Modification of silicon-containing arylacetylene resin and its composite properties by copolymerization with styrene
-
摘要: 含硅芳炔树脂(PSA)/石英纤维(QF)复合材料是极具潜力的新型耐高温透波材料,但由于PSA树脂质脆、极性低,加上石英纤维表面光滑,导致两者间界面粘结弱,突出表现为复合材料层间性能(如层间剪切强度)低。本文采用苯乙烯(ST)对含硅芳炔树脂进行改性,通过ST与PSA分子间发生共聚反应,降低体系的交联密度,均匀化其交联网络结构,提高树脂抗压损伤阻抗,最终达到了改善PSA基复合材料层间剪切强度的目的。通过DSC、TG、DMA等手段测试和表征了改性前后PSA树脂及其复合材料的固化反应性能、流变性能、耐热性能、介电性能和力学性能等,结果表明:添加苯乙烯不会影响PSA树脂的固化规律和工艺。随着ST添加量的增加,改性PSA树脂的耐热性有所下降,但其失重5wt%温度Td5均接近500℃,远高于应用要求的350℃。改性后复合材料保持了良好的介电性能,介电常数为3.09,损耗因子tanδ为2×10−3;在保持较高弯曲强度的同时,改性后复合材料层间剪切强度得到显著提升。当ST质量比为15%时,QF/PSA-15ST在室温下的层间剪切强度提高了53.0%,350℃下提高了98.3%;350℃下层间剪切强度保留率为78.3%,高于改性前的60.4%。
-
关键词:
- 含硅芳炔树脂 /
- 复合材料 /
- 苯乙烯 /
- 增韧 /
- 层间剪切强度(ILSS)
Abstract: Quartz fiber (QF) reinforced poly(silica-containing arylacetylene) (PSA) composite is a new type of highly promising new wave-transparent materials with highly heat-resistance. However, the brittleness and low molecular polarity of PSA resins, combined with the smooth surface of quartz fibers, results in a weak interfacial adhesion, and low interlaminar shear strength (ILSS) of the composites. In this paper, silicon-containing arylacetylene resin was modified by copolymerizing with styrene (ST). As a consequence, the crosslinking density was decreased, the crosslinking network got homogenized, and the crack resistance of the resin against load was improved. Finally, the ILSS of Quartz fiber reinforced PSA composites was improved. The properties of the resin and composites were characterized with differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), mechanical property testing, dielectric property testing, rheological property testing. The results showed that the addition of ST didn’t affect the curing process of the resin. With the increase of ST content, the heat resistance of modified PSA resin decreased to some extent, but its mass loss 5wt% temperature Td5 was still close to 500℃, which was much higher than the expected application temperature of 350℃. The modified composite also maintained the good dielectric properties with dielectric constant of 3.09 and loss factor tanδ of 0.002. The results also showed that the addition of ST significantly improved ILSS. For instance, the ILSS of QF/PSA-15ST increased by 53.0% at room temperature and 98.3% at 350℃. Compared with that at room temperature, the retention rate of interlaminar shear strength at 350℃ was 78.3%, which was much higher than that before modification (60.4% ). -
表 1 含硅芳炔树脂(PSA)-苯乙烯(ST)树脂浇注体的命名
Table 1. Naming of poly(silica-containing arylacetylene) (PSA)-styrene (ST) resin castable
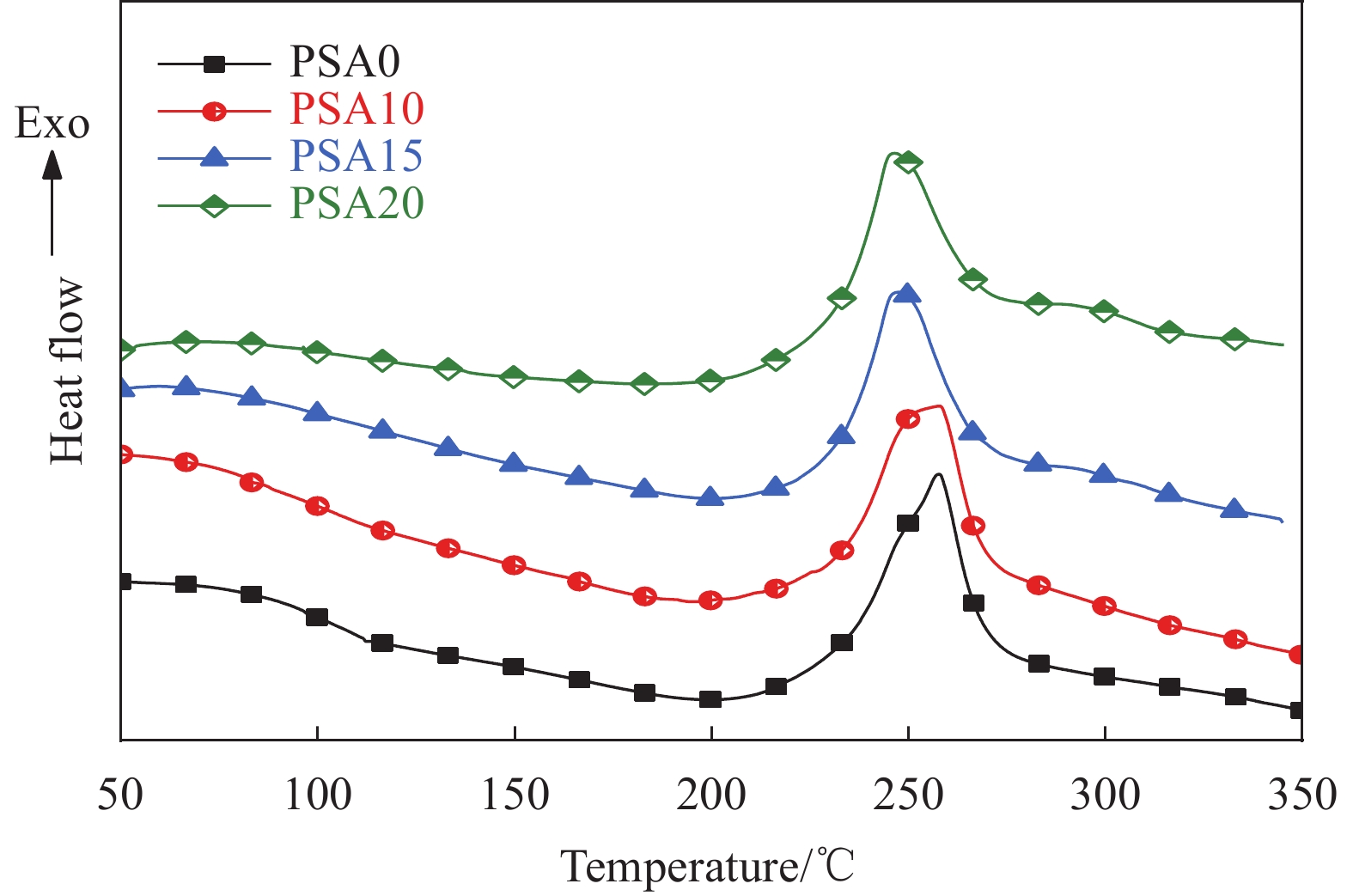
Sample Mass ratio of ST/% Mass ratio of MDPES/% PSA-0ST 0 100 PSA-10ST 10 90 PSA-15ST 15 85 PSA-20ST 20 80 Note: MDPES—Methyldiphenylacetylidene-silane. 表 2 添加不同比例ST的MDPES树脂的DSC数据
Table 2. DSC data of MDPES resin adding with different ratio of styrene
Ti/℃ Tp/℃ Tf/℃ ΔH/(J·g−1) PSA-0ST 210.6 257.7 334.7 196.5 PSA-10ST 206.1 257.9 316.4 191.3 PSA-15ST 205.7 247.6 317.4 191.7 PSA-20ST 201.9 245.9 318.9 196.9 Notes: Ti, Tp and Tf—Initial temperature, peak temperature and final temperature of cure exotherm; ΔH—Enthalpy of cure exotherm. 表 3 添加不同比例ST的MDPES固化树脂的热重数据
Table 3. TGA data of the cured MDPES resin adding with different ratio of Styrene
Tonset/℃ Td5/℃ Tmax/℃ Y350℃/% PSA-0ST 424 504 547 100.0 PSA-10ST 375 497 551 99.6 PSA-15ST 377 494 551 99.6 PSA-20ST 374 480 552 99.6 Notes: Tonset, Td5 and Tmax—Starting decomposition temperature, the temperature at 5wt% mass decomposition and the temperature corresponding to the maximum decomposition rate; Y350℃—Mass residual rate at 350°C. 表 4 QF/PSA复合材料改性前后的力学性能和介电性能
Table 4. Mechanical and dielectric properties of QF/PSA compsites before and after modification
Flexural strength/MPa ILSS/MPa Dielectric properties RT 350℃ RT 350℃ ε tanδ Before modification 66.38
±6.3340.22±5.00 5.02±
1.073.03±0.22 3.05±0.02 0.004±
0.001After modification 83.83
±8.9658.68
±2.547.68
±0.736.01±1.15 3.09±0.01 0.003±
0.001Notes: ILSS—Interlaminar shear strength; RT—Room temperature; ε—Dielectric constant; tanδ—Loss factor. 表 5 改性前后树脂浇注体薄片的洛氏硬度测试结果
Table 5. Rockwell hardness values of flake resin casts before and after modification
HDR/Damage to specimens’ surface Average of HDR Before modification 78.5/SV 69.1/SV 62.0/SV −/SV −/SV 69.9 After modification 94.4/IT 94.3/IT 92.9/IT 88.6/SL 68.3/SV 87.7 Notes: HDR—Rockwell hardness values; SV—Severe damage; SL—Slight damage; IT—Intact. -
[1] ZU Y, ZHANG F F, CHEN D D, et al. Wave-transparent composites based on phthalonitrile resins with commendable thermal properties and dielectric performance[J]. Polymer,2020,12(24):166-198. [2] 姚琪, 张振林, 宫剑. 耐高温/隐身/透波一体化天线罩材料的研究进展[J]. 当代化工研究, 2018, 12:6-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2018.07.004YAO Qi, ZHANG Zhenlin, GONG Jian. Research progress of high temperature resistant/stealth/wave transmitting integrated radome materials[J]. Modern Chemical Research,2018,12:6-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2018.07.004 [3] 张明习, 轩立新, 徐晓燕, 等. 军用透波复合材料的研究进展[C]//2005年南京复合材料技术发展研讨会论文集. 南京: 中国航空工业集团公司济南特种结构研究所, 2005: 13-19.ZHANG Mingxi, XUAN Lixin, XU Xiaoyan, et al. Process in the research of military transparent composites[C]//Proceedings of the 2005 Nanjing Symposium on Composites Technology Development. Nanjing: AVIC Research Institute for Special Structures of Aeronautical Composite, 2005: 13-19(in Chinese). [4] KANDI K K, THALLAPALLI N, CHILAKALAPALLI S P R. Development of silicon nitride-based ceramic radomes-A review[J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology,2015,12(5):909-920. [5] 王飞, 石佩洛. 树脂基复合材料在雷达天线罩领域的应用及发展[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2017, 47(2):10-13. doi: 10.12044/j.issn.1007-2330.2017.02.003WANG Fei, SHI Peiluo. Application and development of resin matrix composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2017,47(2):10-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.12044/j.issn.1007-2330.2017.02.003 [6] KUROKI S, OKITA K, KAKIGANO T, et al. Thermosetting mechanism study of poly[(phenylsilylene)ethynylene-1, 3-phenyleneethynylene] by solid-state NMR spectroscopy and computational chemistry[J]. Macromolecules,1998,31(9):2804-2808. doi: 10.1021/ma971133g [7] YOU X T, DENG S F, HUANG Y C, et al. Thermosetting mechanism study of silicon-containing polyarylacetylene via in situ FTIR and solid-state NMR spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2019,136(13):47301. doi: 10.1002/app.47301 [8] 包建文. 耐高温树脂基复合材料及其应用[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2018: 374-414.BAO Jianwen. High temperature resistant resin matrix composites and their applications[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2018: 374-414(in Chinese). [9] 陈梦怡, 嵇培军, 蔡良元, 等. 石英纤维织物增强复合材料性能研究[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2004(1):12-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2004.01.004CHEN Mengyi, JI Peijun, CAI Liangyuan, et al. Property study of quartz fabric reinforced composites[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites,2004(1):12-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2004.01.004 [10] 孟庆杰, 石军威, 徐亮, 等. 空心石英玻璃纤维增强氰酸酯基低介电复合材料的制备及性能分析[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(S1): 110-112.MENG Qingjie, SHI Junwei, XU Liang, et al. Fabrication and properties of hollow silica fiber reinforced cyanate ester composites with low dielectric property[J]. Materials Review, 2018, 32(S1): 110-112(in Chinese). [11] 郑锡涛, 罗贵, 李宇徒. 复合材料层间性能改善方法研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2013, 56(15):26-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2013.04.001ZHENG Xitao, LUO Gui, LI Yutu. Review of methods on improving interlaminar properties of composites laminate[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2013,56(15):26-29(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2013.04.001 [12] ITOH M, MITSUZUKA M, IWATA K, et al. A novel synthesis and extremely high thermal stability of poly[(phenylsilylene)ethynylene-1, 3-phenyleneethynylene][J]. Macromolecules,1994,27(26):7917-7919. doi: 10.1021/ma00104a056 [13] ITOH M, INOUE K, IWATA K, et al. A heat-resistant silicon-based polymer[J]. Advanced Materials,1997,9(15):1187-1190. doi: 10.1002/adma.19970091514 [14] ITOH M, IWATA K, ISHIKAWA J I, et al. Various silicon-containing polymers with Si(H)-C≡C units[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry,2001,39(15):2658-2669. doi: 10.1002/pola.1242 [15] ZHANG J A, HUANG J X, YU X J, et al. Preparation and properties of modified silicon-containing arylacetylene resin with bispropargyl ether[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society,2012,33(11):3706-3710. doi: 10.5012/bkcs.2012.33.11.3706 [16] 王林靖, 扈艳红, 杜磊, 等. 乙炔基芳酰胺酸硅烷改进石英纤维/含硅芳炔复合材料高温界面性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(2):287-296.WANG Linjing, HU Yanhong, DU Lei, et al. High-temperature interfacial property of quartz fiber/silicon-containing arylacetylene composites with aromatic amic acid-containing alkyne-terminated silane[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(2):287-296(in Chinese). [17] 杨海荟, 扈艳红, 杜磊, 等. 新型硅烷偶联剂对石英纤维/含硅芳炔复合材料界面增强增韧改性[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2016(8):13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2016.08.002YANG Haihui, HU Yanhong, DU lei, et al. Reinforcing and toughening of quartz fiber(QF)/silicon-containing arylacetylene(PSA) composites with new silane coupling agent[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites,2016(8):13-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2016.08.002 [18] 张芳芳, 扈艳红, 杜磊, 等. 含噁嗪环硅烷偶联剂对石英纤维/含硅芳炔复合材料性能的影响[J]. 功能高分子学报, 2017, 30(03): 347-353. doi: 10.14133/j.cnki.1008-9357.2017.03.014ZHANG Fangfang, HU Yanhong, DU Lei, et al. Effects of benzoxazine-containing silane coupling agent on properties of QF/PSA composites. [J]. Journal of Functional Polymers, 2017, 30(03): 347-353(in Chinese). _ doi: 10.14133/j.cnki.1008-9357.2017.03.014 [19] 陈麒, 李扬, 戴泽亮, 等. 甲基二苯乙炔基硅烷及其网络聚合物的合成与表征[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(3):254-258. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2005.03.015CHEN Qi, LI Yang, DAI Zeliang, et al. Synthesis and characterization of methyl-di(phenylethynyl)silane and its network polymer[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica,2005,63(3):254-258(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2005.03.015 [20] 周权, 倪礼忠. 双马来酰亚胺改性甲基二苯乙炔基硅烷复合材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 材料工程, 2009, 37(S2):336-339, 344.ZHOU Quan, NI Lizhong. Preparation and properties of bismaleimide-modified methyl-di(phenylethynyl)silane composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2009,37(S2):336-339, 344(in Chinese). [21] ASTM. Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced plastics and electrical insulating materials: ASTM D790-2017[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM, 2017. [22] ASTM. Standard test method for short-beam strength of polymer matrix composite materials and their laminates: ASTM D2344 M-2016[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM, 2016. [23] SUN Y J, WU Y Y, CHEN L G, et al. Thermal self-initiation in stable free-radical polymerization of styrene[J]. Polymer Journal,2009,41(11):954-960. [24] HUI A W, HAMIELEC A E. Thermal polymerization of styrene at high conversions and temperatures: An experimental study[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2010,16(3):749-769. [25] KIM H D, ISHIDA H. Model compounds study on the network structure of polybenzoxazines[J]. Macromolecules,2003,36(22):8320-8329. doi: 10.1021/ma030108+ -





 下载:
下载: