Microstructure and high-temperature tensile properties of Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminated composites prepared by vacuum hot pressing
-
摘要: 为改善Ti2AlNb合金的本征脆性且不牺牲其高温性能,将其与高温钛合金TA15进行复合,采用真空热压法制备了Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料,研究了不同热压温度对其微观组织及其拉伸性能的影响。研究结果表明:界面层的孔洞缺陷随热压温度的升高逐渐减少,热压温度在
1050 ℃及以上时可以获得无缺陷冶金结合界面。界面反应层厚度随热压温度的升高而增加,且在1050 ℃及以上的扩散温度条件下,反应区和Ti2AlNb层间形成了一定宽度的过渡层,提升了界面结合性能。拉伸实验结果表明,相较于Ti2AlNb合金,Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料的室温和高温拉伸性能均有显著的提升。其中1050 ℃热压温度条件下的叠层复合材料具有较好的综合性能,650℃高温抗拉强度和应变分别为667.85 MPa和16.2%。Abstract: In order to improve the intrinsic brittleness of Ti2AlNb alloy without sacrificing its high-temperature performance, a composite material was prepared by combining it with high-temperature titanium alloy TA15 using vacuum hot pressing. The effects of different hot pressing temperatures on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminated composite materials were investigated. The results show that the pore defects in the interface layer gradually decrease with the increase of the hot pressing temperature. A defect-free metallurgical bonding interface can be achieved at temperatures of1050 ℃ and above. The thickness of the interface reaction layer increases with the rise of the hot pressing temperature. Under the diffusion conditions at1050 ℃ and above, a transition layer of certain width formed between the reaction zone and the Ti2AlNb layers, which improve the properties of the interface bonding. Tensile tests indicate that the room and high-temperature tensile properties of the Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminated composite material are significantly improved compared with Ti2AlNb alloy. The laminated composite material under the hot pressing temperature condition of1050 ℃ exhibits excellent comprehensive performance, with a high-temperature tensile strength and strain of 667.85 MPa and 16.2%, respectively. -
膜分离技术具有高能效、易操作、环境友好和占地面积小等优点,近年来在气体分离领域受到广泛关注[1-4]。传统气体分离膜多以聚合物膜为主,然而由于聚合物分离膜固有的选择性和渗透性的制约关系(Trade-off效应),使其性能很难再提升[5-6]。研究者发现将多孔材料与聚合物基体共混制成混合基质膜,通过结合两种材料的优点,能够同时提升膜的气体渗透性和选择性,从而突破聚合物膜的Trade-off效应[7-8]。因此,制备混合基质膜是改善膜气体分离性能的一种有效方法。
对于混合基质膜,填料和聚合物基体材料的选择尤为重要。聚酰亚胺由于其优异的热稳定性、良好的力学性能以及可加工性,已经在气体分离膜领域发展多年,是混合基质膜聚合物基体候选材料之一[9-11]。对于填料材料的选择,共价有机框架材料(COFs)是一种由有机单元通过共价键构成的多孔材料,由于其具有优异的稳定性,易功能化、永久空隙率以及高比表面积等优点,在气体分离领域展现出不俗的潜力[12]。由于COFs全有机的性质,使其能够均匀地分散在聚合物基质中,减少了混合基质膜中由于界面缺陷产生的非选择性孔[13-14]。然而,大部分COFs的孔径很难做到2 nm以下,相对于气体分子动力学直径(N2:0.36 nm;O2:0.35 nm;CO2:0.33 nm)还是较大,难以实现对气体的高效分离,从而降低了气体选择性[15-16]。因此,需要对COFs的孔径大小调控或引入一些功能性吸附位点进行改善。研究表明,引入氟原子能够有效改善COFs的孔径大小且能够提供与气体相互作用的吸附位点。Alahakoon等[17]通过使用含氟单体制备出两种氟化COFs,将氟化COFs与未氟化的相比,发现氟化COFs具有更大的比表面积、更小且更明确的孔径。Gao等[18]报道了3种具有—H、—Me和—F取代基的同构三维共价有机骨架,对比不含氟的COFs,氟化COFs具有更高的CO2亲和力,对CO2/N2有着更高的IAST选择性。Yang等[19]制备了一种氟化CTF,通过氟原子的强静电作用以及C—F键与CO2的偶极-四极作用,使其具有优异的CO2吸附能力。
基于上述讨论,本文合成出一种具有较小孔径、高比表面积的氟化共价有机框架材料(TpPa-CF3)。随后,以TpPa-CF3为填料,聚酰亚胺(6FDA-ODA)为基体,制备出不同负载量的TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜。表征了其结构和表面、截面的微观形貌,探究了其热性能、力学性能以及疏水性能,最后讨论了混合基质膜的气体渗透性以及在烟道气分离(CO2/N2)和空气分离(O2/N2)上的应用前景。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
4,4-二氨基二苯醚(ODA,98%)、4,4-(六氟异丙烯)二酞酸酐(6FDA,98%+)、2,4,6-三甲酰间苯三酚(Tp,98%)、2-三氟甲基-1,4-苯二胺(Pa-CF3,97%)、1,3,5-三甲基苯(99%+)、1,4-二氧六环(99%)均购自上海阿达玛斯试剂有限公司;乙酸(AR)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF,AR)均购自西陇科学股份有限公司;间甲酚(m-Cresol,99%)、异喹啉(97%)均购自上海阿拉丁试剂有限公司;丙酮(Acetone,AR),成都市科隆化学品有限公司;工业酒精(95%),弘昊实验设备有限公司。
1.2 TpPa-CF3的合成
将Tp (63.0 mg,0.30 mmol)、Pa-CF3 (79.0 mg,0.45 mmol)、1,3,5-三甲基苯(1.5 mL)、1,4-二氧六环(1.5 mL)依次加入到Pyrex管(25 mL)中。为使混合物均匀分散,超声处理0.5 h,再加入3 mol/L乙酸溶液(0.5 mL)。随后,用液氮将Pyrex管骤冻抽出空气,再在室温下解冻,此操作循环3次。密闭封管,将Pyrex管在120℃下油浴3天。反应完毕后冷却至室温,过滤收集产物,先用DMF溶液搅拌洗涤3次,再通过索氏提取法进行提纯(提纯溶剂采用丙酮)。随后,收集产物,在真空烘箱中120℃下干燥12 h后,得到橘红色粉末样品TpPa-CF3。
1.3 聚酰亚胺(6FDA-ODA)的合成
在N2氛围下,向装有机械搅拌、冷凝回流的150 mL三口烧瓶内依次加入ODA (2.00 g,9.99 mmol)、间甲酚(28 mL),待ODA完全溶解后再依次加入6FDA (4.44 g,9.99 mmol)、间甲酚(28 mL),随后将温度升到50℃待反应物完全溶解后,滴加5~6滴异喹啉后升温至80℃反应3 h,120℃反应3 h,180℃反应3 h,最后200℃反应12 h。反应结束冷却至室温后,将聚酰亚胺溶液缓慢倒入大量工业酒精中拉丝沉淀,过滤收集产物,在真空烘箱中150℃干燥8 h。随后,使用适量DMF重新溶解并进行二次沉淀以除去聚酰亚胺中残留杂质。
1.4 TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的制备
取一定量的TpPa-CF3粉末分散在DMF (3 mL)中,使用细胞粉碎机,在300 W功率下超声0.5 h后再搅拌6 h,保证TpPa-CF3粉末在DMF溶液中分散均匀。同时,称取0.2 g 6FDA-ODA溶解在DMF (2 mL)中,用针式滤头(0.45 μm,尼龙)过滤除去杂质。随后,将TpPa-CF3的分散液滴加到6FDA-ODA溶液中搅拌12 h,确保TpPa-CF3和6FDA-ODA充分混合。最后,将混合溶液缓慢流延到光滑平整的玻璃板(5 cm×5 cm)上,在80℃下蒸发12 h除去溶剂,待冷却至室温后在温水中脱膜,最后在150℃的真空烘箱中干燥12 h以除去残留的溶剂分子。按以上步骤分别制备含量为0wt%、1wt%、3wt%、5wt%、7wt%的TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜。
1.5 表征测试
X射线衍射(XRD):采用荷兰帕纳科公司的X'Pert Pro型X射线衍射仪对制备的TpPa-CF3粉末与薄膜进行晶型及结构表征,扫描范围在3°~40°,扫描速度为2°/min。
傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR):采用美国尼高力公司的Nicolette 6700-NXR型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪分析TpPa-CF3和薄膜的化学键组成及官能团。对于粉末样品通过溴化钾压片的方式测试,对于薄膜样品通过制成厚度约为20 μm的薄膜直接测试。扫描范围为400~
4000 cm−1,扫描次数64次以上。固态核磁共振(ssNMR):通过德国布鲁克公司的Avance Neo 400 WB型固体核磁共振波谱仪测试TpPa-CF3的13C NMR,分析其化学键连接方式。所需样品压实后的体积应多于0.5 cm3。
X射线光电子能谱(XPS):采用美国热电公司的Escalab 250 Xi型X射线光电子能谱仪分析TpPa-CF3的化学元素及化学态。采用粉末压片的方式制样。
扫描电子显微镜(SEM):通过日本日立公司的SU 4800型扫描电子显微镜表征TpPa-CF3和薄膜表面、截面的微观形貌。对于粉末样品,用牙签将少量样品涂在导电胶上制样;对于薄膜样品,膜表面直接粘在导电胶上,膜断面通过液氮脆断选取平整截面制样。全部样品在测试前通过喷金处理提高样品导电性。
N2吸附-脱附测试:通过美国康塔公司的Autosorb IQ型比表面及孔隙度分析仪器表征TpPa-CF3的比表面积及孔径分布。采用BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller)法计算比表面积,密度泛函理论(DFT)计算孔径分布。
热重分析(TGA):通过德国耐驰公司的STA 449C型综合热分析仪测试TpPa-CF3和薄膜的热稳定性。在N2氛围下测试,升温速率为10℃/min,测试范围在50~800℃。
差示扫描量热分析(DSC):通过德国耐驰公司的DSC 214型差示扫描量热仪测试薄膜的玻璃化转变温度,在N2氛围下以10℃/min的速率升温,测试范围在30~350℃,所有结果均采用消除热历史后的二次升温曲线。
力学性能:通过美国美特斯公司的CMT2103型万能试验机来表征薄膜的力学性能。薄膜样品尺寸为50 mm×10 mm,拉伸载荷为5 kN,拉伸速率为2 mm/min,标距为20 mm。
水接触角测试:通过中国承德优特仪器有限公司JY-PHb型接触角分析仪测定薄膜的亲疏水性能。薄膜样品尺寸为20 mm×20 mm,测试次数至少3次。
气体渗透性测试:通过中国济南兰光公司的VAC-V1型气体渗透仪测试薄膜的气体渗透性能。测试方法为恒体积变压法,测试气体为高纯气体(CO2、O2、N2),测试条件为4 bar,35℃。测试过程如下,将厚度均匀的待测薄膜装入膜腔中,测试前将上下腔气压抽至20 Pa以下,随后下腔关闭,上腔通入待测纯气体形成压差。压差推动气体自上腔(高压侧)向下腔(低压侧)渗透,通过系统计算得到膜的气体渗透系数P。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 TpPa-CF3的表征
通过粉末X射线衍射(PXRD)对合成的TpPa-CF3的晶体结构进行分析,图1(a)中2θ=4.79°处出现的强峰对应于COF的(100)晶面,其他峰也出现在2θ=7.81°、26.14°处,分别对应于(200)、(001)晶面,其中(001)晶面也是其π-π堆叠峰,通过布拉格方程计算得出其堆叠层间距为0.33 nm。将测试结果与模拟的晶体模型的衍射峰进行对比,结果表明二者衍射峰的位置与强度均匹配良好。TpPa-CF3在Pawley精修后得到的晶胞参数为a=
2.290351 nm,b=2.236760 nm,c=0.423813 nm,α=89.56415 ,β=89.73479 ,γ=120.51471 。实验结果与精修后的PXRD之间的残差值较小,Rwp=1.24%,Rp=0.91%。以上结果初步说明成功合成出了目标晶体结构,且具有良好的结晶性。为进一步说明TpPa-CF3成功合成,通过FTIR对TpPa-CF3以及其构筑单元测试,从图1(b)中可以看到,构筑单元2,4,6-三甲酰间苯三酚(Tp)在
2894 cm−1处醛基的CH=O特征峰和构筑单元2-三氟甲基-1,4-苯二胺(Pa-CF3)在3318 cm−1和3210 cm−1处的—NH2特征峰在产物TpPa-CF3中消失,表明醛胺缩合反应完全。在1282 cm−1处的C—N的特征吸收峰表明烯醇-酮异构的发生。因为框架是以酮的形式存在,结构中有强的分子内氢键及共轭作用,所以在1592 cm−1处的C=C的特征峰和1610 cm−1处的C=O特征峰合并呈肩状[20]。在1128 cm−1处出现了C—F的特征峰。13C固体NMR分析如图1(c)所示,图中显示化学位移在184.2×10−6和108.1×10−6处有两个较明显的信号峰,分别对应于烯醇-酮异构反应所形成的C=O键和C—N键上的C原子,123.6×10−6处归属于C—F上的C原子。其余在119.0×10−6、134.1×10−6和146.5×10−6处的信号峰则归属于芳香单元上的C原子。
FTIR和固体核磁分析结果证实TpPa-CF3的成功合成且以稳定的β-酮胺形式存在。
通过XPS测量TpPa-CF3的全谱和各个元素的光谱,由图2(a)的全谱可知TpPa-CF3是由C、N、O、F 4种元素组成的。图2(b)是C1s的高分辨率XPS光谱,其能够被卷积为4个峰,分别对应于TpPa-CF3中的C=C/C—C(284.8 eV)、C—N(286.2 eV)、C=O(288.9 eV)和C—F(292.9 eV)键,N1s的高分辨率XPS如图2(c)所示,其被卷积为2个峰,分别归属于N—C(400.2 eV)和N—H(403.9 eV)键,F1s的高分辨率XPS如图2(d)所示,其只有一个卷积峰归属于C—F(688.3 eV)。所有以上结果说明TpPa-CF3形成目标结构,由C1s和N1s证明该结构发生了烯醇-酮异构。
通过扫描电镜(SEM)观察TpPa-CF3的微观形貌。如图3(a)所示,TpPa-CF3具有均匀的微观形貌,呈现为“米粒”形颗粒堆积形成的团簇,每一颗“米粒”的尺寸在(100±30) nm。
为了解TpPa-CF3的多孔性,对其进行N2吸附-脱附测试。图3(b)中N2吸脱附曲线呈现出I型曲线特征,TpPa-CF3在相对压力较低的区域(p/p0<0.1),N2的吸附量快速增加,说明材料中存在丰富的微孔结构。通过计算分析得出TpPa-CF3具有较大的比表面积(791.83 m2·g−1),图3(c)显示TpPa-CF3具有较小的孔径(1.18 nm)。这归因于TpPa-CF3中氟原子的高电负性增强了框架中芳香环之间的相互作用力,这种相互作用力有助于COF形成较大的比表面积以及较小的孔径[17]。
通过热重分析TpPa-CF3的热性能。热重曲线如图3(d)所示,从图中看到热损失分为两个阶段,大约在400℃之前的损失可能为残留在孔道里的高沸点溶剂(DMF)的挥发。400℃后出现明显的质量损失,从DTG曲线上可以看到在416℃质量损失的速度最快,这主要归因于TpPa-CF3框架的分解。以上结果可以看出TpPa-CF3具有较好的热稳定性。
2.2 TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的表征
通过XRD对膜结构表征,评价了填料对聚合物链排列的影响。从图4(a)中可以看到所有曲线在2θ=15°左右均出现典型的聚合物宽峰。通过布拉格方程计算,得到膜的分子链间距。纯6FDA-ODA膜的分子链间距为0.574 nm,随着填料TpPa-CF3负载量的增加,链间距呈现先增大后下降的趋势,7%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA膜的链间距最小(0.566 nm)。分子链间距先增大主要是由于小负载量的掺入破坏了分子链的堆积,随着负载量的增大,填料与聚合物基质的相互作用逐渐增强,限制了分子链的迁移率,链间距减小有利于提高气体的选择性。同时,在TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜中没有观察到TpPa-CF3粉末的特征峰,这主要是由于在超声搅拌过程中COF填料的部分剥落[21]。
混合基质膜的FTIR图谱如图4(b)所示,所有膜都表现出6FDA-ODA的特征峰,包括C=O的对称(
1783 cm−1)和不对称拉伸(1733 cm−1)、C—N的拉伸振动(1378 cm−1)、C—O—C的拉伸振动(1157 cm−1)、C—F键的吸收峰(1110 cm−1),以及酰亚胺环的弯曲振动(721 cm−1),值得注意的是在1597 cm−1处的特征峰,随着填料的增加而增强,这主要归因于TpPa-CF3和6FDA-ODA中芳香环上的C=C的吸收峰重叠[22]。以上结果说明聚酰亚胺基体和填料之间具有良好的相容性,填料的加入并没有破坏聚酰亚胺的结构。为分析TpPa-CF3的加入对混合基质膜热稳定性的影响,对6FDA-ODA及TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜进行了热重测试。如图5(a)所示,混合基质膜的分解分为两个阶段,第一阶段是400℃左右TpPa-CF3框架的分解,第二阶段是500℃左右6FDA-ODA基体膜的分解,填料的加入对膜的热稳定性影响不大。所有混合基质膜都表现出高达500℃的良好热稳定性,远高于工业中膜的操作温度,表明这些膜具有良好的适用性。DSC曲线用于分析膜的玻璃化转变温度(Tg)。如图5(b)所示,6FDA-ODA膜的Tg出现在297.5℃。随着TpPa-CF3负载量的增加,TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA膜的Tg从297.5℃逐渐增加到302.1℃,说明TpPa-CF3与6FDA-ODA之间具有良好的界面相互作用,这有利于提升混合基质膜的气体选择性[23]。
膜表面、截面的扫描电镜表征能够反映出填料在膜内的分散情况。如图6(a1)~6(e1)所示,与表面光滑平整的纯膜相比,混合基质膜的表面随着填料负载量的增加逐渐变得粗糙,在负载量达到7wt%时可以看到膜表面出现不平整及大颗粒团聚的现象。图6(a2)~6(e2)为纯膜及其混合基质膜的截面扫描电镜图,纯膜的截面表现出均匀、致密的微观结构,在1wt%~5wt%混合基质膜的截面图中能够观察到随着负载量的增加其截面形貌逐渐变粗糙,同时在膜内能够观察到TpPa-CF3颗粒很好地被聚合物包裹且分散均匀。当填料负载量达到7wt%时膜内出现填料与聚合物基质相分离的现象,说明此时负载量已经达到聚合物基质所能承受的上限,5wt%为其最优负载量。
通过接触角测试仪分析纯膜及其混合基质膜的水接触角(θw)。如图7(a)和表1所示,6FDA-ODA膜的水接触角为79.9°,TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的水接触角为81.4°~89.1°,呈现逐渐增大的趋势。这主要归因于TpPa-CF3框架中含有—CF3疏水基团,因此随着TpPa-CF3含量的增加相应负载量的混合基质膜水接触角也逐渐增加。提升膜的疏水性能有助于阻止水汽进入,提升其气体传输性能。
表 1 不同负载量下TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的力学性能Table 1. Mechanical properties of TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA mixed matrix membranes at different loadingsTpPa-CF3 loadings/wt% Tensile strength/MPa Elongation at break/% Young's modulus/GPa θw/(°) 0 74.1 10.1 1.59 79.9 1 79.6 9.7 1.63 81.4 3 82.9 8.6 1.70 83.1 5 93.0 7.8 1.82 84.1 7 84.5 7.3 1.76 89.1 Note: θw—Water contact angle. 对混合基质膜进行拉伸实验以此来检验其力学性能。测试结果如图7(b)和表1所示。从表中可以看出,TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的抗拉强度和杨氏模量随着TpPa-CF3负载量的增加呈现出先增加后下降的趋势,而断裂伸长率呈现逐渐下降的趋势。这主要归因于,在混合基质膜中TpPa-CF3与6FDA-ODA之间较好的相互作用力使得填料与聚合物之间具有良好的界面相容性,增强了膜的刚性。然而,当负载量达到7wt%时,抗拉强度和杨氏模量略微下降,这主要是过量的TpPa-CF3颗粒之间发生团聚,使得界面出现缺陷导致应力集中,降低了膜的力学性能[24]。
利用3种纯气体(CO2、O2、N2)渗透测试来评估不同负载量下TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的渗透性及CO2/N2和O2/N2的理想选择性。结果如表2所示,每一种膜气体渗透系数的大小均与气体分子动力学直径呈反比,即膜的3种气体渗透系数大小排列为P(CO2)>P(O2)>P(N2),3种气体分子动力学直径大小排列为N2(0.36 nm)>O2(0.35 nm)>CO2(0.33 nm)。同6FDA-ODA膜相比所有混合基质膜的气体渗透性都有所提升。由图8(a)中可得,随着TpPa-CF3含量的增加,膜的气体渗透性呈现出先增大后下降的趋势,其中5%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA膜气体渗透性能最佳,P(CO2)提升了149%,P(O2)提升了138%,P(N2)提升了98%。这主要归因于TpPa-CF3的高孔隙率提高了TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA膜的比表面积及固有孔隙率,为气体传输提供了快速通道。TpPa-CF3负载量到7wt%时,气体的渗透性明显下降,但仍然比6FDA-ODA膜高。这主要是由于负载量过大,造成TpPa-CF3在膜内团聚堵塞了气体传输的孔道。
表 2 6FDA-ODA及TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的气体渗透系数P和理想选择性Table 2. Gas permeability coefficient P and ideal selectivity of 6FDA-ODA and TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA mixed matrix membranesMembrane Permeability/Barrer Ideal selectivity α CO2 O2 N2 α(CO2/N2) α(O2/N2) 6FDA-ODA 12.47 2.55 0.64 19.5 4.0 1%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA 16.91 3.76 0.98 17.2 3.8 3%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA 22.77 4.43 1.03 22.0 4.3 5%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA 31.08 6.08 1.27 24.5 4.8 7%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA 18.62 4.16 1.11 16.8 3.8 Notes: 1 Barrer=10−10 cm3(STP)·cm·cm−2·s−1·cmHg−1; Ideal selectivity α=P(A)/P(B), A and B are two different pure gases. TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA膜的气体选择性变化趋势和气体渗透性变化趋势不同,如图8(b)所示,CO2/N2和O2/N2均呈现出先下降后上升再下降的趋势,CO2/N2及O2/N2的理想选择性范围分别在16.8~24.4和3.8~4.8。其中,当TpPa-CF3负载量为5wt%时,混合基质膜的CO2/N2和O2/N2选择性最好,分别是6FDA-ODA膜的125%和119%。理想选择性的提高主要归因于两个方面:一个方面是CO2和O2的分子动力学直径要小于N2的分子动力学直径,从而CO2和O2分子倾向于优先通过。另一个方面,TpPa-CF3中富含大量对CO2具有亲和力的N、O和F等电负性原子,同时框架内还存在能与CO2发生偶极-四极相互作用的强极性C—F键,因此CO2/N2选择性相较于O2/N2的提升更明显[25]。然而,当负载量到7wt%时,混合基质膜的CO2/N2和O2/N2选择性大幅下降,略低于6FDA-ODA膜,这主要归因于当TpPa-CF3的负载量增加一定程度时,其在膜内发生团聚,并和聚合物基质产生部分相分离,产生一些非选择的孔,从而造成CO2/N2和O2/N2理想选择性的大幅下降。
对TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜进行72 h的连续气体渗透性测试,以验证膜的稳定性。如图8(c)所示,该膜在72 h的运行试验中P(CO2)下降了18%,CO2/N2的选择性下降了16%,总体表现出了良好的分离稳定性。
为了评估混合基质膜的气体分离性能,图9显示了不同负载量的TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜的气体分离性能与Robeson上限的对比。当负载量为5wt%时,其气体分离性能更靠近Robeson上限,气体的渗透性与选择性同步提升。说明适量的引入TpPa-CF3能够改善聚合物膜的气体分离性能。此外,表3显示了文献[26-30]中报道的混合基质膜气体分离性能与本工作的对比,TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜显示出适中的气体渗透性以及适中的气体选择性,说明TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA混合基质膜还有进一步提升的潜力。
表 3 文献中报道的混合基质膜气体分离性能与本工作的对比Table 3. Comparison of gas separation performance of mixed matrix membranes reported in the literature with the present workMembrane type P(CO2)/Barrer P(O2)/Barrer (CO2/N2) (O2/N2) Ref. TpPa-1-nc/Pebax 21 — 72 — [26] COFp-PVAm 270 — 86 — [27] TpBD@PBI-BuI 14.8 — 23 — [28] ZIF-7-I/(BPDA/6FDA-ODA) — 2.9 — 0.19 [29] PBI-PI-based carbon 293.5 93.1 8.3 2.6 [30] 5%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA 31.08 6.08 24.4 4.8 This work Notes: TpPa-1-nc—; COFp—; TpBD—; BPDA—; Pebax—Poly(ether-block-amide); PVAm—Polyvinylamine; PBI-BuI—Tert-butylpolybenzimidazole; ZIF-7-I—Wide-pore ZIF-7; PBI—Polybenzimidazoles; PI—Polyimide. 3. 结 论
(1)采用溶剂热法合成了一种氟化共价有机框架材料(TpPa-CF3),其具有高比表面积(791.83 m2·g−1),较小且均一的孔径(1.18 nm)以及良好的热稳定性。
(2)采用共混法成功制备TpPa-CF3/聚酰亚胺(6FDA-ODA)混合基质膜。通过表征得出,所得膜具有良好的界面相容性以及较高的热稳定性(热分解温度在500℃左右)。水接触角的范围在81.4°~89.1°,且膜具有良好的力学性能,有利于膜在分离过程中的稳定性。
(3) TpPa-CF3的掺入提高了混合基质膜的气体渗透性,随着膜中TpPa-CF3负载量的增加,混合基质膜的气体渗透性呈现先减小后增大再减小的趋势。其中,5%TpPa-CF3/6FDA-ODA膜的气体分离性能最好,其CO2和O2的渗透性能分别提高了149%和138%,CO2/N2和O2/N2的分离性能分别是6FDA-ODA基体膜的125%和119%。
-
表 1 Ti2AlNb和TA15的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Ti2AlNb and TA15
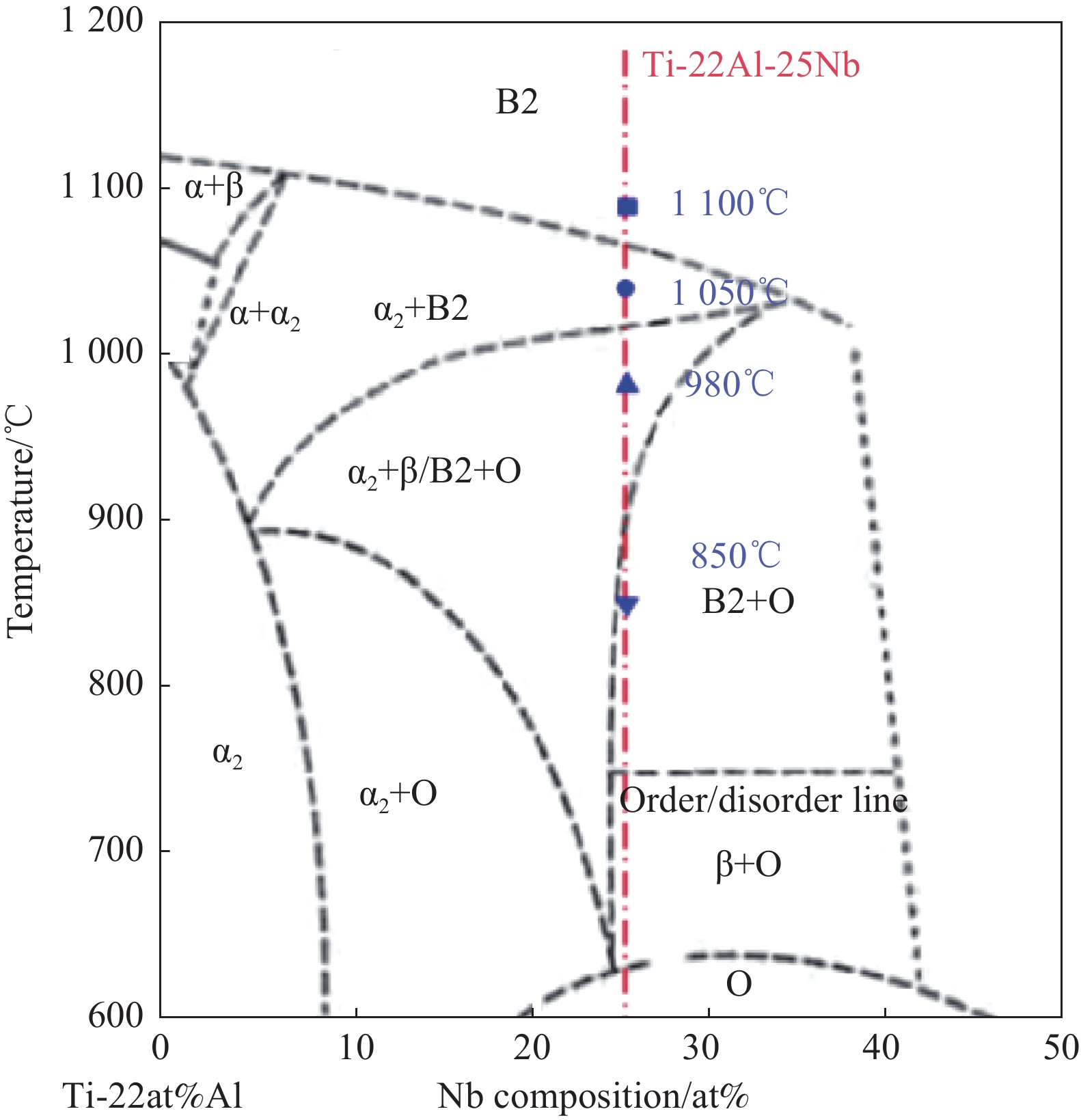
Material Chemical composition TA15/wt% Al: 6.78, Mo: 1.7, V: 2.31, Zr: 2.00, Fe<0.05, Si<0.017, O<0.11, N<0.011, Ti: Balance Ti2AlNb/at% Al: 22.3, Nb: 25.2, Ti: Balance 表 2 Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料制备工艺参数
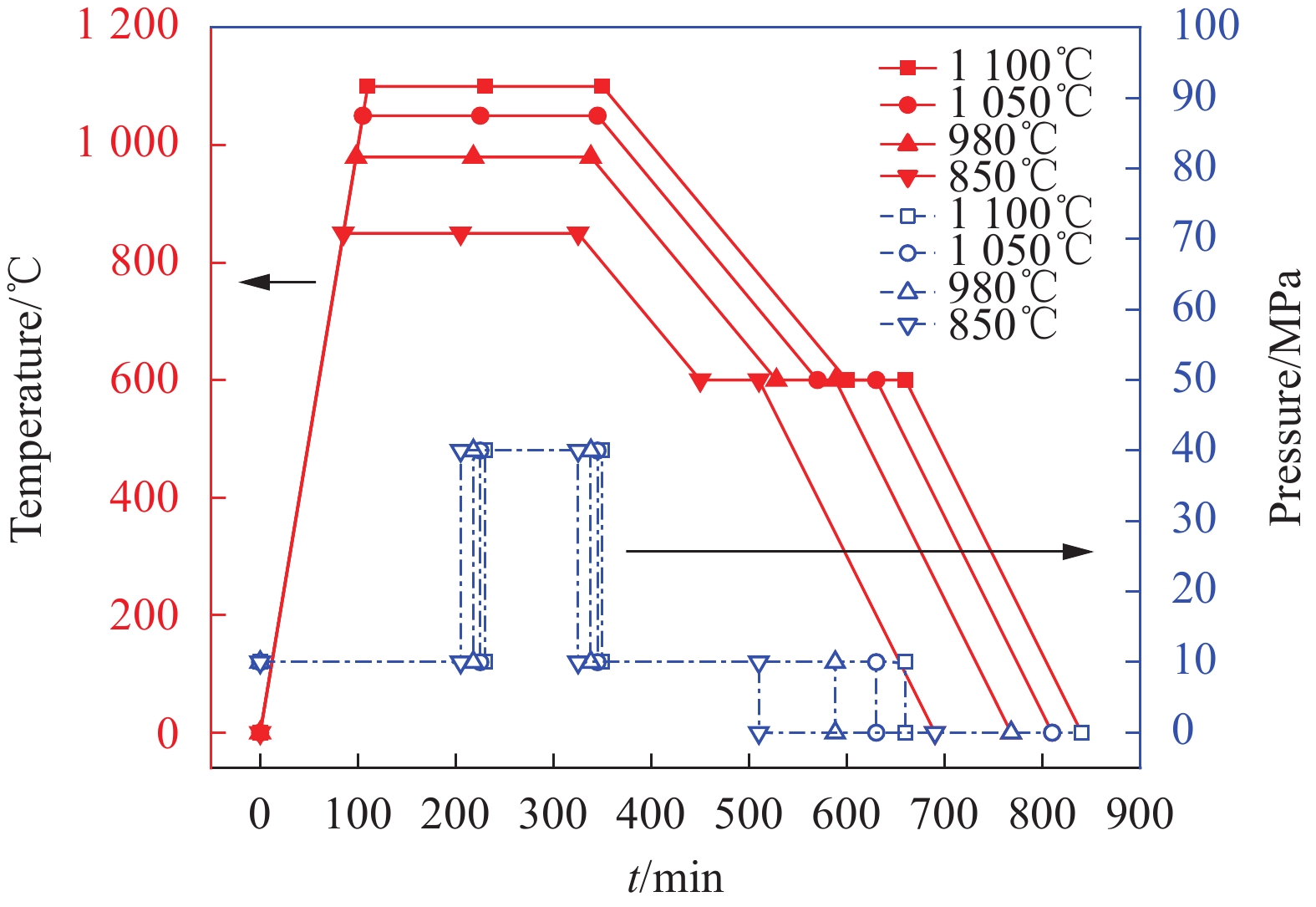
Table 2 Preparation process parameters of Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminated composites
Experiment Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 T1/℃ t1/h P1/MPa T2/℃ t2/h P2/MPa T3/℃ t3/h P3/MPa 1 850 2 10 850 2 40 600 1 10 2 980 2 10 980 2 40 600 1 10 3 1050 2 10 1050 2 40 600 1 10 4 1100 2 10 1100 2 40 600 1 10 Notes:T1, T2 and T3 are the hot-pressing temperature in the first, second and third stage; t1, t2 and t3 are the holding time in the first, second and third stage; P1, P2 and P3 are the hot-pressing pressure in the first, second and third stage. 表 3 Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料室温拉伸强度和应变
Table 3 Room temperature tensile strength and strain of Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminated composites
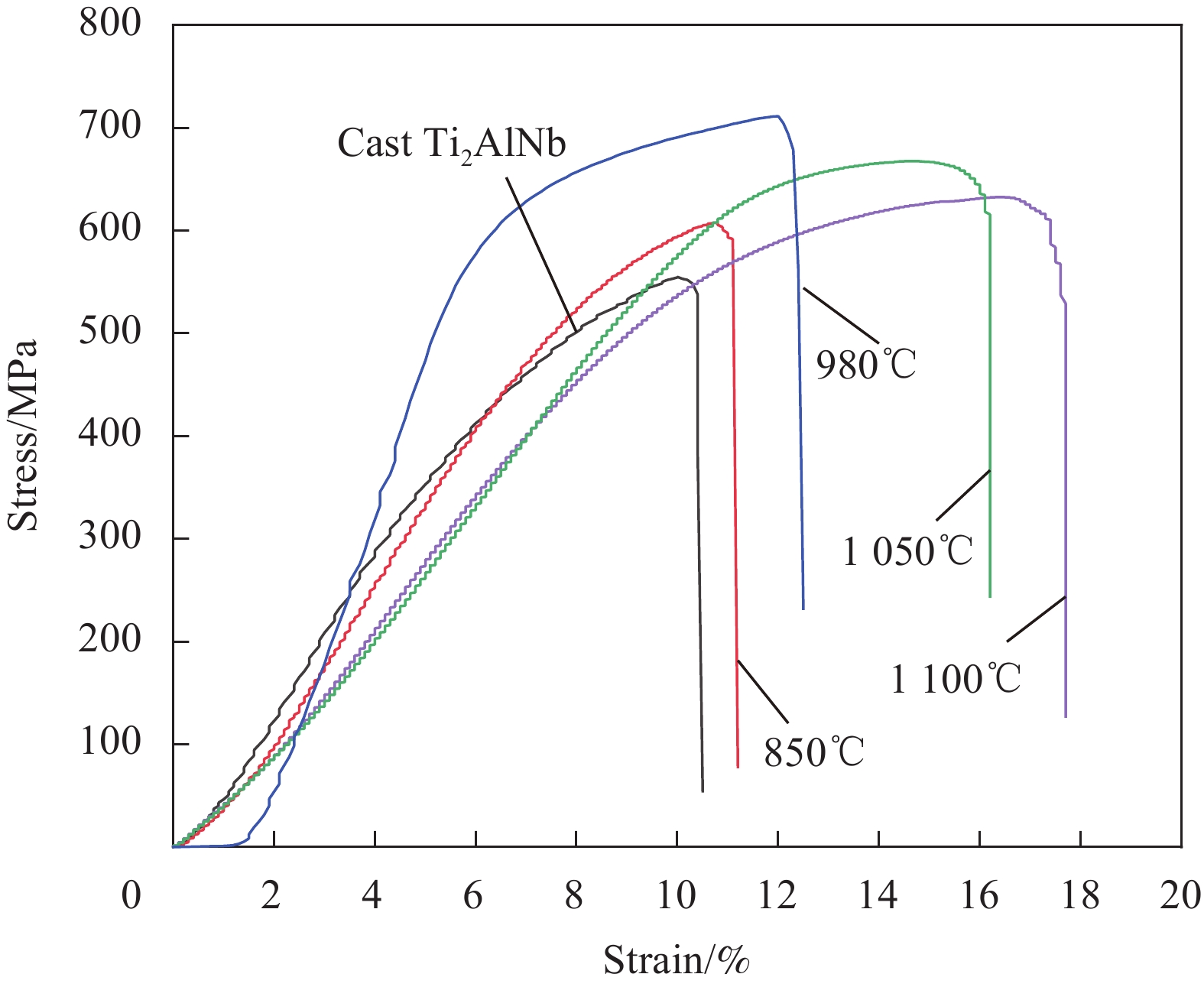
Specimen Hot pressing temperature/℃ Tensile strength/MPa Tensile strain/% TA15/Ti2AlNb 850 726.22 6.42 980 873.21 7.28 1050 817.44 9.37 1100 775.79 10.35 Ti2AlNb (as cast) — 660.09 3.10 表 4 Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料650℃高温拉伸强度和应变
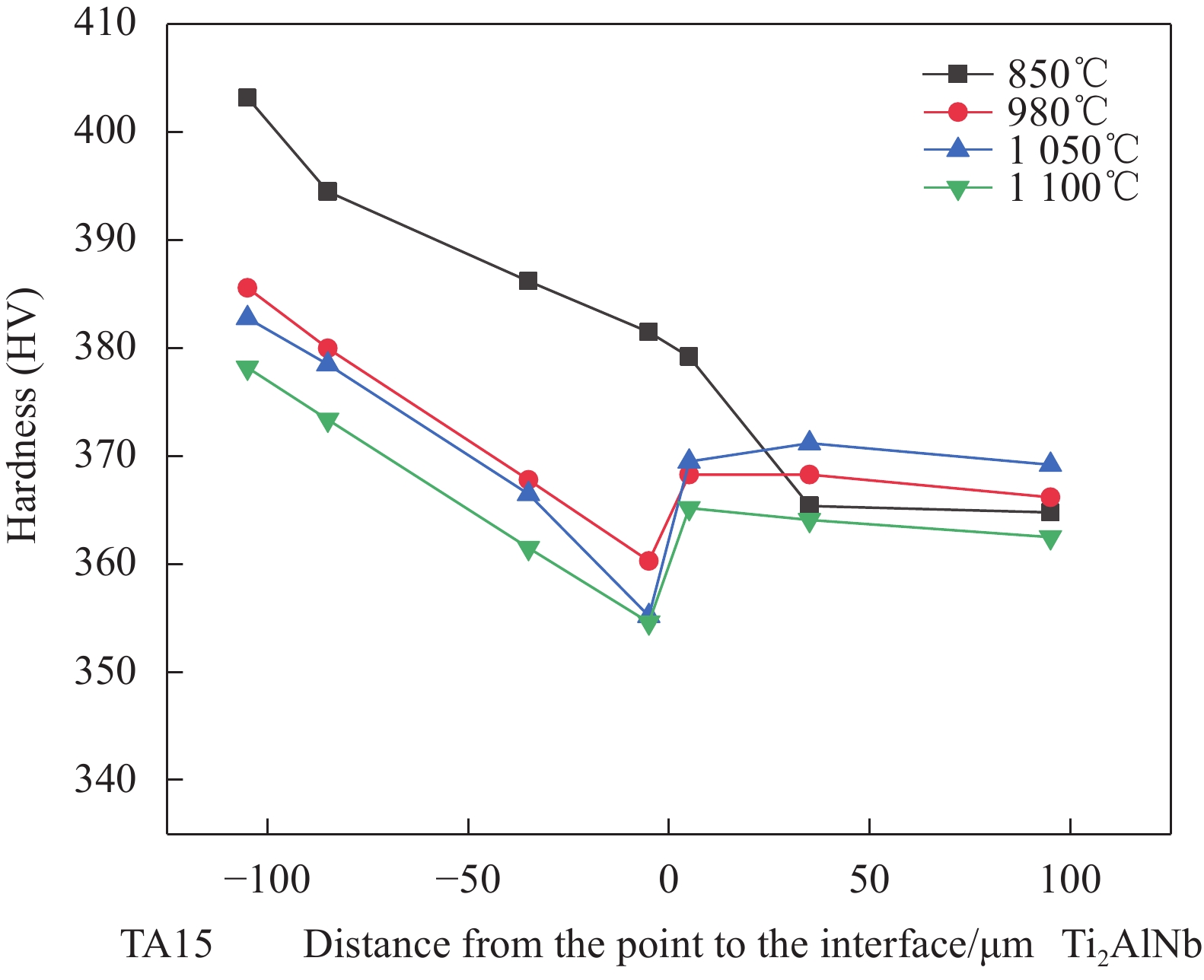
Table 4 650℃ high temperature tensile strength and strain of Ti2AlNb/TA15 laminated composites
Specimen Hot pressing temperature/℃ Tensile strength/MPa Tensile strain/% Ti2AlNb/TA15 850 607.71 11.1 980 711.58 12.5 1050 667.85 16.2 1100 632.76 17.7 Ti2AlNb (as cast) — 555.08 10.5 -
[1] 王兴杰. “爆炸焊接+热处理”制备Ti/Al3Ti叠层复合材料及其性能研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2022. WANG Xingjie. Research on the preparation and properties of Ti/Al3Ti laminated composites by explosive welding and heat treatment [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2022 (in Chinese).
[2] 赵赫威, 郭林. 仿贝壳珍珠母层状复合材料的制备及应用[J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(6): 576-589. DOI: 10.1360/N972016-00754 ZHAO Hewei, GUO Lin. Synthesis and applications of layered structural composites inspired by nacre[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(6): 576-589(in Chinese). DOI: 10.1360/N972016-00754
[3] 尹楚藩. 基于爆炸焊接法的Ti/TiAl3叠层复合材料制备技术研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020. YIN Chufan. Research on the preparation technology of Ti/TiAl3 laminated composites based on explosion welding method [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2020(in Chinese).
[4] 曹阳, 朱世范, 果春焕, 等. 新型金属间化合物基层状装甲防护复合材料[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2014, 37(6): 122-128. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2014.06.039 CAO Yang, ZHU Shifan, GUO Chunhuan, et al. Novel metal-intermetallic laminate composite for armor material[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2014, 37(6): 122-128(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2014.06.039
[5] TRESA M, POLLOCK. Alloy design for aircraft engines[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15: 809-815. DOI: 10.1038/nmat4709
[6] HAGIWARA M, EMURA S, ARAOKA A, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloy[J]. Metals Materials International, 2003, 9: 265-272. DOI: 10.1007/BF03027045
[7] 冯艾寒, 李渤渤, 沈军. Ti2AlNb基合金的研究进展[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2011, 10(1): 30-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.01.007 FENG Aihan, LI Bobo, SHEN Jun. Recent advances on Ti2AlNb-based alloys[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2011, 10(1): 30-38(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6620.2011.01.007
[8] FRONCZEK D M, WOJEWODA-BUDKA J, CHULIST R, et al. Structural properties of Ti/Al clads manufactured by explosive welding and annealing[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 91: 80-89.
[9] FINDIK F. Recent developments in explosive welding[J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(3): 1081-1093.
[10] SUN W, FAN H Y, YOU F H, et al. Prediction of interfacial phase formation and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V-Ti43Al9V laminate composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 782: 139173.
[11] SUN W, YOU F H, KONG F T, et al. Effect of residual stresses on the mechanical properties of Ti-TiAl laminate composites fabricated by hot-pack rolling[J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 166: 110394. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110394
[12] LYU S Y, SUN Y B, LI G D, et al. Effect of layer sequence on the mechanical properties of Ti/TiAl laminates[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 143: 160-168.
[13] SUN W, YOU F H, KONG F T, et al. Enhanced tensile strength and fracture toughness of a Ti-TiAl metal-intermetallic laminate (MIL) composite[J]. Intermetallics, 2020, 118: 106684. DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2019.106684
[14] ZHU H F, SUN W, KONG F T, et al. Interfacial characteristics and mechanical properties of TiAl/Ti6Al4V laminate composite (LMC) fabricated by vacuum hot pressing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 742: 704-711. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.086
[15] 孔凡涛, 陈玉勇. γ-TiA1/TC4复合板材的制备及组织性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(8): 1484-1486. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2009.08.040 KONG Fantao, CHEN Yuyong. Preparation of γ-TiAl/TC4 composite sheet and its microstructure and properties[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(8): 1484-1486(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2009.08.040
[16] 宋志恒. TiAl/Ti合金层状复合材料的制备及组织性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017. SONG Zhiheng. Fabrication and microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl/Ti laminated composities[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[17] FAN M Y, DOMBLESKY J, JIN K, et al. Effect of original layer thicknesses on the interface bonding and mechanical properties of TiAl laminate composites[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 99: 535-542.
[18] 杨蕊鸿, 林飞, 朱岩, 等. TC4/Ti2AlNb异种合金扩散连接接头组织与性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020, 49(5): 20-24. YANG Ruihong, LIN Fei, ZHU Yan, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of diffusion bonded joints of TC4/Ti2AlNb dissimilar alloys[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(5): 20-24(in Chinese).
[19] LI D H, WANG B B, LUO L S, et al. The interface structure and its impact on the mechanical behavior of TiAl/Ti2AlNb laminated composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 827: 142095.
[20] LI P, JI X H, XUE K M. Diffusion bonding of TA15 and Ti2AlNb alloys: Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 26(4): 1839-1846. DOI: 10.1007/s11665-017-2555-4
[21] LI P, WANG L S, WANG B, et al. Diffusion and mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb and TA15 interface: From experiments to molecular dynamics[J]. Vacuum, 2022, 195: 110637. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110637
[22] LIU Y T, ZHANG Y Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TA15-Ti2AlNb bimetallic structures by laser additive manufacturing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 795: 140019. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140019
[23] SUN Z C, YANG H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TA15 titanium alloy under multi-step local loading forming[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2009, 523(1-2): 184-192. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.05.058
[24] WEI M, CHEN S, LIANG J, et al. Effect of atomization pressure on the breakup of TA15 titanium alloy powder prepared by EIGA method for laser 3D printing[J]. Vacuum, 2017, 143: 185-194. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.06.014
[25] ZHANG K, LEI Z, CHEN Y, et al. Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of laser-TIG hybrid welded dissimilar joints of Ti-22Al-27Nb and TA15[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2015, 73: 139-145.
[26] BOEHLERT C J. The phase evolution and microstructural stability of an orthorhombic Ti-23Al-27Nb alloy[J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1999, 20(2): 101-108. DOI: 10.1007/s11669-999-0007-z
[27] ZHANG Y, CAI Q, MA Z, et al. Solution treatment for enhanced hardness in Mo-modified Ti2AlNb-based alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 805(15): 1184-1190.
[28] WANG J Y, GE Z M, ZHOU B Y. Aeronautical titanium alloy [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1985: 120.
[29] 曹京霞, 方波, 黄旭, 等. 微观组织对TA15钛合金力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属, 2004(2): 362-364. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2004.02.018 CAO Jingxia, FANG Bo, HUANG Xu, et al. Effects of microstructure on properties of TA15 titanium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2004(2): 362-364(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2004.02.018
[30] ARDELL A J. Microstructural stability at elevated temperatures [J]. Journal European Ceramic Society, 1999, 19: 2217-2231.
[31] STEFANSSO N, SEMIATIN S L. Mechanisms of globularization of Ti-6Al-4V during static heat treatment[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transaction A, 2003, 34(3): 691-698. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-003-0103-3
[32] HE B, WU D, PAN J L, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser deposited TA15/Ti2AlNb gradient composite structures[J]. Vacuum, 2021, 190: 110309. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110309
[33] ZHAO Y Y, LI J Y, QIU R F, et al. Growth characterization of intermetallic compound at the Ti/Al solid state interface[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(3): 472.
[34] 郑友平, 曾卫东, 王伟, 等. Ti-22Al-25Nb合金等轴组织演变和拉伸性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(S1): 200-203. ZHENG Youping, ZENG Weidong, WANG Wei, et al. Equiaxed microstructure evolution and tensile properties of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(S1): 200-203(in Chinese).
[35] TANG B, XIAN S Q, KOU H C, et al. Recrystallization behavior at diffusion bonding interface of high Nb containing TiAl alloy[J]. Advanced Engineering Material, 2016, 18(4): 657-664. DOI: 10.1002/adem.201500457
[36] ZHANG H, YAN N, LIANG H, et al. Phase transformation and microstructure control of Ti2AlNb-based alloys: A review[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 80(21): 203-216.
[37] ZHOU Y H, WANG D W, SONG L J, et al. Effect of heat treatments on themicrostructure and mechanical properties of Ti2AlNb intermetallic fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Science & Engineering, A. Structural Materials: Properties, Misrostructure and Processing, 2021, 817: 141352.
[38] LI N, ZHAO Z B, SUN H, et al. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-22Al-24Nb-0.5Mo alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 857: 144052. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.144052
-
目的
航空航天、装甲防护以及特种设备领域对金属材料的各项性能要求也越来越高,传统金属的单一性能已经无法满足设计和性能需求。将不同性能的金属材料交替结合,获得更高的比刚度、比强度、断裂韧性等特性的金属基叠层复合材料,有效弥补了单一金属材料在塑性和韧性等方面的不足,大幅提升了材料的整体性能。 TiAlNb由于具有高比强度、断裂韧性、高温强度和抗蠕变性等性能,且能够在600℃~850℃服役,成为具潜力的新型航空航天用轻质高温结构材料。但TiAlNb密度较大,且在室温下存在本征脆性,制约了其制备、加工及应用。因此,研究以TiAlNb合金为基体的叠层复合材料具有重要的工程价值。真空热压法(VHP)具备制备工艺简单,成本较低,应用范围广等优势。而采用热压法制备TiAlNb叠层复合材料的研究相对较少,且主要集中在扩散连接领域。TA15是一种近α钛合金,同时具有α和α+β钛合金的优点,如较高的中高温强度、良好的热稳定性、接近α+β合金的良好可加工性以及类似于α钛合金的良好焊接性,广泛应用于航空航天领域。采用TiAlNb和TA15为基体进行叠层复合材料热压工艺探索,有望制备兼具韧塑性和高温性能的复合材料。同时,该研究能够为这两种材料在宇航部件的异种材料连接、多层中空结构制备等方面提供借鉴。本文以TiAlNb和TA15为原材料,依据TiAlNb的相变温度区间设计了四种热压工艺,通过真空热压法进行TiAlNb/TA15叠层复合材料制备,对叠层复合材料的基体和界面微观组织进行分析,探究热压工艺对基体组织和界面组织演化规律的影响以及叠层复合材料的高温拉伸性能。
方法首先使用线切割将Ti-22Al-25Nb铸锭和TA15铸锭切成长方体层板并使用砂纸对其进行打磨,随后浸入10 vol.% HF溶液以去除材料表面的氧化皮,接着放入10 vol.% CHOH溶液浸泡,并进行超声波清洗,干燥处理后制备叠层复合材料预制体。接着,将置入预制体的模具放入真空热压炉中,进行TiAlNb/TA15叠层复合材料的制备。最后,取出制备好的试样,使用线切割机对试样进行金相试样、拉伸试样制备。经过机械打磨和剖光之后,采用HF: HNO: HO(1: 2: 5)腐蚀液对试样进行腐蚀。使用X射线衍射、扫描电子显微镜、扫描电子显微镜能谱仪等对试样的物相及其微观组织进行测试分析。使用万能电子拉伸机对TiAlNb/TA15叠层复合材料进行室温和650℃高温拉伸实验。
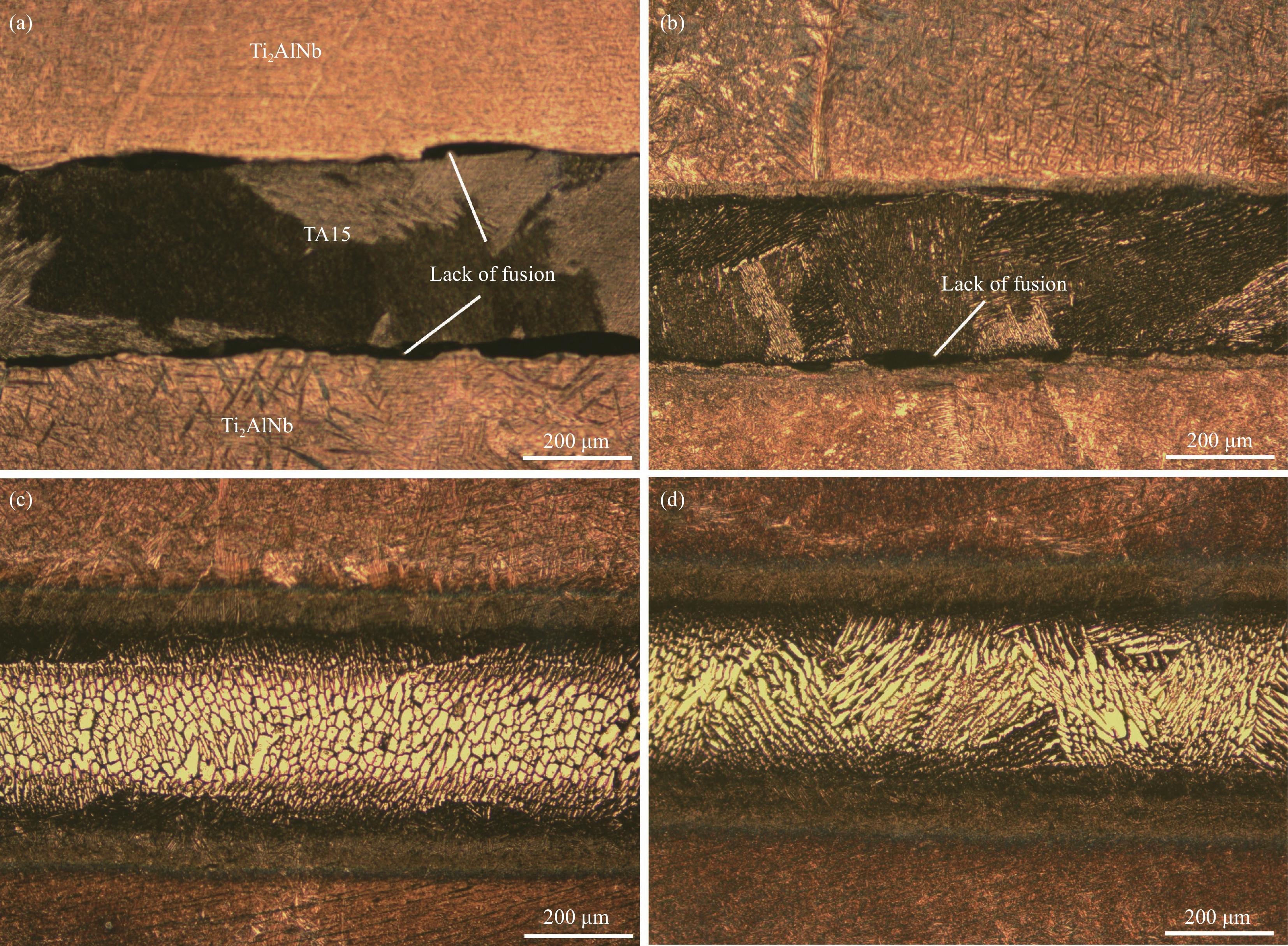
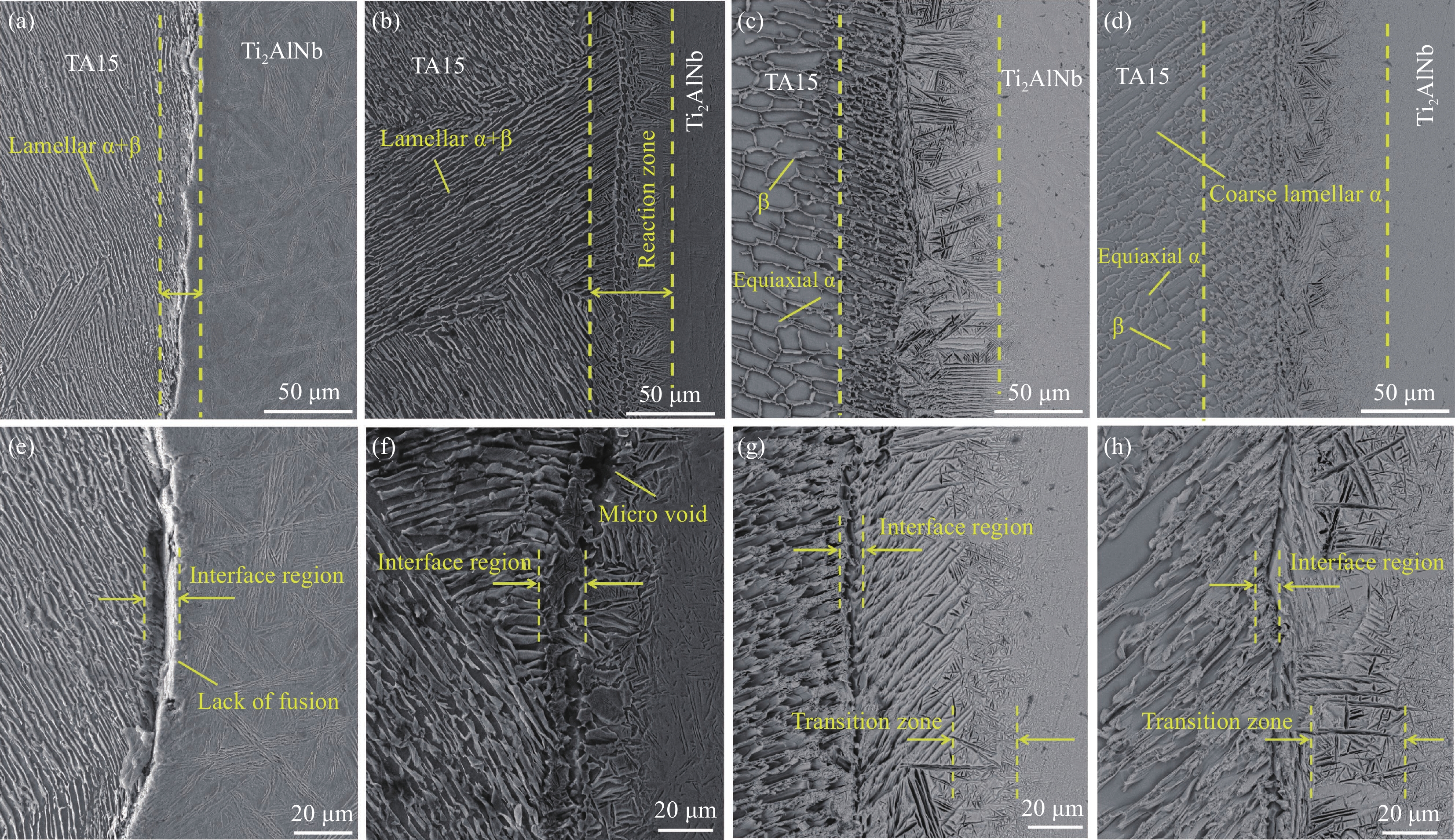
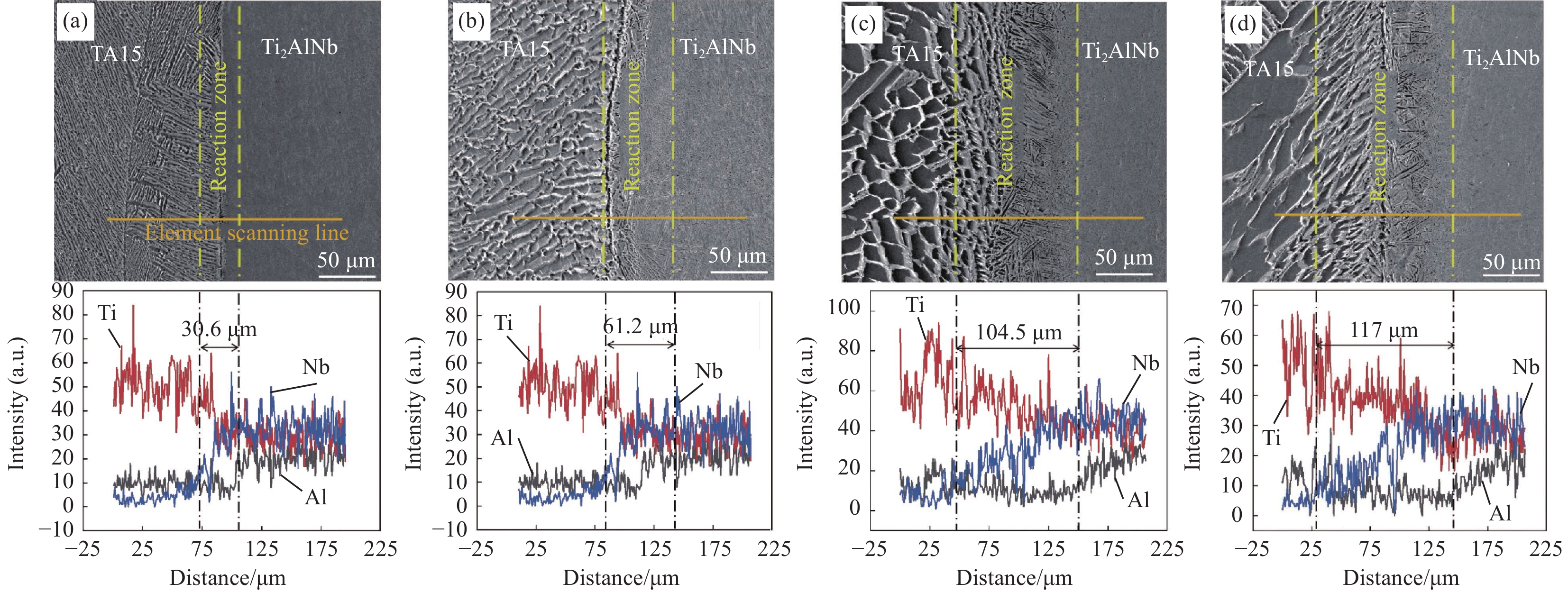
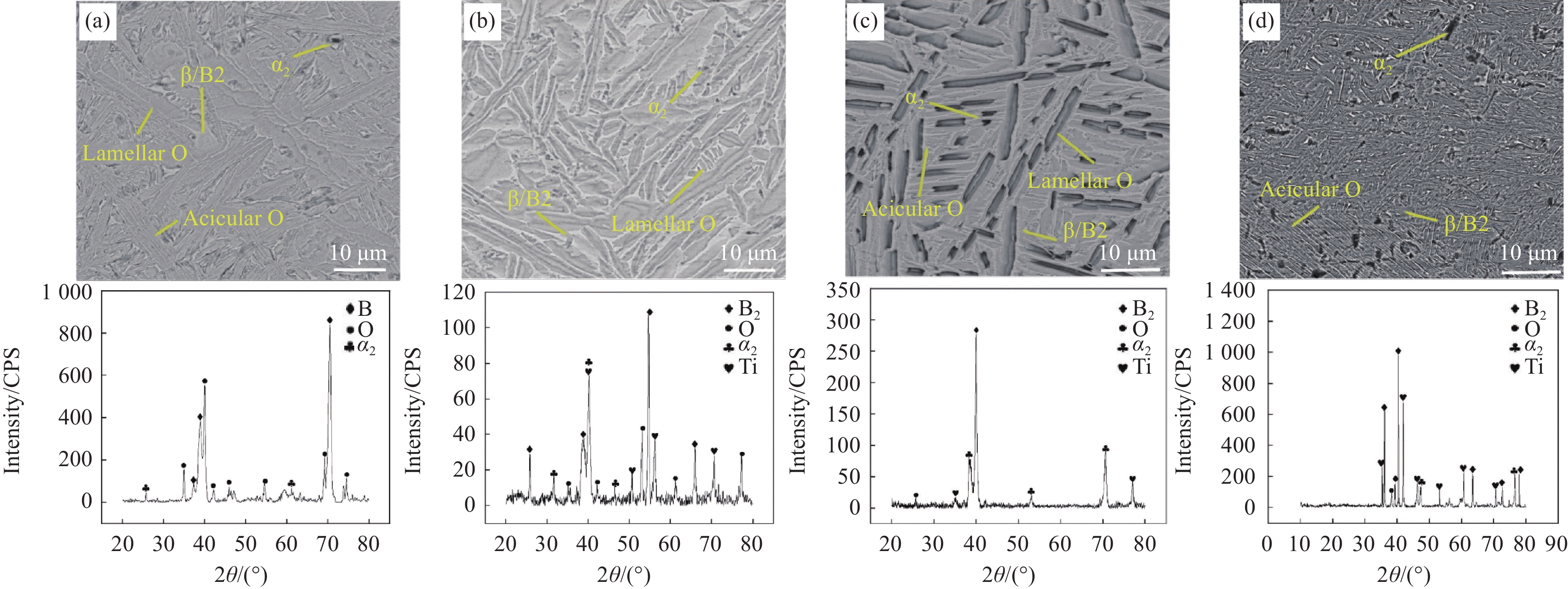
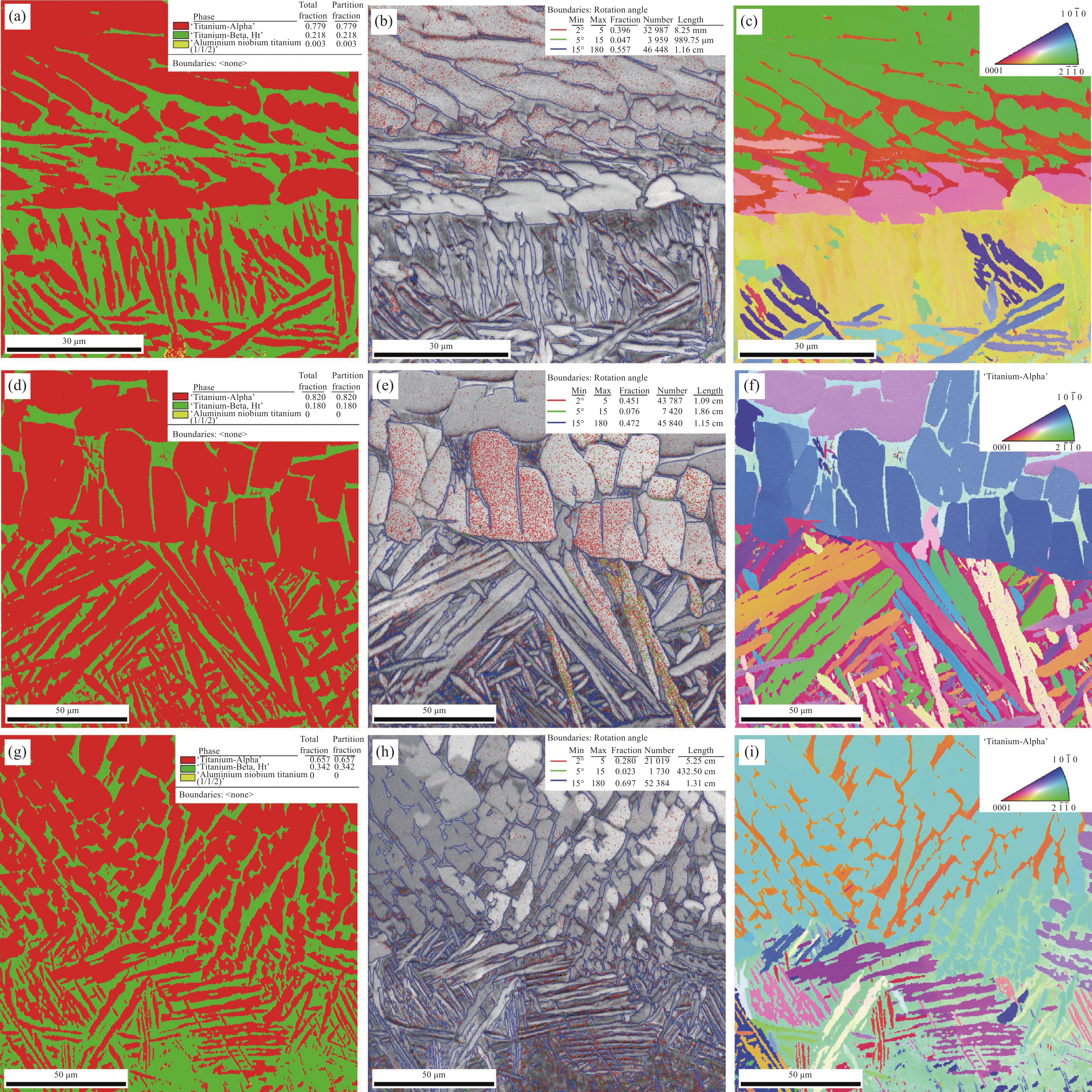
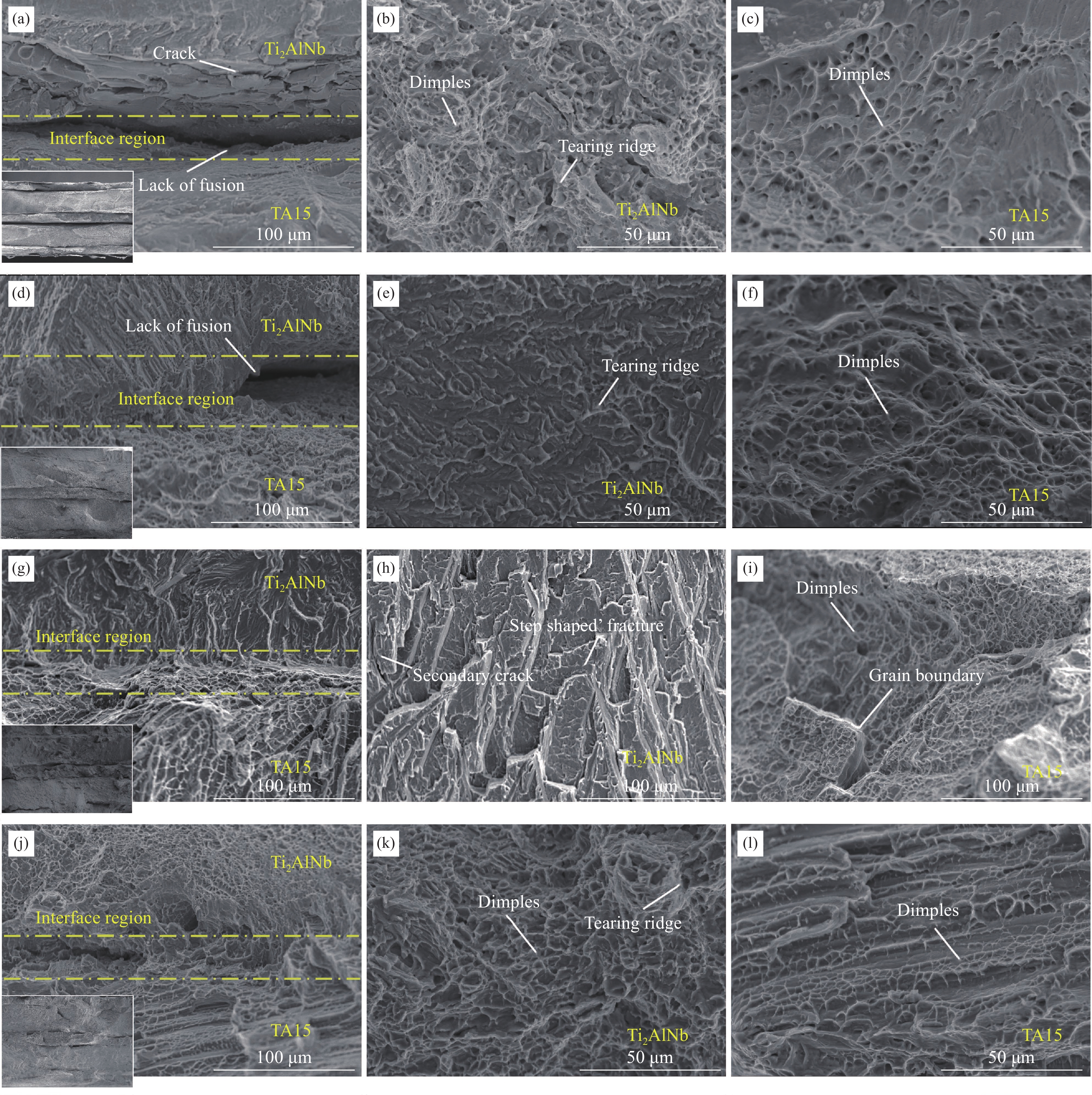
结果从真空热压法制备TiAlNb/TA15叠层复合材料实验结果分析可得以下几点:(1)采用真空热压法制备的TiAlNb/TA15叠层复合材料可以显著改善TiAlNb合金的室温和650℃高温抗拉强度和塑性;随热压温度的升高,抗拉强度有所降低,但塑性显著提高。(2)当热压温度大于1050℃时,可以实现Ti2AlNb和TA15合金的冶金界面结合,且在热压温度为1050℃时复合材料的综合性能较为优异,其中室温抗拉强度和应变为817.44MPa和9.37%,650℃高温抗拉强度和应变分别为667.85MPa和16.2%。(3)基体界面反应区厚度随热压温度的升高而增加,在热压温度在1050℃以上时,在Ti2AlNb一侧形成了针状组织形貌的过渡区。该过渡区的生成有利于减小两种基体材料组织和性能的差异,有利于提升材料的整体性能。
结论真空热压法制备的TiAlNb/TA15叠层复合材料可以显著改善TiAlNb合金的室温和650℃高温抗拉强度和塑性;随热压温度的升高,抗拉强度有所降低,但塑性显著提高;在热压温度为1050℃时复合材料的综合性能较为优异,其中室温抗拉强度和应变为817.44MPa和9.37%,650℃高温抗拉强度和应变分别为667.85MPa和16.2%;基体界面反应区厚度随热压温度的升高而增加。
-
Ti2AlNb具有高比强度、断裂韧性、高温强度和抗蠕变性等性能,但在室温下存在本征脆性,制约了其制备、加工及应用。金属基叠层复合材料可以有效弥补单一金属材料在塑性和韧性等方面的不足,提升材料的整体性能。本文创新性地选用高温钛合金TA15增韧,制备了Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料。
文中研究了热压温度对基体相和界面反应层组织的影响规律,获得了适宜的热压工艺参数;研究了基体与界面层组织与力学性能和断裂行为的关系。相较于Ti2AlNb合金,Ti2AlNb/TA15叠层复合材料室温和高温拉伸性能均有所提升,其中1050℃热压温度条件下的叠层复合材料具有较好的综合性能,650℃高温抗拉强度和应变分别为667.85MPa和16.2%。
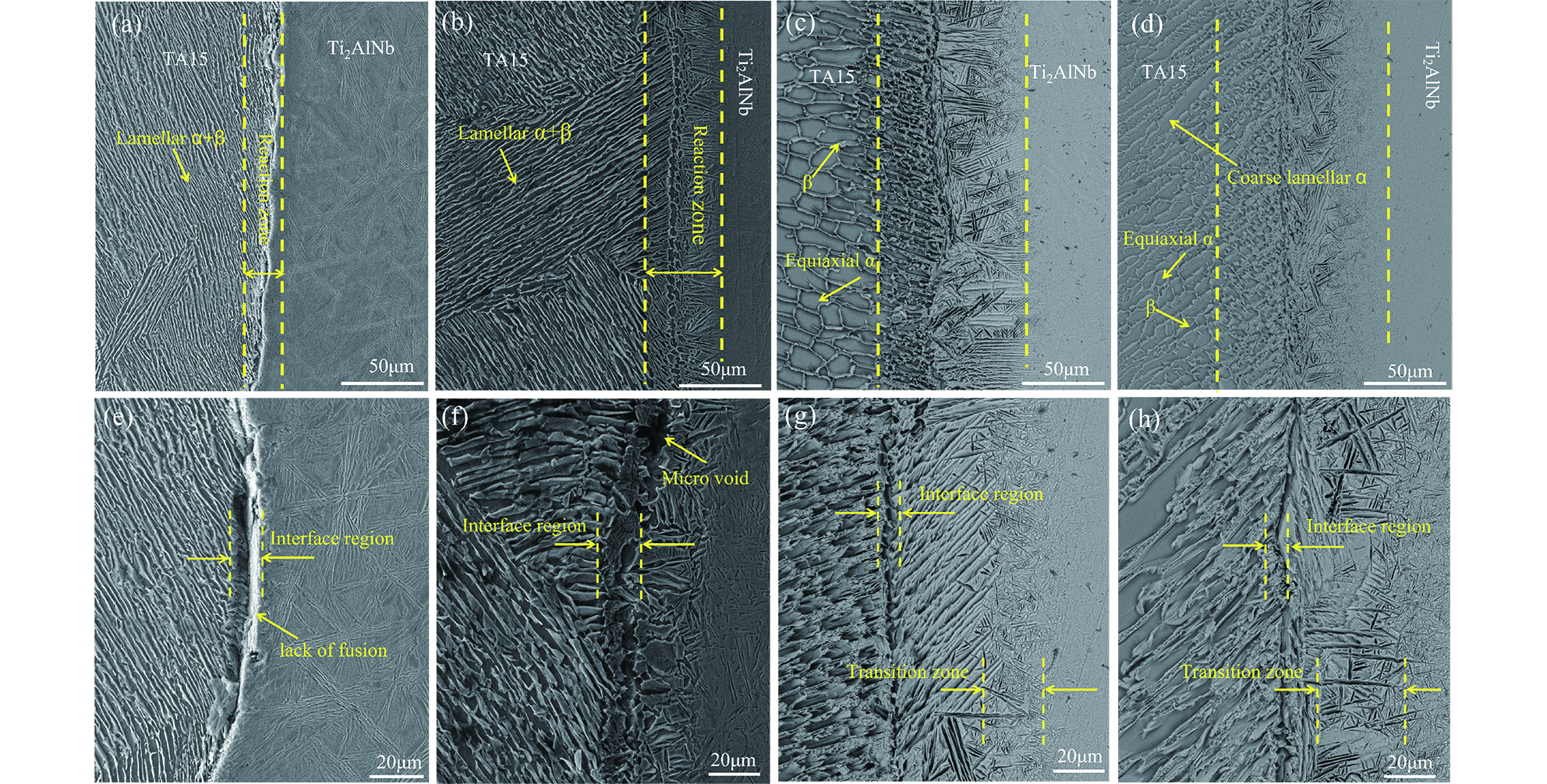
不同热压温度叠层复合材料的SEM组织





 下载:
下载: