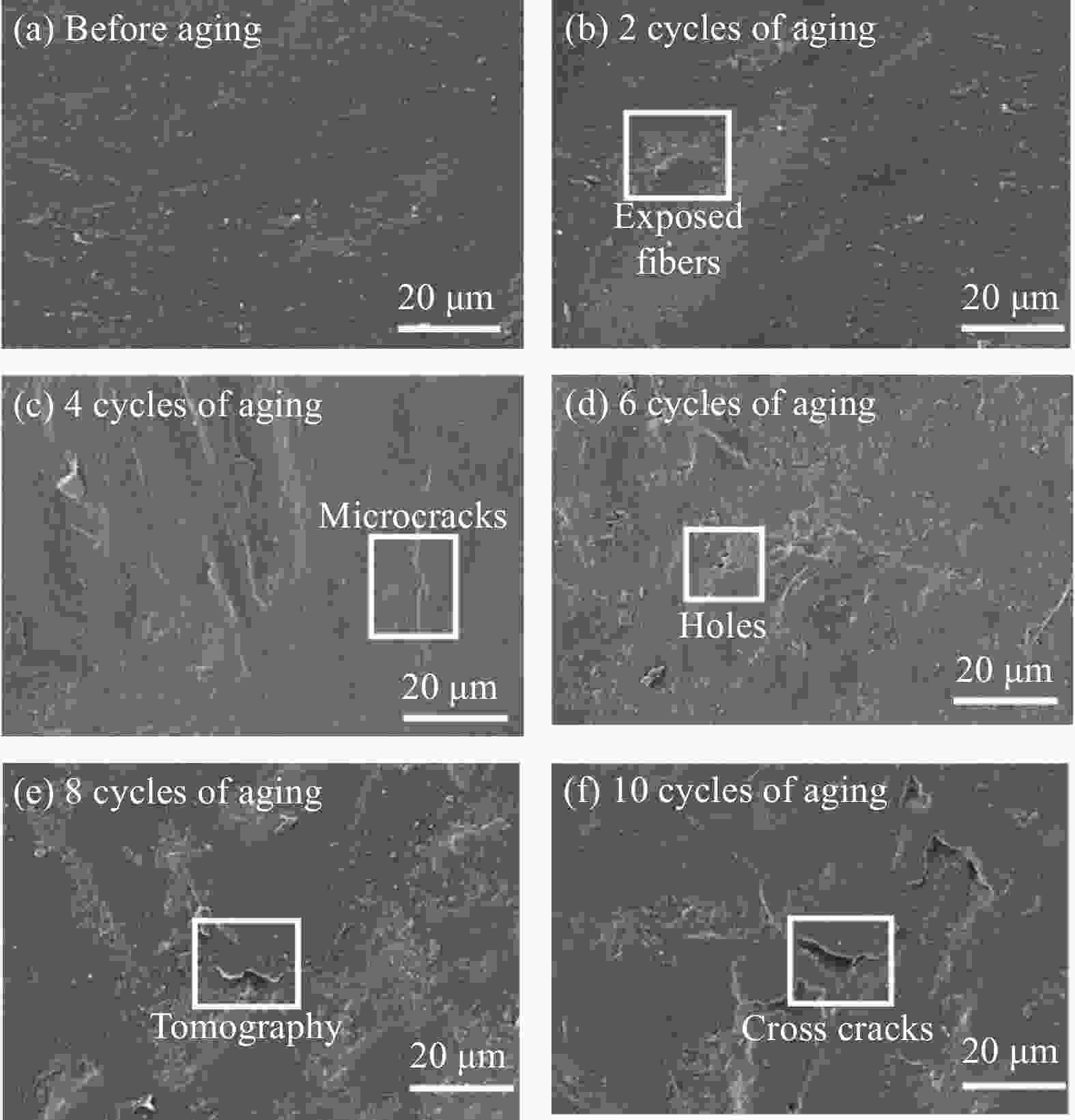
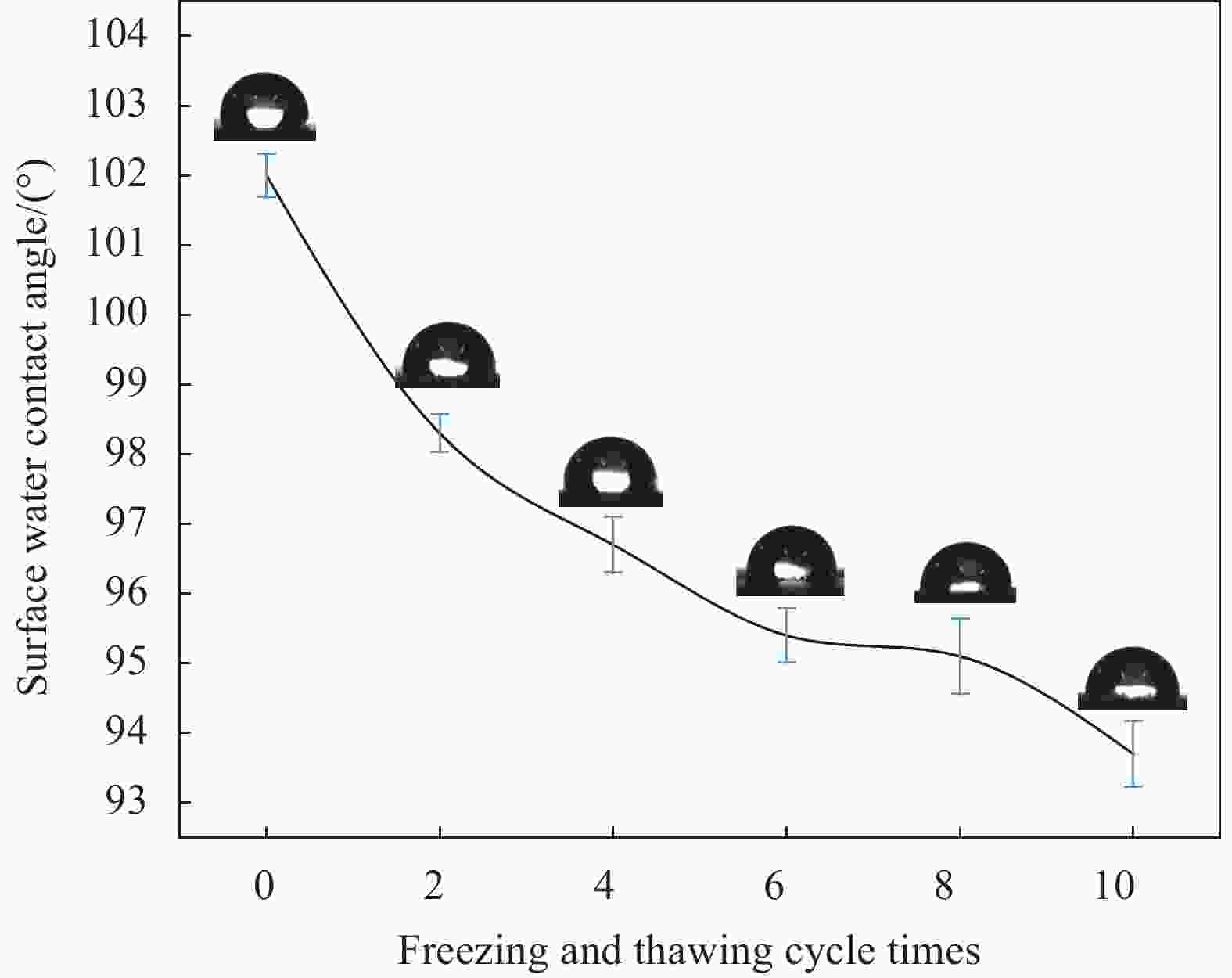
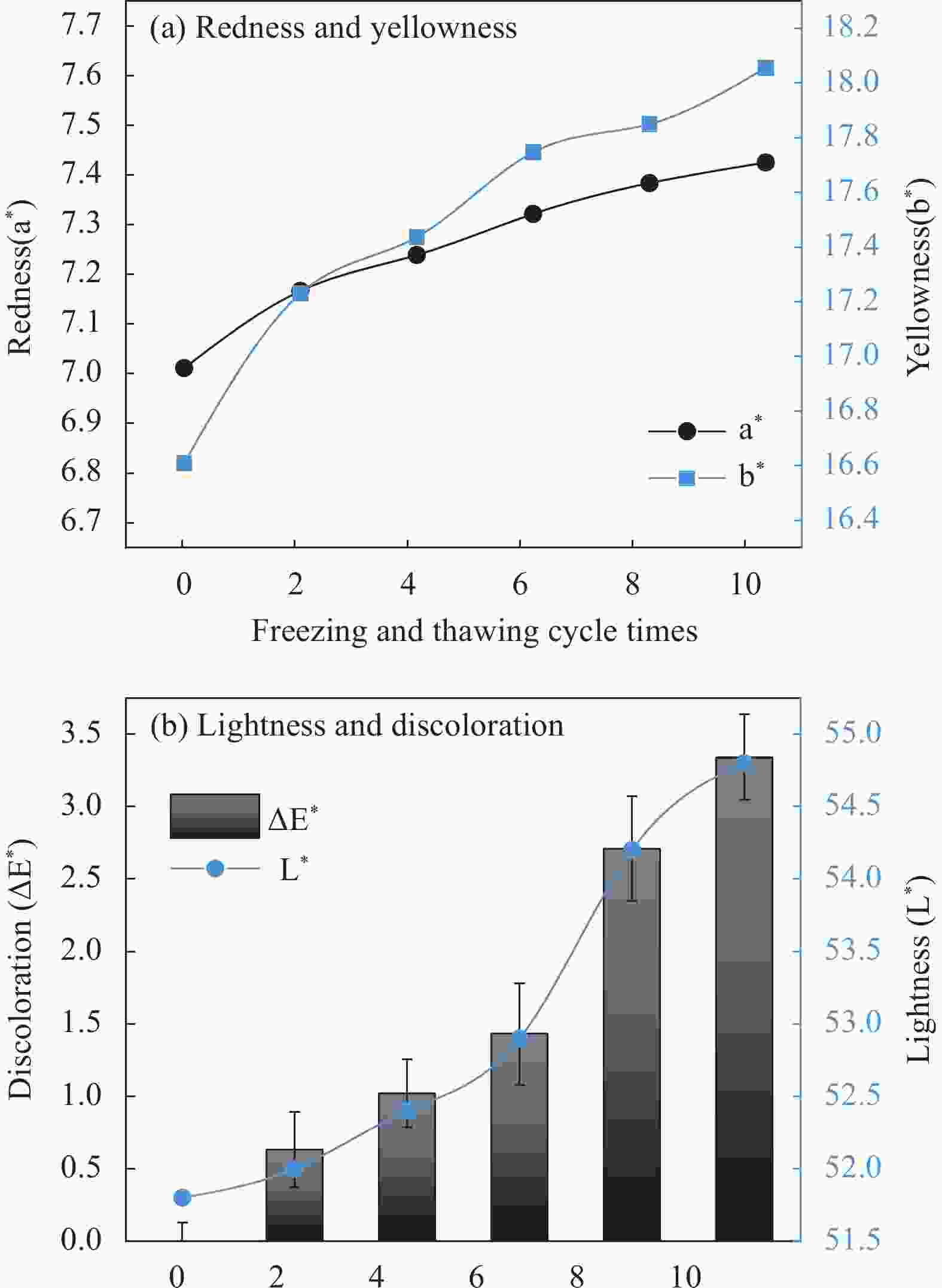
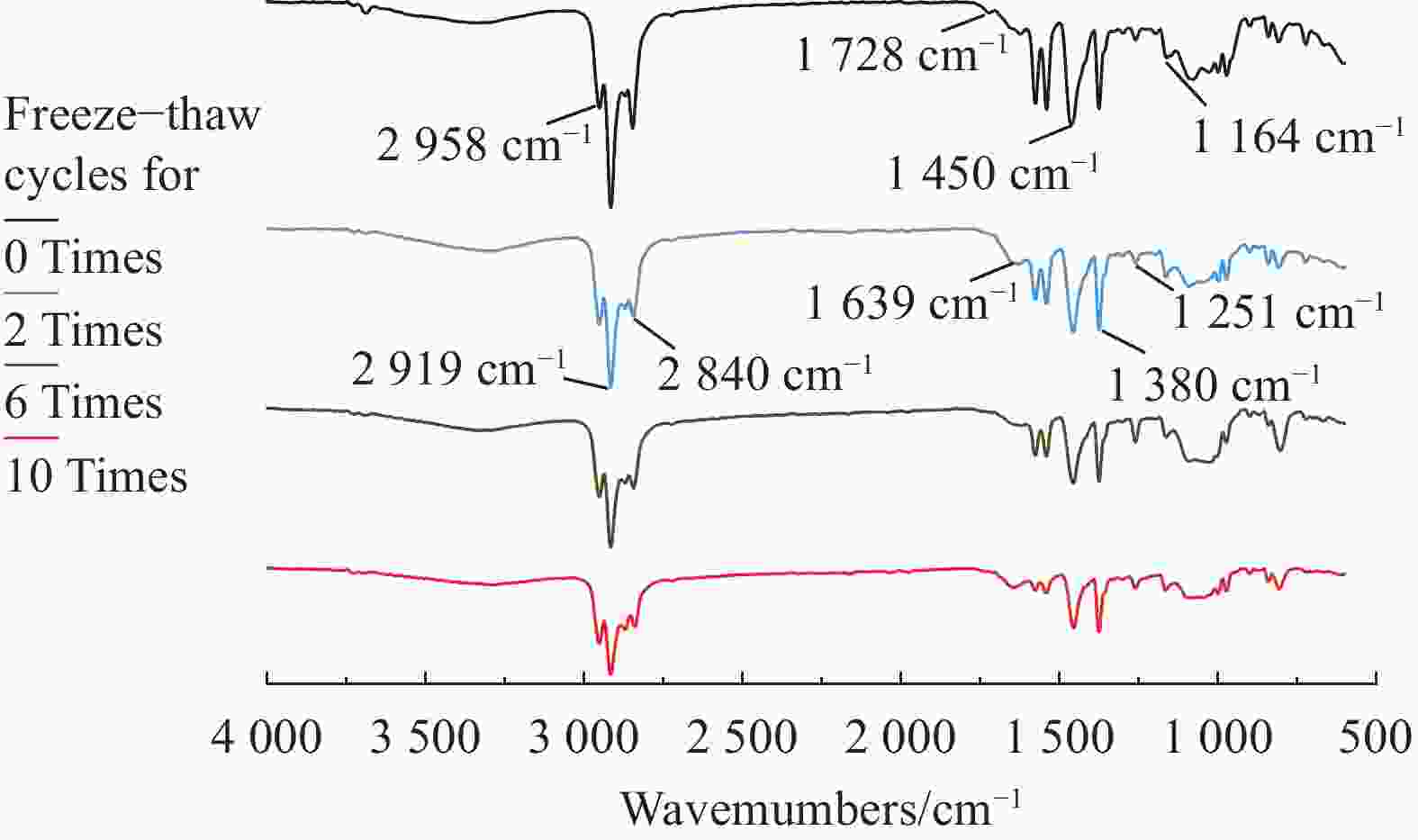
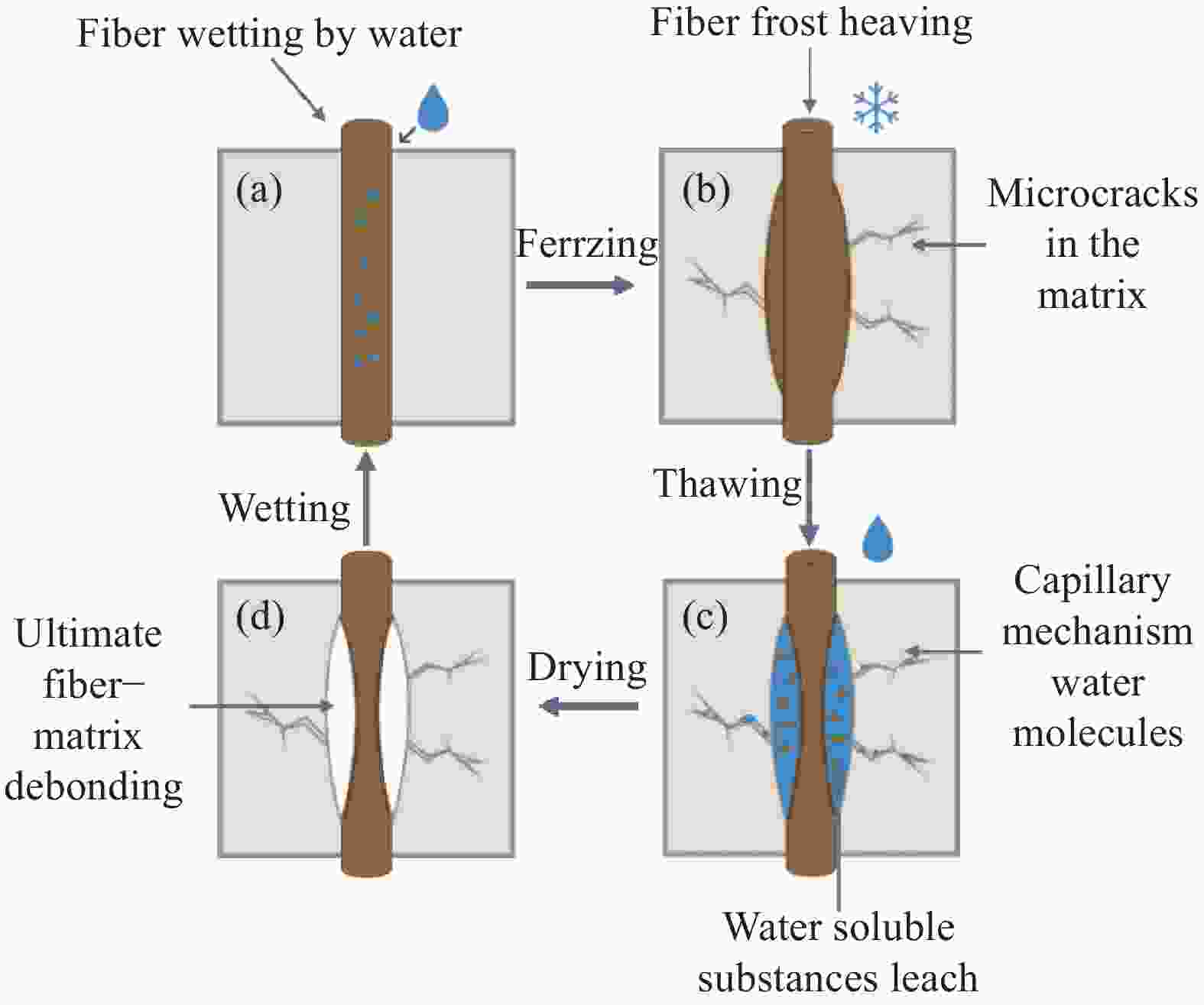
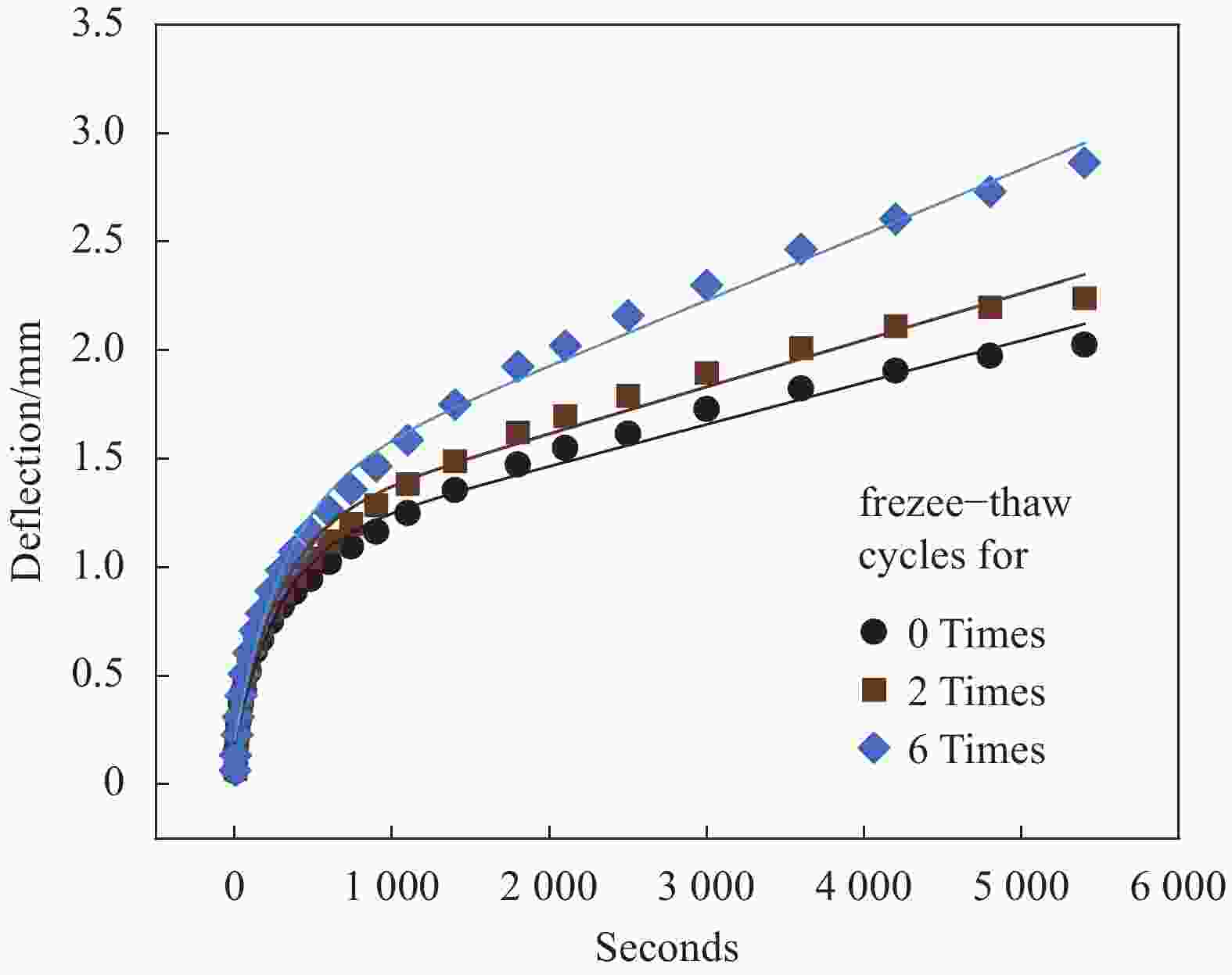
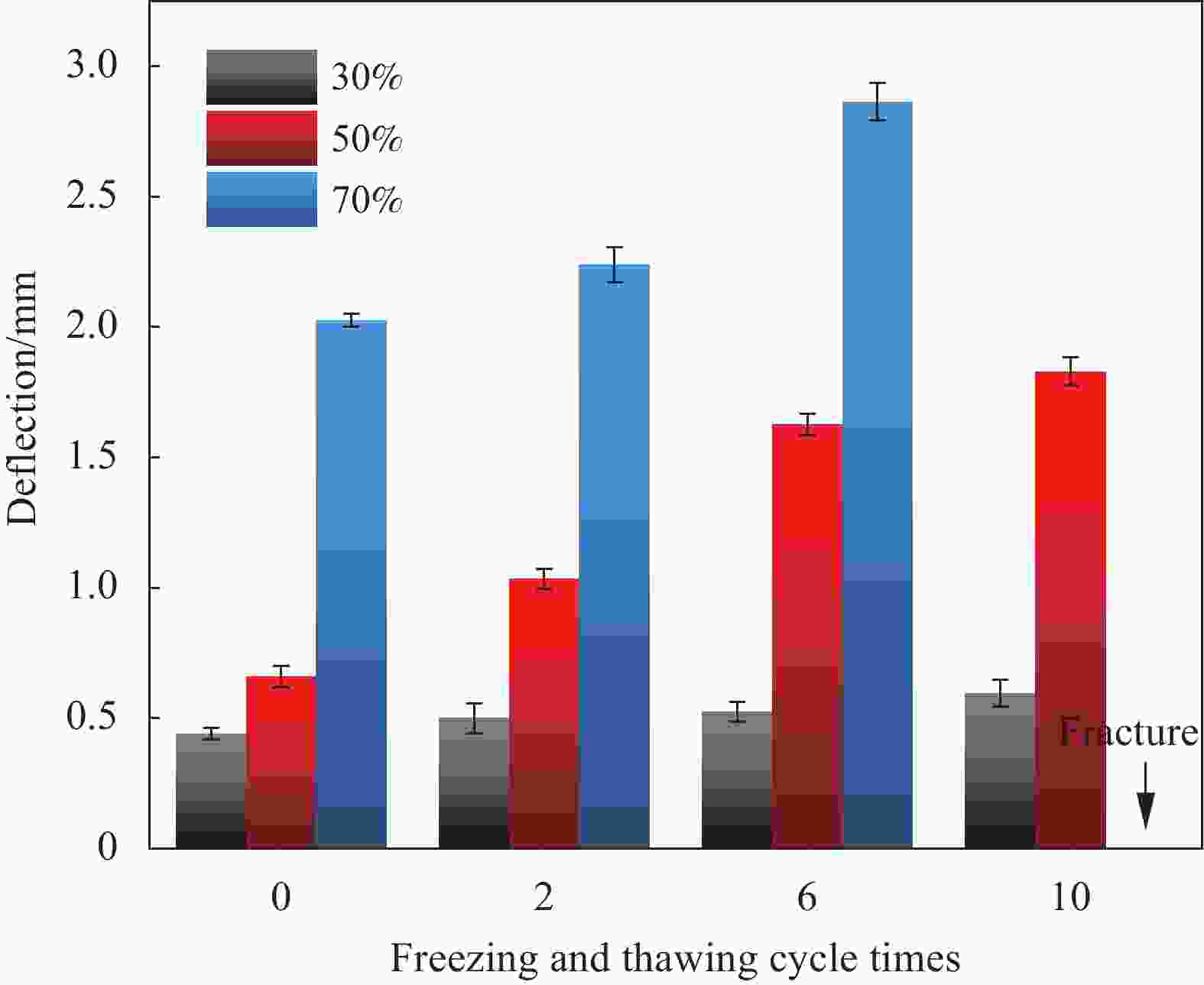
| [1] |
董婕. 竹粉/聚丙烯复合材料的制备及性能研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2017.DONG Jie. Study on preparation and properties of bamboo flour/polypropylene composites [D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2018 (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
QIU Z Y, FAN H L. Nonlinear modeling of bamboo fiber reinforced composite materials[J]. Composite Structures. 2020, 111976-111976.
|
| [3] |
PRZEMYSŁAW M, JERZY M, MAGDALENA Z. The Effect of Thermo-Mechanical Treatment of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys Pubescens) on Its Sorption and Physicomechanical Properties[J]. Drvna industrija:Scientific journal of wood technology, 2019, 70(3): 256-272.
|
| [4] |
向娥琳. 毛竹生长过程中细胞壁结构与性能的变化研究[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2018.XIANG Elin. Study on the cell wall structure and propery during the growth of Moso bamboo [D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Agriculture university, 2018 (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
ZHOU X, HUANG S, YU Y, et al. Outdoor natural weathering of bamboo flour/polypropylene foamed composites[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 2014, 33(19): 1835-1846. doi: 10.1177/0731684414548611
|
| [6] |
邓浩, 刘彤, 张吉润. PP、PCL、PAL/BF 复合材料现状及发展[J]. 塑料, 2020, 49(3): 119-122.DENG Hao, LIU Tong, ZHANG Jirun. Present Situation and Development of PP, PCL and PAL/BF Composite[J]. Plastics, 2020, 49(3): 119-122(in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
LONG H, WU Z, DONG Q, et al. Mechanical and thermal properties of bamboo fiber reinforced polypropylene/polylactic acid composites for 3D printing[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2019, 59(s2): E247-E260.
|
| [8] |
陈家鑫, 徐子然, 宋经纬, 等. 我国木材资源供应与用材林培育建设分析[J]. 林业科技通讯, 2021, (11): 18-21.CHEN Jiaxin, XU Ziran, SONG Jingwei, et al. Analysis of China 's timber resources supply and timber forest cultivation and construction[J]. Forest Science and Technology, 2021, (11): 18-21(in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
KIM J K, PAL K. Recent Advances in the Processing of Wood-Plastic Composites[M]. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
|
| [10] |
张笑梅, 郭万涛. 纤维增强树脂基复合材料环境加速老化性能研究[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2017, 32(2): 41-46.ZHANG Xiaomei, GUO Wantao. Research on accelerated environmental aging properties of the fiber reinforced polymer composites[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2017, 32(2): 41-46(in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
JEANETTE M, MATUANA L. ∙Durability of wood flour-plastic composites exposed to accelerated freeze-thaw cycling[J]. Journal of Vinyl& Additive Technology, 2005, 53(1): 1-8.
|
| [12] |
HAMED K Y. Maleated nanolignin as a new coupling agent for wood-plastic composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2023, 57(30): 4649-4658. doi: 10.1177/00219983231215422
|
| [13] |
CUI Y H, LEE S, NORUZIAAN B, et al. Fabrication and interfacial modification of wood/recycled composite materials[J]. Composites, 2008, 39(1): 655-661.
|
| [14] |
牟堂峰. 聚丙烯/木粉复合材料的研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2008.MU Tangfeng. A Study on polypropylene/wood flour composites[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2008 (in Chinese)
|
| [15] |
刘晓玲. 竹粉/聚丙烯复合材料性能及其界面特征[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2009.LIU Xiaoling. The performance and interface characterization of bamboo flour/PP composites. [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2009. (in Chinese)
|
| [16] |
American Society of Testing. ASTM D 6662-22 Standard Specification for Polyolefin-Based Plastic Lumber Decking Boards[S]. Toronto, America: ASTM international, 2017.
|
| [17] |
中国国家标准化管理委员会(标准制定单位). 塑料弯曲性能的测定: GB/T 9341—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of flexural properties: GB/T 9341—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese).
|
| [18] |
中国国家标准化管理委员会(标准制定单位). 塑料拉伸性能的测定: GB/T 1040—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of tensile properties: GB/T 1040—2006[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2006(in Chinese).
|
| [19] |
中国国家标准化管理委员会(标准制定单位). 塑料简支梁冲击性能的测定: GB/T 1043.2—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of charpy impact properties: GB/T 1043.2—2018[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2018(in Chinese).
|
| [20] |
陈涵. 竹纤维/聚丙烯复合材料的耐老化性能[J]. 福建林业科技, 2012, 390(2): 52-54+78.CHEN Han. Aging Properties of Bamboo Particles Reinforced Polypropylene Composites[J]. Jour of Fujian Forestry Sci and Tech, 2012, 390(2): 52-54+78(in Chinese).
|
| [21] |
周吓星, 陈礼辉, 黄舒晟等. 竹粉/聚丙烯发泡复合材料加速老化性能的研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(7): 287-292.Zhou Xiaxing, Chen Lihui, Huang Shusheng, et al. Performance of bamboo flour/polypropylene foamed composite under accelerated weathering[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(7): 287-292(in Chinese).
|
| [22] |
BUTYLINA S H M K T. Weathering of wood-polypropylene composites containing pigments[J]. European Journal of Wood and Wood Products, 2012, 70(3): 719-726.
|
| [23] |
周吓星, 黄舒晟, 苏国基, 等. 冻融循环老化降低竹粉/聚丙烯发泡复合材料性能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(10): 285-292.ZHOU Xiaxing, HUANG Shusheng, SU Guoji, et al. Freeze-thaw cycles weathering degrading properties of bamboo flour-polypropylene foamed composites[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(10): 285-292(in Chinese).
|
| [24] |
SHUGUANG L, SU L, LIQIANG Y, et al. Mechanical strength model of engineered cementitious composites with freeze–thaw damage based on pore structure evolution[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites. 2022, 134.
|
| [25] |
龚新怀, 戴忠豪, 王兆礼, 等. 冻融循环老化对 PLA/TW 生物质复合材料性能的影响[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2018, 46(10): 39-43.GONG Xinhuai, DAI Zhonghao, WANG Zhaoli, et al. Effects of Freeze-Thaw Cycling Accelerated Weathering on Properties of Poly(lactic acid)/Tea Waste Biomass Composites[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2018, 46(10): 39-43(in Chinese).
|
| [26] |
张显, 蔡明, 孙宝忠. 植物纤维增强复合材料的湿热老化研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(5): 226-236.ZHANG Xian, CAI Ming, SUN Baozhong. Research progress of hygrothermal aging of plant fiber reinforced composites[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(5): 226-236.
|
| [27] |
熊小艺. 竹纤维增强聚丙烯复合材料的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2017.XIONG Xiaoyi. The Research on Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composite[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese)
|
| [28] |
陈冬梅, 姜良朋, 刘丁宁, 等. 四种壳类纤维/聚氯乙烯木塑复合材料的蠕变及磨损性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(6): 1464-1471.CHEN Dongmei, JIANG Liangpeng, LIU Dingning, et al. Creep and wear properties of four different types of husk fibers/polyvinyl chloride composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2018, 35(6): 1464-1471(in Chinese).
|
| [29] |
肖伟. 加速老化对木塑复合材料性能的影响——冻融、氙灯加速老化[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2010.XIAO Wei. The influence of accelerated aging on the properties of wood-plastic composite materials freeze-thaw, xenon accelerated aging[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University , 2010. (in Chinese)
|
| [30] |
段洁利, 蒋恩臣, 胡圣荣. 松木粉/PVC 复合材料蠕变性能研究[J]. 农机化研究. 2013, 35(02): 142-145.DUAN Jieli , JIANG Enchen , HU Shengrong. Study of the Creep Behavior of Pine Powder/Polyviny Chloride Composites[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2013, 35(02): 142-145. (in Chinese)
|
| [31] |
周冬艳. 聚乙烯木塑复合材料胶接接头设计与耐久失效行为[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2019.ZHOU Dongyan. Design and durable failure behavior of bonding joint for polyethylene wood plastic composites[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2019. (in Chinese)
|
| [32] |
REGAZZI A, CORN S, IENNY P, et al. Coupled hydro-mechanical aging of short flax fiber reinforced composites[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2016, 130300-306.
|

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图




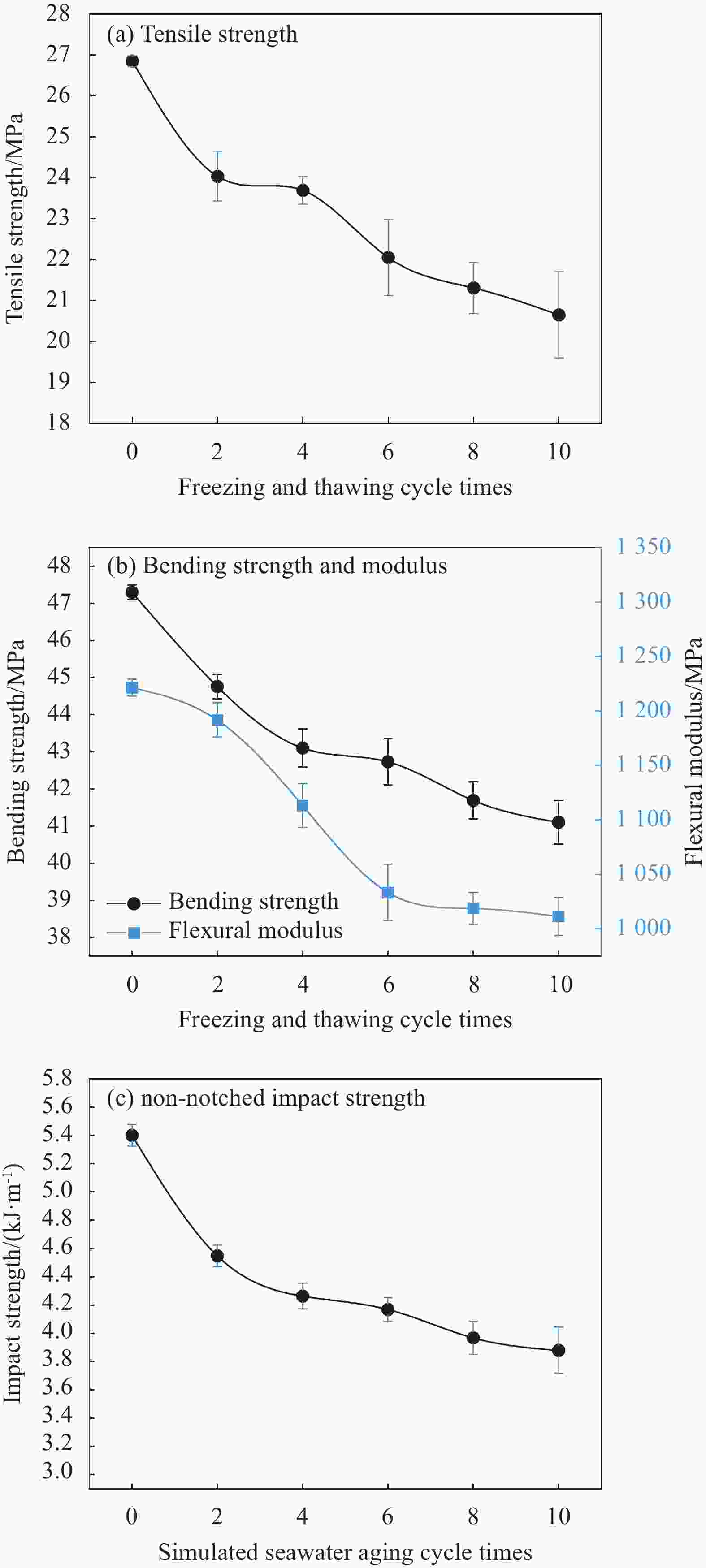
 下载:
下载: