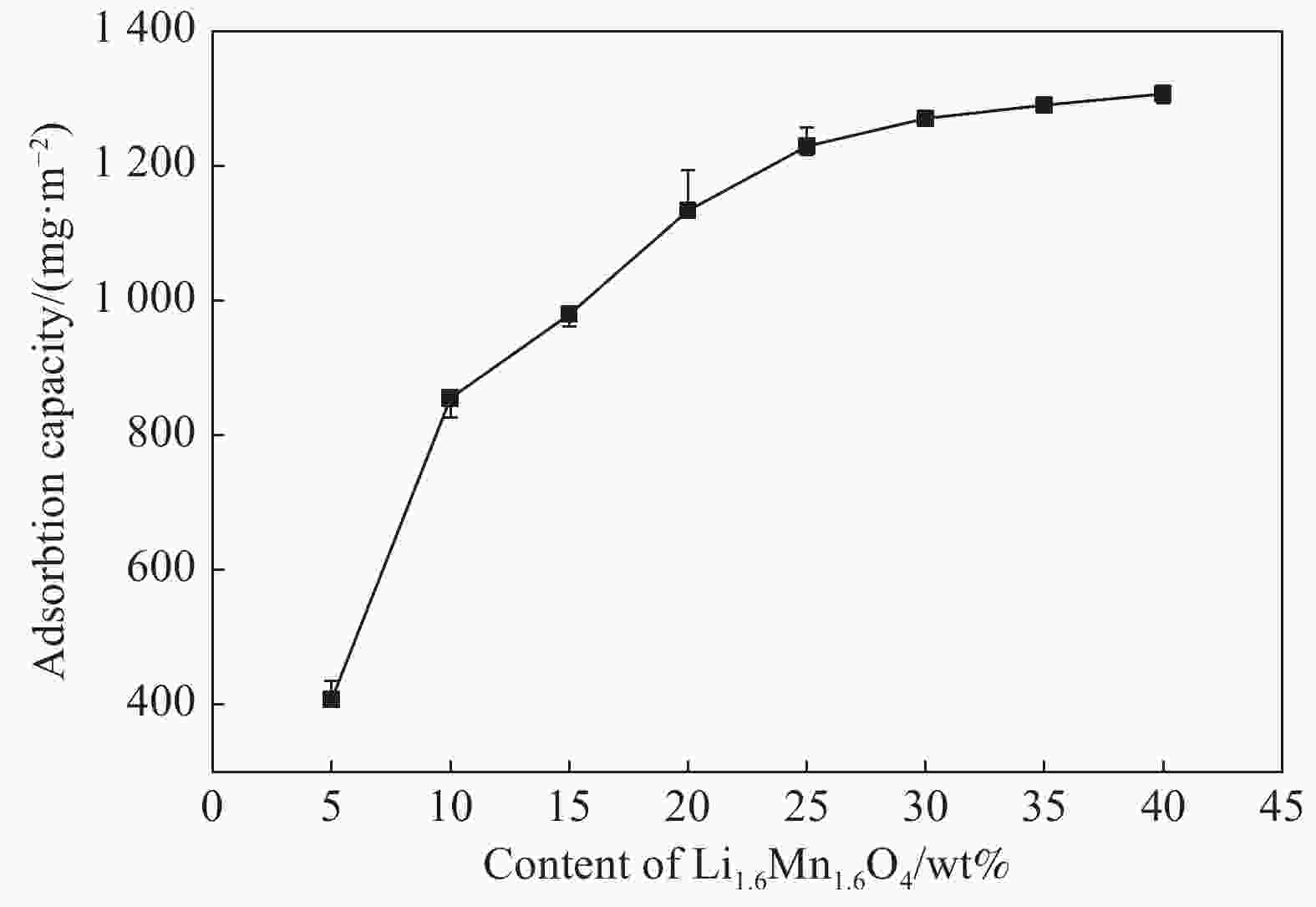
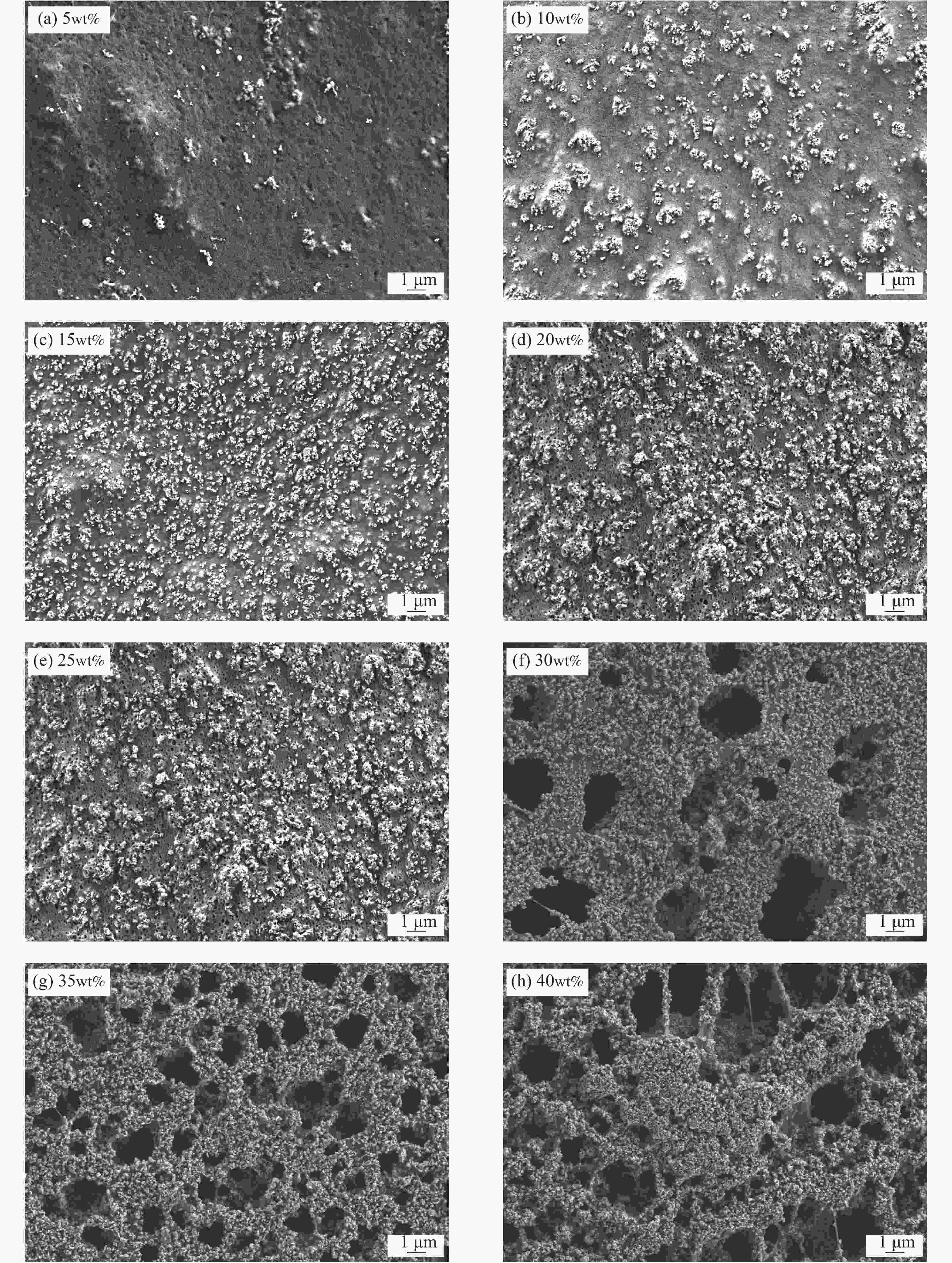
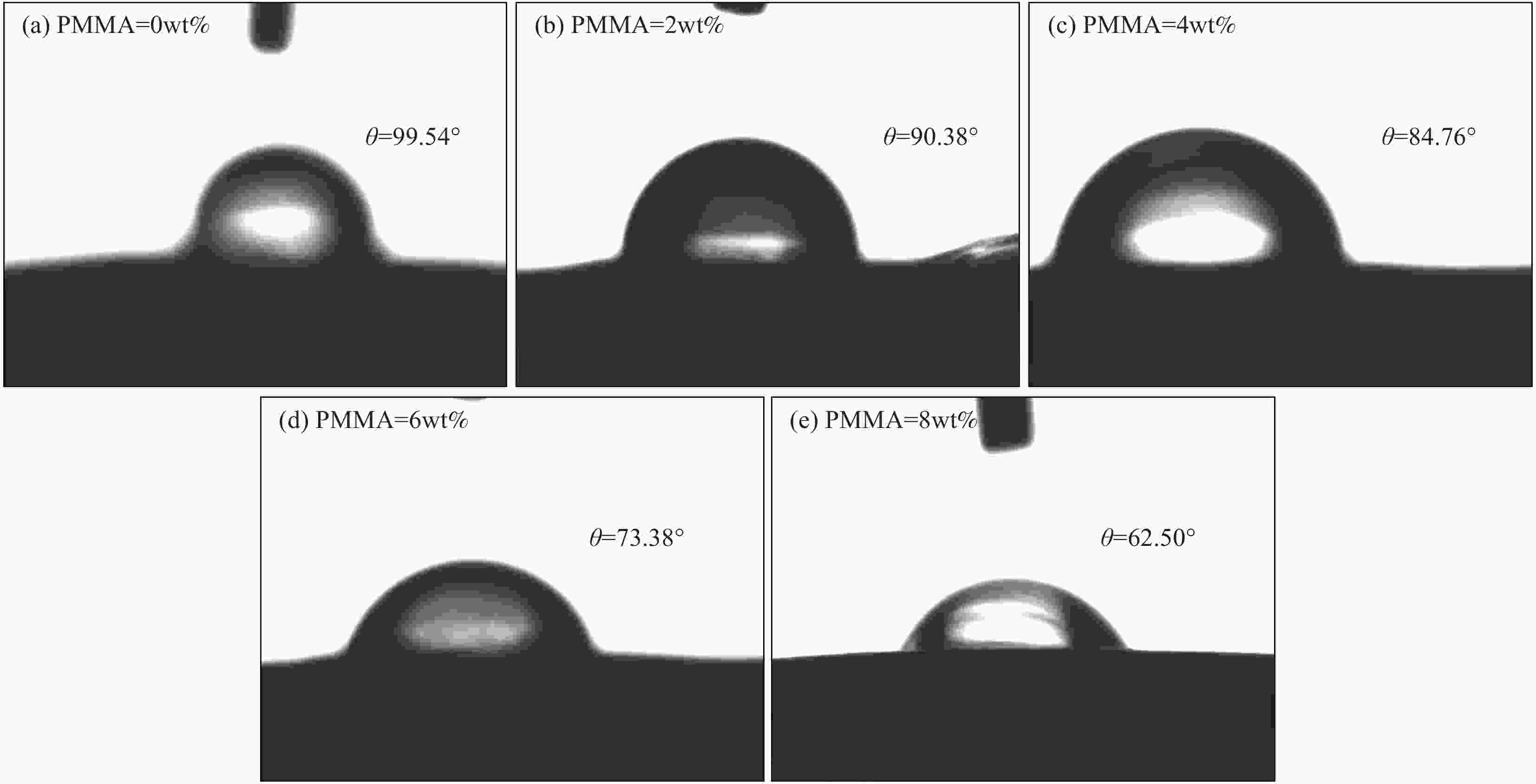
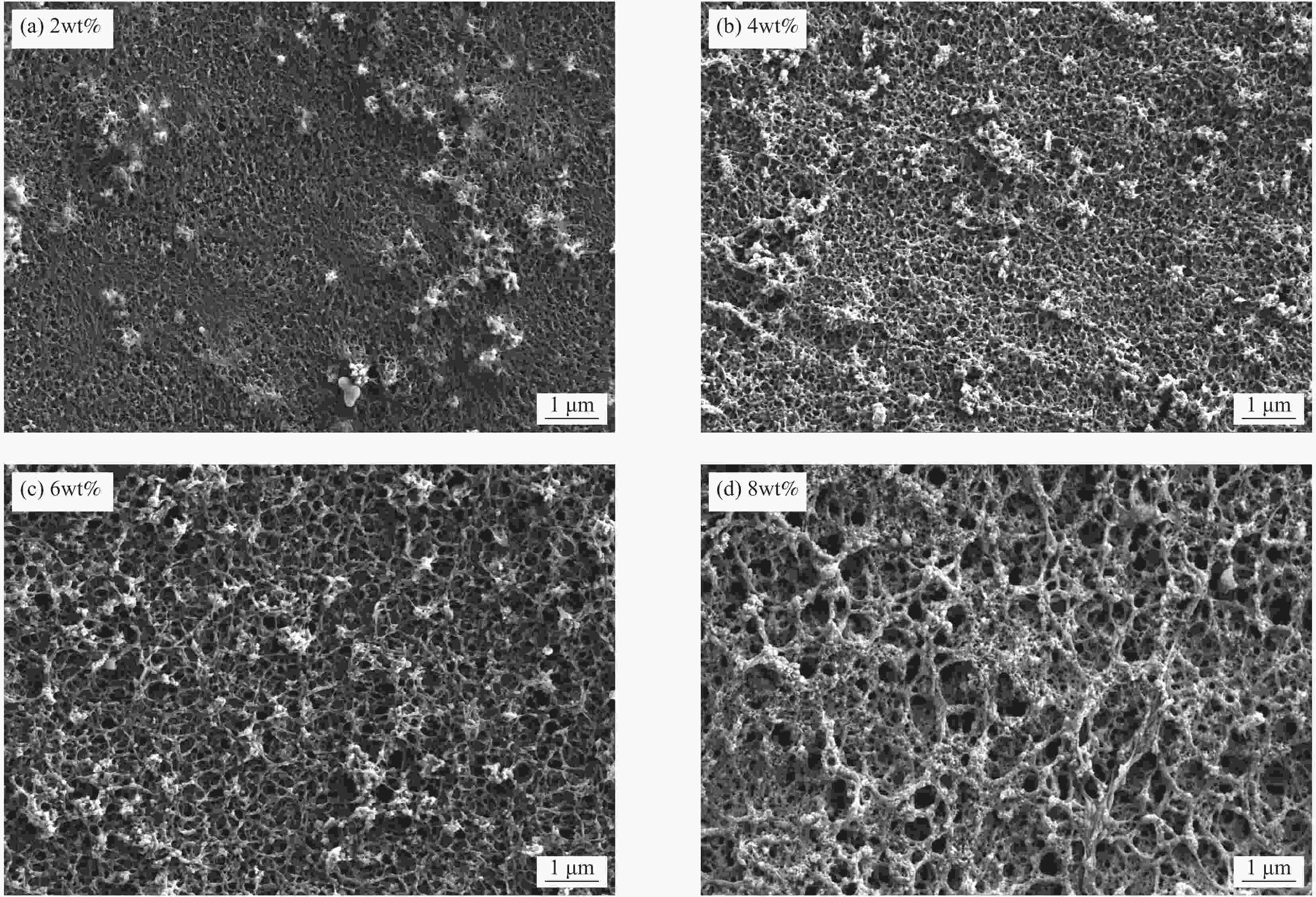
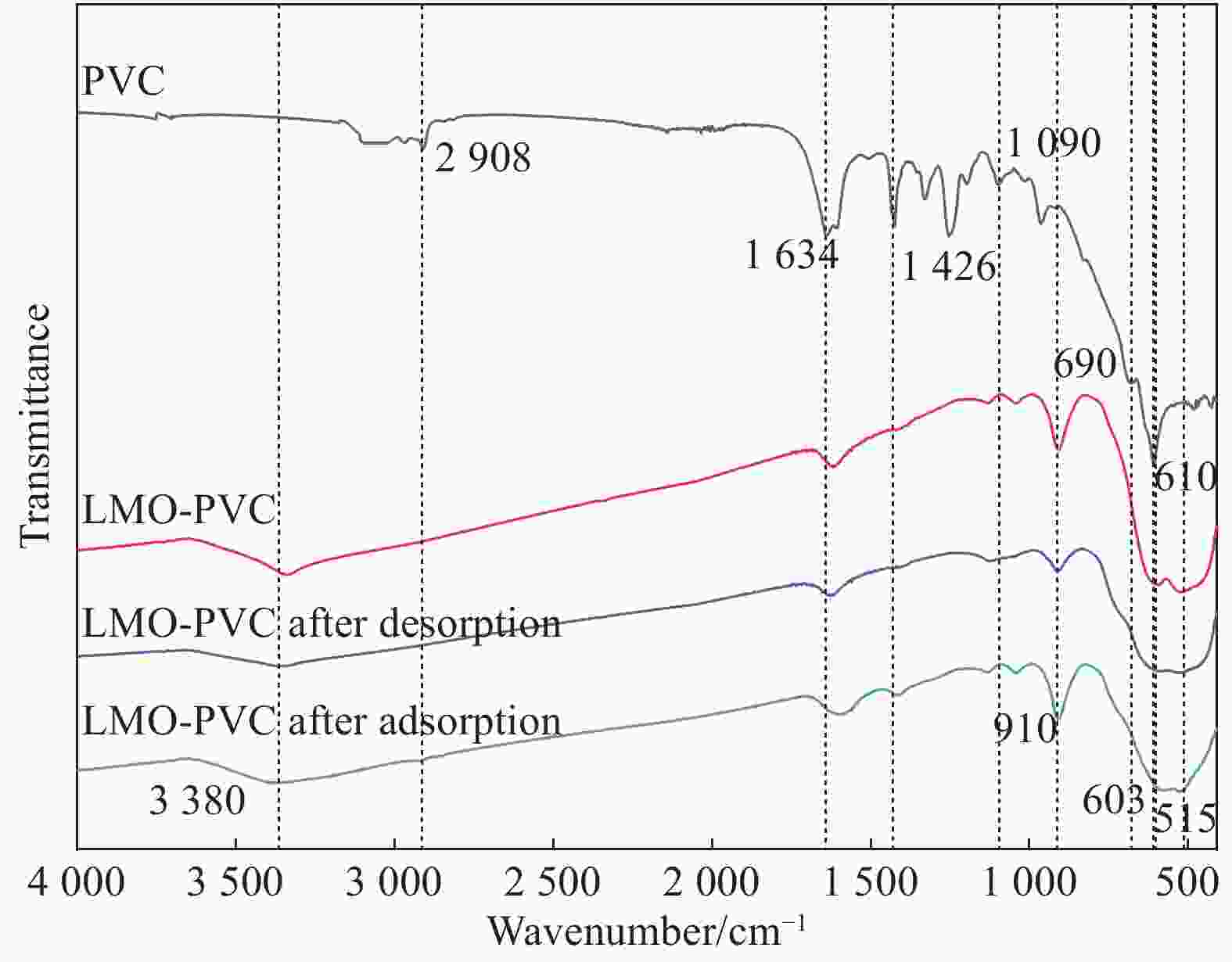
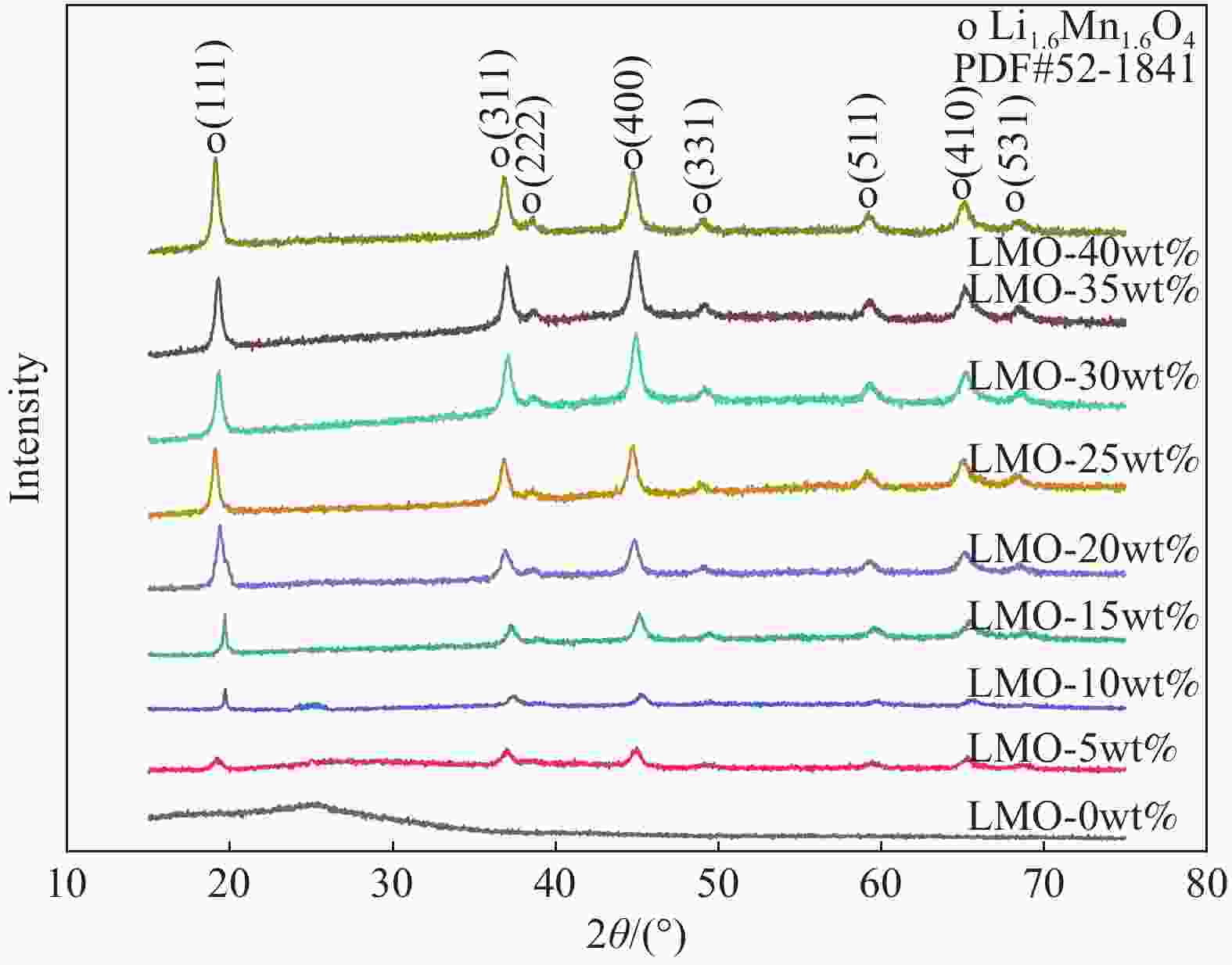
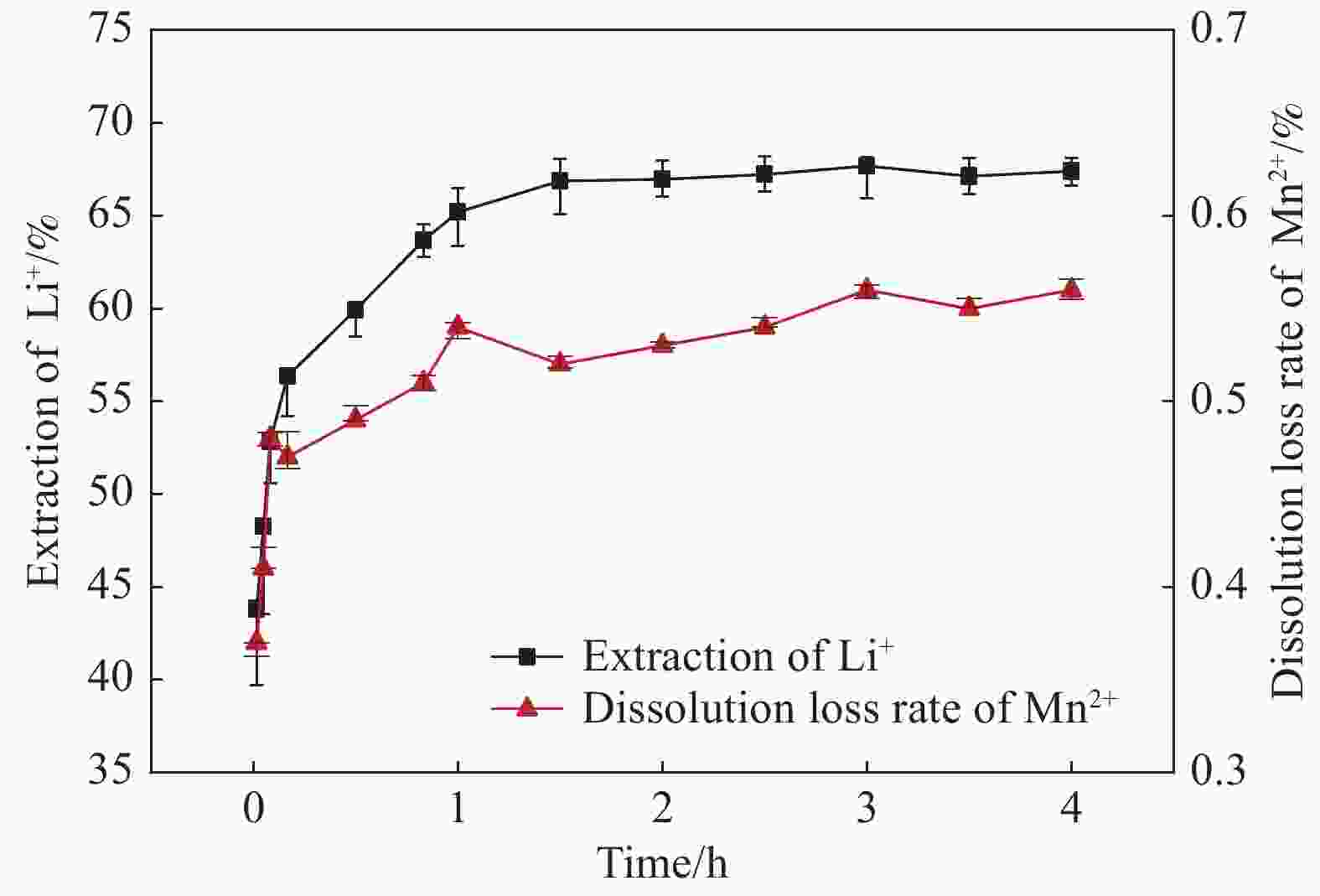
摘要: 锂离子筛的成型技术对于其在卤水中的工业化生产应用具有重要意义。以聚氯乙烯(PVC)为成膜材料,聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA)和聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVPk30)为改性剂,制备了负载Li1.6Mn1.6O4的PVC锂离子筛前驱体膜,研究了膜经稀盐酸抽锂后得到的PVC锂离子筛膜对锂的吸附性能及循环吸附解吸性能等,并对离子筛膜进行了吸附动力学及吸附等温模型分析。结果表明:PVC浓度为10wt%,PMMA的添加量为6wt%,PVPk30的添加量为2wt%,Li1.6Mn1.6O4含量为20wt%联用时,制得的离子筛膜吸附量为1336.30 mg/m2。经0.1 mol·L−1 HCl溶液解吸,约2 h时解吸达到平衡,锰的溶损率为0.56%左右。在卤水中进行了10次循环吸附解吸过程,吸附量降至1294.16 mg/m2,吸附量仅损失了3%。在含有多种复杂离子如Na+、K+、Mg2+和Ca2+的卤水中,锂离子筛膜对Li+有很高的选择性。说明该PVC锂离子筛膜结构稳定,循环利用性能优异,有利于其工业化应用。PVC锂离子筛膜的吸附过程更符合伪二级动力学方程及Langmuir吸附等温模型,说明该吸附过程的吸附类型为单分子层化学吸附。膜状的离子筛对于从盐湖卤水等液态锂资源中提取锂具有很大的开发潜力。Abstract: Lithium ion sieve formation technology for Li+ recovery industrial production and application from brine is very important. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)-Li1.6Mn1.6O4 lithium ion sieve precursor membrane was prepared by blend of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 with PVC, polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVPk30). After the precursor membrane was treated with HCl solution it can uptake lithium. A series of experiments for examining its adsorption and cyclic performance were carried out. The adsorption isotherm model and the adsorption kinetics of PVC lithium ion sieve membrane were analyzed. The results showed that the adsorption capacity of PVC lithium ion sieve membrane was 1336.30 mg/m2 when the concentration of PVC was 10wt%, the content of PMMA was 6wt%, the content of PVPk30 was 2wt%, and the amount of loading of Li1.6Mn1.6O4 was 20wt%. After treated with 0.1 mol·L−1 HCl for 2 h, the lithium extraction reached equilibrium and the dissolution loss rate of Mn2+ was about 0.56%. After 10 cycles of adsorption and desorption in brine, the Li+ adsorption capacity was lost only 3.0% (from 1336.30 mg/m2 to 1294.16 mg/m2). The PVC lithium ion sieve membrane showed great selectivity for Li+ in brine containing a variety of complex ions such as Na+, K+, Mg2+ and Ca2+. The PVC lithium ion sieve membrane has stable structure and excellent recycling performance, which is conducive to its industrial application. The PVC lithium ion sieve membrane accords with the pseudo second order kinetic equation and Langmuir adsorption isotherm model, indicating a monolayer chemisorption. It is potential to be used in enrichment and recovery of lithium from salt lake brine and other liquid lithium sources.
-
Key words:
- lithium ion-sieve /
- polyvinyl chlorides /
- brine /
- absorption /
- membranes /
- separation
-
表 1 青海昆特依盐湖卤水水质成分
Table 1. Components of the Qinghai Kunty salt lake brine
Metal ion Li+ Mg2+ Ca2+ K+ Na+ Mn2+ Cd2+ Cr3+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Mg2+/Li+ Initial concentration/(g·L−1) 0.15 10.52 0.072 3.63 5.39 − 0.0034 0.0069 0.0024 0.01 70 表 2 不同致孔剂聚乙烯吡咯烷酮PVPk30添加量的PVC锂离子筛膜的膜通量参数
Table 2. Membrane flux performance of PVC lithium ion sieve membrane with different pore-causing agent polyvinylpyrrolidone PVPk30 contents
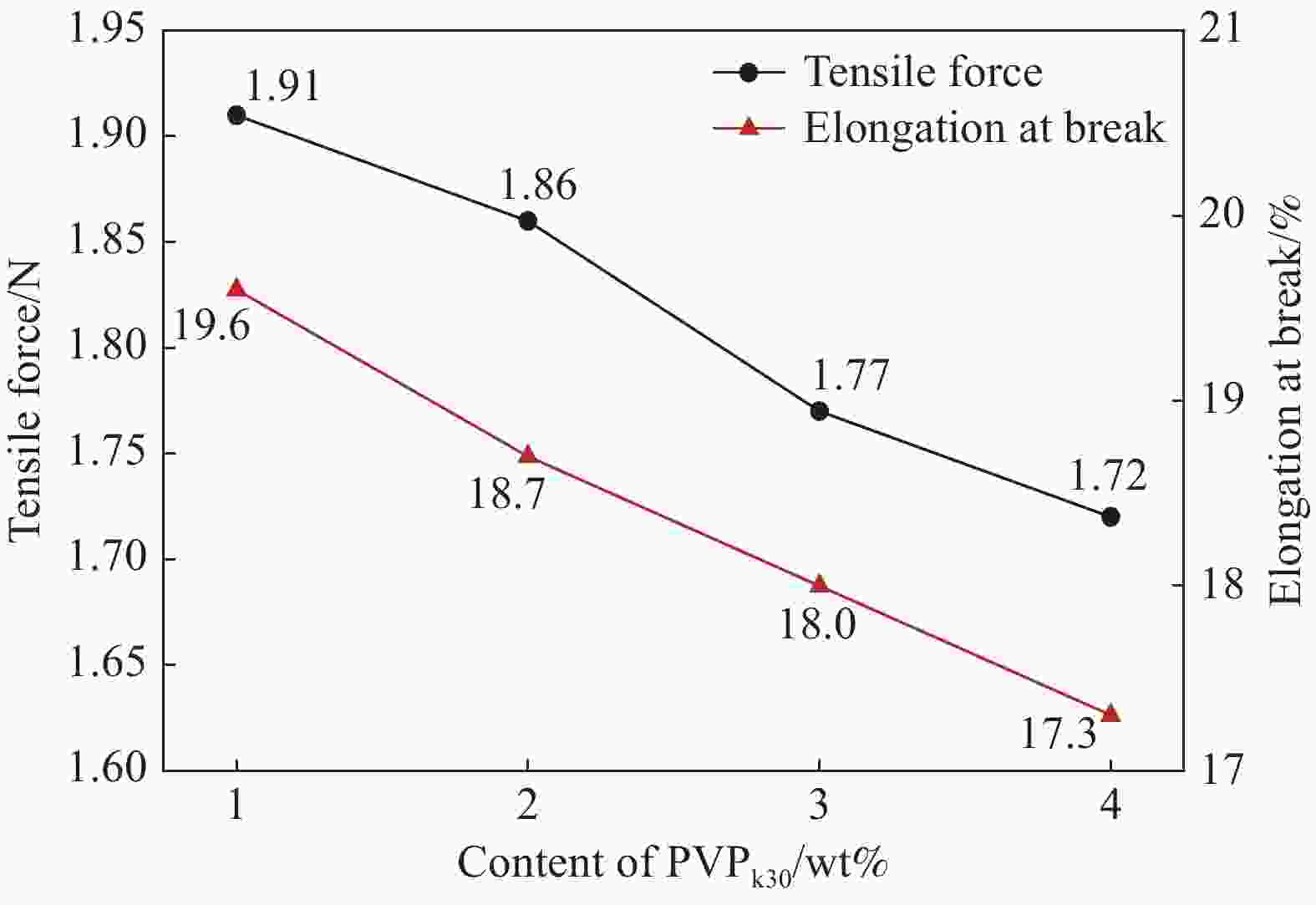
PVPk30 content/wt% Brine flux
/(L·m2·h−1)0 228.06 1 311.20 2 488.83 3 593.78 4 669.69 表 3 锂离子筛膜从卤水中分离锂离子的性能
Table 3. Performance of PVC lithium ion sieve membrane the separation of Li+ from other cations in brine
Cations C0/(mg·L−1) Ce/(mg·L−1) Q/(mg·m−2) Q/(mmol·m−2) Kd/(L·m−2) $\alpha_{\rm{M}}^{{\rm{L i}}} $ CF/(L·m−2) Li+ 128.98 89.22 1335.78 192.45 14.972 1.00 10.356 Mg2+ 10155.32 10054.91 3373.78 138.81 0.335 44.69 0.332 K+ 3820.16 3804.65 521.14 13.33 0.137 109.28 0.136 Na+ 4370.87 4336.58 1152.14 50.09 0.266 56.29 0.264 Ca2+ 72 71 – – – – – Notes: C0 and Ce—Initial and equilibrium Li+ concentrations in brine, respectively; Q—Li+ adsorption capacity; Kd—Distribution coefficient; α—Separation factor; CF—Concentration factor; M—Li, Na, K, Mg and Ca. -
[1] LU L G, HAN X B, LI J Q, et al. A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2013,226:272-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.10.060 [2] LIU G, ZHAO Z W, GHAHREMAN A. Novel approaches for lithium extraction from salt-lake brines: A review[J]. Hydrometallurgy,2019,187:81-100. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.05.005 [3] KESLER S E, GRUBER P W, MEDINA P A, et al. Global lithium resources: Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2012,48:55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.05.006 [4] RYU T, RYU J C, SHIN J, et al. Recovery of lithium by an electrostatic field-assisted desorption process[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research,2013,52(38):13738-13742. doi: 10.1021/ie401977s [5] TABELIN C B, DALLAS J, CASANOVA S, et al. Towards a low-carbon society: A review of lithium resource availability, challenges and innovations in mining, extraction and recycling, and future perspectives[J]. Minerals Engineering,2021,163(1-4):106743. [6] WANG L, MA W, LIU R, et al. Correlation between Li+ adsorption capacity and the preparation conditions of spinel lithium manganese precursor[J]. Solid State Ionics,2006,177(17-18):1421-1428. [7] WENG D, DUAN H Y, HOU Y C, et al. Introduction of manganese based lithium-ion sieve—A review[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International,2020,30(2):139-152. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2020.01.017 [8] 漆贵财. 锂离子筛复合材料的制备及性能研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019.QI Guicai. Synthesis of lithium ion sieve composites and research of the properties[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019(in Chinese). [9] SUN D S, MENG M J, YIN Y J, et al. Highly selective, regenerated ion-sieve microfiltration porous membrane for targeted separation of Li+[J]. Journal of Porous Materials,2016,23(6):1411-1419. doi: 10.1007/s10934-016-0201-4 [10] SARAVAIA H, GUPTA H, KULSHRESTHA V. Single step synthesis of a magnesium doped lithium manganese oxide ion sieve nanomaterial and a SPES/ion sieve composite membrane for the separation of lithium[J]. RSC Advances,2016,6(108):106980-106989. doi: 10.1039/C6RA14230C [11] YU Z J, LIU X Y, ZHAO F B, et al. Fabrication of a low-cost nano-SiO2/PVC composite ultrafiltration membrane and its antifouling performance[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2015,132(2):467-470. [12] ARYANTI P T P, YUSTIANA R, PURNAMA R E D, et al. Performance and characterization of PEG400 modified PVC ultrafiltration membrane[J]. Membrane Water Treatment,2015,6(5):379-392. doi: 10.12989/mwt.2015.6.5.379 [13] BODZEK M, KONIECZNY K. The influence of molecular mass of poly (vinyl chloride) on the structure and transport characteristics of ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Jour-nal of Membrane Science,1991,61:131-156. doi: 10.1016/0376-7388(91)80011-T [14] 邢丹敏, 武冠英, 胡家俊. 改性聚氯乙烯超滤膜的研究(I)-等离子体改性膜结构和性能的研究[J]. 膜科学与技术, 1996, 16(1):49-55.XING Danmin, WU Guanying, HU Jiajun. Study on the modified PVC UF membrane(I)-study on the structure and performance of the membrane treatmented by O2-plasma[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,1996,16(1):49-55(in Chinese). [15] 高以烜, 马炳伦, 李佩衍, 等. 聚氯乙烯超滤膜及其稳定性[J]. 水处理技术, 1988, 14(5):278-283. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.1988.05.005GAO Yixuan, MA Binglun, LI Peiyan, et al. PVC ultrafiltration membrane and its stability[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,1988,14(5):278-283(in Chinese). doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.1988.05.005 [16] 任松洁, 林伟青. 聚氯乙烯超滤膜的改性研究进展[J]. 广州化工, 2018, 46(18):34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.18.015REN Songjie, LIN Weiqing. Research progress on modification of PVC ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2018,46(18):34-36(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.18.015 [17] 郝慧博. PVC/PU共混超滤膜制备及其对多糖的分离[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2010.HAO Huibo. Preparation of PVC/PU blend ultrafiltration membrane and separation of the Astragalus[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University of Technology, 2010(in Chinese). [18] 马兴法, 魏丽萍, 吴崇光, 等. PVC/CEVA共混体系相容性研究[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 1996, 12(2):136-138. doi: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.1996.02.029MA Xingfa, WEI Liping, WU Chongguang, et al. Study on compatibility of PVC/CEVA blends[J]. Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering,1996,12(2):136-138(in Chinese). doi: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.1996.02.029 [19] DAS G, BANERJEE A N. Role of methods of blending on polymer-polymer compatibility[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1996,61(9):1473-1478. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19960829)61:9<1473::AID-APP6>3.0.CO;2-G [20] BODZEK M, KONIECZNY K. Ultrafiltration membranes made of vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer[J]. Jour-nal of Membrane Science,1993,76(2-3):269-279. [21] 谭欣, 张唏晨, 王同生. 分离乙醇和水的聚氯乙烯光化学接枝膜的接枝方法研究[J]. 膜科学与技术, 1992, 12(4):41-46.TAN Xin, ZHANG Xichen, WANG Tongsheng. The PVC photochemical grafting membrane separating ethanol and water[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,1992,12(4):41-46(in Chinese). [22] 李系蕴, 张振家, 乔向利. PVC/PES相容性及对共混超滤膜性能的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2006, 29(7):28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2006.07.012LI Xiyun, ZHANG Zhenjia, QIAO Xiangli. Compatibility properties of PVC/PES and its impact on Co-blend ultrafiltration membrane[J]. Environmental Science and Technology,2006,29(7):28-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2006.07.012 [23] RAHIMPOUR A, MADAENI S S, TAHERI A H, et al. Coupling TiO2 nanoparticles with UV irradiation for modification of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2008, 313(1-2):158-169. [24] PENG Y L, SUI Y. Compatibility research on PVC/PVB blended membranes[J]. Desalination,2006,196(1-2-3):13-21. [25] 隋燕, 彭跃莲, 钱英. 聚氯乙烯共混超滤膜研究[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2005, 25(3):30-33, 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2005.03.008SUI Yan, PENG Yuelian, QIAN Ying. Compatibility research of PVC/PVB blend membrane[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,2005,25(3):30-33, 79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2005.03.008 [26] 丁马太, 余乃梅, 何旭敏, 等. PVC/PAN共混超滤膜的研究 Ⅱ:铸膜液组成对膜结构与性能的影响[J]. 水处理技术, 1991, 17(5):295-299.DING Matai, YU Naimei, HE Xumin, et al. Studies on PVC/PAN blend UF membrane Ⅱ:The effect of the polymer-concentration of casting solution on the performance and the structure of PVC/PAN blend UF membrane[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,1991,17(5):295-299(in Chinese). [27] 丁马太, 何旭敏, 丁俊琪, 等. 聚氯乙烯/聚丙烯腈共混超滤膜的研究Ⅲ:制膜工艺条件对共混超滤膜结构与性能的影响[J]. 水处理技术, 1992, 18(3):155-161.DING Matai, HE Xumin, DING Junqi, et al. Studies on PVC/PAN blended UF membrane Ⅲ:The effect of technological conditions for membrane-making on the performance and the structure of PVC/PAN blended UF membrane[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,1992,18(3):155-161(in Chinese). [28] ULUTAN S, BALKÖSE D. Diffusivity, solubility and permeability of water vapor in flexible PVC/silica composite membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,1996,115(2):217-224. doi: 10.1016/0376-7388(96)00030-0 [29] 李浩, 陈健波, 刘湛红, 等. 用正交设计研究PVDF/PVC/PMMA共混中空纤维膜[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2007, 27(6):32-36, 41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2007.06.008LI Hao, CHEN Jianbo, LIU Zhanhong, et al. Investigation of PVDF/PVC/PMMA blend hollow fiber membrane by orthogonal design[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,2007,27(6):32-36, 41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2007.06.008 [30] 戎静, 奚旦立, 李运清. 聚偏氟乙烯/聚氯乙烯/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯共混多孔中空纤维膜的制备与性能测试[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2008, 39(5):65-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2008.05.018RONG Jing, XI Danli, LI Yunqing. Preparation of PVDF/PVC/PMMA blend porous hollow fiber membrane and performance testing thereof[J]. Industrial Water and Wastewater,2008,39(5):65-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2008.05.018 [31] UMENO A, MIYAI Y, TAKAGI N, et al. Preparation and adsorptive properties of membrane-type adsorbents for lithium recovery from seawater[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(17): 4281-4287. [32] ZHU G R, WANG P, QI P F, et al. Adsorption and desorption properties of Li+ on PVC-H1.6Mn1.6O4 lithium ion-sieve membrane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2014,235:340-348. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.068 [33] 王盼. 锂离子筛膜的制备及其吸附性能研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.WANG Pan. Peparation and adsorption properties of lithium ion sieve membrane[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013(in Chinese). [34] PARK M J, NISOLA G M, BELTRAN A B, et al. Recyclable composite nanofiber adsorbent for Li+ recovery from seawater desalination retentate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 254: 73-81. [35] NISOLA G M, LIMJUCO L A, VIVAS E L, et al. Macroporous flexible polyvinyl alcohol lithium adsorbent foam compo-site prepared via surfactant blending and cryo-desiccation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,280:536-548. [36] TAN I A W, HAMEED B H, AHMAD A L. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on basic dye adsorption by oil palm fibre activated carbon[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2007,127(1-3):111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2006.09.010 [37] CHEN J H, LIU Q L, HU S R, et al. Adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution by glutaraldehyde crosslinked humic acid-immobilized sodium alginate porous membrane adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Jour-nal,2011,173(2):511-519. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.023 [38] EASTOE J, DALTON J S. Dynamic surface tension and adsorption mechanisms of surfactants at the air-water interface[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2000,85(2-3):103-144. [39] HUANG X J, AN L Y, ZHAO X Y, et al. Preparation of ammonium tungstophosphate-calcium alginate composite adsorbent and its adsorption properties of rubidium[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2013,652-654:2524-2528. [40] 郑凤, 黄征青. 聚偏氟乙烯有机-无机超滤膜性能影响因素的研究进展[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2010, 27(6):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2010.06.005ZHENG Feng, HUANG Zhengqing. Study of impact factors of performance for polyvinylidene fluoride organic-inorganic ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Chemistry and Bioengineering,2010,27(6):17-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2010.06.005 [41] 赵晨阳, 孙本惠. PVC/PMMA合金微滤膜的研制[J]. 中国塑料, 2001, 15(2):46-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9278.2001.02.013ZHAO Chenyang, SUN Benhui. Preparation of PVC/PMMA alloy microfiltration membrane[J]. China Plastics,2001,15(2):46-49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9278.2001.02.013 [42] SINGH Y P, SINGH R P. Compatibility studies on solutions of polymer blends by viscometric and ultrasonic techniques[J]. European Polymer Journal,1983,19(6):535-541. doi: 10.1016/0014-3057(83)90206-9 [43] 胡亮平, 贺高红, 赵薇, 等. PVP添加剂对聚醚酰亚胺超滤膜的影响[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2008, 28(5):110-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2008.05.022HU Liangping, HE Gaohong, ZHAO Wei, et al. Effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone on the morphology and properties of polyetherimide ultra-filtration membranes[J]. Membrane Science and Technology,2008,28(5):110-113(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8924.2008.05.022 [44] 蒋炜, 江成璋. 聚乙烯吡咯烷酮添加剂对聚醚砜制膜体系的影响[J]. 水处理技术, 1996, 22(2):63-68. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.1996.02.001JIANG Wei, JIANG Chengzhang. Influence of PVP additive on polyethersulfone casting system[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,1996,22(2):63-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.1996.02.001 [45] 石西昌, 余亮良, 陈白珍, 等. 锂锰氧化物离子筛结构和掺杂研究进展[J]. 中国锰业, 2009, 27(3):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4336.2009.03.004SHI Xichang, YU Liangliang, CHEN Baizhen, et al. Research progress on structure and doping of lithium manganese oxide ion-sieve[J]. China’s Manganese Industry,2009,27(3):17-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4336.2009.03.004 [46] SHANNON R D, PREWITT C T. Effective ionic radii in oxides and fluorides[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry,1969,25(5):925-946. doi: 10.1107/S0567740869003220 [47] ROSSEINSKY D R. Electrode potentials and hydration energies. Theories and correlations[J]. Chemical Reviews,1965,65(4):467-490. doi: 10.1021/cr60236a004 -






 下载:
下载: