Ultra-thin magnetic biochar composite absorbing material derived from sycamore catkins
-
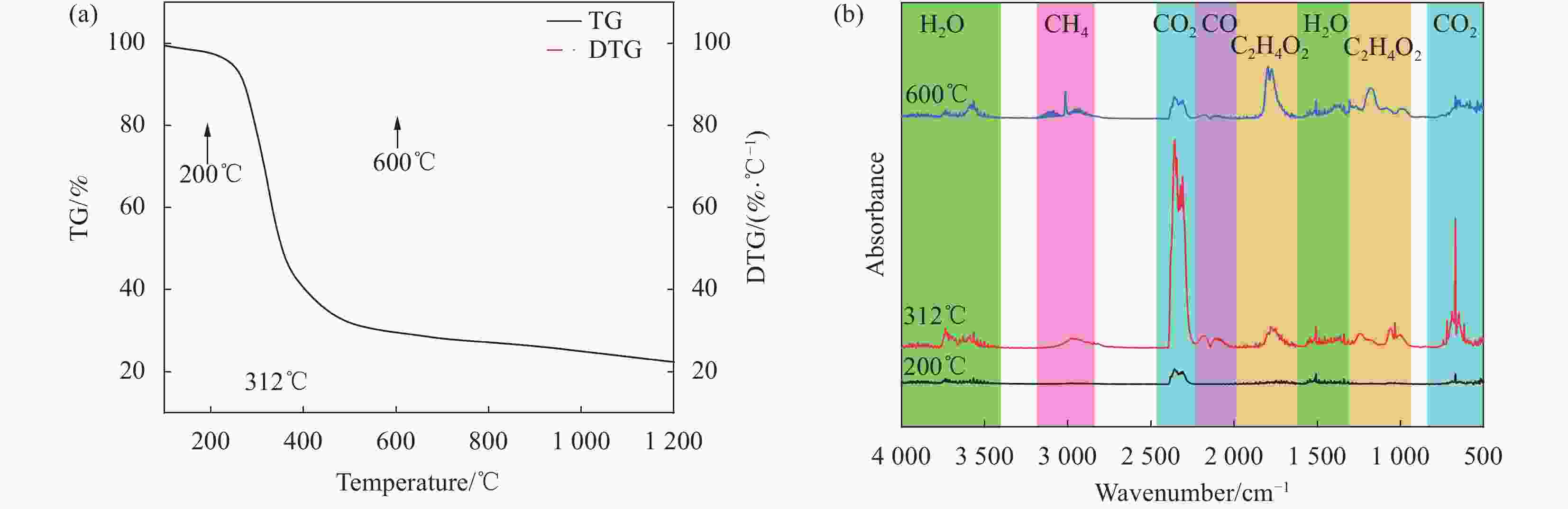
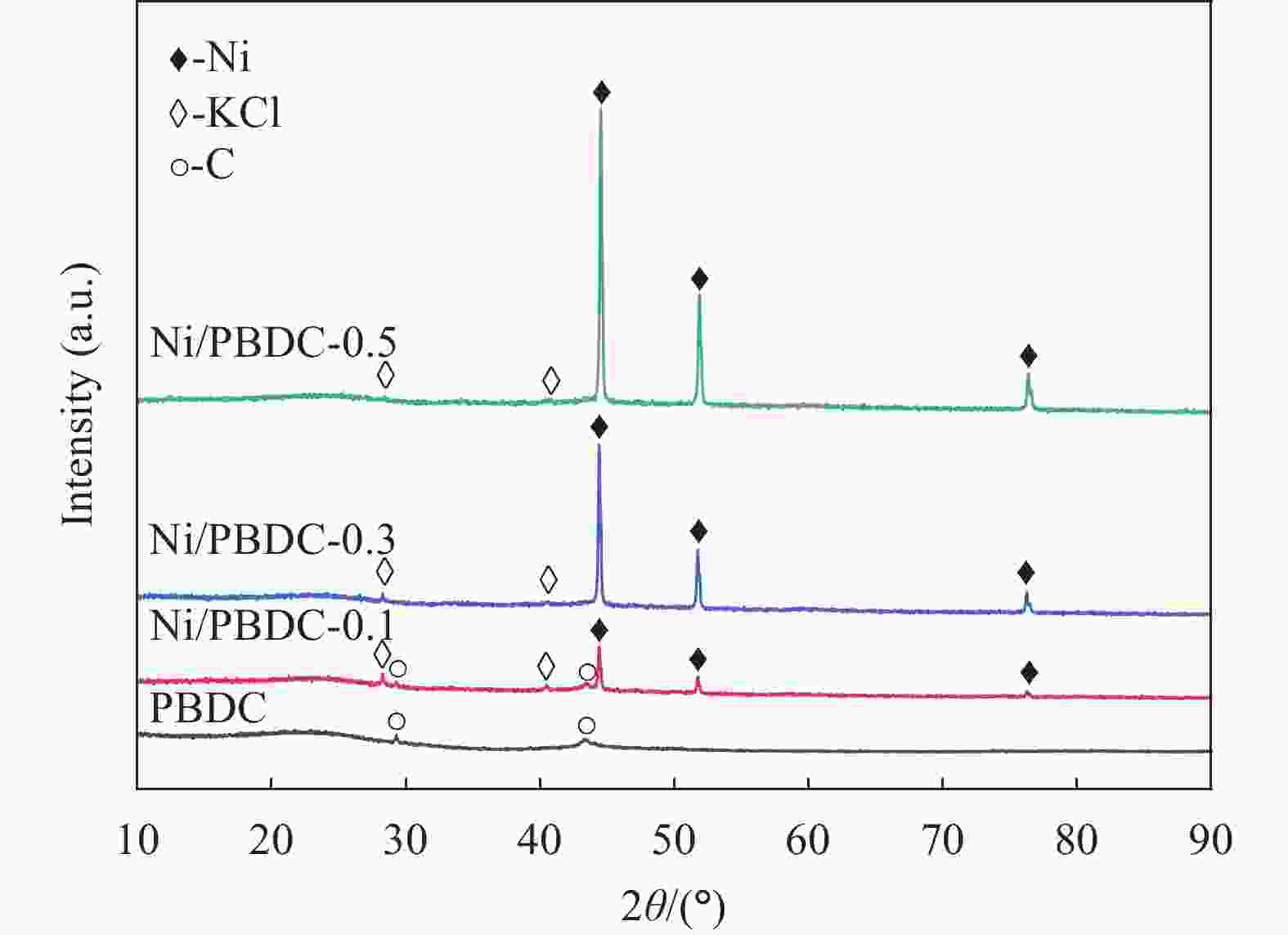
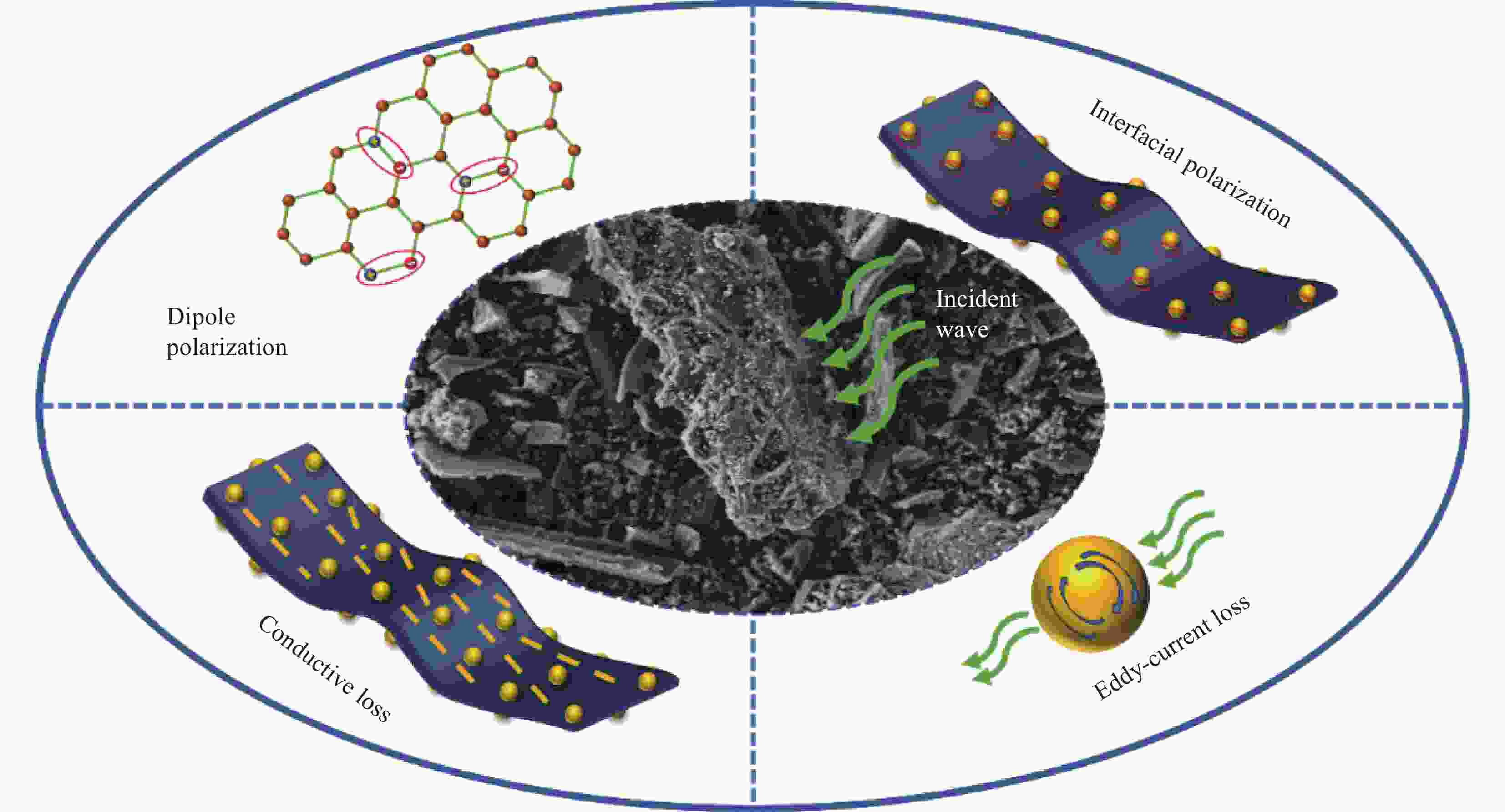
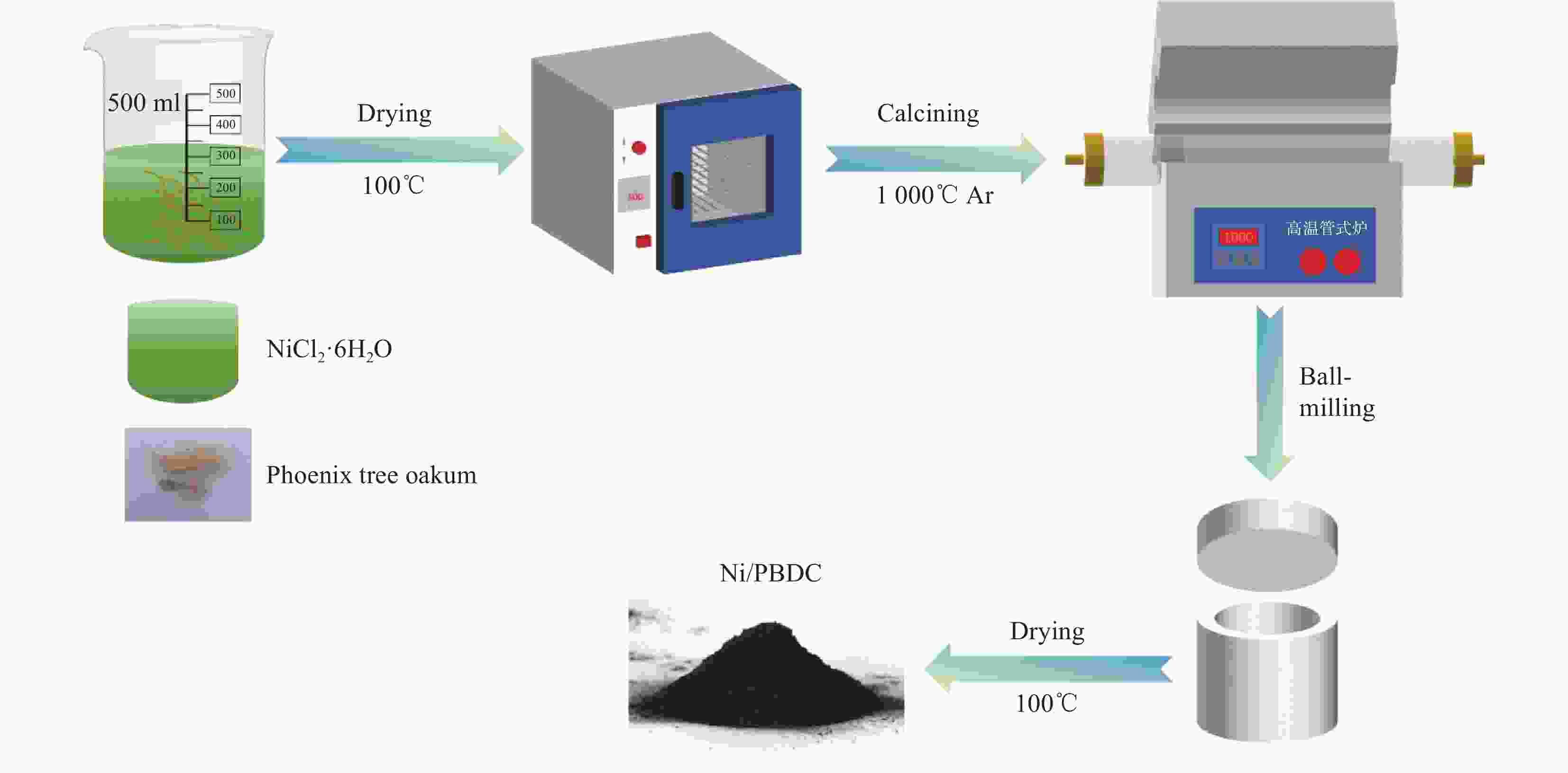
摘要: 生物质衍生炭因其环保性和可持续性在微波吸收领域引起了广泛的关注。本研究主要以生物质废料梧桐絮为原料,采用绿色环保的浸渍碳化工艺,通过原位生长法来制备镍/梧桐絮衍生炭(Ni/PBDC)复合吸波材料。研究表明,在梧桐絮的碳化过程中,木质素内的官能团经历热解转化为气体释放出来,此过程同步伴随着生物炭的生成以及进一步的石墨化转变。镍颗粒生长在碳的表面和内部,这种分布增强了复合吸波材料的界面极化损耗;磁性颗粒镍的加入增加了磁损耗和界面极化损耗,但是镍含量过高会导致材料阻抗失配从而降低电磁衰减能力。性能最佳的Ni/PBDC复合吸波材料的最小反射损耗为−40 dB,有效吸收带宽为4.16 GHz,对应的匹配厚度为1.4 mm。值得注意的是,不同镍含量的Ni/PBDC复合吸波材料的最佳吸波性能的响应厚度均在1.5 mm以下。该复合吸波材料具有厚度薄、吸收性能强且带宽宽的优点,因此在吸波领域具有巨大的应用潜力。Abstract: Biomass derived carbon has attracted extensive attention in the field of microwave absorption due to its environmental protection and sustainability. In this study, Ni/phoenix tree oakum biomass derived carbon(Ni/PBDC)absorbent composite material was prepared by in-situ growth method using green impregnation carbonization process and biomass waste phoenix tree oakum as raw material. Research has shown that during the carbonization process of the phoenix tree oakum, the functional groups within the lignin undergo pyrolysis and transform into gases that are released, while this process is simultaneously accompanied by the formation of biochar and further graphitization. The growth of nickel particles on the surface and within the carbon enhances the interfacial polarization loss of the composite absorbing material. The addition of magnetic nickel particles increases both magnetic loss and interfacial polarization loss, but an excessively high nickel content can lead to impedance mismatch in the material, thereby reducing its ability to attenuate electromagnetic waves. The optimal Ni/PBDC composite absorbing material exhibits a minimum reflection loss of −40 dB, with an effective absorption bandwidth of 4.16 GHz at a corresponding matching thickness of 1.4 mm. It is worth noting that the response thickness of Ni/PBDC composite absorbing materials with the same nickel content is less than 1.5 mm. The composite absorbing material has the advantages of thin thickness, strong absorption performance and wide band, so it has great application potential in the field of wave absorption.
-
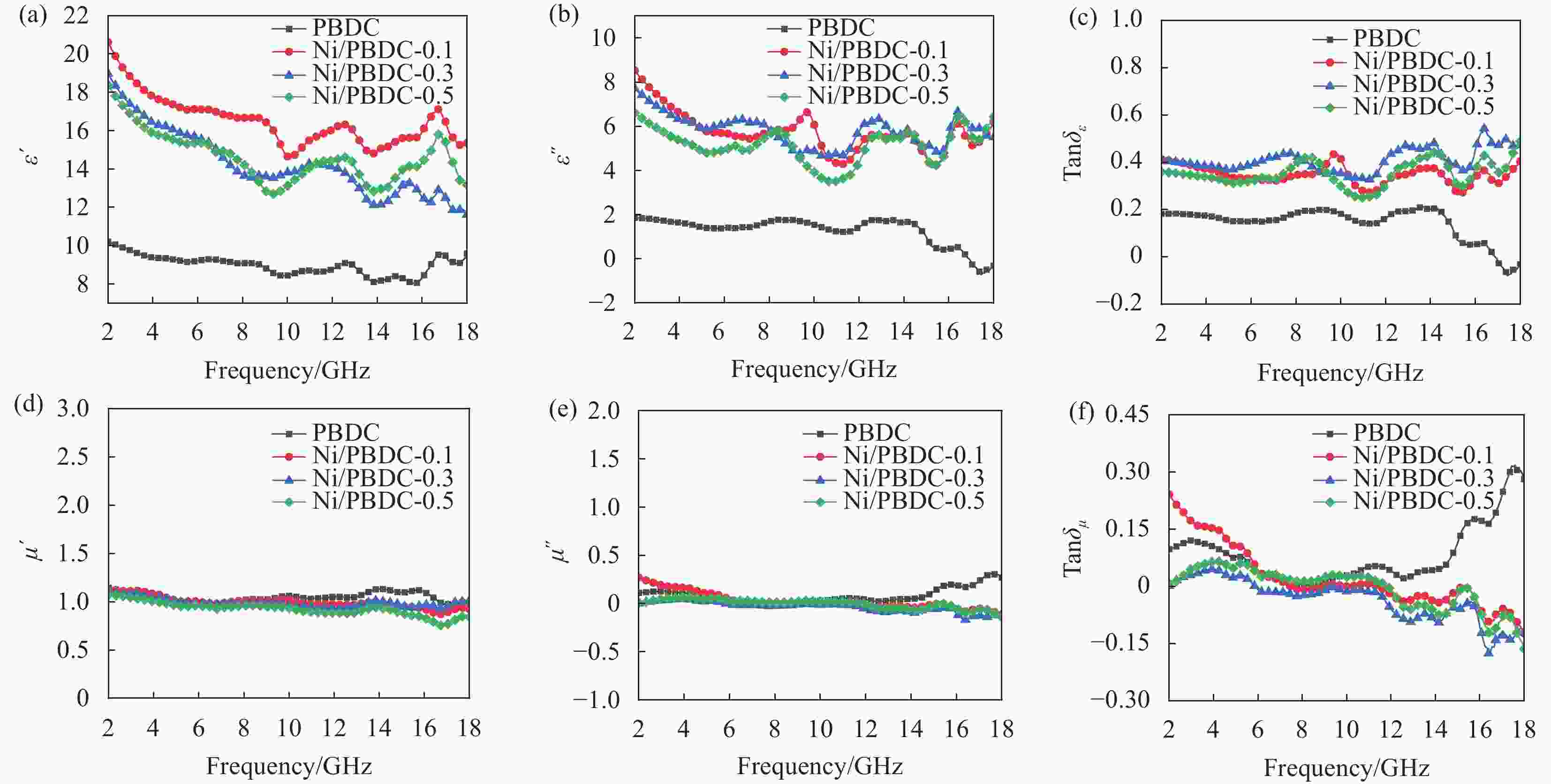
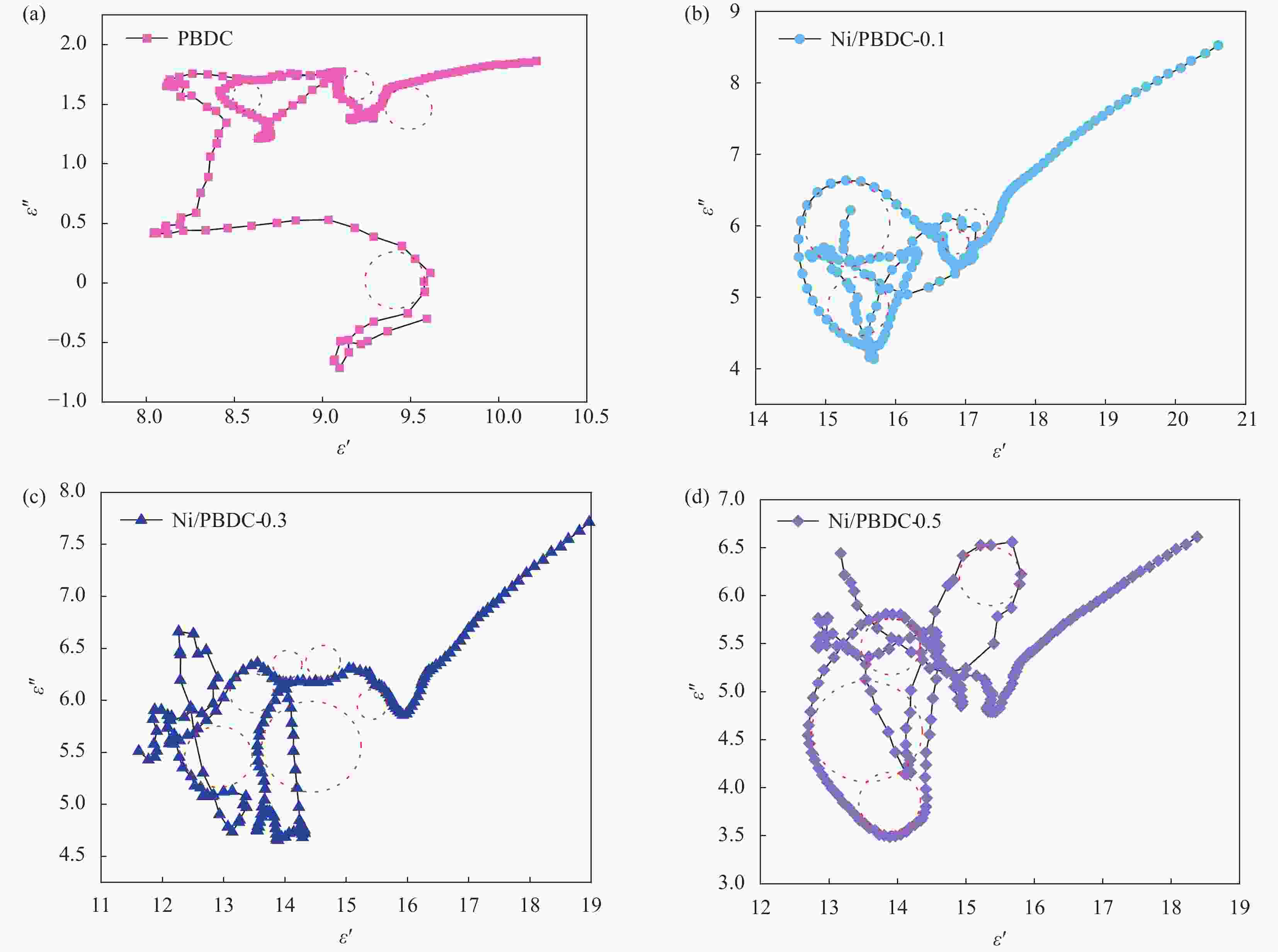
图 7 Ni/PBDC样品的电磁参数: 介电常数实部$ {\varepsilon' } $ (a)、介电常数虚部$ {\varepsilon ''} $ (b)、介电损耗正切$ \text{tan}{\delta }_{\varepsilon } $ (c)、磁导率实部$ {\mu }^{\prime } $ (d)、磁导率虚部$ {\mu'' } $ (e)、磁损耗正切$ \text{tan}{\delta }_{\mu } $ (f)
Figure 7. Electromagnetic parameters of the Ni/PBDC sample: Real part of permittivity $ {\varepsilon' }$ (a), imaginary part of permittivity $ {\varepsilon'' } $ (b), tangent of dielectric loss $ \text{tan}{\delta }_{\varepsilon } $ (c), real part of permeability $ {\mu' } $ (d), imaginary part of permeability $ {\mu ''} $ (e), tangent of magnetic loss $ \text{tan}{\delta }_{\mu } $ (f)
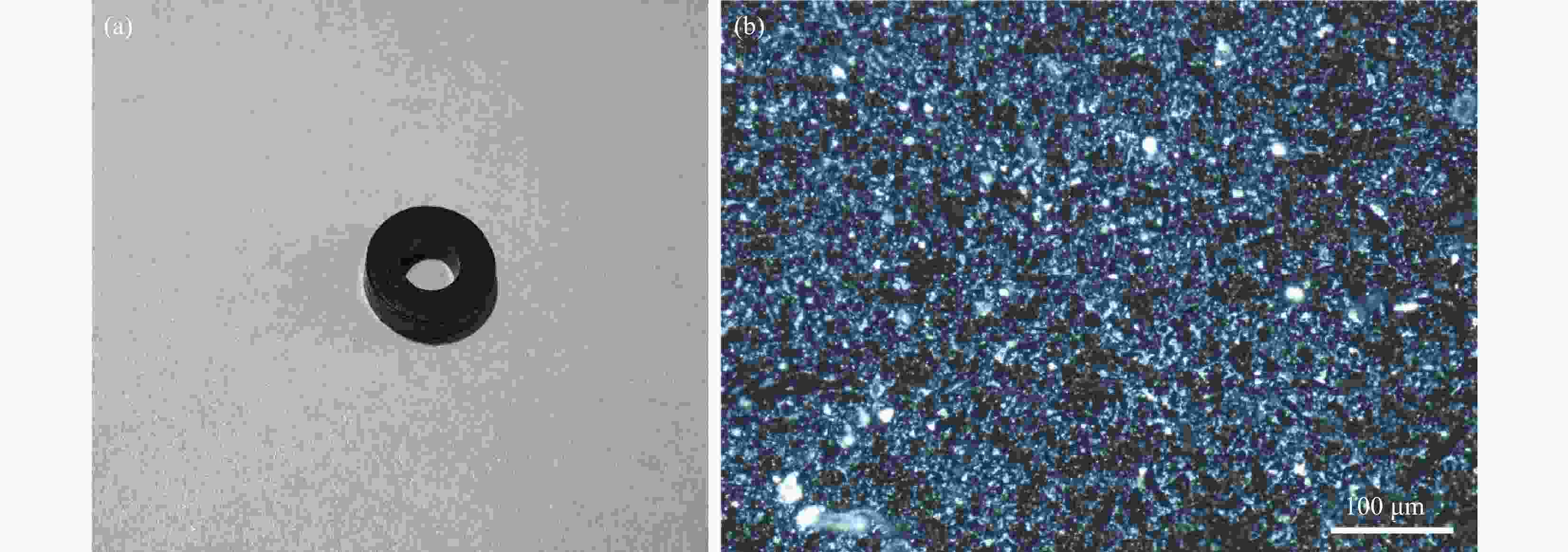
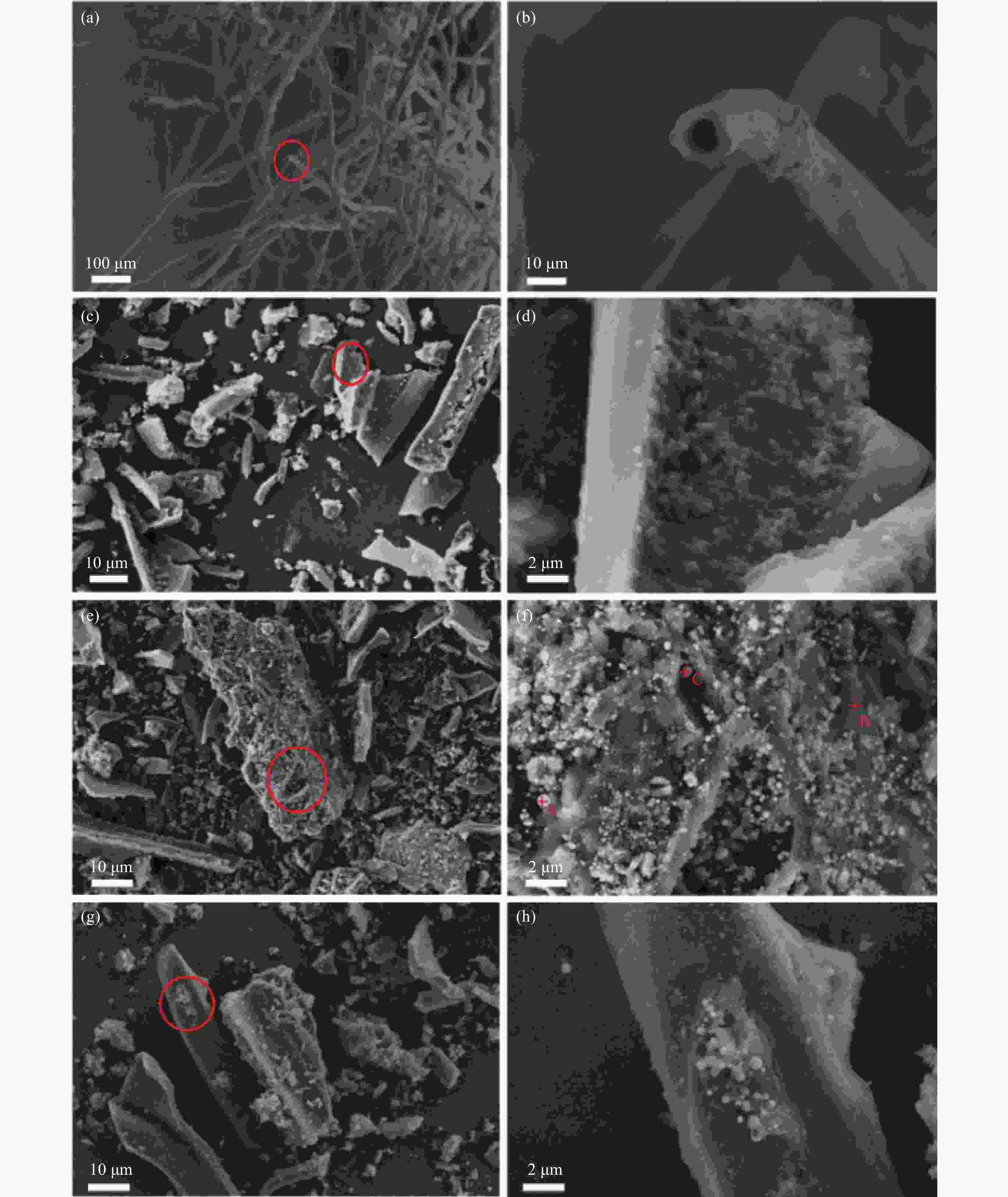
表 1 Ni/PBDC-0.3 EDS结果
Table 1. Ni/PBDC-0.3 EDS results
Elemental Point A/wt% Point B/wt% Point C/wt% Ni 88.94 7.64 68.93 C 9.21 59.81 21.01 O 1.44 5.42 3.61 K 0.00 11.69 0.96 Ca 0.40 7.36 4.39 Cl 0.00 8.08 1.10 表 2 Ni/PBDC复合吸波材料与文献报道的其他生物质碳吸波材料的对比
Table 2. Comparison of Ni/PBDC composite absorbing materials with other biomass carbon absorbing materials reported in the literature
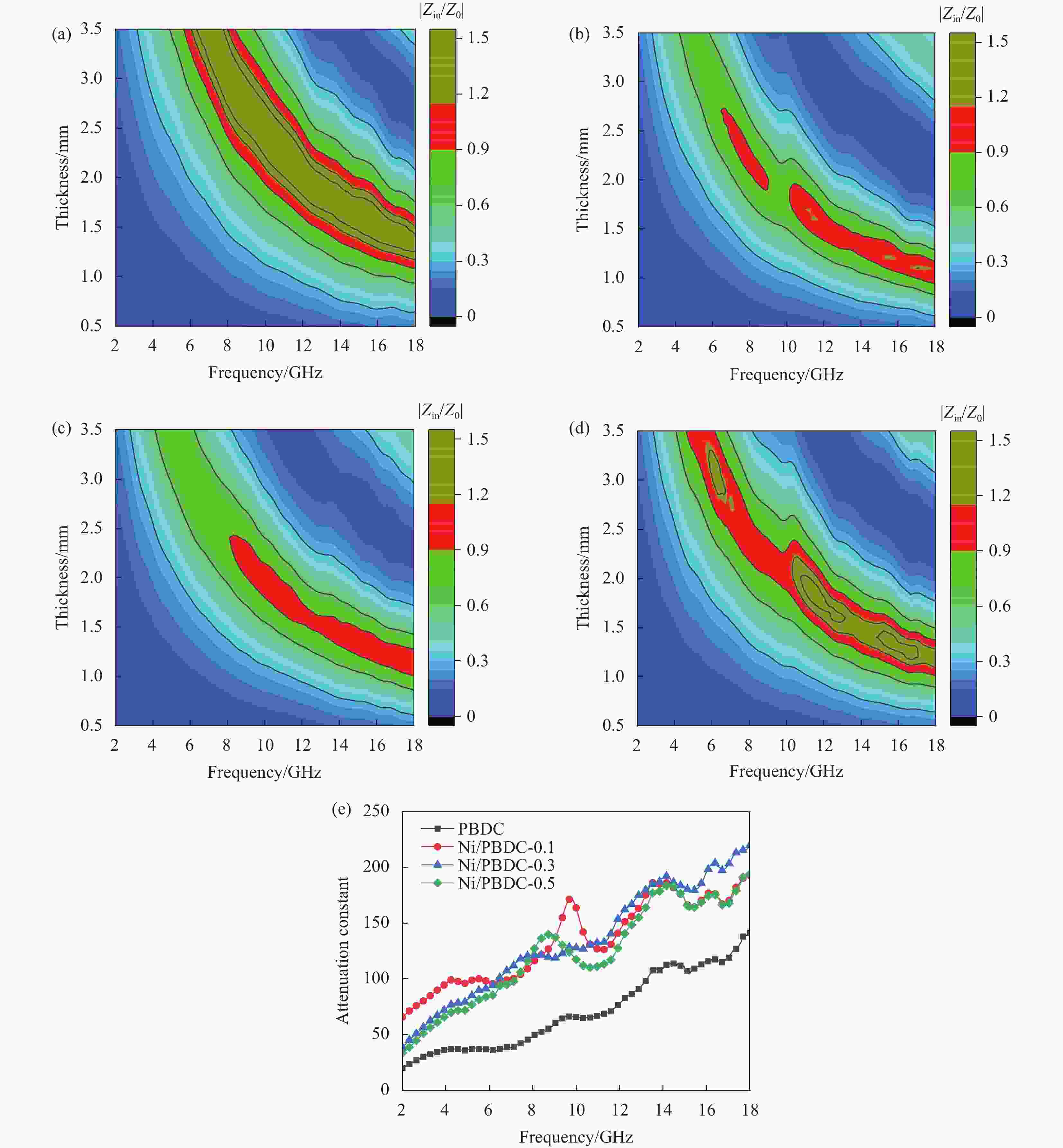
Absorber RLmin/dB EAB/GHz T/mm Ref. Fish skin −29.5 5.8 1.7 [19] Phragmites australis/ Fe3O4 −45.7 3.4 1.7 [20] Rice husk/NiSO4 −58.5 3.53 2.7 [38] Walnut shell −42.4 1.76 2 [39] Cotton/Co(NO3)2·6H2O −14.98 2.6 2.5 [40] Rice husk −47.46 3.4 2.8 [41] Pine pollen /NiO −52.6 4.9 3 [42] Fir wood /NiFe2O4 −17.5 2.6 2.4 [43] Walnut shell /Fe3O4 −56.61 2.72 2.46 [44] Agaric / Fe3O4 −30.41 2.45 2.06 [45] Mango leaves −22.7 5.17 1.75 [46] Juncus effusus −40.4 3.48 1.75 [47] Phoenix tree oakum/NiCl2·6H2O −40 4.16 1.4 This work Notes: RLmin, EAB, and T are minimum reflection loss, effective absorption bandwidth, and thickness of the absorber,respectively. -
[1] LV H, YANG Z, PAN H, et al. Electromagnetic absorption materials: Current progress and new frontiers[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 127: 100946. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100946 [2] ZHANG C, WU Z, XU C, et al. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotubes hollow microsphere with confined magnetic nanospheres for broadband microwave absorption[J]. Small, 2022, 18(3): 2104380. doi: 10.1002/smll.202104380 [3] AHMAD H S, HUSSAIN T, NAWAB Y, et al. Effect of various dielectric and magnetic nanofillers on microwave absorption properties of carbon fiber reinforced composites structures[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(14): 19882-19890. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.03.263 [4] DAI D, LAN X, WANG Z. Hierarchical carbon fiber reinforced SiC/C aerogels with efficient electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2023, 248: 110376. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110376 [5] YUAN R, LYU J, FU C, et al. Carbonized Kevlar Nanofiber/Carbon Nanotube/Magnetic Nanoparticle Hybrid Aerogel Fibers for Microwave Absorption[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2023, 6(13): 10944-10952. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c01606 [6] WANG Y Y, ZHOU Z H, ZHU J L, et al. Low-temperature carbonized carbon nanotube/cellulose aerogel for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 220: 108985. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108985 [7] CAO Y, CHENG Z, WANG R, et al. Multifunctional graphene/carbon fiber aerogels toward compatible electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding in gigahertz and terahertz bands with optimized radar cross section[J]. Carbon, 2022, 199: 333-346. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.07.077 [8] 乔明涛, 齐靖泊, 王佳妮, 等. 3D 石墨烯气凝胶复合吸波材料的研究现状[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(2): 548-560.QIAO M T, QI J B, WANG J N, et al. Research status of 3D graphene aerogel composite absorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(2): 548-560 (in Chinese). [9] RAN K, WANG W, HOU X, et al. Oxygen plasma modulates the interfacial impedance of microwave reduced graphene oxide for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 924: 166568. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166568 [10] ZHENG H, NAN K, LU Z, et al. Core-shell FeCo@ carbon nanocages encapsulated in biomass-derived carbon aerogel: Architecture design and interface engineering of lightweight, anti-corrosion and superior microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 646: 555-566. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.05.076 [11] WU Z, CHANG J, GUO X, et al. Honeycomb-like bamboo powders-derived porous carbon with low filler loading, high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2023, 215: 118415. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118415 [12] WANG S, LI Q, HU K, et al. A facile synthesis of bare biomass derived holey carbon absorbent for microwave absorption[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 544: 148891. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148891 [13] Wan H, Hu X. Nitrogen doped biomass-derived porous carbon as anode materials of lithium ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2019, 341: 115030. doi: 10.1016/j.ssi.2019.115030 [14] SHI Q, ZHAO Y, LI M, et al. 3D lamellar skeletal network of porous carbon derived from hull of water chestnut with excellent microwave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 641: 449-458. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.03.062 [15] ZHANG R, QIAO J, ZHANG X, et al. Biomass-derived porous carbon for microwave absorption[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 289: 126437. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126437 [16] WU N, LIU C, XU D, et al. Ultrathin high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with facilely fabricated hierarchical porous Co/C crabapples[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(6): 1659-1669. doi: 10.1039/C8TC04984J [17] WANG Y, GAO X, LIN C, et al. Metal organic frameworks-derived Fe-Co nanoporous carbon/graphene composite as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 785: 765-773. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.271 [18] WANG B, ZHANG Y, YANG Y, et al. Facile preparation of carbon nanosheet frameworks/magnetic nanohybrids with heterogeneous interface as an excellent microwave absorber[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 838: 155586. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155586 [19] GU W, SHENG J, HUANG Q, et al. Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13: 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-00525-y [20] 简煜, 范勋娥, 邱柏杨, 等. 铁氧体/芦苇秆炭复合吸波材料的制备与性能[J/OL]. 复合材料学报, 1-112024-0711]. https: //doi. org/10.13801/j. cnki. fhclxb. 20240018.001. JIAN Y, FAN X E, QIU B Y, et al. Ferrite/reed stem carbon composite absorbing material preparation and properties of [J/OL]. Journal of composite materials, 1-11 [2024-07-11]. https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20240018.001(in Chinese). [21] 李雪菲, 陈辰, 赵珺瑞, 等. 梧桐絮制备多孔纤维碳材料及其在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2020, 37(05): 52-57.LI X F, CHEN C, ZHAO J R, et al. Preparation of porous fiber carbon materials from Chinese buttonwood and its application in Supercapacitors[J]. Chemical & Biological Engineering, 2019, 37(05): 52-57(in Chinese). [22] 孔祥恺, 吴佩琨, 严寒, 等. 生物质碳管/高岭岩-双废材料的复合及其吸波应用[J/OL]. 复合材料学报, 1-10 [2024-07-11]. https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20240022.002.KONG X K, WU P K, YAN H, et al. Composite of biomass carbon tube/Kaolinite and double waste material and its wave absorption application [J/OL]. Journal of composite materials, 1-10 [2024-07-11]. https://doi.org/10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20240022.002(in Chinese). [23] 粟婉婷, 李鹏辉, 王欢, 等. 木质素基多孔碳材料的制备与应用的研究进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2023, 42(7): 130-140. doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2023.07.015SU W T, LI P H, WANG H, et al. Research progress on the preparation and application of lignin-based porous carbon materials[J]. China Paper Making, 2023, 42(7): 130-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2023.07.015 [24] WEI Y, LIU H, LIU S, et al. Waste cotton-derived magnetic porous carbon for high-efficiency microwave absorption[J]. Composites Communications, 2018, 9: 70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2018.06.007 [25] WANG L, LI X, LI Q, et al. Oriented polarization tuning broadband absorption from flexible hierarchical ZnO arrays vertically supported on carbon cloth[J]. Small, 2019, 15(18): 1900900. doi: 10.1002/smll.201900900 [26] ZHAO X, NIE X, LI Y, et al. A layered double hydroxide-derived exchange spring magnet array grown on graphene and its application as an ultrathin electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(39): 12270-12277. doi: 10.1039/C9TC03254A [27] WANG J, LIU L, JIAO S, et al. Hierarchical carbon fiber@ MXene@ MoS2 core-sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(45): 2002595. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002595 [28] WU Z, PEI K, XING L, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption performance from magnetic coupling of magnetic nanoparticles suspended within hierarchically tubular composite[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(28): 1901448. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201901448 [29] LI B, MA Z, ZHANG X, et al. NiO/Ni heterojunction on N-doped hollow carbon sphere with balanced dielectric loss for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Small, 2023, 19(12): 2207197. doi: 10.1002/smll.202207197 [30] LI Y, LIAO Y, JI L, et al. Quinary high-entropy-alloy@ graphite nanocapsules with tunable interfacial impedance matching for optimizing microwave absorption[J]. Small, 2022, 18(4): 2107265. doi: 10.1002/smll.202107265 [31] LIANG J, YE F, CAO Y, et al. Defect-engineered graphene/Si3N4 multilayer alternating core-shell nanowire membrane: a plainified hybrid for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(22): 2200141. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202200141 [32] DENG L, HAN M. Microwave absorbing performances of multiwalled carbon nanotube composites with negative permeability[J]. Applied physics letters, 2007, 91(2). [33] DUAN Y, GAO M, PANG H, et al. FeCoNiMnAl high-entropy alloy: Improving electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2021, 36(10): 2107-2117. doi: 10.1557/s43578-021-00242-1 [34] XU J, LIU M, ZHANG X, et al. Atomically dispersed cobalt anchored on N-doped graphene aerogels for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption with an ultralow filler ratio[J]. Applied Physics Reviews, 2022, 9(1): 011402. doi: 10.1063/5.0067791 [35] ZHANG X, SHI Y, XU J, et al. Identification of the intrinsic dielectric properties of metal single atoms for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14: 1-17. doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00751-y [36] ZHANG F, CUI W, WANG B, et al. Morphology-control synthesis of polyaniline decorative porous carbon with remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 204: 108491. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108491 [37] ZHU X, DONG Y, XIANG Z, et al. Morphology-controllable synthesis of polyurethane-derived highly cross-linked 3D networks for multifunctional and efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2021, 182: 254-264. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.06.028 [38] WU Z, GUO X, MENG Z, et al. Nickel/porous carbon derived from rice husk with high microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 925: 166732. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166732 [39] QIU X, WANG L, ZHU H, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(22): 7408-7418. doi: 10.1039/C7NR02628E [40] LI W, QI H, GUO F, et al. Co nanoparticles supported on cotton-based carbon fibers: a novel broadband microwave absorbent[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 772: 760-769. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.075 [41] WU Z, MENG Z, YAO C, et al. Rice husk derived hierarchical porous carbon with lightweight and efficient microwave absorption[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 275: 125246. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125246 [42] WANG H, WU X, WANG Q, et al. NiO nanosheets on pine pollen-derived porous carbon: construction of interface to enhance microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32: 25656-25667. doi: 10.1007/s10854-020-04057-4 [43] JI C, LIU Y, XU J, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of biomass-derived carbon decorated with transition metal alloy at improved graphitization degree[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 890: 161834. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161834 [44] LI Z, LIN H, DING S, et al. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@ C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon[J]. Carbon, 2020, 167: 148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.070 [45] SU J, YANG R, ZHANG P, et al. Fe/Fe3O4/biomass carbon derived from agaric to achieve high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2022, 129: 109386. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109386 [46] NEGI P, CHHANTYAL A K, DIXIT A K, et al. Activated carbon derived from mango leaves as an enhanced microwave absorbing material[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2021, 27: e00244. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2020.e00244 [47] MAO Y, LIU K, SHENG Y, et al. Hierarchical porous carbon frameworks derived from Juncus effusus biomass with robust electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12(12): 4442-4452. doi: 10.1039/D4TC00223G -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 27
- HTML全文浏览量: 11
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: